[PCOL and TOXICOLOGY] PPT Air Pollutants (Part 2 of intro)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Carbon monoxide
• Colorless, tasteless, odorless and nonirritating gas
• Byproduct of incomplete combustion
• Average concentration in the atmosphere is about 0.1ppm in heavy traffic it may exceed 100ppm
Carbon Monoxide
• Combines tightly but irreversibly with oxygen-binding sites of hemoglobin and has an affinity for hemoglobin 220x that of oxygen
• Reduces the transfer of oxygen to tissues especially the organs with the highest oxygen demand (brain, heart and kidney)
• Product form: Carboxyhemoglobin
Carboxyhemoglobin
Product of CO and Hemoglobin
brain, heart and kidney
The CO Reduces the transfer of oxygen to tissues especially the organs with the highest oxygen demand such as what
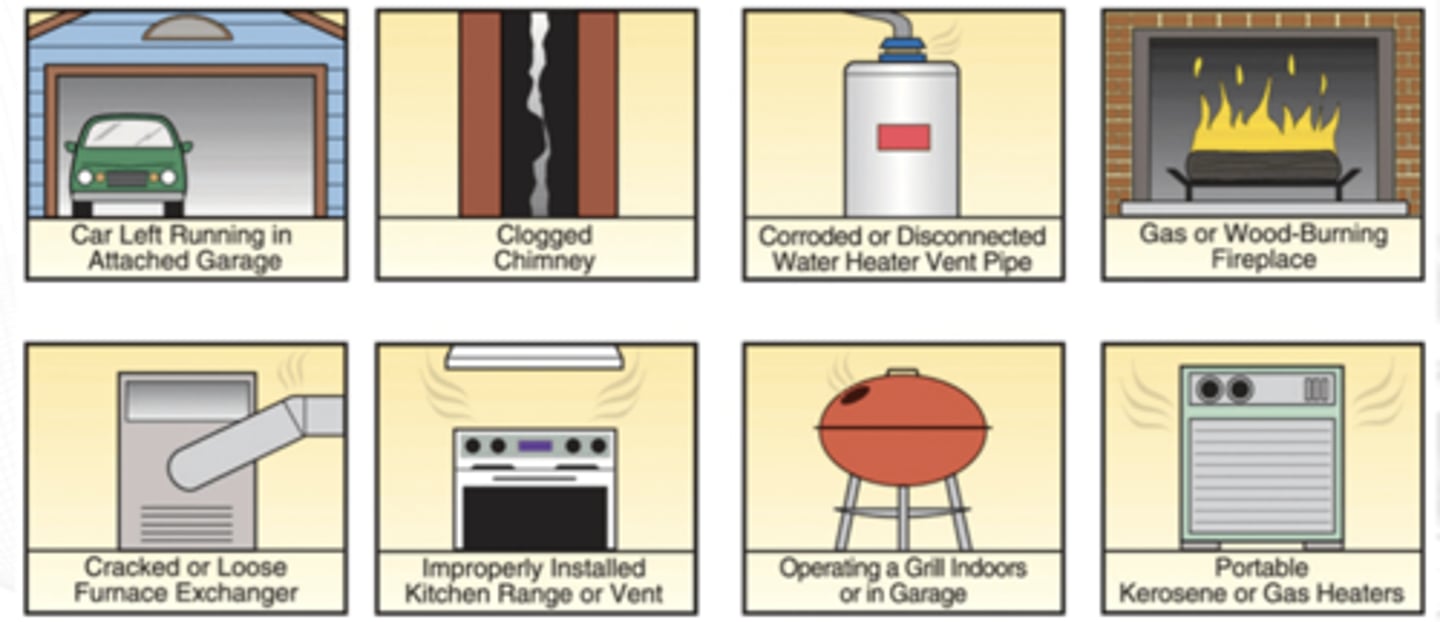
Sources of CO at home
hypoxia
Principal signs of CO intoxication are those of _____:
• Psychomotor impairment
• Headache and tightness in the temporal area
• Confusion and loss of visual acuity
• Tachycardia, tachypnea, syncope and coma
• Deep coma, convulsions, shock and respiratory failure
High Labor (Trabaho)
High Altitudes (Taas)
High Temperatures (Temp)
3 factors that can aggravate the effect of CO
Key: 3 Ts
Acute toxicity
What type of exposure is usual for CO intoxication
cardiac effects
neurologic disturbances
emotional disorders
Chronic exposures to low CO levels may lead to adverse effects on what body systems
Elevated CO exposure
The ff are effects of what intoxication
critical periods of fetal development may cause fetal death or serious and irreversible but survivable birth defects
removal of exposure
Respiration (high oxygen)
Mechanical ventilation
Hypothermic Therapy
4 ways to treat CO intoxication
Short period of time
when experiencing CO intoxication, should high concentration treatment be in short or long period of time?
Mechanical ventilation
CO intoxication treatment if respiratory failure is present
Hypothermic Therapy
CO intoxication treatment to reduce metabolic demand of the brain
Sulfur Dioxide
Emitted by volcanoes
Colorless, irritant gas generated primarily by the combustion of sulfur- containing fossil fuels
Sulfur Dioxide
• high solubility of _____ in moist membranes forms sulfurous acid.
• severe irritant on the eyes, mucous membranes, respiratory tract and skin
• 90% of inhaled form is absorbed in the Upper Respiratory tract causing Acute Irritant Asthma
sulfurous acid
high solubility of SO2 in moist membranes forms ________
Acute Irritant Asthma
90% of inhaled form of SO2 is absorbed in the Upper Respiratory tract causing ____________
Sulfur Dioxide
• eye, nose and throat irritation, reflex bronchoconstriction and increased bronchial secretions
> Eyes nose (mucosal), bronchial (lungs)
• Asthmatic subjects exposed to ____ may result in acute asthmatic episode
• When combined exposure to high respirable particulate loads and ____ the mixed irritant load may increase the toxic respiratory response
respirable particulate loads
When SO2 is combined exposure to high ___________ , the mixed irritant load may increase the toxic respiratory response
depends on respiratory tracts and asthma
Treatment of SO2 intoxication/irritation
Nitrogen Oxides (NO2)
• Brownish irritant gas associated with fires
• Farmers exposed to fresh silage
• Miners exposed to diesel equipment
• Automobile truck traffic emissions
Nitrogen Oxides (NO2)
• Relatively insoluble deep lung irritant, producing lung edema and adult pulmonary respiratory distress syndrome
Nitrogen Oxides (NO2)
• Inhalation damages the lung infrastructure that produces the surfactant necessary to allow smooth and low-effort lung alveolar expansion
• Type I pneumocytes of the alveoli appears to be the cells chiefly affected by acute low to moderate inhalation exposure
Type I pneumocytes
________ pneumocytes of the alveoli appears to be the cells chiefly affected by acute low to moderate inhalation exposure of Nitrogen Oxides (NO2)
Nitrogen Oxides (NO2)
Acute: Irritation of eyes and nose, cough, mucoid or frothy sputum production, dyspnea and chest pain; Pulmonary edema, fibrotic destruction of terminal bronchioles
1-2hours
Pulmonary edema appears how many hours after exposure to Nitrogen Oxide
Emphysematous changes
Chronic exposure effect of Nitrogen Oxides
No specific Treatment
What is the specific treatment for acute exposure to NO2
Deep lung irritation management (for Non-cardiogenic Pulmonary edema)
Bronchodilators
Sedatives
Antibiotics
Therapeutic Measures for NO2
Ozone (O3) and other Oxides
• Bluish irritant gas naturally found in the earth’s atmosphere
• Ground level ____ pollution is derived from photolysis of oxides, nitrogen, volatile organic compounds, and heat and sunlight
• Compounds are produced primarily from fossil fuels such as gasoline, oil or coal or when some chemicals evaporate
• Emitted from power plants, motor vehicles and other sources of high heat compounds
• High-voltage electrical equipment and air and water purification systems
• Agricultural sources of ______ are also important as well, as there are numerous adverse effects to plants
Ozone (O3) and other Oxides
• Irritant of mucous membranes
• Produces upper respiratory tract irritation to deep lung irritation with pulmonary edema
• Formation of reactive free radicals
Shallow
rapid breathing
decrease in pulmonary compliance
Clinical effect of Ozone and other oxides
changes to visual acuity
Irritation and dryness to throat
substernal pain
dyspnea
ARDS
Clinical effects of Acute exposure to ozones and other oxides
Chronic Bronchitis
Bronchiolitis
Empyshema
effects of chronic exposure to Ozones and other oxides (BOBOE)
No specific Treatment
Treatment for Acute exposure to O3
Reduce time
Management varies
deep lung irritation management - noncardiogenic pulmonary edema to ARDS
Treatment for O3 exposure
Particulate matter
Complicated topic due to different sizes of particulate matter and health effect depending on the size
PM 10
this micron of particulate matter elicit health effects
PM 2.5
this micron of particulate matter or smaller elicits most profound effects, this can be emitted from construction sites, industries (smokestacks), vehicles, and fires
2.5-10
Coarse particles of particulate matter in the range of _____ microns tend to deposit in the upper thoracic airways
< 2.5 microns
Fine particulate matters in microns can deposit in gas exchange areas
< 0.1 microns
Ultrafine particles suspected to cause serious health effects
No specific treatment
time reduction of exposure
N95 or KN95 masks (w/ Hepa filter)
Treatment or mitigation of Particulate matter exposures