MGMT 3661 Exam #3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
1
New cards
the Big Five personality dimensions
1. extraversion
2. agreeableness
3. openness
4. conscientiousness
5. emotional stability
2
New cards
extraversion (Big Five)
outgoing, talkative, sociable, assertive
3
New cards
agreeableness (Big Five)
trusting, good-natured, cooperative
4
New cards
openness (Big Five)
intellectual, imaginative, curious
5
New cards
conscientiousness (Big Five)
dependable, responsible, achievement-oriented
6
New cards
emotional stability (Big Five)
relaxed, secure, unworried
7
New cards
self-efficacy
belief in one’s ability to do a task
8
New cards
self-esteem
extent to which people like or dislike themselves
* HIGH:
* more apt to handle failures
* emphasize the positive
* take more risks
* LOW:
* tend to focus more on one’s weakness
* may be more dependent of others
* HIGH:
* more apt to handle failures
* emphasize the positive
* take more risks
* LOW:
* tend to focus more on one’s weakness
* may be more dependent of others
9
New cards
locus of control
people believe they control their fate through their own efforts
10
New cards
internal locus of control
you believe you control your destiny
11
New cards
external locus of control
you believe external forces control you
12
New cards
emotional stability
extent to which people feel secure and unworried and to which they are likely to experience negative emotions under pressure
13
New cards
HIGH levels of emotional stability
tend to show better job performance
14
New cards
LOW levels of emotional stability
prone to anxiety and tend to view the world negatively
15
New cards
emotional intelligence (EQ)
the ability to monitor your and others feelings and the ability to use this information to guide your thinking and actions
16
New cards
four aspect of emotional intelligence
1. self-awareness
2. self-management
3. social awareness
4. relationship management
17
New cards
self-awareness (EQ)
most essential trait…the ability to read your own emotions and gauge your moods accurately, so you know how you’re affecting others
18
New cards
self-management (EQ)
the ability to control your emotions and act with honesty and integrity in reliable and adaptable ways. can leave occasional bad moods out of the office
19
New cards
social awareness (EQ)
includes empathy, allowing you to show others that you care, and organizational intuition, so you keenly understand how your emotions and actions affect others
20
New cards
relationship management (EQ)
ability to communicate clearly and convincingly, disarm conflict, and build strong personal bonds
21
New cards
five distortions in perception
1. stereotyping
2. implicit bias
3. the halo effect
4. the recency effect
5. causal attribution
22
New cards
stereotyping (distortion in perception)
the tendency to attribute to an individual the characteristics one believes are typical of the group to which that individual belongs
23
New cards
implicit bias (distortion in perception)
is the attitudes or beliefs that affect our understanding, actions, and decisions in an unconscious manner
24
New cards
the halo effect (distortion in perception)
an effect in which we form a positive impression of an individual based on a single trait
25
New cards
the recency effect (distortion in perception)
the tendency of people to remember recent information better than earlier information
26
New cards
causal attribution (distortion in perception)
the activity of inferring causes for observed behavior
27
New cards
rational model of decision making
also called classical model; the style of decision making that explains how managers should make decisions; it assumes that managers will make logical decisions that are the optimal means of furthering the organization’s best interests
28
New cards
four stages of rational decision making
1. identify the problem
2. think up alternative solutions
3. evaluate alternatives and select a solution
4. implement and evaluate the solution chosen
29
New cards
what’s wrong with rational model
* it is *prescriptive*, doesn’t describe how managers *actually* make decisions
30
New cards
nonrational models of decision making
models of decision-making style that explain how managers make decisions; they assume that decision making is nearly always uncertain and risky, making it difficult for managers to make optimum
* satisficing
* intuition
* satisficing
* intuition
31
New cards
bounded rationality
one type of nonrational decision making; the ability of decision makers to be rational is limited by numerous constraints such as complexity, time, money, and other resources
32
New cards
satisficing model
one type of nonrational decision making; managers seek alternatives until they find one that is satisfactory, not optimal
33
New cards
intuition model
making a choice without the use of conscious thought or logical inference, “going with your gut”
\-stems from expertise, known as *holistic hunch*
\-stems from feelings, known as *automated experience*
\-stems from expertise, known as *holistic hunch*
\-stems from feelings, known as *automated experience*
34
New cards
**advantages** of group decision making
* greater pool of knowledge
* different perspectives
* intellectual stimulation
* better understanding of decision rationale
* deeper commitment to the decision
* different perspectives
* intellectual stimulation
* better understanding of decision rationale
* deeper commitment to the decision
35
New cards
**disadvantages** of group decision making
* few people dominate or intimidate
* groupthink
* satisficing
* goal displacement
* groupthink
* satisficing
* goal displacement
36
New cards
four characteristics of group decision making
1. they are less efficient
2. their size affects decision quality
3. they may be too confident
4. knowledge counts
37
New cards
groupthink
agreeing for the sake of unanimity & thus avoid accurately assessing the decision situation
38
New cards
consensus
occurs when members are able to express their opinions and reach agreement to support the final decision
39
New cards
brainstorming
used to help groups generate multiple ideas and alternatives for solving problems; individuals in a group meet and review a problem to be solved, then silently generate ideas, which are collected and later analyzed
40
New cards
devil’s advocacy
assigns someone the role of critic; helps uncover & air all possible objections
41
New cards
project post-mortem
review of recent decisions in order to identify possible future improvements
42
New cards
extrinsic rewards
the payoff, such as money, that a person receives from others for performing a particular task
43
New cards
intrinsic rewards
the satisfaction, such as a feeling of accomplishment, a person receives from performing a task
44
New cards
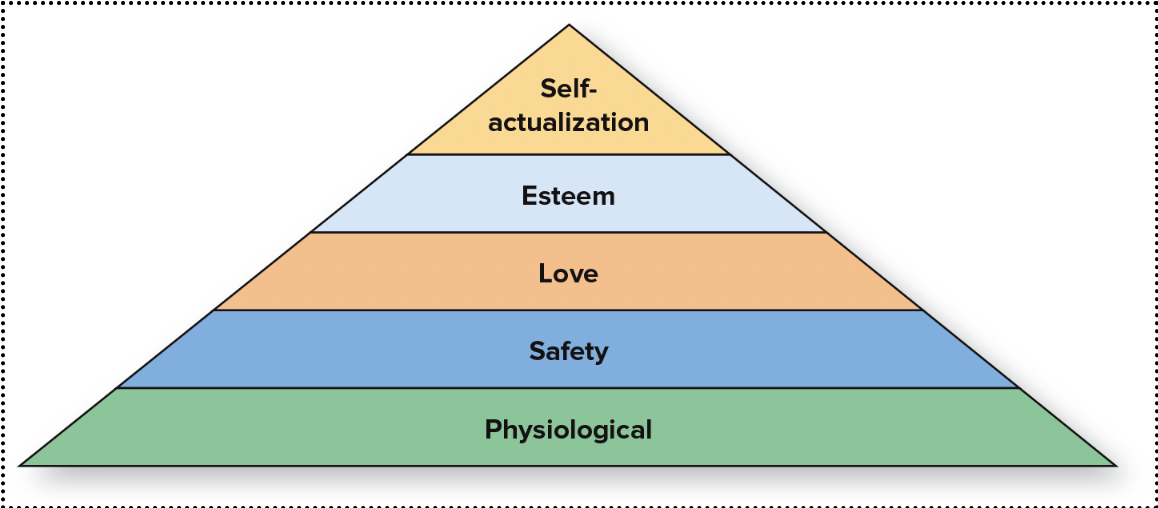
maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory
theorizes that people are motivated by five levels of needs:
1. physiological need (most basic need)
2. safety need
3. love need
4. esteem need
5. self-actualization need (highest level)
1. physiological need (most basic need)
2. safety need
3. love need
4. esteem need
5. self-actualization need (highest level)
45
New cards
mclleland’s aquired needs theory
theory that states that there are three needs—**achievement, affiliation, and power**—that are the major motives determining people’s behavior in the workplace
46
New cards
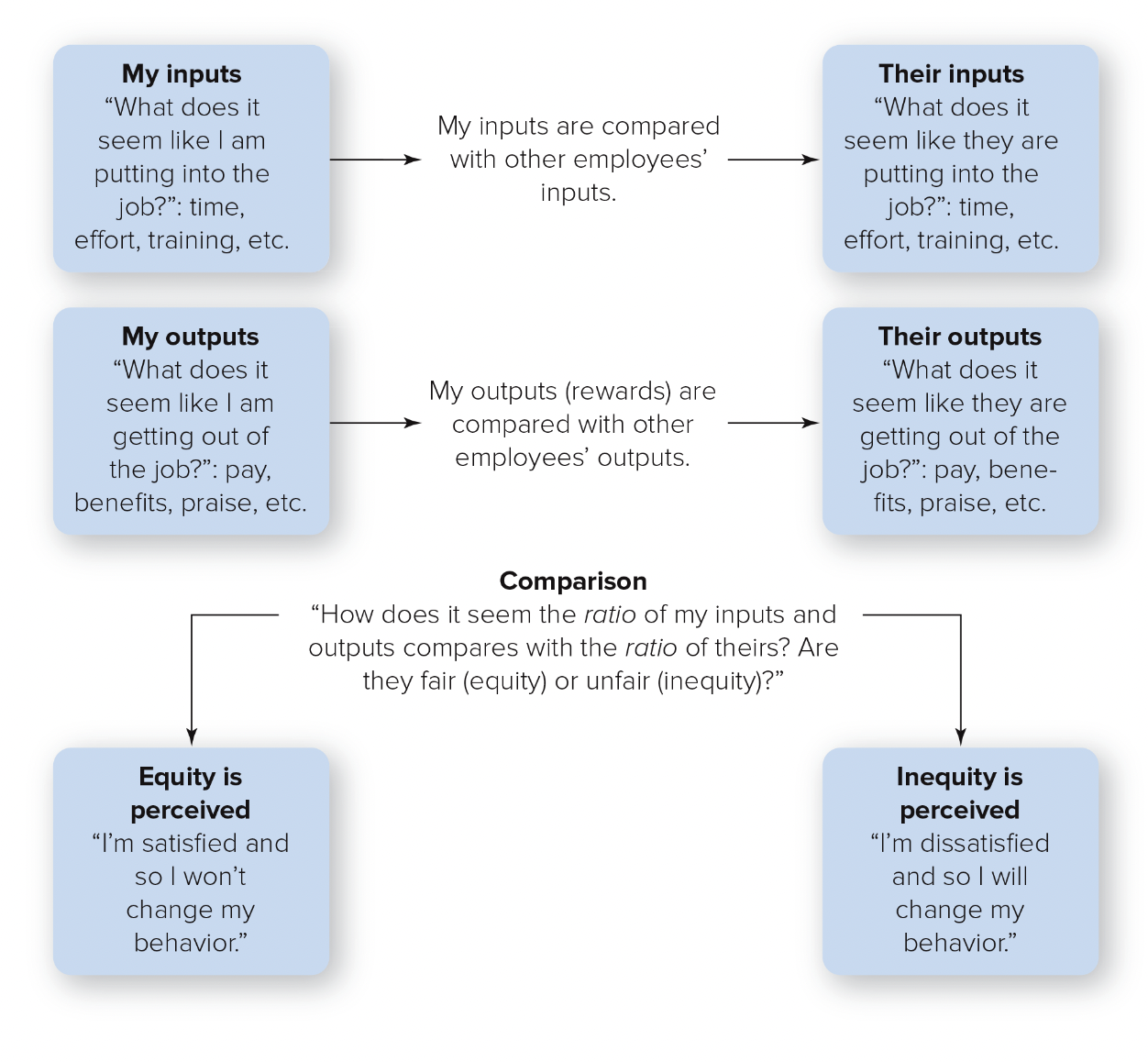
equity theory
the focus on how employees perceive how fairly they think they are being treated compared with others
47
New cards
justice theory
extension of equity theory, concerned with the extent to which people perceive they are treated fairly at work
48
New cards
procedural justice (justice theory)
the perceived fairness of the process and procedures used to make allocation decisions
* “how fair is the process for handing out rewards?”
* “how fair is the process for handing out rewards?”
49
New cards
distributive justice (justice theory)
reflects the perceived fairness of how resources and rewards are distributed or allocated
* “how fair are the rewards that are being given out?”
* “how fair are the rewards that are being given out?”
50
New cards
interactional justice (justice theory)
relates to how organizational representatives treat employees in the process of implementing procedures and making decisions
* “how fair is the treatment i receive when rewards are given out?”
* “how fair is the treatment i receive when rewards are given out?”
51
New cards
goal setting theory
employee-motivation approach that employees can be motivated by goals that are specific and challenging but achievable. the goal setting process is useful only if people *understand, accept,* and are *committed* to the goals
52
New cards
four motivational mechanisms of goal-setting theory
1. direct attention
2. regulate effort
3. increase persistence
4. foster the use of strategies and action plans
53
New cards
four types of behavior modification
1. positive reinforcement
2. negative reinforcement
3. extinction
4. punishment
54
New cards
positive reinforcement
the use of positive consequences to strengthen a particular behavior
55
New cards
negative reinforcment
process of strengthening a behavior by withdrawing something negative
56
New cards
extinction
the weakening of behavior by ignoring it or making sure it is not reinforced
57
New cards
punishment
the process of weakening behavior by presenting something negative or withdrawing something positive
58
New cards
groups
two or more freely interacting individuals who share collective norms, share collective goals, and have a common identity
59
New cards
work teams
* have a clear purpose that all members share
* usually permanent, and members must give complete commitment
* usually permanent, and members must give complete commitment
60
New cards
project teams
* assembled to solve a particular problem
* can come from same or different departments
* can come from same or different departments
61
New cards
cross-functional team
a team that is staffed with specialists pursuing a common objective
* include members from different areas (i.e. finance, operations, sales)
* can be work teams or project teams
* include members from different areas (i.e. finance, operations, sales)
* can be work teams or project teams
62
New cards
self-managed teams
groups of workers who are given administrative oversight for their task domains
63
New cards
five stages of team development
1. forming
2. storming
3. norming
4. performing
5. adjourning
64
New cards
forming (five stages of team development)
first stage of team development; people get oriented and get acquainted
65
New cards
storming (five stages of team development)
second stage of team development; individual personalities, roles, and conflicts within the group emerge
66
New cards
norming (five stages of team development)
third stage of development; conflicts are resolved, lose relationships develop, and unity and harmony emerge
67
New cards
performing (five stages of team development)
fourth stage of team development; members concentrate on solving problems and completing the assigned task
68
New cards
adjourning (five stages of team development)
fifth stage of team development; members of an organization prepare for disbandment
69
New cards
two roles in teams
task and maintenance role
70
New cards
task role
behavior that concentrates on getting the team’s task done
* ex: coordinators, initiators, energizers
* ex: coordinators, initiators, energizers
71
New cards
maintenance role
relationship-related role consisting of behavior that fosters constructive relationships among team members
* ex: encouragers, standard setters, compromisers
* ex: encouragers, standard setters, compromisers
72
New cards
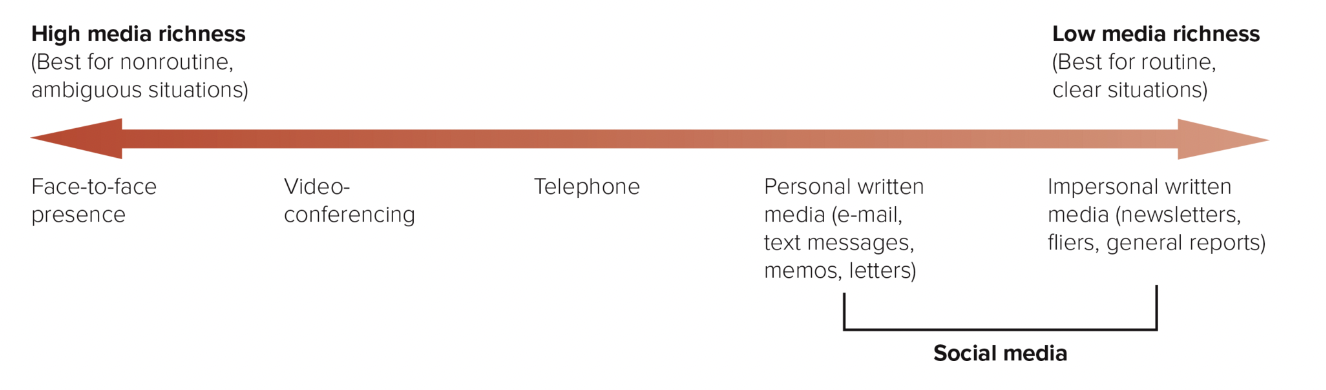
media richness
indication of how well a particular medium conveys information and promotes learning
73
New cards
downward communication
communication that flows from a higher level to a lower level
74
New cards
upward communication
communication that flows from lower levels to higher levels
75
New cards
sideways (horizontal) communication
communication that flows within and between work units; its main purpose is coordination
76
New cards
outward (external) communication
communication between people inside and outside an organization
77
New cards
formal communication channels
communications that follow the chain of command and are recognized as official
* upward
* downward
* sideways
* outward
* upward
* downward
* sideways
* outward
78
New cards
informal communication channels
communication that develops outside the formal structure and does not follow the chain of command
* grapevine
* face-to-face
* grapevine
* face-to-face
79
New cards
grapevine
the unofficial communication system of the informal organization (ex: workplace gossip)