BIOLOGY LAB MIDTERM REVIEW PT. 2
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
osmosis
The flow of water across a selectively permeable membrane
diffusion
the movement of molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration
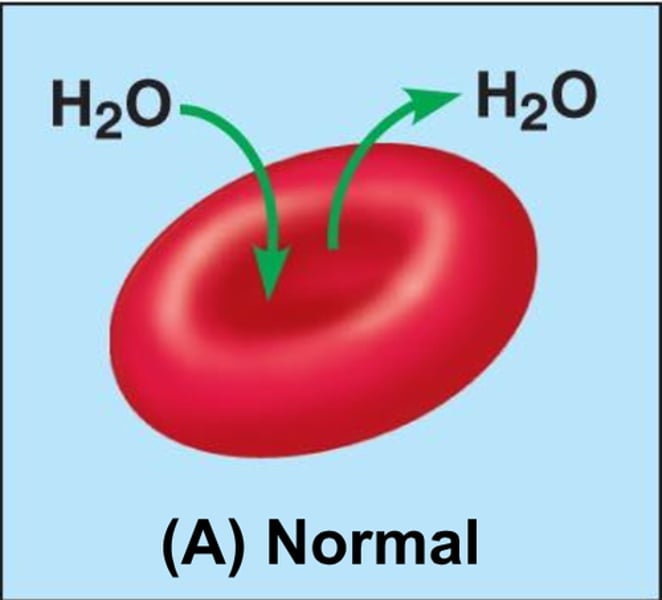
isotonic
Cells retain their normal size (same solute/water concentration)
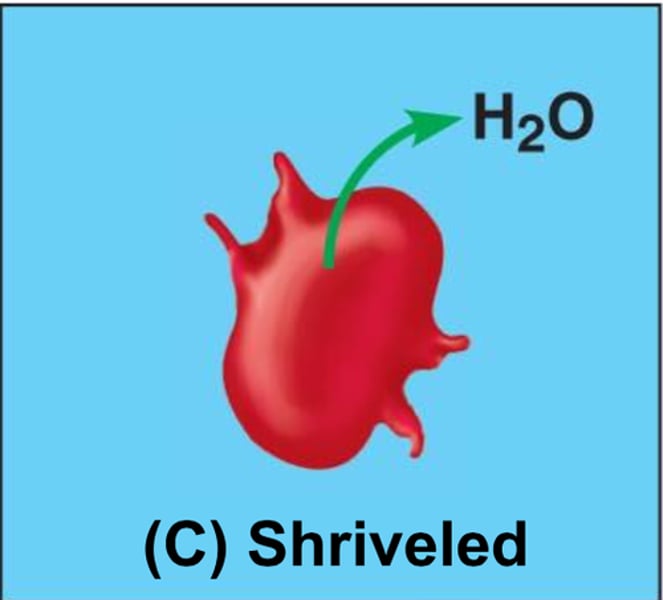
hypertonic
Cells lose water by osmosis and shrink (crenation)
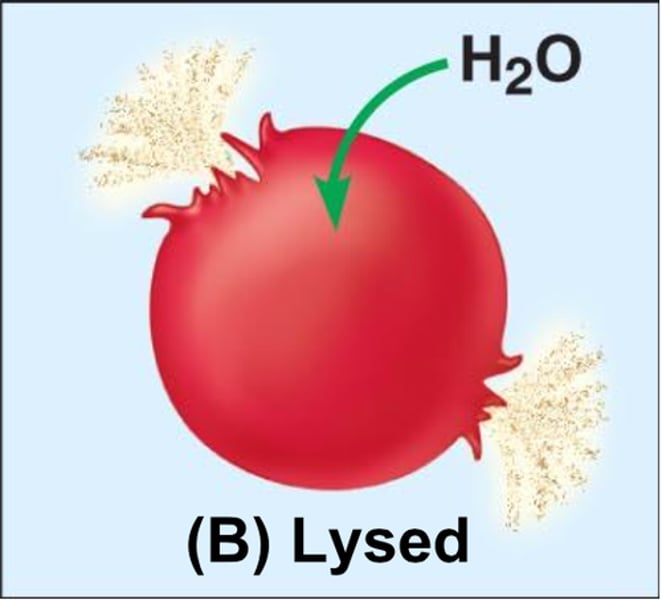
hypotonic
Cells take on water by osmosis until they become bloated and burst (lyse)
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
water and iodine
Which substances was the dialysis tubing used in lab permeable to?
starch
Which substances was the dialysis tubing used in the lab Impermeable to?
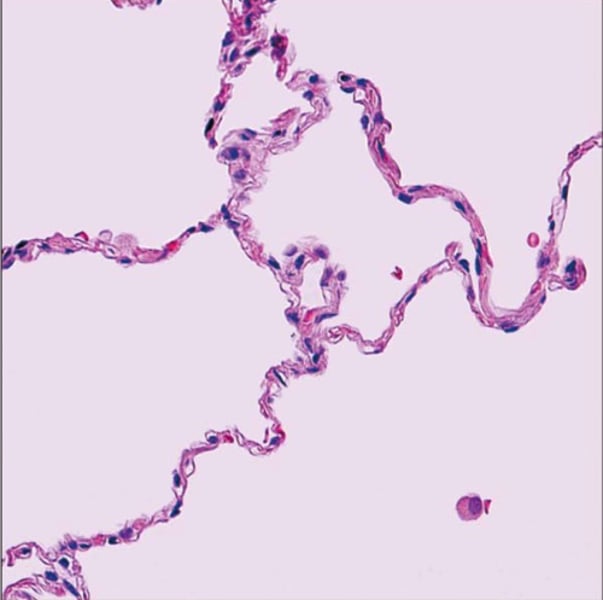
simple squamos epithelium
found in airsacs of lungs
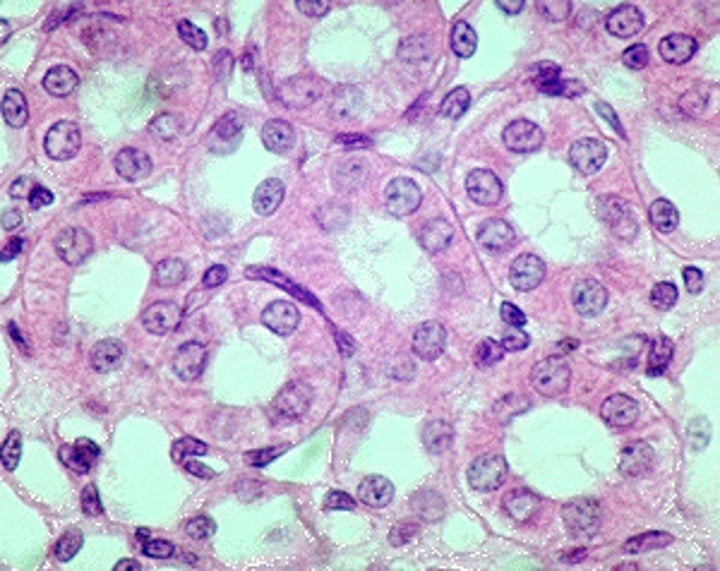
simple cuboidal epithelium
found in kidney tubules
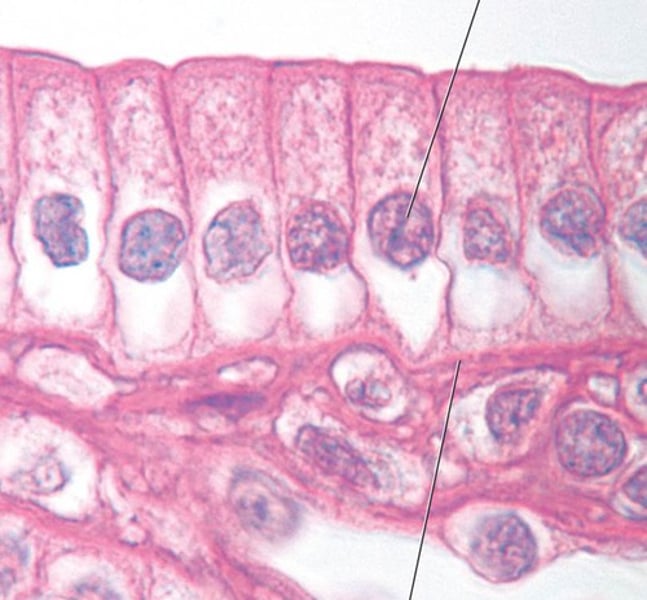
simple columnar epithelium
found in the gallbladder and digestive tract
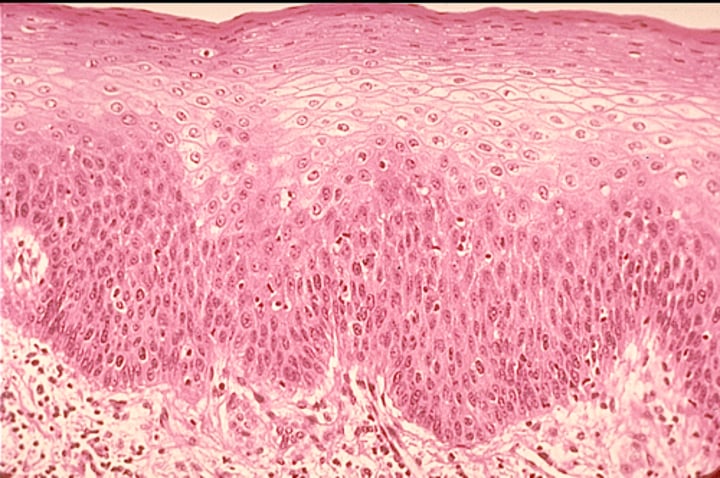
stratified squamous epithelium
found in the linings of esophagus, mouth and vagina
stratified cuboidal epithelium
found in sweat, salivary and mammary glands
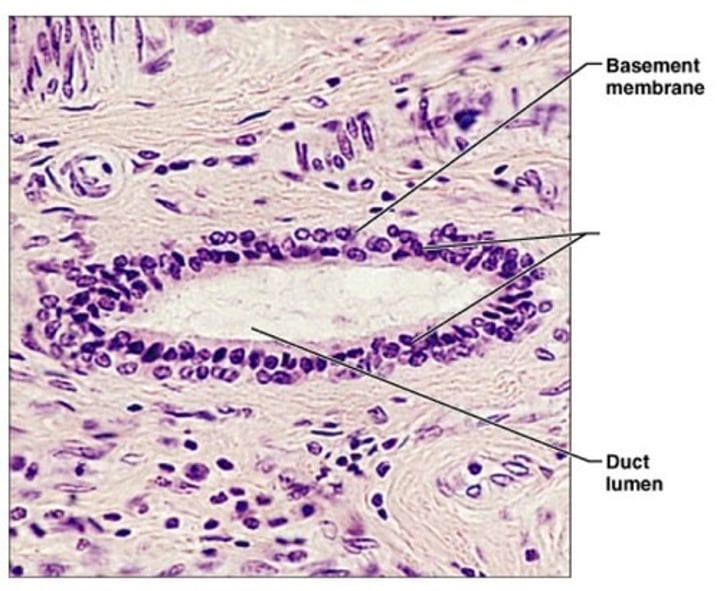
stratified columnar epithelium
found in male urethra
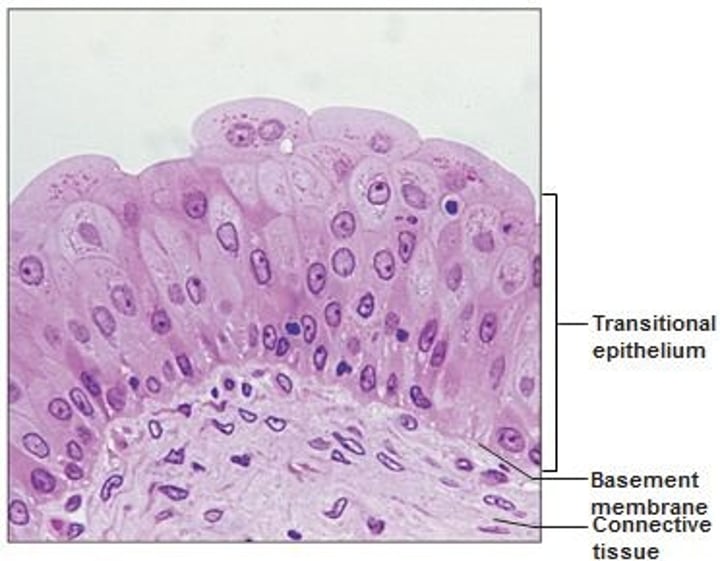
transitional epithelium
found in ureters, urethra and urinary bladder
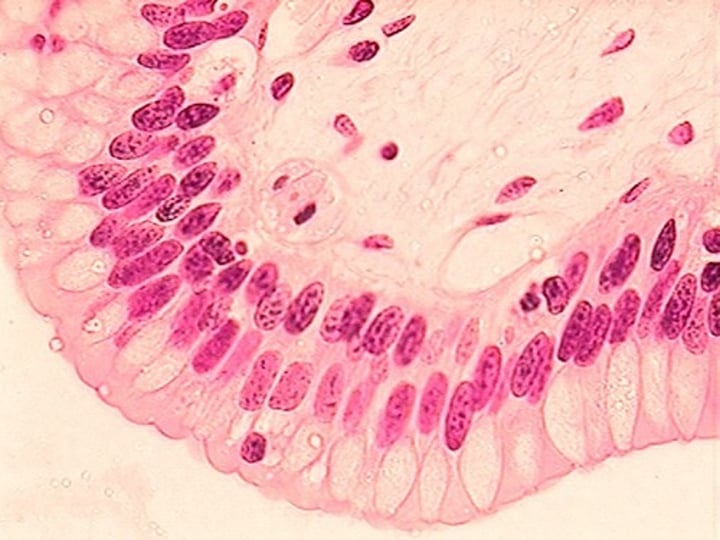
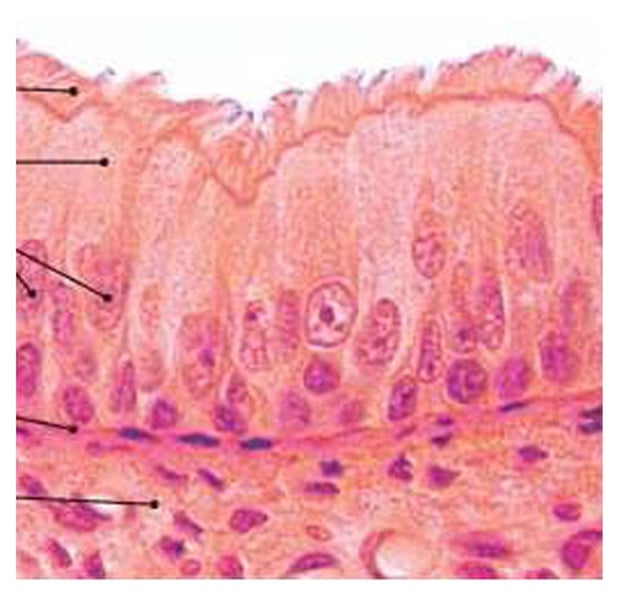
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
found in the trachea and sperm-carrying ducts
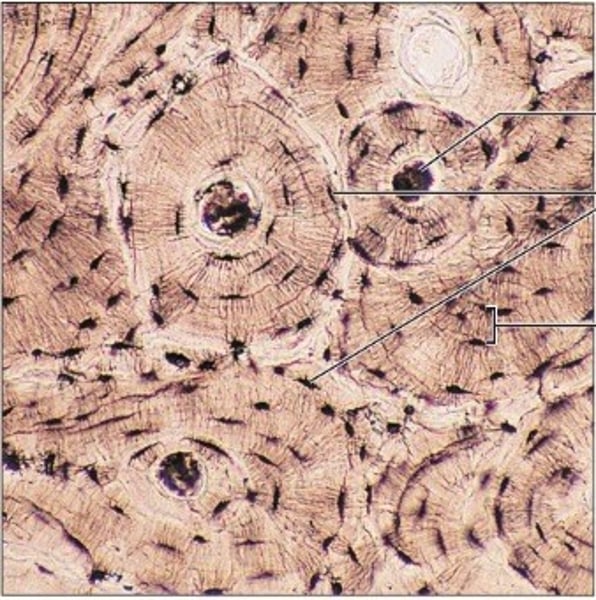
connective osseous tissue
found in bones
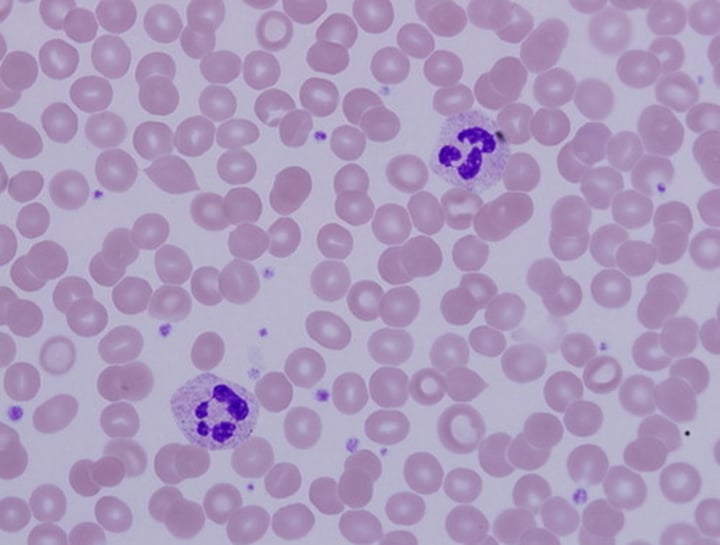
blood
found within blood vessels
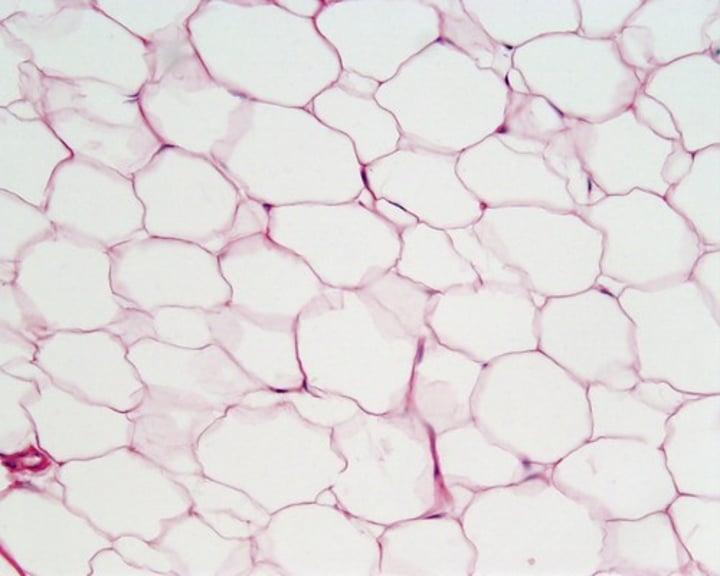
loose connective tissue, adipose
found around kidneys, eyeballs and breasts
loose connective tissue, areolar
found under epithelia of body (packages organs)
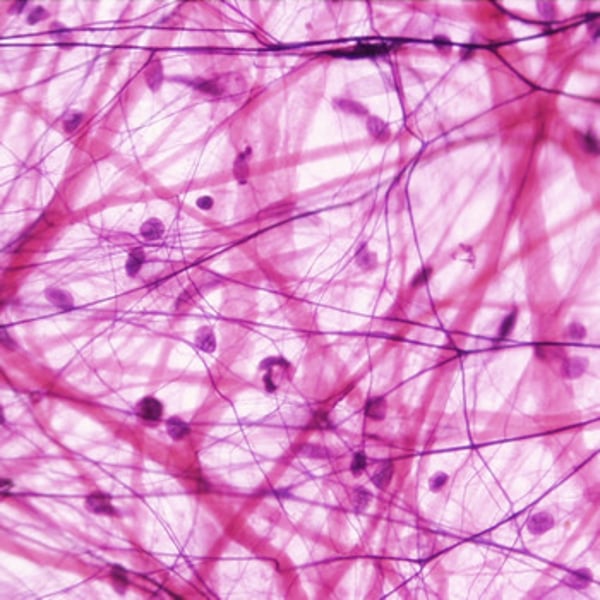
loose connective tissue, reticular
found in lymph nodes, bone marrow and spleen
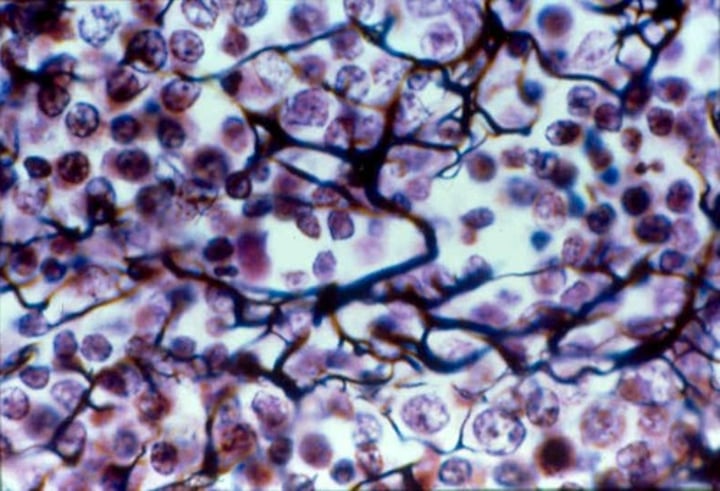
Cartilage: Hyaline
cover ends of long bones, nose, trachea and larynx
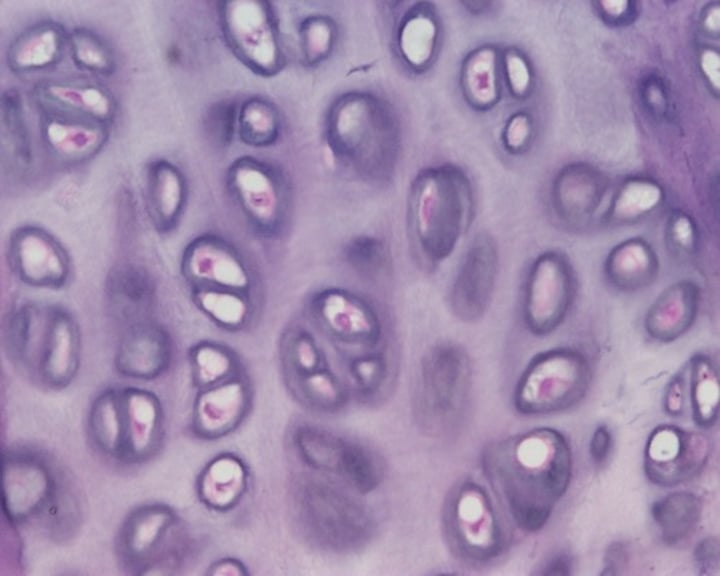
elastic cartilage
supports the external ear; epiglottis
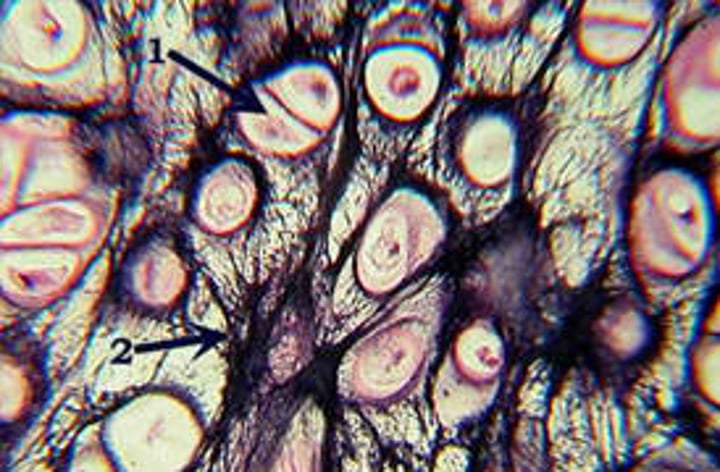
fibrocartilage
found in intervertebral discs and knee joint
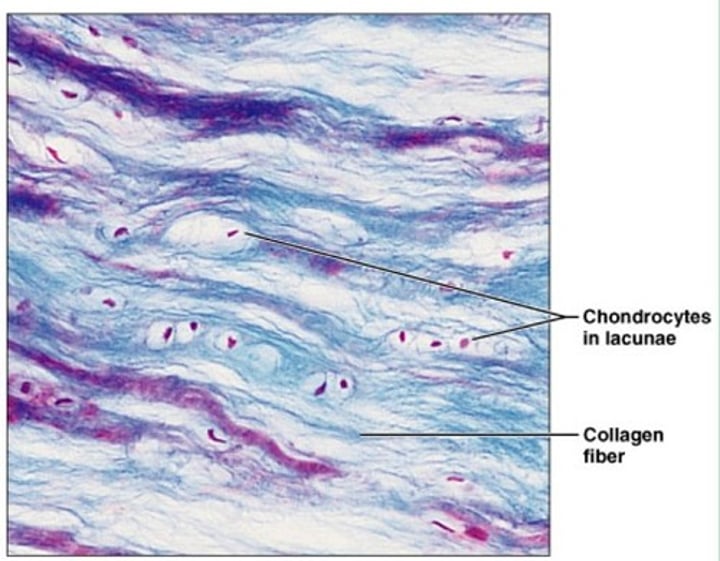
dense regular connective tissue
found in tendons and ligaments
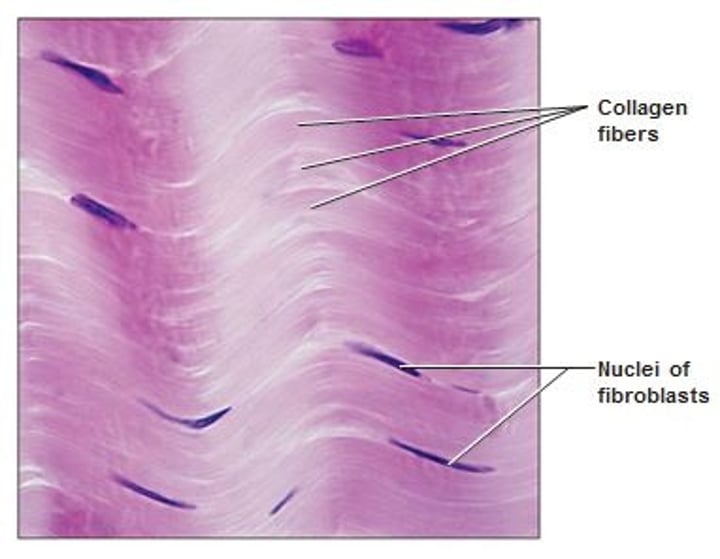
dense irregular conncetive tissue
found in dermis of skin and submucosa of digestive tract
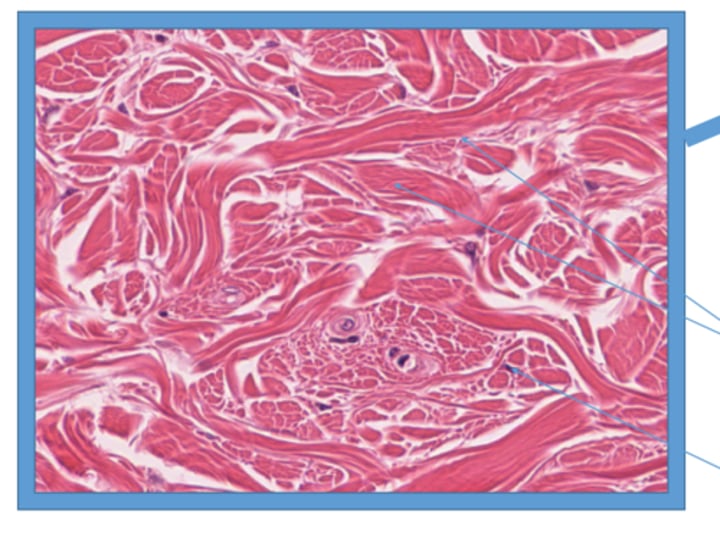
Embryonic Connective Tissue: Mesenchyme
found in embryo
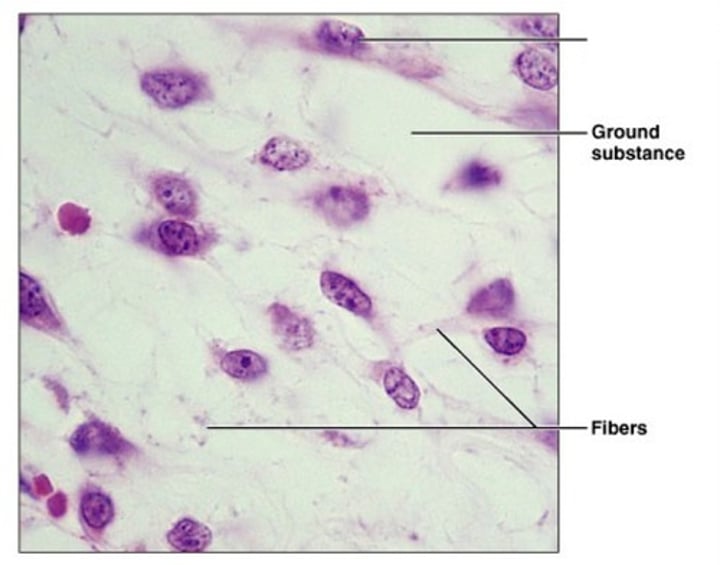
skeletal muscle
found in skeletal muscles attached to bones

cardiac muscle
found in the walls of the heart
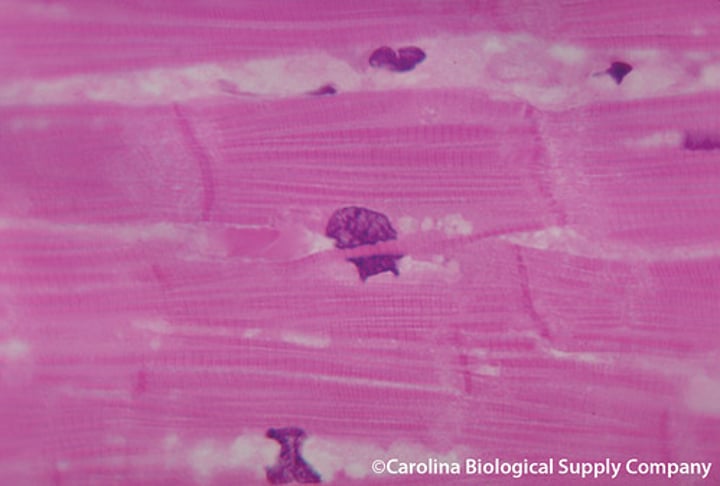
smooth muscle
found in the walls of hollow organs
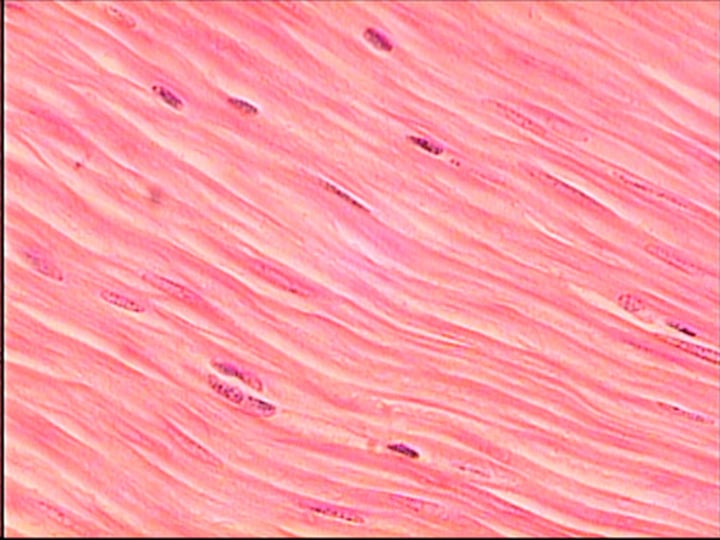
nervous tissue, neurons
found in brain, spinal cord, and nerves
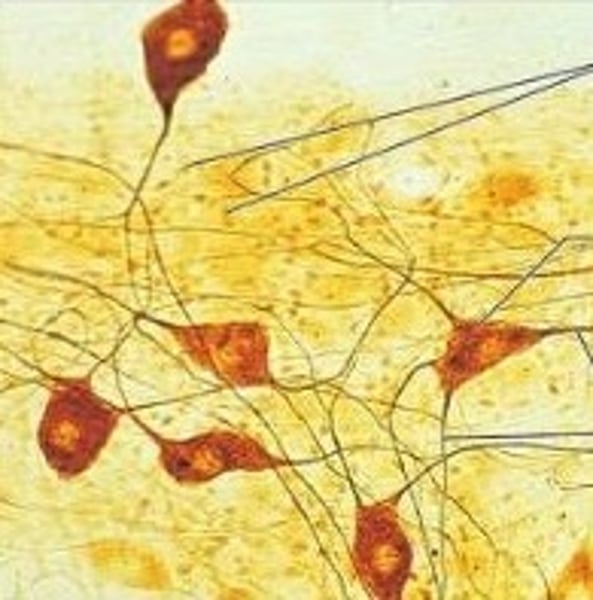
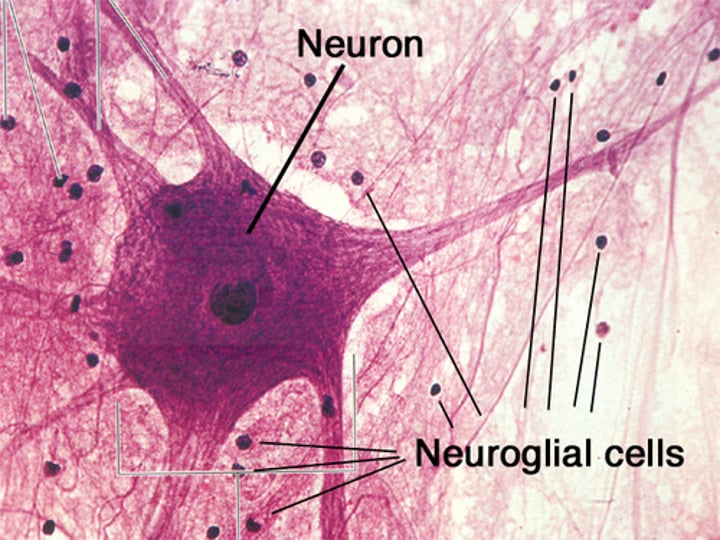
Neuroglia
found in the nervous sytem
Keratinocytes
produce keratin fibrils that give the epidermis durability and protection
melanocytes
produce the brown to-black pigment called melanin that protects from ultraviolet radiation
Langerhans cells (dendritic cells)
They ingest foreign substances and play a key role in activating the immune response
Tactile epithelial cells (Merkel cells)
form sensitive touch receptors located at the epidermal-dermal junction
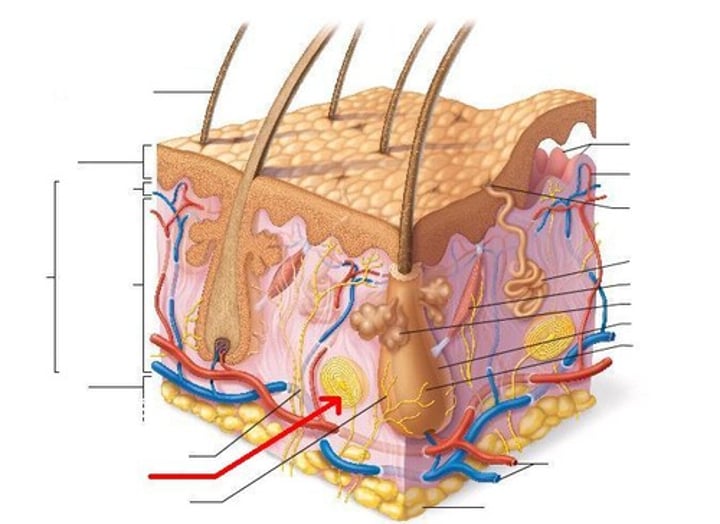
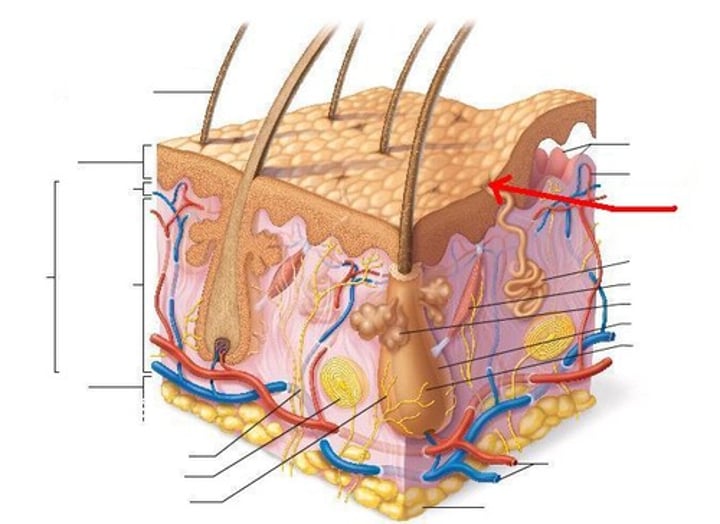
Epidermis
Outer layer of skin
Dermis
Inner layer of skin (papillary layer and reticular layer)
papillary layer
produces fingertips and heat, pain and touch receptors found here
reticular layer
contains sweat and sebaceous glands, and pressure receptors
Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
the layer of skin beneath the dermis, which serves as a storage repository for fat
Stratum corneum (horny layer)
outermost layer consisting of 20-30 layers of dead, scalelike keratinocytes. Theyre constantly being exfoliated and replaced by the division of the deeper cells
Stratum lucidum (clear layer)
Present only in thick skin. A very thin transparent band of flattened, dead keratinocytes with indistinct boundaries
stratum granulosum (granular layer)
thin layer named for the abundant granules its cells contain: lamellar granules, keratohyaline granules.
stratum spinosum (spiny layer)
Several layers of cells that contain thick, weblike bundles of intermediate filaments made of a pre-keratin protein
stratum basale (basal layer)
-Deepest epidermal layer firmly attached to the dermis
single row of stems
-also called stratum germinative: cells undergo rapid division
-journey from basal layer to surface- takes 25-45 layers
hair follicle
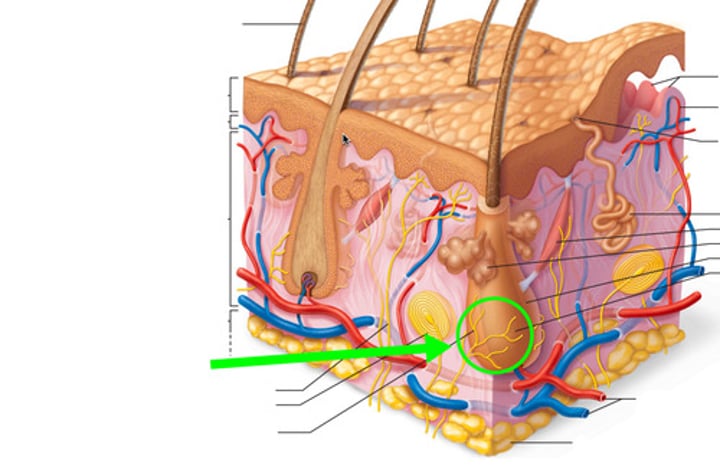
eccrine sweat gland
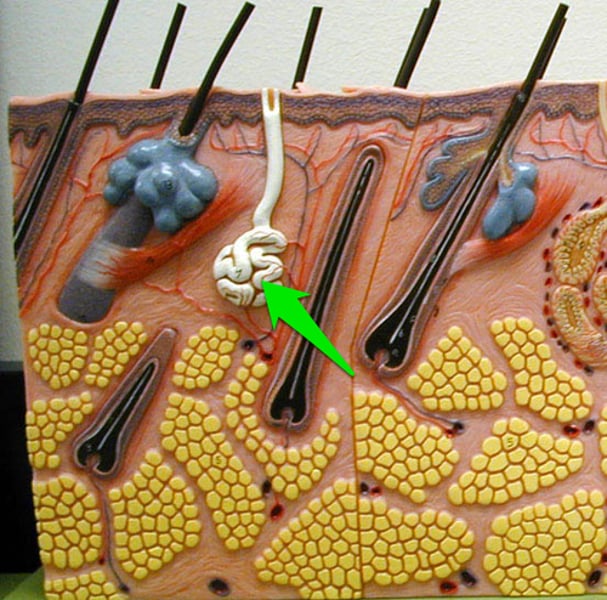
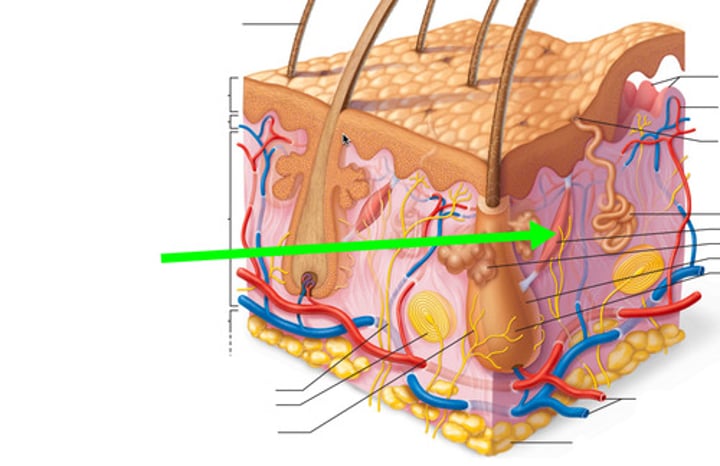
arrector pili muscle
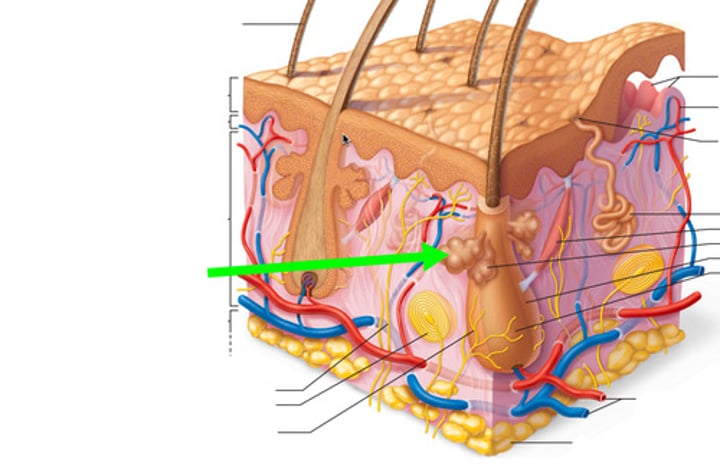
Sebaceous (oil) glands
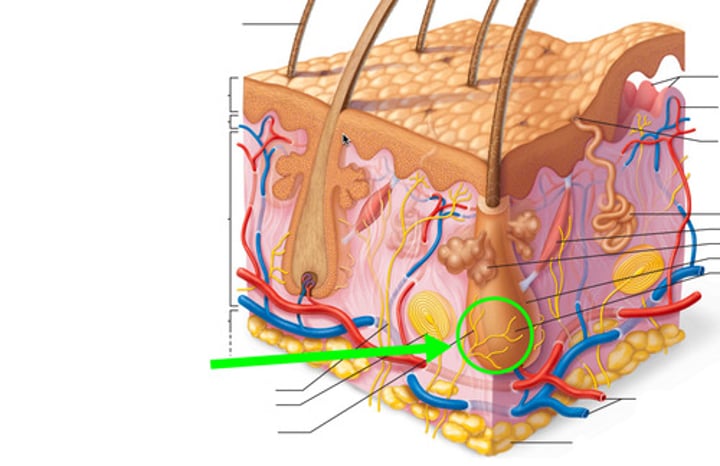
hair root
lamellar corpuscle
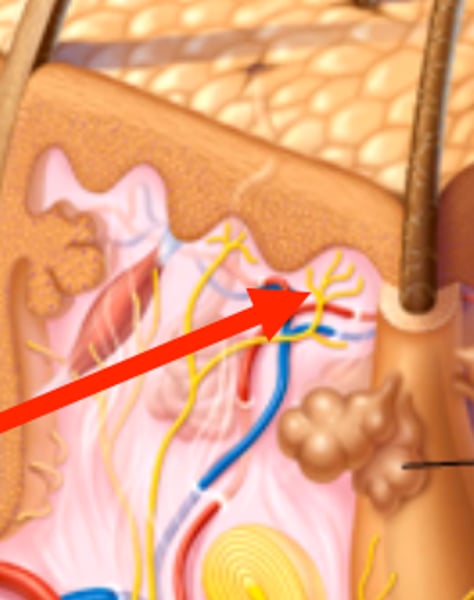
tactile corpuscles
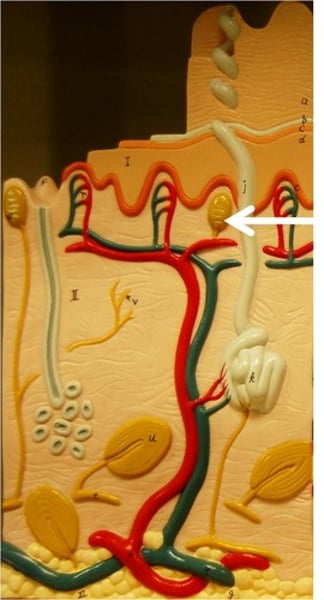
free nerve endings
pore
Adipose (hypodermis)
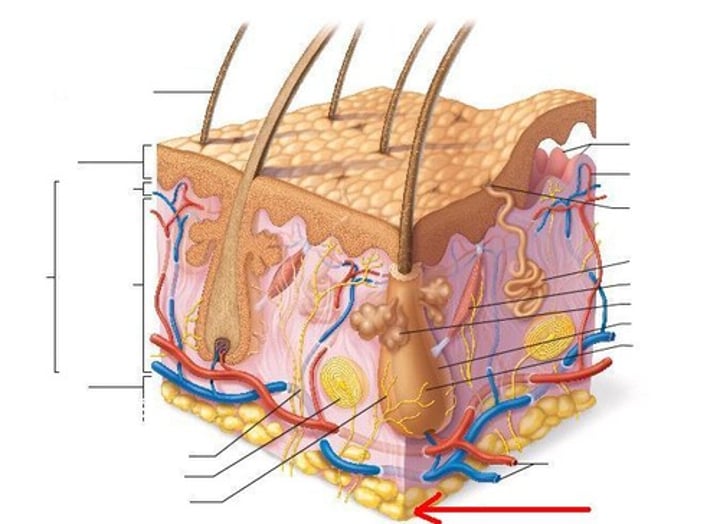
artery
red in skin model
vein
blue in skin model
accessory organs of the skin
hair, nails, and cutaneous glands
5 functions of the skeletal system
protects & supports the body, lever for skeletal muscles, store lipids & minerals, blood cell formation
hyaline cartilage
Most common type of cartilage; it is found on the ends of long bones, ribs, and nose
elastic cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage. found in external ear and epiglottis
Fibrocartilage
Pads between vertebrae that are shock absorbers, found in intervertebral discs, and knee & hip joints
How many bones are in the adult skeleton?
206
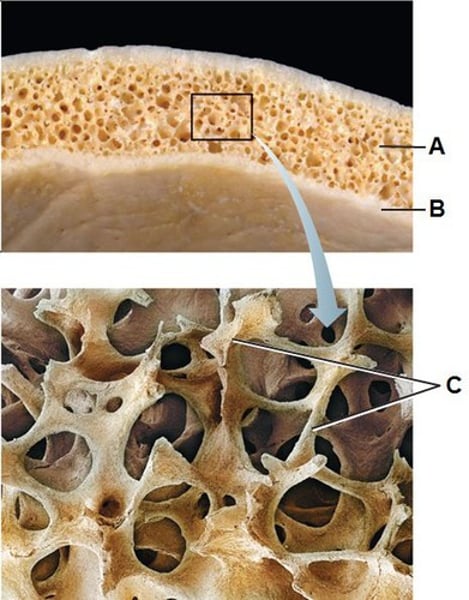
compact bone
dense and made up of organizational units called osteons, looks dense and homogeneous
spongy (cancellous) bone
composed of small trabeculae (columns) of bone and lots of open space, found in the long bones
long bones
bones that are longer than they are wide, consist of a shaft with heads at either ends, mostly compact bone. arms and legs
short bones
cube shaped, more spongy bone than compact bone, wrist and ankles
flat bones
thin & curved, with two waferlike layers of compact bone sandwiching a thicker layer of spongy bone between them
irregular bones
bones of the vertebrae and face, dont fall under long, short or flat categories
sesamoid bones
special types of short bones formed within tendons (kneecaps)
wormian (sutural) bones
tiny bones between cranial bones
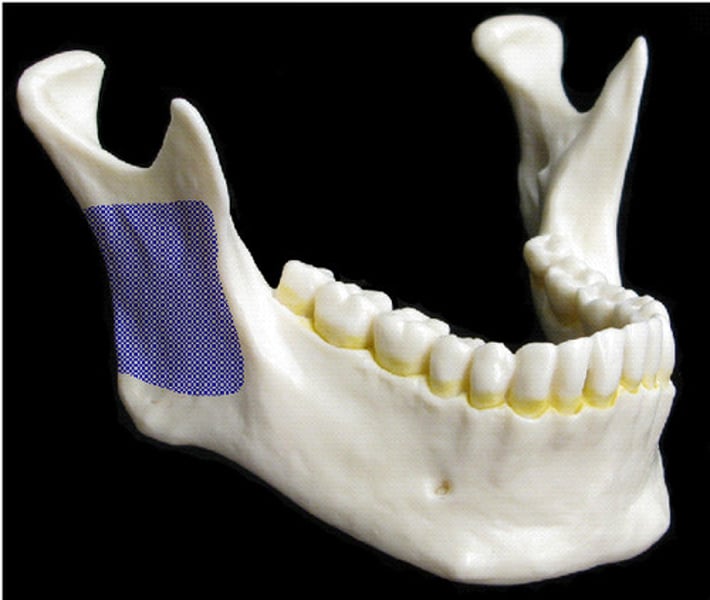
ramus
armlike bar of bone
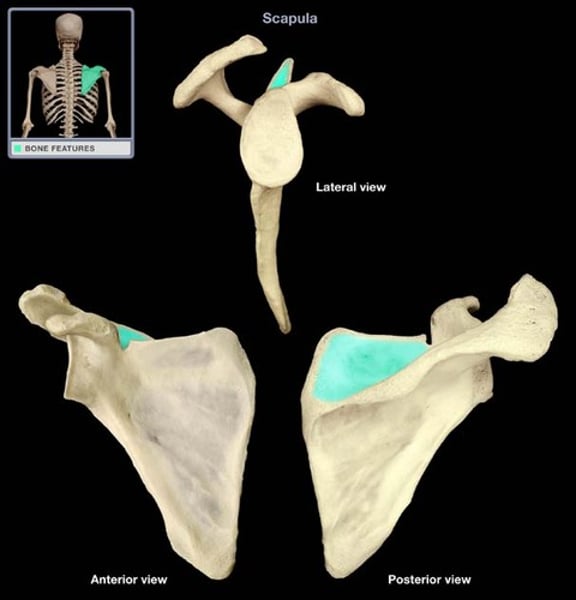
fossa
Shallow, basinlike depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
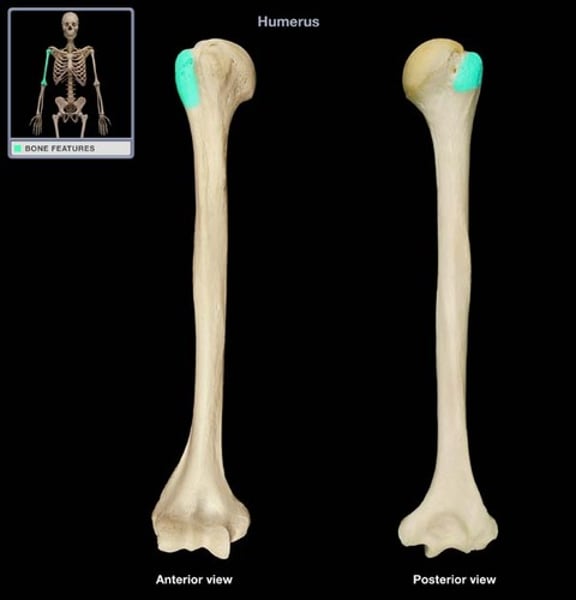
tubercle
Small rounded projection or process
Epicondyle
Raised area on or above a condyle
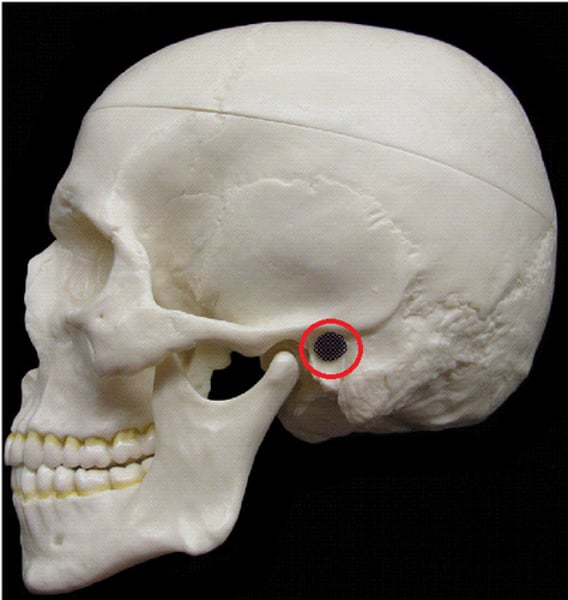
meatus
Canal-like passageway
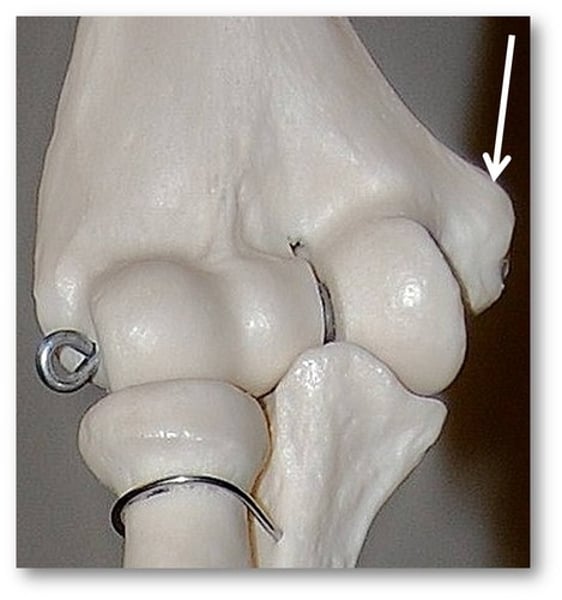
tuberosity
Large rounded projection; may be roughened
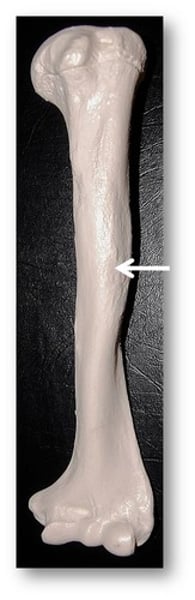
spine
Sharp, slender, often pointed projection
groove
furrow
Condyle
Rounded articular projection
crest
Narrow ridge of bone; usually prominent
head
Bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
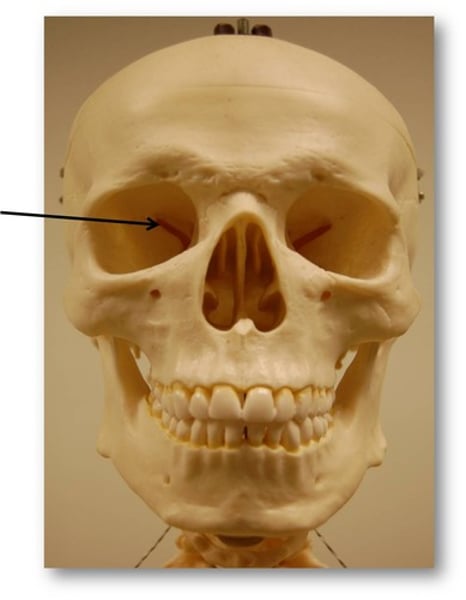
foramen
Round or oval opening through a bone
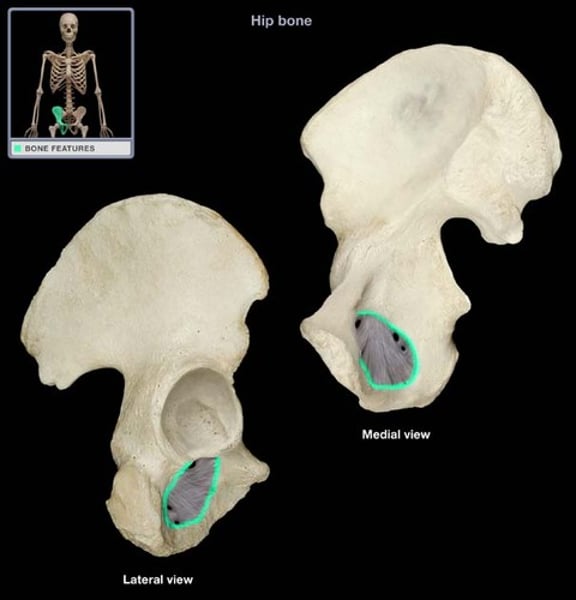
trochanter
Very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process
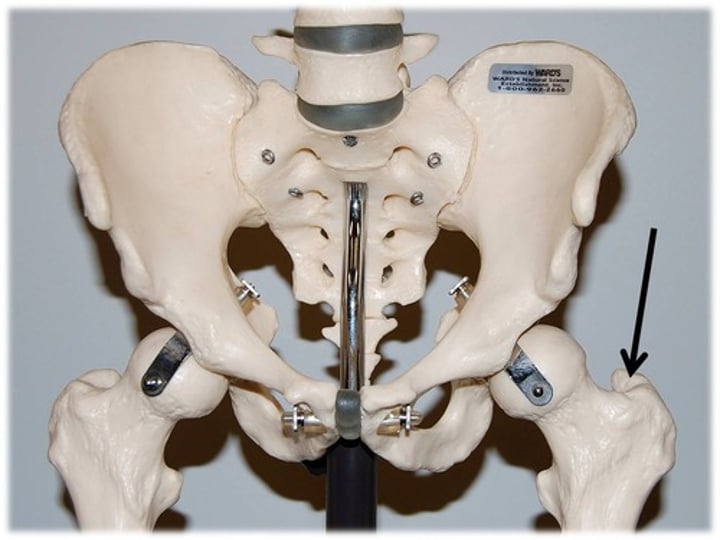
fissure
Narrow, slitlike opening
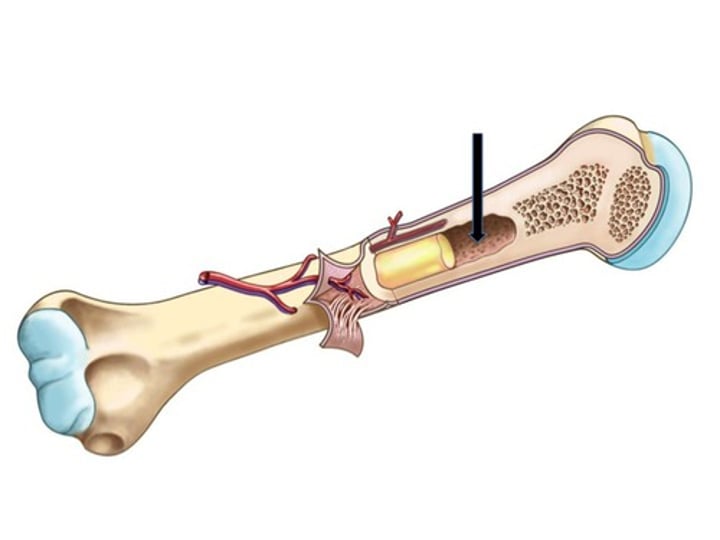
Diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
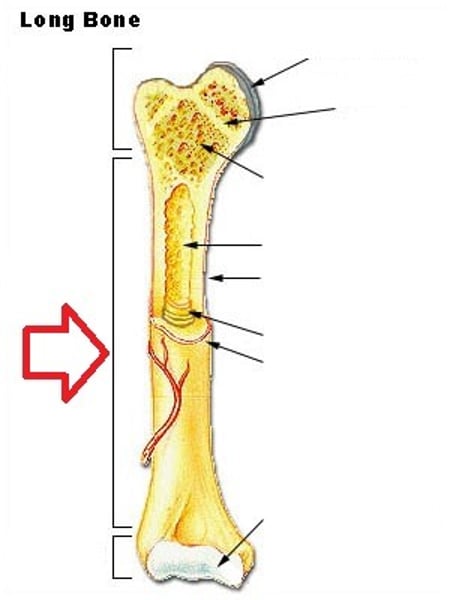
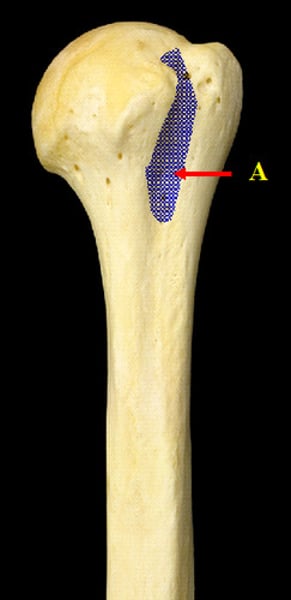
Endosteum
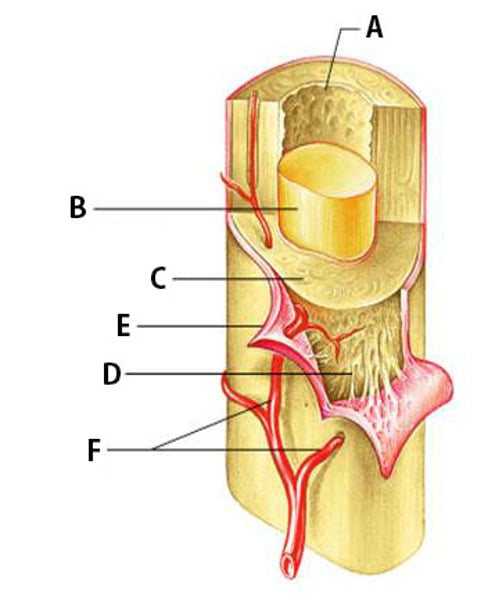
membranous lining of the hollow cavity of the bone (A in the picture)
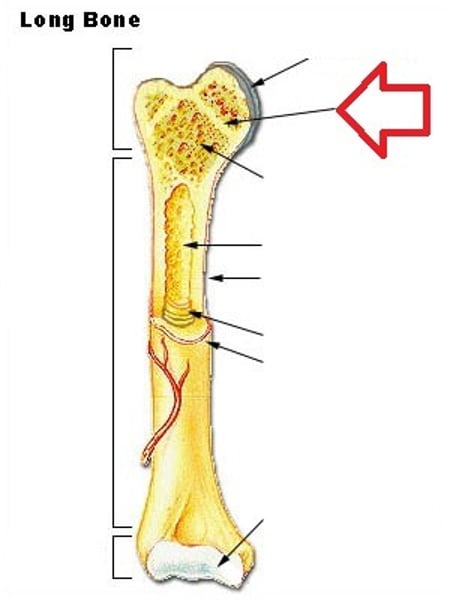
Epiphysis
End of a long bone
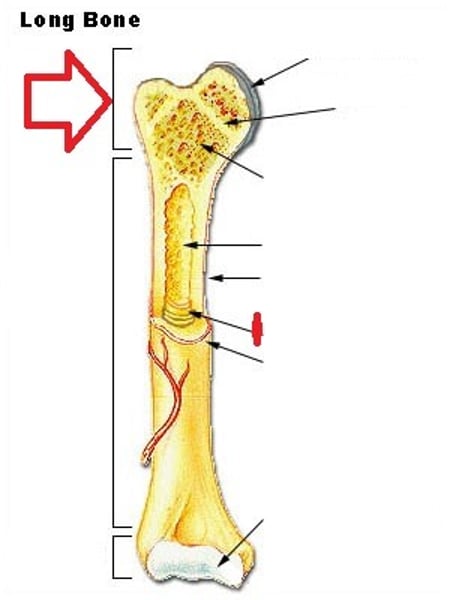
epiphyseal line
smooth line between parts of spongy bone
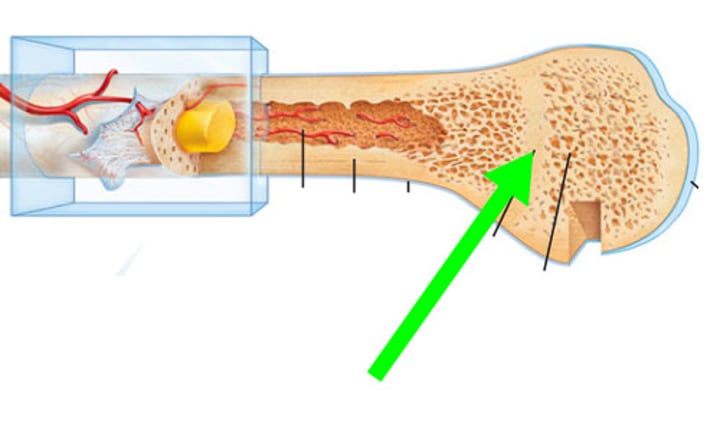
epiphyseal plate
cartilaginous area at the ends of long bones where lengthwise growth takes place in the immature skeleton
medullary cavity
cavity within the shaft of the long bones filled with bone marrow
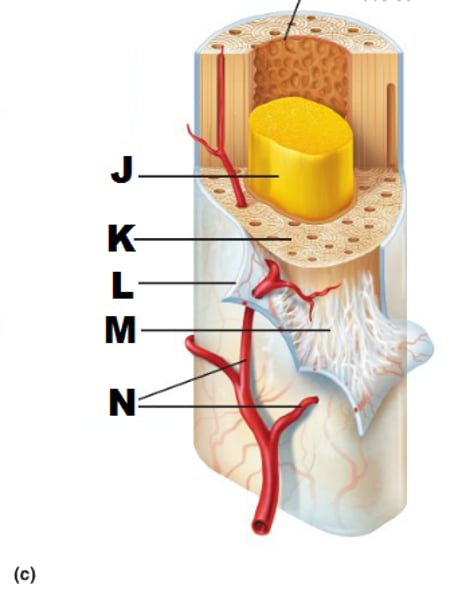
Perforating (Sharpey's) fibers
hundreds of connective tissue fibers that secure the periosteum to the underlying bone (M in picture)
Osteoblasts
bone forming cells
osteoclasts
Bone-destroying cells
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones
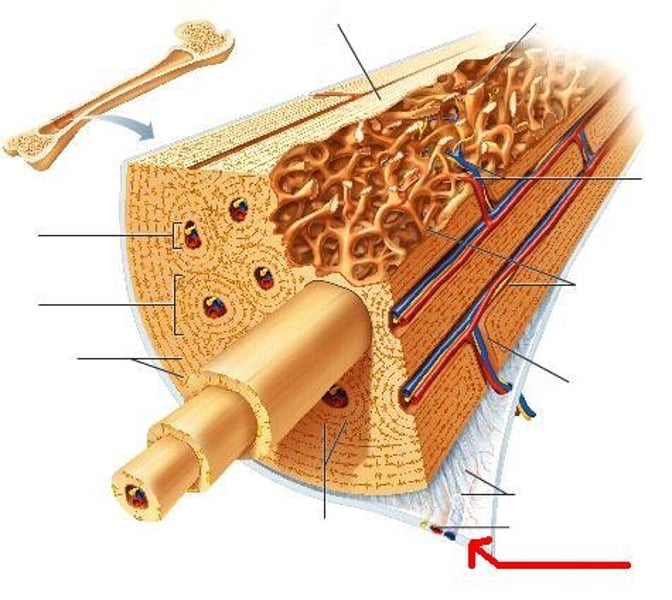
red bone marrow
found in cancellous bone
yellow bone marrow
fatty tissue found in the medullary cavity of most adult long bones
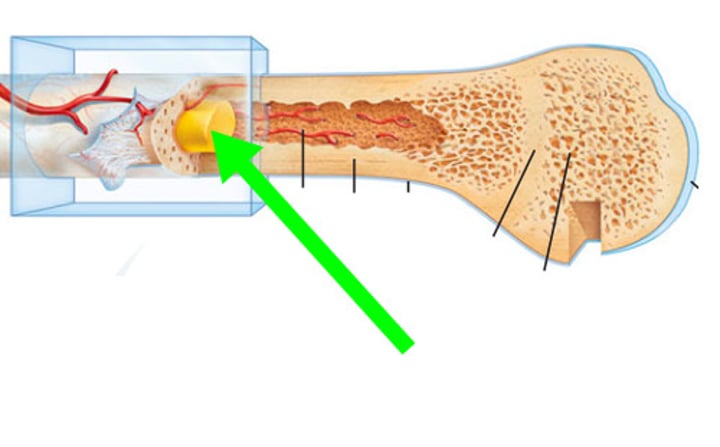
trabeculae
supporting bundles of bony fibers in cancellous (spongy) bone