Lecture 67: Dermatopathology Response to Injury
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is thinning of skin due to decreased epidermal/dermal thickness caused by steroids, chronic ischemia, radiation, or autoimmune cytotoxicity?
atrophy
Smooth skin with loss of surface detail indicates what type of skin lesion?
atrophy
What type of skin lesion is common on pressure points?
callus
What is localized thickening (lichenification) from chronic pressure or friction?
callus
What is a dilated follicle filled with keratin and sebum that can rupture and cause inflammation?
comedone
What skin lesion is seen in chronic solar injury, endocrine disorders, or breed syndromes (Schnauzers)?
comedone
What is skin crusts?
dried serum, necrotic cells, or exudate on surface
What type of skin lesions are secondary lesions in infections such as dermatophilosis or pemphigus foliaceus?
crusts
What are fluid or keratin-filled sacs lined by epithelium?
cysts
What is a circular ring of exfoliating stratum corneum with erythematous margin?
collarette
What skin lesion is characteristic of staphylococcus pseudointermedius infection (superficial spreading pyoderma)?
collarette
What skin lesion is most, nonhemorrhagic, and involves partial-thickness epidermal loss?
erosions
What type of skin lesion common in self-trauma or mild injury heals without scarring?
erosions
What is full thickness epidermal loss exposing dermis, often hemorrhagic and granular?
ulcers
What is the fibrotic remodeling following injury? These can be atrophic (depressed) or hypertrophic (raised)?
scars
What type of skin lesion can cause permanent hair loss or pigmentation loss?
scars
What is the difference between vesicles and bullae?
vesicles < 1 cm and bullae > 1 cm
What type of fluid filled skin lesion is seen in viral, autoimmune, or hereditary blistering diseases?
vesicles/bullae
What are raised solid lesions caused by cellular infiltration or tissue deposition?
papules/nodules/plaques
What skin lesion commonly seen in pyoderma or pemphigus is elevated and filled with pus?
pustules
What is the dry or oily accumulation of keratin seen in seborrhea, ectoparasitism, lupus, or ichthyosis?
scale
What are the hard conical keratin projections associated with papillomas, SCC, or viral infections?
cutaneous horns
What is the thickened, folded skin from chronic trauma or inflammation common in chronic dermatitis?
lichenification
What skin lesion is characterized by white hair from melanocyte loss in follicles and commonly seen in vitiligo, alopecia areata, trauma, or aging?
leukotrichia
What is excess dermal hyaluronic acid deposition, causing thickened, pitted skin seen in Shar Pei dogs (genetic) or hypothyroidism?
mucinosis
What are the epidermal injury reaction patterns?
hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, dysplasia, necrosis, vesiculation
What are the skin inflammatory patterns:
perivascular/interstitial dermatitis, vasculitis, folliculitis, panniculitis
What are the two types of radiation injury?
ionizing radiation (x-rays): high-energy, causes DNA ionization and tissue necrosis
nonionizing radiation (UVR): damages DNA through chemical reactions, causing photoaging and neoplasia
What are the results of UVA and UVB solar injury?
sunburn, solar dermatitis, actinic keratosis, and squamous cell carcinoma affecting poorly pigmented or sparsely haired areas
What is the difference between UVA and UVB solar injury?
UVA: penetrates deeper, generates free radicals → DNA and membrane damage
UVB: directly damages DNA, forming pyrimidine dimers → apoptosis or mutation
What is chronic solar dermatitis?
result of prolonged UV exposure that leads to epidermal hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, and comedone formation → ruptured actinic comedones can lead to pyogranulomatous dermatitis
What is moderate heat dermatitis?
dermatitis caused by chronic radiant head from pads, heaters, or surfaces → erythema, alopecia, hyperpigmentation
What are the four types of thermal burns?
first-degree: epidermal erythema, edema
second-degree: vesicle/blister formation
third-degree: full-thickness necrosis of dermis and adnexa
fourth-degree: extends to subcutis or muscle
What is acute solar injury (sunburn)?
acute UVB injury affecting nonpigmented, sparsely haired skin → keratinocyte necrosis, inflammation and pain → if chronic = hyperpigmentation, scaling, lichenification
What can chronic UV damage lead to?
actinic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma, hemangiomas, and hemangiosarocmas
True or false: prognosis of UV-induced hemangiosarcomas is better than non-sun-induced types
true
What is the cold injury causing vascular ischemia and cellular dehydration, leading to pale necrotic skin on extremities and coagulative necrosis and thrombosis in microvasculature?
frostbite
What is type I - primary (phototoxic) photosensitivity?
ingestion of preformed photodynamic compounds in plants (ex. St. John’s wort, buckwheat) or drugs (tetracyclines, phenothiazine) causing lesions on white-haired, sun-exposed skin (commonly in herbivores)
What is type II - congenital (porphyric) photosensitivity?
defective porphyrin metabolism → accumulation of uroporphyrins and coproporphyrins (ex. bovine congenital porphyria) ; affects poorly pigmented areas, commonly seen in cattle, pigs, and cats
What is type III - secondary hepatogenic photosensitivity?
(most common type) liver unable to excrete phylloerythrin (chlorophyll breakdown product), triggered by lantana, tribulus, or mycotoxins and causes erythema, edema, blisters, and necrosis (facial eczema) in cattle and sheep
What is the pathophysiological pathway of photosensitivity?
Photodynamic compounds + sunlight (UVA/UVB) → reactive oxygen species → membrane and DNA damage → necrosis and inflammation in lightly pigmented skin
What can cause skin atrophy?
excess steroids (systemic or topical), chronic ischemia, and radiation injury
What is a morphologic characteristic and important clinical lesion of skin atrophy in dogs?
loss of cobblestone appearance of nasal planum (skin smoothing)
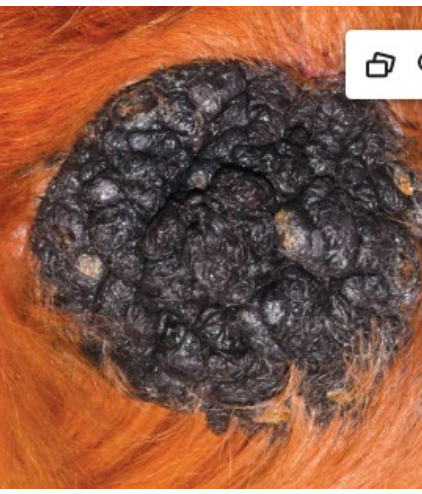
What skin lesion is present on this dog’s elbow?
callus
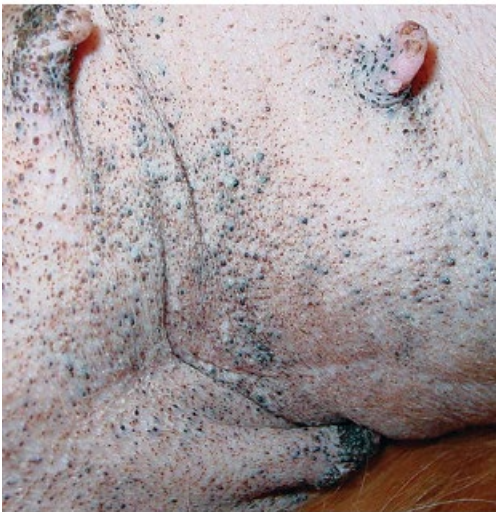
comedone
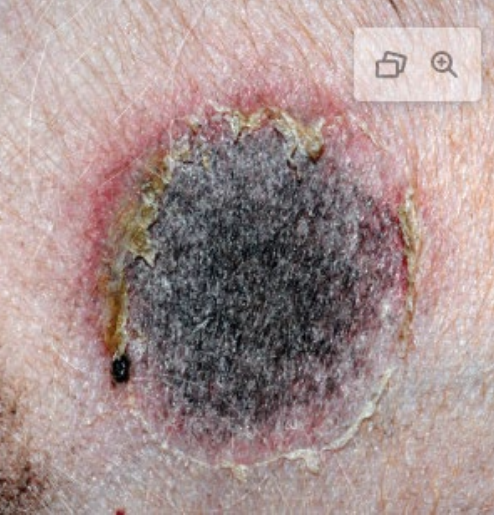
collarette
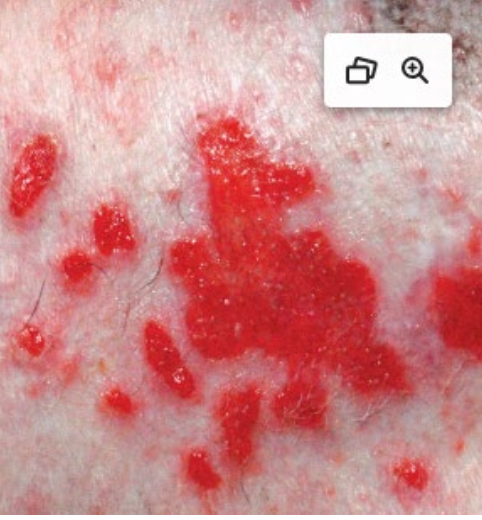
erosions
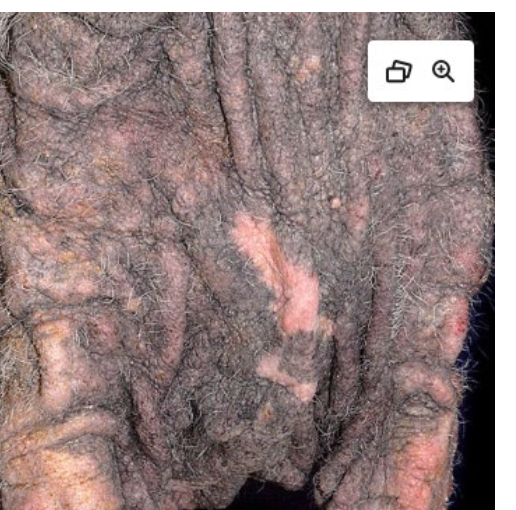
lichenification
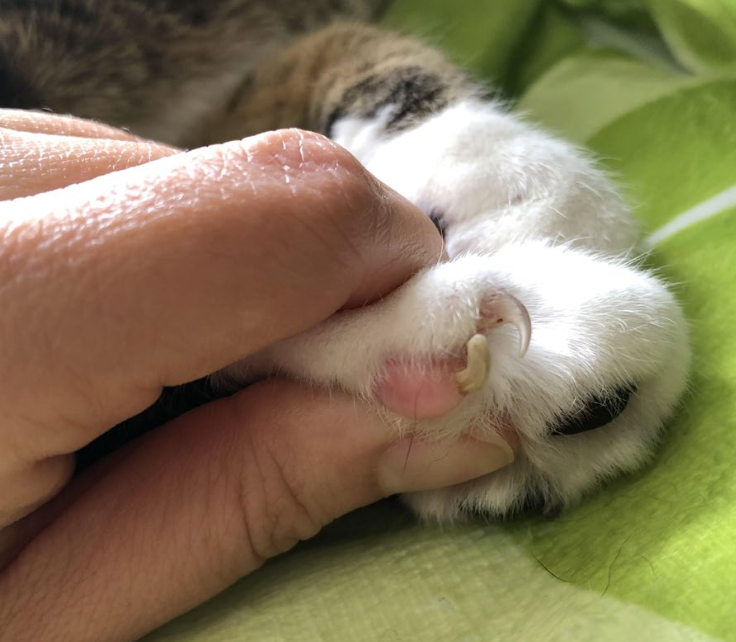

cutaneous horn
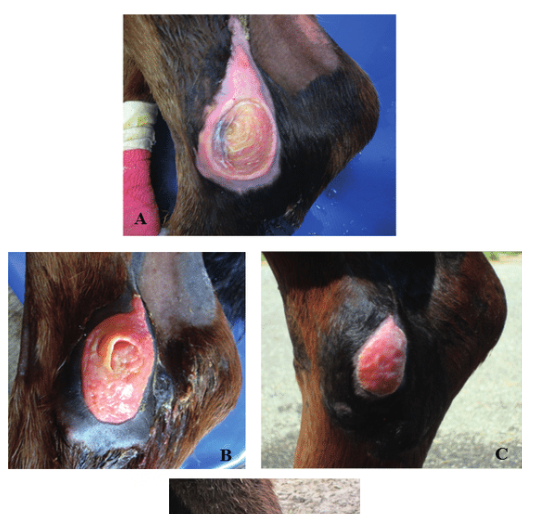
This injury was a result of sustained pressure injury to the skin causing ischemic necrosis.
decubitus ulcer
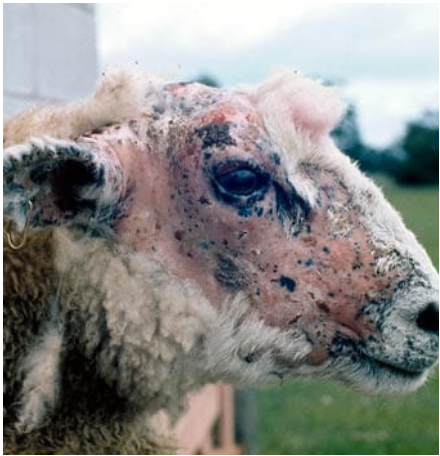

What is affecting this sheep?
type III phototoxicity