Exam 2 Intro to Animal Science
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
female reproductive responsibilities
provide ____ ovum and release it at the ____ time
provide viable ovum and release it at the right time
female reproductive responsibilities
successfully _____
successfully conceive
female reproductive responsibilities
provide for the ____ during pregnancy
provide for the fetus during pregnancy
female reproductive responsibilities
successfully ____ fetus
successfully deliver fetus
female reproductive responsibilities
____ and ____ the newborn
accept and nourish the newborn
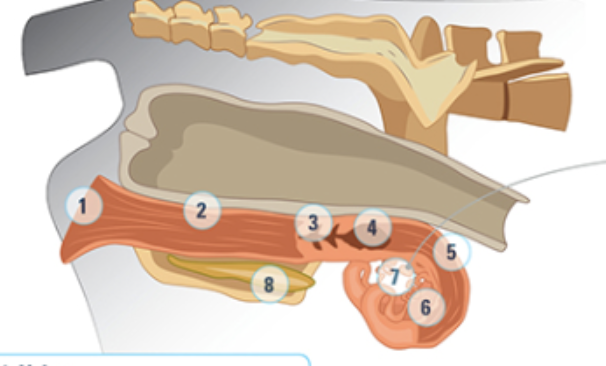
what is #1
Vulva: most outside part, as animal approaches estrus, the vulva will swell and be moist and red
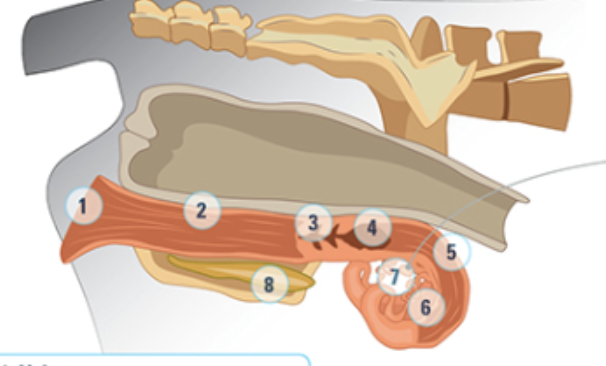
what is #2
the vagina
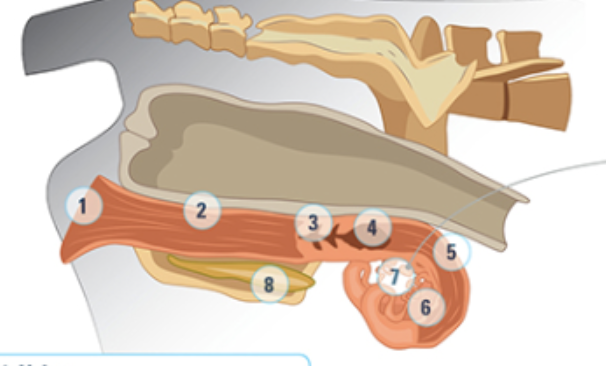
what is #3
the cervix: a thick walled organ that forms the connection between the vagina nd the uterus. It protects the uterus from the external environment
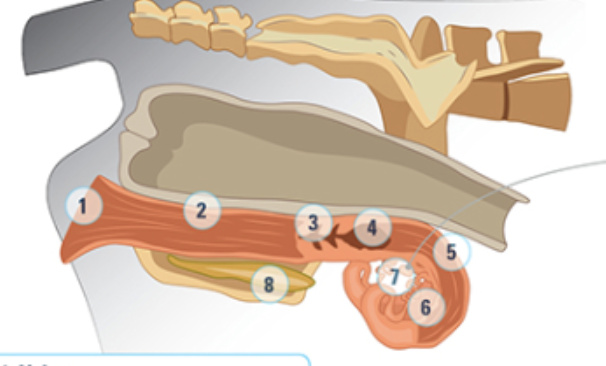
what is #4
the uterine body: where semen is deposited at artificial insemination
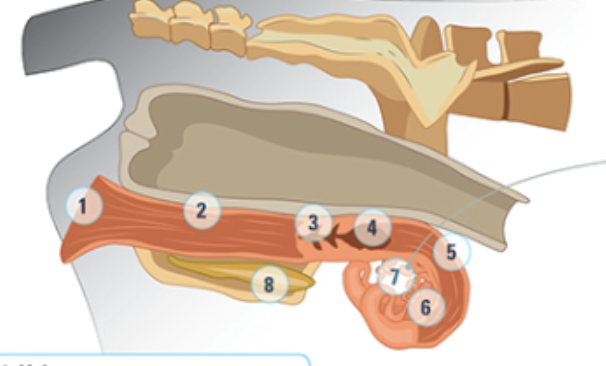
what is #5
the uterine horn: three layers of muscle strongly vascularized. Under the influence of oxytocin and estrogen these muscles rhythmically contract to aid the transport of sperm into the oviducts
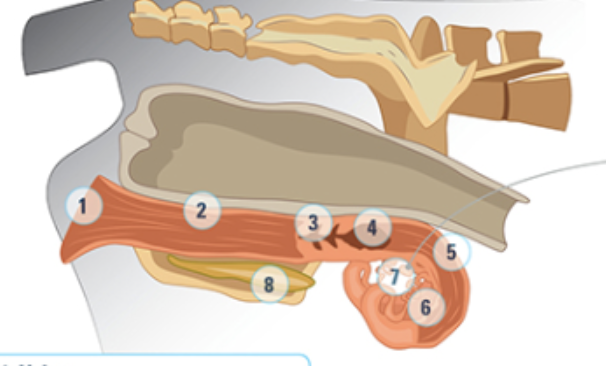
what is #6
the oviduct: where the eggs are
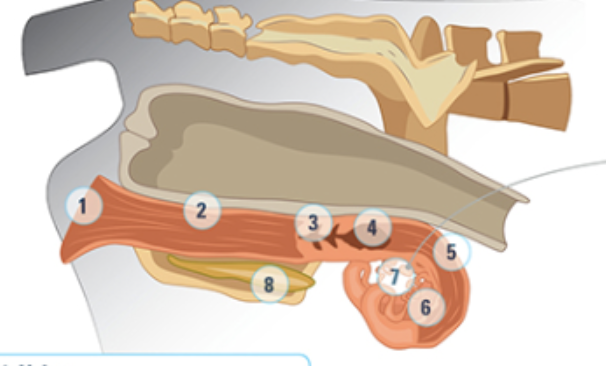
what is #7
the ovary
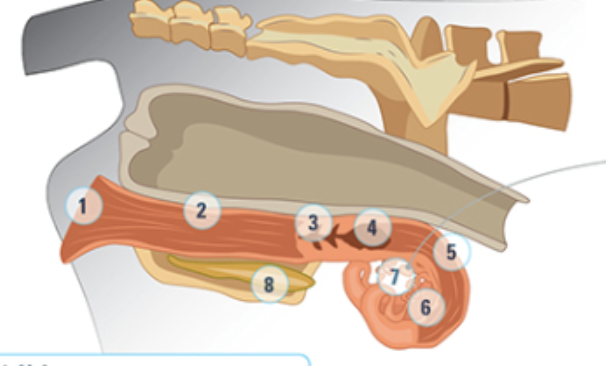
what is #8
bladder
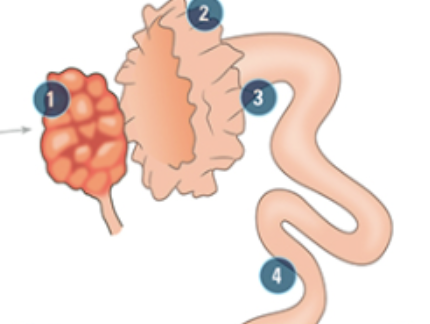
what is #1
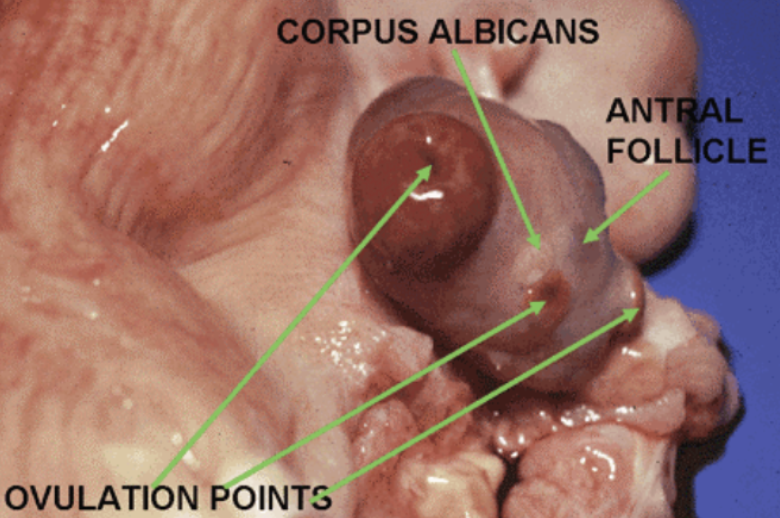
the ovary: produces oocytes and hormones throughout the Estes cycle. Hold multiple follicles and the corpus lutes and the site where previous ovulation took place.
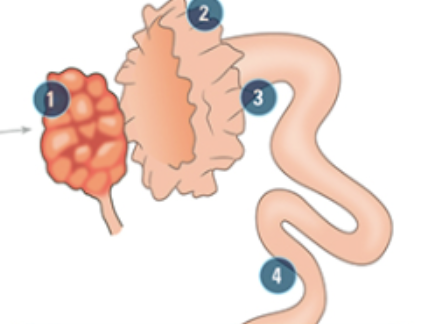
what is #2
Infundibulum: on the open end of the oviduct, it surrounds the very and keeps eggs from falling into the body cavity
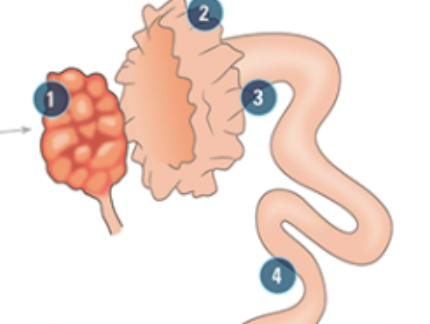
what is #3
Ampulla: part closest to the oviduct where the actual fertilization happens
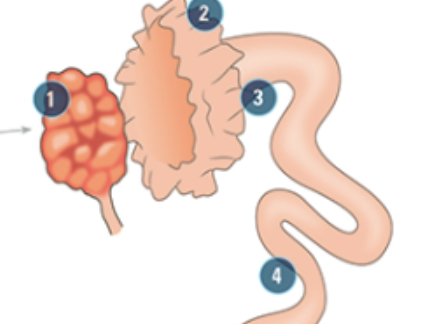
what is #4
the Isthmus: holds spermatozoa as they mature in a process called capacitation
major structures of the female reproductive tract
ovary, oviduct, uterus, cervix, vagina, external genitalia
the ovary
produce oocytes, estrogen, and progesterone
what is oocytes
a cell in. an ovary which may undergo meiotic division to form and ovum
parts of the ovary
what are follicles
blister-like structures, contain ovum; there is 4 types of follicles in the ovary
types of follicles
primordial follicles
most immature and are the smallest encountered in the ovarian cortex
types of follicles
primary follicle
what the primordial follicles develop into, more advanced. surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal epithelium
types of follicles
secondary follicle
two or more layers of follicle cells, without an antrum (cavity); also surrounded by a thick translucent layer called zonapellucida
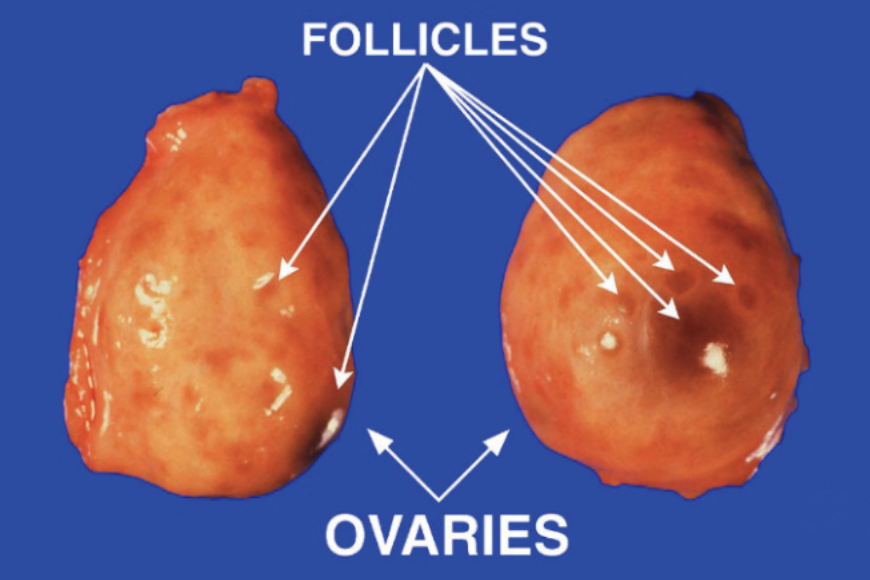
types of follicles
tertiary follicle (developing antral follicle)
fluid (follicular fluid) filled cavity and can be observed with the naked eye because it is on the surface of the ovaries
folliculogenesis
process of when an immature follicle develop into more advanced follicles and become “candidates” for ovulation
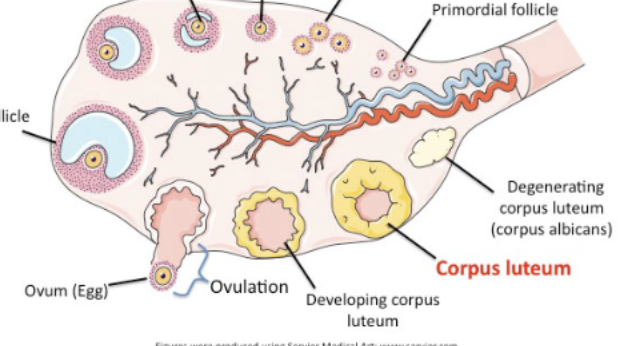
parts of the ovary
corpus luteum
“yellow body” (yellow mass of cells), produces progesterone, is essential for establishing and maintaining pregnancy in females
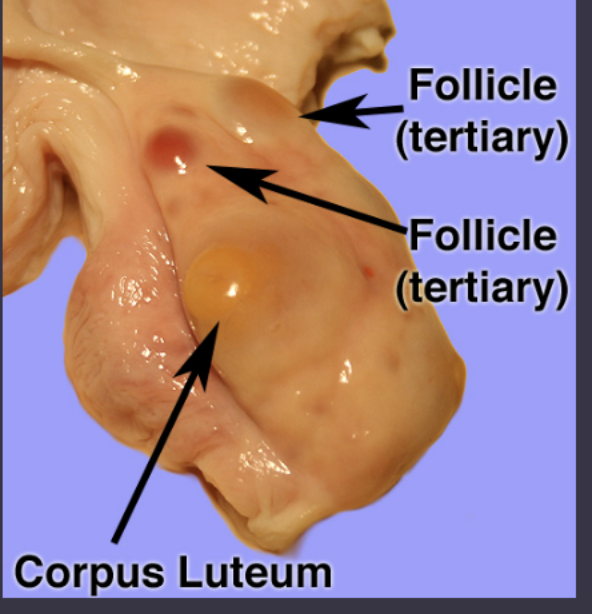
progesterone
steroid hormone responsible for the decidualization of the endometrium and maintenance
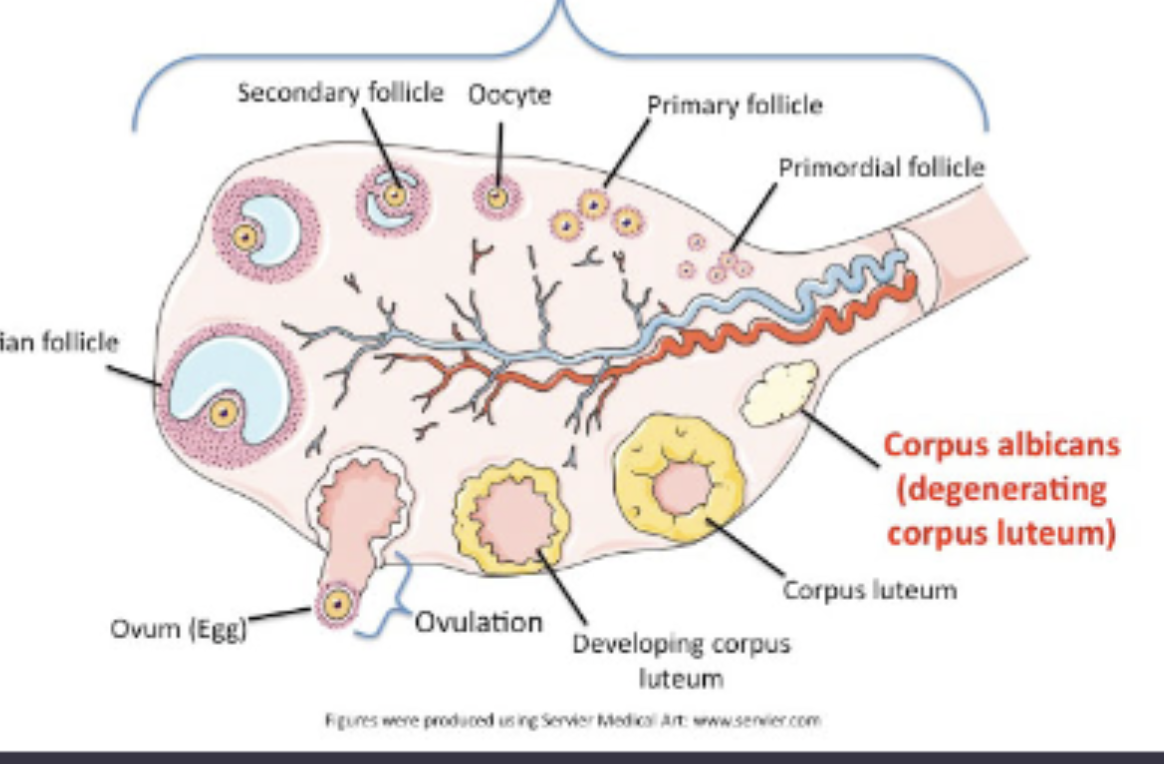
parts of the ovary
corpus albicans
“white body,” it is the degenerating version of the corpus luteum, scar like structure, presence and function doesn’t contribute to fertility but indicates healthy reproductive system.
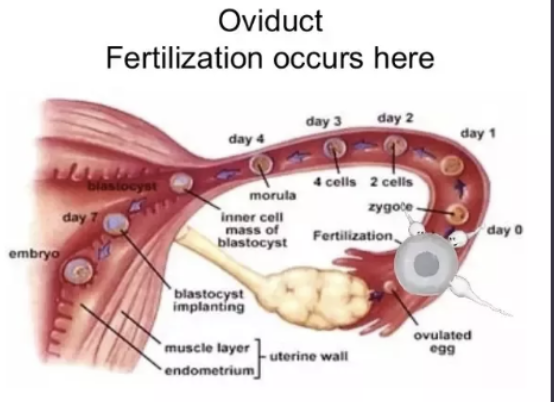
reproductive tract
oviduct
transport ova and sperm, site of fertilization and early cleavage safe environment for fertilization, transports egg to the central channel of the uterus
reproductive tract
uterus
assist in sperm transport, regulates corpus luteum, glandular secretions nourish embryo prior to placenta
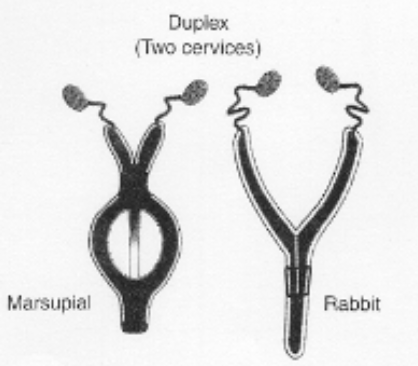
types of uteri
duplex
two uterine horns each with separate cervical canal opening directly into the vagina
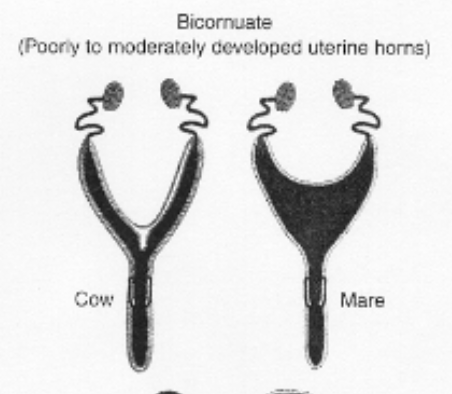
types of uteri
bicornuate
small uterine body and two long uterine horns. Upper parts of the uterus remain separate, but lower parts are fused into a single structure
types of uteri
bipartite
prominent uterine body and two uterine horns, share single cervix
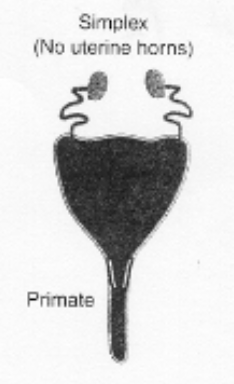
types of uteri
simplex
pear shaped body with no uterine horns. Entire uterus is fused into a single organ
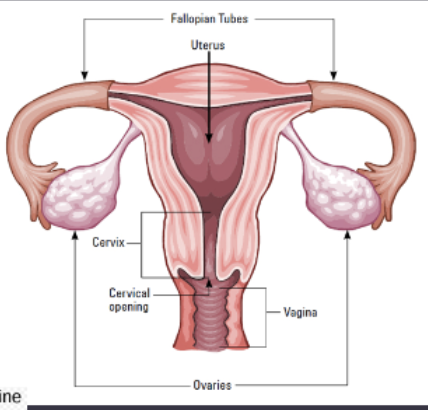
reproductive tract
cervix
facilitating sperm transport and prevents uterine contamination
reproductive tract
vagina
copulation organ and the birth canal
estrus
a noun: means standing heat (phase of sexual receptivity) and the act of ovulation (expulsion of ova)
estrous
adjective: the cycle of ovulation in females; used to describe things related to estrus like behaviors
estrous cycle
the period from one estrus to the next
the estrous cycle
the follicular phase: 20% of cycle, large antral follicles, estradiol is primary hormone
luteal phase: 80% of cycle, corpora lutea, progesterone is primary hormone
three type of estrous cyclicity
polyestrus, seasonally polystrus, monoestrus, and diestrus
polyestrus
animals that cycle continuously through the year if not pregnant
seasonally polyestrus
animals with seasonal variations in estrous cycle, continuously cycle during specific season
monoestrus
animals with one cycle per year
diestrus
animals with two cycles per year, one in the spring and one the fall
FSH hormone
comes from the brain, stimulated follicular growth in ovaries, stimulates estrogen secretion
LH hormone
comes fro the brain, surge causes ovulation, relsutls in formation of a corpus luteum
Estrogen hormone
comes from ovaries, thickens uterine lining, inhibits FSH and LH for most of cycle, stimulates release of FSH and LH release pre-ovulation
progesterone hormone
Gomes from ovaries, thicken uterine lining and inhibits FSH and LH
what does the mammary glad do
provides nutrition to offspring, source of passive immunity to offspring
the Mammary gland
what is colostrum
first milk, higher in protein, minerals, and milk fat, also extremely high immunoglobulin content
the mammary gland
what is the exocrine gland
produces secretions that pass into a system of ducts that leave the body
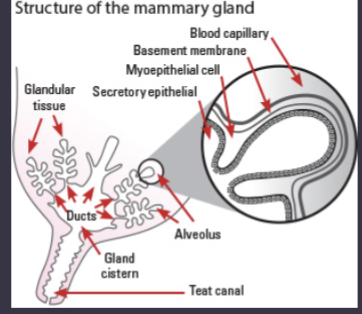
the mammary gland
what is the Alveoli
has milk secreting cells, storage of milk prior to it leaving; each alveolus has its own blood supply because the blood
why does each alveolus have its own blood supply?
The blood delivers the milk components and then the milk components are absorbed by the epithelial cells
gland cistern
where the milk is collected during milk letdown and then sucked through the teat
cow mammary gland
has 4 mammary glands and 4 teats
sheep/goats mammary glands
3 mammary glands, and 2 teats
mare mammary glands
4 mammary gland terminate into 2 teats
sow mammary glands
6- 20 mammary glands/teats (2 rows) (10-14 are functional)
mammary gland development
develops rapidly post-puberty, all the hormones help form the different parts
oxytocin
essential for milk let down and secreted from posterior pituitary
prolactin (PRL)
essential for milk production
growth hormone somatotropin
essential for lactation, supports synthesis of lactose protein and fat in mammary glands
Glucocorticoid (cortisol)
can reduce secretion and production
oxytocin release
if oxytocin is inhibited, there will be no milk let down
factors that inhibit oxytocin
pain, loud noises, stressful stimuli
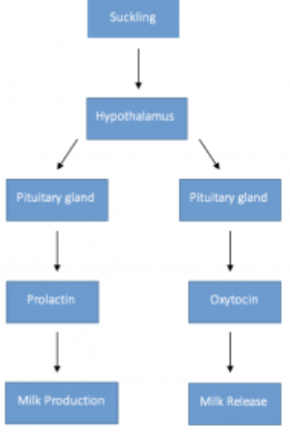
what hormones MAINTAIN lactation
somatotropin, cortisol, prolactin, and oxytocin
world milk production
over 80% comes from dairy cows, buffalo and sheep % is increasing, goats is there but not much
composition of milk
88% water, 8.6% solids-not-fat (protein, lactose, and minerals), 3-4% milk fat
milk fat
3-4% of milk composition, homogenized, 48% of calories, has vitamins D,A,K,E, over 400 different fatty acids, and it provides the flavor.
carbohydrates in milk
Lactose takes up 4.8% of milk composition, milk is the only natural source of lactose
proteins in milk
38% of SNF, contains All amino acids required by humans, contains Casein
Casein
protein only found in milk, takes of 82% of the total milk protein
vitamins in milk
milk has all vitamins essential for humans, A,D,E, K (fat-soluble), C, and B (water soluble)
minerals in milk
rich source of calcium, good source of phosphorus and zinc, has only a little iron
reproductive technologies today
artificial insemination (AI), estrus synchronization, embryo transfer, sexed semen
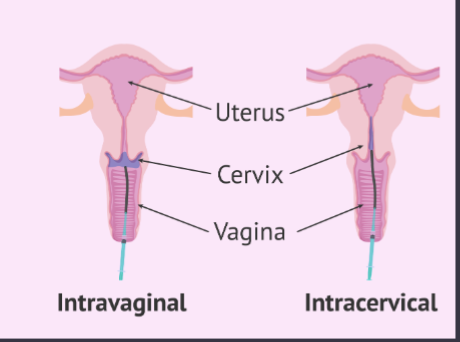
Artificial Insemination in cows, sheep, and goats
semen deposited in uterine body
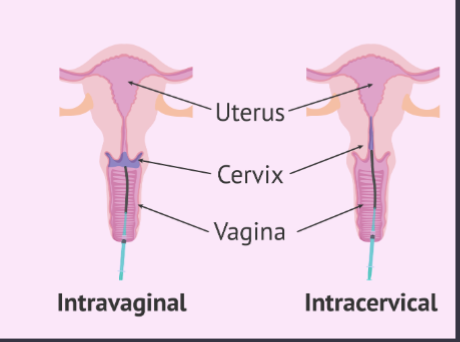
Artificial Insemination in pigs and horses
within the cervix
Artificial Insemination in poultry
into the oviduct
artificial imsemination
used to deposit stored semen directly into the family reproductive tract and can improve reproductive performance and genetic quality of livestock
heat detection aids
make it easier to identify females that are in standing heat
types of heat detection aids
gamer male, chin-ball markers, marking harness, heat detection patch, animal temperature, activity monitors, and tail chalking
Gomer/ Vasectomized Male
masectromized male animal who can still identify cows in heat but not breed them
animal behaviors when in heat
nervous/excited behavior, swelling of vulva, mounting, mucus discharge from vulva
semen collection
obtaining/collecting semen with the use of various methods
common techniques for collecting semen
the technique used depends on species and the male, techniques are the use of artificial vagina, digital manipulation, electroejaculation
artificial vagina
used to collect semen from many species (cattle and horses), the male is conscious, not afraid of people and wants to ejaculate
mounting surrogates
mounting dummies, easy to clean, minimize risk of injury, and minimize risk of disease transmission
estrus synchronization
controlling the Estrous cycle so females express estrus around the same time (used for AI or embryo transfer)
hormones used in estrous synchronization
lutalyse, estrumate, and prostamate (eliminates source of progesterone)
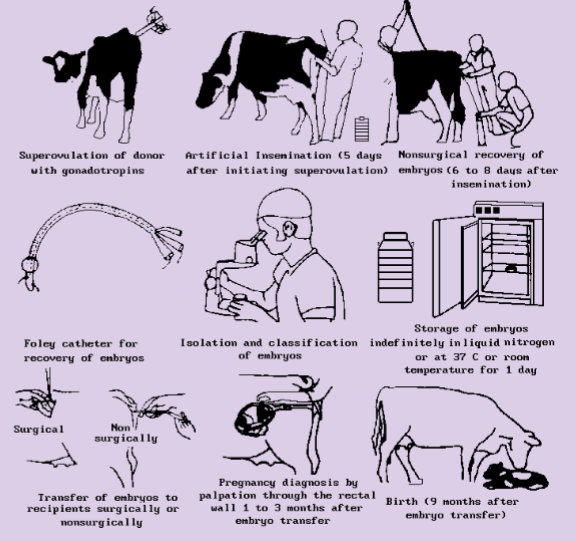
Embryo transfer benefits
can select donor female and donor male in recipient female, can evaluate quality of embryos
super ovulation
animal is ovulating super amount of egg cells than they normally would
reproduction
the process where animals produce offspring
reproductive process depends on
age, nutrition, post partum, males, length of day, parity
reproduction needs
tremendous coordination between the hypothalamus, pituitary glands, and the gonads
sexual reproduction
sperm and egg cell unite, needs two parents
sperm
male sex cell produced in the testes
egg (ovum)
female sex cell produced in the ovaries
asexual reproduction
occurs without interaction of cells or gametes. No mates required, no genes are being exchanged thought sex