lecture 6- membrane structure and composition
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Biological membranes are responsible for _____ cells and
intracellular organelles.
delimit
Biological membranes does what? and what is it made of
enclosing or separating
layers of material made of amphiphilic molecules that act as a selective permeability barrier
What is the structure of the plasma membrane and most intracellular membranes that encapsulate organelles are described as what?
Lipid bilayer
polar head are hydrophobic or hydrophilic and they face what ?
Hydrophilic
Face the cytoplasm and the extracellular space
Fatty acyl chains tails are hydrophobic or hydrophilic and they face what ?
Hydrophobic
Face each other in the plane of the membrane
Amphipathic
Molecules containing hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains
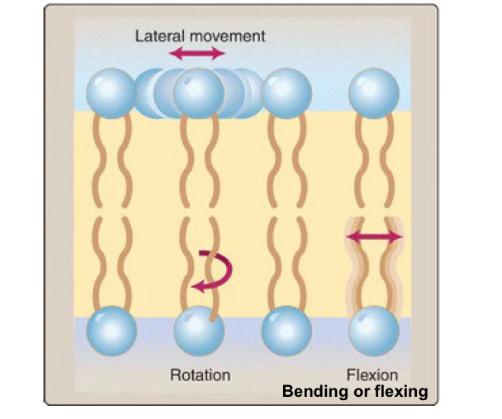
Unsaturated fatty acid tails are ___ because the kinks prevent tight packing.
more fluid
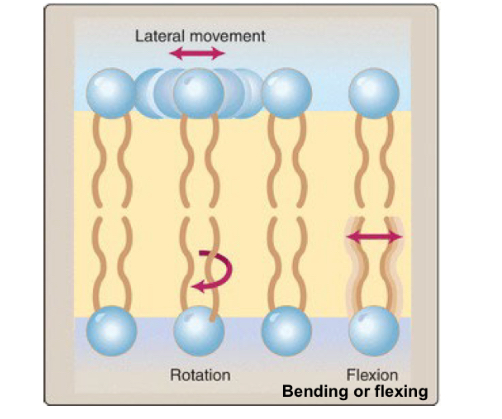
longer chains are more or less fluid
longer chains are less fluid.
Membrane lipids with saturated fatty acid tails are more ___ because they pack tightly.
Rigid
When heat is added to membrane what consistent would be seen?
Fluid like consistency
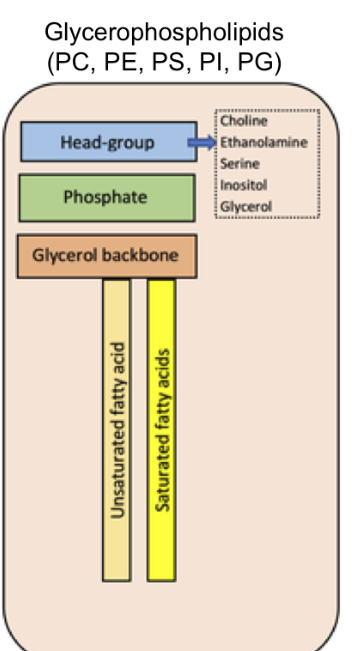
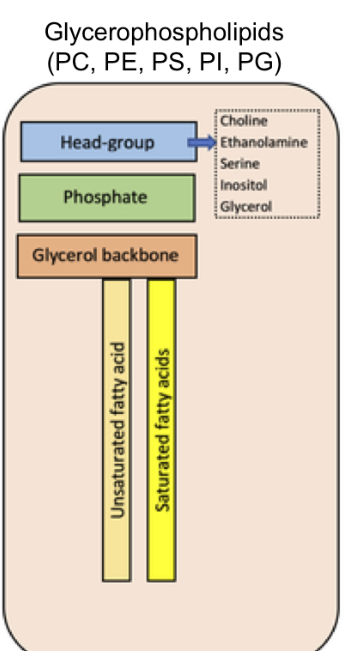
Glycerophospholipids structure
Head group with choline, ethanlamine, serine,glycerol, inositol
phosphate
glycerol back bone
one saturated and one unsaturated fatty acids
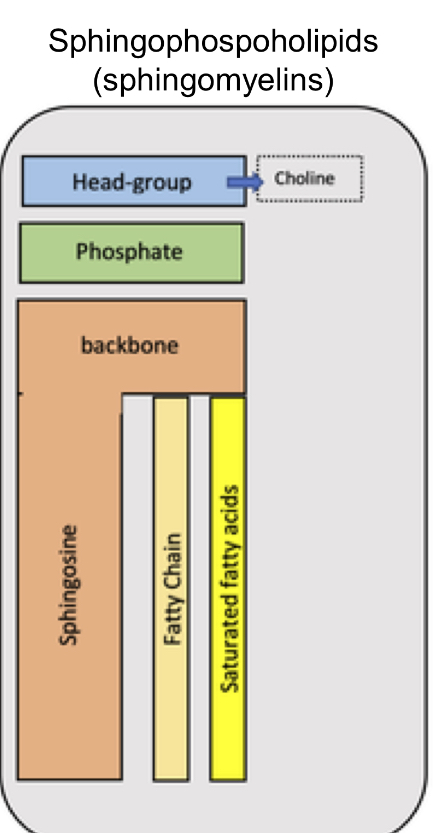
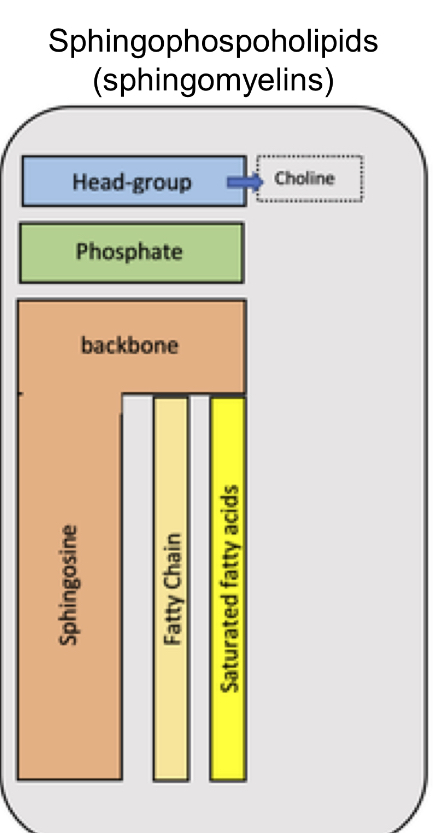
Sphingophospoholipids
(sphingomyelins) Structure
Head group with choline
Phosphate
Sphingosine Backbone
Fatty chain tail
saturated fatty acids
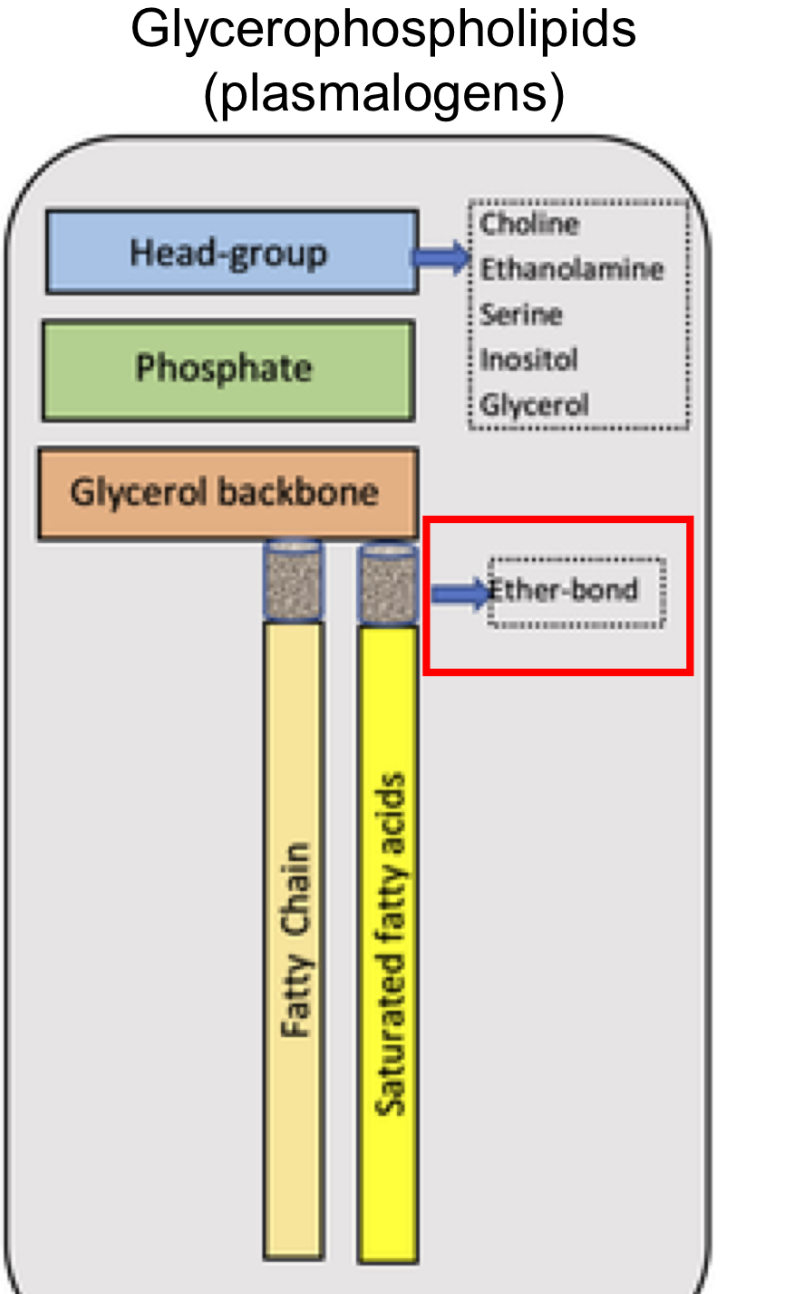
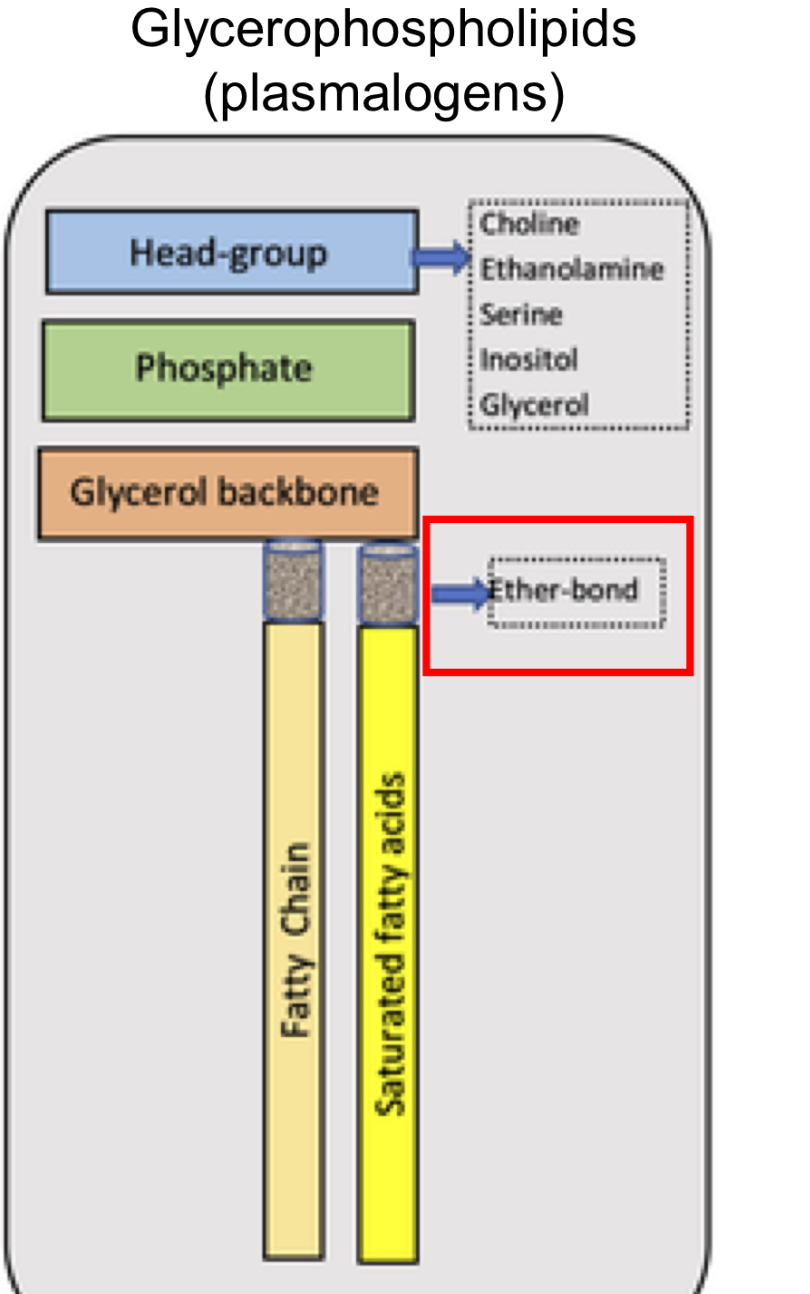
Glycerophospholipids
(plasmalogens) Structure
Head group with choline, ethanlamine, serine,glycerol, inositol
phosphate
glycerol back bone With ether bond
Fatty chain tail saturated fatty acids
Phosphatidylinositol is a key component of many what?
many signaling pathways, and is located primarily in the cytoplasmic leaflet of the plasma membrane
Pulmonary Surfactant is a ?
a surface-active lipoprotein complex formed by alveolar cells in lungs.
DiPalmitoyl-PhosphatidylCholine (DP-PC) is the ___ of surfactant, sometimes called Lecithin (a generic name for amphiphilic films).
main lipid component
DPPC ___(and allows air to inflate the lungs more easily) by adsorbing to the air-water ___ of alveoli, with hydrophilic head groups in the water and the hydrophobic tails facing towards the air.
reduces water surface tension….interface
Respiratory Distress Syndrome can occur in ____; It is the most common cause of death in premature babies.
in neonates;
The molecular basis of respiratory distress syndrome is an _____ of surfactant caused by abnormal Lecithin / Sphingomyelin ratio in amniotic fluid.
insufficiency of surfactant
Glycolipids are what?
Glycolipids are lipids with one or more carbohydrates
attached
Are glycolipids more abundant or less abundant than phospholipids ?
less
Carbohydrates of glycolipids are always oriented to face
the ___ of the cell
outside
Glycolipids are a component of the “____” on cells,
known as the ___
“coating” on cells,
known as the glycocalyx
Glycolipids participate in what interactions?
cell-cell
Sphingoglycolipids are a source of ____, and can act as receptors for toxins, such as cholera toxin and tetanus toxin
blood group antigens
• Glycolipids also protect what?
epithelial cell membranes exposed to harsh environments, such as low pH and degradative enzymes
Reduced degradation causes
Lipid accumulation diseases
Neumann pick disease
sphingomyelin in brain and RBCs
Fabry disease
Glycolipids → ceramide trihexoside in brain heart kidney
Krabbe disease
Glycolipids , particularly galaocerebroside in ogliodendrocytes
Gaucher disease
Glucocerebrosides in RBCs liver and spleen
Tay sachs disease
GM2 gangliosides In neurons
Meracheomaric leukodystrophy
Sulfatide compounds in neural tissue
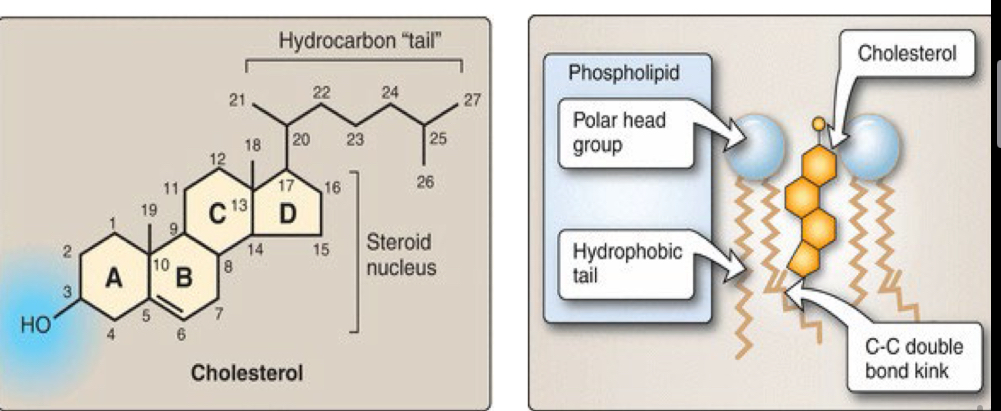
What’s the characteristics of cholesterol?
Cholesterol is also amphipathic, with a polar hydroxyl group, and hydrophobic steroid nuclei and hydrocarbon tails.
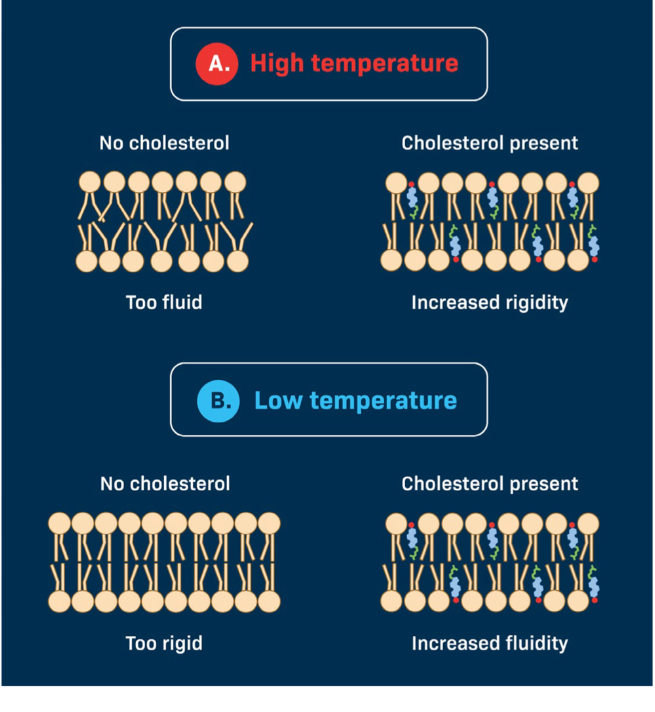
Cholesterol influences what at both low and high temperatures?
Membrane fluidity
Cholesterol does what with phospholipids ?
it “slips through” or insert itself between phospholipids and fills spaces between rails of phospholipids with unsaturated , lined fatty acid tails
Integral membrane proteins
span the entire membrane one or more times
Lipid anchored membrane proteins –
proteins with covalent attachment to a lipid
Glycoproteins –
transmembrane or lipid anchored proteins with extracellular-facing carbohydrate groups
Peripheral membrane proteins –
proteins associated with lipids (always face the cytoplasm)
Lipid-anchored proteins are also considered to be integral membrane proteins , why?
because they can only be removed from membranes by disrupting the entire membrane structure
Hydropathy plots are used for what?
to determine the overall structure of integral membrane proteins by identifying regions with a-helical segments
Integral membrane proteins associated with?
Cell-cell and cell-extracellular
matrix adhesion proteins
• Ion channels
• Transport proteins
• Hormone and growth factor
receptors
lipid anchored membrane proteins associated with ?
G-proteins – signaling, post-translational modification of effector molecules
Glycoproteins – glycocalyx, adhesion, signaling, antigenic immune regulation
Peripheral membrane proteins associated with
Cytoskeletal filaments – corralling integral and lipid-anchored proteins, “stabilizing” peripheral proteins
Enzymes – signal transduction, protein processing
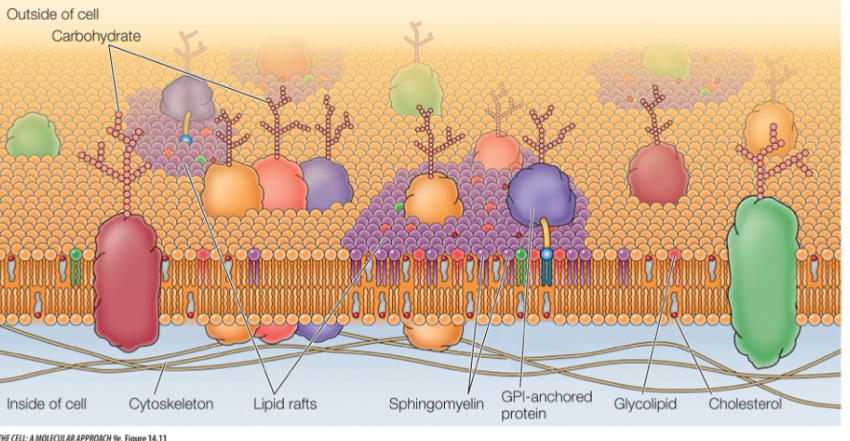
The fluid mosaic model of membranes
Although the biological membranes are stable structures, the lipids and proteins with them are relatively relatively fluid
What physical barriers restricts movement?
tight junctions, or anchoring to the cytoskeleton
Phosphatidylserine has the ability to what?
Act as “eat me “ signals to attract macrophages
What’s a plasmalogin ?
A special lipid restricted to the peroxisome
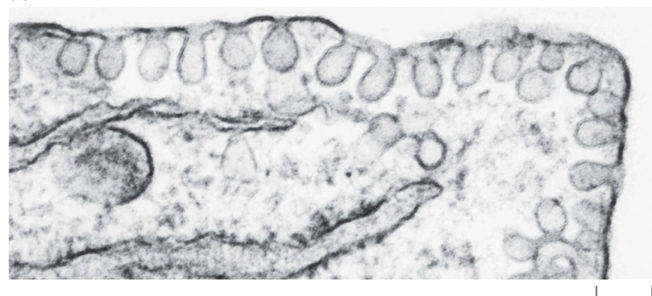
Caveolae do what
Cholesterol homeostasis
Endocytosis
Signaling
Mechanoprotection
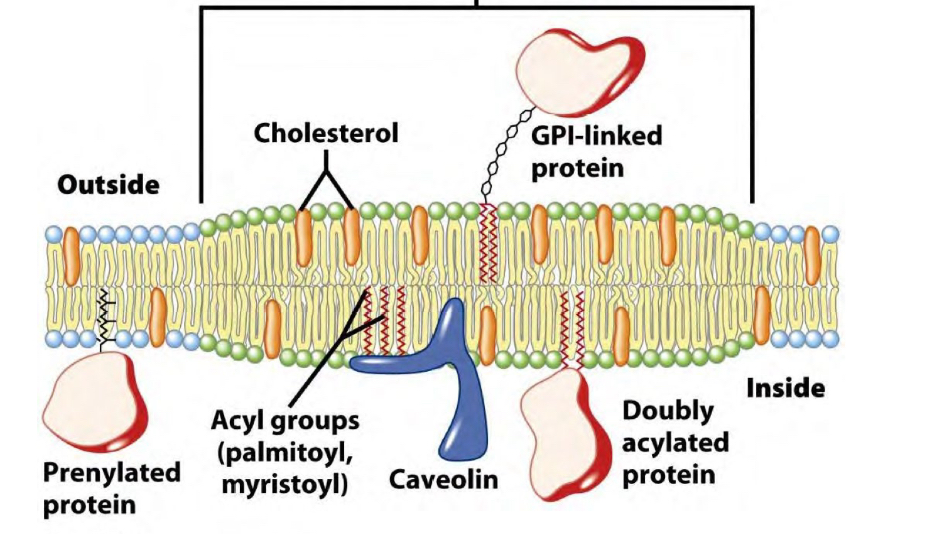
Lipid rafts have what and do what?
Enriched in shingolipids, cholesterol
Cholesterol transport
Endocytosis
Signal transduction
Molecules can be clustered Tg and considered “micro compartmentalization