Understanding Vital Signs and Body Temperature
Vaporization
Evaporation of moisture from body (Insensible water and heat loss) ie expired air and evaporation of skin moisture.
O2 saturation
How much oxygen does your blood have. It is usually checked by pulse oximeter. 95% - 100%.
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Vaporization
Evaporation of moisture from body (Insensible water and heat loss) ie expired air and evaporation of skin moisture.
O2 saturation
How much oxygen does your blood have. It is usually checked by pulse oximeter. 95% - 100%.
Diurnal Variations
Circadian rhythms affecting body temperature.
Body Temperature
Reflects the balance between the heat produced and heat loss. Measured in heat units called degrees.
Core Temperature
Temperature of the deep tissues in the body. Relatively constant - i.e. Abdominal cavity pelvic cavity.
Surface Temperature
Temperature of the skin, subcutaneous tissues, & fats. In contrast to Core Temperature, it rises and falls in response to the environment.
Hyperpyrexia
A very high fever.
Febrile
A client who has a fever (Prefix: Afebrile, meaning no fever).
Pyrexia
A fever but not as high as hyperpyrexia.
Hypothermia
Abnormally low temperature.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Rate of energy utilization required to maintain essential activities.
Muscle Activity
The more you move the more heat you will produce.
Thyroxine Output
Effect: chemical thermogenesis.
Stress
Increase our cellular metabolism.
Fever
Abnormally high body temperature.
Intermittent Fever
Alternating temperature at regular intervals between periods of fever and periods of normal or subnormal temperatures.
Remittent Fever
Wide range of temperature fluctuations (more than 2°C [3.6°F]) occurs over the 24-hour period, all of which are above normal.
Relapsing Fever
Short febrile periods of a few days are interspersed with periods of 1 or 2 days of normal temperature.
Constant Fever
Body temperature fluctuates minimally but always remains above normal.
Radiation
Transfer of heat from one surface to another without contact between the two objects.
Conduction
Transfer of heat between two objects in contact.
Convection
Dispersion of heat by air currents.
Types of Thermometer
Includes mercury in glass thermometer, electronic thermometer, chemical disposable thermometer, temperature sensitive tap, infrared thermometers, and temporal artery thermometers.
Fever Spikes
A temperature which rises to fever level rapidly following a normal temperature and then returns to normal within a few hours.
Celsius
Centigrade temperature scale.
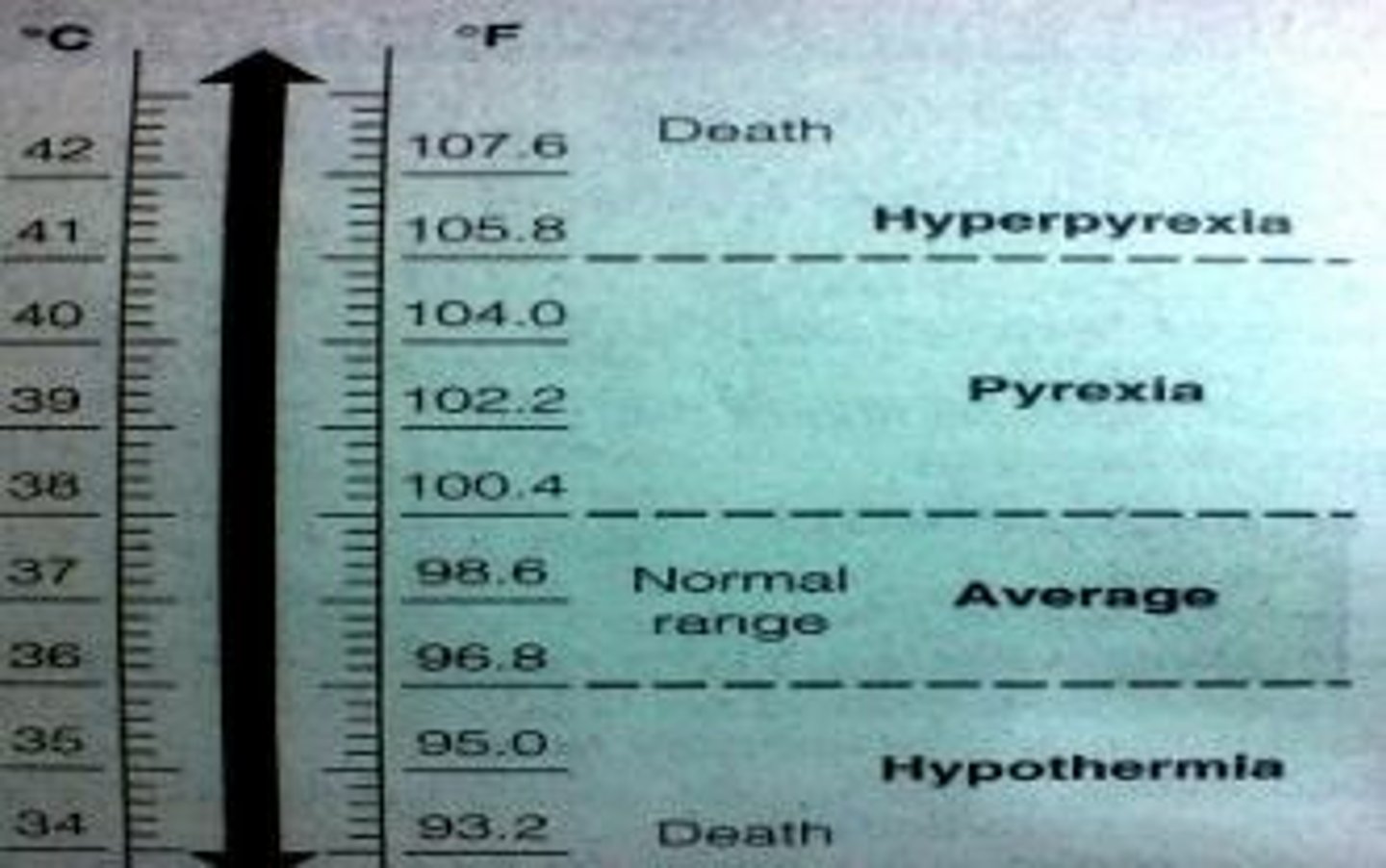
Fahrenheit
Temperature scale where 100F indicates fever.
Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion
C= (Fahrenheit temperature- 32) x 5/9
Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion
F= (Celsius temperature x 9/5) +32
Resolution By Crisis
Patient took medication to address the fever.
Resolution By Lysis
Fever slowly decreases.
Pulse
Wave of blood created by contraction of the left ventricle of the heart.
Stroke Volume
Normal stroke volume is 70cc each contraction of the left ventricle.
Heart Rate (HR)
Expressed in beats per minute (BPM).
Hypothermia
Body temperature that is lower than normal.
Accidental Hypothermia
Exposure to cold environment, immersion in cold water, or lack of adequate clothing.
Induced Hypothermia
Usually done during surgery.
Compliance
Ability to contract and expand (arteries).
Cardiac Output
Volume of blood pumped into the arteries by the heart, calculated as CO = SV X HR.
Peripheral Pulse
Pulse located away from the heart.
Apical Pulse
Central pulse located at the apex of the heart.
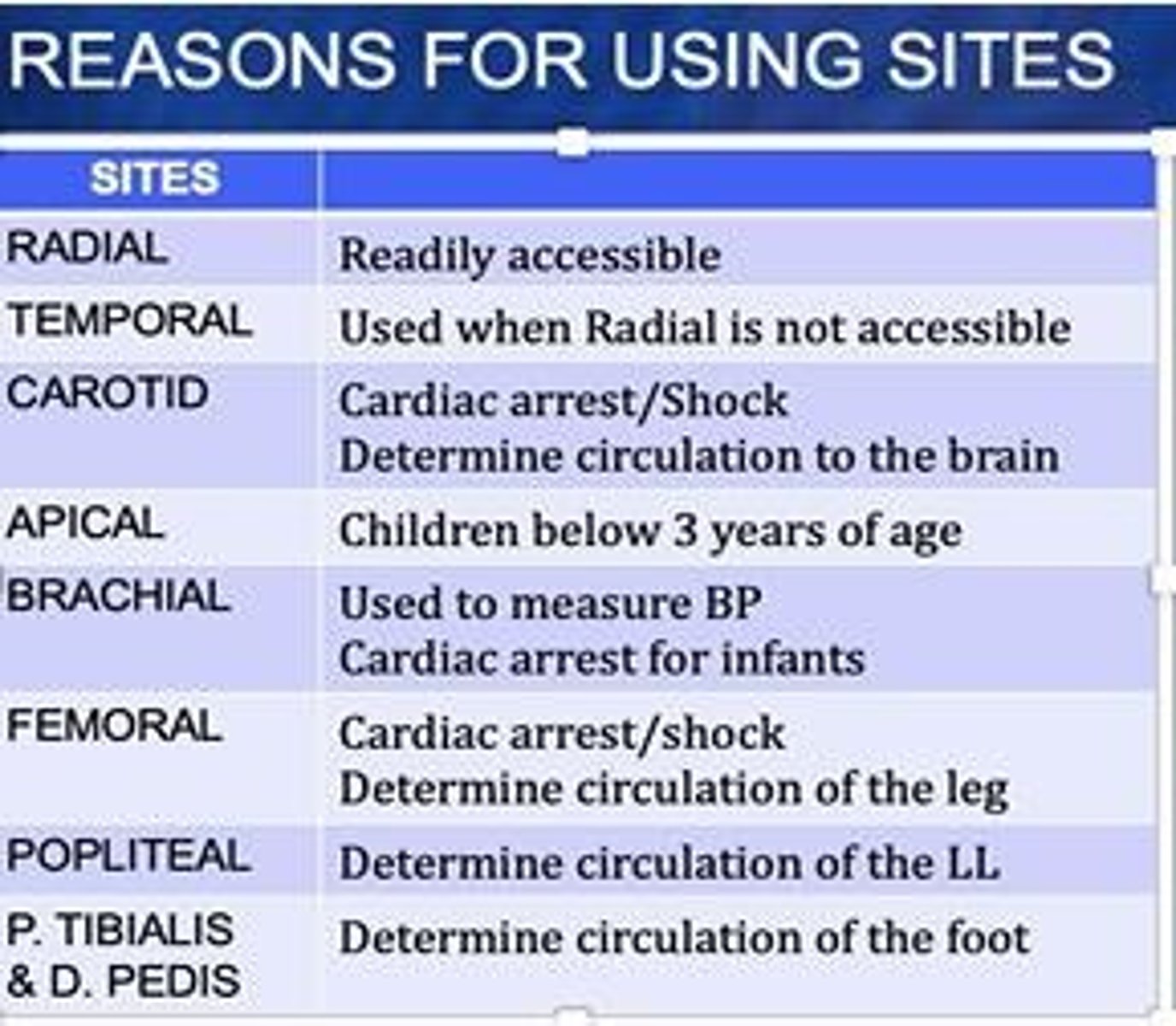
Rectal Temperature Measurement
Reliable measurement for core temperature but contraindicated for certain conditions.
Axillary Temperature Measurement
Preferred site for measuring temperature in newborns but may not accurately detect fever.
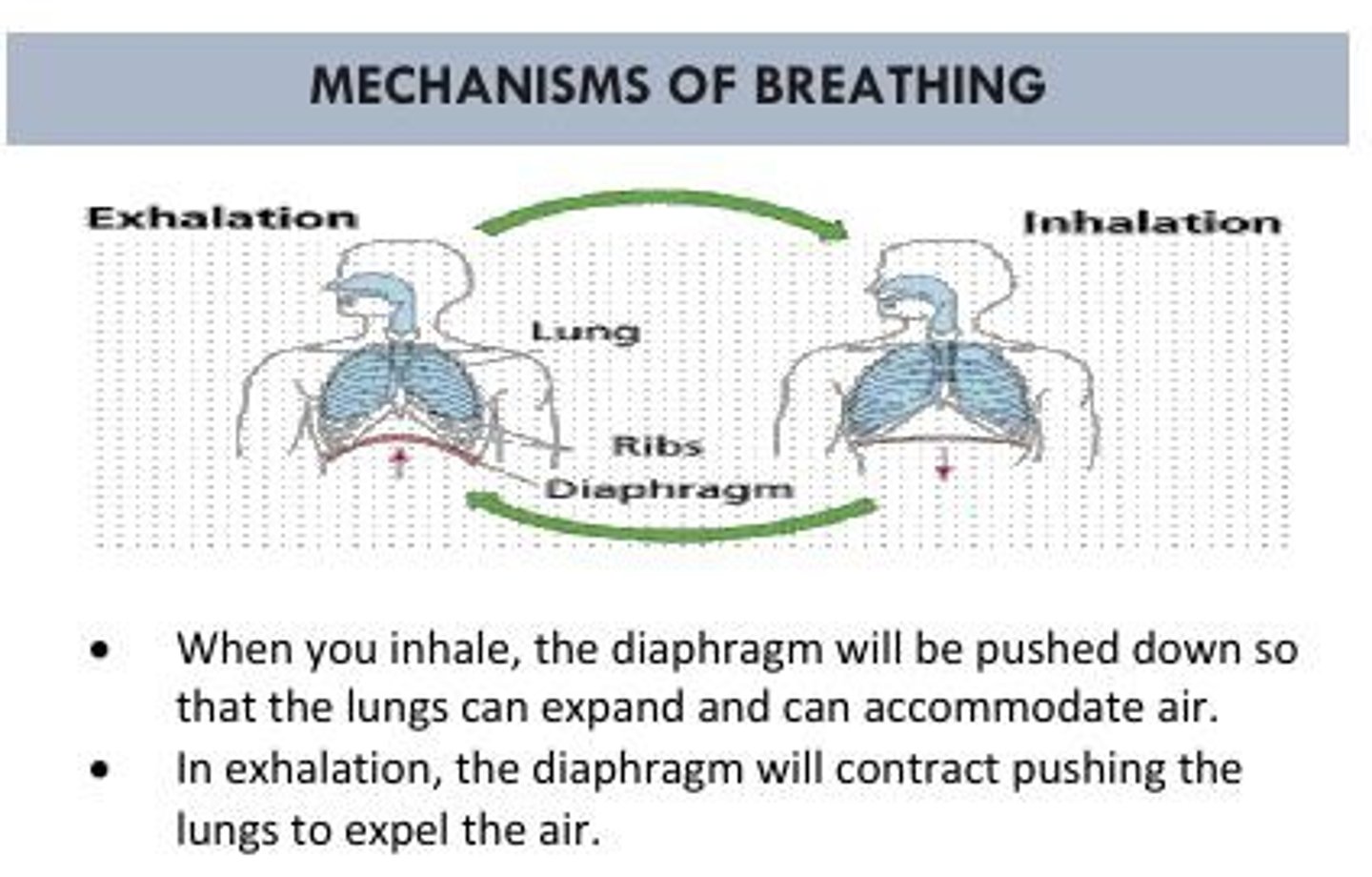
Respiration
The act of breathing.
Tachycardia
Excessively fast heart rate.
Bradycardia
Decreased heart rate than normal.
Dysrhythmia
Pattern of the beats and the intervals between the beats.
Costal Breathing
Involves the external intercostal muscles and accessory muscles.
Diaphragmatic Breathing
Involves the contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm.
Pulse Volume
Refers to the force of blood with each beat, also known as pulse strength.
Apnea
Absence of breathing.
Eupnea
Normal breathing.
Apical-Radial Pulse
Normal if apical and radial rates are identical; abnormal if apical pulse rate is greater than radial pulse.