BIOS 1300 lab exam 1 osmosis, transport, celular structures (lab 3)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
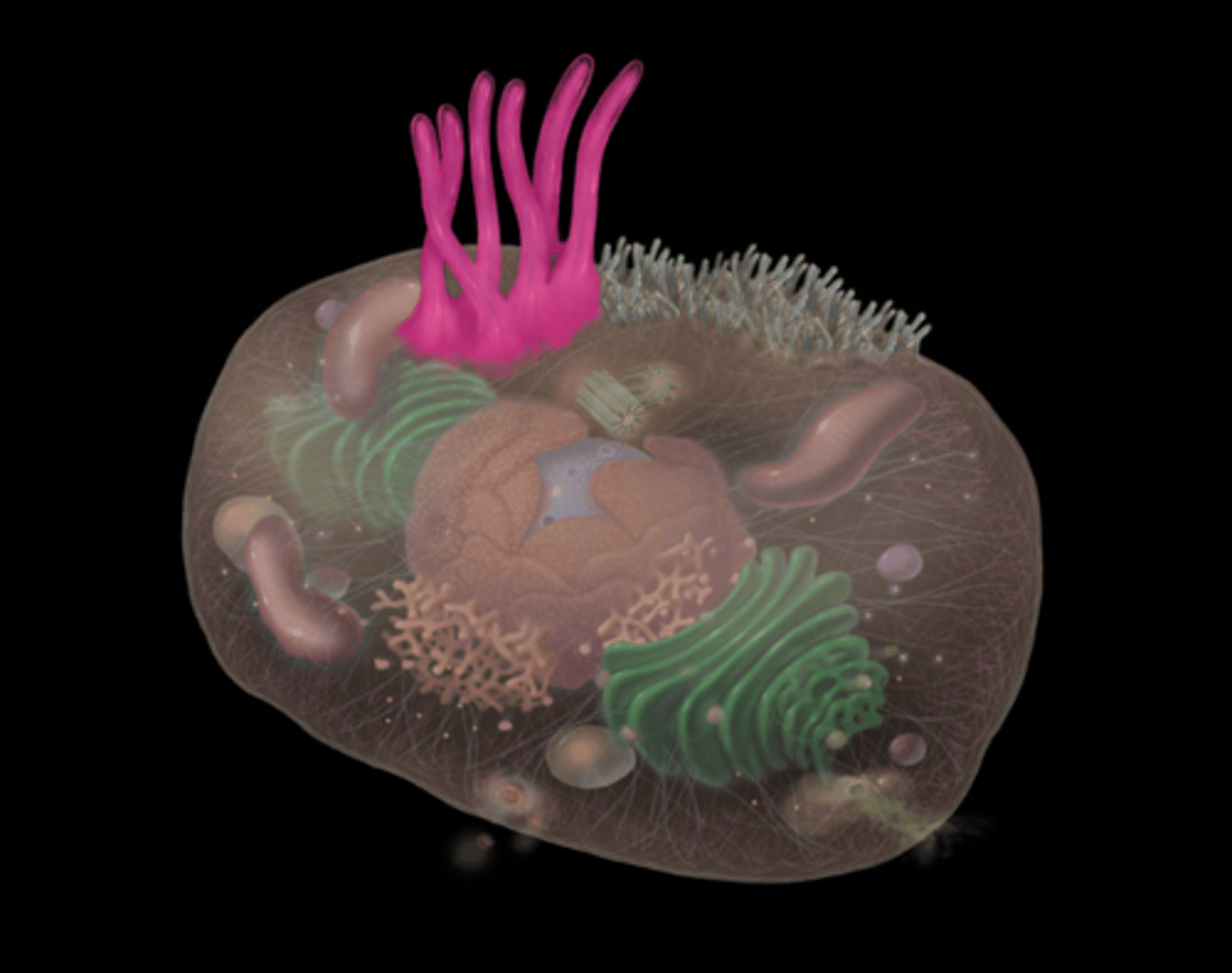
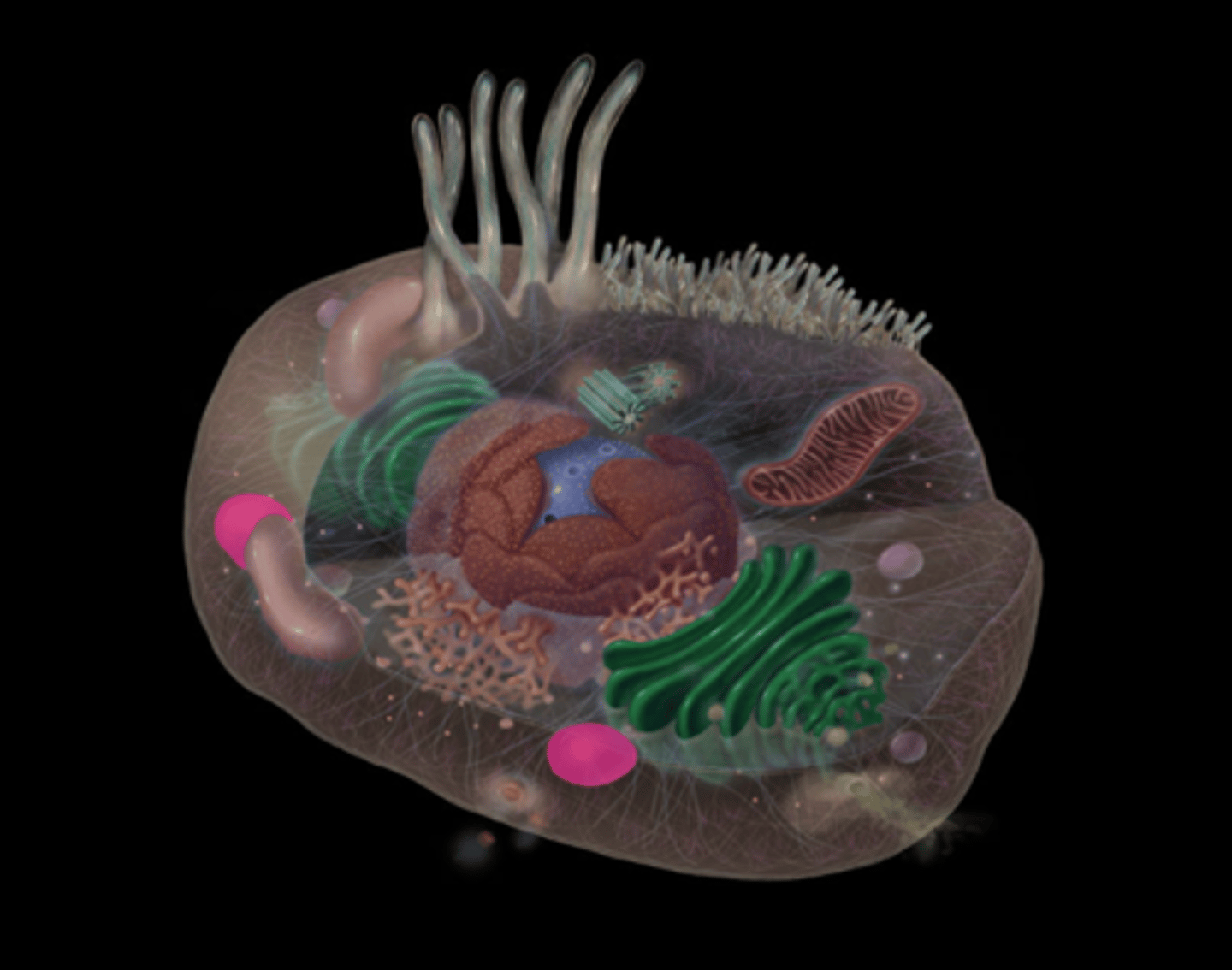
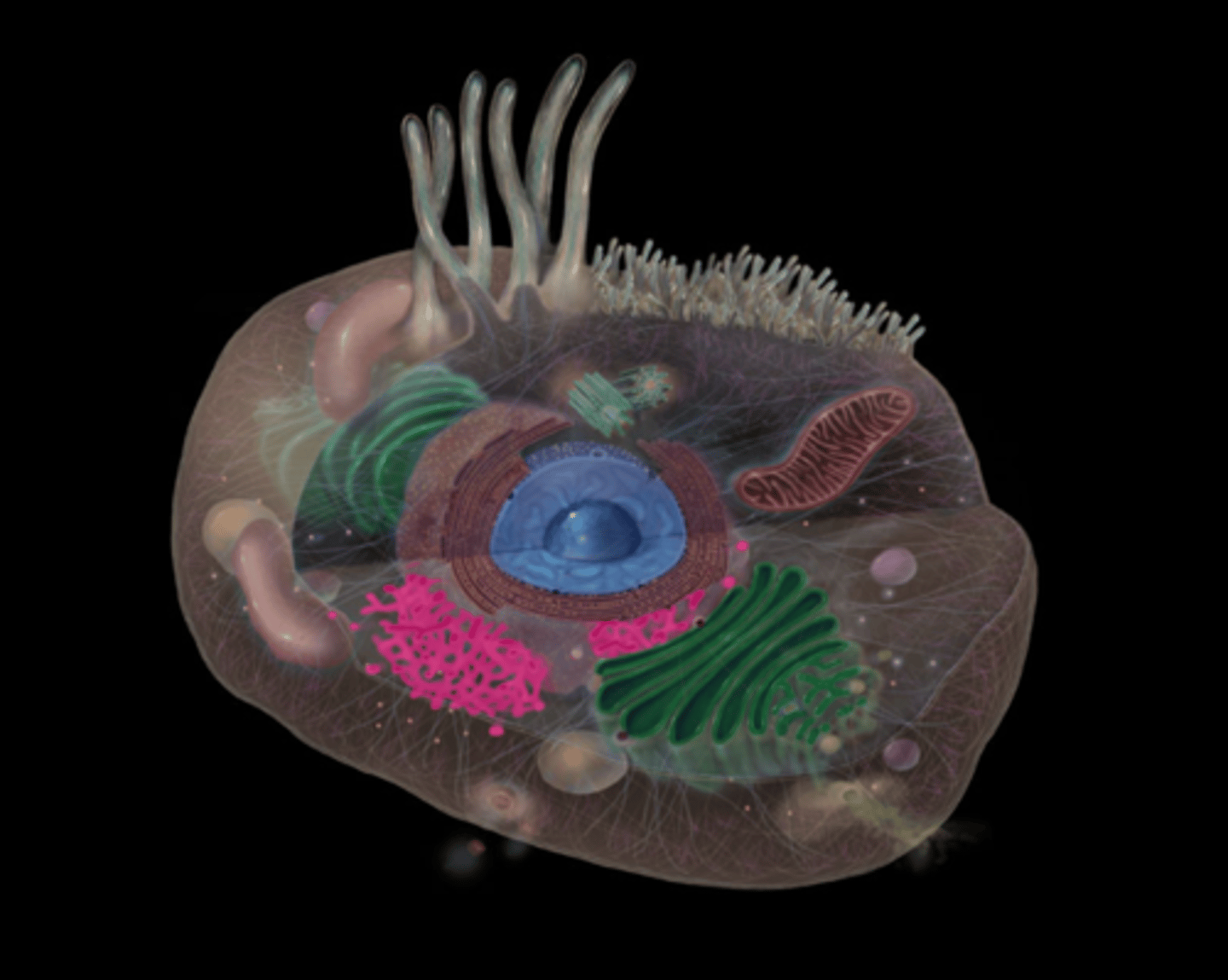
centrosomes
highlighted in pink
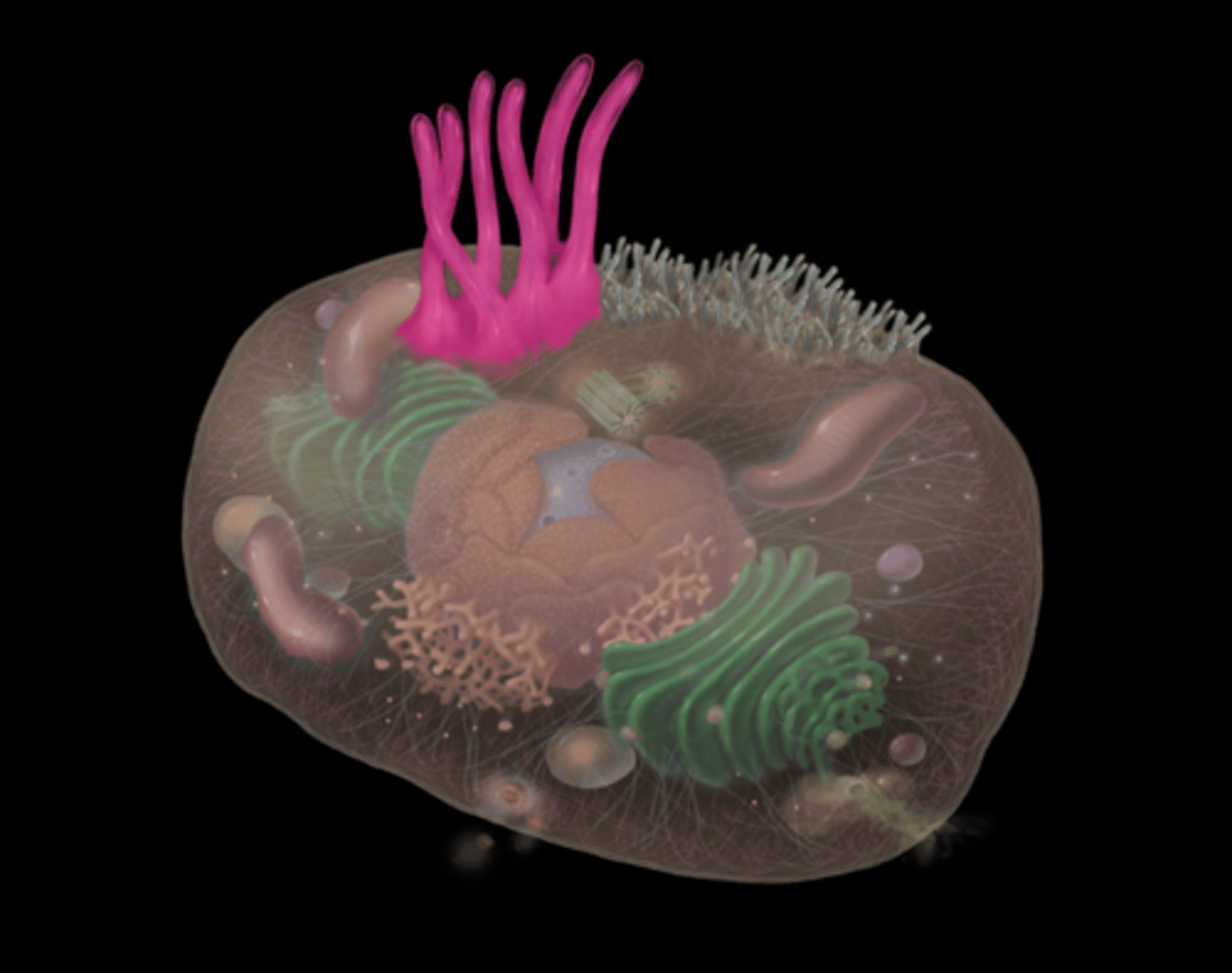
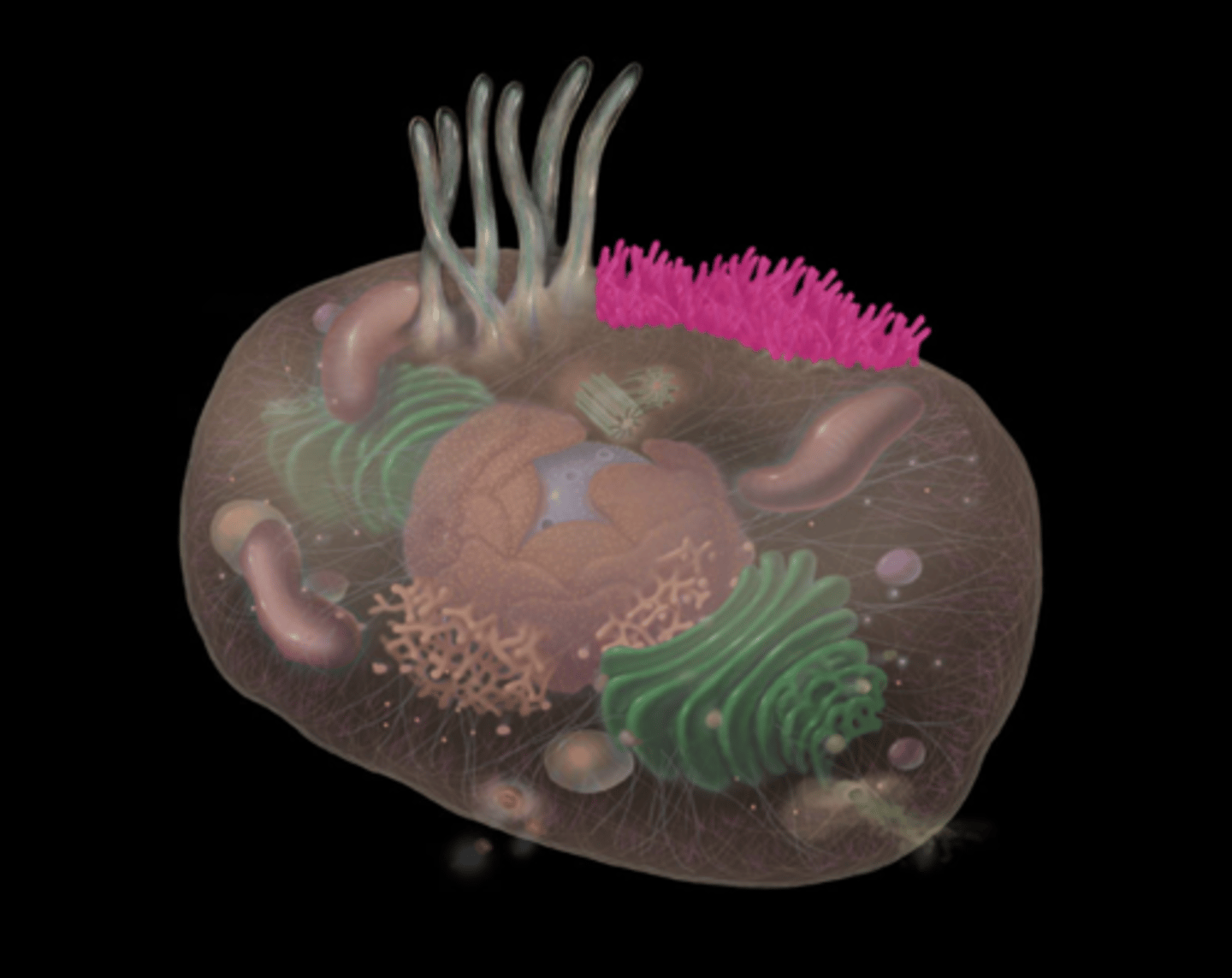
cilium
highlighted in pink
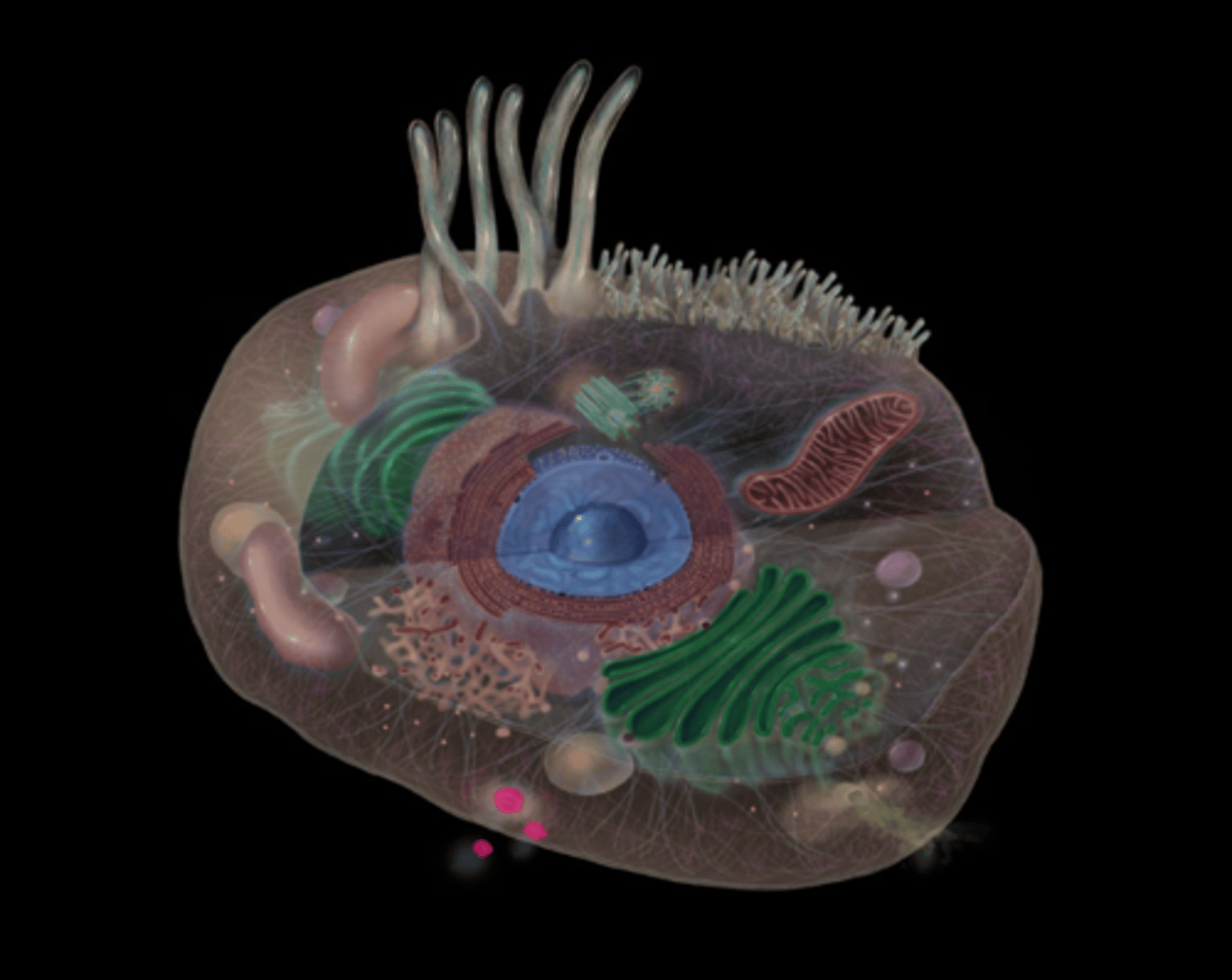
endocytic vesicles
highlighted in pink
free ribosomes
highlighted in pink
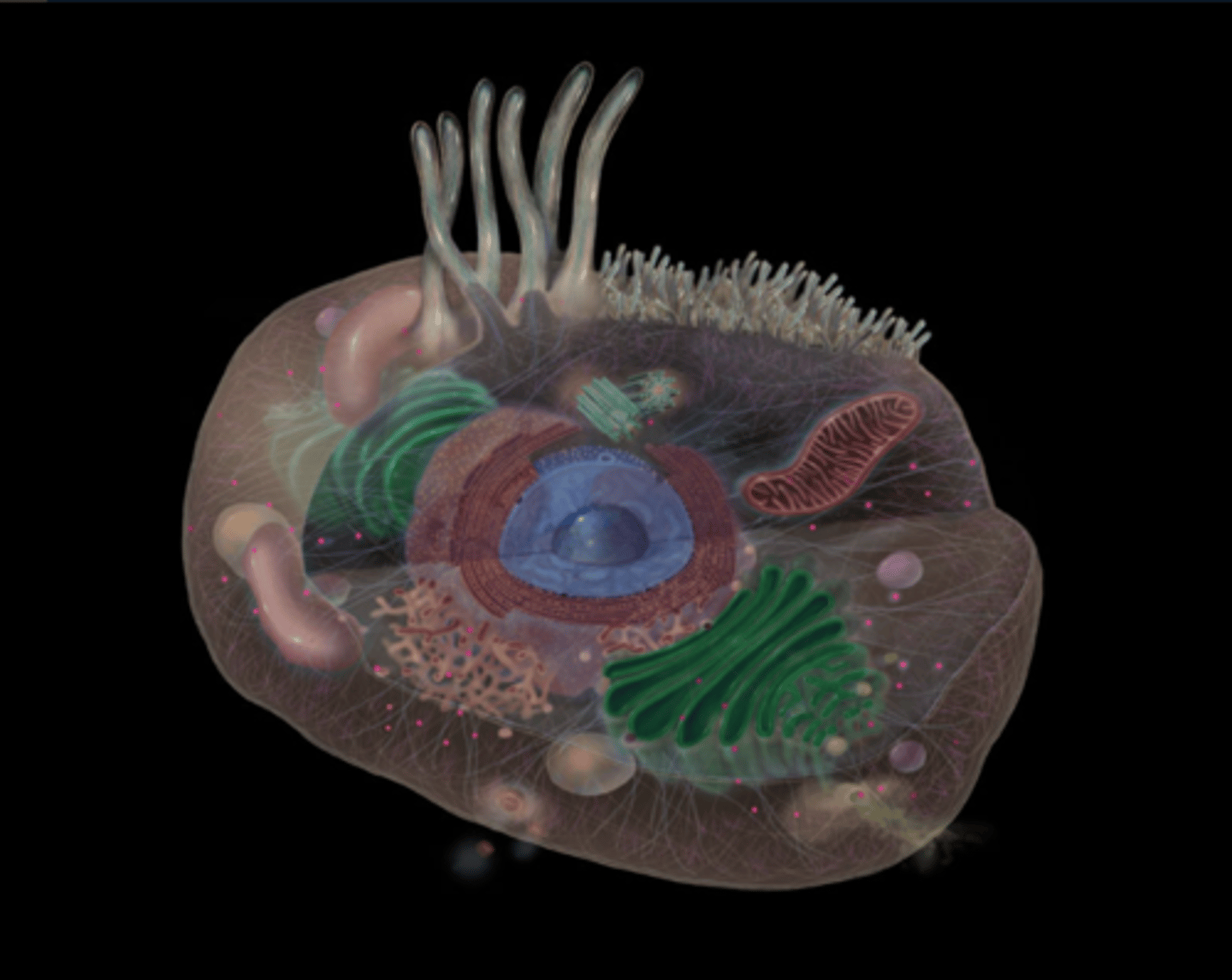
Golgi apparatus
highlighted in pink
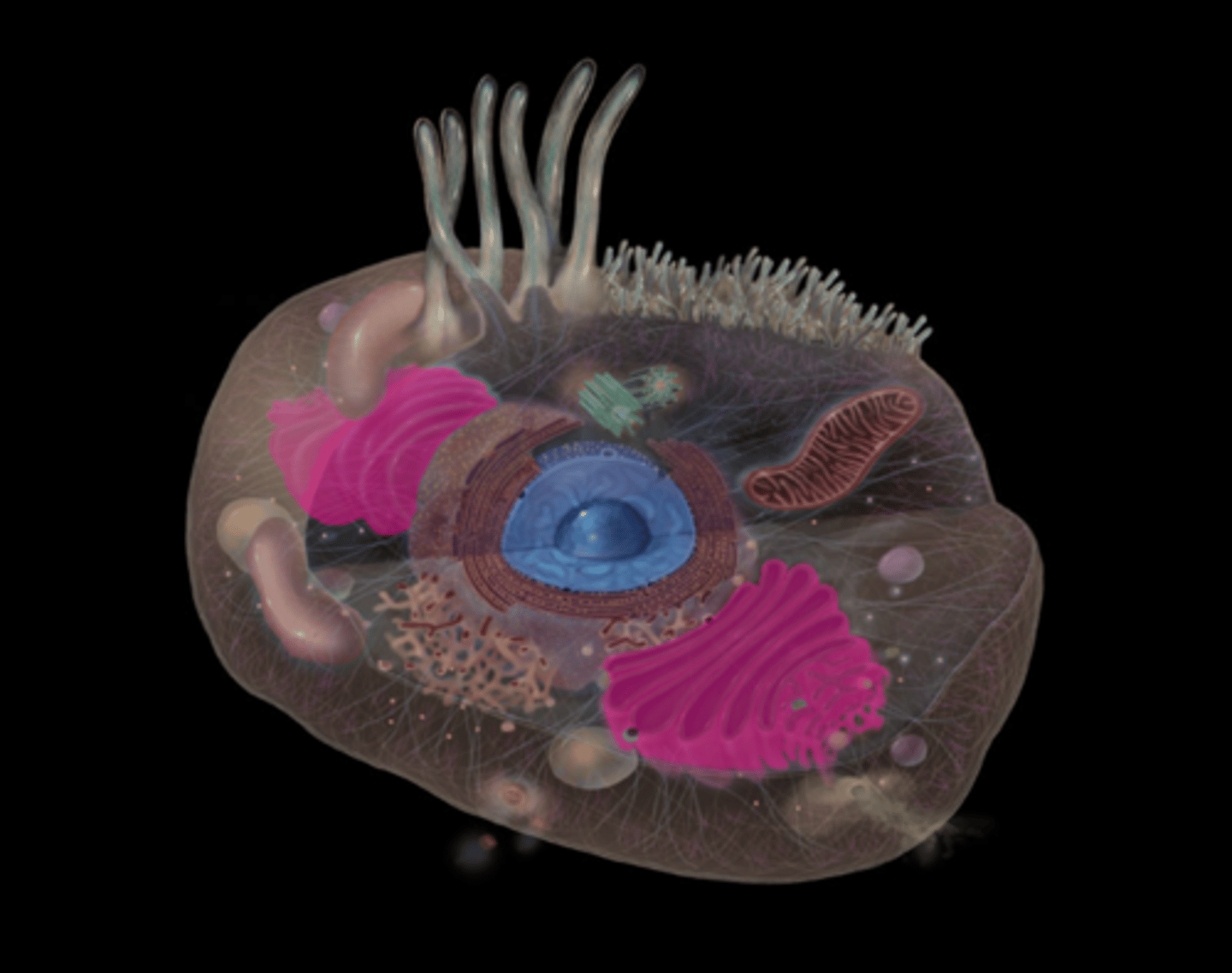
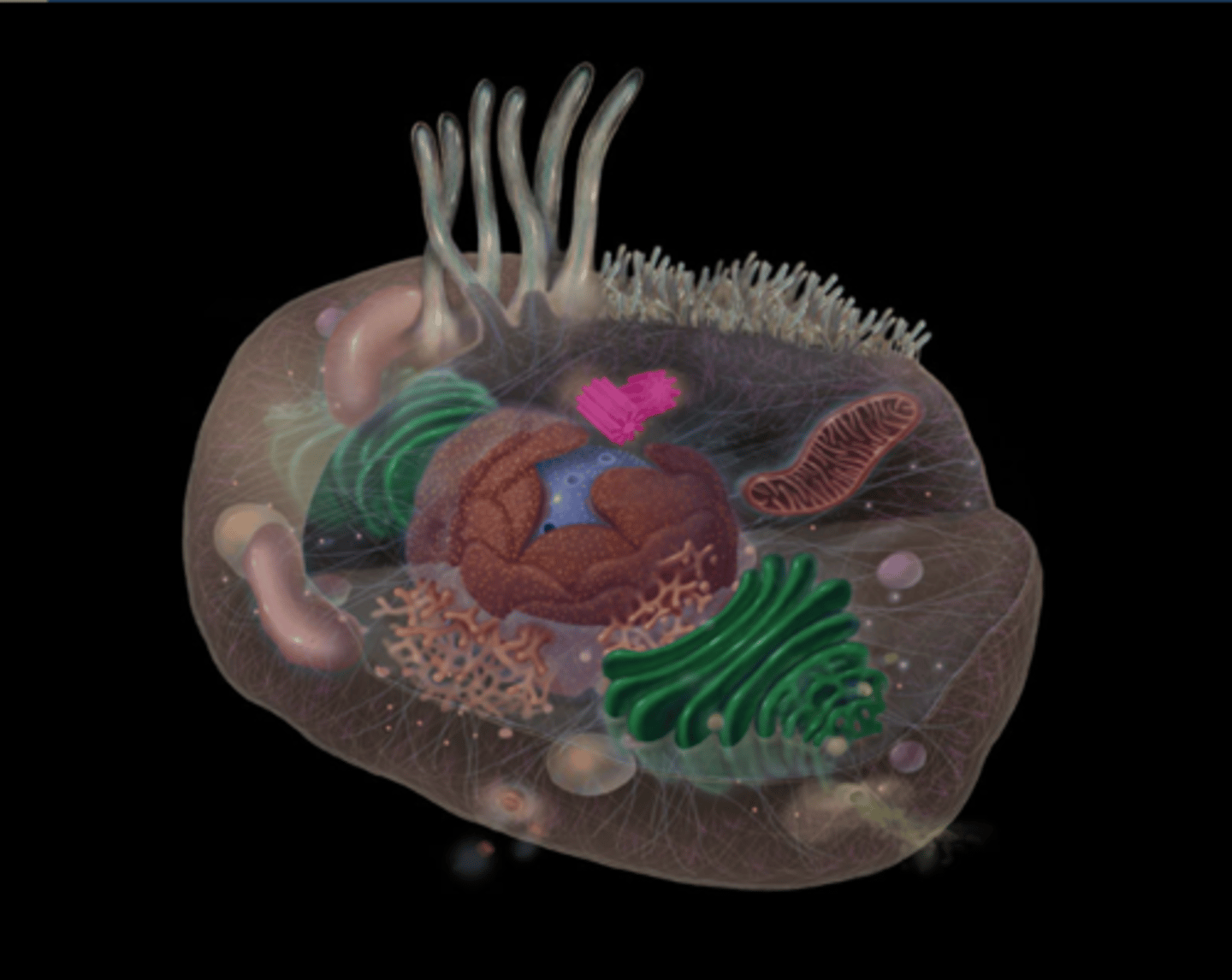
Lysosomes
highlighted in pink
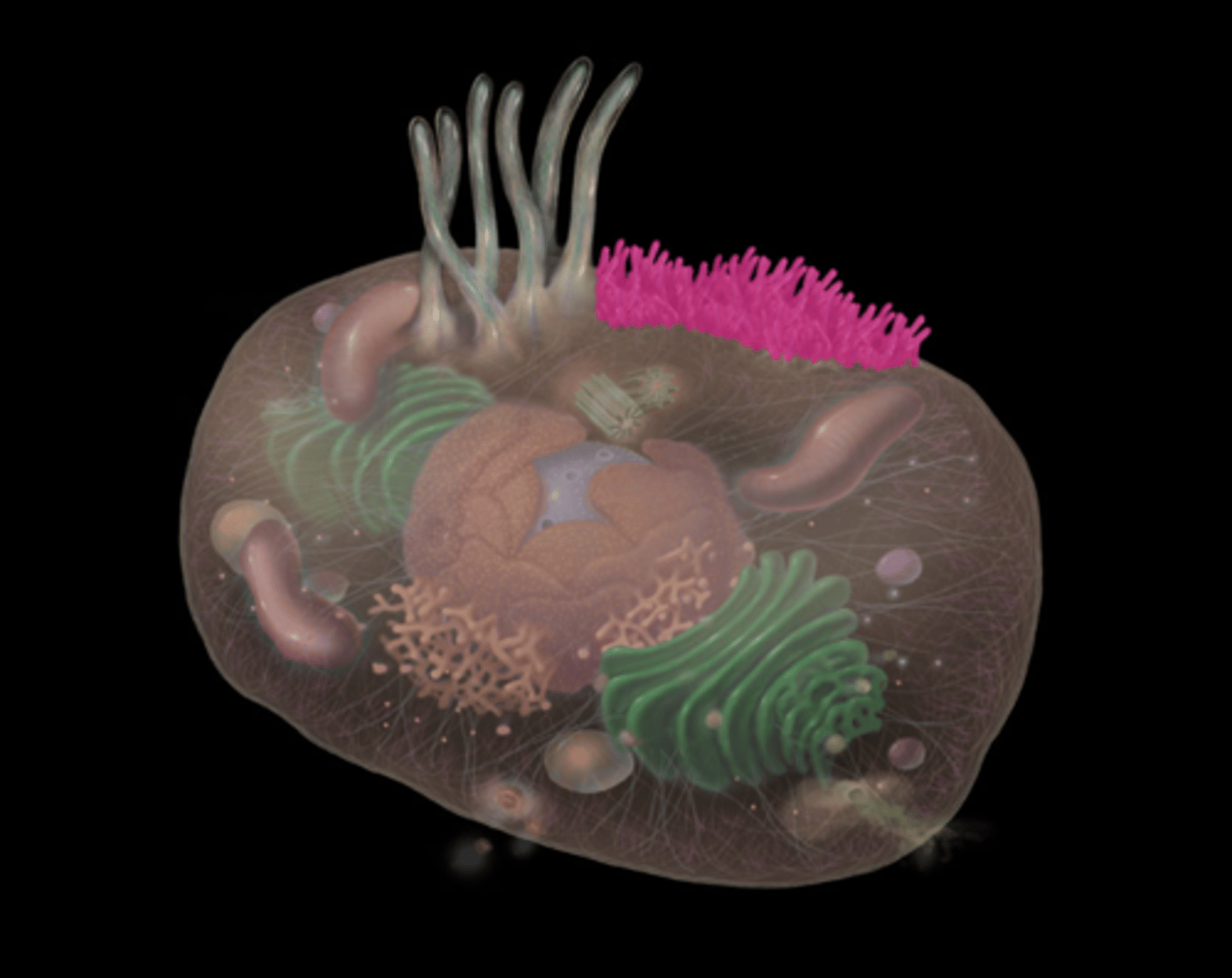
Microvilli
highlighted in pink
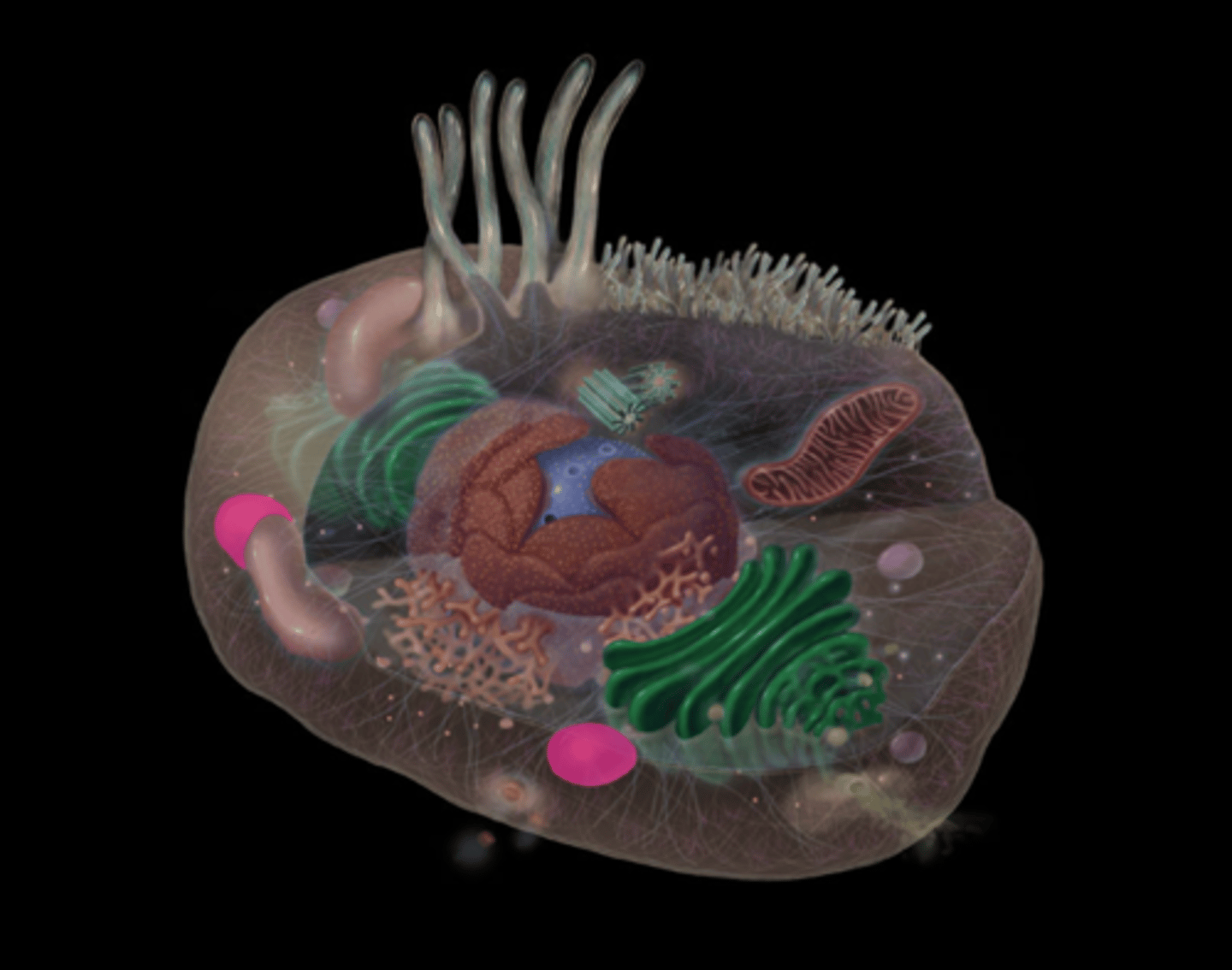
Mitochondria
highlighted in pink
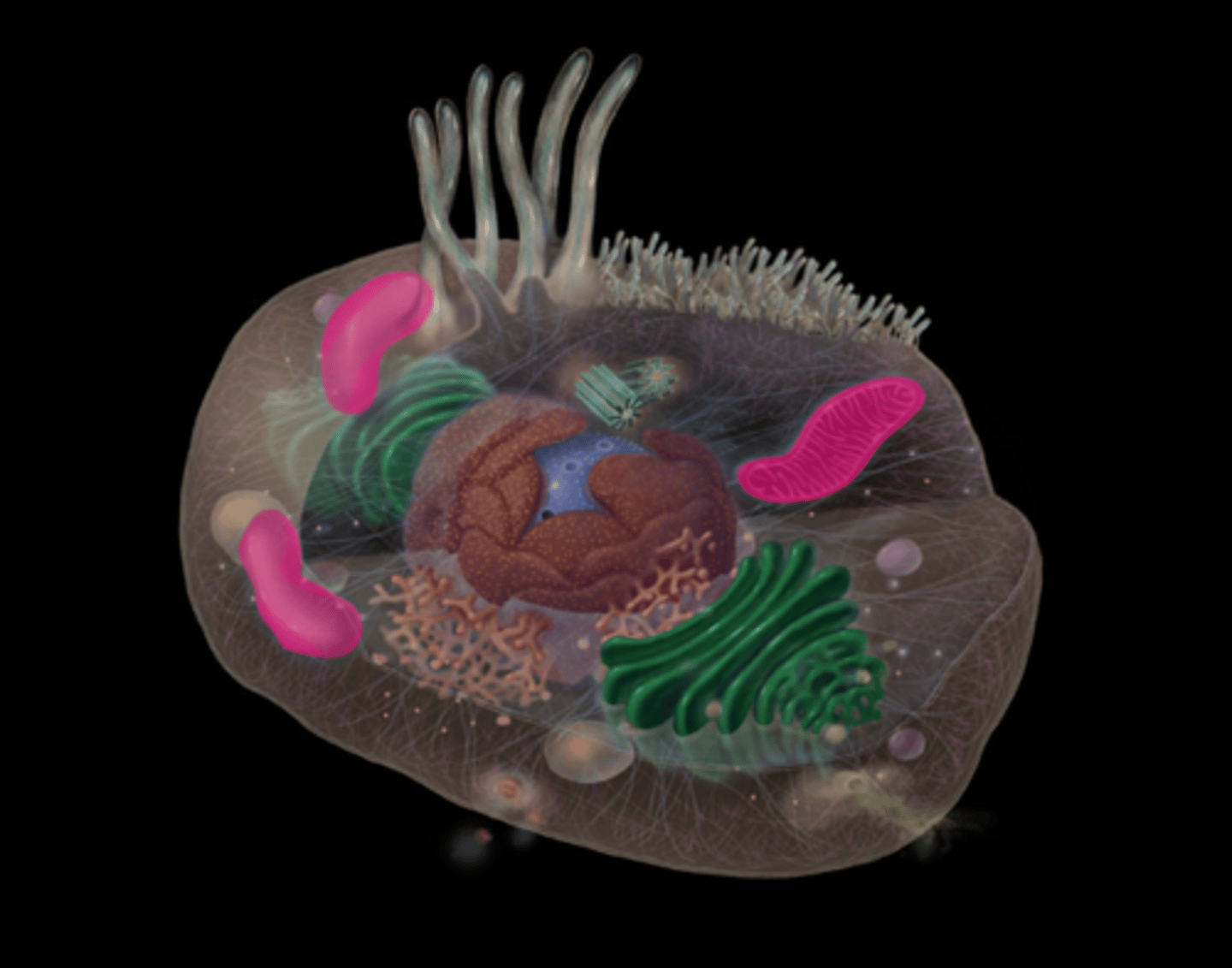
nuclear pores
highlighted in pink
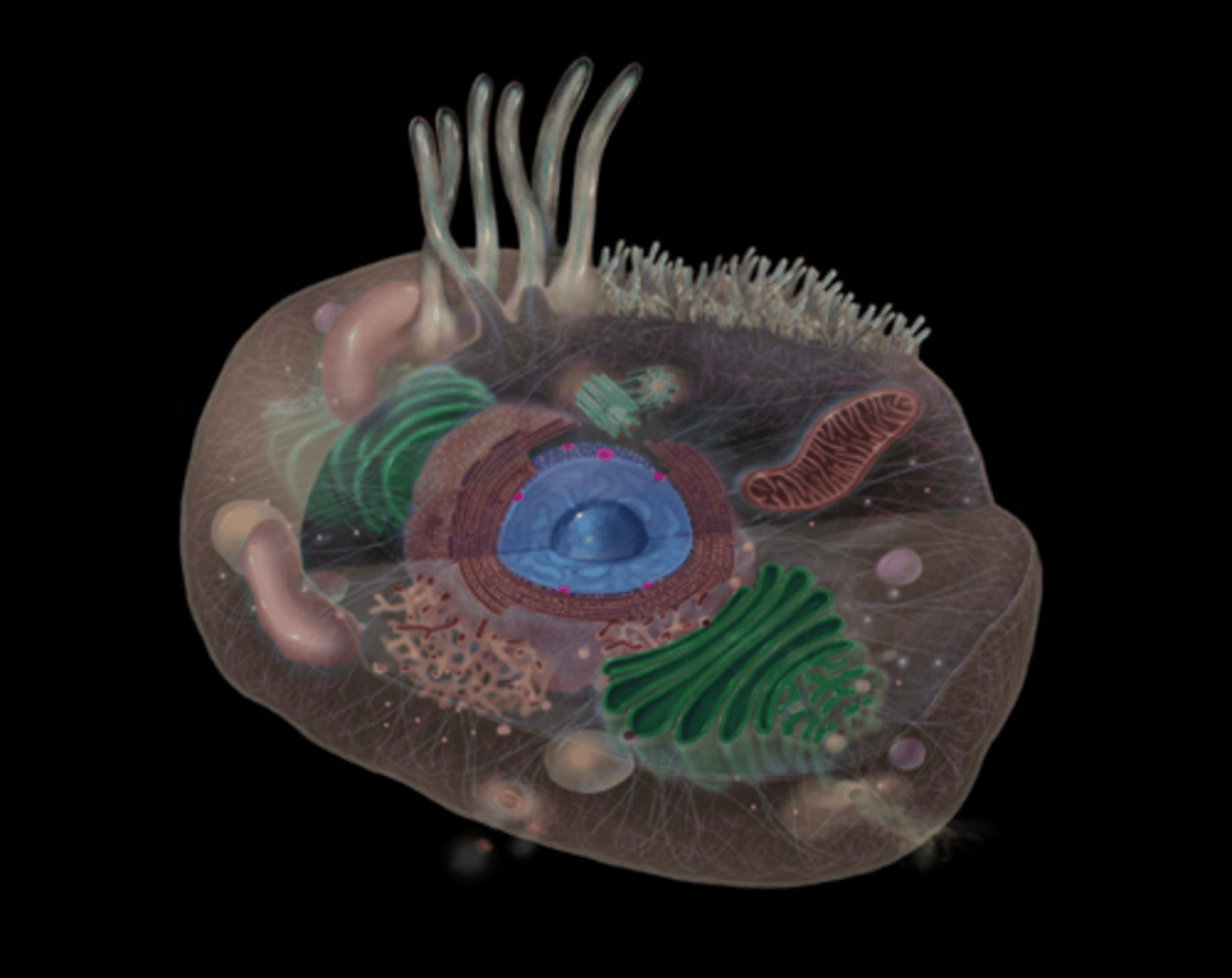
Nucleolus
highlighted in pink
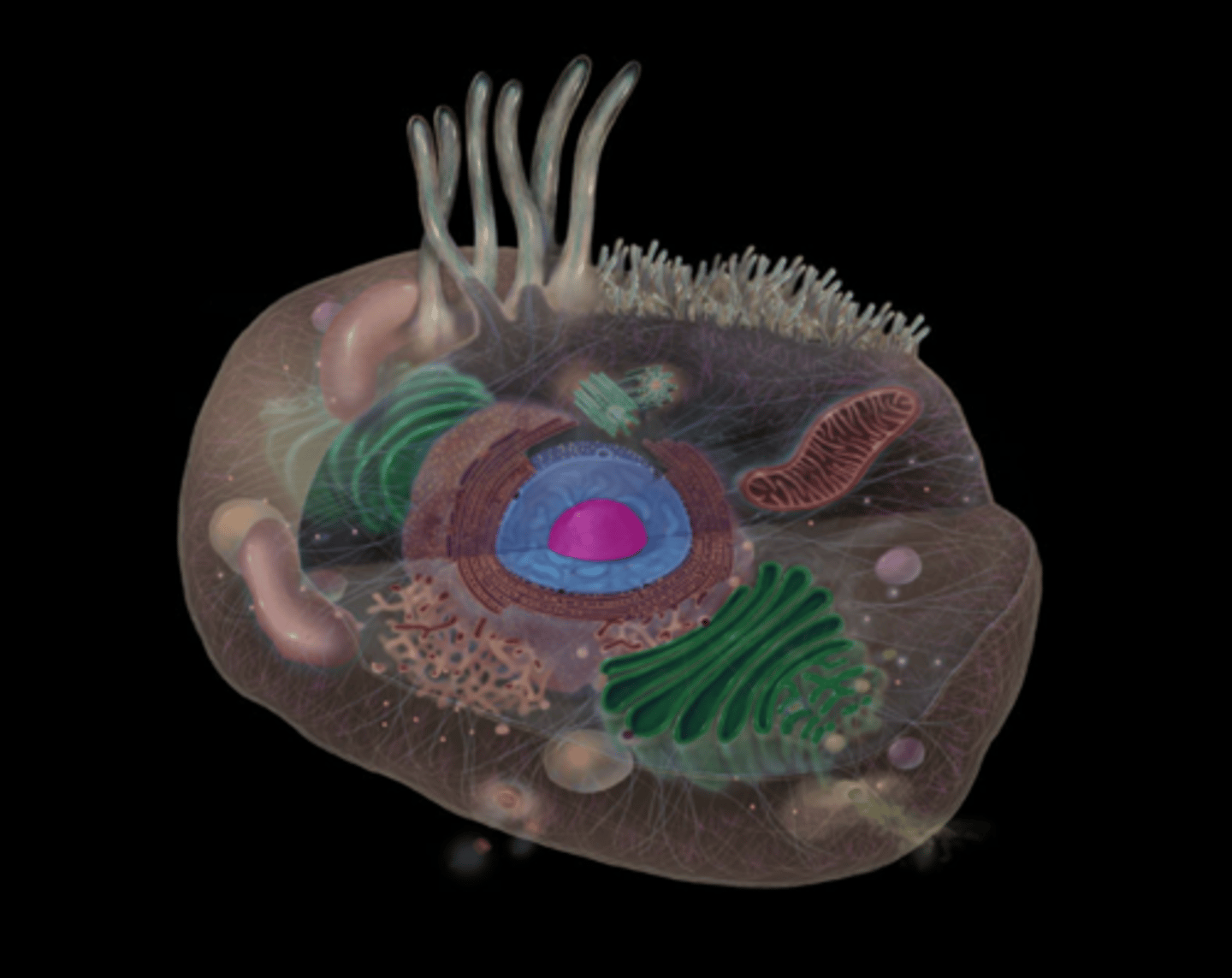
Nucleus
highlighted in pink
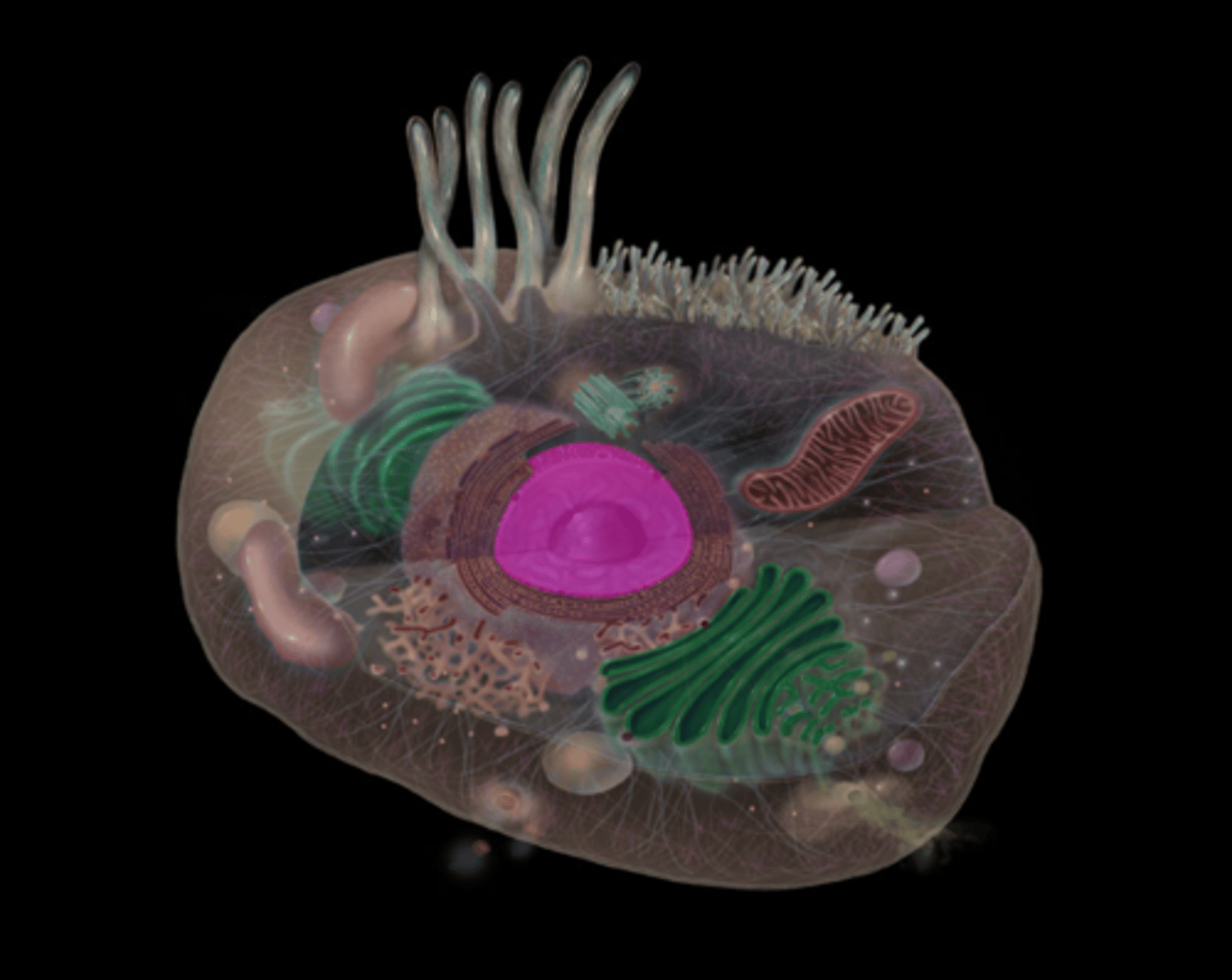
Peroxisomes
highlighted in pink
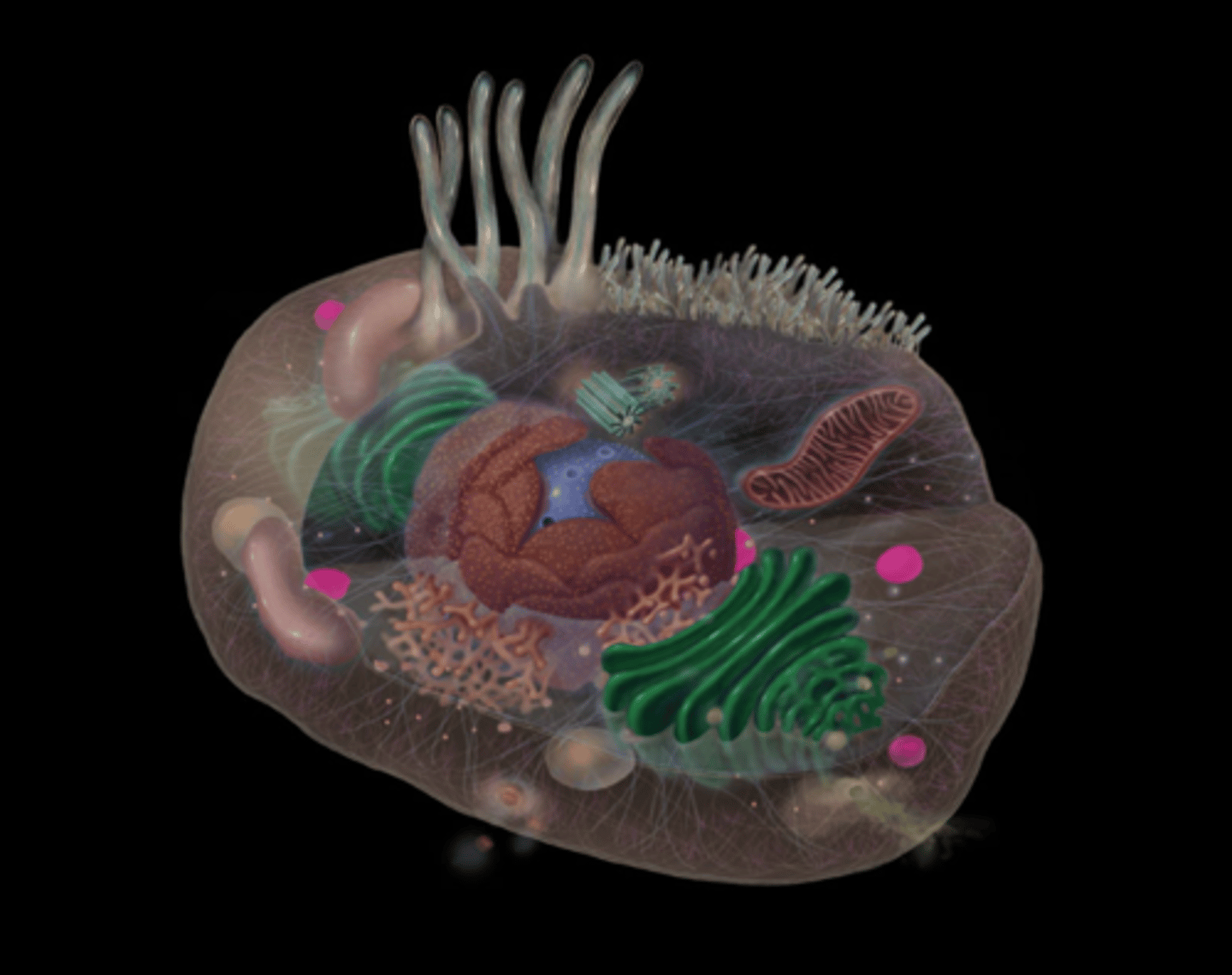
plasma membrane
highlighted in pink
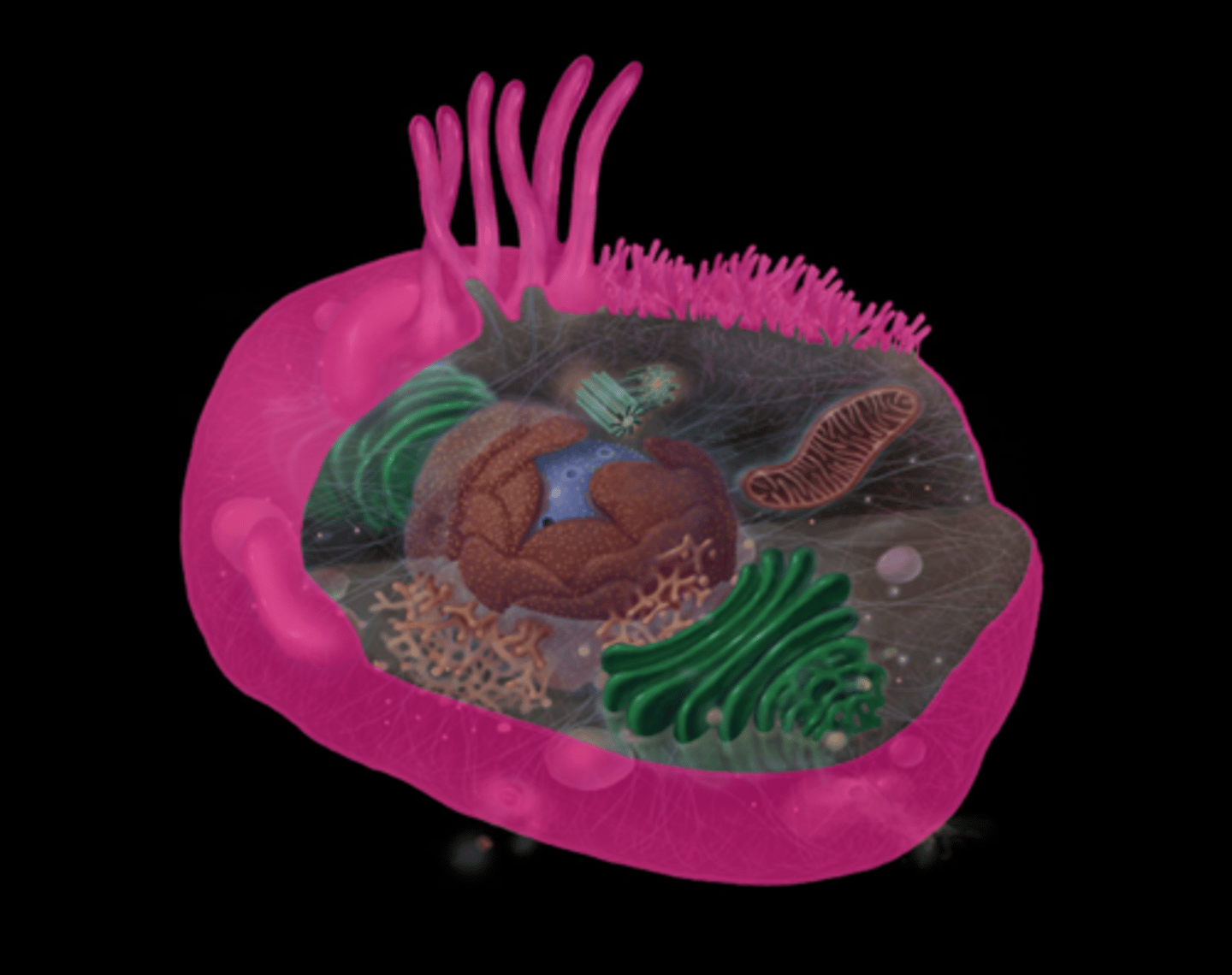
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
highlighted in pink
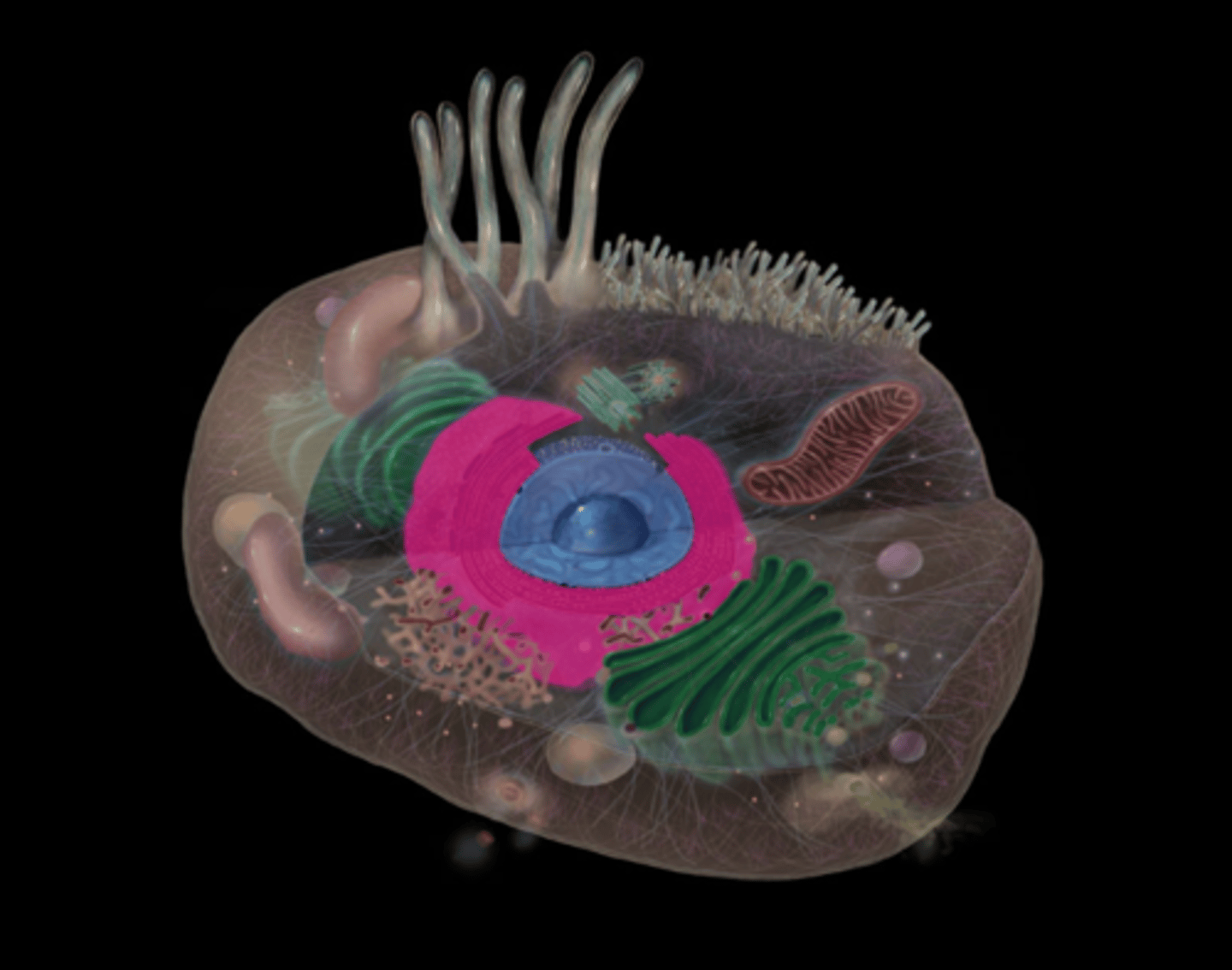
secretory vesicle of the Golgi apparatus
highlighted in pink
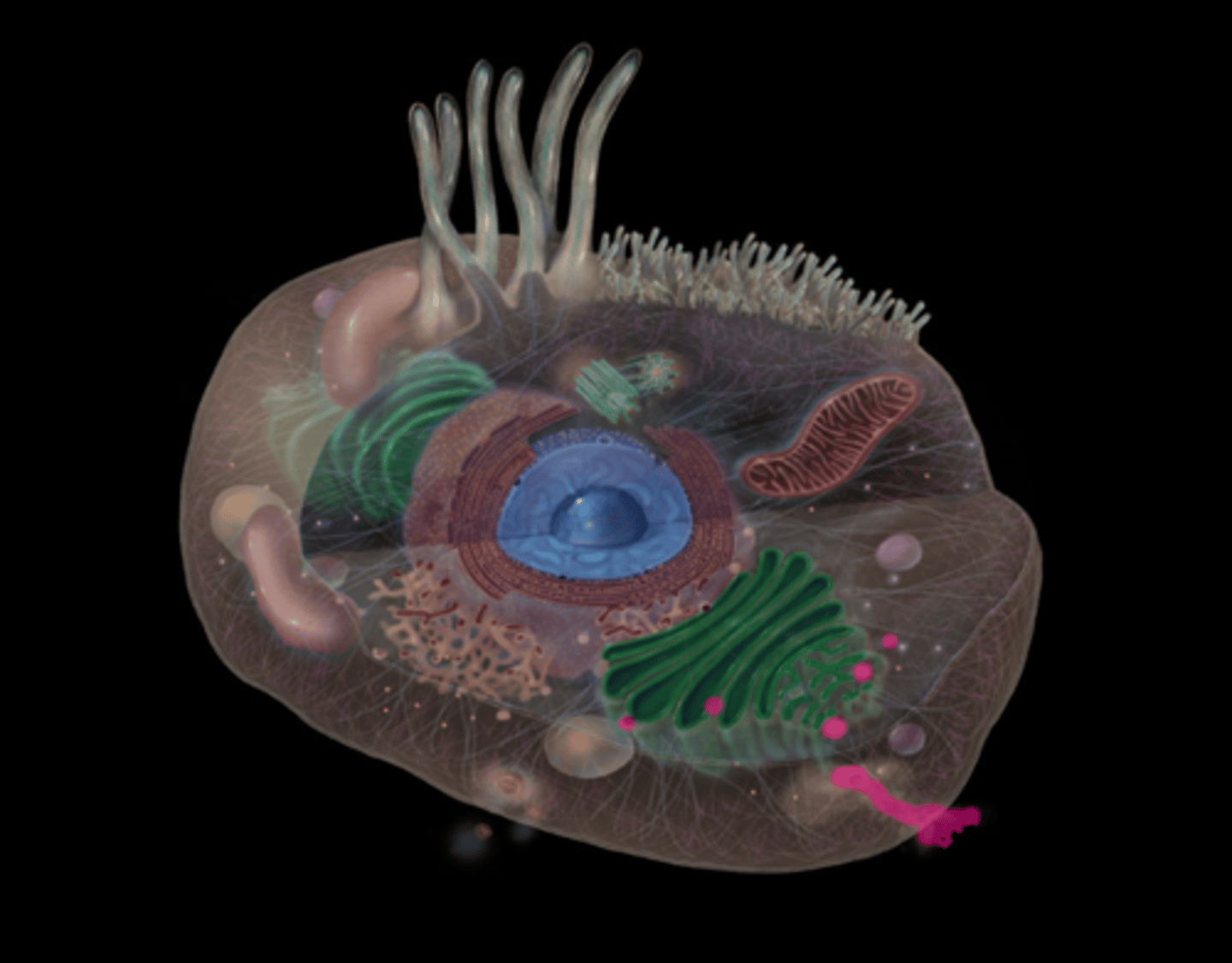
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
highlighted in pink
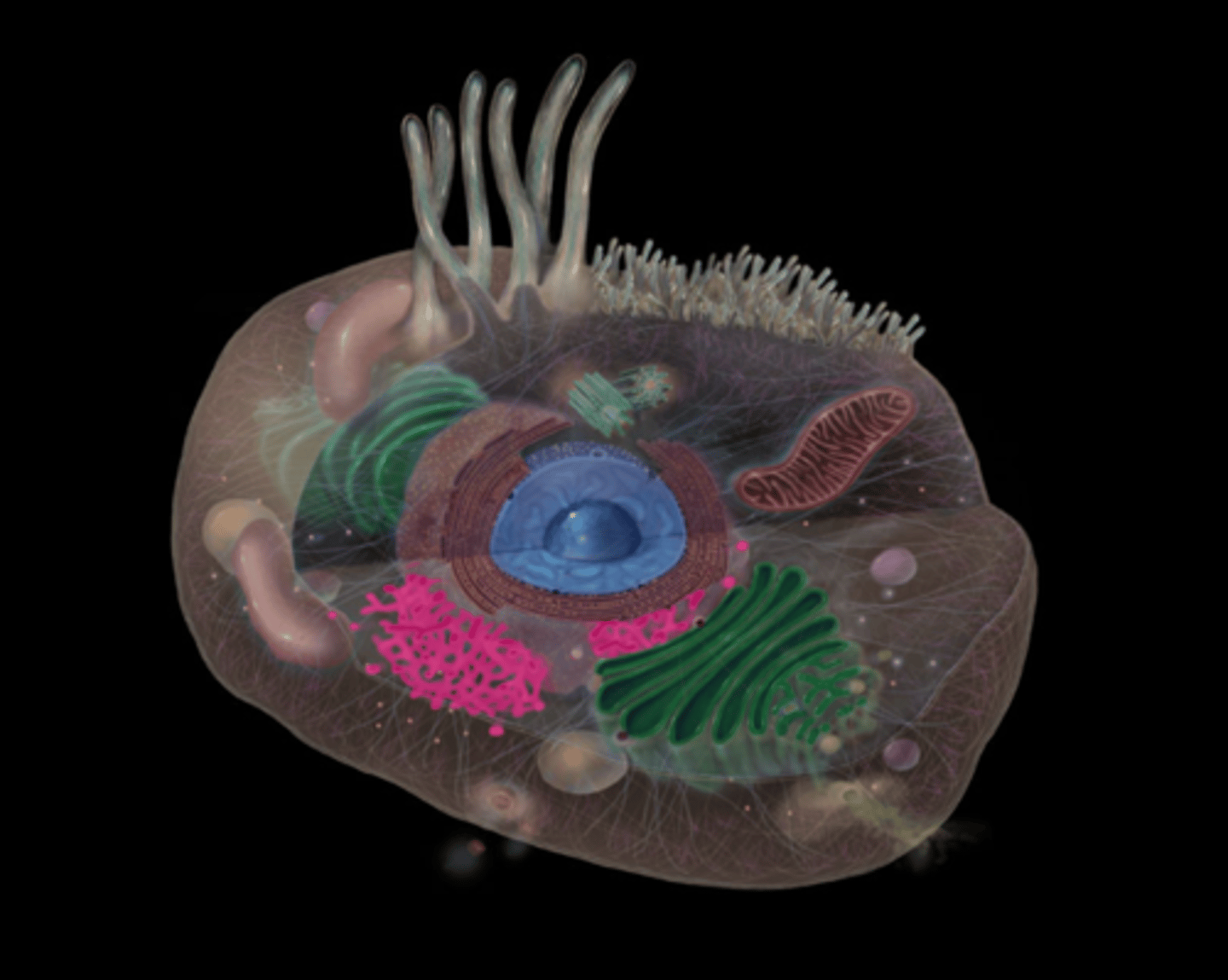
what does the centrosomes do?
Assists in formation and organization of microtubules and
Responsible for spindle formation during mitosis
What does cilium do?
Oscillations (bending to-and-fro) of cilia move substances (e.g., mucus, cells, and debris) over cell surface
Ciliary motion (bending) created by axoneme microtubules sliding past one another
what does endocytic vesicles do?
Used for transport into the cell, endocytosis• Phagocytosis= cellular "eating"• Pinocytosis=cellular "drinking"
What do free ribosomes do?
Sites of protein synthesis
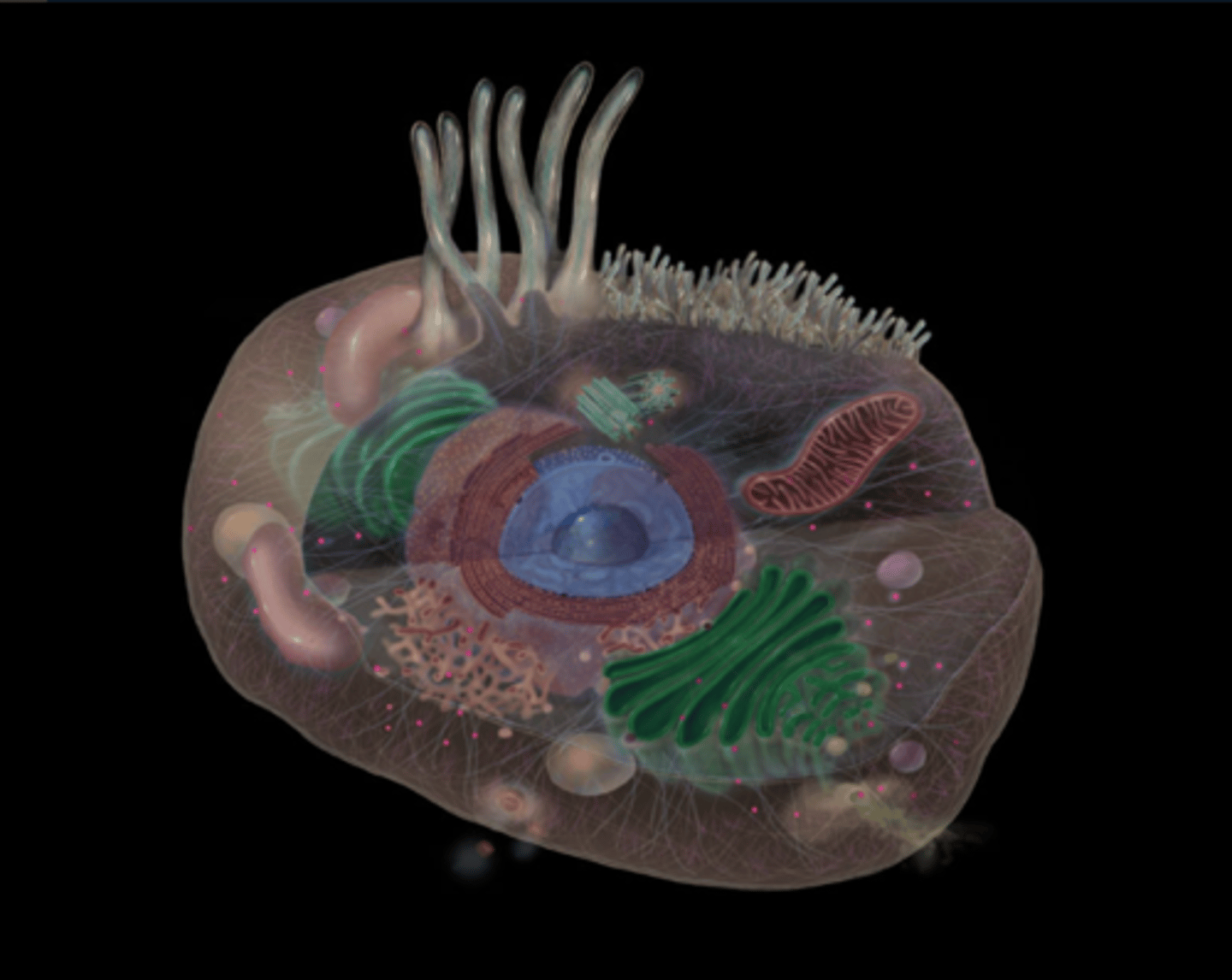
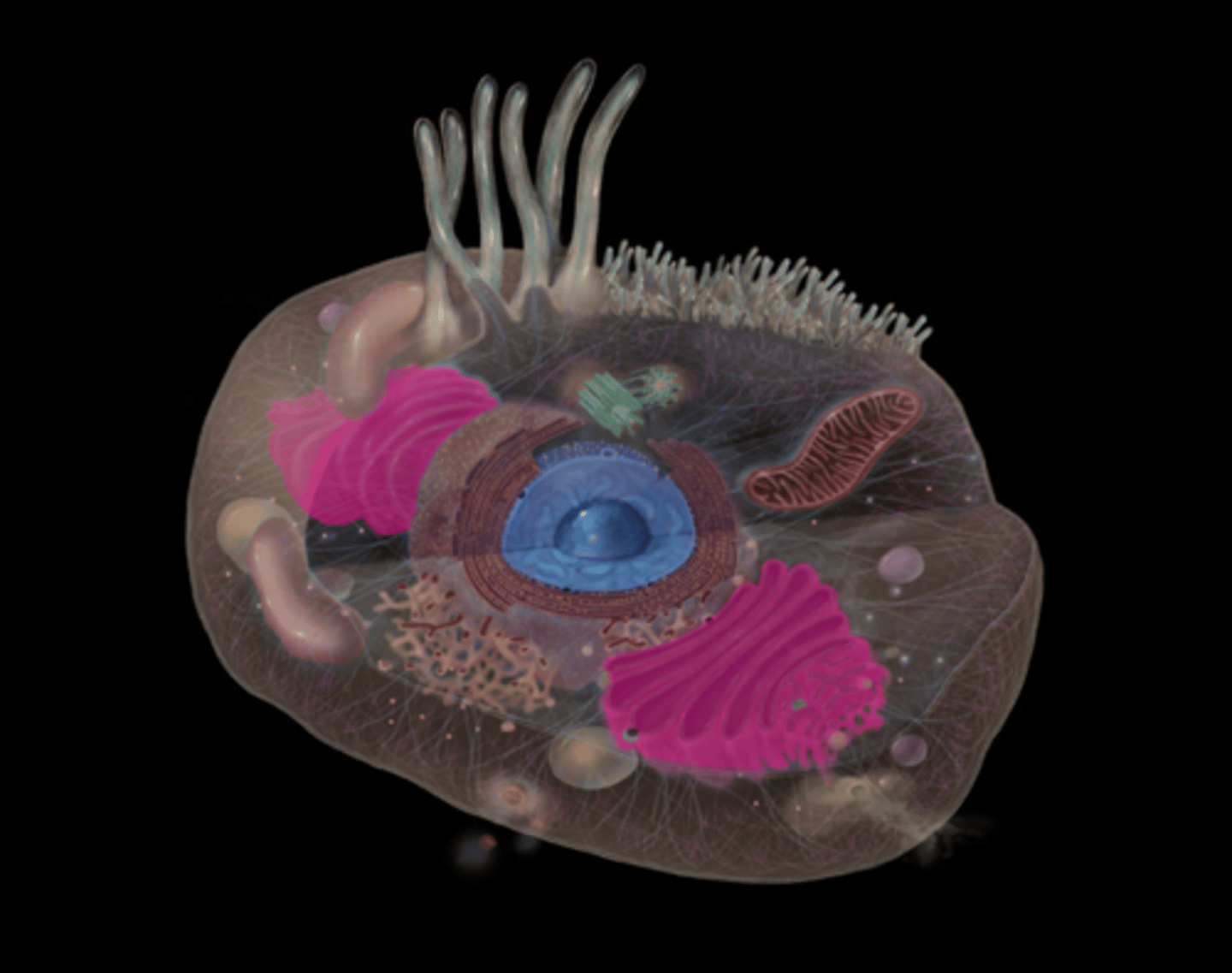
What does the Golgi apparatus do?
Protein sorting
What do lysosomes do?
Contains hydrolases that digest intracellulardebris; garbage-disposal of the cell
What do microvilli do?
Increase cell surface area
Facilitate transport and absorption (e.g., nutrients) across membrane
What does the mitochondria do?
Site of ATP synthesis; powerhouse of cell
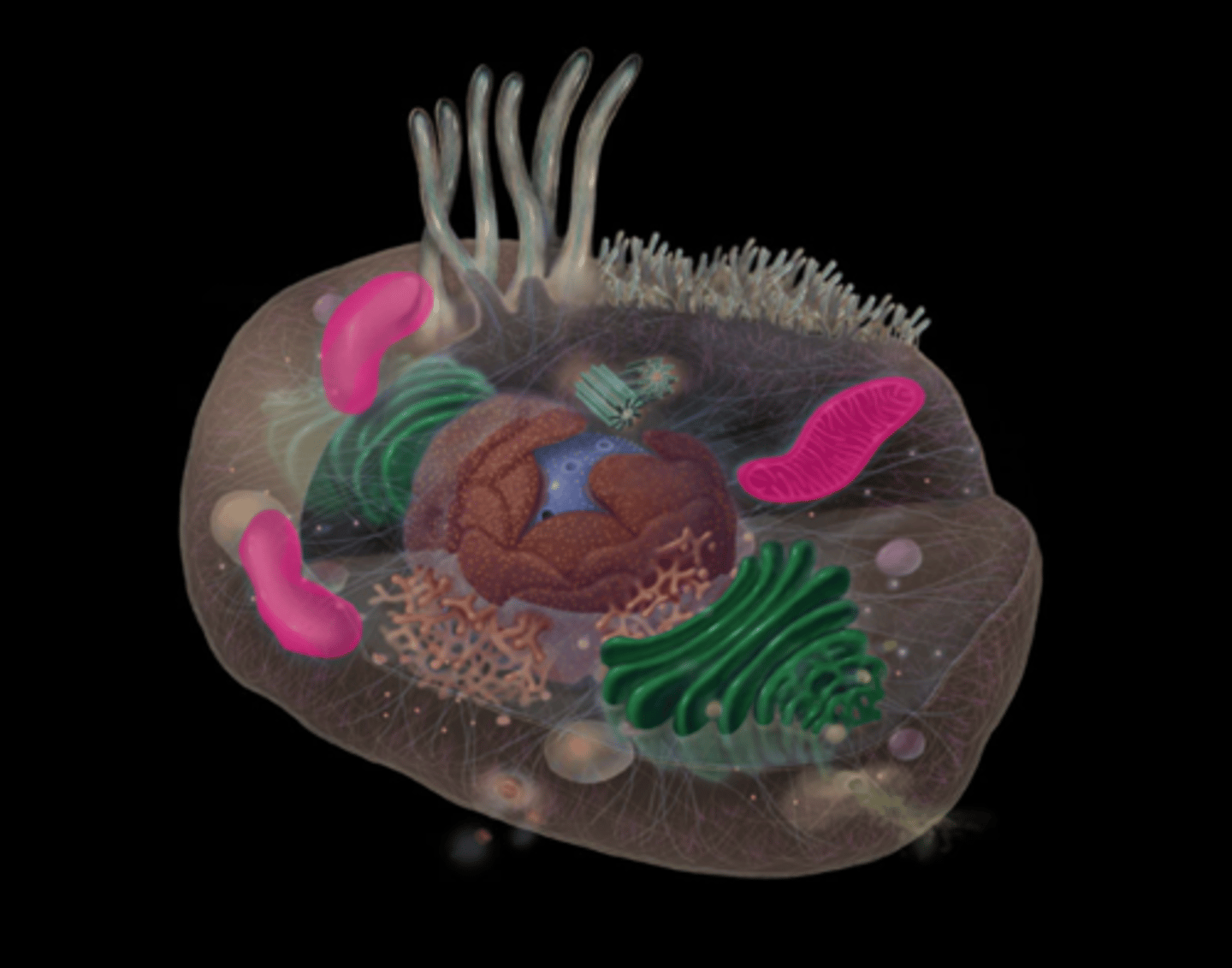
what do nuclear pores do?
Allows for, and regulates, passage of materials between cytoplasm and nucleus
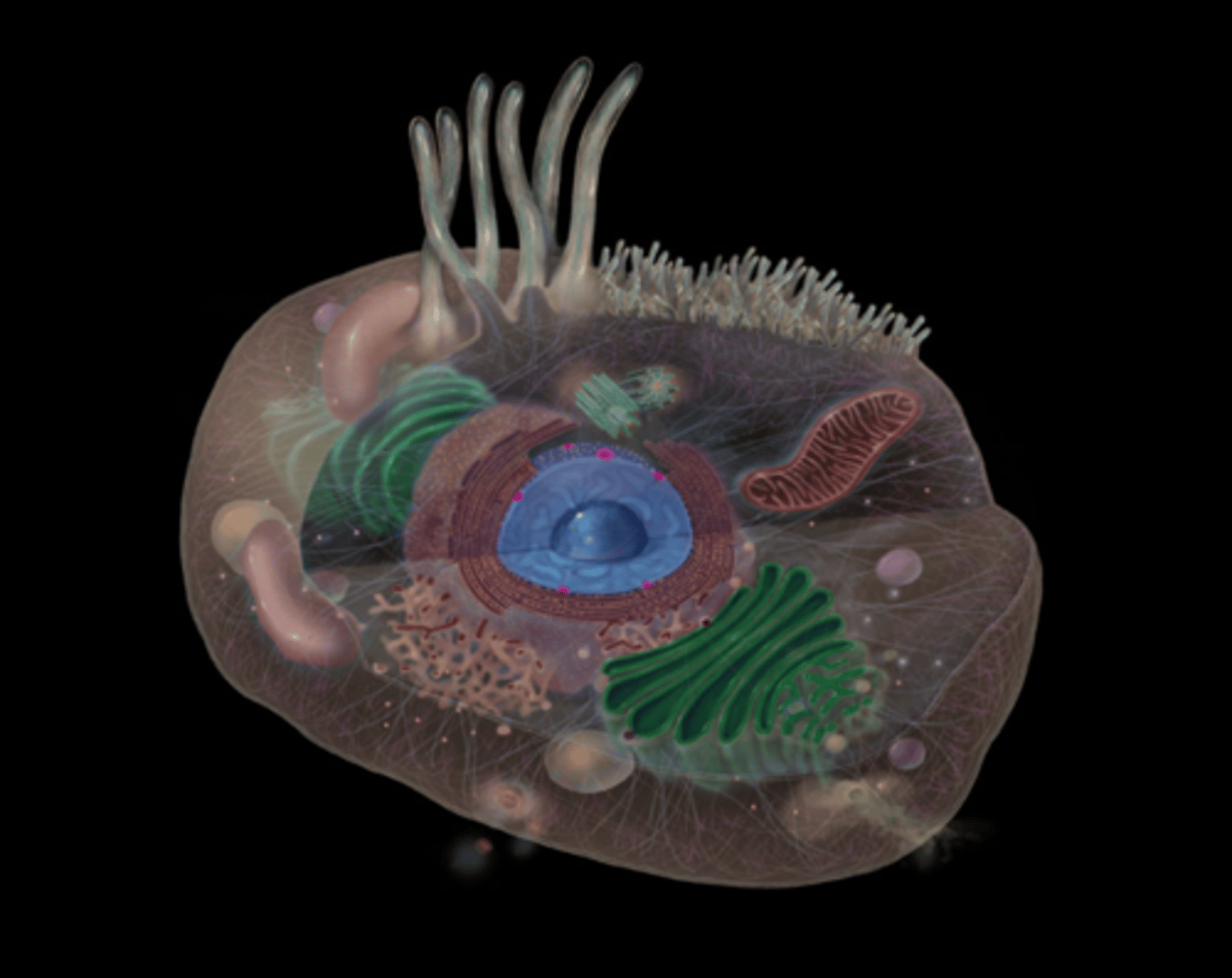
what does the nucleosus do?
Ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosome assembly
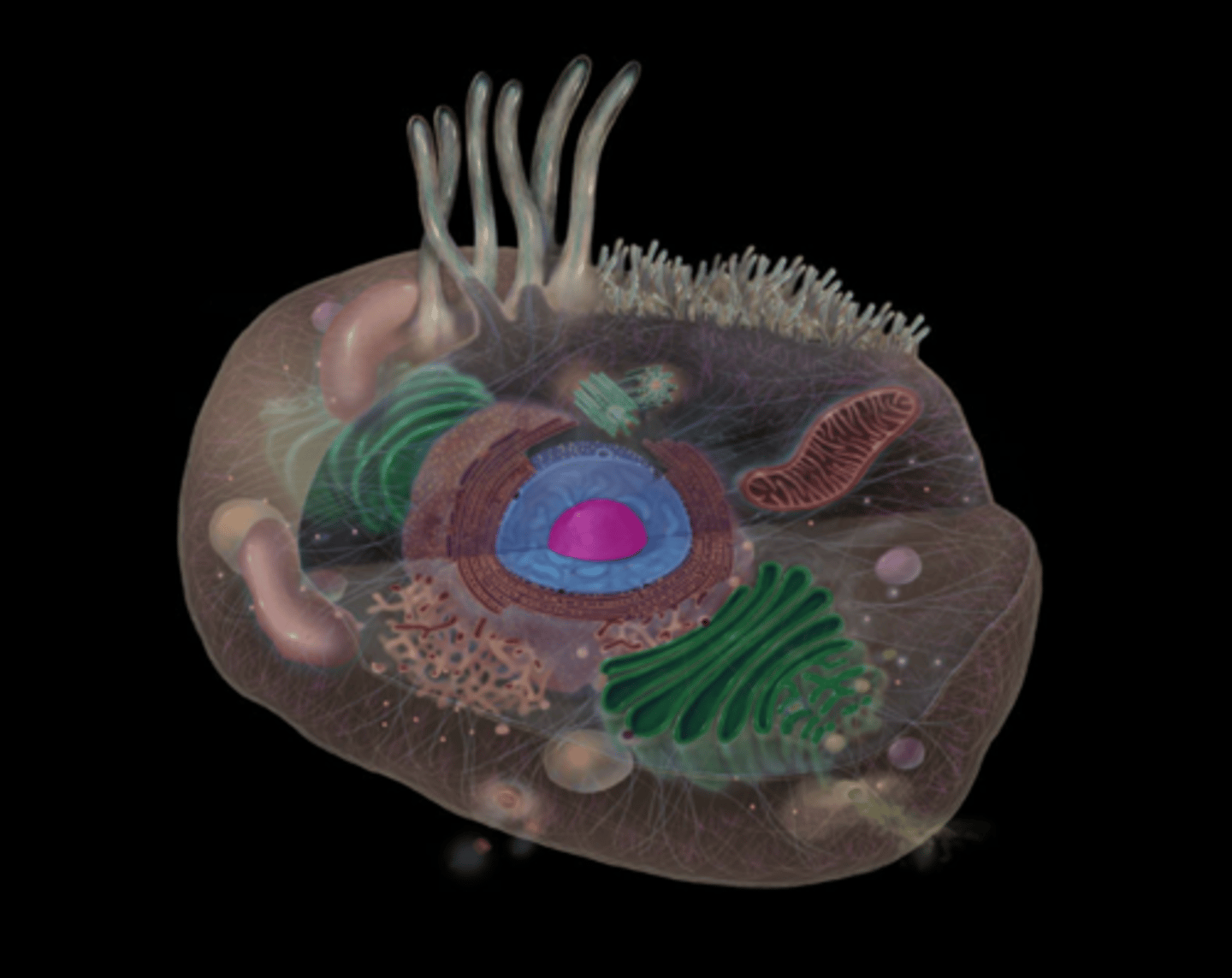
what does the nucleus do?
DNA replication
DNA transcription into mRNA
Ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosome subunit assembly (in nucleolus)
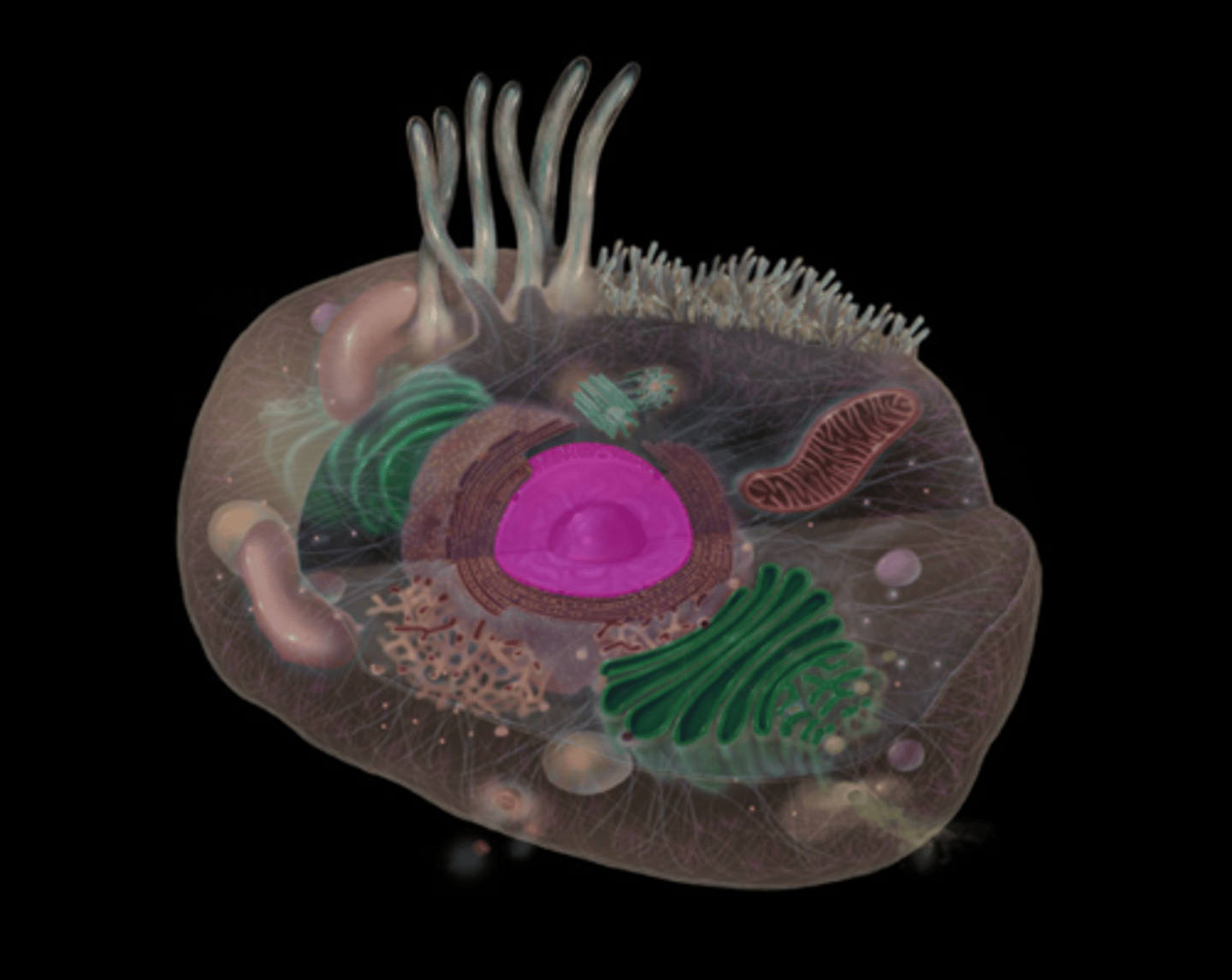
what do the peroxisomes do?
Oxidation of fatty acids, a major source ofmetabolic energy. Synthesis of cholesterol/bile.
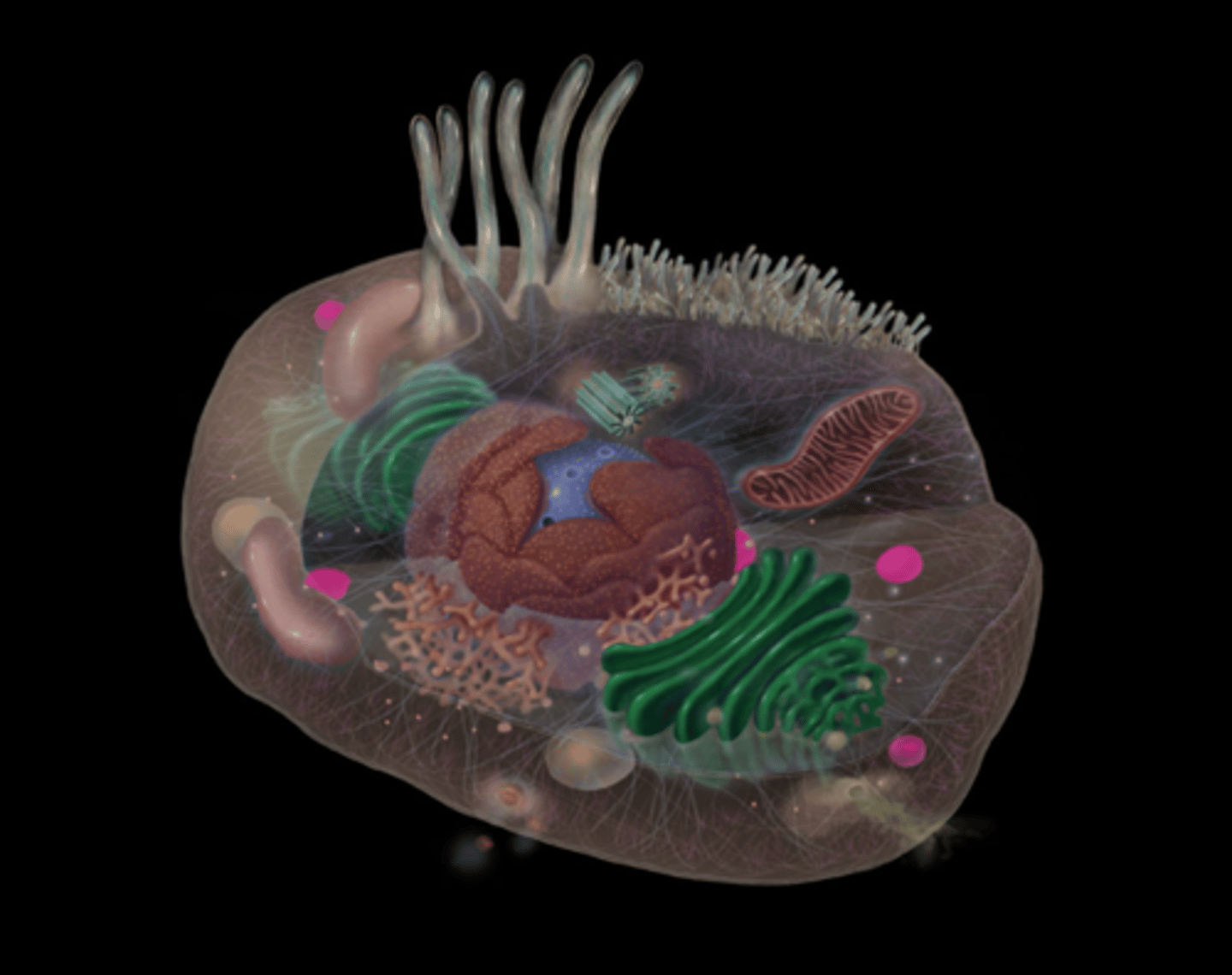
what does the plasma membrane do?
Encloses cell contents
Communication (receptors)
Intercellular connections
Regulates movement of materials into and out of cell
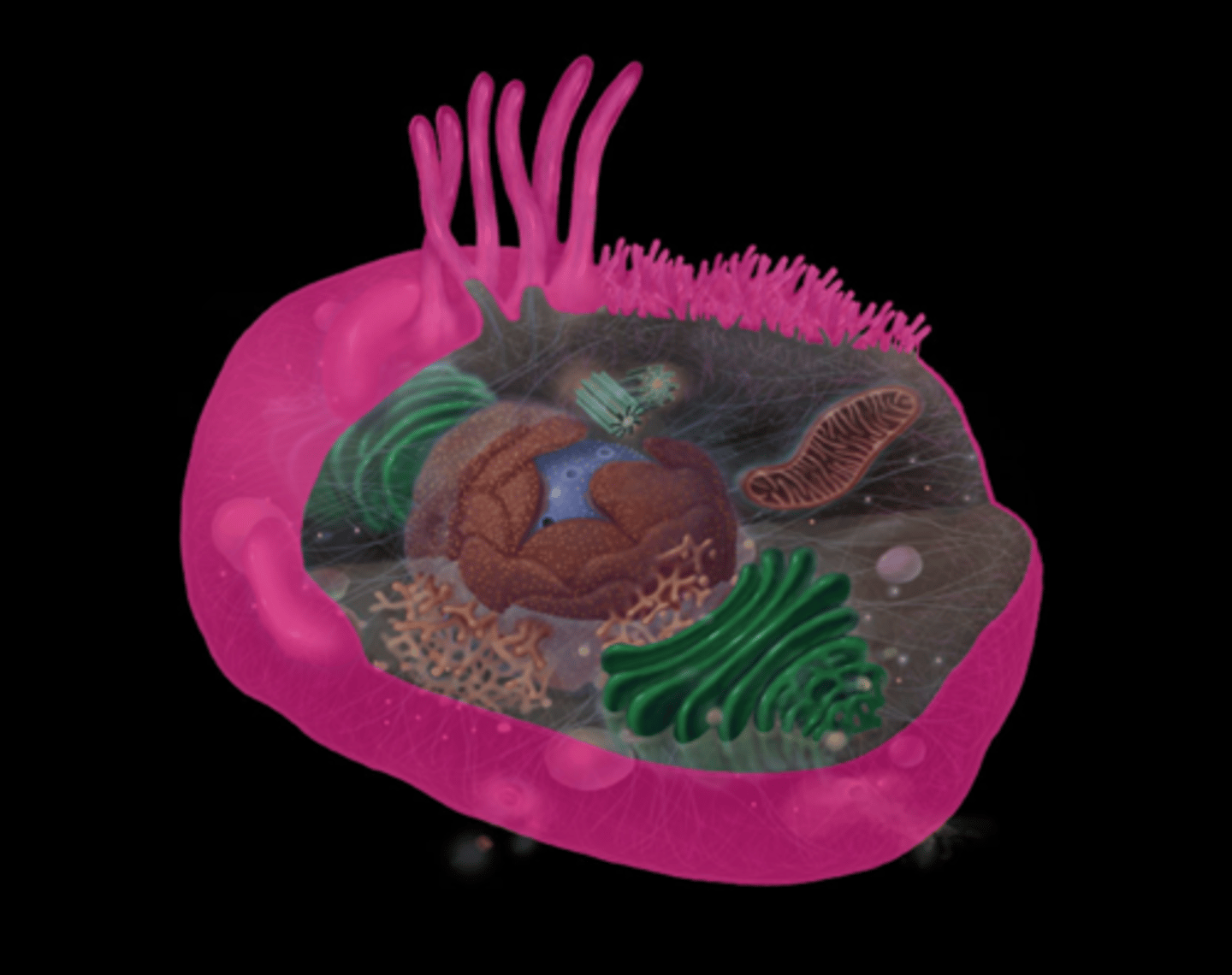
what does the rough endoplasmic reticulum do?
Modify proteins after they are made andtransports them to Golgi and other sites
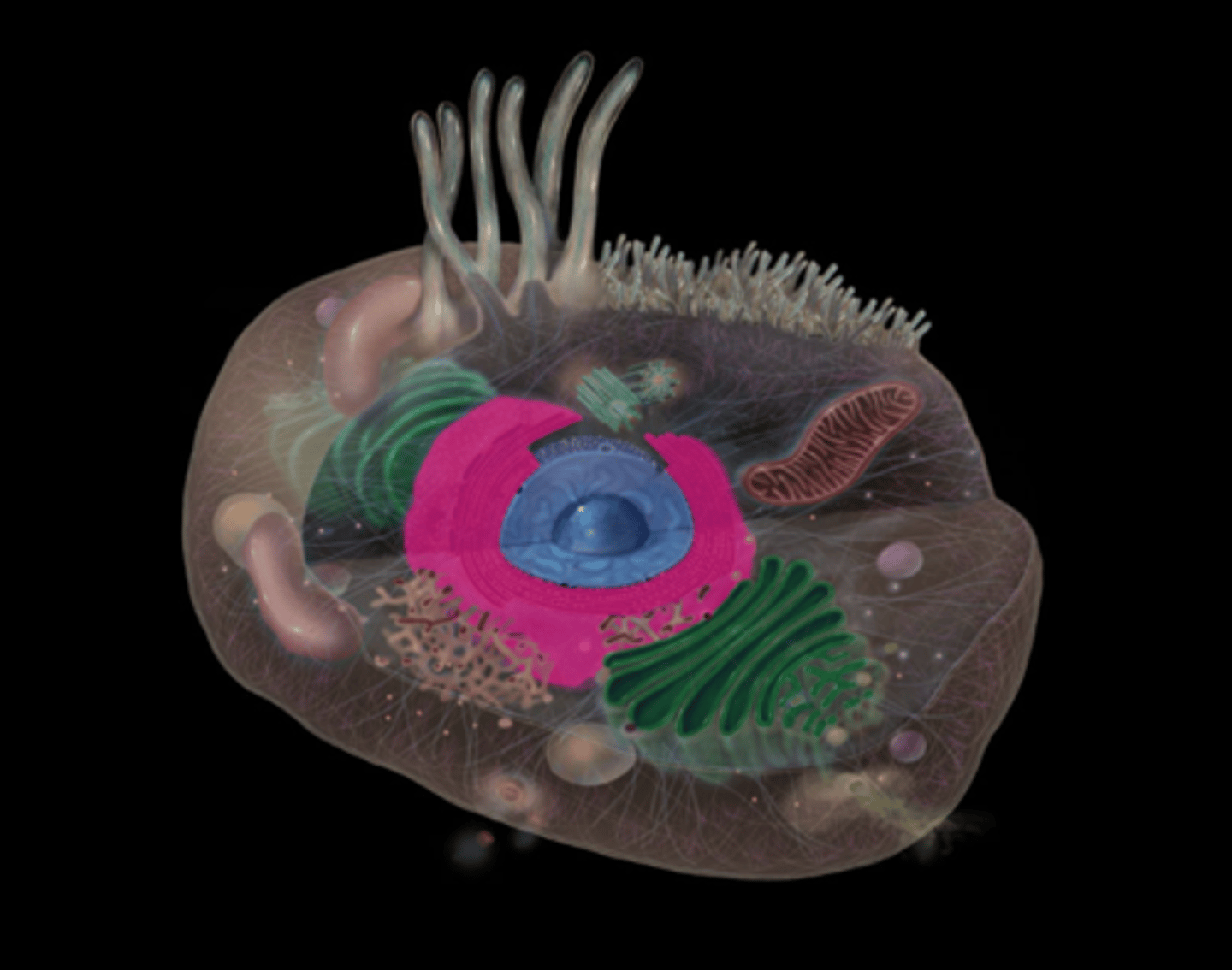
what do the secretory vesicles of the Golgi apparatus do?
Carries protein products from Golgi apparatus to cell surface for exocytosis
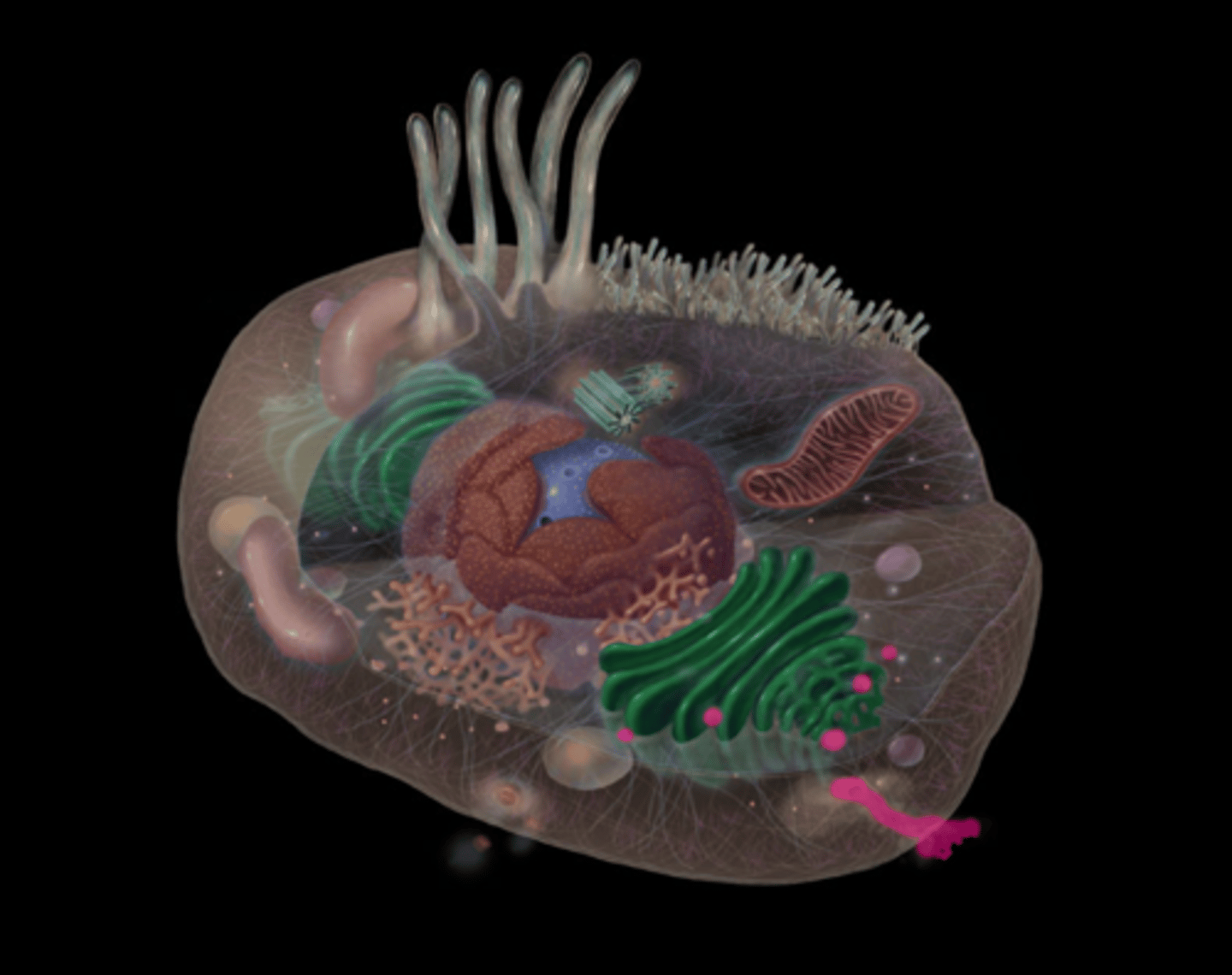
What does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum do?
Lipid synthesis , detoxification of drugs,glycogen breakdown
transcription
DNA---> mRNA
translation
mRNA---> protein
simple diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Tonicity
the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
hypertonic solution
Solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell; cell loses water
hypotonic solution
Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
isotonic solution
A solution with the same concentration of water and solutes as inside a cell, resulting in the cell retaining its normal shape because there is no net movement of water.
Crenation
This happens when a cell shrinks and shrivels; can result in cell death if severe.
lyse
Cell bursting.
growth 1 in cell cycle
Cell growth
Synthesis in cell cycle
DNA replication
growth 2 in cell cycle
more growth and preparation for mitosis
mitosis
division of the nucleus
prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms

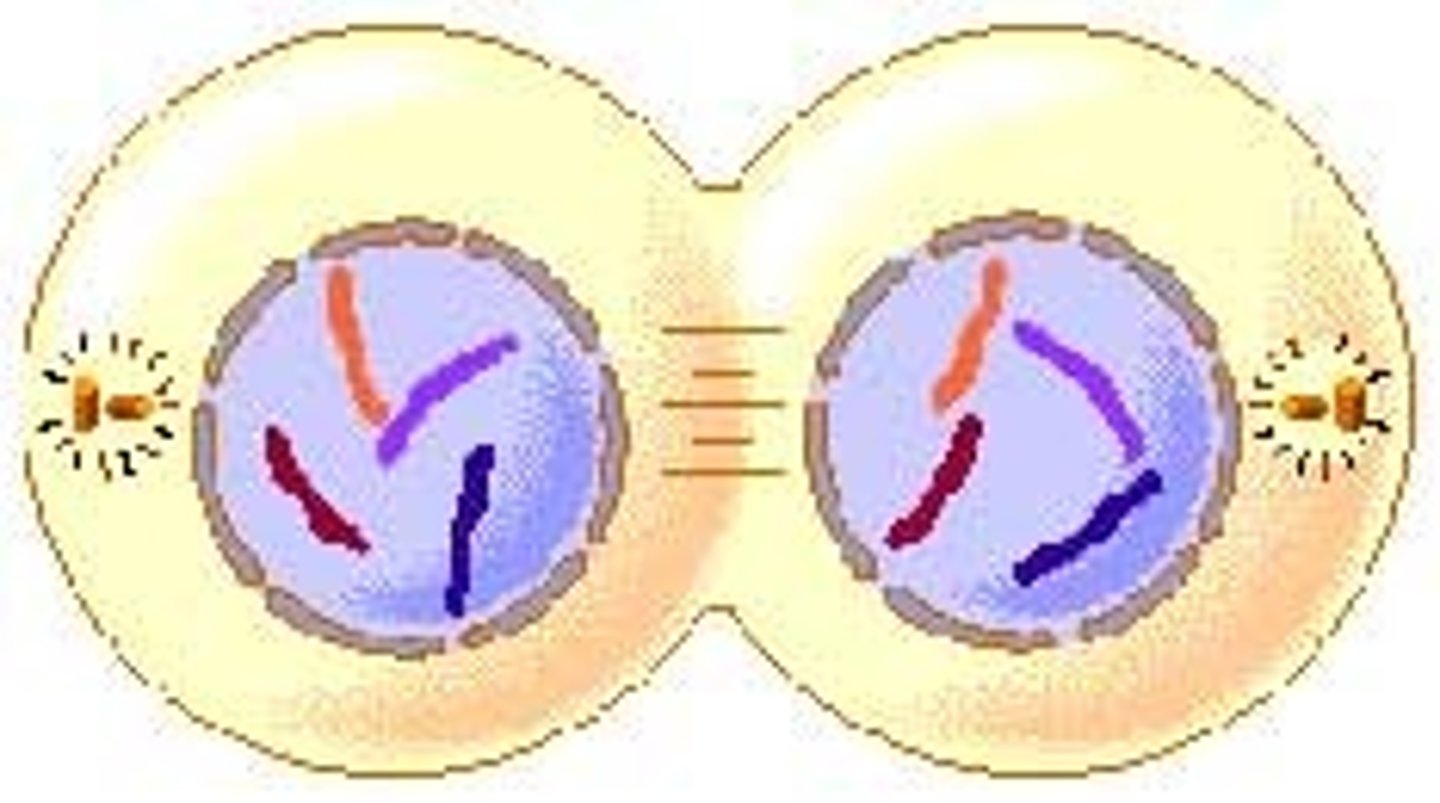
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
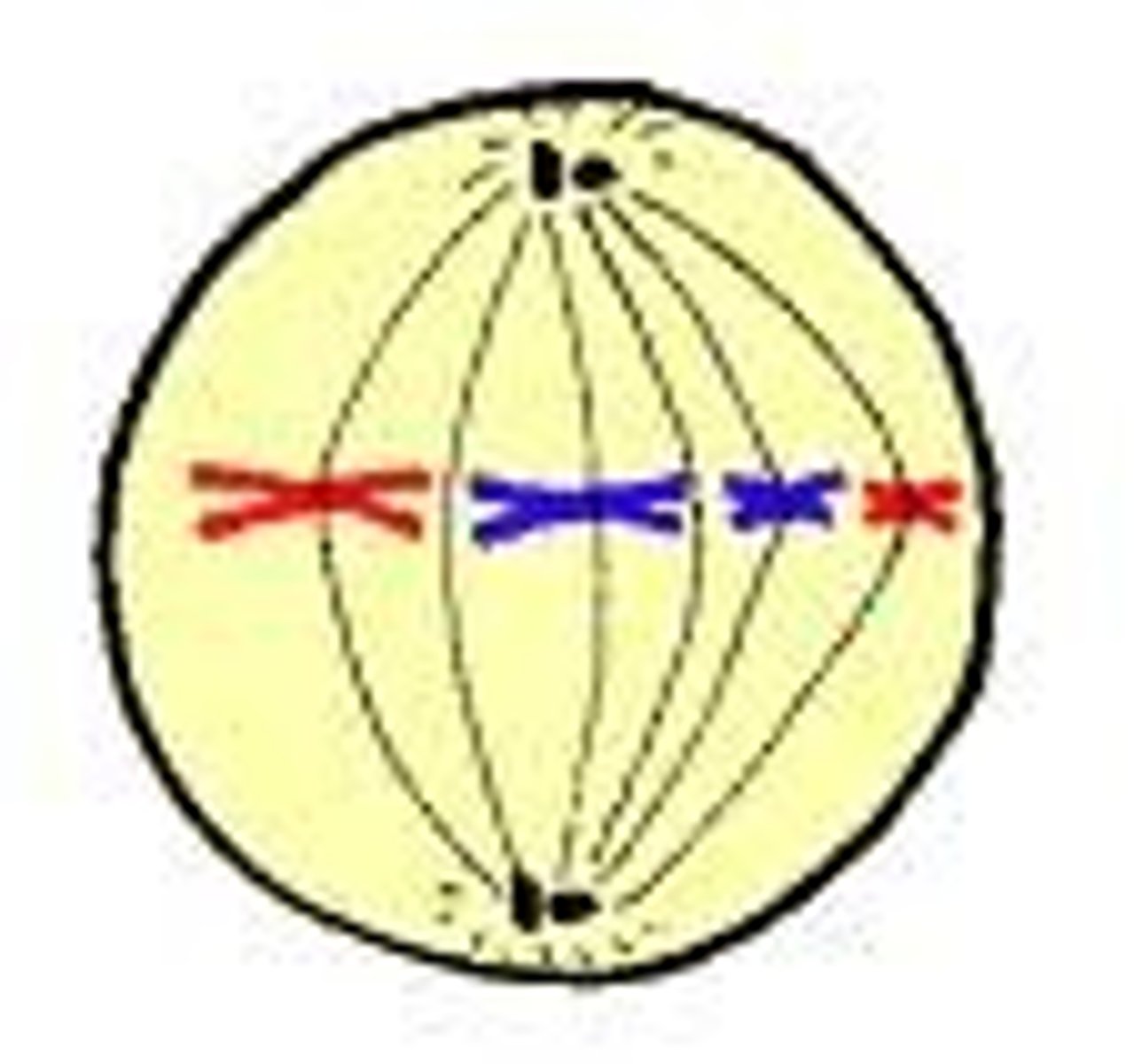
anaphase
chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
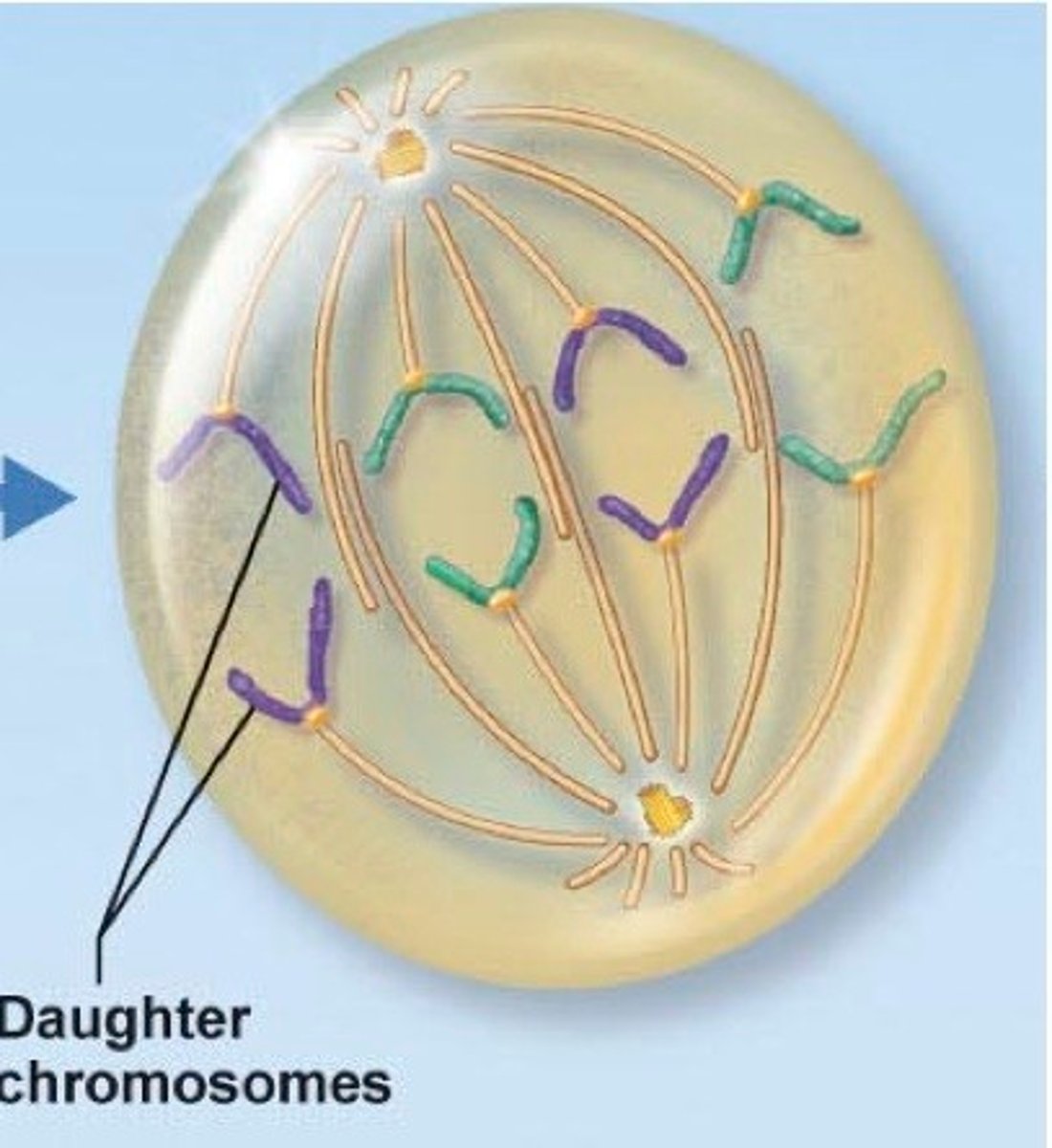
telophase
After the chromosome seperates, the cell seals off, Final Phase of Mitosis.
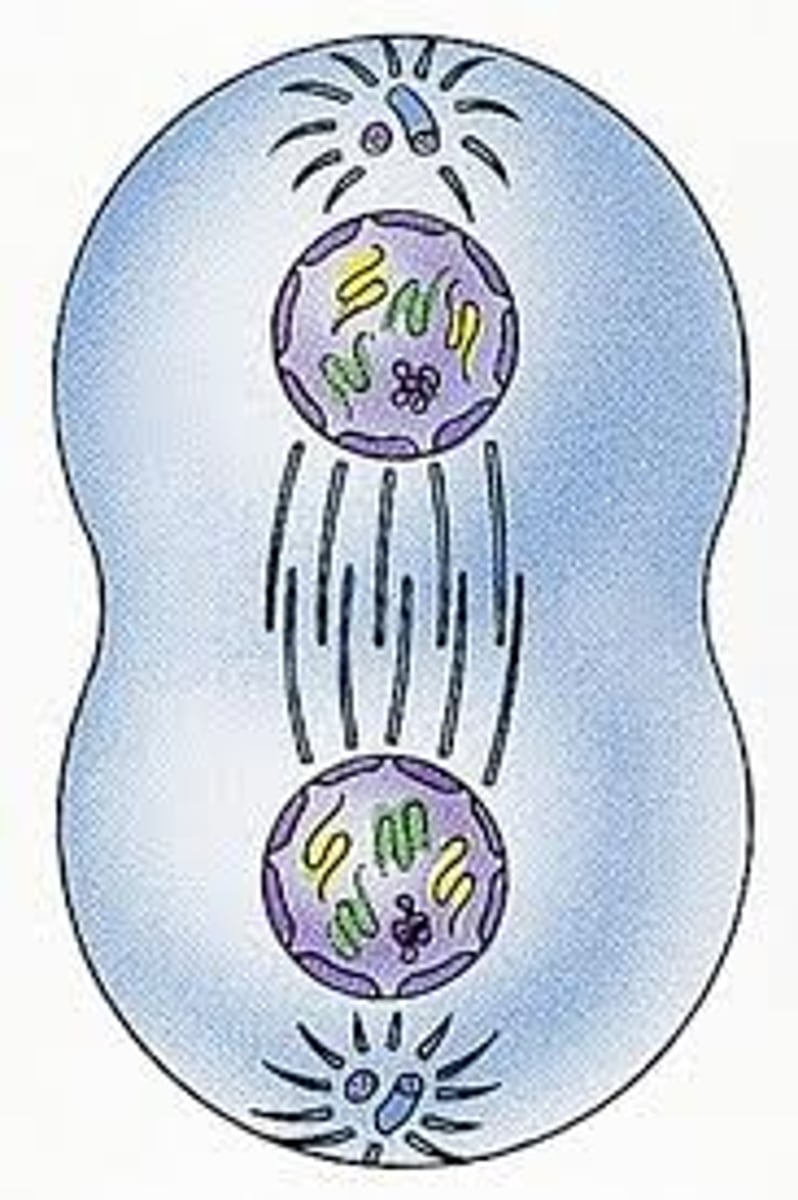
Cytokinisis
division of the cytoplasm