Chapter 16 plant hormones and growth
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
directional growth in response to a stimulus or environmental cues
Tropism definition?
auxins, gibberelllins, ethene and ABA
4 main plant hormones
seed absorbs water and starts to produce gibberellins
stimulate the production of enzymes to break down food stores
Gibberellins switch on genes that code for amylases and proteases to germinate
ABA acts as an antagonist
How do hormones cause seed germination?
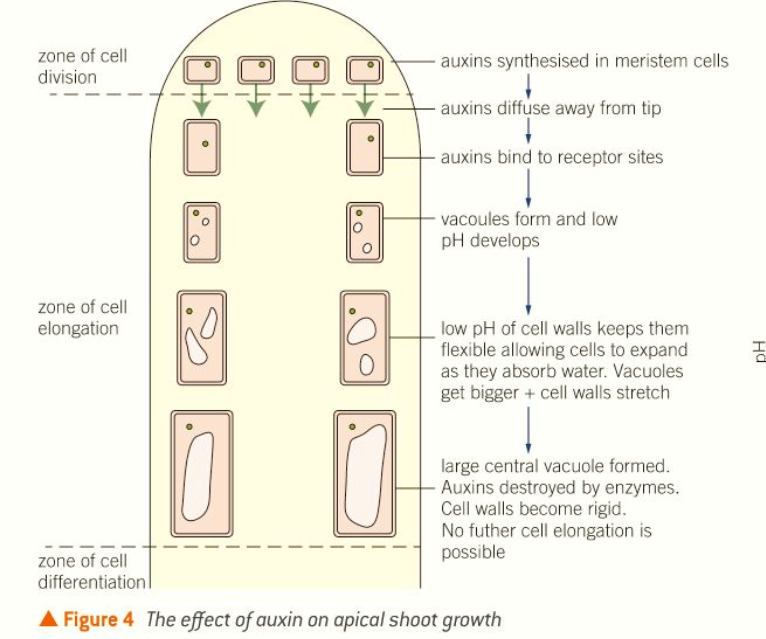
made in the tips of roots and shoots, in the meristems
stimulate the growth of the main apical shoot, suppress growth of lateral shoots.
low conc promote root growth
presence of auxins means cells stretch more easily
auxins bind to receptors in the cell membrane causing a fall in pH which is the optimum pH.
What are some of the ways auxins affect growth in plants? and where are they made?
elongation of plant stems
affect the length of the internodes (regions between leaves on a stem)
What do gibberellins do?
Synergisms - when hormones work together, giving greater response than they would on their own
Antagonism - opposite effects, promoting and inhibiting
what is synergism and antagonism?
change in day length
lack of or excess water
high winds
Changes in salinity
examples of abiotic stress?
leaf loss due to very cold temps and lack of light. The energy needed to keep leaves is more than what is produced by photosynthesis.
daylight sensitivity - germinating or flowering at certain times of day
leaf abcission
making chemicals to stop freezing like solutes and antifreeze
stomatal control under control of ABA
what happens in abiotic stress?
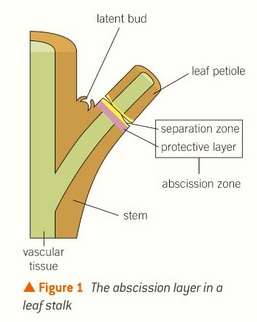
light levels fall and so does auxin
plants therefore make ethene
base of leaf stalk has an abcission zone which has two layers of cells
ethene stimulates gene switching which makes enzymes to digest and weaken cell walls in abcission zone
vascular bundles sealed off and protective layer deposited
leaf abcission process
physical - thorns, barbs, spikes, spiny leaves, folding when touched
chemical - chemicals made to stop animals from eating them
what are the two types of plant responses to herbivory?
tannins - bitter tasting and toxic to insects
alkaloids - bitter, nitrogenous compounds, act as drugs like caffeine, nicotine
terpenoids - form essential oils but can be toxic to insect and fungi, insect repellents
pheromones - affects the social behaviour of the same species
VOCs - made when plant detects attack by insect through saliva, affect the behaviour of predatory insects
chemical defences to herbivory?
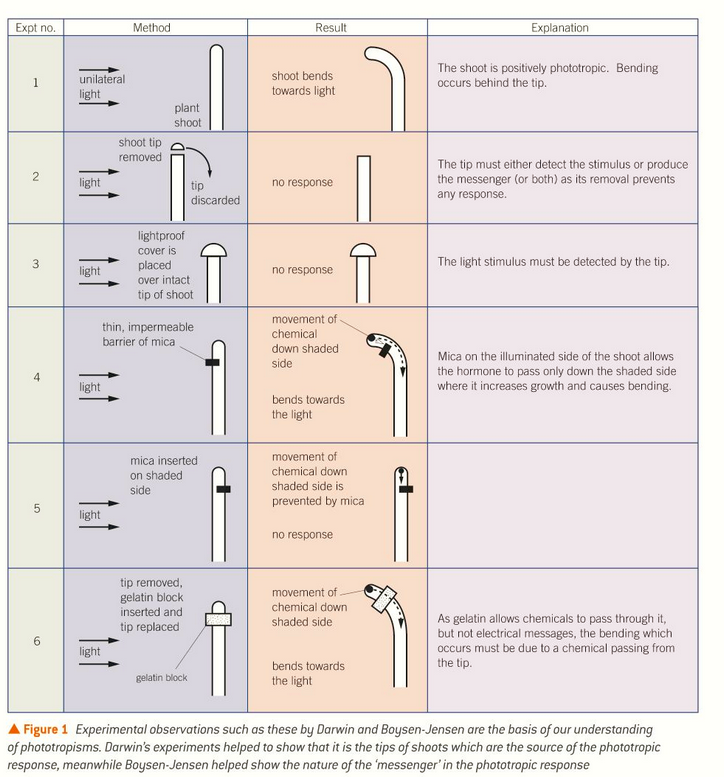
growth of plants in response to light
result of movement of auxins across the shoot or root
auxins move towards the shaded side of the plant and result in cell elongation on that side
this means the plant grows towards the light
roots grow away from the light
how does phototropism work?
in shaded conditions plants grow very fast to get to the light
auxins move away from light and causes cell elongation
when shoot is growing directly towards the light, the unilateral stimulus is removed and plants grow straight towards the light
effect of unilateral light?
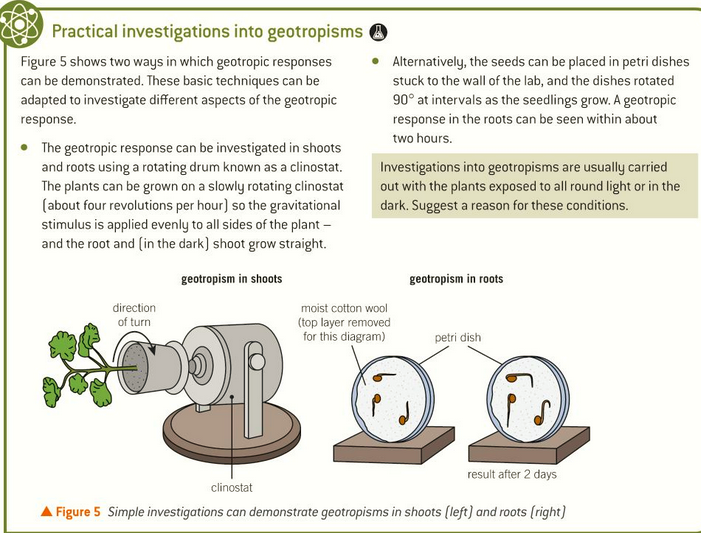
roots are positively geotropic and shoots are negatively geotropic
Response of plants to gravity
what happens due to geotropisms?
ethene from ripe fruits can stimulet other unripe fruit to ripen
when fruits are needed for sale they are exposed to ethene gas so they ripen at the same rate
contro of ripening by hormones?
application of auxins to cut shoots to stimulate the new production of roots
A cutting is a small piece of the stem of a plant
synthetic auxins can cause plants to grow too fast and they die
what are hormone rooting powders and weedkillers?
auxins can be used in the making seedless fruit
ethene to promote fruit dropping
gibberellins used to delay ripening and ageing in fruit
other uses of plant hormones?