Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is PES?
How much QS will change in responsive to a change in price
What is the formula for PES?
Percentage change in QS/ Percentage change in price
If the price goes down, what will be the % change in price?
Negative
If the price decreases, what will happen to the quantity supplied?
It will decrease because suppliers have less of an incentive to supply due to a lower price, so % change in Qs will be negative
If the price went up, then the % change in price on the bottom would be:
Positive
This increase in price means that the % change in quantity supplied will be:
Positive
When a good has a PES greater than 1, we say that supply for the good is:
elastic
If the PES is between 0 and 1, supply for our good is:
inelastic
If the PES is between 1 and infinity , supply for our good is:
elastic
What does it mean for the supply to be inelastic?
If the % change in price will lead to a smaller % change in quantity supplied
What does it mean for the PES if it was equal to 1?
If the % change in price will lead to % change in quantity supplied of the same size
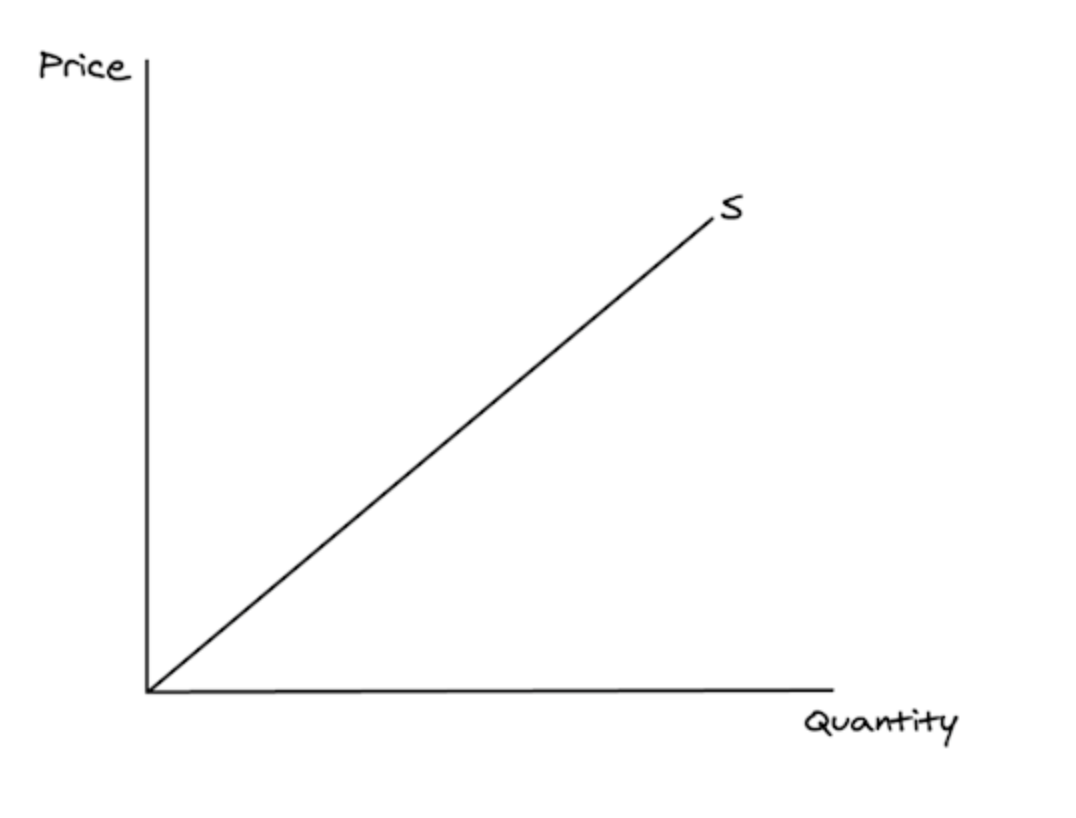
What does an elastic supply curve look like?
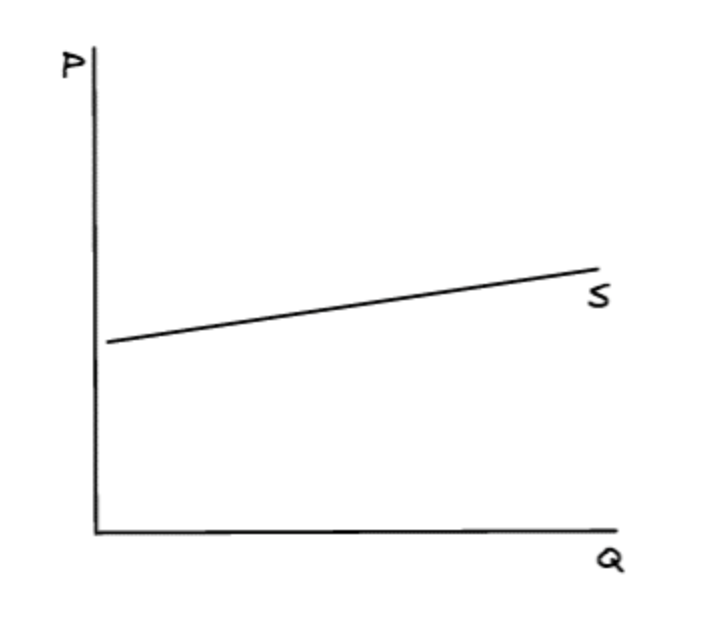
What does an inelastic supply curve look like?
What are the factors that influence PES?
Spare capacity
Availability of FOP
State of the economy
Stockpiles and perishability
Time period
There are two factories: factory one which is using all of it capacity and factory two which has a lot of spare capacity. What are the elasticities of these factories?
Factory 1 has little spare capacity so if the price were to rise, for instance, Factory 1 would not have the space or machinery to increase its output by much in response. This suggests firms with little spare capacity cannot respond much to changes in price, which implies inelastic supply.
Factory 2, however, has a lot more spare capacity so if the price were to rise, Factory 2 would be able to use up its spare capacity and increase output to take advantage of the higher price. This suggests that more spare capacity means a company is more responsive to a change in price, which implies that supply will be more elastic.
What are the four factors of production?
land
labour
capital
entrepreneurship or enterprise
Understanding that diamond rings require factors with little availability and cucumber sandwiches require factors which are very available, which of them is more likely to be elastic or inelastic? and why?
Because it's so easy to find the inputs required to produce cucumber sandwiches, if the price of cucumber sandwiches, producers would easily be able to find more resources to produce more sandwiches. They would therefore be able to respond a lot to a change in price, suggesting elastic supply.
However, it's very difficult to find the factors of production to produce a diamond ring. So, if the price of diamond rings were to rise, although producers would like to supply more diamond rings, it would be very difficult for them to find the resources to do so. As a result, they wouldn't be able to increase their supply of diamond rings by a large %, so the supply of diamond rings would be unresponsive to price, suggesting inelastic supply.
If cheese is hard to stockpile whereas sharpeners are much easier to stockpile, which of them is more likely to be elastic or inelastic? and why?
Sharpeners are more likely to be elastic.This is because sharpeners can be easily stockpiled, so if the price of sharpeneres were to rise, producers could react quickly by selling the sharpeners they have in storage, increasing quantity supplied by a large %, suggesting elastic supply.
Cheese, however, is more likely to be inelastic. This is because cheese cannot be easily stored due to its perishability: cheese will go off if stored for too long, so large quantities of cheese cannot be stockpiled long-term. As a result, if the price of cheese were to rise, producers wouldn't have a large stockpile of cheese to begin selling to consumers, they would have to make additional cheese from scratch which takes a long time. This means producers would not be able to respond much, suggesting inelastic supply.
If the price of a race car were to go up in the short run, would race car producers be able to increase their quantity supplied by a small % or a large %?
In the short run, race car producers would only be able to increase quantity supplied by a small % because they will be limited by their fixed factors of production. For instance, they might have a fixed amount of factory space, a fixed number of machines, and so even if the price of race cars goes up massively, race car producers will not be able to produce many more race cars because they don't have enough space or machinery.
n the long run, supply will be:
more elastic
What does a perfectly inelastic supply curve look like?
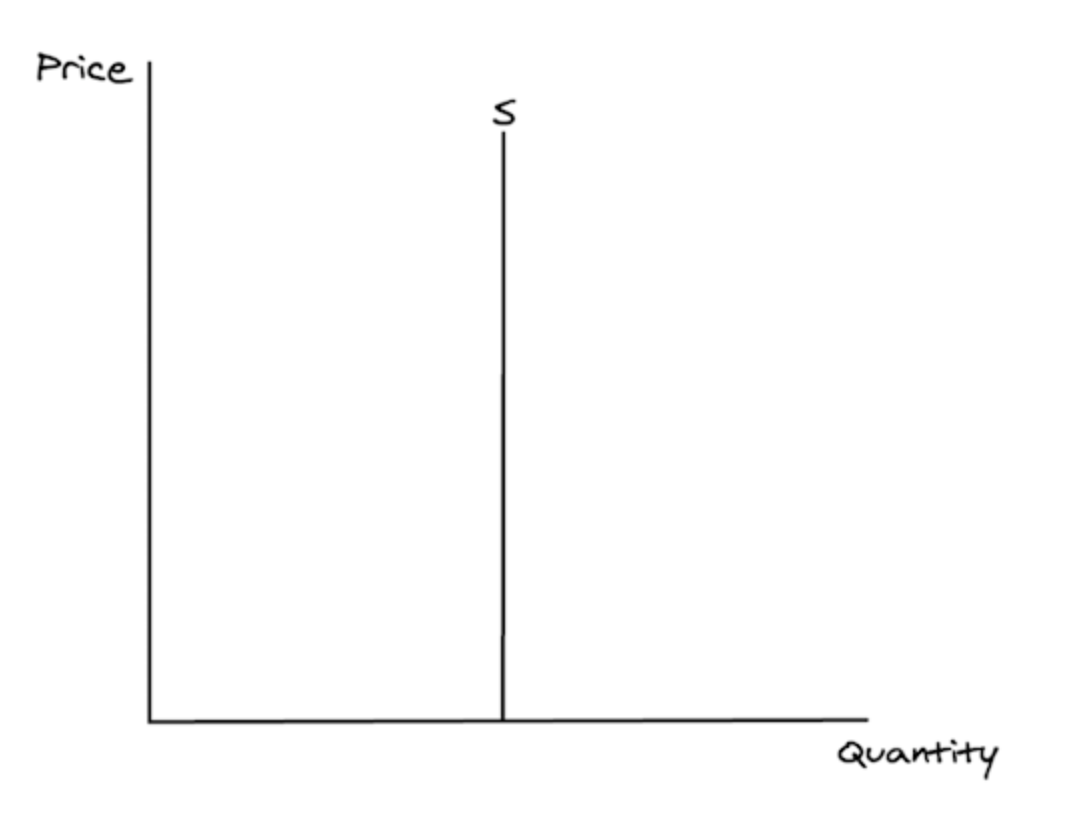
What are examples of perfectly inelastic supply?
In the short run, even if the price went up massively, producers of agricultural goods (wheat, strawberries, beef), wouldn't be able to increase the quantity they supply at all because it takes so long to grow new crops or raise more animals.
When PES=0, we say that supply is:
perfectly inelastic
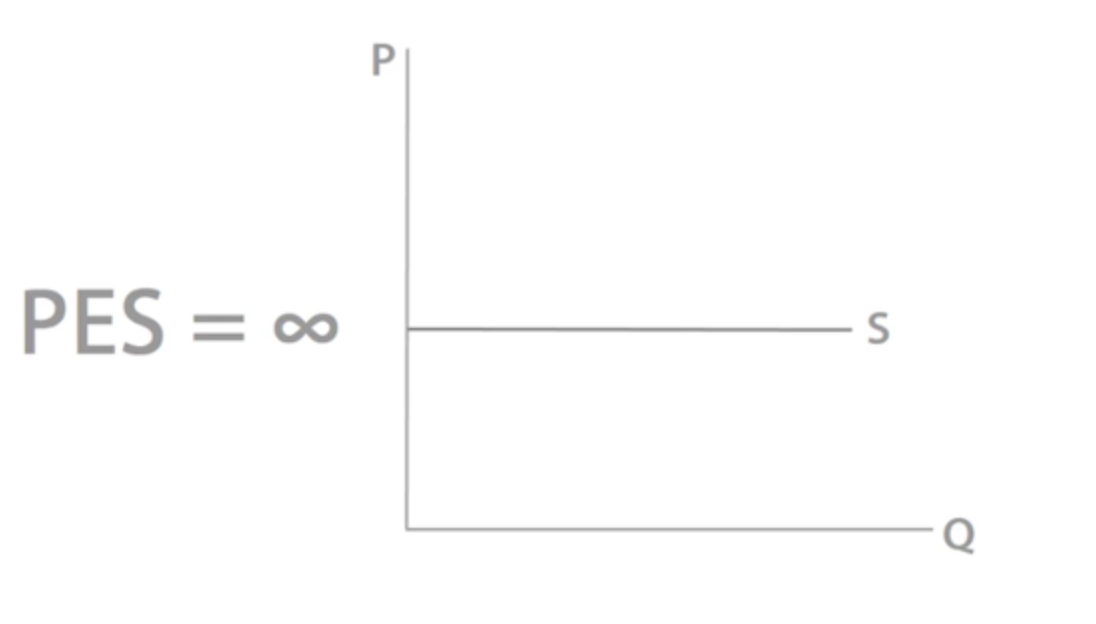
What does a perfectly elastic supply curve look like?
What does the unitary supply graph look like?