6.1 The objectives of government economic policy
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
The government has 4 main macroeconomic objectives
These aim to provide macro stability
A policy objective
is a target or goal that a government wishes to achieve or ‘hit’
The 4 objectives are to
achieve economic growth and improve living standard and levels of economic welfare
create and maintain full employment or low unemployment
limit or control inflation, or to achieve some measure of price stability
attain a satisfactory balance of payments, usually defined as the avoidance of an external deficit which might create an exchange rate crisis
Economic Growth
In the UK, the long run trend of economic growth is about 2.5%
Governments aim to have sustainable economic growth for the long run
In emerging markets and developing economies, governments might aim to increase economic development before economic growth, which will improve living standards, increase life expectancy and improve literacy rates
short-run economic growth
which occurs when there are unemployed resources or ‘slack’ in the economy, is when there is a movement from a point inside the economy’s production possibility frontier to a point on the frontier. short-run growth is also called economic recovery.
Long-run economic growth
an increase in the economy’s potential level of real output, and an outward shift of the economy’s production possibility frontier.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The sum of all goods and services, or level of output, produced in the economy over a period of time, e.g. one year.
real GDP
A measure of all the goods and services produced in an economy, adjusted for price changes or inflation. These adjustments transforms changes in nominal GDP, which is measured in money terms, into a measure that reflects changes in the total output of the economy.
Recession
A fall in real GDP for 6 months or more
nominal GDP
GDP measured at the current market prices, without removing the effects of inflation
Minimising unemployment
Governments aim to have as near to full employment as possible. They account for frictional unemployment by aiming for an unemployment rate of around 3%. The labour force should also be employed in productive work.
full employment
according to Beveridge’s definition, full employment means 3% or less of the labour force unemployed. According to the free-market definition, it is the level of employment occurring at the market-clearing real-wage rate, where the number of workers whom employers wish to hire equals the number of workers wanting to work.
Claimant count
The method of measuring unemployment according to those people who are claiming unemployment-related benefits (Jobseekers allowance)
Labour Force Survey
a quarterly sample survey of households in the UK. Its purpose is to provide information on the UK labour market. The survey seeks information on respondents’ personal circumstances and their labour market status during a period of 1-4 weeks.
Price Stability
In the UK, the government inflation target is 2% measured with CPI. This aims to provide price stability for firms and consumers, and will help them make decisions for the long-run. If the inflation rate falls 1% outside this target, the Governor of the Bank of England has to write a letter to the Chancellor of the Exchequer to explain why this happened and what the Bank intents to do about it.
Inflation
A persistent or continuing rise in the average price level
Deflation
A persistent or continuing fall in the average price level
Disinflation
when the rate of inflation is falling, but still positive
price index
an index number showing the extent to which a price, or a ‘basket’ of prices, has changed over a month, quarter or year, in comparison with the price(s) in a base year.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The official measure used to calculate the rate of consumer price inflation in the UK. The CPI calculates the average price increase of a basket of 700 different consumer goods and services.
Retail Price Index
The RPI is an older measure used to calculate the rate of consumer price inflation in the UK. Currently, the UK government uses the CPI for the indexation of state pensions and welfare benefits and for setting a monetary policy target, and the RPI for uprating each year the cost of TV and motor vehicle licenses, together sometimes with taxes and goods such as alcoholic drinks.
indexation
the automatic adjustment oof items such as pensions and welfare benefits to changes in the price level, through the use of a price index.
Stable balance of payments on current account
Governments aim for the current account to be satisfactory, so there is not a large deficit. This is usually near to equilibrium. A balance of payments equilibrium on the current account means the country can sustainably finance the current account, which is important for long term growth.
Balance of payments
A record of the currency flows into and out of a country in a particular time period
Current account of the balance of payments
measures all the currency flows into and out of a country in a particular time period in payment for export and imports, together with income and transfer flows.
exports
domestically produced goods or services sold to residents of other countries.
imports
goods or services produced in other countries and sold to residents of this country
Balance of trade
The difference between the money value of a country’s imports and its exports. Balance of trade is the largest component of a country’s balance of payments on current account.
Balance of trade deficit
The money value of a country’s imports exceeds the money value of its exports
Balance of trade surplus
the money value of a country’s exports exceeds the money value of its imports
Additionally, the government might have the following macroeconomic objectives
Balanced government budget
Greater income equality
Potential conflicts and trade-offs between the macroeconomic objectives(generally in the short run)
Balanced government budget
This ensures the government keeps control of state borrowing, so the national debt does not escalate. This allows governments to borrow cheaply in the future should they need to, and makes repayment easier.
Greater income equality
income and wealth should be distributed equitably, so the gap between the rich and poor is not extreme. It is generally associated with a fairer society.
The importance of each objective changes over time.
Potential conflicts and trade-offs between the macroeconomic objectives (generally in the short run)
Economic growth vs inflation
A growing economy is likely to experience inflationary pressures on the average price level. This is especially true when there is a positive output gap and AD increases faster than AS.
Economic growth vs the current account
During the periods of economic growth, consumers have high levels of spending. In the UK, consumers have a high marginal propensity to import, so there is likely to be more spending on imports. This leads to a worsening of the current account deficit. However, export-led growth, such as that of China and Germany, means a country can run a current account surplus and high levels of economic growth.
Economic Growth vs the government budget deficit
Reducing a budget deficit requires less expenditure and more tax revenue. This would lead to a fall in AD. however, and as a result there will be less economic growth.
Economic Growth vs the environment
High rates of economic growth are likely to result in high levels of negative externalities, such as pollution and the usage of non-renewable resources. This is because of more manufacturing, which is associated with higher levels of carbon dioxide emissions.
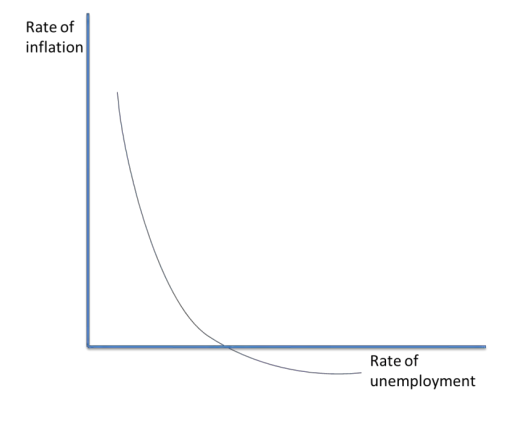
Unemployment vs inflation
In the short run, there is a trade-off between the level of unemployment and the inflation rate. This is illustrated with a Phillips curve.
As economic growth increases, unemployment falls due to more jobs being created. However, this causes wages to increase, which can lead to more consumer spending and an increase in the average price level.
The extent of this trade off can be limited if supply side policies are used to reduce structural unemployment, which will not increase average wages.