Business Information Systems | Quizlet
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
234 Terms
Information Systems (IS)
the combination of people and information technology that create, collect, process, store and distribute useful data.
Digital Innovation
a product, process, or business model that is perceived as new, requires some significant changes on the part of the adopters and is embodied in or enabled by IT.
3 characteristics of Digital Innovation
1. Digitalization -> transforming something digital to something digital.
2. Moore's Law -> Rapid performance improvements of IT components due to doubling of the number of transistors in an integrated circuit approx. every 2 years.
3. Network effects -> value of innovation increases when more people use it.
Digital Density
the amount of connected data per unit of activity.
3 drivers of
1. Connections: between people/organizations/computers, as well as the ability to connect almost any physical object to the digital world.
2. Data: the ability to connect elements of the physical to the digital world.
3. Interactions: human interactions vs. automation.
Information Technology (IT)
includes hardware (for filing), software (to execute business processes more efficiently), and telecommunication networks (to share data globally).
Data
Raw symbols such as characters and numbers. Don't have meaning and are of little value until processed.
we want data of quality that has completeness, accuracy, etc. to turn it into something useful.
Information
Data that has been formatted, organised and processed.
information helps us answer questions about who, what, where, when.
Knowledge
Required to sue information. it is the ability to understand information, form opinions and make decisions or predictions based on information.
It is skills + experience + accumulated learning + judgement.
IS & Performance
IS and performance are positively related in 3 ways:
1. Automation: doing things more accurately, efficiently and consistently.
2. Learning: doing things better, based on available information.
3. Supporting strategy: doing things smarter, fundamentally redefining business and industry processes and relationships.
Business Processes
the activities organisations perform to reach their business goals, including core activities that transform inputs and produce outputs, supporting activities that enable the core activities to take place.
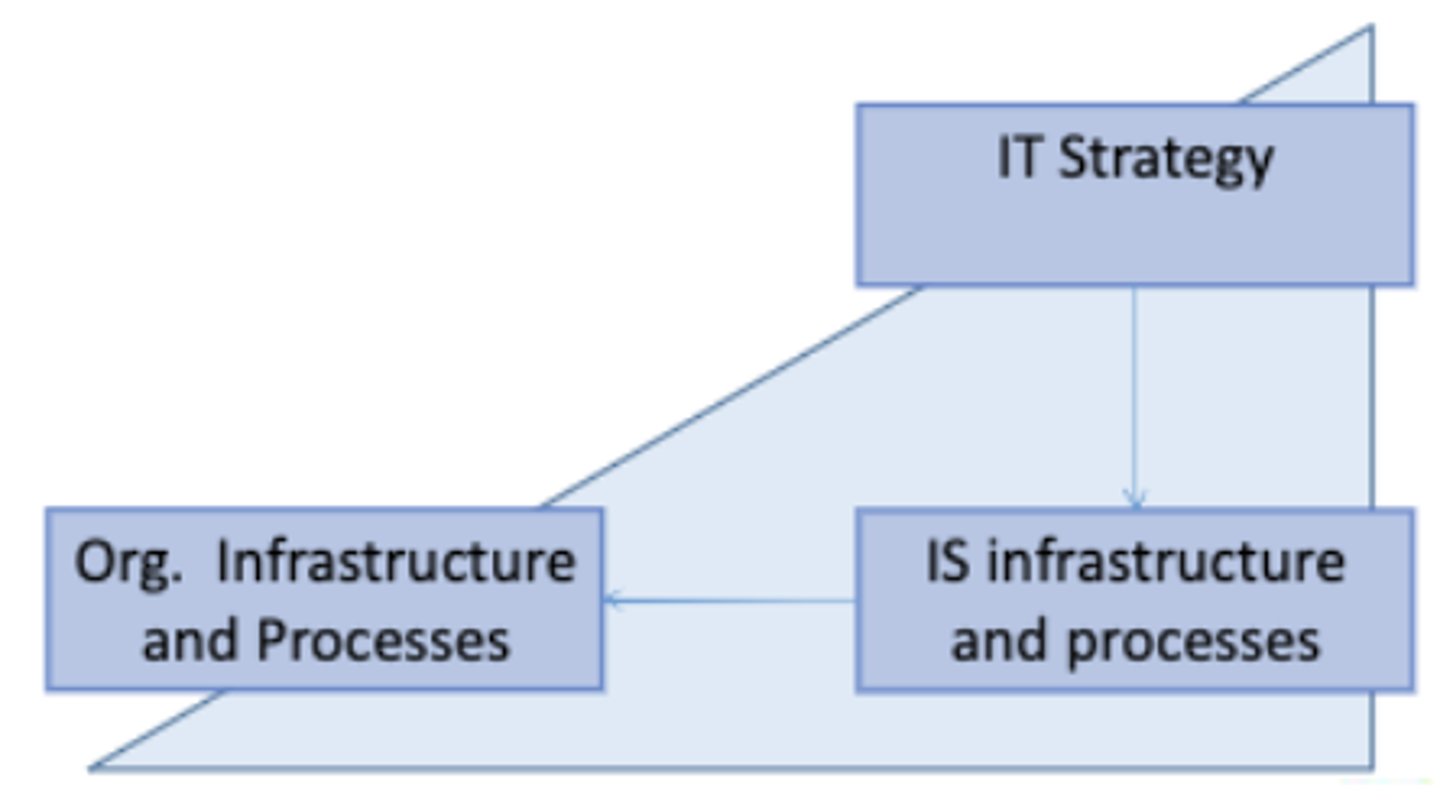
IS strategy
the organizational perspective on the investment in deployment, use and management of information systems.
IS Strategy Process
The process of identifying a portfolio of computer-based applications that support an organisation's business plans, enabling the organisation to align its IS with its business needs and achieve its goals.
5 Phases of IS Strategy Process
1. Strategic awareness
2. Situation Analysis
3. Strategy conception
4. Strategy formulation
5. Strategy implementation
strategic awareness
organise the process, identify objectives for business and IS strategy, then find integration among business strategy, IT strategy, business infrastructure, and IT infrastructure.
Strategic alignment
1. Henderson & Venkatraman
-> Focuses on external and internal domain, so the strategic and operational level.
-> Focuses on business and IT domain.
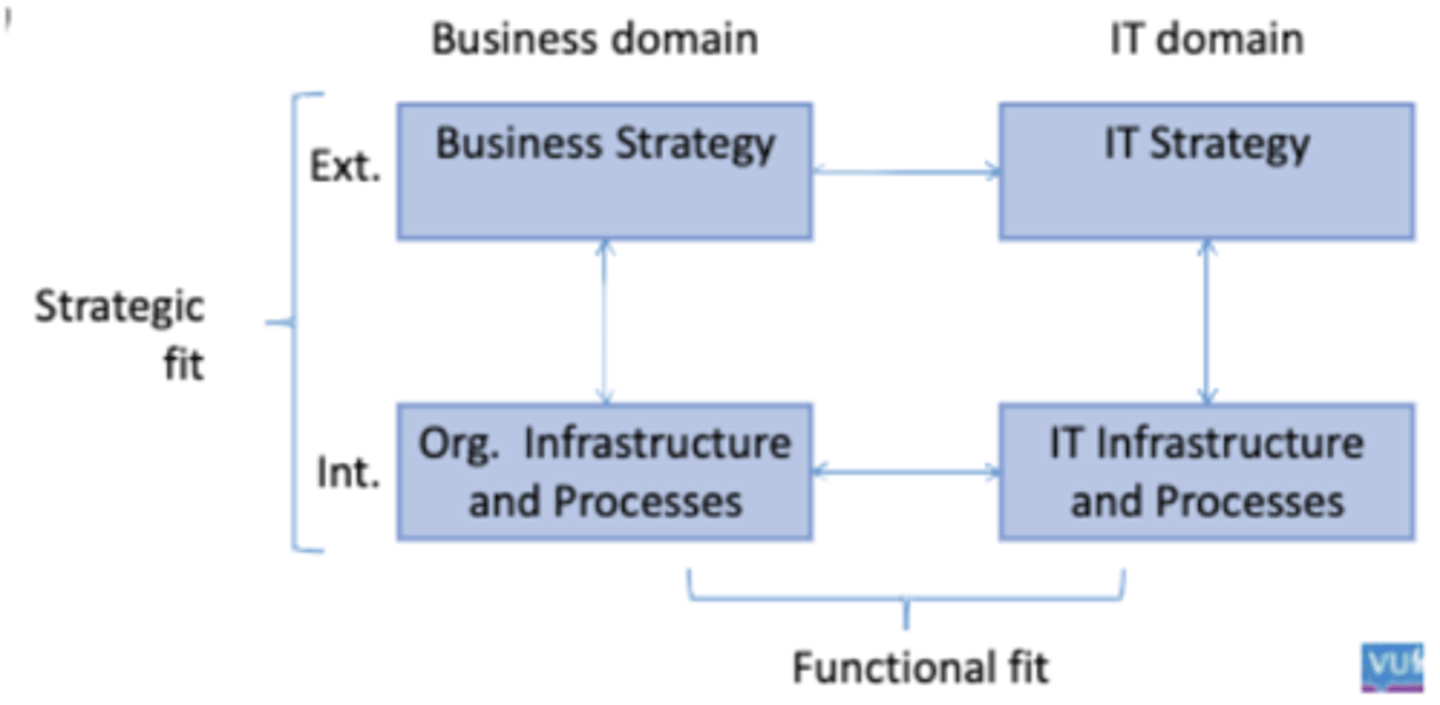
Strategic alignment
2. Technology Potential
-> Business strategy is the driver.
-> What IT strategy will achieve that business strategy.
-> Should not be constrained by the current organisation.
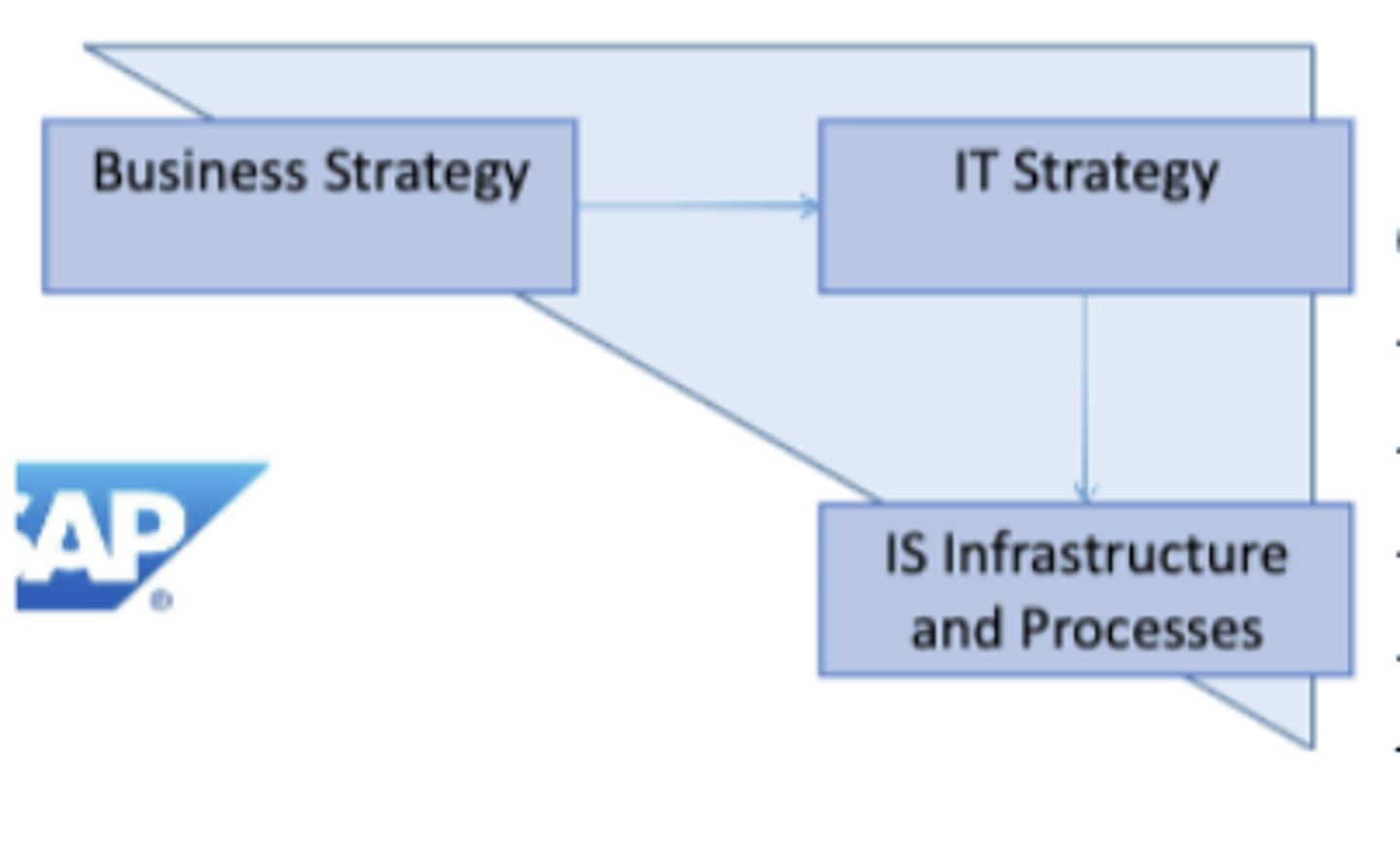
Strategic Alignment
3. Competitive Potential
-> IT strategy is the driver!
-> What business strategy will achieve that IT strategy?
-> You adapt your organization to IT possibilities
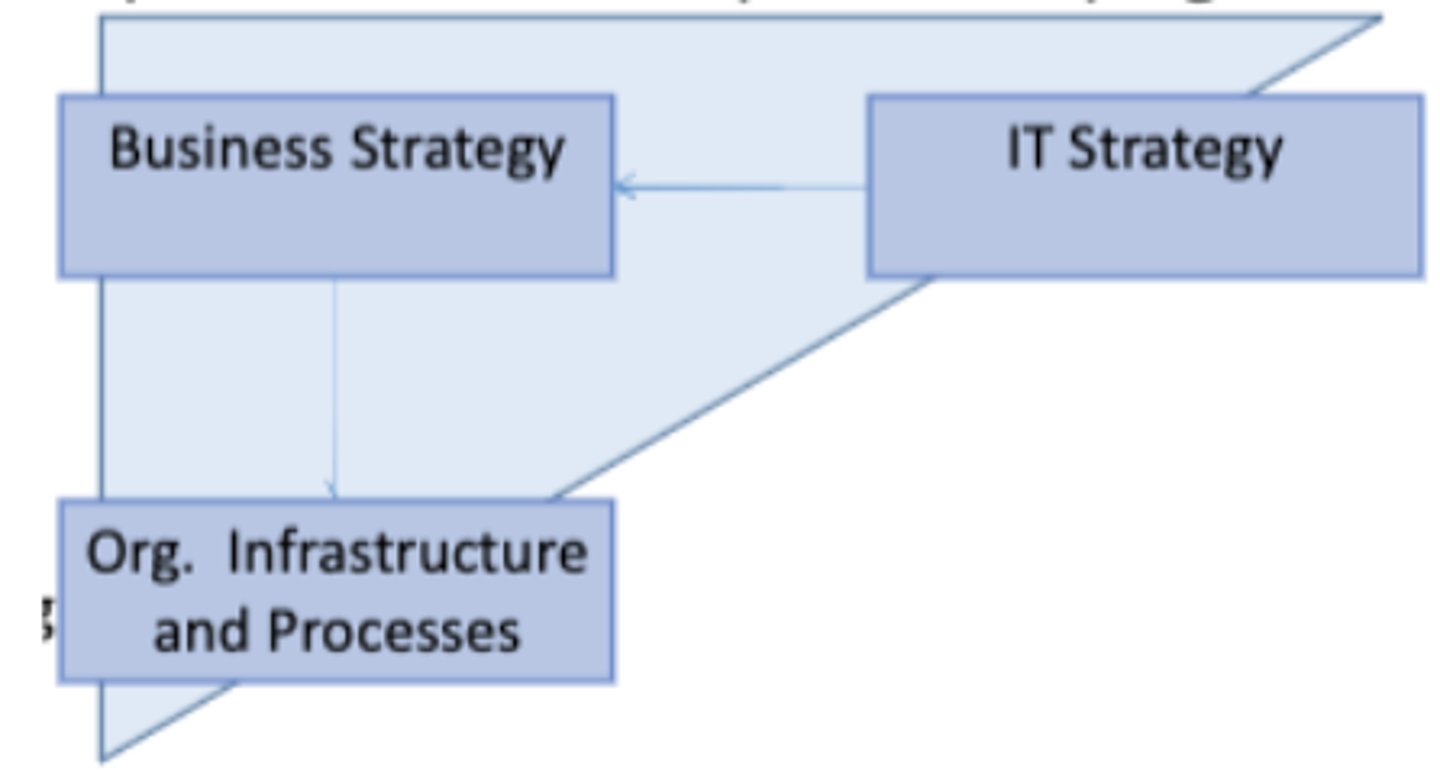
Strategic Alignment
4. Strategy Execution
-> Business strategy is the driver !
-> Determines organizational structure and processes, "How can IS optimally support the current organisation?"
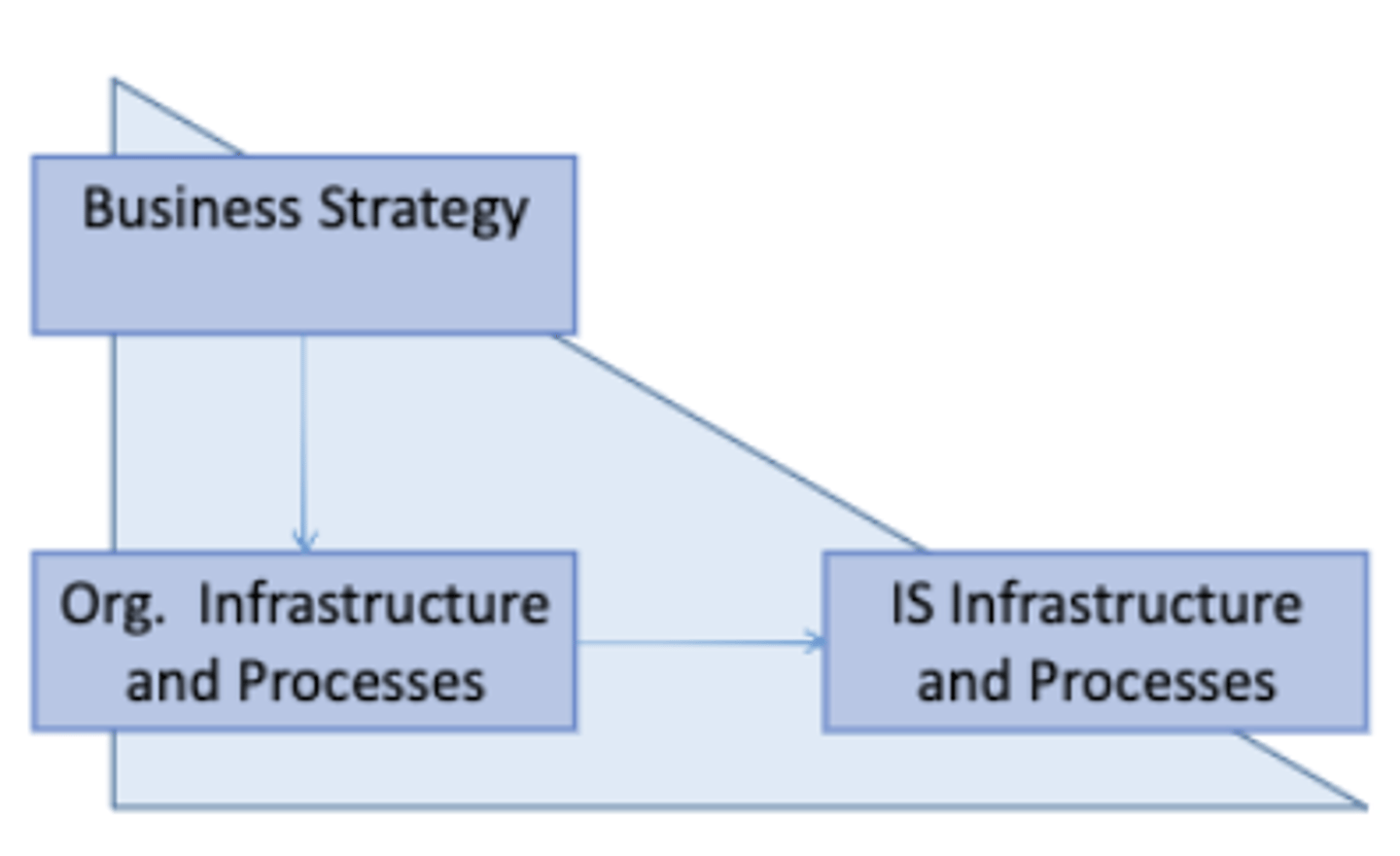
Strategic Alignment
5. Service level alignment
-> IT strategy is the driver
-> Determines IT infrastructure and processes to achieve the IT strategy.
-> "How can we build an optimal IS organization?"
SWOT Analysis
Strength: Internal & Helpful
Weakness: Internal & Harmful
Opportunities: External & Helpful
Threats: External & Helpful
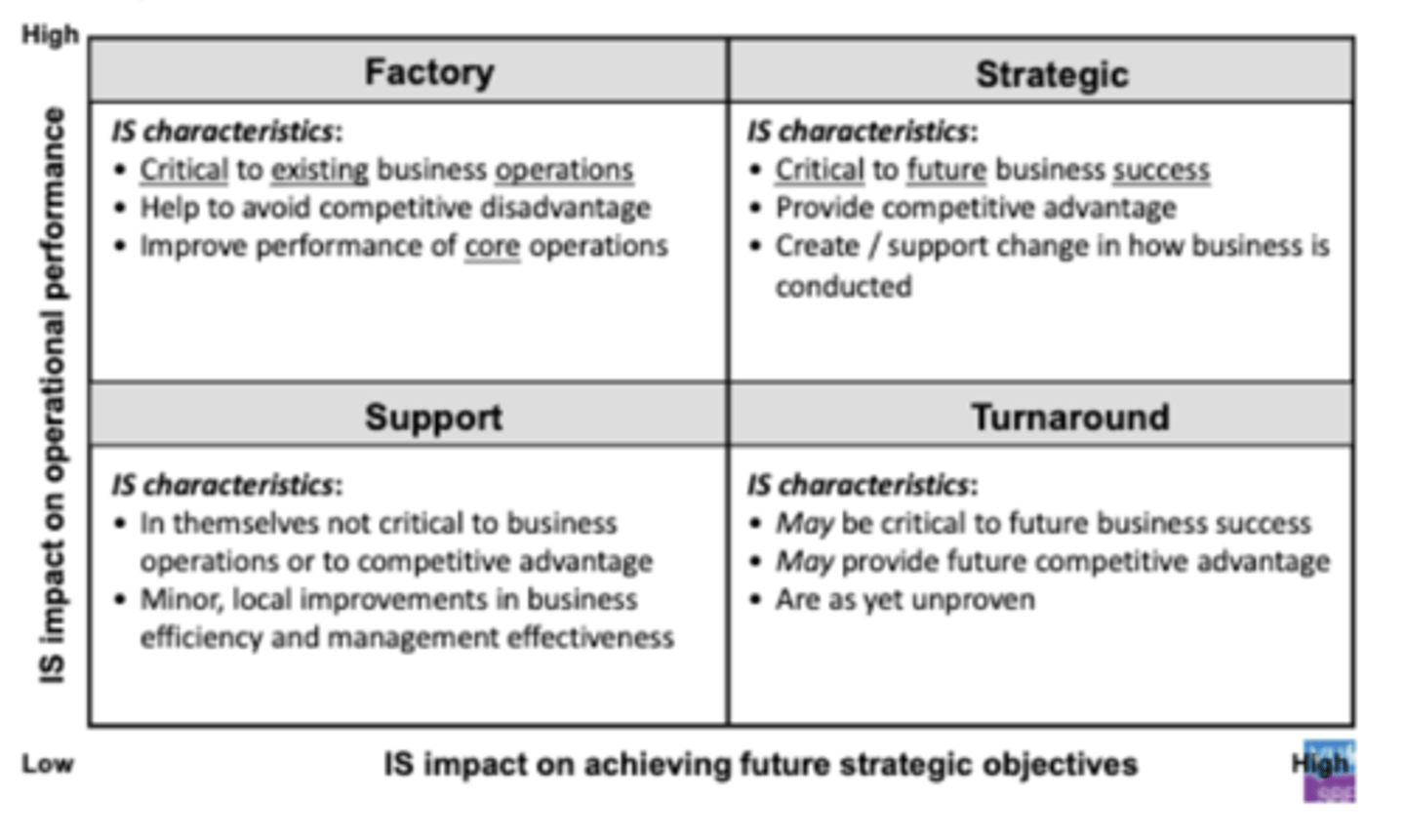
McFarlan's strategic grid
asseses the importance of IS, to match IS with strategic objectives and to match IS with IS management.
Strategy Conception
-> General objectives for IS strategy
-> Focusing on opportunities (&threats)
Strategy Formulation
-> Formulate the IS strategy goals
-> Determine what the organisation should look like
-> Determine what IS portfolio should look like
Strategy Implementation
-> defining change management approach
-> Concrete change projects
How to compete- Choosing a Generic Strategy
1. Rivalry among existing firms
2. Threat of potential new entrants
3. Bargaining power of buyers
4. Bargaining power of suppliers
5. Threat of substitute products/services
Platform based business models
1. Same-side network effect: increase/decrease in value as additional users join the same side of the network.
2. Cross-side network effect: the change in value for a user if users join on the other side.
Service-based business models
here a business can offer equipment services, information services, etc. E.g. hours of usage instead of buying equipment
Data-driven business models
here data is a key resource and key source of revenue.
IS strategy- Boeing and the 787 Dreamliner case
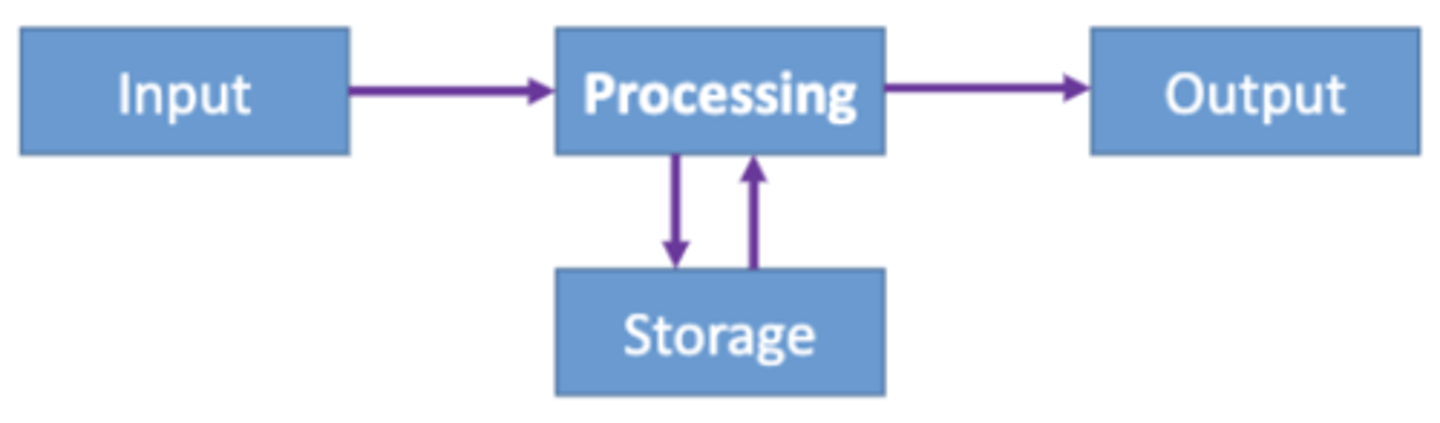
How does a computer work?
-> Computer's brain is the CPU (Central Process Unit)
-> Has a control unit: that fetches and decodes instructions, retrieves and stores data.
-> Arithmetic logic unit: performs mathematics and logical operations
--> now its all processes with 1's and 0's: Bits
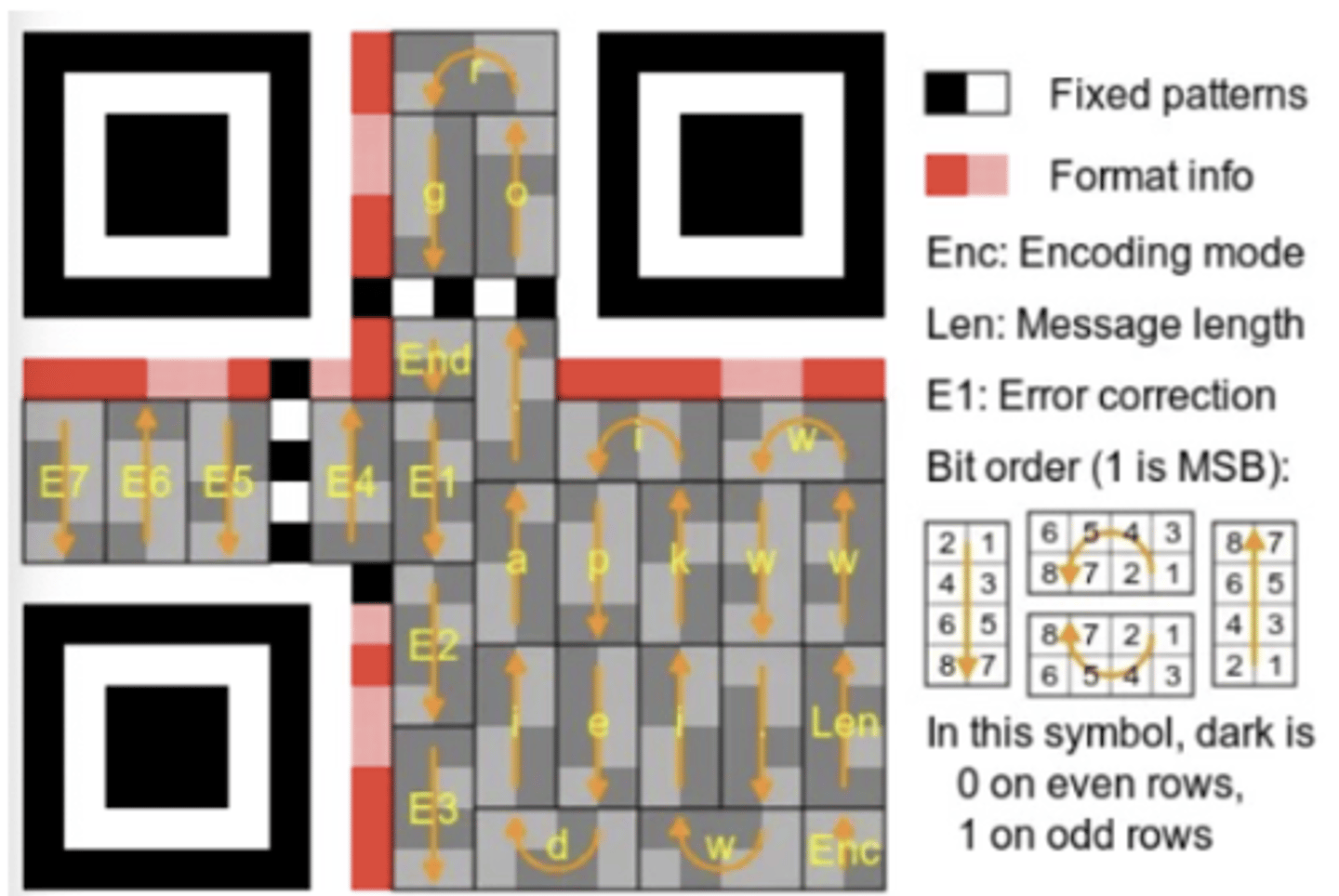
What happens when you scan a QR code?
-> Black and white pixels gor for 1's and 0's.
-> Instructions are in the processor and the programme knows how to read it. The scanner knows where it starts and then it codes from the bottom right all the way till top left.
Bit
A contraction of "Binary Digit". A bit is the single unit of information in a computer, typically represented as a 0 or 1.
Byte
a group of 8 bits.
Databases
Places where things are stored like Wikipedia, Spotify, Reddit, and Amazon.
Oversimplification
The fallacy of oversimplification occurs when we attempt to make something appear simpler by ignoring certain relevant complexities.
Different types of databases
1. Relational Databases (RDBMS)
-> most common and is easy to implement
-> attempts to balance efficiency to storage needs.
2. NoSQL (newer)
->Flexible/scalable, often have ad-hoc depending on company needs
->Easier than RDBMS which is why its more popular
Database design - data model
Operational system and BI
-Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) -> Interact with users and processes and generate and update data.
- Data Warehouse -> stores data from different business processes, and quick access to historical info for business intellegence.
- CoolBlue sells the speaker, the databasechceks how much is stored and available, and the database then also suggests other speakers. this is done in the data warehouse.
Moore's Law
The number of transistors per square inch on an integrated chip doubles every 2 years. --> exponential growth in processing power
Networks
When a system connects two or more devices.
-> transmitting bits in networks happens through electricity, lights or radio waves.
-> there also is media, which is divided into: Guided (cables), and unguided (no cables -> electromagnetic waves, wireless, infrared)
Protocols
agreements for data exchange -> OSI model in Tech Briefing
e.g. bluetooth, 3G/4G/5G, TCP/IP(internet)
Developments in networking
-> increase in capacity, e.g. transfer speed, bits/second.
-> increase in interconnectedness, e.g. internetworking, standardisation.
-> Increase in mobility (wireless)
-> Increasing diversity and complexity (combinig multiple networks and devices).
Cloud Computing
a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable network resources (e.g. network, servers, storage)
--> advantages:
+ Rapid elasticity, on-demand service
+ Broad network access
+ Resource pooling
+ Measured service

Internet of Things (IoT)
A network of broad range of physical objects that can automatically share data over the internet.
-> billions of devices generate and use data.
->Hardware is small (sensors, chips, etc.)
-> have connectivity
Software
A set of instructions that allow hardware to perform tasks.
-> often this is for office applications, mobile apps, enterprise systems, etc.
Smart Software
-> = smarter algorithms (get up to 4300 faster)
-> new intelligent software includes machine learning, AI, Gen-AI
-> Hardware and software developments
-> Processing power and smarter algorithms
price ceiling
a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good or service
Mirrlees Review
A good tax system has the following properties
1)Simple
2)Holistic
3)Avoids distortions
4)Efficient
equity-efficiency trade-off
refers to the trade-off between ensuring an equitable allocation of resources (equity) and increasing social surplus or total output (efficiency)
Producing optimal price
The quantity level is MR=MC, so then you trace up to where it hits dmeand an dthen fuund in that way the price
Compettive firm set
P=MR=MC
Monopilist set
P>MR=MC
How a monopolist calculates profits
Profits= Total revenue-Total cost=(PQ)-(ATCQ)=(P-ATC)*Q
-Profit is only in the area between ATC and Demand
Broken Invisible Hand
A firm exercises market power causes a reallocation of resources toward itself, thereby sacrificing social surplus.Here the invisble hand is broken because there only 1 company
simultaneous move games
In game theory, there are 3 elements:players,stratgies,payoffs.
->Simultaneous move games means that players pick their actions at the same time without knowing what the other person is doing.
Strategy for the prioner´s dilemma
A stratgey of a player is a best response to the stratgies of the others in the game if, taking the other players' stragy as given,it gives her greater payoffs than other stratgey she has available
Dominat Strategy
Is best response to very possible stratgey of the other player
->Dominat stratgey equilibrium if the relevant stratgey for each player is a dominat strategy
Nash Equilibrium
if each strategy is a best response to the strategies of others
->In Equilibrium, no player in a game can change strategy and improve his or her payoff.
zero-sum game
a situation in which an economic gain by one country results in an economic loss by another
pure strategy
A simple strategy that uses just one option, such as hiring and firing workers, for meeting demand.
extensive form game
a representation of games that specifies the order of play
game tree
a graphical representation of the consequences of different actions in a strategic setting
Backward Indicution
The procedure of solving an extensive-form gamr by first consindering the last mover's decision in order to deduce the decisions of all previous movers
First mover adavantage &Commitment
=When the first player to act in sequential game gets a benefit from doing so.
=The ability to choose and stick with an action that misght later be costly
Oligipoly
a state of limited competition, in which a market is shared by a small number of producers or sellers.
(Not a monopoly but also not a perfect market)
The Oligopolist's proplem:
a) Like a monopolist, has signifigant barriers to entry, resulting in long-run economic profits
b)High degree of iinterdependecne between the few firms that occupy the market
Producing the optimal quantity
Marginal Revenue has to be bigger than MC
->Its b etter to decrease producction to the point of MR=MC
consumer sovereignty
the power of consumers to decide what gets produced
price effect
after a price increase, each unit sold sells at a higher price, which tends to raise revenue
Relationship among Price, Marginal Revenue, and total Revenue (In a monopol)
Demand curve and MR;
-Begins at the same point on the axis
-after that MR lies below th edemadn curve
-and as quantiy increase, the difference between them grows larger
-MR Curve is twice as steep as the demand curve
total Revenue:
-When total revnue is rising, MR is positive.
-When the TR is falling, MR is negative
quantity effect
after a price increase, fewer units are sold, which tends to lower revenue
labour-leisure trade-off
If you dont work it is considered leisure/play/not-work
->The price of leisure is the opportunity cost of leisure and that opportunity cost is the lost wages from not working
2Factors that shift labour damand
1)Price of the good that the firm is producing
2)Technology of the Firm
Factors that shift labour supply
1)Populataion changes
2)Changes in worker prefernces and tastes
3)Opportuinty costs
legal market power
occurs when a firm obtains market power through barriers to entry created not by the firm itself, but by the government
monopolist problem
->Increase price and lose all of its business
->Demand curve is downwards sloping, as they can increase the price
natural market power
occurs when a firm obtains market power through barriers to entry created by the firm itself
a)The monopolist own or controls a key resource necessary for production of a good or service
b)There are economies of scale in producion over the relevant range of output
Wage inequality
3Big Reason;
1) Differences in human capital
2)Differences in compensating wages
3)Discrimaniation in the job market
Monopoly
Is an industry in which only 1 seller provides a good or service that has no close substitues.
A monopoly is a price-maker and have all the market power
Sources of Market Power
The ability to contol a market power, relies on barriers of entry(=provides a seller with protection from potential competiors entering the market)
Market for other factors of production-physical capital and land
->Vlaue of marginal product of physical capital=The contribution of an additional unit of physical capital to a firm revenues
->Land includes the soild surface of the rath and natural resources
->The rental price of a good is the cot of using that good for some specif period of time
labour-saving technology
A Tech that substitutes for existing labour inuts, reducing the marginal product of labour.
(These are also labour-complementary technologies)
value of marginal product of labor
the contribution of an additional worker to a firm's revenues
Firm maximises profits by optimapply choosing its labor by expending its workforce until the marginal product of labor * price =VMPL=Wage
> price = Wage/MPL
>Marginal product of labor*Price =Wage
>Margianl cost=Wage/MPL=Price
The competitive labour market & Demad for labour
All firms rely on labour as a major of production and affects all of us. You are direcetly influenced by the labour market when you are looking for a job or are employed and earning money.
The main factors of production are machines(Physical capital) and land.
Paternalism
the policy or practice on the part of people in positions of authority of restricting the freedom and responsibilities of those subordinate to them in the subordinates' supposed best interest.
Government Failures
refers to inefficiencies caused by a government's interventions
1)Direct costs of bureaucracies
2)Corruption
3)Underground economy
price floor
A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold
2 main types of regulations
1)Direct regulation=Refers to direct actions by the government to control the amount of a certain activity.
2)Price Control=attempts by the government to control the price of an activity
Big data - Instagram
Volume -> Instagram has 1.44 Billion users and around 50 Billion photos n 2021.
Velocity -> 1074 photos uploaded per second which is around 95M posts per day.
Variety -> Instagram also needs big data with its massive variety of things you can do, like, follow, comment, and upload pictures or videos.
Tracking private jets to discover deals
-> Using corporate jet flight data in 2019 a hedge fund saw that managers from occidental petroleum were in Omaha. They inferred a possible contract between OP and Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway fund who later confirmed a 10 bill dollar investment in OP.
-> from the box above, this example shows us how the flight company is data-driven organisation

5 Strategic Alignment
1. Henderson & Venkatraman
2. Technology Potential
3. Competitive Potential
4. strategic executing
5. Service level Alignment
Regulation & Price Ceilings
Refers to actions by the federal or local government dirceted at influencing market outcomes, such as the quantity traded of a good or service, its price, or its quality and safety.
Henderson & Venkatraman
-> Focuses on external and internal domain, so the strategic and operational level.
-> Focuses on business and IT domain
-> 4 approaches to alignment
-> The point is to align them together so that they translate into operations and be able to implement, otherwise it just fails
Tax Burden and the effects of demand and supply Elasticities
The elasticity of market is usally not idential to the elasticity of market supply
"The tax burden falls less heavily on the side of the market that is more elastic- that is , more responsive to price changes.
When supply is more elastic than demand, the tax burden falls more heavily on buyers.
When demand is more elastic than supply, the tax burden falls more heavily on sellers."
Where does the money come from?
Federal taxes
1. Individual income taxes
2. Social insurance taxe
3. Corporate income tax
4. All other taxes
Different stakes, similar approaches
-> All want to use data to customise their platform to match your behaviourism.
-> If Tinder learns what you like more, Tinder gets a better competitive advantage over other apps, as well as good marketing as you recommend the app more.

Why does the government tax and spend?
1. Raising reveunes
->Most taxation is intended to rais revenues for the funding of public goods such as national defence, puplic education, police protection and infrastructure projects
2. Redistributing funds via transfer payments
-> This is in order to reduce tax inequality and making wealth gaps not get too big.
->Transfer payments occur when the government gives part of its tax revenue to some individual groups such as the elderly or the unemployed
- Average tax rate
-Margianl tax rate
-Progressive tay system
3.Financing operations
4.Correcting market failures and externaiities
tax incidence
how the burden of taxation is distributed
->Tax burdens are both on buyers and sellers, not just one
Proportional tax system
households pay the same percentage of their incomes in taxes regardless of their income level
Data-driven organisations
-> Access to data ( this is up to date).
->Access to analytics (advanced).
-> Analytics and domain knowledge collaboration (data engineer and business manager work together and understand one another).
-> Data-informed decision making (actually making decisions based on the evidence from data).
regressive tax system
involves lower tax rates on those earning higher incomes
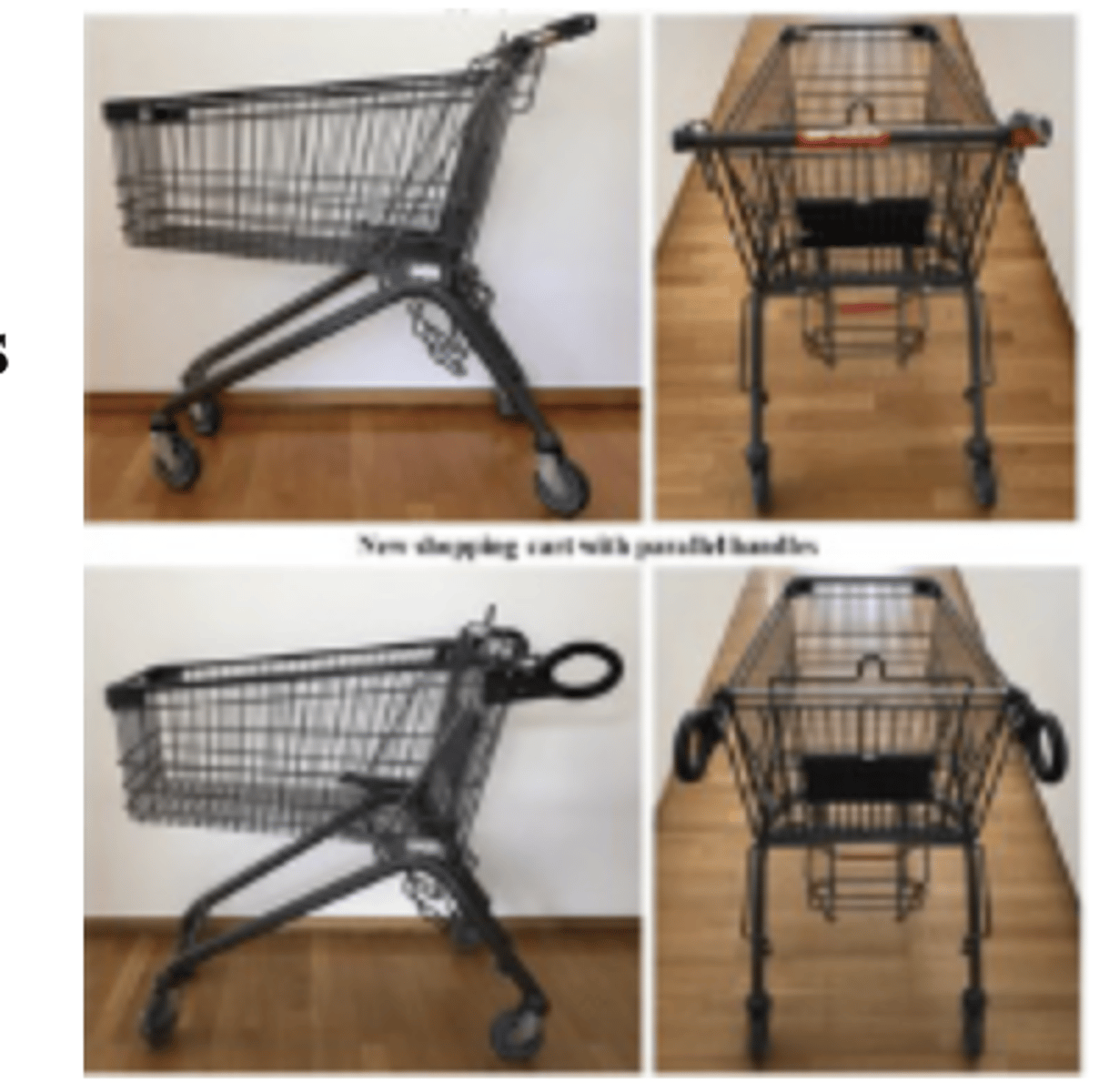
Cart Handle design in supermarkets
-> Using sales and biometric data
-> Researchers find that changing the design of shopping cart handles activates different physiological processes and leads to higher sales.
-> The way that we push a shopping cart changing how our mind thinks apparently. if you are forced to push from the side, it makes you want more things. so just by tweaking the handle, there were more sales.
