Parasitology: Key Concepts, Hosts, Transmission, and Diagnosis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is Parasitology?
The study of organisms that live at the expense of a host.
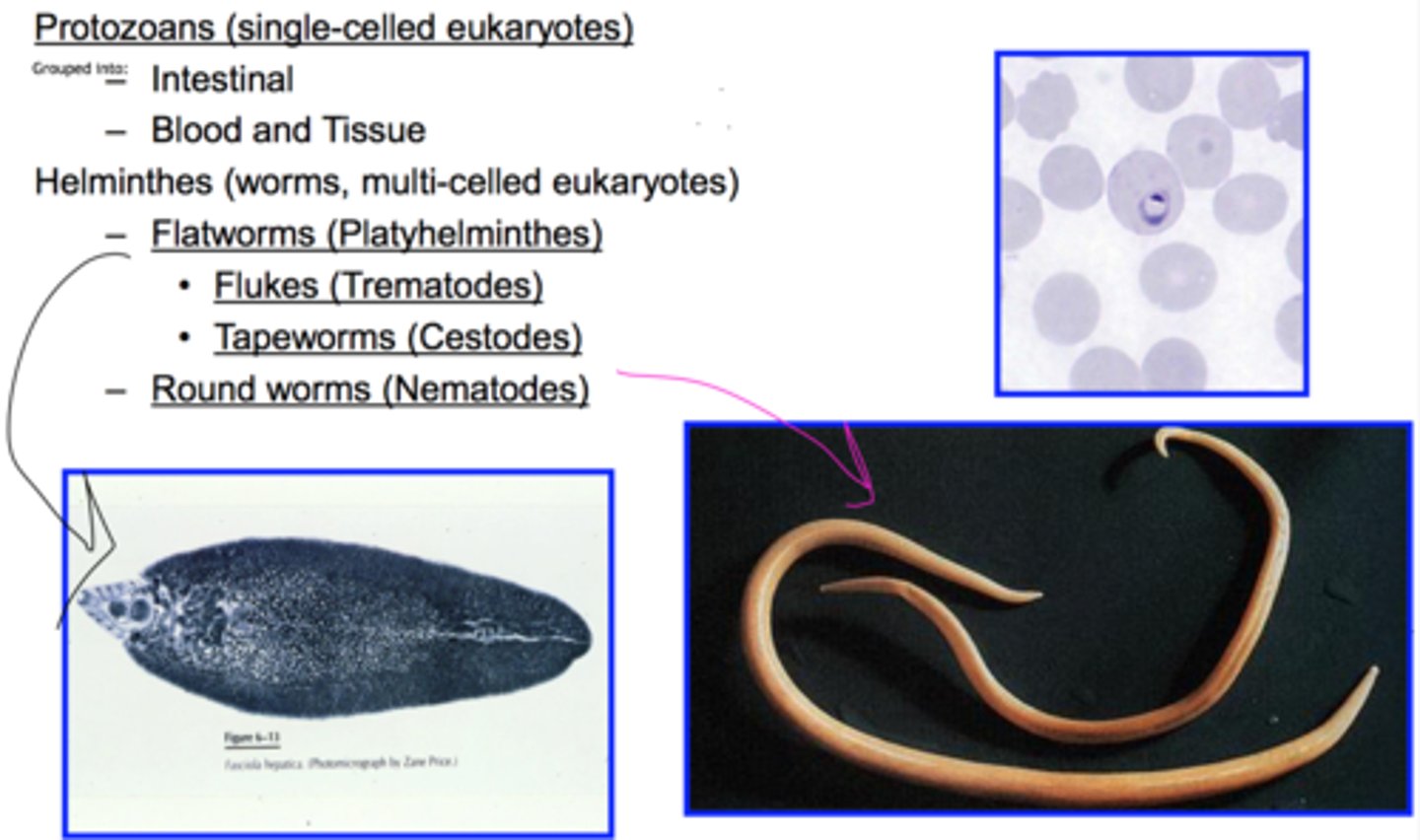
What are the two types of Parasitism?
Obligate (must have a host) and Facultative (can live independently or as a parasite).
What is the difference between a Definitive and an Intermediate Host?
Definitive hosts are where the parasite reaches sexual maturity; Intermediate hosts are required for larval/developmental stages.
What are the three main morphological groups of parasites?
Protozoa (unicellular), Helminths (multicellular worms), Ectoparasites (live on host surface).
What are the primary transmission routes for human parasites?
Ingestion (contaminated food/water), skin penetration, and vector-borne (insect bites).
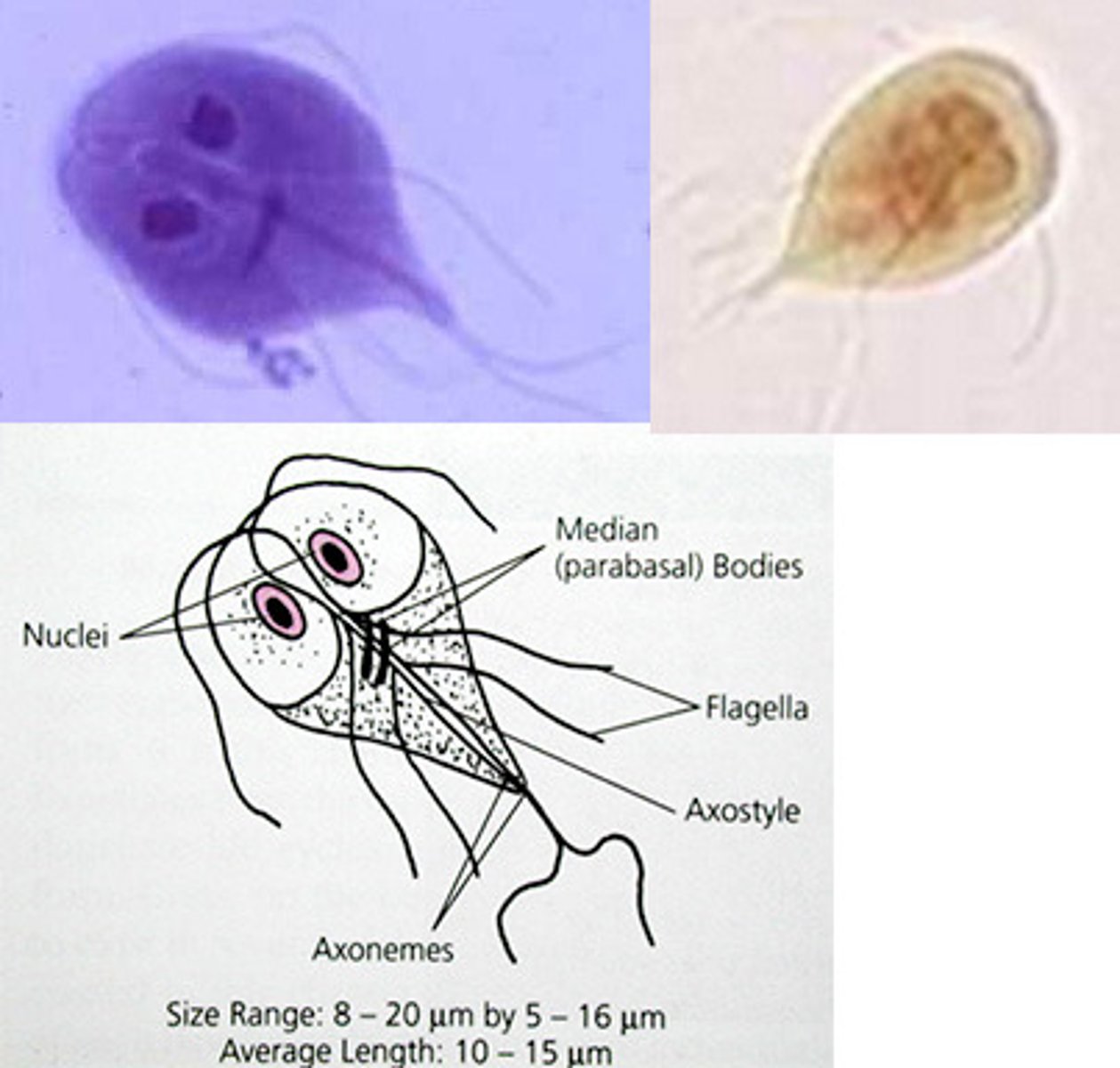
What is the 'Ventral Sucking Disk' in Giardia?
A specialised attachment organ that allows the protozoan to "suction" onto the intestinal wall, leading to malabsorption and foul-smelling, fatty diarrhoea
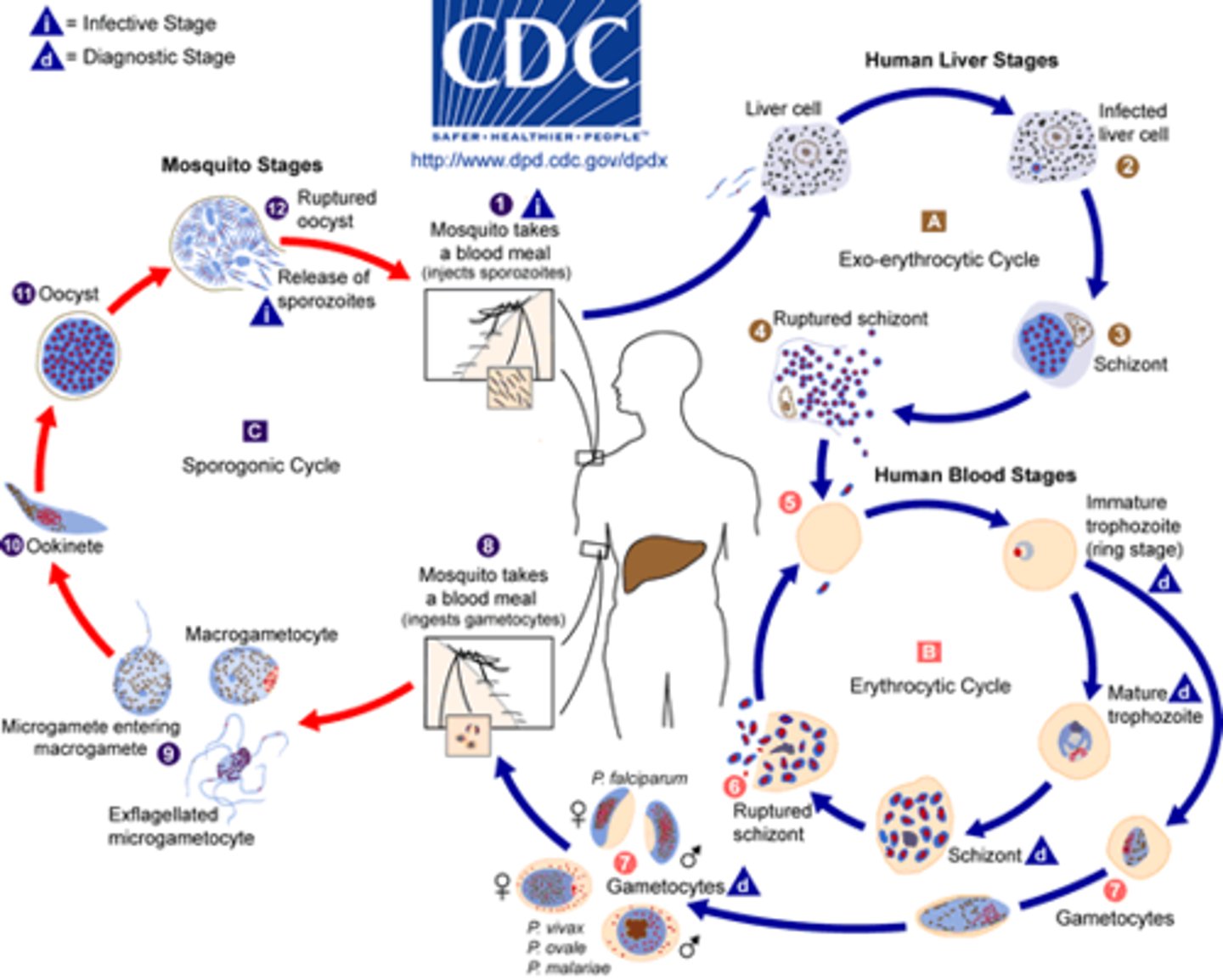
What is the difference between the 'Infective Stage' and 'Diagnostic Stage'?
Infective stage is the form that enters the host; Diagnostic stage is the form found in laboratory samples.
Why is 'Eosinophilia' a critical diagnostic marker for Helminths?
Eosinophils are WBC which attack large, multicellular parasites, and a high eosinophil count suggests a parasitic infection.
What is the global impact of 'Neglected Tropical Diseases' (NTDs)?
They affect billions of people and cause roughly 100 million DALYs, often in the poorest regions.
What is Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)?
rare, almost always fatal brain infection caused by Naegleria fowleri (the "brain-eating amoeba").
Entry: Via the nose from warm freshwater (>25°C).
Pathology: Migration through the olfactory nerve to the brain.

How is Naegleria fowleri diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis: CSF microscopy or PCR; Treatment: Amphotericin B.
What are the key clinical features of Loa loa (African Eye Worm)?
: It causes Calabar swellings (localised itchy swellings) and visible migration of the adult worm across the conjunctiva (surface of the eye).
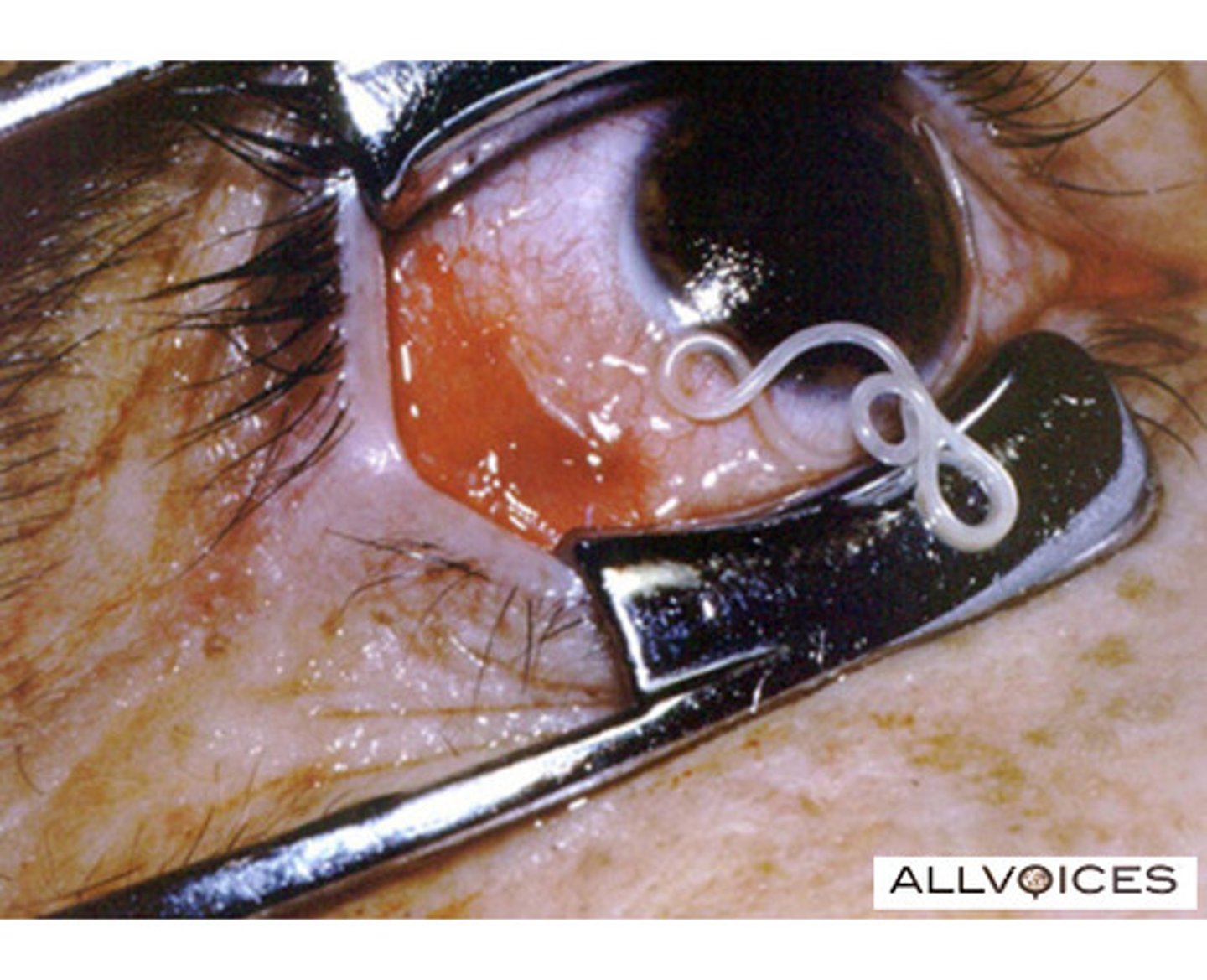
How do you diagnose and treat Loa loa?
Diagnosis: Daytime blood microscopy or PCR; Treatment: Diethylcarbamazine (DEC).
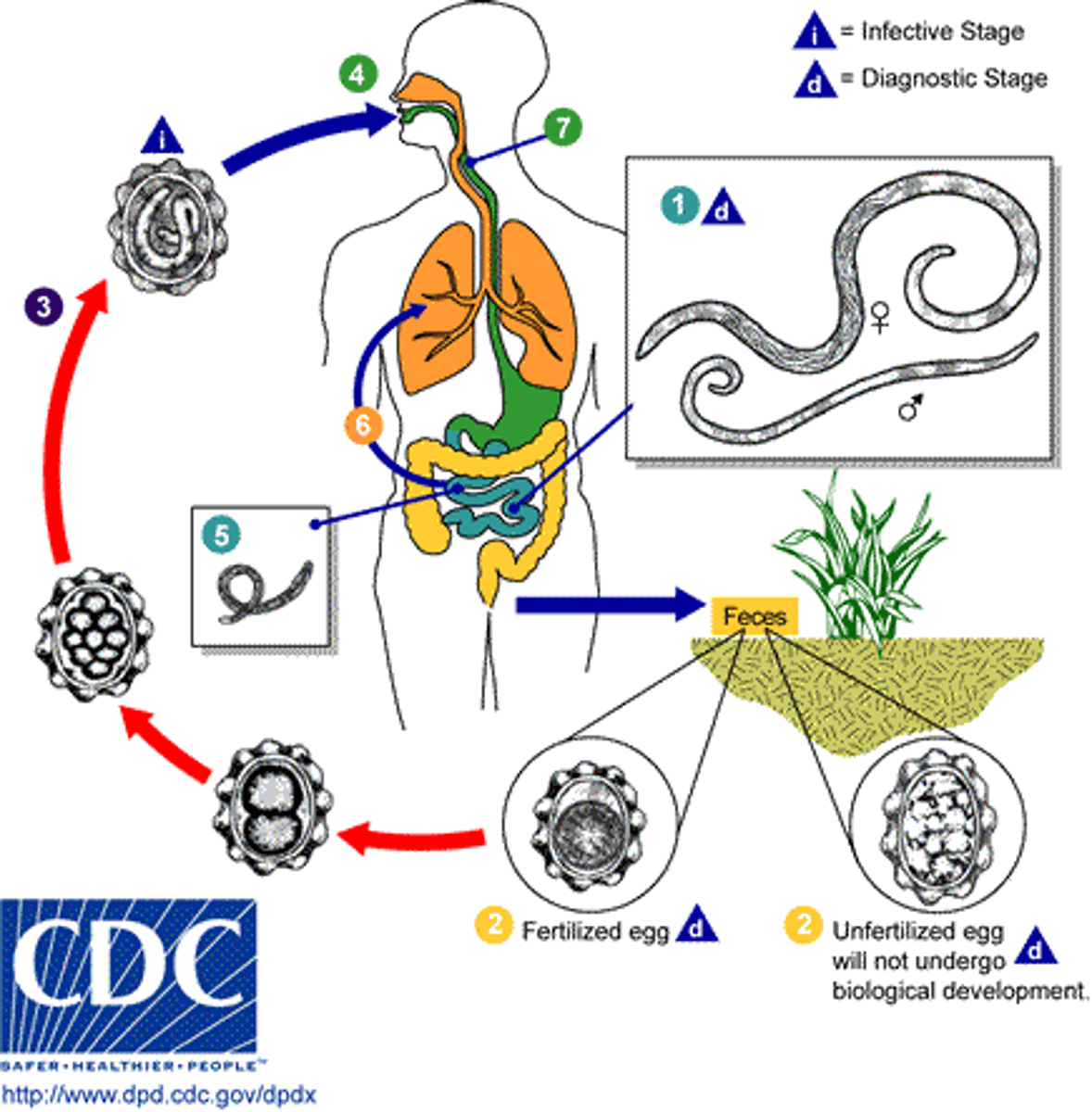
Describe the 'Human Stage' of a Soil-Transmitted Helminth (STH).
Larvae penetrate skin, migrate through lungs/heart, swallowed into gut, mature into adults.
Why is PCR often preferred over microscopy for parasitic diagnosis?
PCR is more sensitive and can detect parasite DNA at low organism levels.
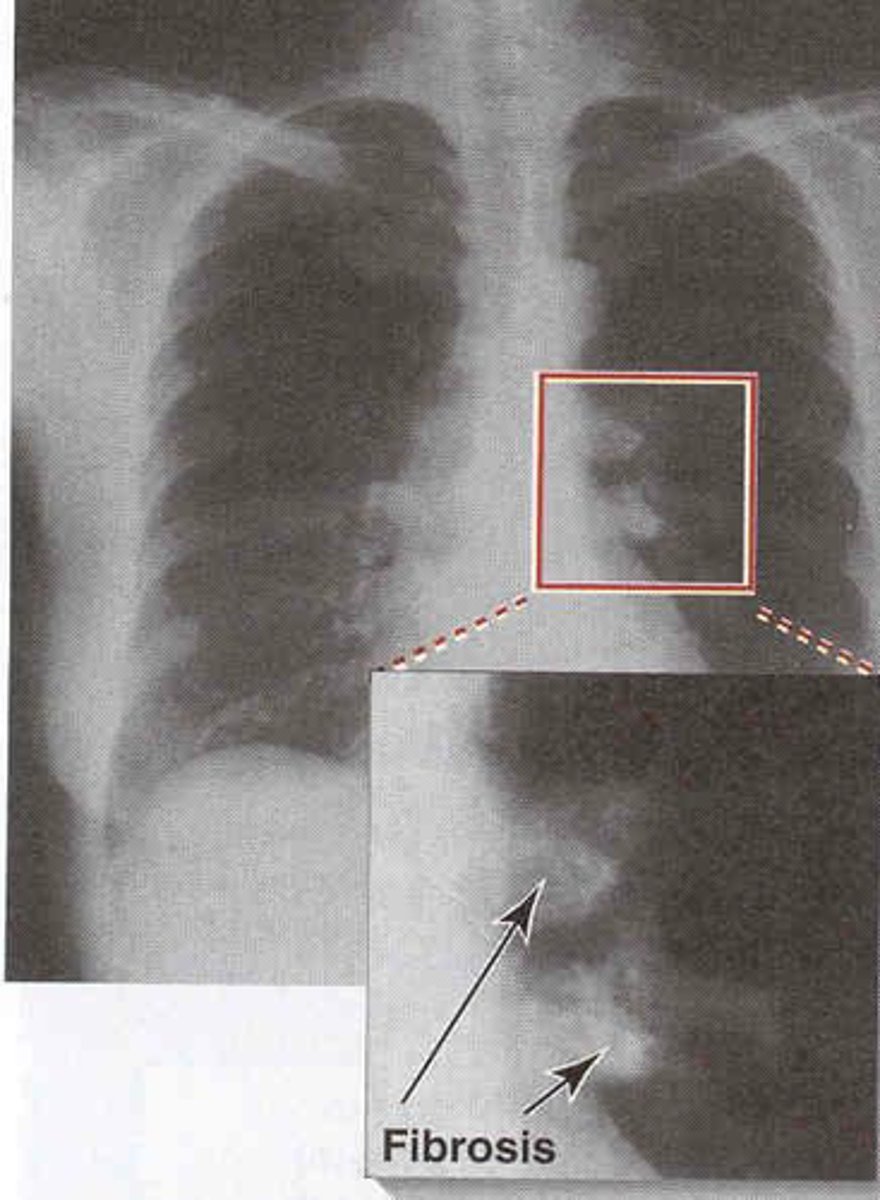
What causes 'Miliary TB'?
Systemic spread of Mycobacterium tuberculosis via blood, appearing as tiny spots on X-ray.
Why are parasitic diseases increasing in non-endemic countries?
Increased global travel/migration and Climate Change allowing vectors to survive in colder regions.