lecture 9/10: adrenal medulla and cortex I
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
mesoendodermal
embryologic origin of adrenal corotex
transcortin and albumin
90% of cortisol is bound to plasma proteins. What is the plasma protein?
albumin, transcortin
60% of aldosterone is bound to what plasma proteins?
-cortisol has a longer half life due to more of it being bound
-60 min to 20 min
compare half lives of cortisol and aldosterone
absolutely! most potent mineralcorticoid
is aldosterone necessary for life?
-cytosol receptor on the principal cells of renall collecting ducts
where does aldosterone bind?
sodium reabsorption, potassium and hydroen excretion
-water reabsorption
major effects of aldosterone:
-RAAS system has greatest control
-ACTH is permissive
-extracellular potassium concentration
controllers of aldosterone secretion:
aldosterone
hormone associated with salt sparing, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis
mostly.... it is necessary during stress
-the most potent glucocorticoid
is cortisol necessary for life?
-binds cytosol receptor on various cells in liver, muscle/bone, and adipose tissue
site of action of cortisol
-catabolic on MSK, diabetogenic, anti-inflammatory
what are the major effects of cortisol
-ACTH controlled, and induced by stress
controllers of cortisol secretion
cortisol
hormone associated with hyperglycemia
no, they are very weak androgens
-tho they do serve as precursors to more important sex hormones
is androstenedione/DHEA necessary for life?
in early age, contributes to normal development of pubic and axillary hair
-contributes to systemic testosterone/estrogen levels which are esp important for post-menopausal women
-virilizing effect pathologically in women
Major effects of DHEA
ACTH
DHEA secretion is controlled by
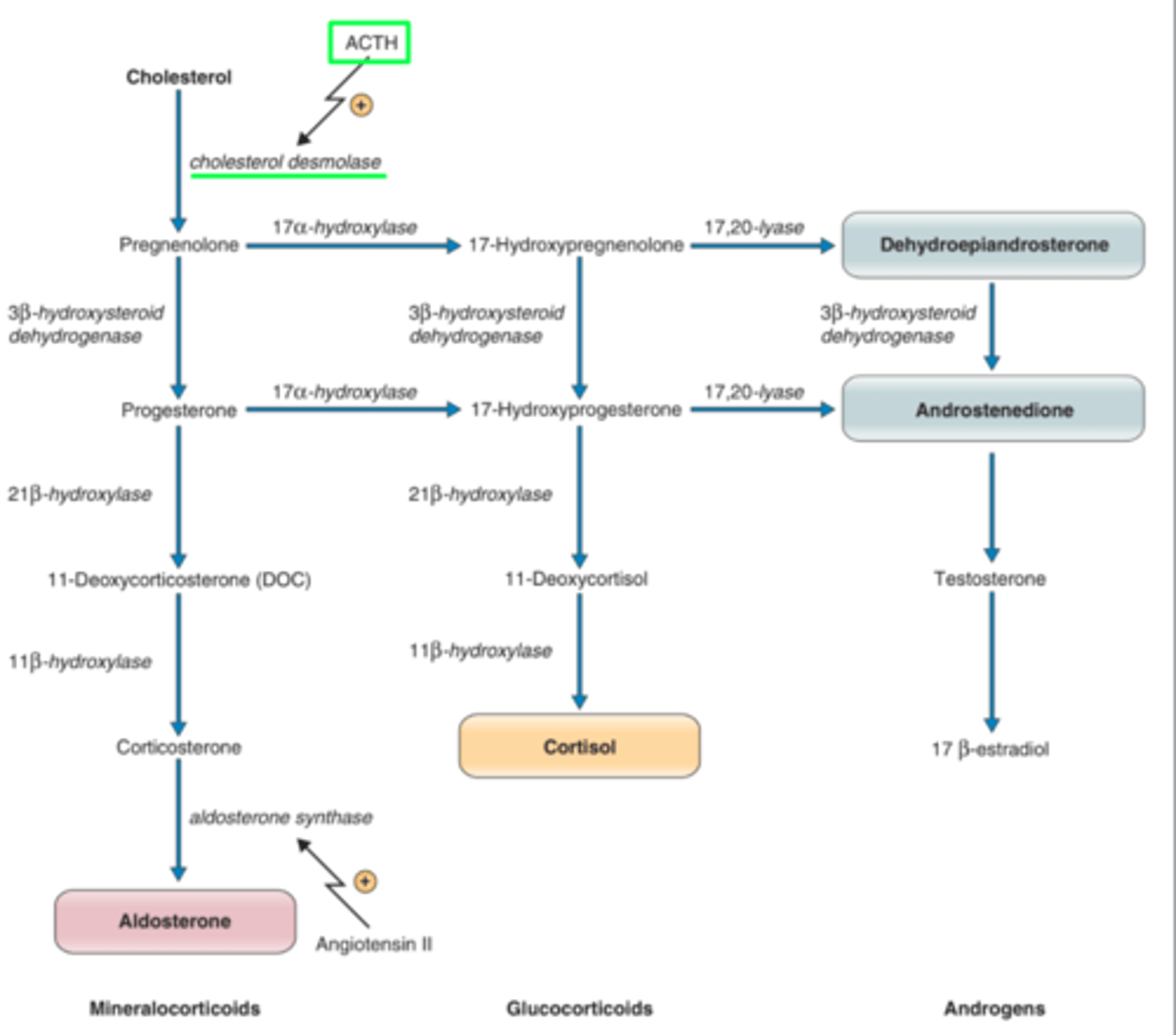
conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone by cholesterol desmolase
-performs cholesterol side chain cleavage
the first step in synthesis of the steroid hormones:
cholesterol desmolase
what is the rate limiting enzyme in steroid hormone biosynthesis
there is none! all steroid hormones coome from de novo synthesis from cholesterol
storage of steroid hormones
steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR)
a protein that mediates the transport of intracellular cholesterol across the inner mitochondrial membrane to cholesterol desmolase enzyme
progesterone, cortisol, 11-deoxycorticosterone, corticosterone, aldosterone
name the 21 carbon pregnanes
27
how many carbons is cholesterol
androgens: 19
estrogen: 18
how many carbons are androgens and estrogens
17-hydroxylase
__________ enzyme is not in the glomerulosa layer so only the fasciculata and reticularis can synthesize cortisol
ACTH and CRH
circulating cortisol exerts negative feedback control of
POMC
corticotrophs synthesize ACTH by post-translational processing of what large precursor protein?
-increase cholesterol binding to cholesterol desmolase
-increase pregnenolone production
-increase StAR protein
generates all substrates needed to make cortisol
what are the most immediate actions of ACTH when it binds to MC2R receptor on adrenal cortex?
free cortisol
negative feedback of both cortisol and DHEA
melanocortin-2 receptor (MC2R)
What receptor does ACTH bind to in adrenal cortex?
cortisol, despite multiple other secretory products
what is the main regulator of the transcription of POMC?
binds to cytosolic receptor, which then moves to the nucleus where it binds to GREs and modulates gene expression and thus inhibits the synthesis of both the CRH receptor and ACTH.
does coortisol bind cytosolic or nuclear receptors?
-plasma cortisol decreases the mRNA and peptide levels of CRH iin paraventricular hypothalamic neurons
cortisol's negative feedback on CRH in hypoothahlamus
-episodic and circadian; lowest during sleep, highest in morning
-
pattern of cortisol and ACTH secretoni
-decreases fibroblast proliferation, decreasing connective tissue
-blocks collagen formation resulting in poor wound healing
effect of cortisol on skin
-catabolic effect on amino acids results in muscle wasting
-increased resorption of bone
effect of cortison on bone and muscle
-increases glycogen via gluconeogenesis
-inhibits insulin uptake of glucose by muscle and fat
effect of cortisol on the liver
-down regulates AA transporters, decreasing protein synthesis and increasing protein degradation
-promotess FFA release form adipose cells, induces expression of hormone sensitive lipase
describe the catabolic effects of cortisol
Hormone Sensitive Lipase (HSL)
• Enzyme in the adipose cell that is responsible for the hydrolysis of triglyceride into FFAs and glycerol, which then leave the adipose cell and enter circulation
• Inhibited by the hormone insulin
-interferes with insulin receptor, increasing blood glucose
-increases expression of gluconeogenic enzymes
-promotes FFA oxidation and ketone body production
describe the diabetogenic effect of cortisol
osteoporosis
chronic glucocorticoid exposure always leads to
-induces osteoblast apoptosis, also decreases colllagen synthesis
-osteoblast death leads to increased levels of RANKL, stimulatinig osteoclasts to resorb bone
-decrease calcium uptake from GI
detail cortisol's effect on bone
-bone resorption; RANKL stiimiulates osteoclasts
increased RANKL indicates
-increase synthesis of proteins that maintain lysosomal membrane (damaged lysosomes release many inflammatory cells)
-down regulate inflammatory cytokinens
-increase expression of lipocortins
-inhibits lymphocyte replication
detail the antiinflammatory effects of cortisol
-enhances myocardial performance; increased response to catecholamines
-decrease production of prostaglandins
-decreases vascular permeability
cortisol's effect on vascular system
increase GFR by causing vasodilation of afferent arterioles
effects of cortisol on the kidney
decrease REM sleep, can cause insomnia
-lower threshold for seizures
effects of cortisol on the CNS
-facilitates development of disaccharidase necessary for milk digestion and lung surfactant
-much of fetal cortisol comes from mom during early gestation
effect of cortisol on fetal development
3B-hyroxysteroid dehydrogenase
oxidizes pregnenolone to form progesterone in aldosterone synthesis
21 B hydroxylase
converts progesterone to 11-deoxycorticosterone in production of aldosterone
11 B-hydroxylase
converts 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone in production to aldosterone
aldosterone synthase
-UPREGULATED by angiotensin II
converts corticosterone to aldosterone
•No storage pool of pre-synthesized aldosterone is available in the glomerulosa cell for rapid secretion.
•Secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal is limited by the rate at which the glomerulosa cells can synthesize the hormone
is there a storage form of aldosterone?
increasing activity of desmolase (SCC enzyme) and aldosterone synthase
ACTH, extracellular K+, and ang II increase secretion of aldosterone by
depolarizes glomerulosa cell membrane to activate calcium channels
how does increased plasma K+ increase aldosterone secretion?
-low plasma K+
-atrial natriuretic peptide (secrete from heart with high blood pressure)
inhibitors of aldosterone secretion:
hyperkalemia and loss of sodium
what causes death within a few days from lack of aldosterone?
increase sodium reabsorption
increase K+ and H+ excretion
-lack of aldosterone---> salt wasting, hypovolemia, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis
main effects of aldosterone
11-B-hydroxysteroid converts cortisol to cortisone, which has a weaker mineralcorticoid activity
-allows the aldosterone to bind more tightly to its receptor!
the affinity of mineralcorticoid receptors for cortisol is nearly the same as their affinity for aldosterone. how does the kidney overcome this to to use aldosterone?
11-B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
this enzyme converts high levels of cortisol to a weaker form, cortisone, allowing for increased action of aldosterone
11-B hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
-prevents cortisol from being converted to cortisone, thus more cortisol can bind to mineralcorticoid--> aldosterone like effects without high aldosterone
natural black licorice contains glycrrhizin which has a binding affinity to what enzyme?
-high consumption of black licorice
-mutation in gene coding for 11-B-dehydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 enzyme
2 ways by which a pt may present with signs of hyperaldosteronism, but have normal serum aldosterone and high cortisol metabolites
9a Fludrocortisone
synthetic, more potent form of aldosterone given pharmacologically
dexamethason> methylprednisone>prednisone
synthetic glucocorticoid with highest level of cortisol activity
testosterone, DHT or estrogen
DHEA and androstenedione convert to what in peripheral tissues?
males: little importance in childhood, hair growth; testes produce DHEA
females: MAJOR source of androgens, esp after menopause
rule of adrenal cortex androgens in males and females
adrenal androgens
__________ are called 17-ketosteroids and their metabolites can be measured in urine
autosomal recessive
inheritance of congenital adrenal hyperplasias
congenital adrenal hyperplasia
in ALL of these conditions, cortisol will not be synthesized and thus ACTH will be high; this continuous stimulation will cause hyperplasia of adrenals
increase in progesterone (aldosterone production
-increase 17-hydroxyprogesterone (cortisol production)
-100 fold increased androgen production due to shunting of pathway
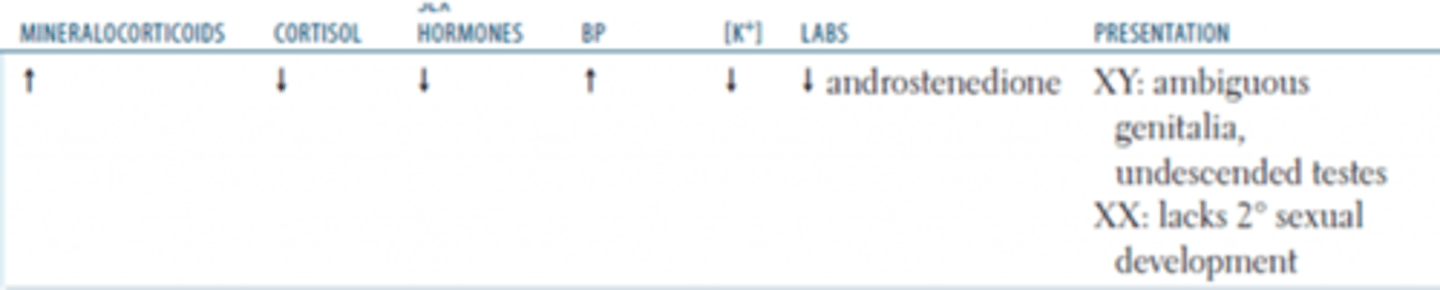
a 21-hydroxylase defect will result in increase in what substrates?
-no aldosterone: hypotension, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis
-no cortisol: hypoglycemia
-females: masculination of genitalia, enlarged clitoris
-males: precocious puberty, aggressiveness
signs and symptoms of 21-hydroxylase defect
21-hydroxylase deficient CAH
-complete block is incompatible with life
most common CAH
test urine for weak androgen metabolites: 17-ketosteroids
how can you test for 21-OHase deficent CAH?
- 11-deoxycorticosterone in aldosterone production
-11-deoxycortisol in cortisol production
-these substrates act as weak mineralcorticoids
defect in 11-B hydroxylase will increase what substrates?
-decreased cortisol--> hypoglycemia
-increased (weak) mineralcorticoids: hypertension, hypokalemic, metabolic alkalosis
-increased weak androgens: virilization of females, precocious puberty in males
signs and symptoms of 11B-hydroxylase defect
precursors for aldosterone synthesis: pregnenolone and progesterone
defect in 17a-hydroxylase result in an increase in what substrates?
-hypertension, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, mild hypoglycemia, undeveloped genitalia in males, genetic females affected later on
-HIGH aldosterone
presentation of 17a-hydroxylase defect
-11-deoxycorticosterone and corticosterone
-allows some cortisol activity in 17-hydroxylase CAH
substrates in aldosterone synthesis pathhway that may act as weak glucocorticoids
17a-hydroxylase CAH
which CAH?
21 hydroxylase CAH
which CAH?

11B-hydroxylase CAH
which CAH?

11-deoxycorticosterone
aldosterone precursor that can act as a mineralcorticoid and has some cortisol like effects
3B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency
enzyme in pivotal in production of all cortex hormones; fatal if deficient
cholesterol desmolase deficiency
fatal in utero as it prevents placenta from making necessary progesterone, which is essential to maintaining pregnancy
17,20 lyase deficiency
presents as a 17-OHase defect
you're chill :) produce adequate 11-DOC
effect of aldosterone synthase defect
Primary cushing's syndrome
•Elevated cortisol due to cortisol producing tumor of Adrenal Gland
•Low ACTH
•Increased Mineralocorticoid activity (high Cortisol = high Cortisone)
secondary cushing's disease
•Elevated Cortisol AND Androgens
•Due to hyper-secretion of ACTH
•AP tumor or sometimes lung tumor
Cushing's syndrome
pt presents withh muscles loss/weakness in arms and legs, decreased bone density, immune suppression, diabetes mellitus, think
cushings on kidney and vasculature
-effects capacity of body to convert cortisol to cortisone
-excess cortisol mimics aldosterone-- HTN, hypokalemia---> arrhythmia
cushings on the liver
-cortisol increases gluconeogennesis and increases insulin resistance causing hyperglycemia
cushings on repro
-cortisol exerts negative feedback on hypothalamus, decreasing GnRH release
-infertiliity, decreased libido, irregular menses
cushings on adipose tissue
-cortisol increases fat breakdown, preferentially in tissues not in the central area/face/ neck
-results in central obesity, moon facies
cushingss on skin and connective tissue
-increased cortisol decreases fibroblast prolferation, decreasing collagen synthesis
-result in skin atrophy, easy bruissing, puruple striae
cushings on muscle
-increasesd cortisol increases proteolysis, decreases protein synthesis, thus decreasing muscle growth in cardiac and skeletal muscle
-cardiomyopathy, heart failure, proximal muscle weakness
cushing syndrome caused by adrenal tumor
what causes these findings from dexamethasone suppression test?
Low dose: no decrease in blood cortisol
ACTH level: Low
In most cases, the high dose test is not needed
ectopic cushing syndrome
what causes these findings from dexamethasone suppression test?
Low dose: no decrease in blood cortisol
ACTH: high
High-dose test: no decrease in blood cortisol
cushing syndrome cauused by pit tumor
what causes these findings from dexamethasone suppression test?
Low dose test: no decrease in blood cortisol
High dose test: expected decrease in blood cortisol
most common: cushing disease
most common cause of ACTH dependent cushing synddrome
exogenous intake
most common cause of ACTH independent cushing syndrome