UNIT 2 -BIO120
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
epithelial tissue
lines the outer surface of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels
connective tissue
provides support, protection, and connection to other tissue and organs, acts as “cellular glue”
muscle tissue
composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts
nervous tissue
specialized tissue composed of two main types of cells, neurons and glia
neurons
responsible for generating and conducting electrical nerve impulses
the main cell type in nervous tissue
glia
provides support, insulation, and nutrients for neurons
gap junctions
channels that connect two cells
hemidesmosome
a junction that connects a cell to a basement membrane
desmosomes
connect cells to adjacent cells
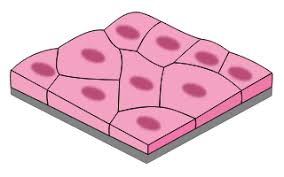
squamous
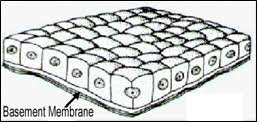
cuboidal
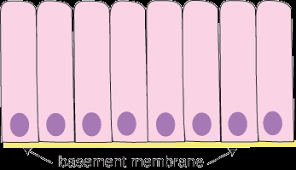
columnar
simple cell layer
a single layer of cells
stratified cell layer
made up of more than one layer of cells
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
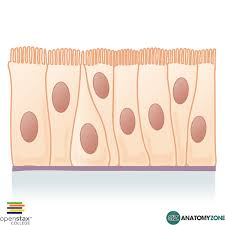
goblet cells
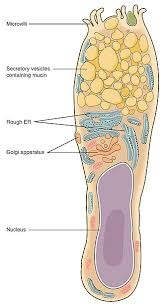
connective tissue
composed of living cells in an extracellular matrix that contains protein fibers called collagen and elastin
loose connective tissue
serves as a soft, elastic, and cushioning padding withing the body, filling space between organs and tissues and protecting them
includes areolar, adipose, and reticular
dense connective tissue
high density fibers, primary collagen, supports, protects, and hold bones, muscles, and other tissues and organs in place
includes regular, irregular, and elastic
cartilage
strong flexible connective tissue that protects joints and bones
includes hyaline, fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage
bone
hard, mineralized tissue that provides structural support, protection, and a framework for movement
includes spongey and compact bone
blood tissue
transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body
includes living cells in a liquid matrix called plasma
erythrocytes (red blood cells) lack nuclei
some white blood cells have polymorphic (multi-lobed) nuclei
hyaline cartilage
found between long bones, ex. knee joint
fibrocartilage
found between vertebrae
elastic cartilage
found in the outer ear
endocrine glands
secrets hormones directly into the bloodstream, not into the ducts
exocrine ducts
secretes substances into ducts
holocrine ducts
entire cells are shed and secreted into a duct
apocrine glands
part of each cell is shed and secreted into a duct
merocrine glands
secrete substances into ducts without cell damage
skeletal muscle tissue
muscles attached to bones that facilitate voluntary movement and maintain posture
cardiac muscle tissue (myocardium)
found exclusively in the heart, responsible for the heart’s rhythmic contractions
smooth muscle tissue
lines the walls of many internal organs and blood vessels and is responsible for involuntary movements like digestion and blood pressure regulation
dendrites
branches of a neuron’s plasma membrane
synovial membranes
inner and outer layer with synovial fluid between
ex. knee joint capsule
digestive mucous membranes
aids in digestion
ex. esophagus, stomach, and intestines
respiratory mucous membranes
protects the respiratory tract
ex. trachea, bronchial tubes
serous membranes
inner (visceral) and outer (parietal) layers with serous fluid between
ex. peritoneal serous membrane and pleural serous membrane
skin
largest organ in the body
integumentary system functions
temperature regulation, protection, and sensation
layers of the integumentary system
epidermis (outer) and dermis (inner)
epidermis
composed of stratified squamous epithelial tissue
avascular (contains no blood vessels
contains specialized cell types like keratinocytes, langerhans cells, melanocytes, and merkel cells
merkel cells
function in tactile sensation
langerhans cells
immune cells of the integumentary system
melanocytes
produce melanin pigment to protect against UV damage
keratinocytes
produce keratin protein to protect against dehydration and damage
stratum corneum
outermost layer composed of keratinized dead cells
stratum lucidum
only found in thick skin (skin of palms and soles
stratum granulosum
contains keratohyalin granules
stratum spinosum
contains abundant desmosomes and langerhans cells
stratum basale
hemidesmosomes connect epidermis to basement membrane
dermis
vascular (contains blood vessels)
papillary layer
the most superficial layer of the dermis
reticular layer
the deeper layer of the dermis
pacinian corpuscle
functions as a sensor for changes in pressure
sebaceous gland
secretes oils
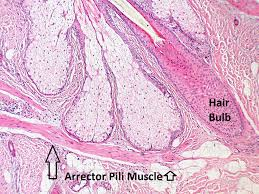
arrector pilli muscles
attach to hair follicles and cause hair to stand up (goosebumps)
composed of smooth muscle
factors in skin color
carotene, erythrocytes (blood flow), and melanocytes (melanin)
sudoriferous glands
include eccrine and apocrine sweat glands
sebaceous glands
produce oils (sebum)
ceruminous glands
produce ear wax (cerumin)
mammary glands
produce milk
hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue)
about half of total body fat is stored here
primarily composed of adipose tissue and some areolar connective tissue
hair
layers of a strand from outside to inside include cuticle, medulla, and cortex
functions of the skeletal system
stores calcium, fat and hematopoietic stem cells
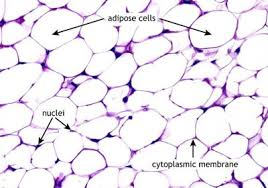
adipose tissue
a specialized connective tissue primarily composed of adipocytes (fat cells) and other non adipocyte cells
dense connective tissue
supports, protects, and holds bones, muscles, and other tissues and organs in place
red bone marrow
contains hematopoietic stem cells (develops into blood cells)
spongey bone tissue
contains red bone marrow
ex. occipital bone, pelvic bone, parietal bones, and sternum
yellow bone marrow
contains adipocytes (fat cells)
long bone anatomy
there are two epiphyses in one long bone (one on each end)
there is one diaphysis in one long bone (the shaft)
endosteum
the inner surface of the medullary cavity of a long bone
periosteum
the outer surface of a long bone
fontanelles
soft spots in a newborn’s skull where ossification is incomplete
anterior fontanelle
not fully ossified at birth
ossification
the hardening of tissue due to the deposition of mineral salts
endochondral bone formation
happens during embryonic development, where mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondrocytes
leads to the development of long bones
intramembranous bone formation
produces flat bones like those of the skull
interstitial growth
describes elongation of a long bone at an epiphyseal plate until the epiphyseal plate ossifies
appositional growth
describes an increase in the diameter of a long bone
primary ossification center
located in the diaphysis of a long bone
secondary ossification center
appears in the epiphyses of a long bone
osteoclasts
remove calcium phosphate to form the medullary cavity of a long bone
remove calcium phosphate from bone and deposits it into blood plasma
osteoblasts
deposits calcium phosphate to form bone matrix
osteogenic cells
stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts
osteocytes
mature bone cells that regulate bone remodeling through osteoblast vs. osteoclast activities
spongey bone
organized in structures called trabeculae
compact bone
dense, hard outer layer of bone tissue, providing strength and support
osteons
a central (haversian) canal with blood vessels and nerves, surrounded by concentric rings called lamellae
lamellae
contains spaces called lacunae in which osteocytes are found
volkmans’s (perforating) canals
permit fluid to move between two osteons
canaliculi
small channels connecting lacunae within an osteon
thyroid gland
secretes calcitonin in response to hypercalcemia (high blood calcium)
parafollicular cells
found in the thyroid gland and produce calcitonin
calcitonin
suppresses osteoclast activity to decrease blood calcium levels
ex. a patient with damage to thyroid parafollicular cells reducing calcitonin production is at risk of becoming Hypercalcemic (due to less suppression of osteoclasts)
parathyroid gland
secretes PTH (parathyroid hormone) in response to hypocalcemia
PTH activates osteoclasts to increase blood calcium levels.
example: A patient with a glandular tumor overproducing PTH is at risk of becoming Hypercalcemic (due to excessive osteoclast activation)
hypocalcemia
low blood calcium
hypercalcemia
high blood calcium
adipose tissue
arrector pilli