P4 - Radioactivity
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Why do some isotopes have an unstable nuclei, and what do they do to make it stable?
Too much mass or too many neutrons compared to protons causes this. To become stable they do radioactive decay (release radiation). This is random as you can’t predict which nucleus will decay next
What is radiation activity and what is it measured in?
Rate at which radioactive sample decays, measured in Becquerels (Bq)
What is radiation count rate?
Number of decays detected by a GM tube in one second
Why is radiation count rate smaller than radiation activity?
Not all radiation reaches detector as it spreads in all directions from source
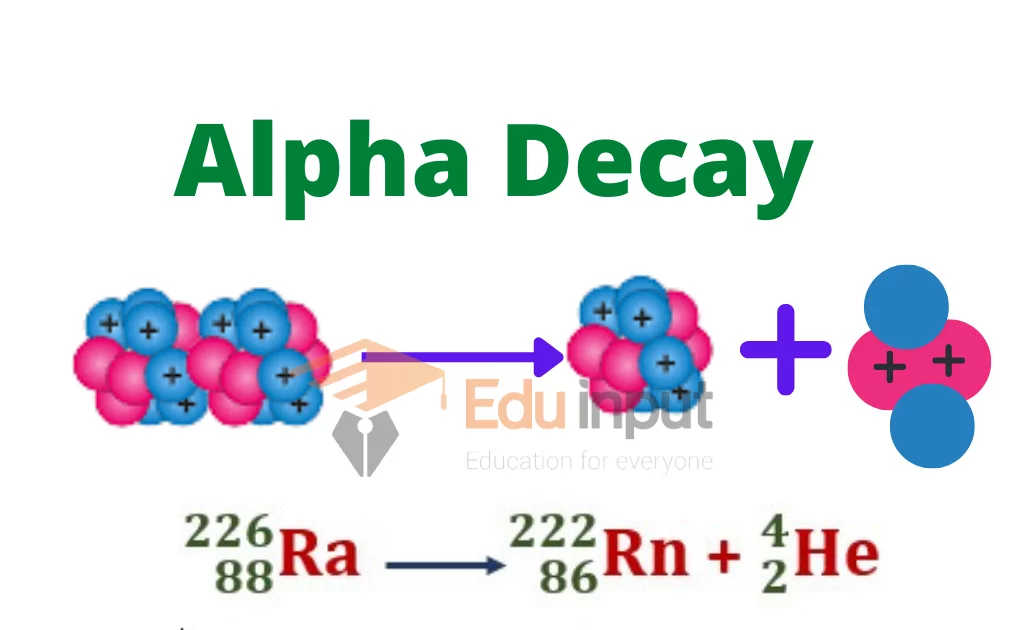
What happens during an alpha decay?
Atomic number goes down by 2 and its mass number decreases by 4
What happens during a beta decay?
Atomic number goes up by 1 and there is no change in mass
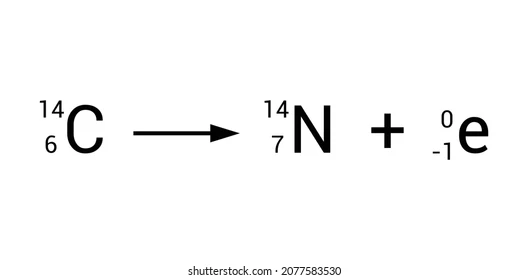
What happens during a gamma decay?
Nucleus emits gamma radiation in order to get rid of excess energy
What is half life?
Time taken for number of radioactive nuclei in an isotope to halve
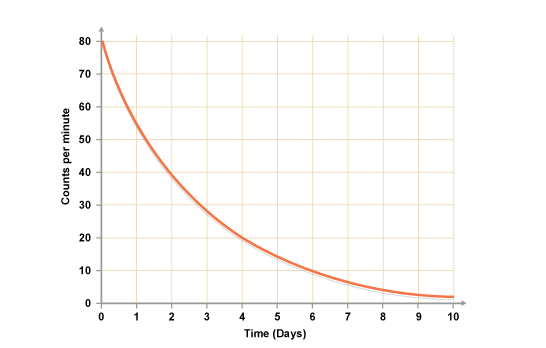
How do you calculate the half life of a material using a graph?
Find half of the maximum y axis reached by line and use that with the line to find the x axis. Judging from the graph, radioactive material has a half life of 2 days
Give some details about alpha radiation
2 protons and 2 neutrons (helium)
Positive (2+)
Low penetrating ability
Strong ionising ability
Stopped/absorbed by paper, skin, few cm of air
Deflected by a magnetic field as it has a charge
Give some details about beta radiation
Fast moving electron
Negative (-1)
Medium penetrating ability
Weak ionising ability
Stopped/absorbed by a thin piece of metal, few metres of air
Deflected by a magnetic field as it has a charge
Give some details about gamma radiation
Electromagnetic wave
No charge
High penetrating ability
Very weak ionising ability
Stopped/absorbed by a thick piece of lead
Can’t be deflected by a magnetic field as it has no charge
Give some details about neutron radiation
Neutron
No charge
High penetrating ability
Not directly ionising
Stopped/absorbed by a thick source of hydrogen based material, like water
Can’t be deflected by a magnetic field as it has no charge
What is irradiation?
Exposure to radiation, usually short term and alpha radiation has the least risk with irradiation as it can’t penetrate through the skin
What is contamination?
When radioactive substance is on the object or inside the body, providing more of a risk with alpha radiation as it’s already in the body and is the most ionising