Chapter 13 Diffusion
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
diffusion
the movement of atoms/ions/molecules within a material; integral to many important treatments used in the processing of materials (heat treatment, ceramics manufacture)
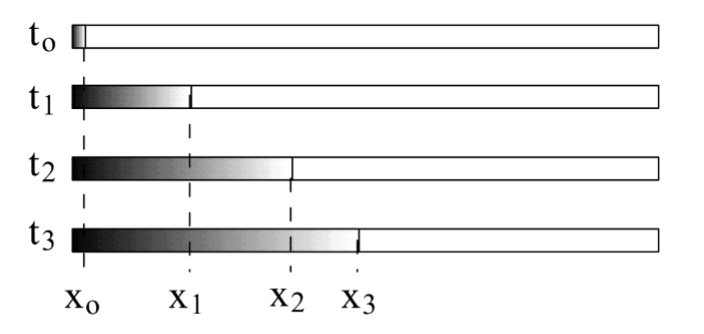
glass capillary tube
this is filled with water, and at time t = 0, add a drop of ink to one end. The diffusion distance, x, varies over time as the ink molecules move through the water molecules.
diffusion occurs in…
solids, liquids, and gases. Pure materials (self-diffusion). Impure materials (impurity diffusion, interdiffusion)
diffusion in solids, liquids, and gases
for solids, atoms not moving much → things can more at relatively high temperature
for liquids, depends on viscosity
for gases, molecules fairly far apart, so diffusion occurs rapidly
concentration gradient
before diffusion occurs, this is equal to infinity. Diffusion is very slow compared to convection, and as the material diffuses into the other, this becomes smaller.
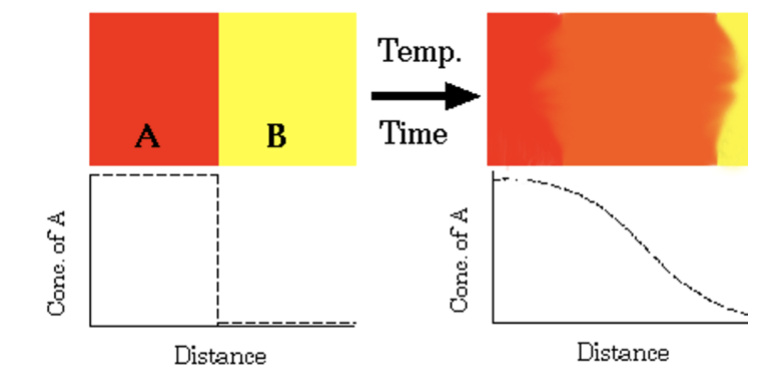
interdiffusion
a process of diffusional exchange of atoms across two materials that are in contact
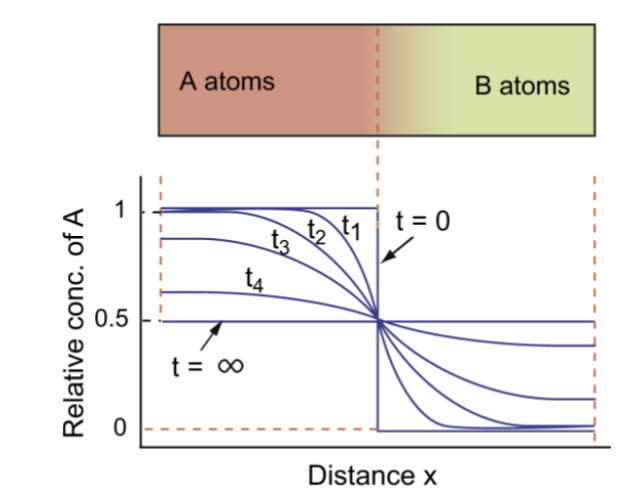
self-diffusion
Atoms move from one lattice position to another in pure solid crystalline materials by ____________ (detectable using radioactive tracers).
isotopes
Identify atoms differing only as ______ will diffuse into pure material. Some of these are radioactive and can be used as markers to track diffusion
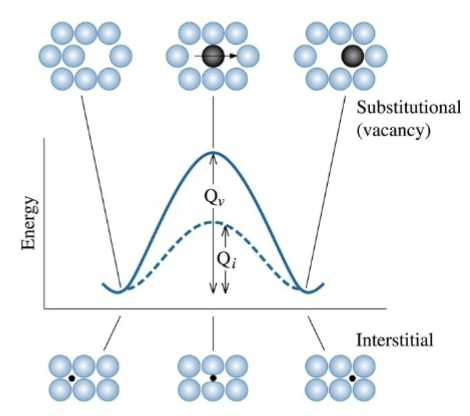
Vacancy Diffusion
Atoms jump into adjacent vacancy sites. Vacancy concentration is strongly temperature-dependent, and so is the atomic jump rate.
Happens for substitutional atoms + point defects in crystal.
Interstitial Diffusion
Small interstitial atoms can move from site to site without vacancies. More rapid.
Interstitial sites between atoms in crystals - smaller atoms can’t typically fit in these sites. Faster → smaller atoms can squeeze + moves around without distorting the crystal
opposite direction
for vacancy diffusion, only adjacent atoms can move into a vacancy, and it moves in _________ of atomic motion.
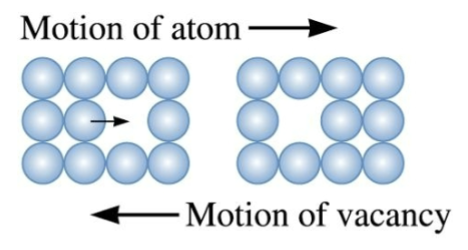
rate of vacancy diffusion
Depends on concentration of vacancies and energy of atom-vacancy exchange (frequency of jumping)
small atoms
interstitial diffusion is generally limited to __________ (eg. H, B, C, N)
They can move into any adjacent empty interstitial position
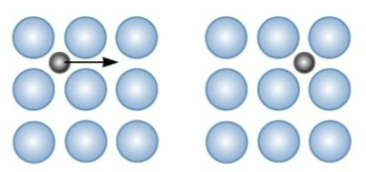
rate of interstitial diffusion
depends on concentration of interstitial atoms and energy of migration.
interdiffusion
Diffusion of copper atoms into nickel. Eventually, the copper atoms are randomly distributed throughout the nickel.
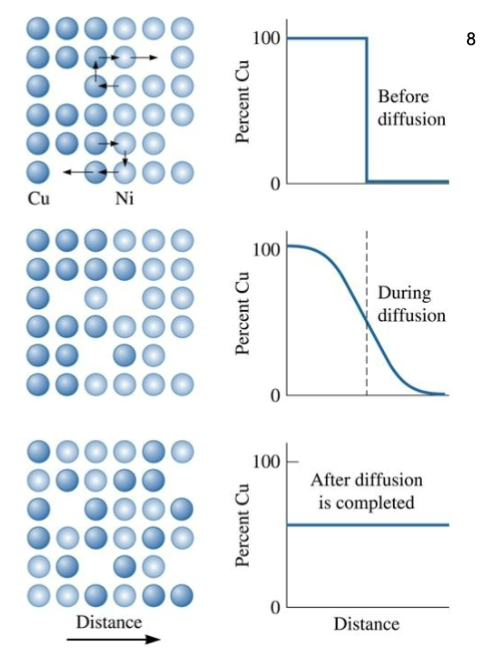
high to low
Generally, atoms migrate from regions of ______ concentration to regions of _____ concentration.
case hardening of steel gear
Diffuse carbon atoms into the host steel (iron) at the surface. The resulting C-enriched surface (the “case”) is in compression and is strong and hard. Diffusion causes significant changes in properties.
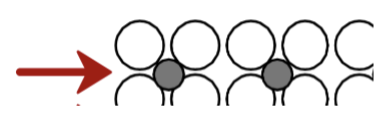
gear teeth
want to prevent wear on these; want high hardness and strength
body of gear
more tough, make it more difficult for dislocations to move by diffusing carbon atoms into the surface, so the teeth can be strengthening while this part is not
activation energy
Energy is required for an atom to squeeze past its neighbors from one low-energy site to the next. This barrier must be overcome, and heat supplies this energy. When Q is small, diffusion is easy.
increasing diffusion rate
increasing temperature does this because more molecules are at a sufficiently high energy to overcome the activation energy barrier
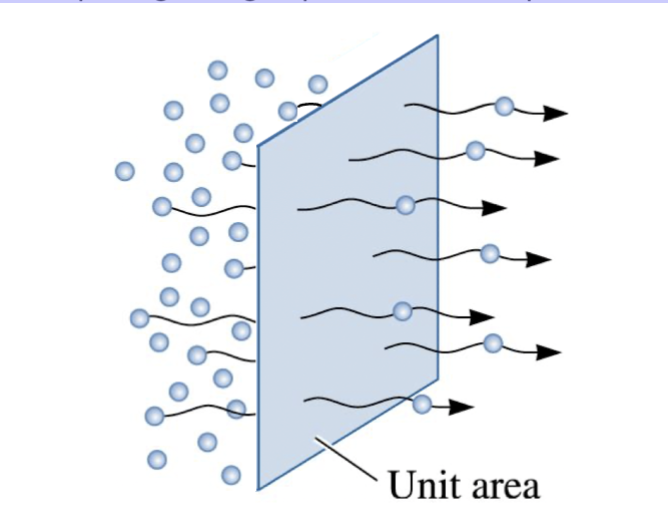
flux
The rate of diffusion is measured by the ______, J, which is the number of atoms passing through a plane of unit area per unit time
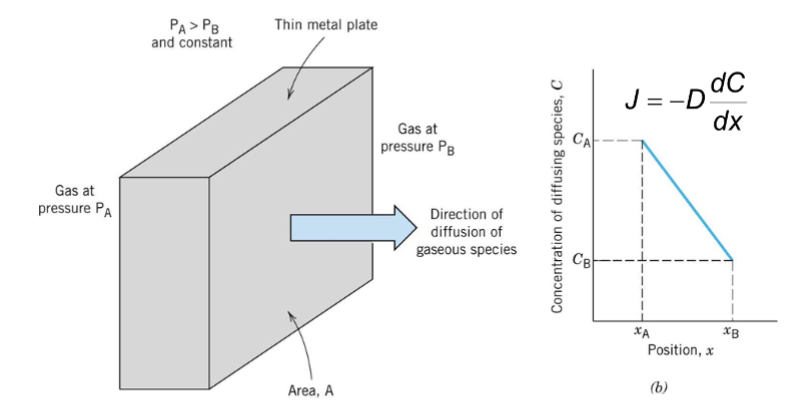
Fick’s First Law
J = -D dc/dx
J = flux (atoms/m²/s)
D = diffusivity (diffusion coefficient) (m²/s)
dc/dx = concentration gradient (atoms/m³/m)
this equation applies everywhere *assuming molecules randomly jump
flux during diffusion
defined as the number of atoms passing through a plane of unit area per unit time
concentration gradient
change in concentration with distance (slope of concentration vs. distance curve). For a given T, the flux is constant only if this is also constant.
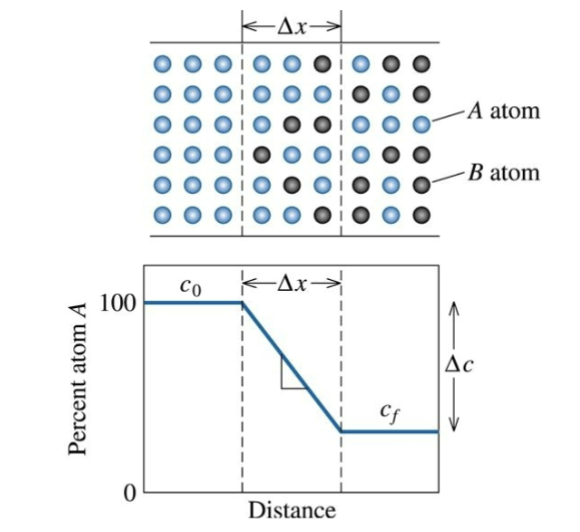
reduced with time
This is not true in typical cases where the gradient is __________, and therefore the flux decreases with time. → transient
steeper; higher
The ______ the concentration profile, the _______ the flux.
steady-state diffusion
takes place at a constant rate - that is, once the process starts the number of atoms (or moles) crossing a given interface (the flux) is constant with time.
Units of J: kg/(m²s)
purify a gas
Thin metal plate separates two regions of different pressures, and the diffusion of gaseous species allows you to do this.
mobile
atoms are _____. They may jump into a vacancy, across a grain boundary, etc. How often or how fast is dependent on temperature
thermally activated
atom mobility is _______; diffusion increases as temperature increases
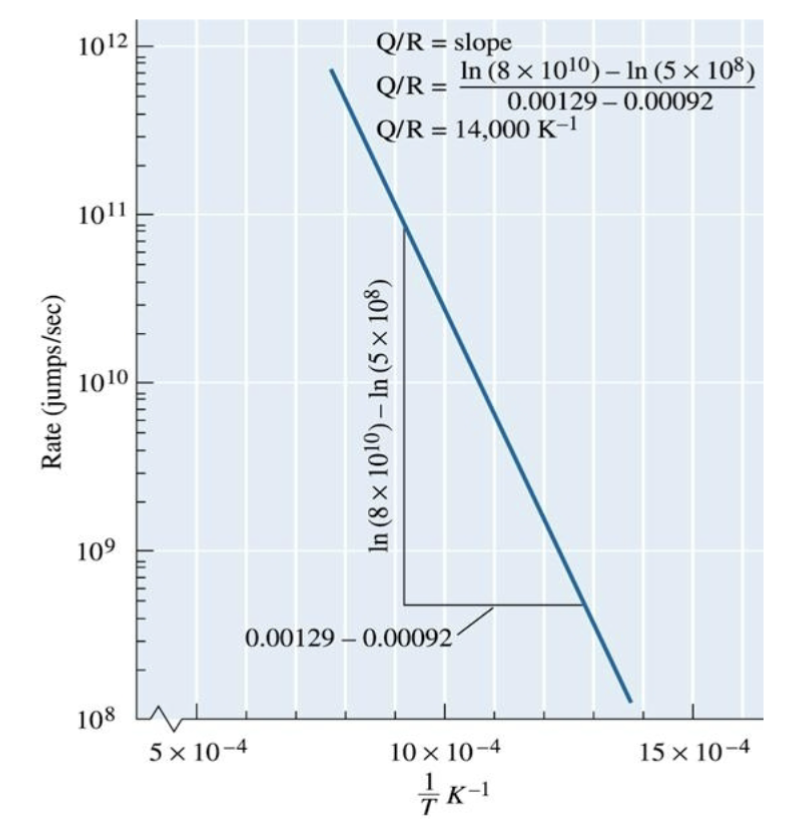
Arrhenius equation
kinetics of atom jumps are described by this
Rate = c0 exp[-Q/(RT)]
c0 = constant; e is base of natural log; R is gas constant,; T is absolute temp (K); Q is activation energy to move the atom
plotting ln(Rate) vs 1/T
slope of curve is -Q/R
ln(c0) is intercept when 1/T is zero
this graph can be used to determine activation energy required for a reaction
temperature and diffusion coefficient
D = D0 exp[-Q/(RT)]
D0 is a constant for a given system (hypothetical diffusion at infinite temperature)
![<p>D = D<sub>0 </sub>exp[-Q/(RT)]</p><p>D<sub>0</sub> is a constant for a given system (hypothetical diffusion at infinite temperature)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cb7f9828-782c-49bf-ad21-9fefa67631a3.png)
increases
as temperature _______, so does D and diffusion flux
insignificant
at low temperature, diffusion may be ________ from a practical point of view
steep slope
of a diffusion coefficient D as a function of 1/T graph, this denotes a high activation energy
characteristic diffusion distance
for a time t, given by x = √(Dt)
For a case of mixing atoms between two materials with different concentrations, this distance is the depth to which the concentration has changed by one-half of the difference in concentrations between the two materials
time required
the diffusion distance formula can also be used to estimate this to achieve a desired depth of diffusion