Key Concepts in Biology and Physiology 9
1/345
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
346 Terms
Acronym for anterior pituitary hormones
FLAT PiG
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
A hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
A hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
A hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
A hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Prolactin
A hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Growth Hormone (GH)
A hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Zymogen
Inactive precursor of an enzyme.
Amylopectin
Branched form of plant starch.
Advantage of compound light microscopes
They can be used to view 2D images of living samples.
Advantage of dark field optical microscopy
Excellent contrast on unstained cells (black background).
Advantage of SEM
High resolution, 3D images of sample surfaces.
Allosteric site
A different location that is not the active site of enzyme catalysis.
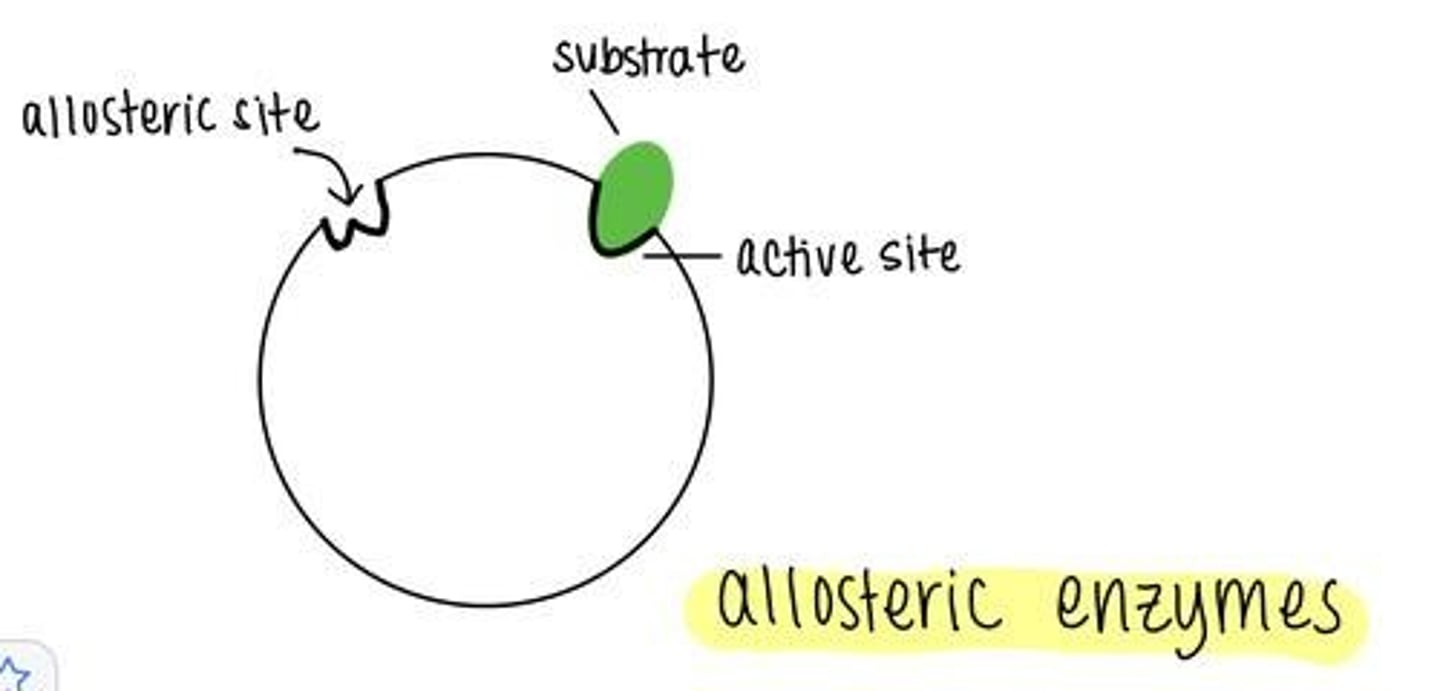
Apoenzyme
An enzyme that is lacking (not bound to) its cofactor.
Example of a eukaryotic organism that uses budding
Yeast (fungus).
Example of a condition that may cause hypotonicity in a skeletal muscle
Carpal tunnel (results in weakness/numbness).
Example of a condition that may cause hypertonicity in a skeletal muscle
Stroke.
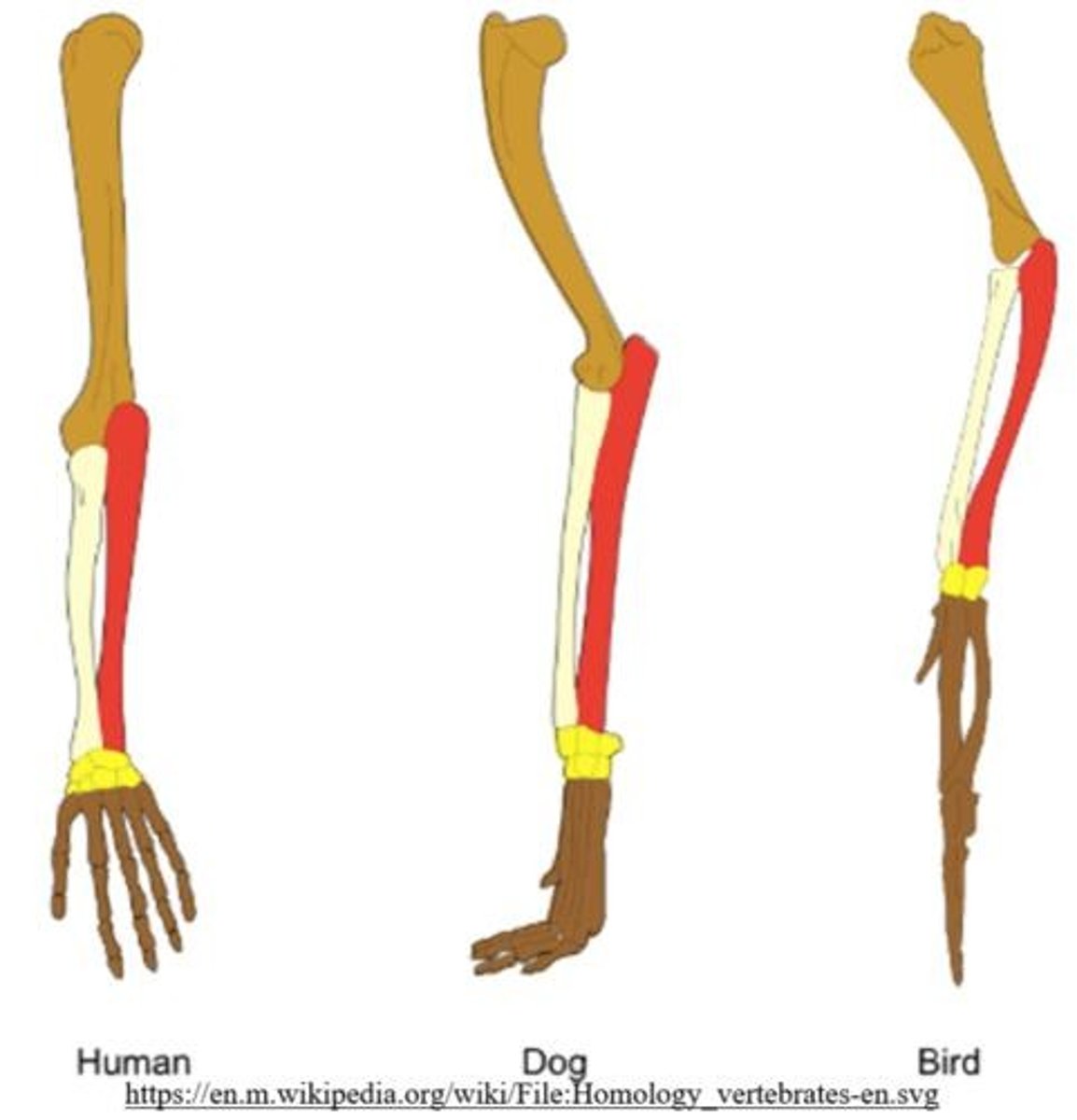
Example of homologous structures
The forearm of a bird and the forearm of a human.
Example of a haplodiploid organism
Bees.
Example of directional selection for bacteria
Antibiotic resistance.
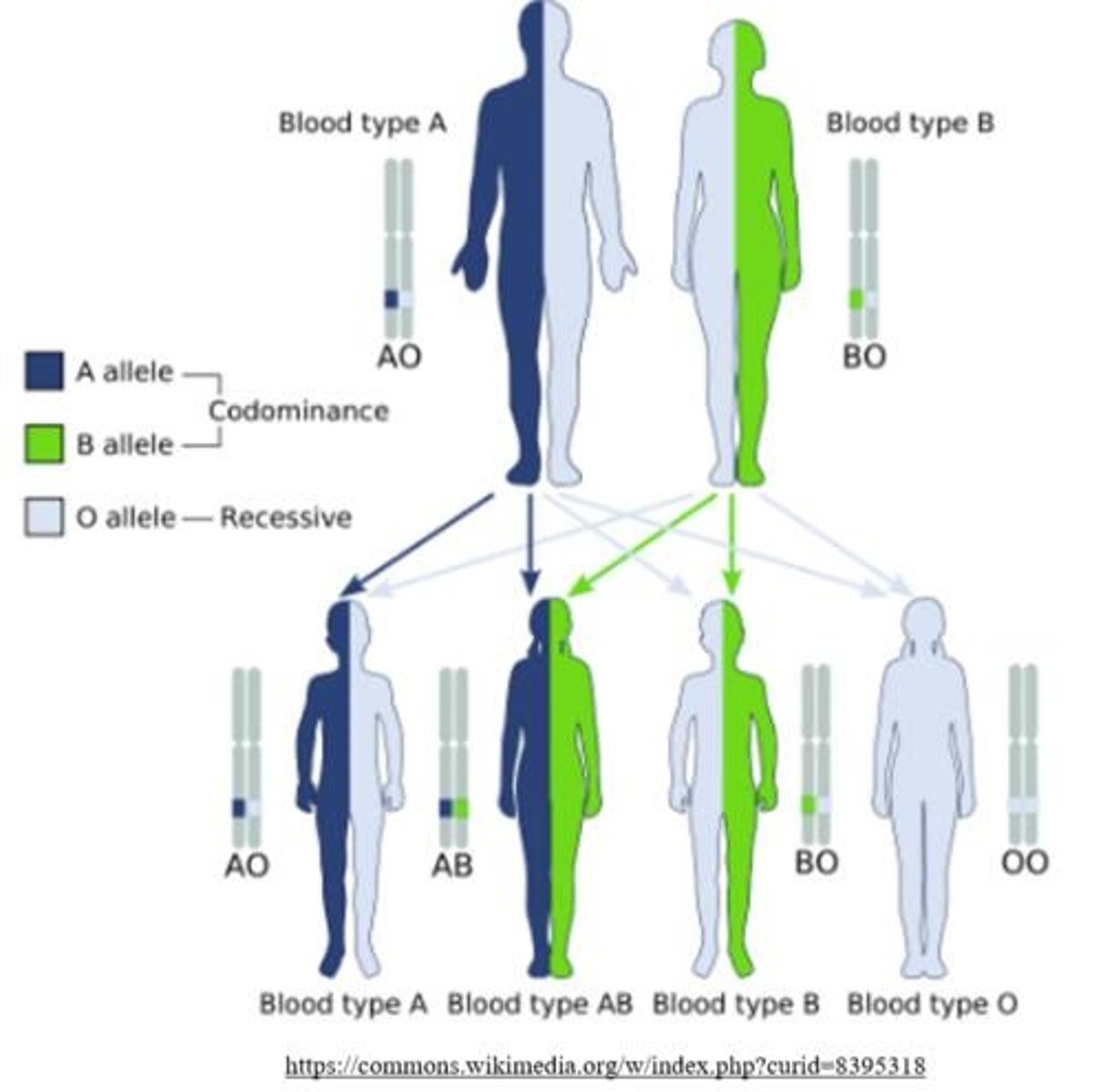
Example of multiple alleles in humans
The ABO blood typing. A person can be type A, AB, B, or O.
Example of pleiotropy in humans
Cystic fibrosis. A single gene will lead to the expression of different symptoms in different tissues.
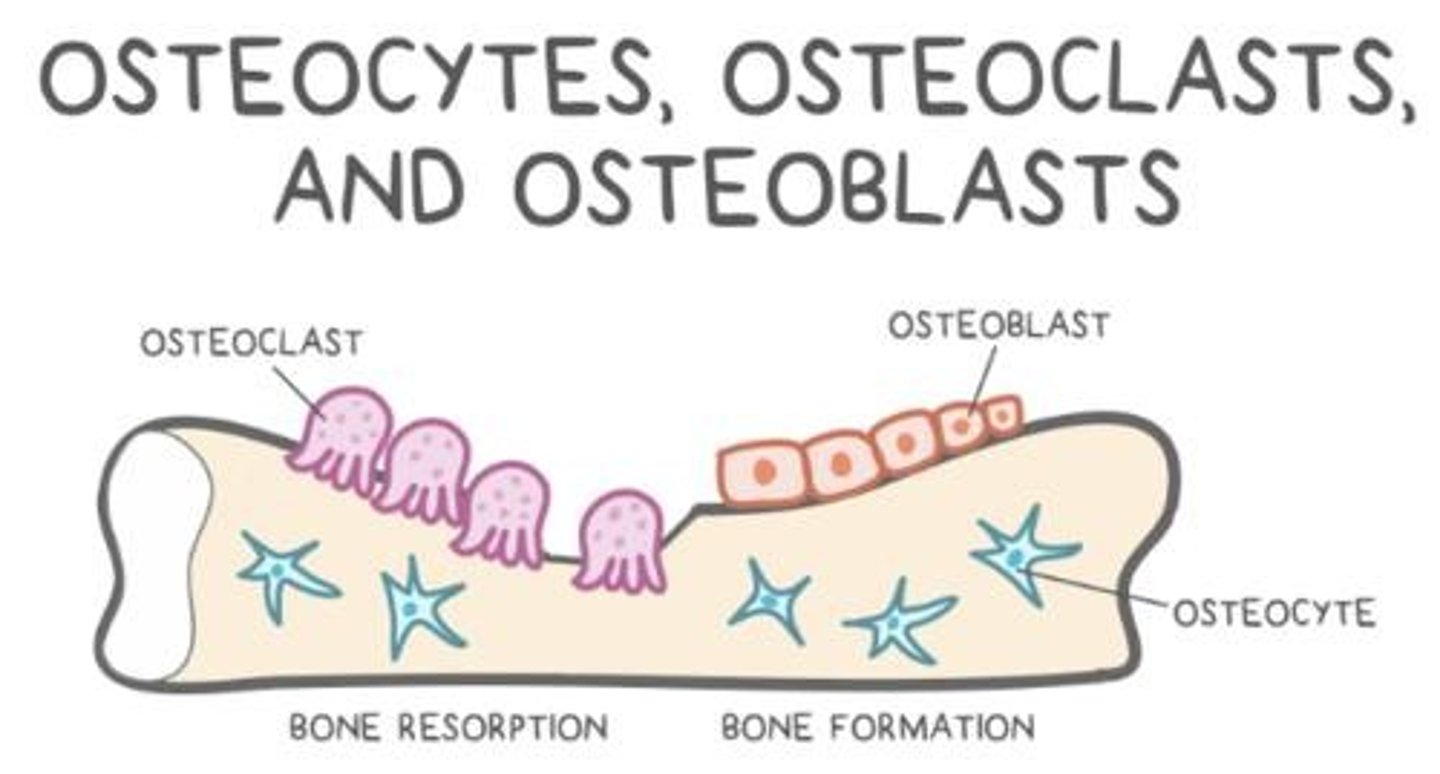
Bone remodeling
The back and forth between resorption (osteoclasts) and ossification (osteoblasts).
Calcitonin's effect on the kidneys and intestines
It decreases Ca2+ reabsorption in these areas.
Cardiac output (CO)
Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
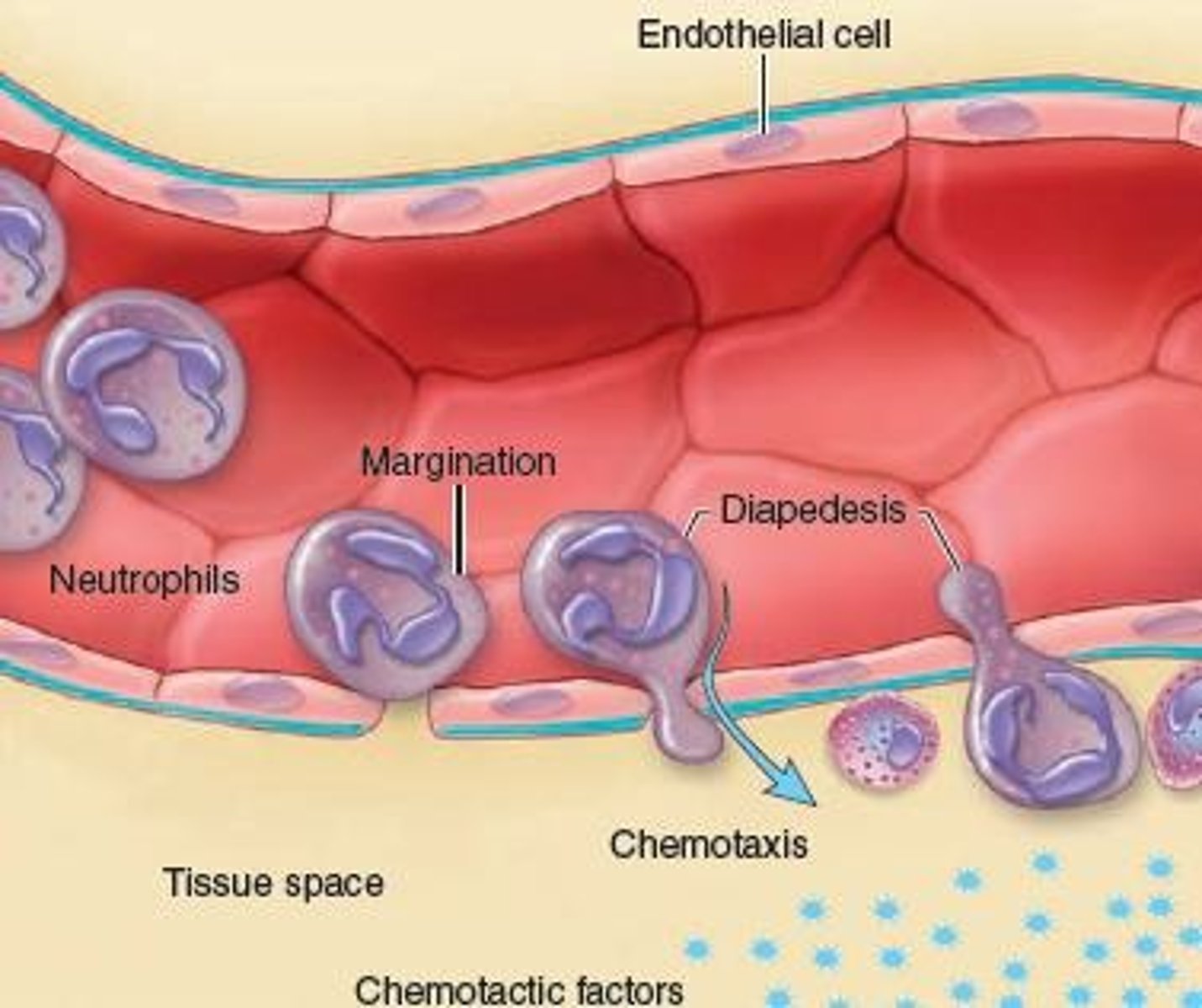
Chemotaxis
The process of moving to a location in response to a chemical signal.
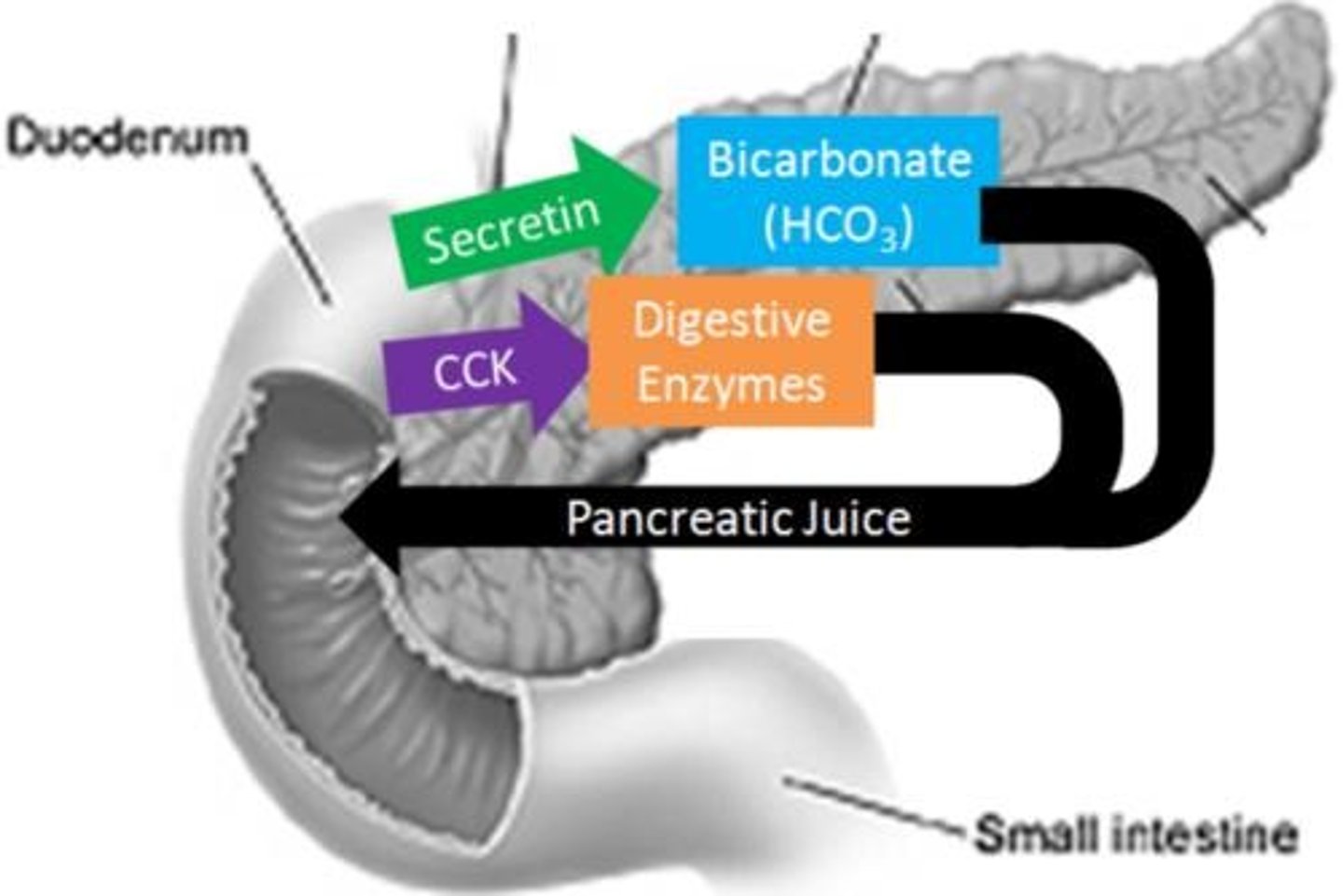
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Hormone secreted by the small intestine that signals for accessory organs to help in the process of digestion.
Characteristic of daughter cells that result from cleavage
They have less cytoplasm than the mother cell.
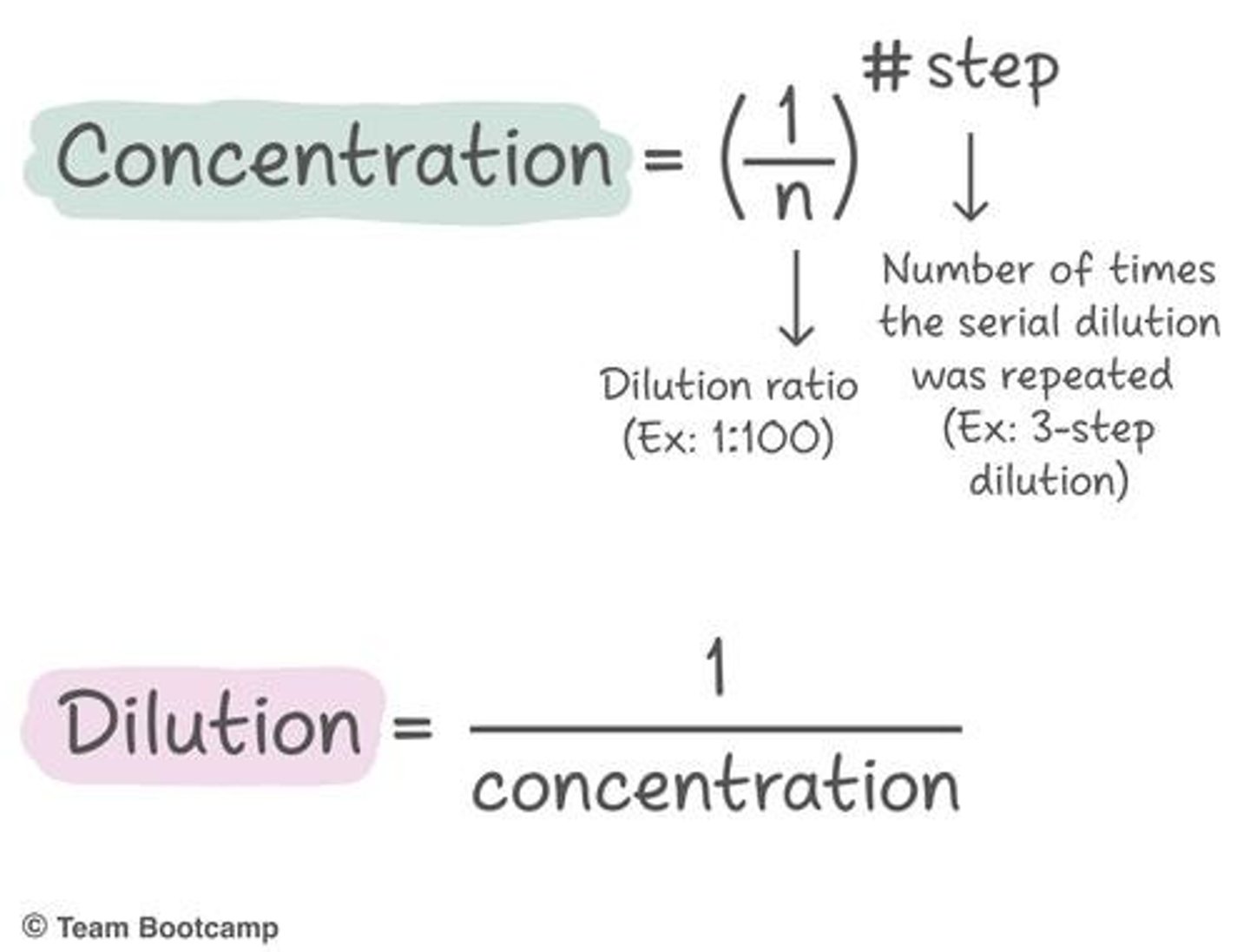
Dilution
It is the process of decreasing the concentration of a solute in a solution, e.g. adding water to orange juice to make it less sweet.
End-diastolic volume (EDV)
The amount of blood in ventricles before contraction.
End-systolic volume (ESV)
The amount of blood in ventricles after contraction.
Enzyme saturation
All active sites are occupied.
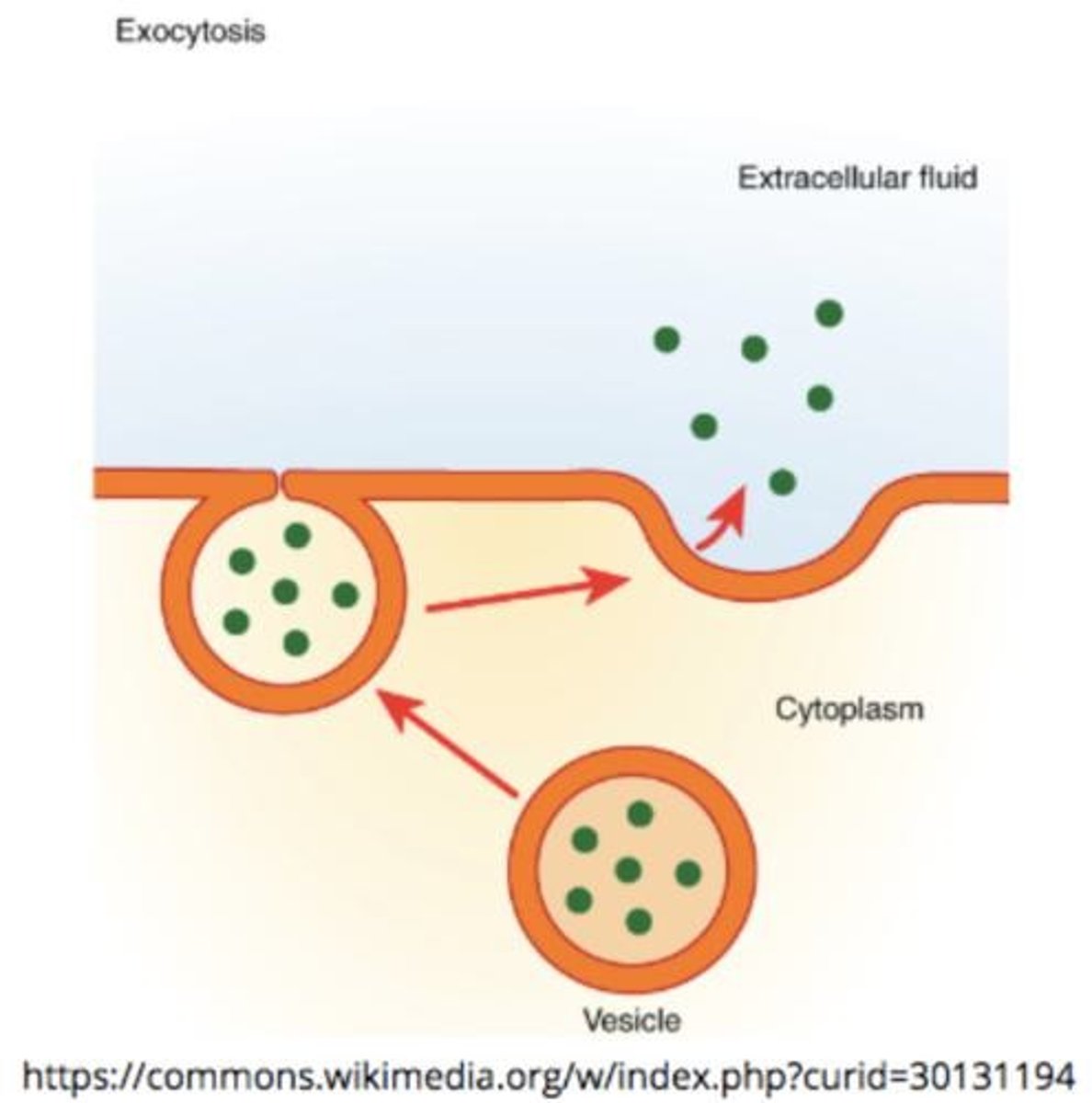
Exocytosis
Process by which materials exit the cell (opposite of endocytosis).
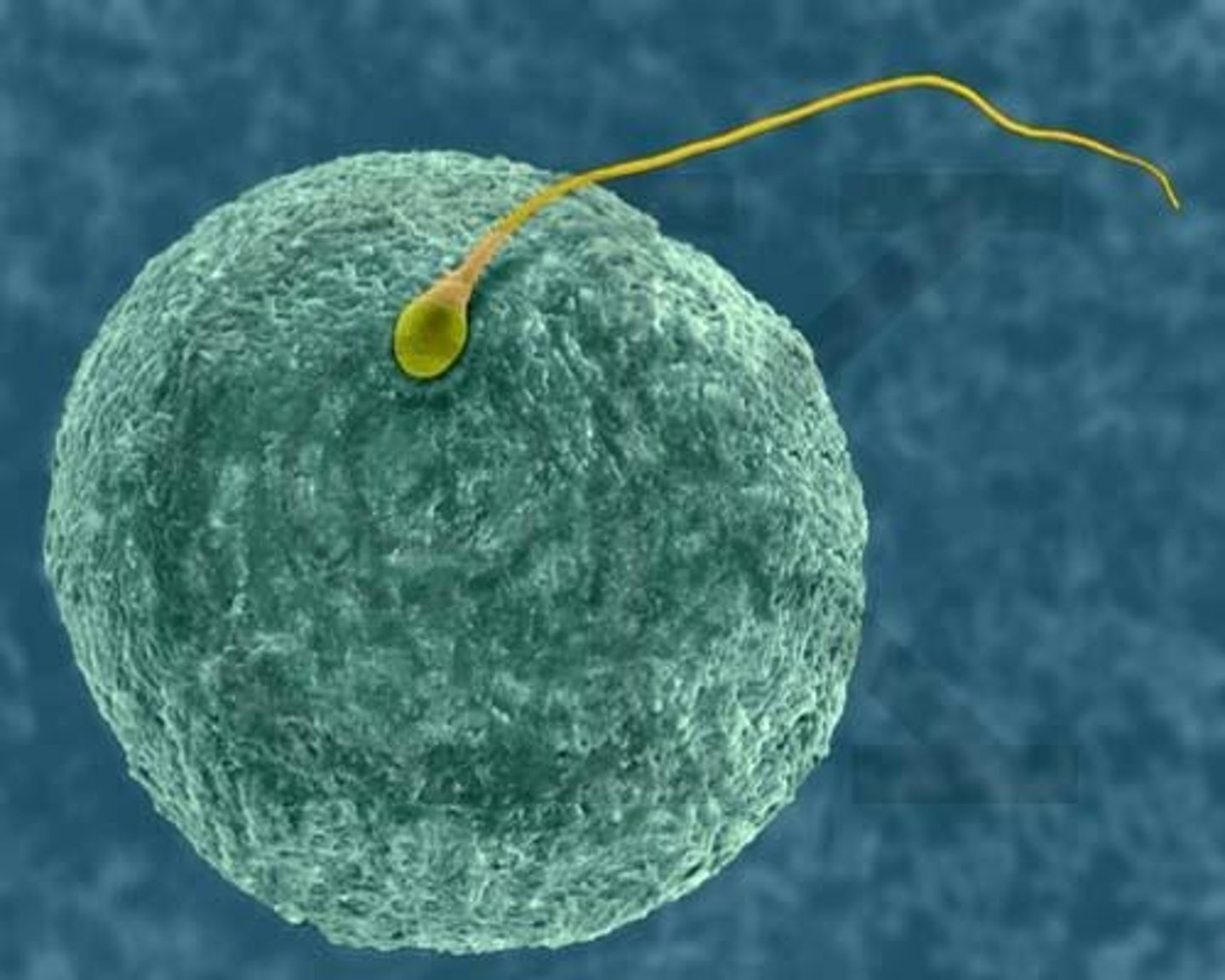
Fertilization
The fusion of 2 haploid gamete nuclei to make 1 diploid zygote.
Erythroblastosis fetalis
Rh- mother gives birth to a Rh+ baby; blood mixing causes mother to develop antibodies against Rh antigens (Rh+ blood).
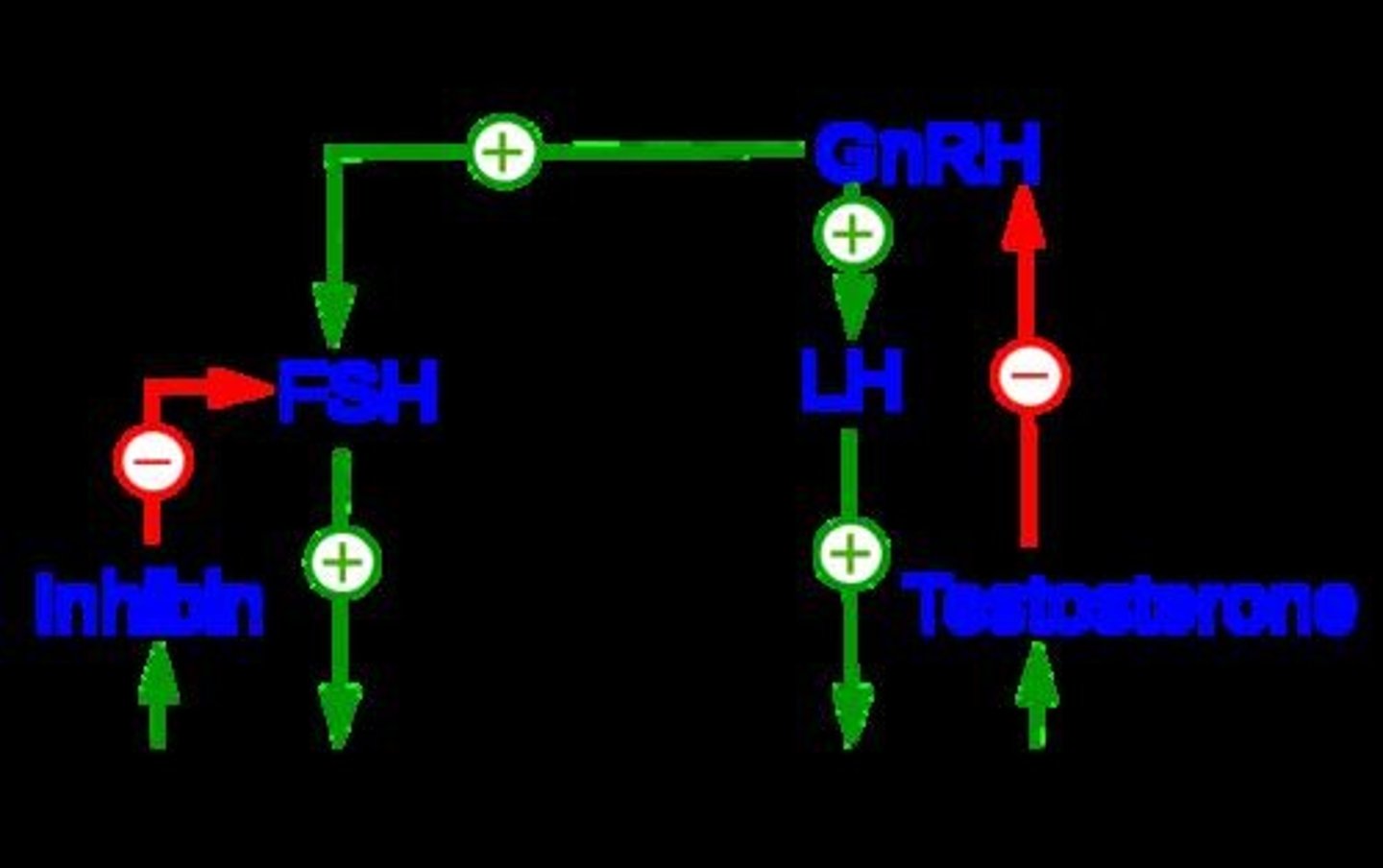
Function of inhibin (from Sertoli cells)
Inhibits the further release of FSH (peptide hormone) by acting on the anterior pituitary.
Heart rate (HR)
Is how fast or slow the heart beats.
Imbibition
The absorption of water by the seed.
Muscle tone (tonus)
Weak, involuntary twitches of small groups of motor units, which keeps muscles firm.
Organogenesis
Formation of new organs.
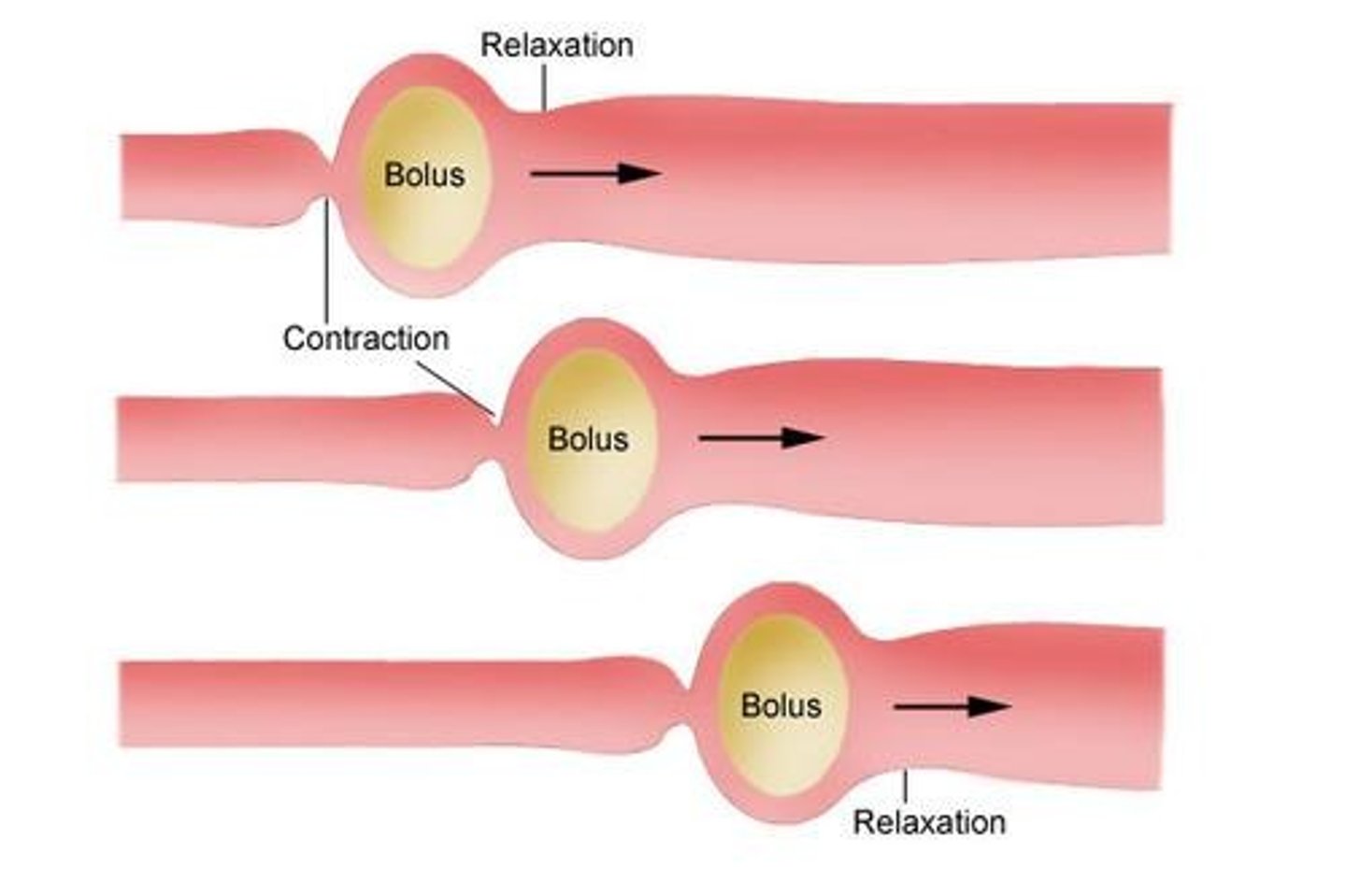
Peristalsis
A rhythmic wave-like contraction that moves food boluses.
Carbaminohemoglobin
Hemoglobin bound to CO2.
plasmogamy
the process where two hyphae of filamentous fungi fuse their cytoplasm
increased Ca2+ significance
it causes hyperactivity, making the flagellum beat harder
saltatory propagation
the action potential 'jumps' from one node of Ranvier to the next
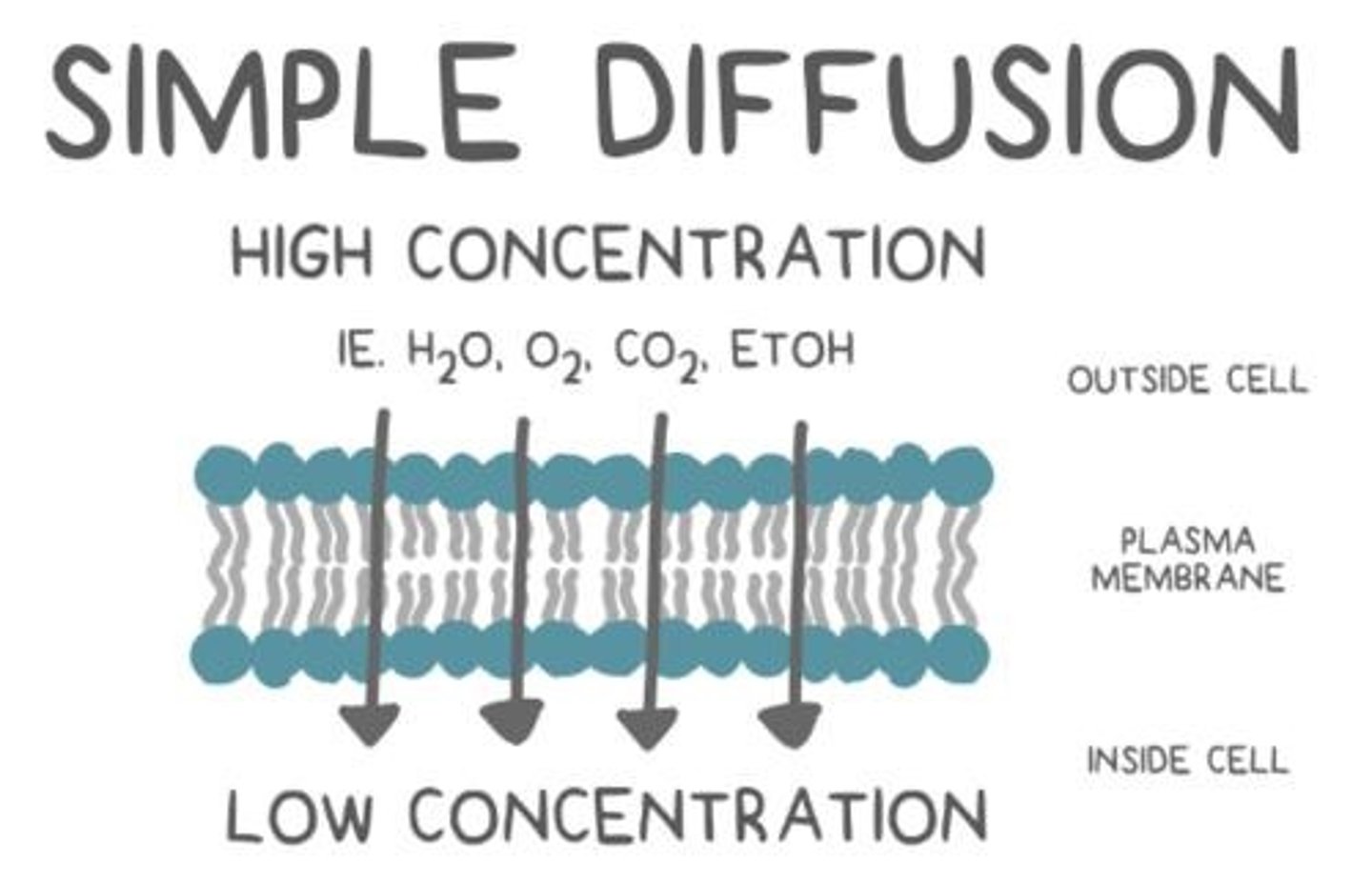
simple diffusion
passive movement of dissolved substances due to concentration gradient
speciation
the process that describes how species actually form
taxonomy
the science of classifying organisms
benefit of saltatory propagation
it provides faster conduction than propagating the signal down the entire axon
bundle sheath cells in C4 photosynthesis
they do not contain as much O₂, so photorespiration is less likely to occur
Casparian strip
a fatty, waxy substance that makes it impenetrable
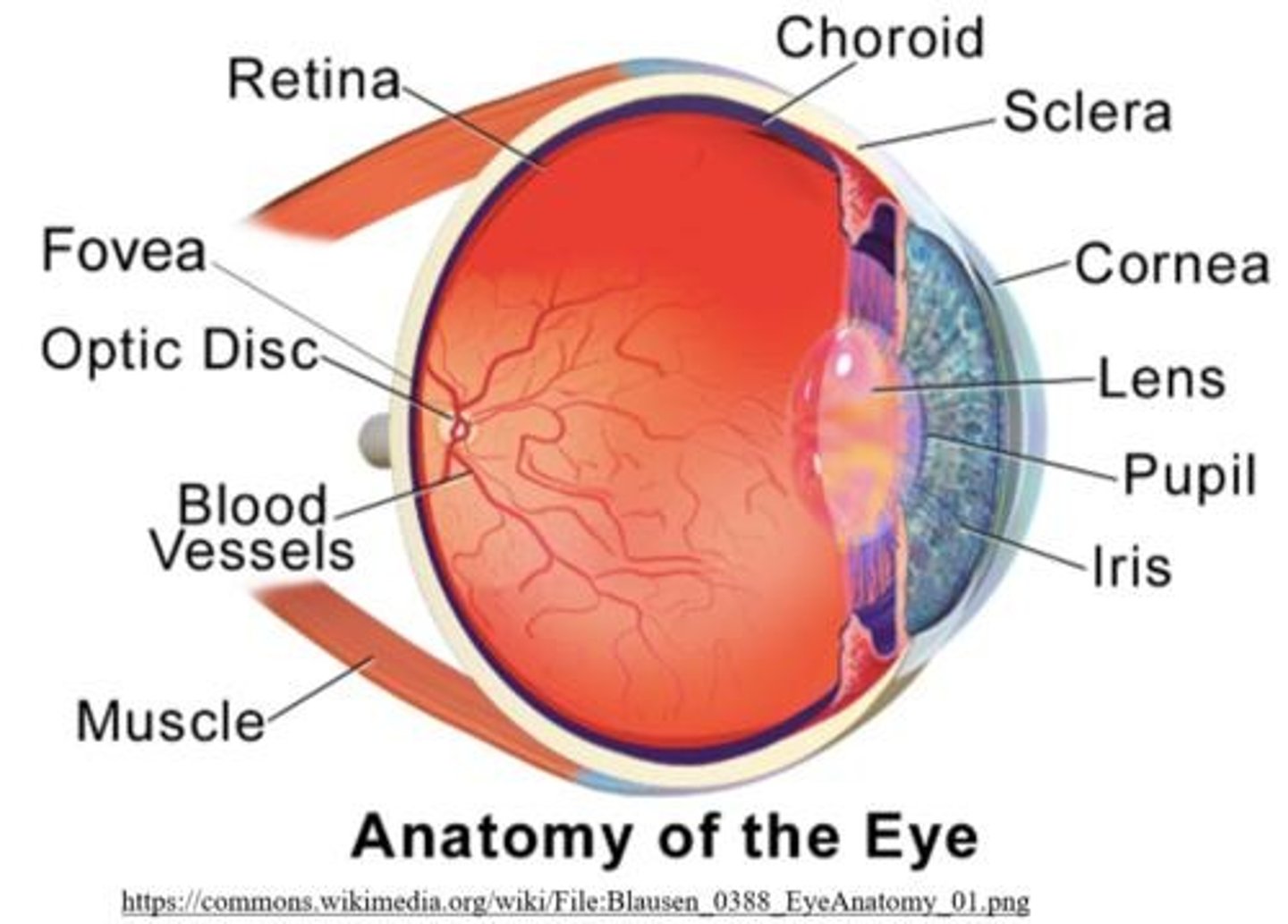
blind spot of the eye
the optic disc (where the optic nerve exits)
central importance of the homeobox
it plays a crucial role during organismal structural organization during development
chemical digestion in the mouth
saliva (salivary amylase)
connective vascular tissue between the sclera and the retina
the choroid
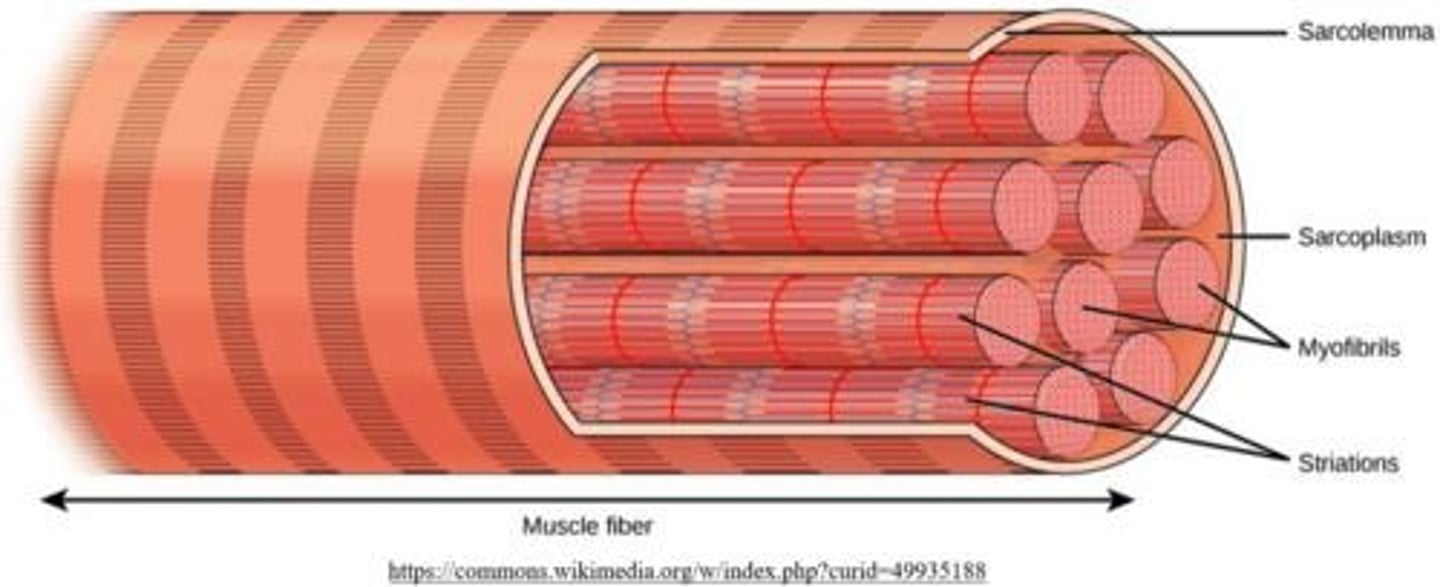
cytoplasm of a muscle fiber
the sarcoplasm
definition of an ecological community
all of the populations living in a certain area where the different species interact
dilution factor
it is the factor by which your original solution was diluted (typically done in factors of 10 or 100)
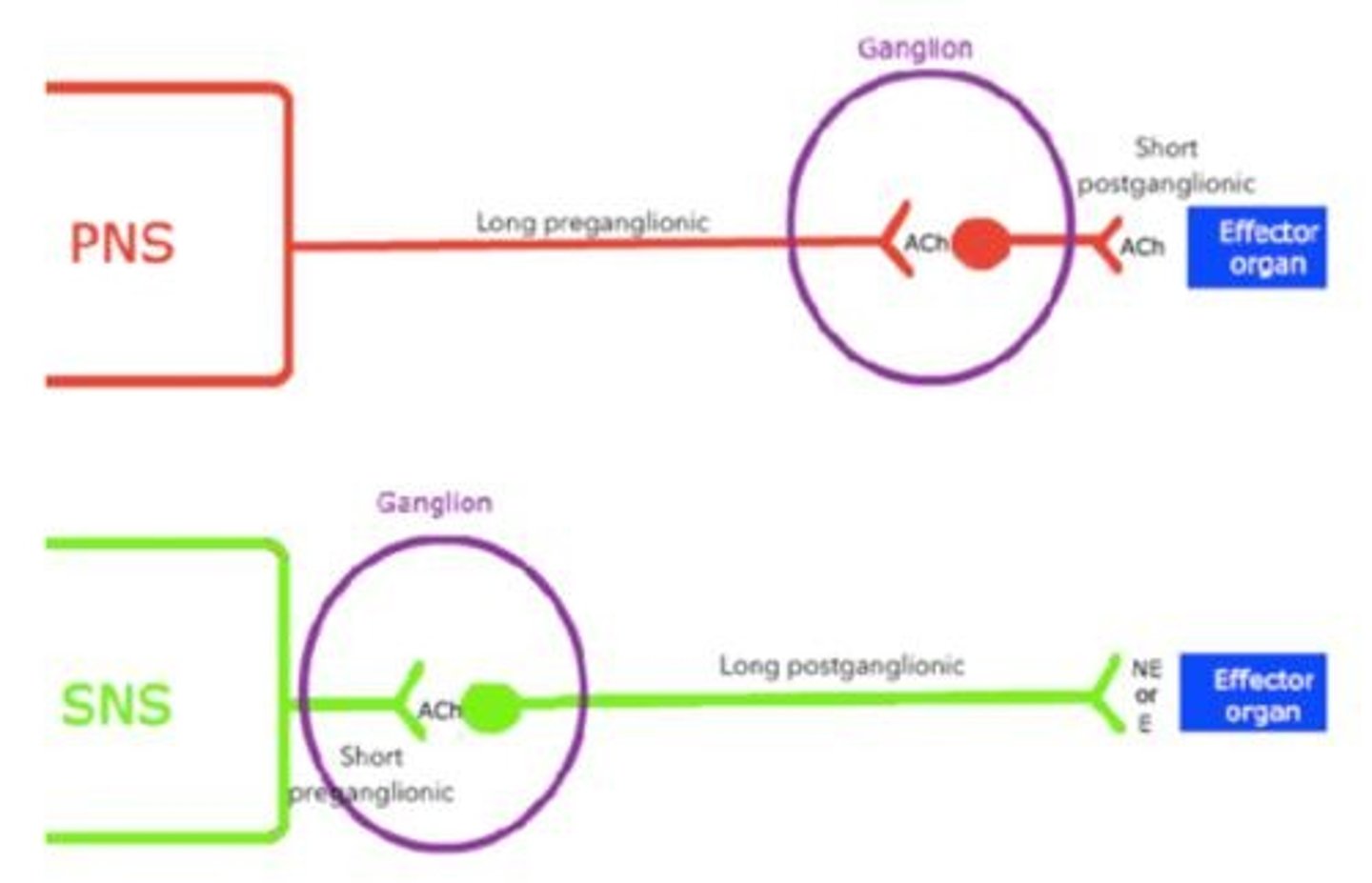
distance of PNS ganglia from effector organs
close
difference between a B cell receptor (BCR) and an antibody
structurally they are identical; however, a BCR is bound to the B cell membrane, while antibodies are freely floating immunoglobulins
distance of SNS ganglia from effector organs
far
embryonic cleavage of protostomes
spiral and determinate
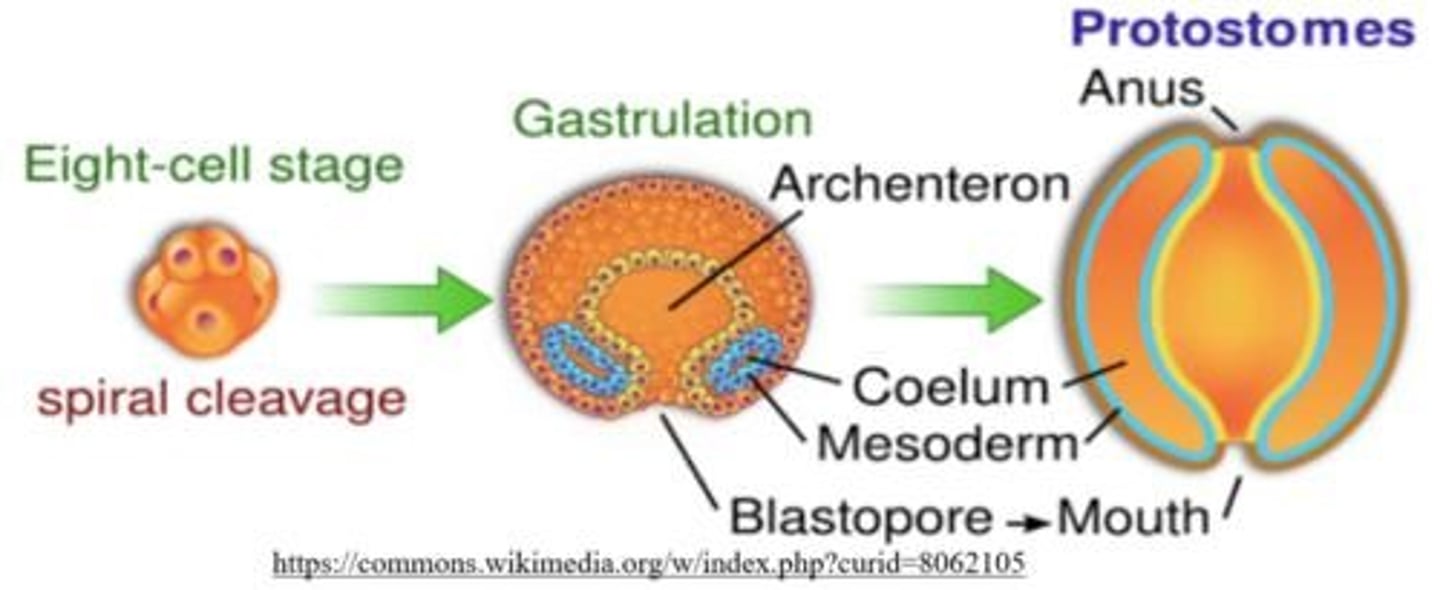
embryonic development of nematoda
protostome
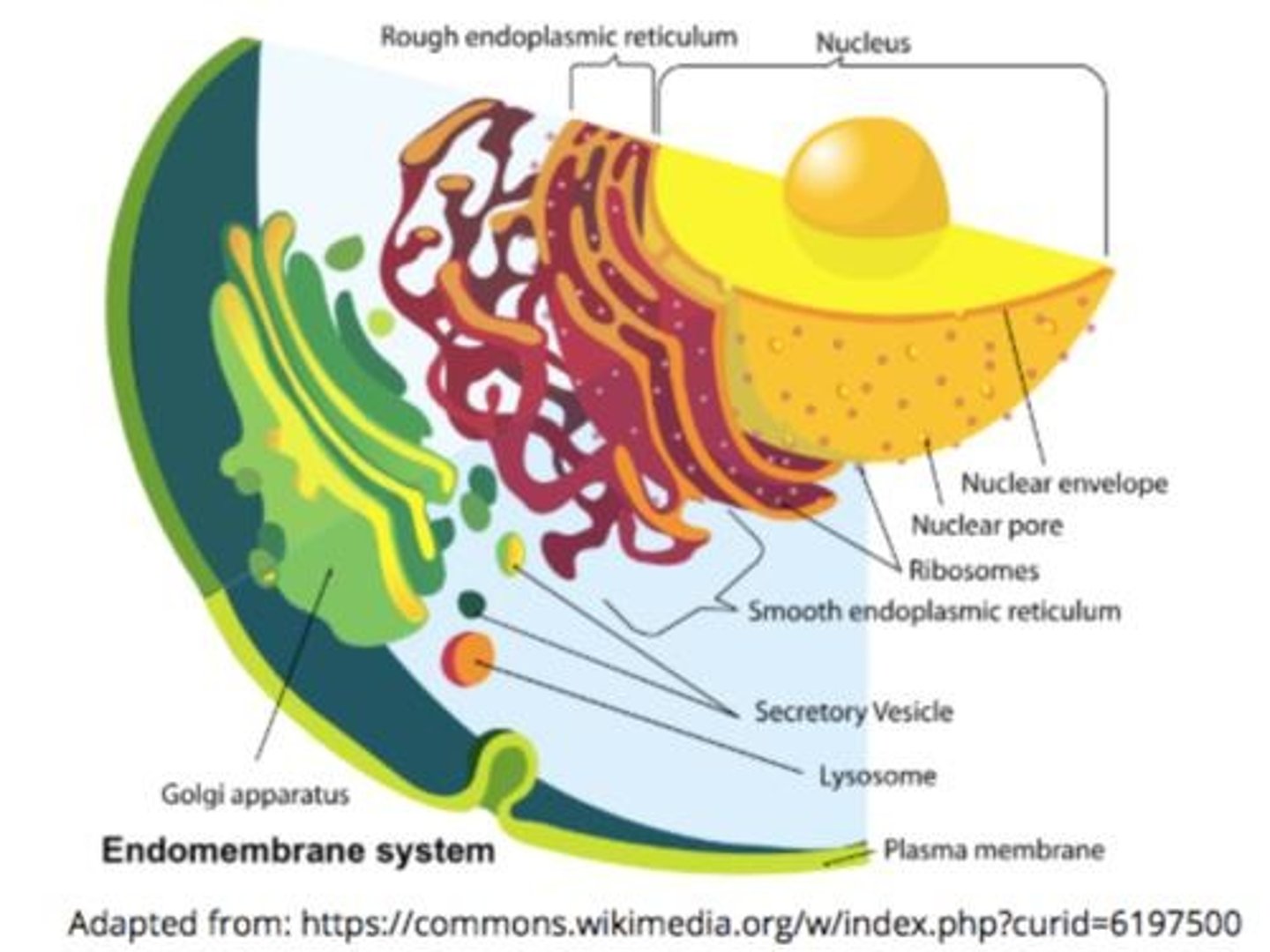
endomembrane system
group of organelles/membranes that work together to modify, package, and transport proteins and lipids that are entering/exiting a cell
enzyme that breaks hydrogen bonds during DNA replication
DNA helicase
fate of the rest of the hypoblast
it undergoes apoptosis
excitatory neurotransmitter of a neuromuscular junction
acetylcholine
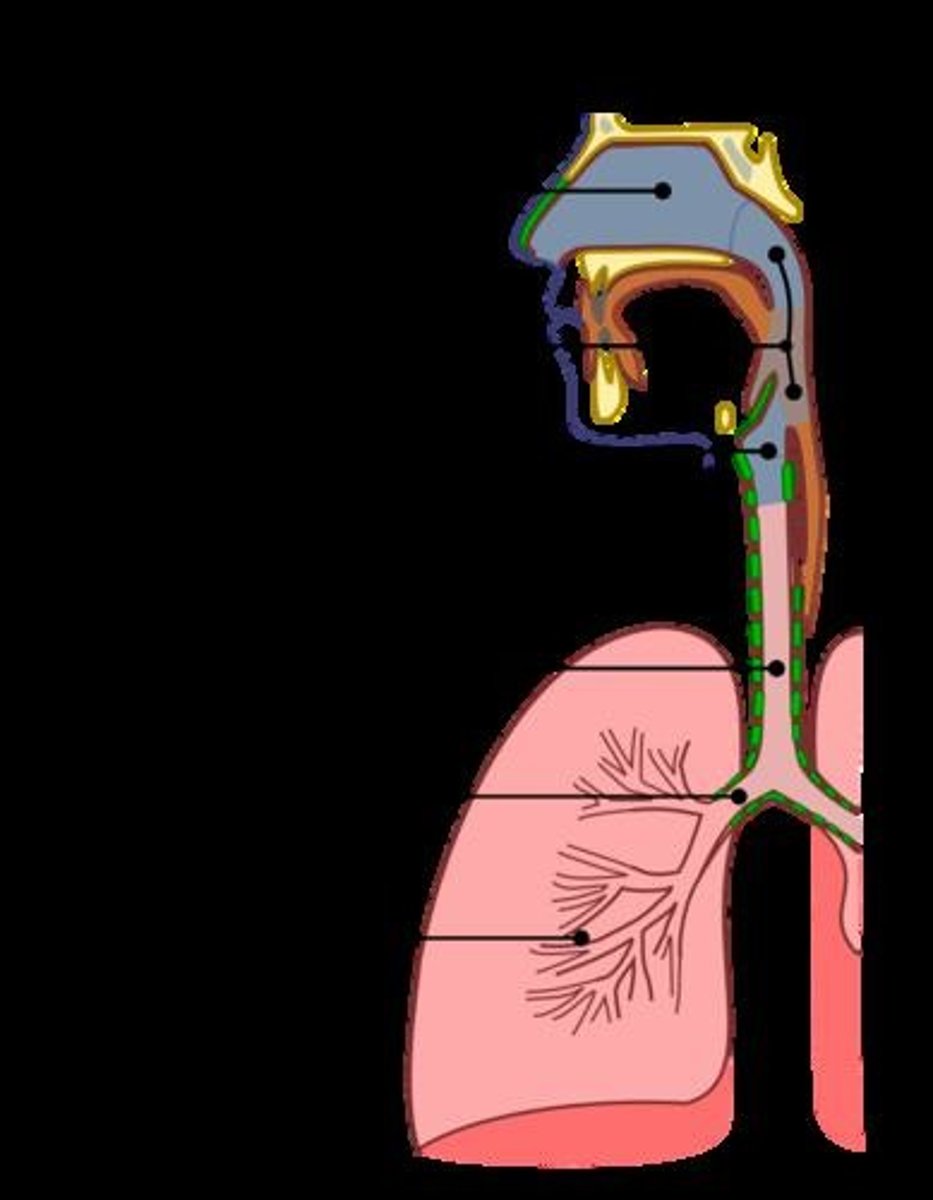
first respiratory structure air makes contact with when inspired
the nasal cavity
first step of growth after formation of the zygote
cleavage
fluid in the lymphatic system
lymph
function of central chemoreceptors
detect the concentration of pH in the cerebrospinal fluid
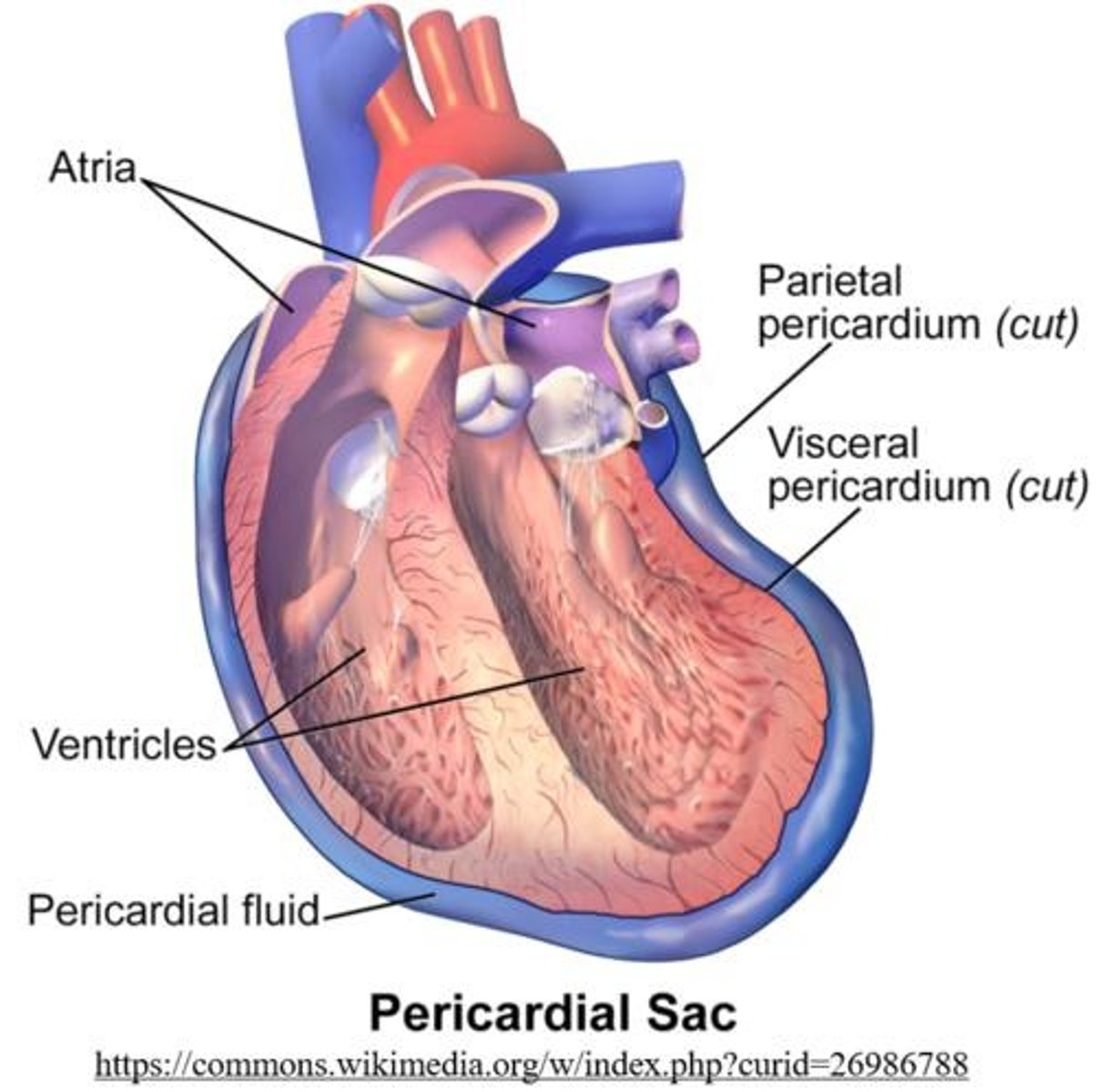
fluid in the pericardium
serous fluid
function of arachnid book lungs
their flat vascularized sheet membranes provide a large surface area for respiration
function of glucagon secreted from alpha cells
increase blood glucose levels
function of insulin secreted from beta cells
decrease blood glucose level
function of intrapleural pressure
it prevents the lungs from collapsing
function of peripheral chemoreceptors
detect changes in the concentration of O2, CO2, and H+ in arterial blood
function of somatostatin secreted from delta cells
inhibits secretion of somatotropin (GH), glucagon, and insulin
function of the AV node
add a brief delay between atrial and ventricular contractions
Function of the mitochondria
Produce ATP to power flagellar motion.
Function of the nasal cavity
It warms and moistens incoming air.
Function of the stamen anther for male angiosperms
The anther is the site of microspore formation via meiosis.
Function of the sperm midpiece
Contains mitochondria to produce ATP for movement.
Function of the sperm tail
Facilitates movement of sperm.
General mechanism of dizygotic twin creation
The mother ovulates 2 eggs, both are individually fertilized by 2 different sperms, resulting in 2 different zygotes with slightly different genetic material.
Functional unit of a muscle fiber
Sarcomeres; they shorten to facilitate muscle contraction.
Function of the stamen filament for male angiosperms
To support the anther.
General process of the acrosomal reaction
Sperm binds to the egg, leading to membrane fusion and fertilization.
General mechanism of the fast block to polyspermy
Sperm penetration leads to Na+ influx, causing membrane depolarization that repels additional sperm.
General mechanism of the slow block to polyspermy
Cortical reaction releases Ca2+ to egg membrane, leading to fusion between sperm and egg.
Genotypic ratio for a monohybrid cross
1:2:1 for XX : Xx : xx.
Function of the hippocampus (limbic system)
Responsible for learning and long-term memories.
Homeobox
A short sequence of about 180 nucleotides (60 amino acids) that is homologous across many different organisms.
Innermost layer of the eye containing photoreceptors
Retina.
Hypothesis for the creation of the first cell
The RNA world hypothesis.
Insecta symmetry of body plan
Bilateral.
Key function of aldosterone (mineralocorticoid)
Increase blood volume and pressure.
Label for the first generation of offspring in a cross
F1 = filial 1 hybrid = offspring of parental generation.
Label for the parental generation in a cross
P = parental generation.
Label for the second generation of offspring in a cross
F2 = filial 2 hybrid = offspring of F1 generation.