AP Environmental Science-Unit 1-Ecosystem Interactions and TOC
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Abiotic Factors
Nonliving components of environment.
Biotic Factors
All the living organisms that inhabit an environment
Habitat
Where an organism lives and any aspect of the location
Niche
Full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions
Organism
Any form of life. Belongs to any of the 6 kingdoms
Species
Group of organisms of same type that can reproduce to have fertile offspring
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment. All abiotic and biotic factors.
Producers/Autotrophs
Organisms that make their own food from compounds and energy obtained from the environment
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy
Salinity
A measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid
Plankton
Small, weakly-swimming, free floating organisms
Decomposers
Organisms that break down the dead remains of other organisms
Phytoplankton
Photosynthetic algae found near the surface of the ocean
Coral Reef
The most diverse marine biome on Earth, found in warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline. Only in waters 18-30 degrees celsius
Consumers
An organism that obtains energy and nutrients by feeding on other organisms or their remains
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Coral bleaching
A phenomenon in which algae inside corals die, causing the corals to turn white. When this happens, the habitat for the animals are destroyed
What are some major threats to coral reefs?
Overfishing, fishing using cyanide and dynamite, pollution from sewage and agriculture, massive outbreaks of predatory starfish, invasive species, and sedimentation from poor land use practices
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The amount of energy lost through respiration by producers sublated from the gross primary productivity of an ecosystem.
Food Chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
Food web
A community of organisms where there are several interrelated food chains
What limits the number of trophic levels in an ecological pyramid?
Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels limits this. When the number of links keep increasing, the amount of energy available decreases, as only 10% of energy gets transferred from one trophic level to the next
Ecological Efficiency
Percentage of energy transferred from one trophic level to another in a food chain or web
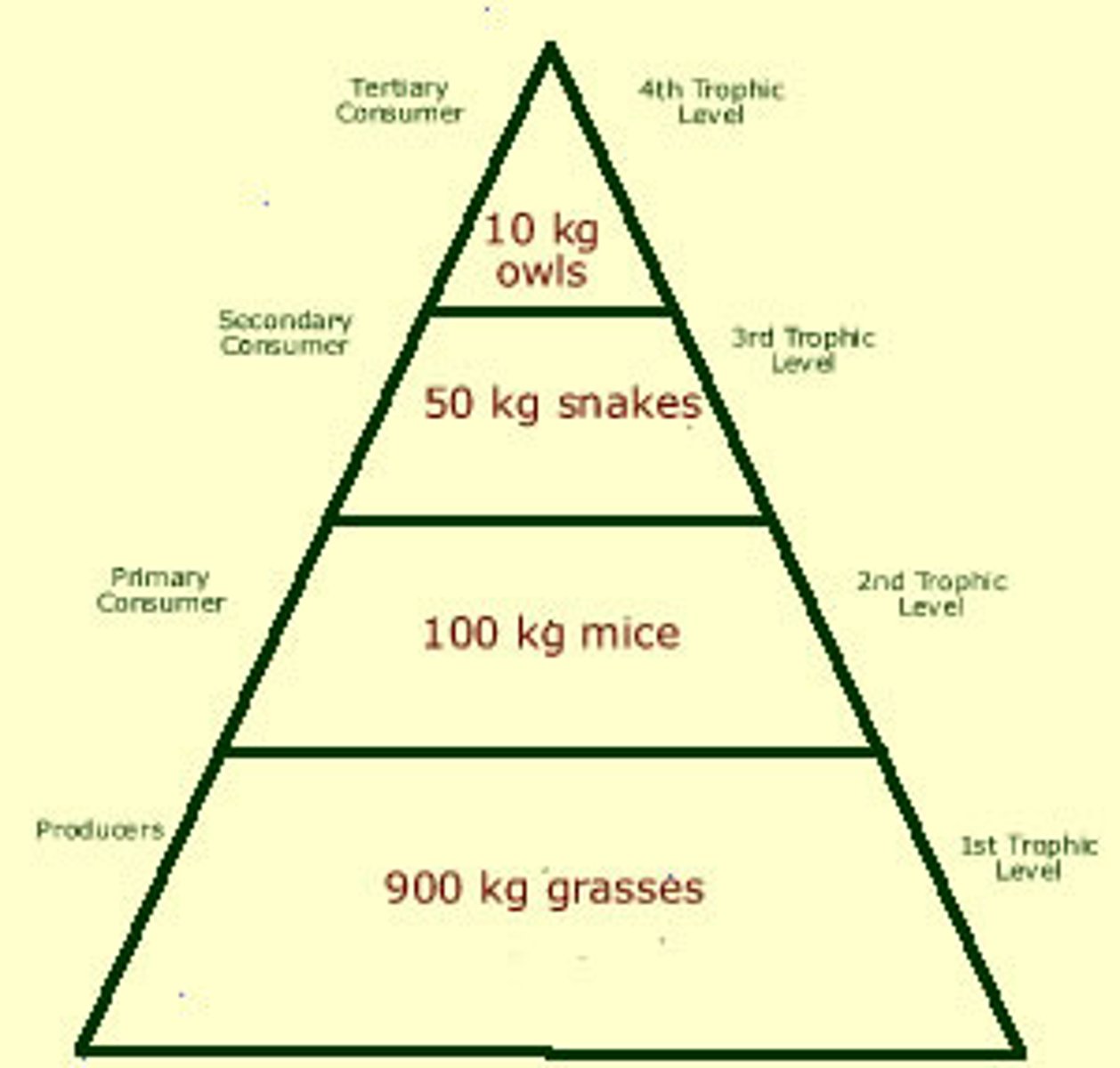
Biomass
A measure of the total dry mass of organisms within a particular region
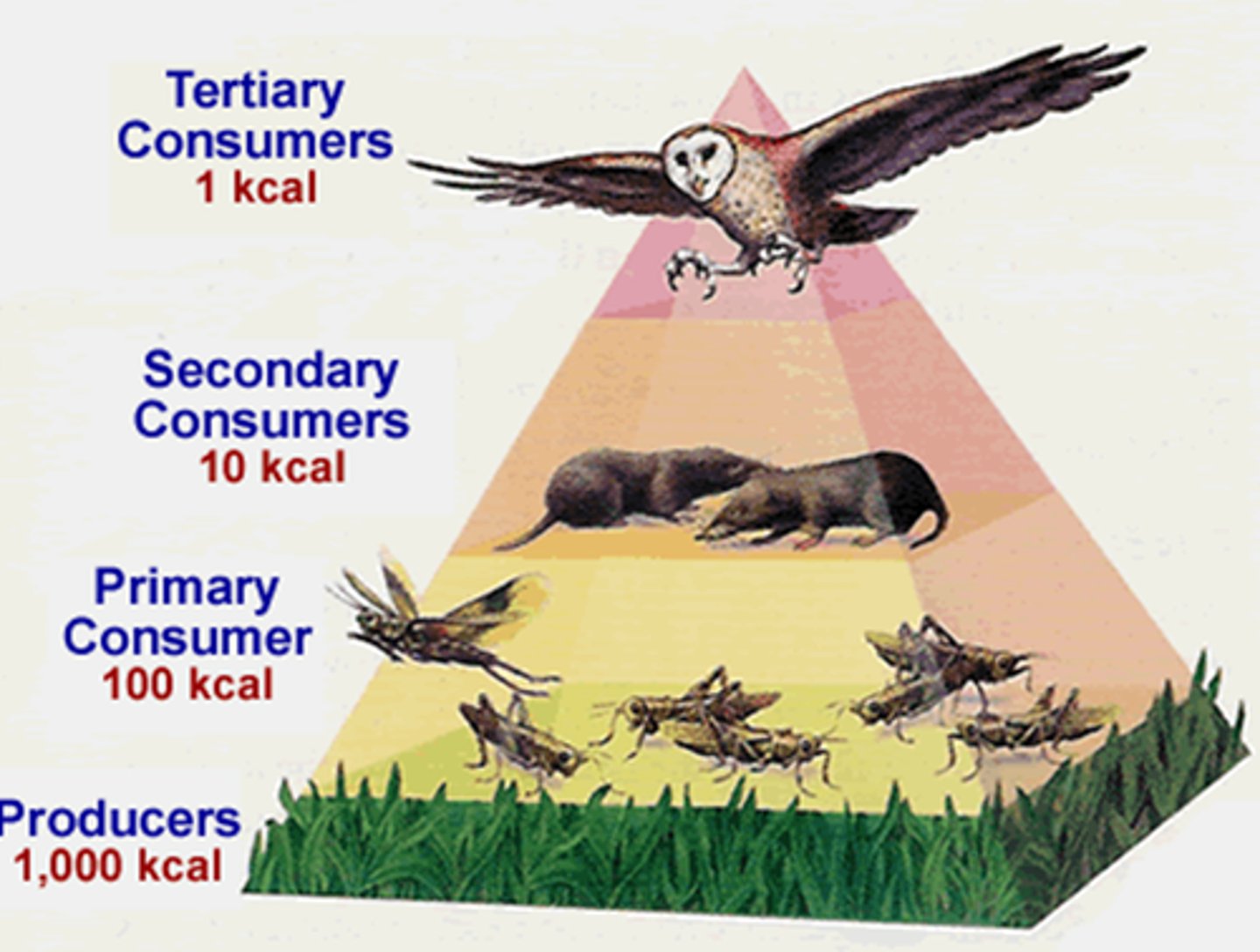
Pyramid of energy
A pyramid that shows the total amount of energy available at each trophic level
Biomass Pyramid
Diagram representing the biomass in each trophic level of an ecosystem
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
Fresh Water Biomes
ponds, lakes, streams, rivers. **Vital source of drinking water**
For a primary producer, the main function of photosynthesis is to manufacture
glucose
10% rule
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed up to the levels of the food pyramid reduces as you go up.
The two major processes involved in the carbon cycle are
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
The ultimate source of energy for terrestrial ecosystems is the
sun
The approximate efficiency of the conversion of light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis
1%
Tragedy of the Commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community
invasive species
plants and animals that have migrated to places where they are not native
invasive species solutions
1. sterilization
2. lampricides
3. barriers/ traps
4. pheromones and alarm cues
5. regulations
indicator species
Species that serve as early warnings that a community or ecosystem is being degraded.
foundation species
species that plays a major role in shaping a community by creating and enhancing a habitat that benefits other species
endangered species
A species whose numbers are so small that the species is at risk of extinction
threatened species
A species that could become endangered in the near future
endemic species
species that are native to and found only within a limited area
generalist species
species with a broad ecological niche
specialist species
Species with a narrow ecological niche. They may be able to live in only one type of habitat, tolerate only a narrow range of climatic and other environmental conditions, or use only one type or a few types of food.
keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
Net Primary Productivity (NPP) formula
NPP = GPP - R where R = respiratory loss
units for Primary Productivity
kcal/m2/yr.
Net Primary Productivity
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers use for respiration
provisioning
provides humans natural resources (production of food, water, wood…)
regulating
benefits from ecosystem processes. climate regulation, flood regulation, water purification.
cultural
cultural benefits like recreation education or spiritual benefits
supporting
services that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services. (nutrient cycling, soil formation,habitat provision, primary production)