ANATOMY EXAM NO.1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
1
New cards
Chapter 1
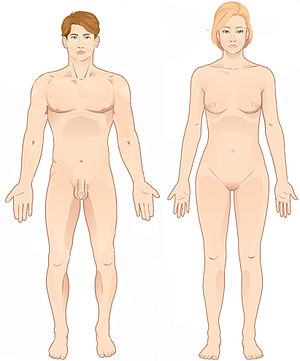
What is anatomical position
What is anatomical position
Feet flat on the ground, arms to your side, palms facing forward
2
New cards
Chapter 1
Supine definition
Supine definition
Laying down face up
3
New cards
Chapter 1
Prone definition
Prone definition
Laying down face down
4
New cards
Chapter 1
Levels of organization (from least complex - most complex)
Levels of organization (from least complex - most complex)
Chemical/Molecular level → Cellular level → Tissue level → Organ level → Organ system level → Organism level
5
New cards
Chapter 1
Abdominopelvic Quadrants (lines shaped like +, intersect at the belly button): Number of sections and name of the sections
Abdominopelvic Quadrants (lines shaped like +, intersect at the belly button): Number of sections and name of the sections
4 sections : right upper quadrant, left upper quadrant, right lower quadrant , left lower quadrant
6
New cards
Chapter 1
Abdominopelvic Regions (lines shaped like #, // lines are the right and left lateral lines, = are the transpyloric and transtubercular planes lines): Number of sections and name of the sections
Abdominopelvic Regions (lines shaped like #, // lines are the right and left lateral lines, = are the transpyloric and transtubercular planes lines): Number of sections and name of the sections
9 Sections
Right side: right hypochondriac region (top), right lumbar region (middle), and right inguinal region (bottom)
Middle side: Epigastric region (top), Umbilical region(middle), Hypogastric -pubic- region (bottom)
Left side: left hypochondriac region (top), left lumbar region (middle), and left inguinal region (bottom)
Right side: right hypochondriac region (top), right lumbar region (middle), and right inguinal region (bottom)
Middle side: Epigastric region (top), Umbilical region(middle), Hypogastric -pubic- region (bottom)
Left side: left hypochondriac region (top), left lumbar region (middle), and left inguinal region (bottom)
7
New cards
Chapter 1
Define Superior and Inferior
Define Superior and Inferior
Superior: Towards or above the head
Inferior: Towards or below the feet
Inferior: Towards or below the feet
8
New cards
Chapter 1
Define Cranial and Caudal
Define Cranial and Caudal
Cranial: Toward head
Caudal: toward tailbone
Caudal: toward tailbone
9
New cards
Chapter 1
Define Medial and Lateral
Define Medial and Lateral
Medial: Toward midline
Lateral: Away from midline
Lateral: Away from midline
10
New cards
Chapter 1
Define Anterior and Posterior
Define Anterior and Posterior
Anterior: The front
Posterior: The back
Posterior: The back
11
New cards
Chapter 1
Define Ventral and Dorsal
Define Ventral and Dorsal
Ventral: Front
Dorsal: Back
Dorsal: Back
12
New cards
Difference between Anterior/Posterior and Ventral/Dorsal
Anterior/Posterior is more general whereas Ventral/Dorsal is more specific
13
New cards
Chapter 1
Define Superficial and Deep
Define Superficial and Deep
Superficial: Closer to the surface
Deep: Further from the service
Deep: Further from the service
14
New cards
Chapter 1
Define Proximal and Distal
Define Proximal and Distal
Proximal: Toward Attached base
Distal: Away from attached base
Distal: Away from attached base
15
New cards
Chapter 1
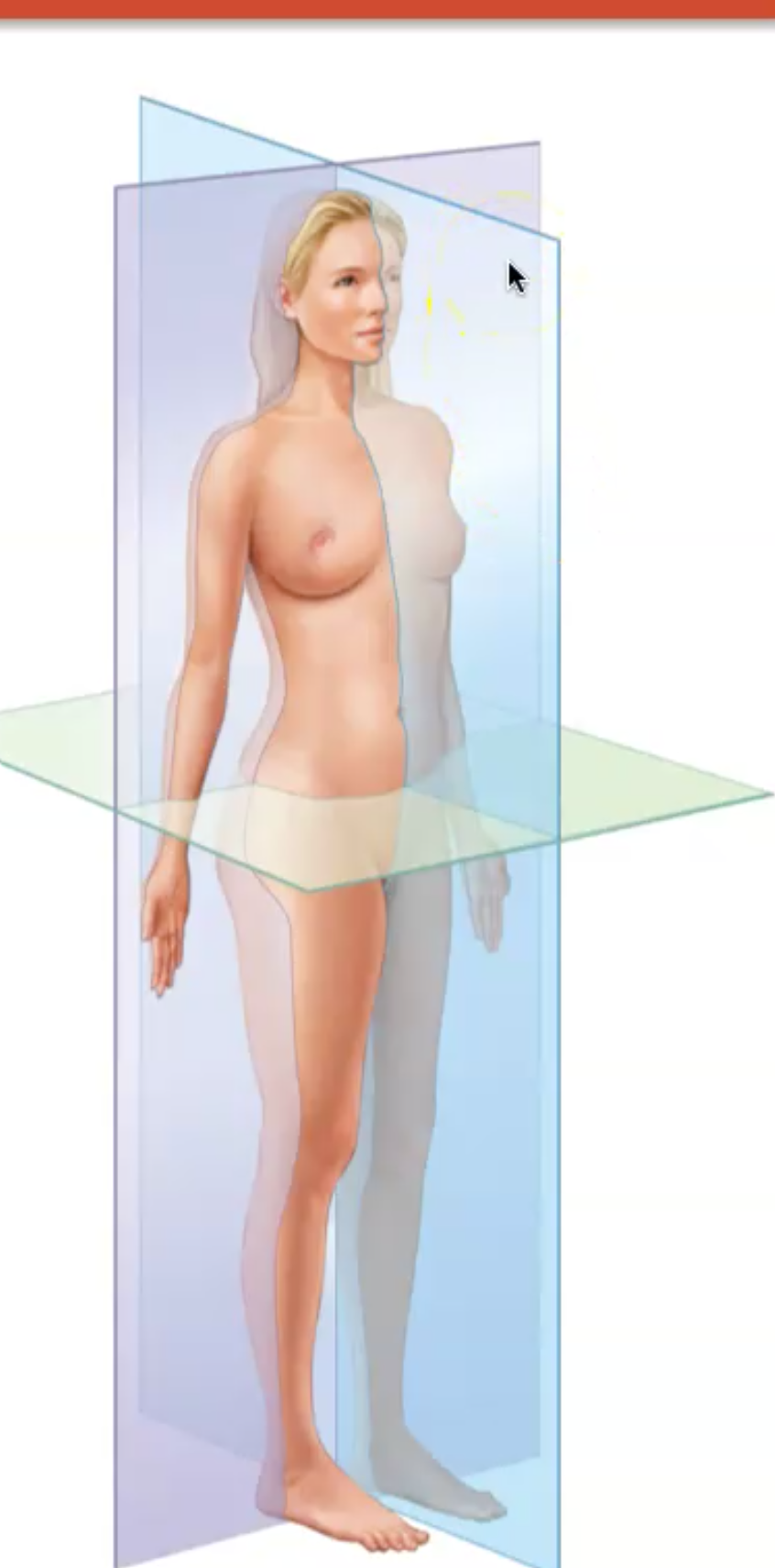
What is a Sagittal Plane
What is a Sagittal Plane
Body divided into left and right pieces
16
New cards
Chapter 1
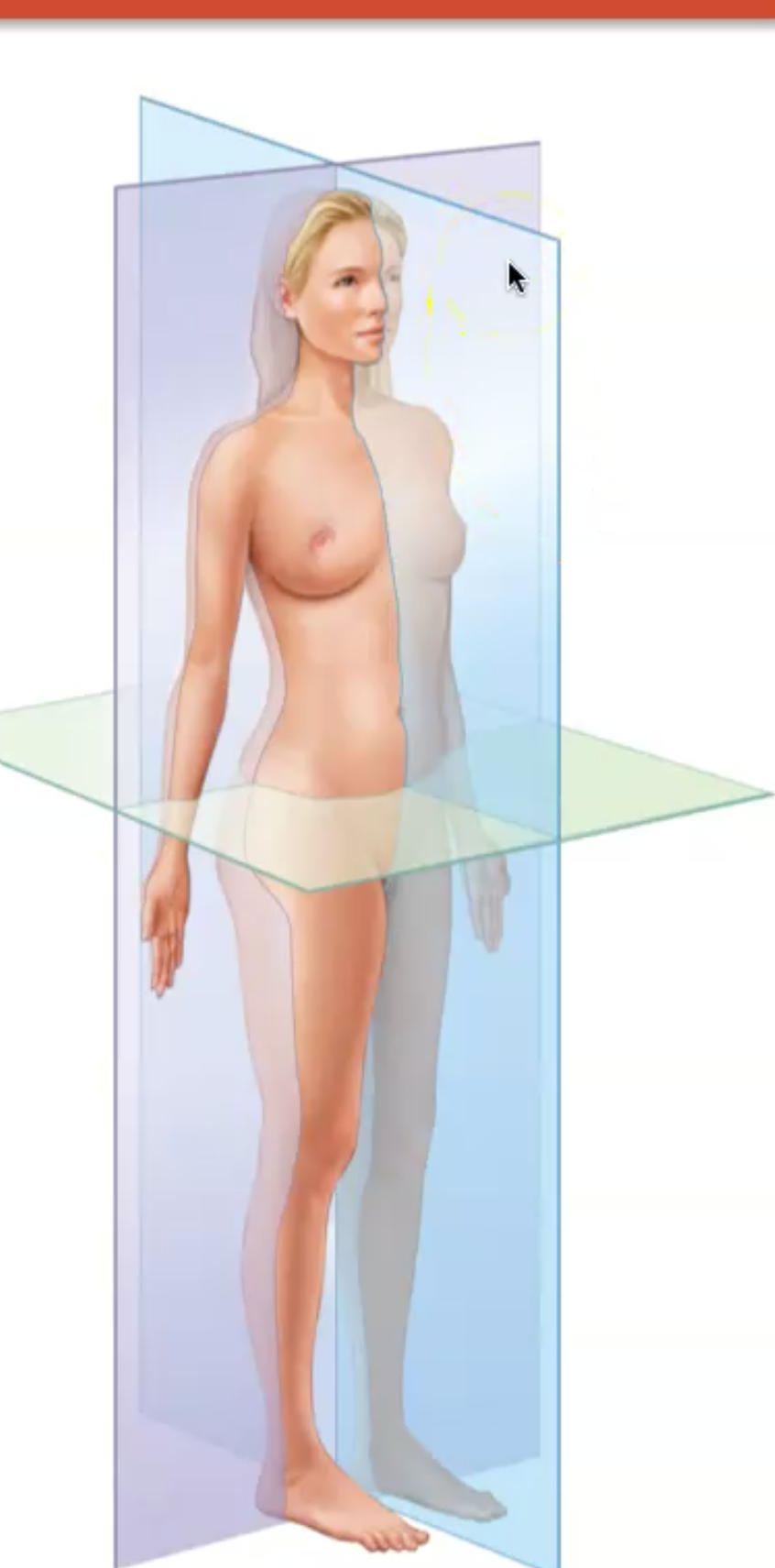
What is a Midsagittal Plane
What is a Midsagittal Plane
Equally divided left and right pieces
17
New cards
Chapter 1
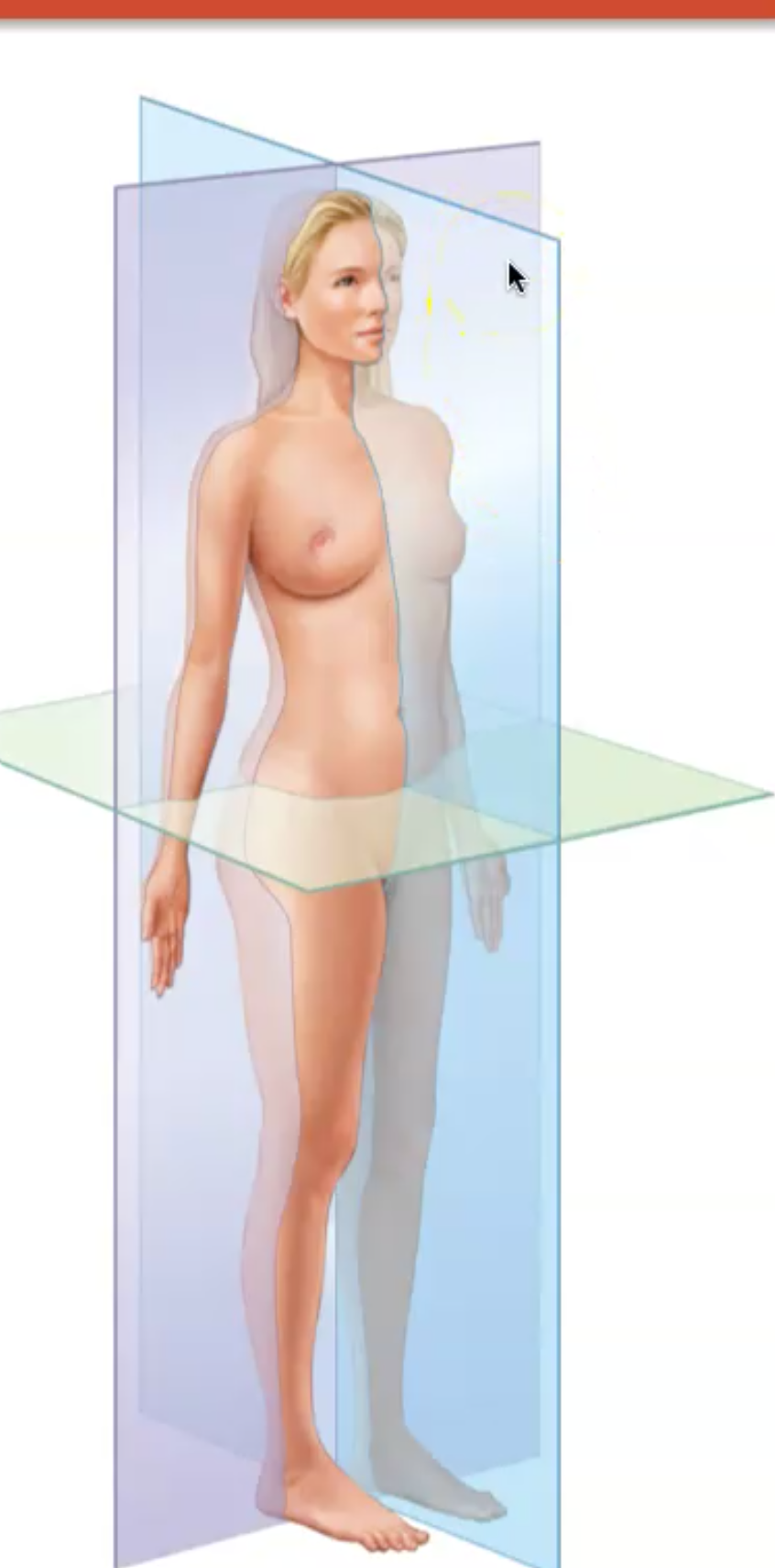
What is a Parasagittal Plane
What is a Parasagittal Plane
Unequally divided left and right pieces
18
New cards
Chapter 1
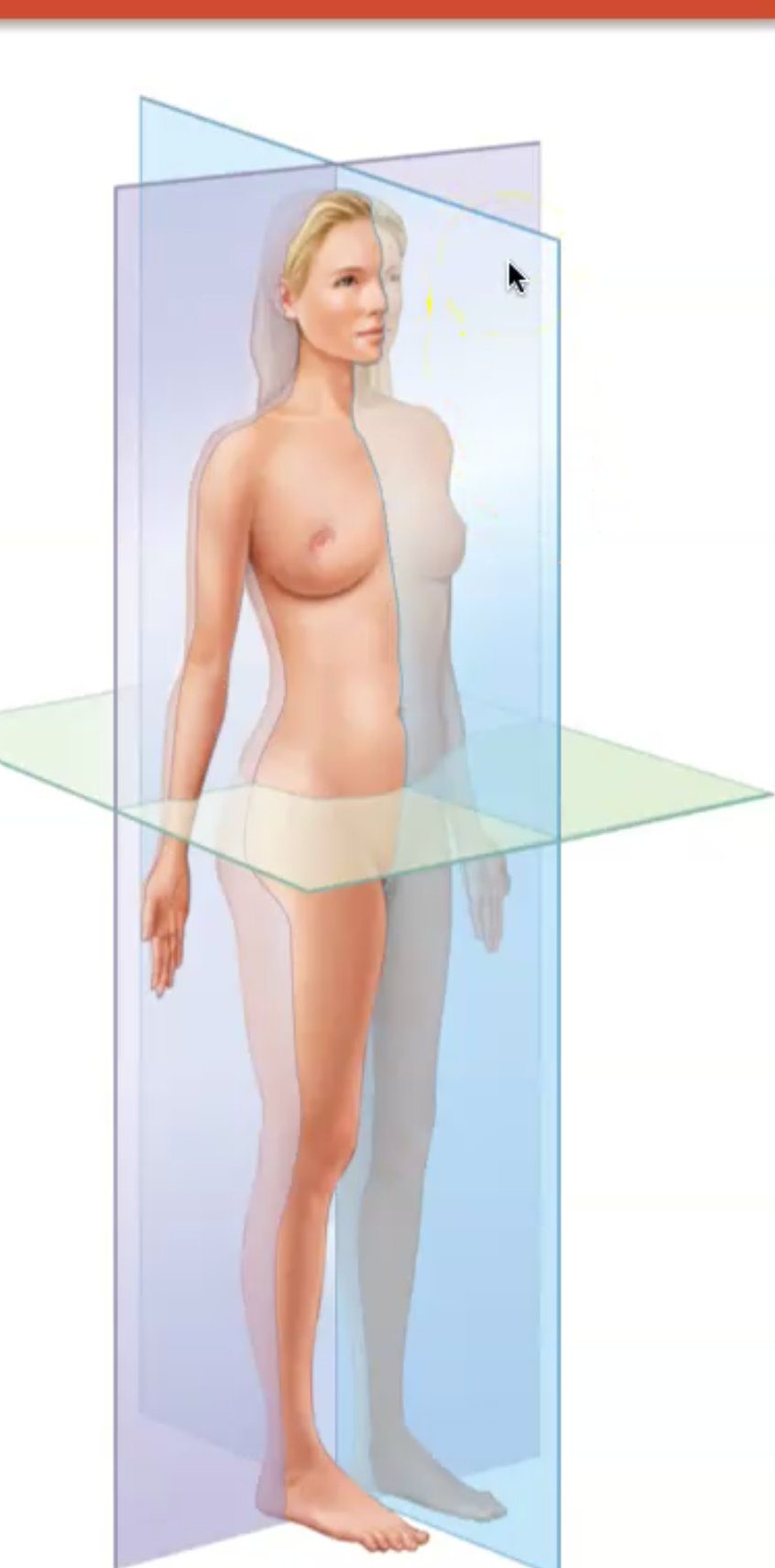
What is a Transverse Plane
What is a Transverse Plane
Body divided into upper and lower body pieces
19
New cards
Chapter 1
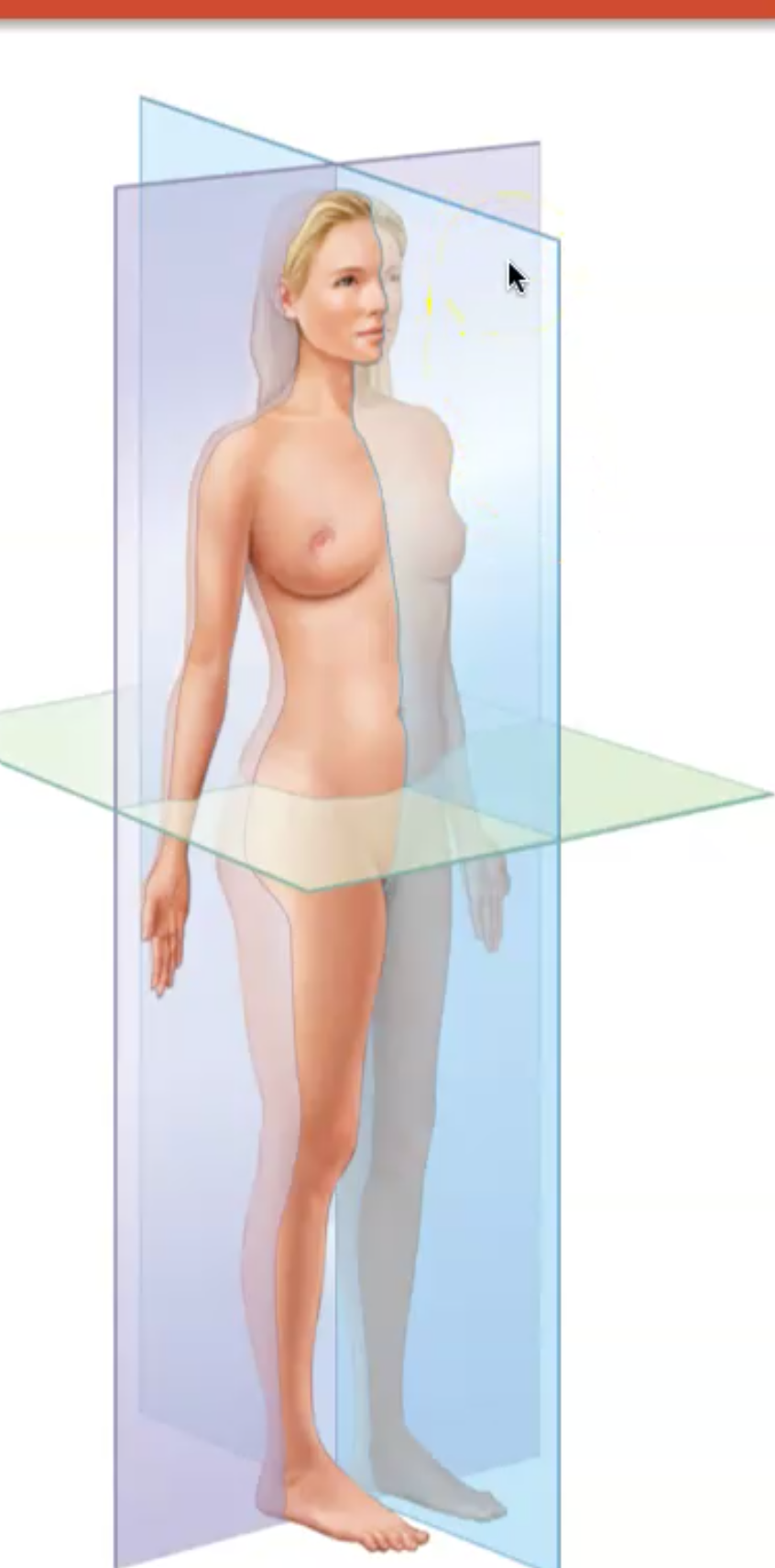
What is a Frontal Plane
What is a Frontal Plane
Divides the front of the body from the back of the body, anterior and posterior pieces
20
New cards
Chapter 1
What is it called when you divide the front of the skull from the back of the skull?
What is it called when you divide the front of the skull from the back of the skull?
coronal
21
New cards
Chapter 1
What are body cavities?
What are body cavities?
The space left when organs are removed
22
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the two functions of body cavities
What are the two functions of body cavities
protecting delicate organs and allow changes in size and shape of organs
23
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the 2 main body cavities
What are the 2 main body cavities
Posterior (dorsal) cavity and Anterior (ventral) cavity
24
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the subdivisions (the cavities of) the posterior cavity
What are the subdivisions (the cavities of) the posterior cavity
Cranial Cavity and Spinal Cavity
25
New cards
Chapter 1
What is the cranial cavity
What is the cranial cavity
the brain enclosed by the skull
26
New cards
Chapter 1
What is the spinal cavity
What is the spinal cavity
the spinal cord enclosed by spinal vertebrae
27
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the subdivisions (the cavities of) the anterior cavity
What are the subdivisions (the cavities of) the anterior cavity
Thoracic cavity and Abdominopelvic cavity
28
New cards
Chapter 1
What is the thoracic cavity
What is the thoracic cavity
enclosed by chest wall and diaphragm
29
New cards
Chapter 1
what is diaphragm
what is diaphragm
the muscle that poses as the divider for the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
30
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the subdivisions (the cavities of) the thoracic cavity
What are the subdivisions (the cavities of) the thoracic cavity
Pericardial cavity (the heart), Mediastinal cavity (trachea, esophagus, and major vessels), and the Pleural cavity (Right and left lungs)
31
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the subdivisions (the cavities of) the abdominopelvic cavity
What are the subdivisions (the cavities of) the abdominopelvic cavity
the abdominal cavity (superior) and pelvic cavity(inferior, enclosed by pelvis)
32
New cards
Chapter 1
What is inside the abdominal cavity
What is inside the abdominal cavity
liver, spleen, stomach, kidneys, pancreas, small intestine, and most of large intestine
33
New cards
Chapter 1
What is inside the pelvic cavity
What is inside the pelvic cavity
rest of the large intestine, urinary bladder, various reproductive organs
34
New cards
Chapter 1
What lines body cavities
What lines body cavities
Serous membranes
35
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the two layers of serous membranes
What are the two layers of serous membranes
Parietal Membranes and Visceral Membranes
36
New cards
Chapter 1
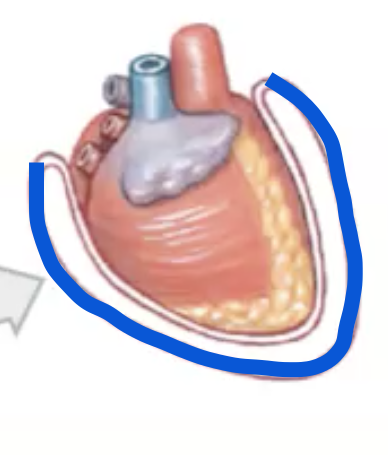
What do Parietal Membranes do
What do Parietal Membranes do
Line cavity wall
37
New cards
Chapter 1
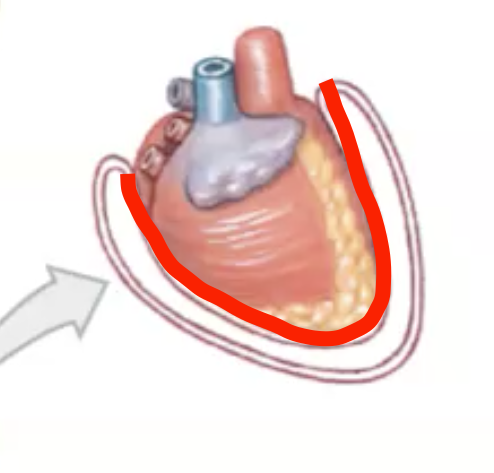
What do Visceral Membranes do
What do Visceral Membranes do
Surround the organ itelf
38
New cards
Chapter 1
What determines the name of the serous membrane lining the cavities
What determines the name of the serous membrane lining the cavities
Where they are located
39
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the names of the serous membranes lining the pleural cavity
What are the names of the serous membranes lining the pleural cavity
visceral and parietal pleura
40
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the names of the serous membranes lining the pericardial cavity
What are the names of the serous membranes lining the pericardial cavity
visceral and parietal serous pericardium
41
New cards
Chapter 1
What are the names of the serous membranes lining the peritoneal cavity
What are the names of the serous membranes lining the peritoneal cavity
visceral and parietal peritoneum
42
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the functions of cells
What are the functions of cells
they form all of the structures and perform all the vital functions
43
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the two kinds of cells
What are the two kinds of cells
Sex cells and somatic cells
44
New cards
Chapter 2
What are sex cells
What are sex cells
the product of meiosis
45
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the male and female sex cells
What are the male and female sex cells
males- sperm, females- oocytes
46
New cards
Chapter 2
What determines the function of a cell
What determines the function of a cell
Their form (what they look like)
47
New cards
Chapter 2
What is the study of cells
What is the study of cells
cytology
48
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the two parts of a cells
What are the two parts of a cells
The plasma membrane and the cytoplasm
49
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the four major functions of the plasma membrane
What are the four major functions of the plasma membrane
1. protection
2. regulation(regulates what goes in and out of cell)
3. sensitivity (responds to change outside cell)
4. allows cell-to-cell communication, adhesion, and structural support
50
New cards
Chapter 2
What is the plasma membrane made up of
What is the plasma membrane made up of
* phospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic heads stick out in the water while the hydrophobic tails stick together)
* proteins (either integrated or peripheral)
* glycolipids(used as receptors)
* sterils (cholesterol)- helps give structure and rigidity
* proteins (either integrated or peripheral)
* glycolipids(used as receptors)
* sterils (cholesterol)- helps give structure and rigidity
51
New cards
Chapter 2
The plasma membrane
The plasma membrane
Closer look
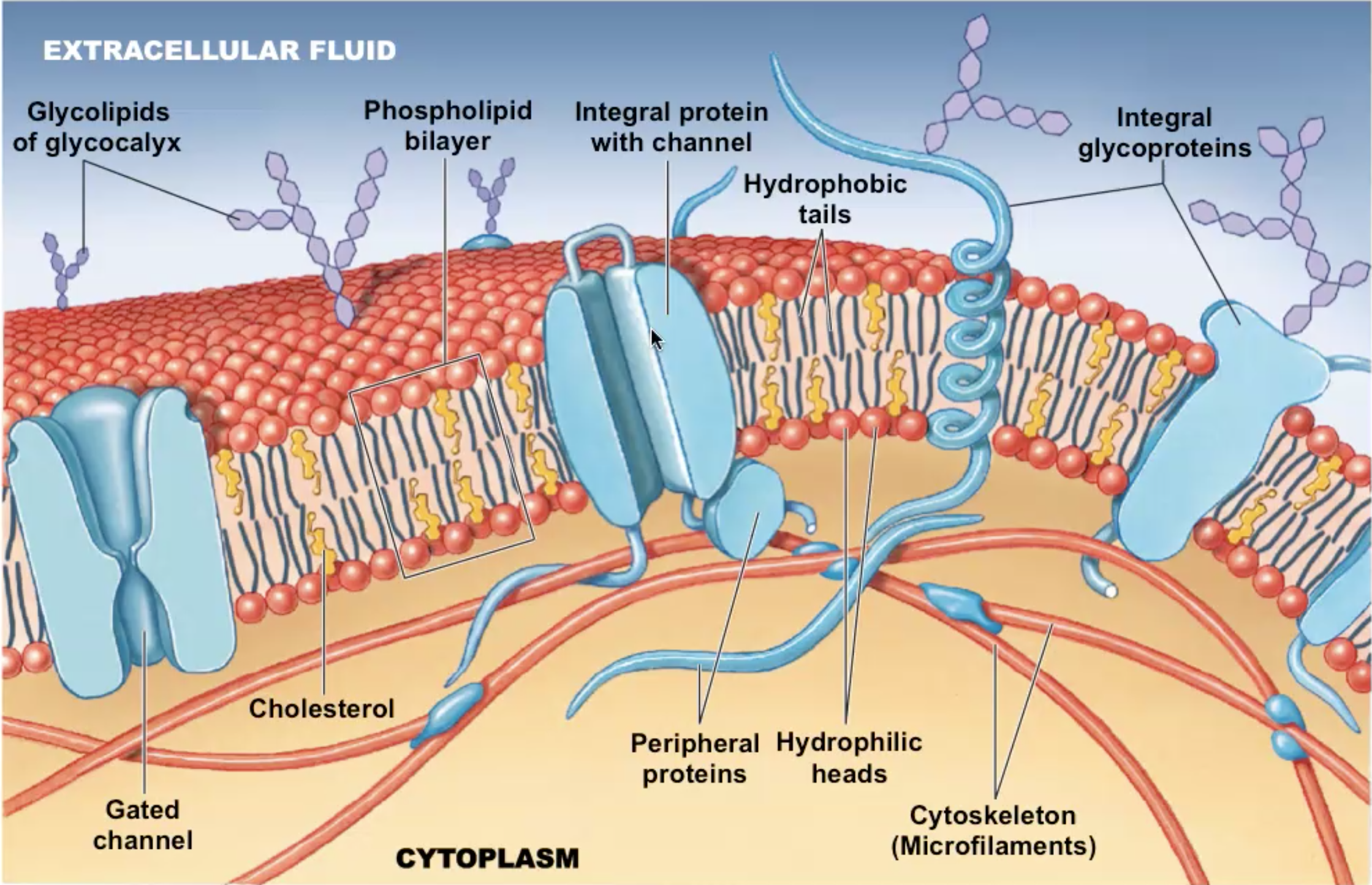
52
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the two processes of the plasma membranes permeability
What are the two processes of the plasma membranes permeability
* Passive Processes
* Active Processes
* Active Processes
53
New cards
Chapter 2
What is passive processes
What is passive processes
* Does not require ATP to occur, meaning it doesn’t need energy for materials to pass in and out of the cell
54
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the three processes of passive processes
What are the three processes of passive processes
1. Diffusion
2. Osmosis
3. Facilitative diffusion
55
New cards
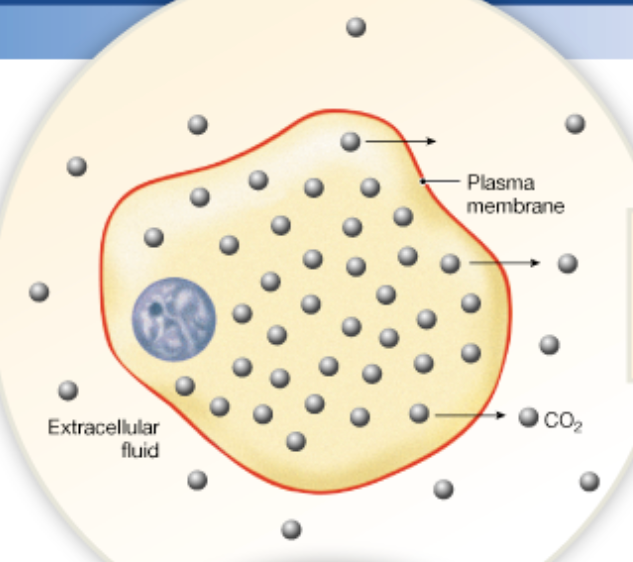
Chapter 2
What is diffusion
What is diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from and area of high concentration to and area of low concentration (concentration gradient) The movement stops at equilibrium
56
New cards
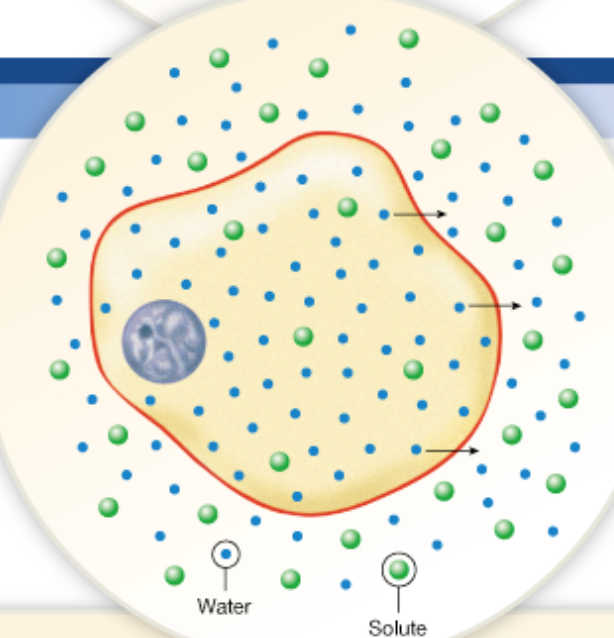
Chapter 2
What is osmosis
What is osmosis
Similar to diffusion except only water molecules are moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration
57
New cards
Chapter 2
What makes it osmosis
What makes it osmosis
water and a semipermeable membrane
58
New cards
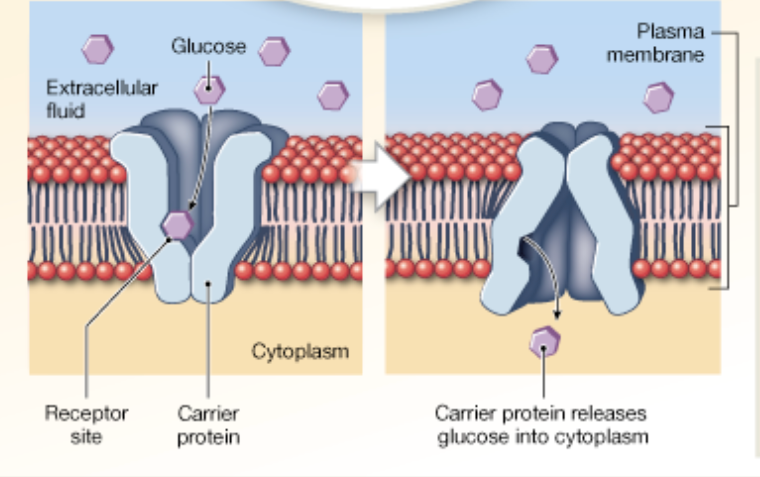
Chapter 2
What is facilitative diffusion
What is facilitative diffusion
Diffusion but a protein is needed to help move from high concentration to low concentration because the molecules are too big.
59
New cards
Chapter 2
What is active processes
What is active processes
* Requires ATP (energy)
* It goes against the concentration gradient, meaning it moves molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
* It goes against the concentration gradient, meaning it moves molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
60
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the three processes of active processes
What are the three processes of active processes
1. Active transport
2. Endocytosis
3. Exocytosis
61
New cards
Chapter 2
What is endocytosis
What is endocytosis
moves materials inside the cell
62
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the three kinds of endocytosis
What are the three kinds of endocytosis
1. pinocytosis
2. phagocytosis
3. recepter mediated endocytosis
63
New cards
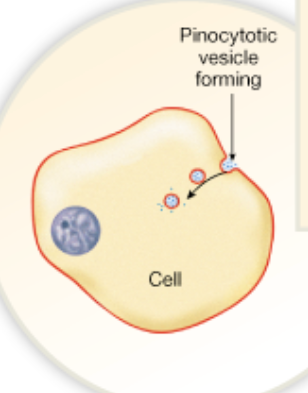
Chapter 2
What is pinocytosis
What is pinocytosis
Also known as cell drinking. it takes in some of the cellular fluid
64
New cards
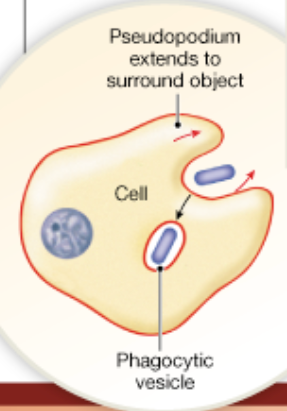
Chapter 2
What is phagocytosis
What is phagocytosis
Also known as cell eating. It takes in some solid particles of the cell
65
New cards
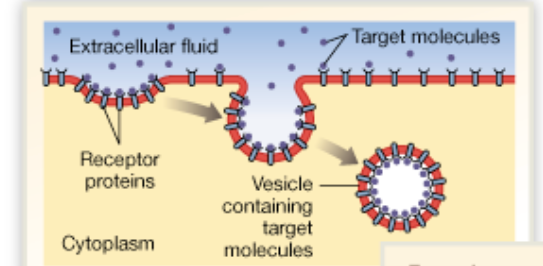
Chapter 2
What is receptor mediated endocytosis
What is receptor mediated endocytosis
Uses a chemical called ligands to bind to specific receptors on plasma membrane and cause vesicles to form and bring target molecules into cell
66
New cards
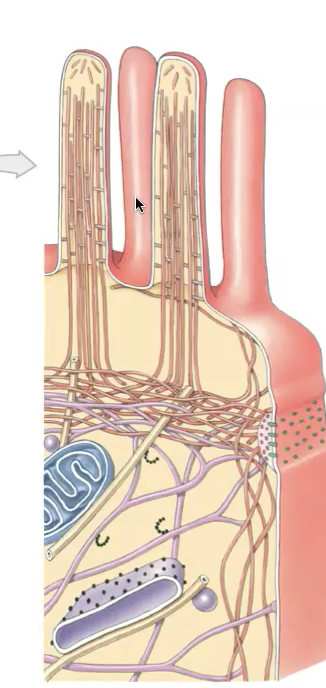
Chapter 2
What are the extensions that come out of a plasma membrane called
What are the extensions that come out of a plasma membrane called
Microvilli
67
New cards
Chapter 2
What do microvilli do
What do microvilli do
They are fingerlike projections that absorb material from extra cellular fluid, they are important for increasing surface area, which increases the amount of nutrients absorbed
68
New cards
Chapter 2
Where do you find microvilli
Where do you find microvilli
In areas where absorption is important
69
New cards
Chapter 2
What does the cytoplasm consist of
What does the cytoplasm consist of
All the intracelluar material.
1. The cytosol
2. The organelles
1. The cytosol
2. The organelles
70
New cards
What is the cytosol
It consists of the intracellular fluid. (nutrients, proteins, waste products)
71
New cards
Chapter 2
What are organelles
What are organelles
Intracellular structures that perform specific functions
72
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the two different kinds of organelles
What are the two different kinds of organelles
membranous and non membranous
73
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the nonmembranous organelles
What are the nonmembranous organelles
cytoskeleton, microvilli, centrioles, cilia, flagella, and ribosomes
74
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the membranous organelles
What are the membranous organelles
mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes
75
New cards
Chapter 2
Cytoskeleton (non membranous) Function
Cytoskeleton (non membranous) Function
* Structural support
* Anchor and stabilizes organelles
* Anchor and stabilizes organelles
76
New cards
Chapter 2
What are Cytoskeletons made up of
What are Cytoskeletons made up of
* Filaments: different sizes
* Microtubules: important for creating cilia, centrioles, and flagella
* Microtubules: important for creating cilia, centrioles, and flagella
77
New cards
Chapter 2
Why are Flagella and Cilia important (both are non membranous)
Why are Flagella and Cilia important (both are non membranous)
They are important for movement within the cell
78
New cards
Chapter 2
Why are centrioles important (nonmembranous)
Why are centrioles important (nonmembranous)
They are important for cell division
79
New cards
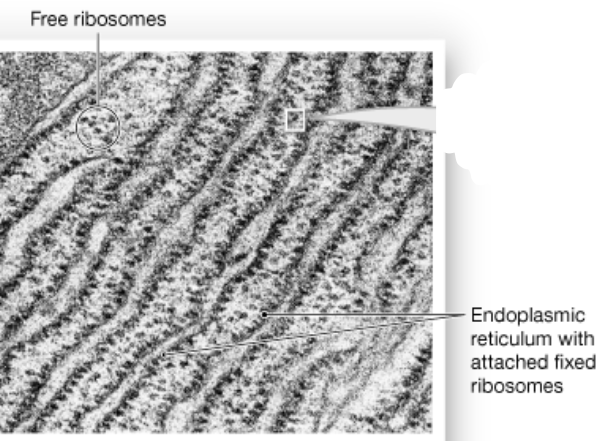
Chapter 2
Ribosome (nonmembranous) function
Ribosome (nonmembranous) function
They are the location of protein synthesis
80
New cards
Chapter 2
What are the two kind of ribosomes
What are the two kind of ribosomes
* Free ribosomes- float in cytoplasm
* Attached ribosomes- attached to endoplasmic reticulum
* Attached ribosomes- attached to endoplasmic reticulum
81
New cards
Chapter 2
Mitochondria (membranous) function
Mitochondria (membranous) function
* produce ATP via cellular respiration
82
New cards
Chapter 2
Nucleus (membranous) function
Nucleus (membranous) function
* “control center” - contains all the chromosomes of the cell
83
New cards
Chapter 2
Endoplasmic reticulum (membranous) two kinds
Endoplasmic reticulum (membranous) two kinds
* rough endoplasmic reticulum
* smooth endoplasmic reticulum
* smooth endoplasmic reticulum
84
New cards
Chapter 2
Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum rough?
Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum rough?
it is studded with ribosomes
85
New cards
Chapter 2
What is the function of a rough endoplasmic reticulum
What is the function of a rough endoplasmic reticulum
protein synthesis
86
New cards
Chapter 2
What is the function of a smooth endoplasmic reticulum
What is the function of a smooth endoplasmic reticulum
carbohydrate and lipid synthesis
87
New cards
Chapter 2
What is the golgi apparatus (membranous)
What is the golgi apparatus (membranous)
* stores, refines, and sends products
88
New cards
lysosomes and peroxisomes (membranous)
PROBABLY NOT NEEDED FOR THE EXAM.
PROBABLY NOT NEEDED FOR THE EXAM.
* lysosomes: carry enzymes for digestion
* peroxisomes: carry hydrogen peroxide to break down compunds
* peroxisomes: carry hydrogen peroxide to break down compunds
89
New cards
What is intracellular attachment
How cells attach together in order to make tissues
90
New cards
What are the 2 different ways of cell attachment
1. Cell adhesion molecules (CAMS): transmembrane proteins that buckle cells to each other
2. Cellular cement (proteoglycan)
91
New cards
What are Cell adhesion molecules (CAMS)
transmembrane proteins that buckle cells to each other
92
New cards
What are Cellular cement
proteoglycans (protein sugar) that glue cells together
93
New cards
Analogy for CAMS
stapling paper; it goes through both in order to stick together
94
New cards
Analogy for cellular cement
gluing paper; liquid pastes it together
95
New cards
What are Cell adhesion molecules (CAMS) important for
making cell junctions
96
New cards
What are the three kinds of cell junctions found in body
1. Gap junction
2. Tight junctions
3. Desmosomes
97
New cards
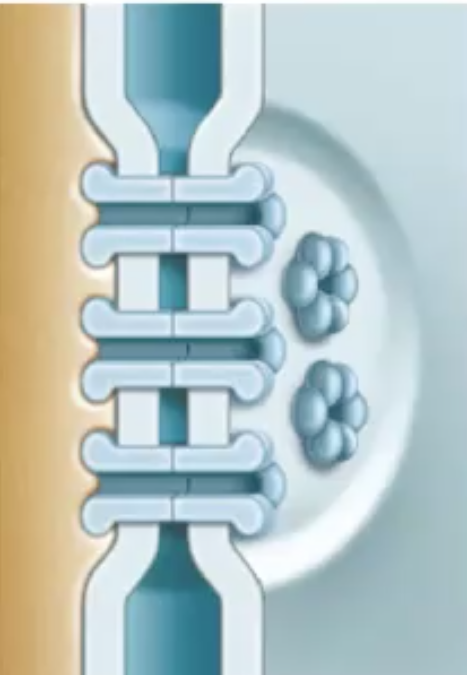
Gap junctions function
* also known as connexons
* allow for communication to occur between cells
* allows for info to be passed from one cell to the other
* allow for communication to occur between cells
* allows for info to be passed from one cell to the other
98
New cards
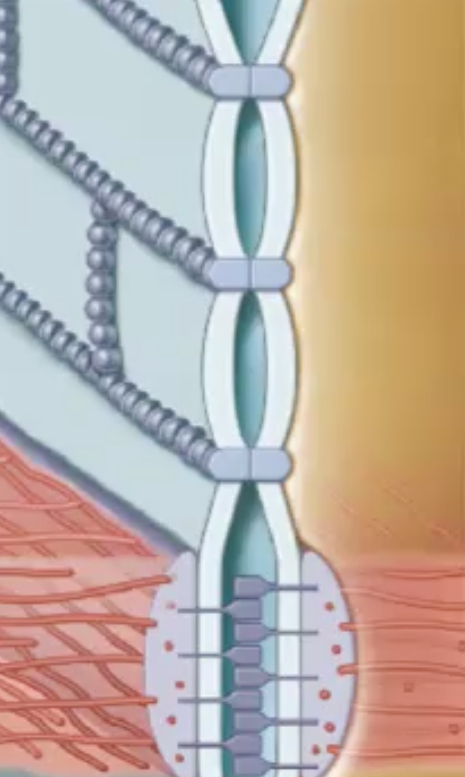
Tight Junctions function
* do not allow any communication
* they glue and hold cells to each other
* they prevent water and solute from passing in between cells
* they glue and hold cells to each other
* they prevent water and solute from passing in between cells
99
New cards
Desmosomes
* they are really strong
* have 2 different kinds
* have 2 different kinds
100
New cards
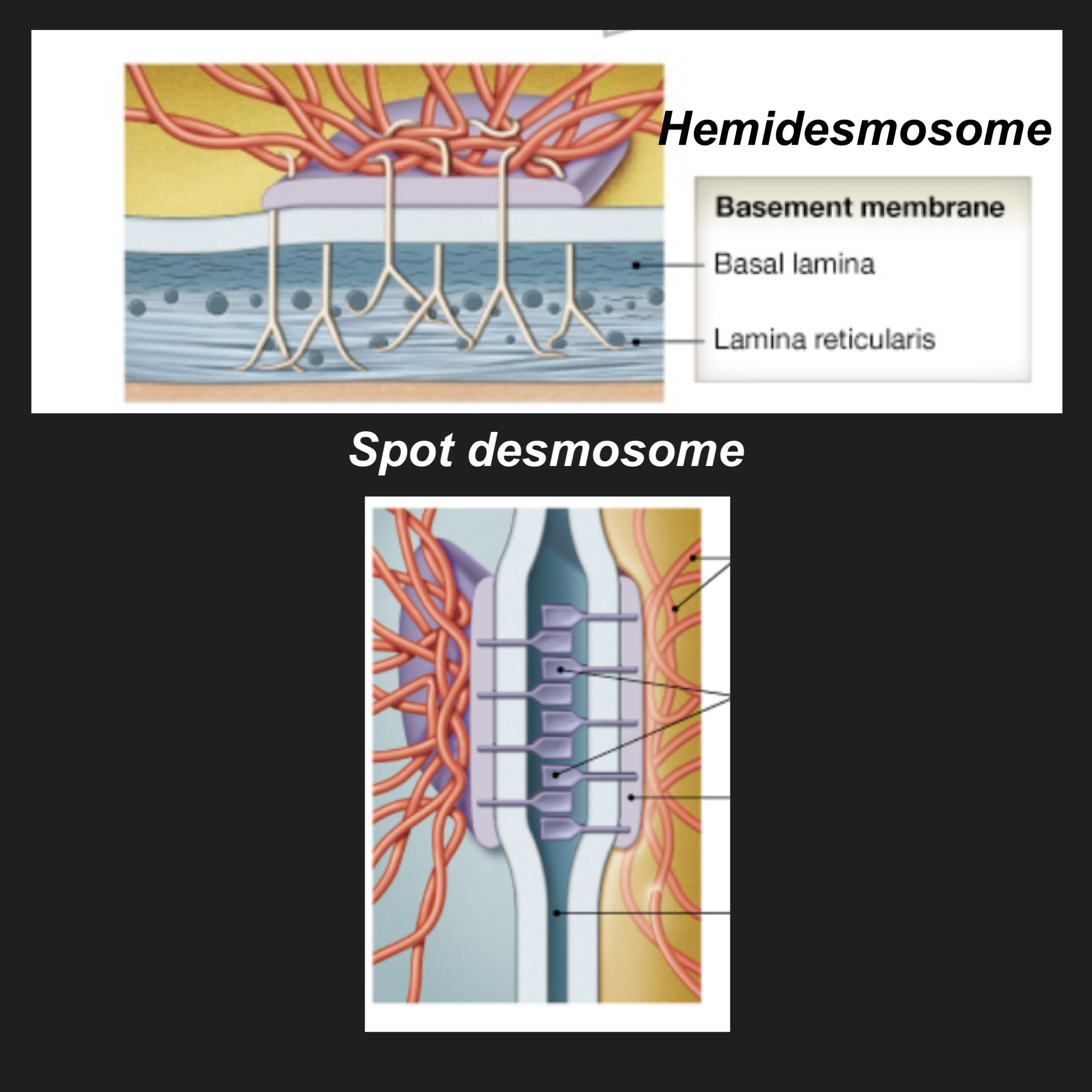
What are the two kinds of desmosomes and what do they do
1. spot desmosomes: link cells
2. hemidesmosomes: link cells to basement membranes