SKULL
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Skull
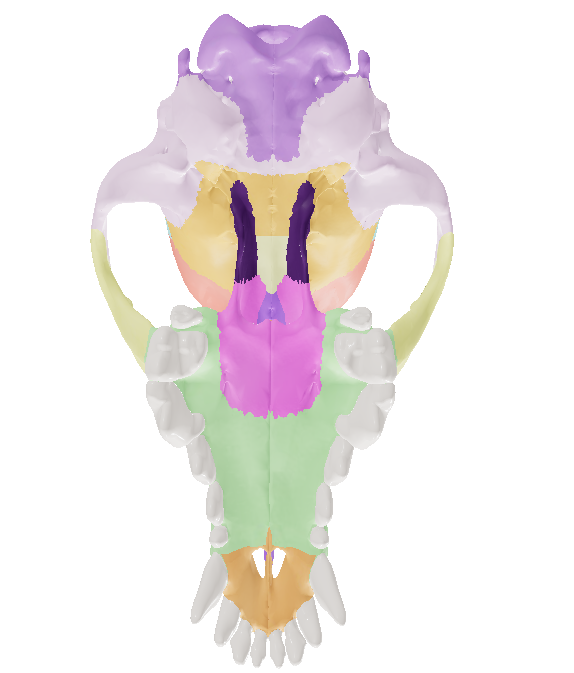
The __ is consisting of the cranial part or braincase (occipital, frontal, parietal, temporal, ethmoid, sphenoid) which surrounds the brain, and the facial part (pterygoid, vomer, incisive, maxilla, nasal, palatine, zygomatic, lacrimal).
Occipital Bone
the most caudal bone of the skull. It contains the foramen magnum, through which spinal cord passes.
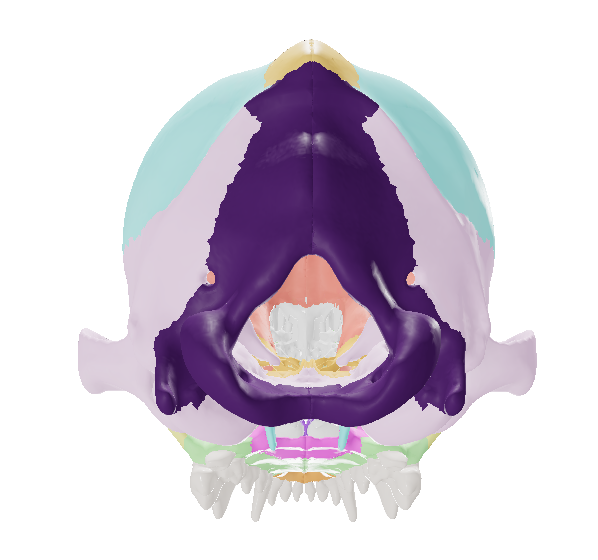
Occipital condyles
On the either side of the occipital bone is a pair of bony prominences, the __ which articulate with the atlas.
Pointed jugular or paracondylar processes
Lateral to the condyles are the ___.
Frontal Bone
forms the rostral part of the roof of the cranial cavity.
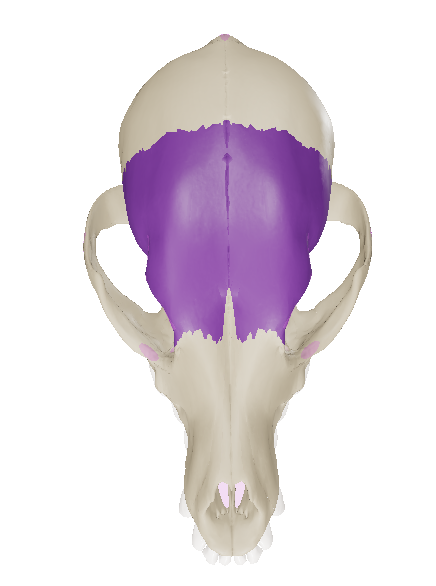
Zygomatic process
Frontal bones has a pointed process called the __ of the temporal bone that partly forms the orbit.
Parietal bone
together with the frontal bone, it forms the roof of the cranial cavity
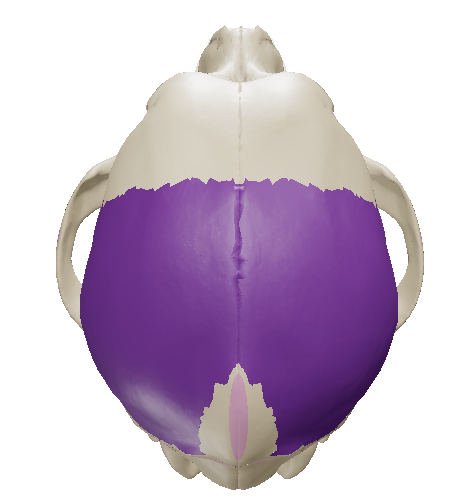
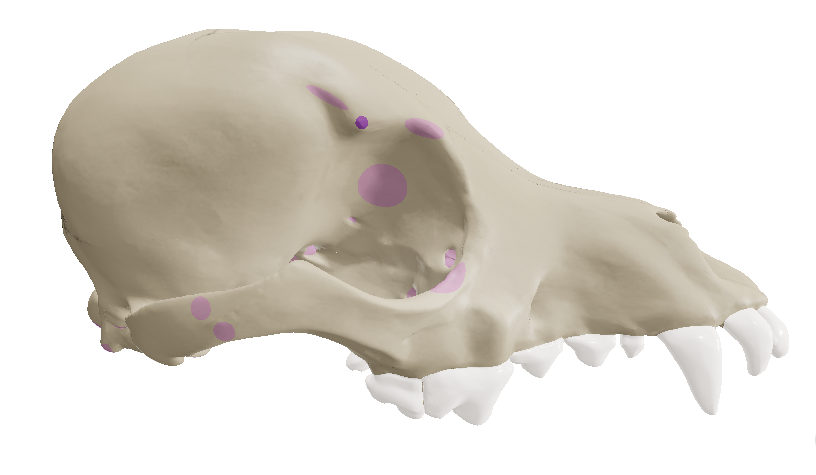
Temporal Bone
lies below the parietal bone on the caudolateral surface of the skull.
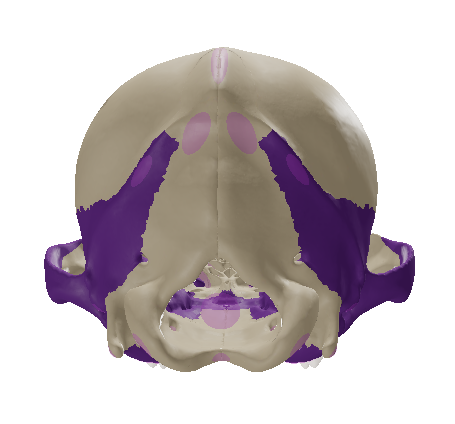
Tympanic bulla
The most ventral part of the temporal bone forms a rounded prominence called the ___, which houses the structures of the middle ear.
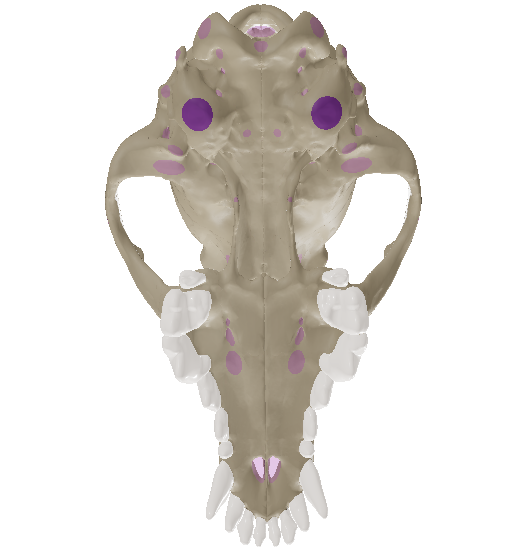
Ethmoid Bone
unpaired bone, forms the rostral wall of the cranial cavity.
Sphenoid Bone
unpaired bone, lying on the ventral aspect of the skull, forming the floor of the cranial cavity. It houses the pituitary gland via a depression. It is divided into presphenoid and basisphenoid.
Pterygoid Bone
forms part of the lateral wall of the air passageway dorsal to the soft palate

Vomer (plowshare bone)
gutter-shaped bone that longitudinally separates the right and left nasal passages. Errol Jay Y. Balagan, DVM, MSc
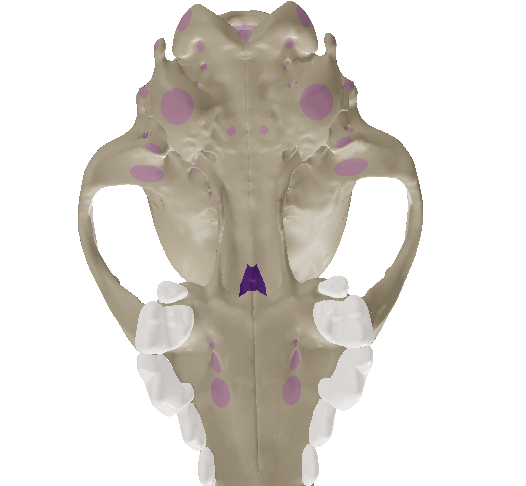
Pterygoid Bone
forms part of the lateral wall of the air passageway dorsal to the soft palate
Vomer (plowshare bone)
gutter-shaped bone that longitudinally separates the right and left nasal passages.
supports the upper incisors and contributes to the formation of palatine fissure. Most rostral bone of the skull
Incisive Bone (Premaxilla)
Nasal Bone
longitudinal bone forming the roof of nasal cavity
Maxillary Bone (Maxilla)
forms the osseous lateral walls of the face and major part of the hard palate
Lacrimal Bone (Prefrontal Bone)
lies at the medial surface of the orbit, which houses the eye
Zygomatic Bone- (Jugal, Malar)
the zygomatic arch is an arch of bone that projects laterally from the skull, forming the cheekbone.
Palatine Bone
forms part of the hard palate, along with the maxilla and incisive bone.
Zygomatic Arch
the bony arch forming the lateral wall of the orbit. It consists of the temporal process of the zygomatic bone and zygomatic process of the temporal bone.
Orbit
the bony socket holding the eyes.
Lacrimal Fossa
the depression in the medial margins of the orbit. It collects tears and sends them through the lacrimal canal which opens into the nasal cavity.
Infraorbital Foramen
the rostral opening of the infraorbital canal, located in the maxillary bone.
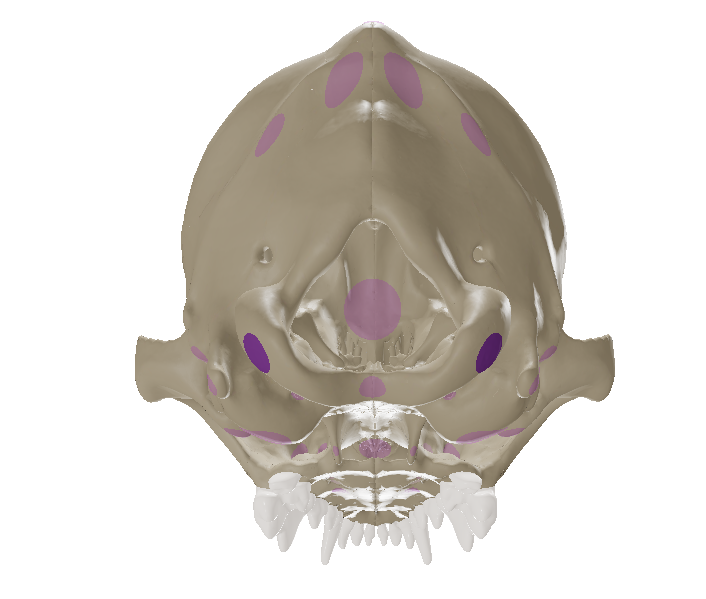
Occipital Condyles
the paired structures lateral to the foramen magnum that articulate with the atlas.
Paracondylar Process (Jugular Process)
ventral projection lateral to the occipital condyle
External Acoustic Meatus
the large opening caudal to the zygomatic arch where the external ear attaches. In living animal, it is being covered by the ear drum (tympanic membrane).
Mastoid Process
located caudal to the external acoustic meatus which serves for muscle attachment.
External Occipital Protuberences
caudal process of the occipital bone.
Foramen Magnum
large opening into the cranial cavity for the continuity of the spinal cord and brain.
Tympanic Bulla
the smooth bulbous enlargement on the ventral side of the temporal bone housing the middle ear.
Mandibular Fossa
area on the zygomatic arch for the articulation with the condylar process of the mandible
Optic Canal
- the passageway for the optic nerve from the eyeball to the brain. It is rostal to all other foramina.
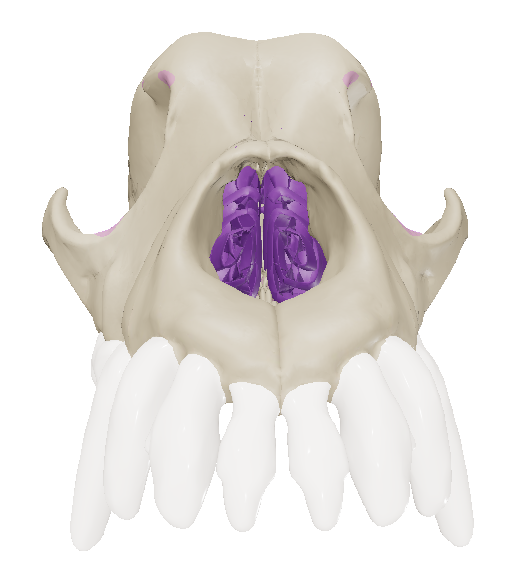
Choanae (Caudal Nares)
the two bony openings at the caudal end of the hard palate, leading from the nasal cavity into the pharynx.
Hard Palate
horizontal parts of the incisive, maxillary bone and palatine bone, separating nasal and oral cavity
Nuchal Crest
transverse ridge at the transition from the dorsal to the caudal surface of the skull
Temporal Fossa
depression formed by the temporal and parietal bone.
Nasal Aperture
the rostral bony opening into the nasal cavity.
Median Sagittal Crest
extends rostrally from the external occipital protuberance on the midline