1.5 Cell Physiology
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Define Diffusion
The net movement of molecules/ions from a region of higher conc. to a region of lower conc.
What does Diffusion Involve?
Diffusion of small, lipid soluble, or non polar molecules
EG Oxygen, carbon dioxide, water (small molecule)
Factors Affecting Diffusion
• Temperature- higher temps give molecules more kinetic energy
• Size- smaller molecules diffuse faster
• Difference in conc. gradient- bigger difference = faster diffusion
• Surface area- larger SA = faster diffusion
• Thickeness of surface- thinner surface = faster diffusion
Osmosis
The net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane
Factors Influencing Water Potential
Presence of solutes
Will make water potential more negative due to there being space for fewer free water molecules per unit vol.
Effect on water potential as a consequence of presence of solute molecules is called solute potential- always negative
External pressure on cell membrane
As cell takes in water by osmosis and expand, the cell wall will squeeze on cell membrane
pressure potential is increased pressure made by cell wall pushing against cell surface membrane- usually positive but can be 0
Equation for water potential of a cell
Solute potential + Pressure potential = Water potential of a cell
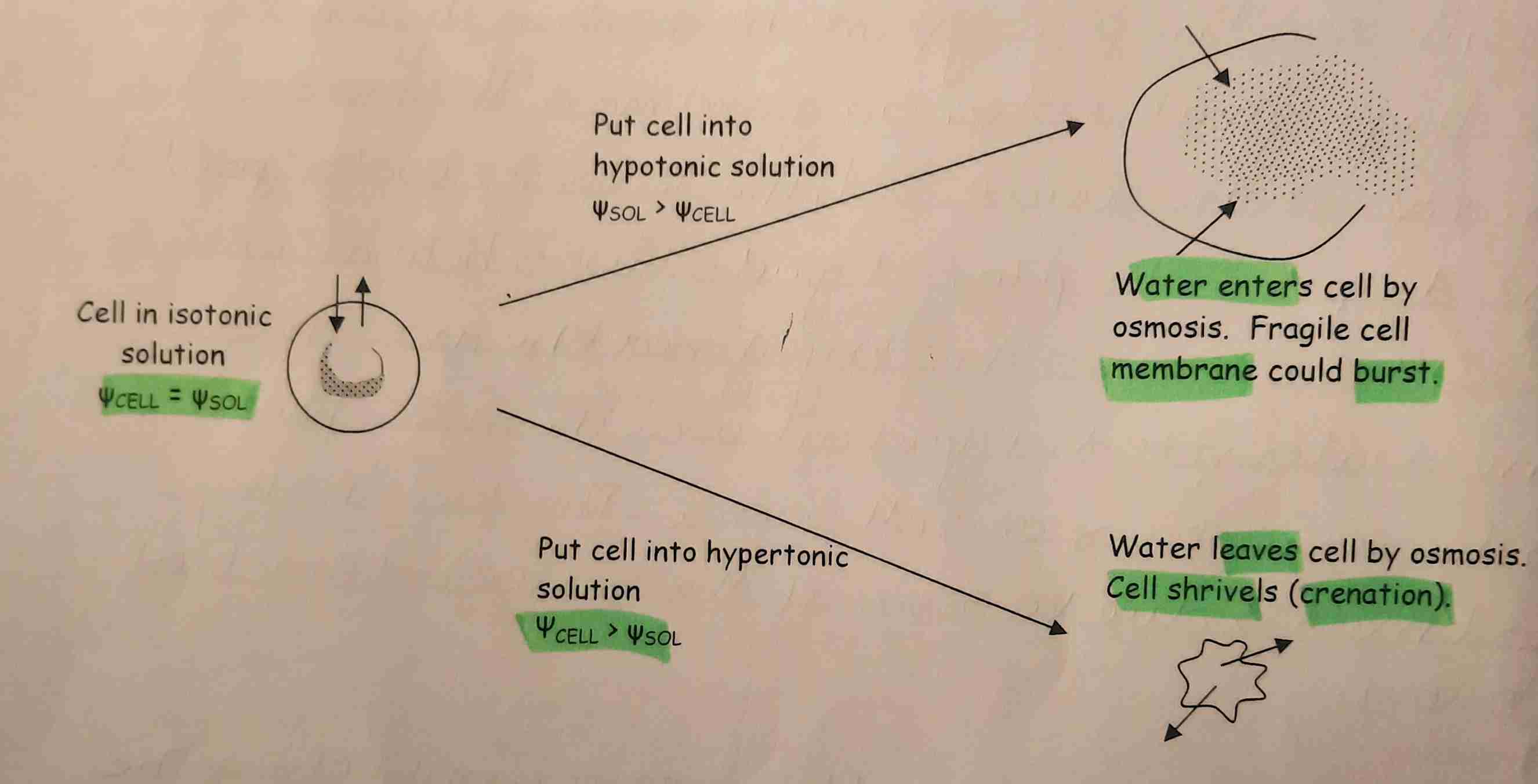
Lysis & crenation in Animal Cells
Place cell in to hypotonic sol. (higher potential than cell's). Water enters by osmosis. Cell membrane can burst. (Lysis)
Place cell into hypertonic sol. (cell potential higher than sol.’s). Water leaves cell by osmosis & shrivels. (Crenation)
Osmosis & Plant cells
Cell in hypotonic sol. (sol. potential>cell)-
Water enters cell bt osmosis. Protoplast push against wall. Wall pushes- resisting entry of water - TURGID
Cell in hypertonic sol. (cell potential>sol)-
Water leaves by osmosis. Protoplast shrink & membrane pulls away from wall. - PLASMOLYSED
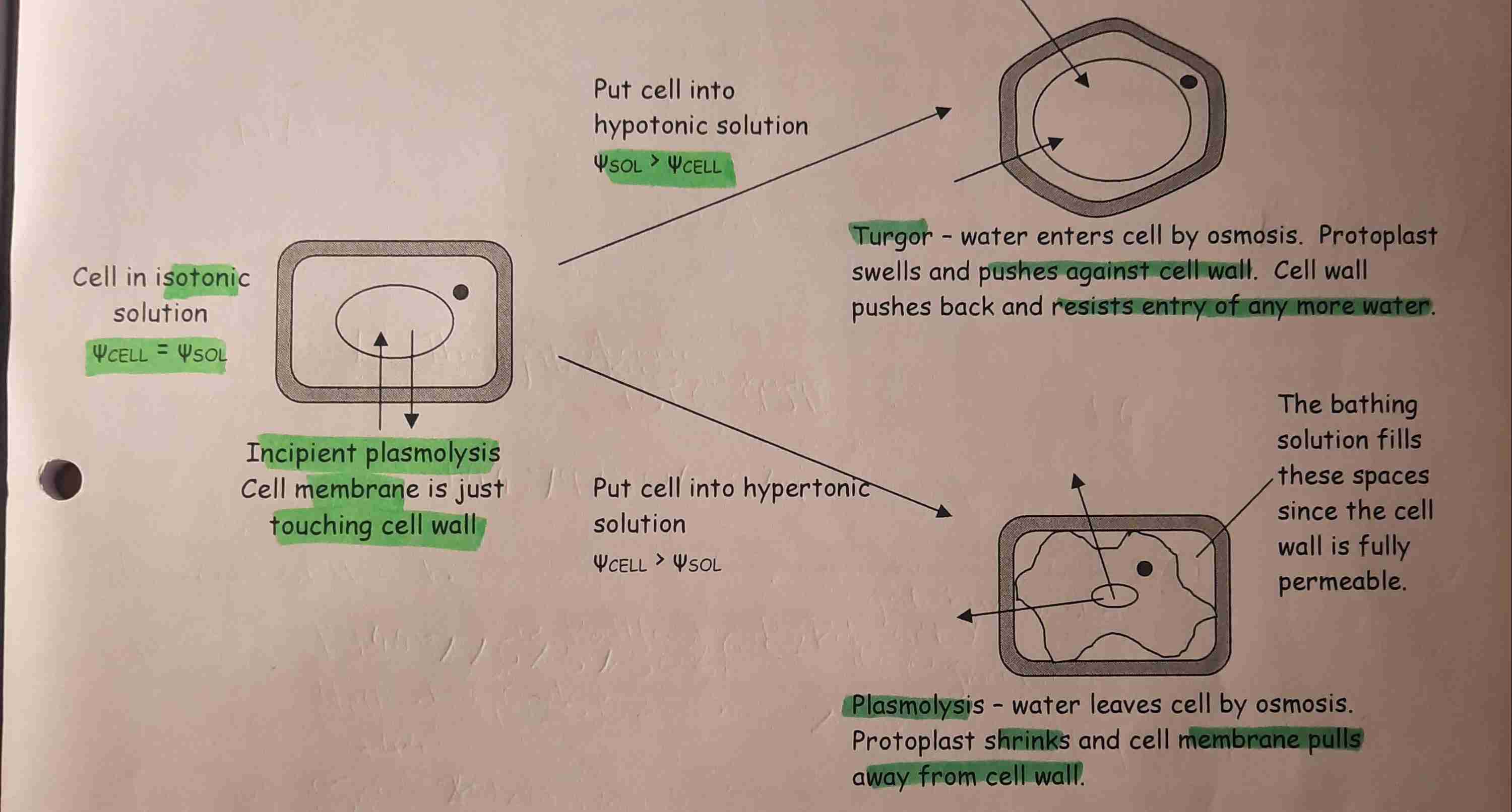
Incipient Plasmolysis
The point at which the membrane just begins to lose contact w/ wall
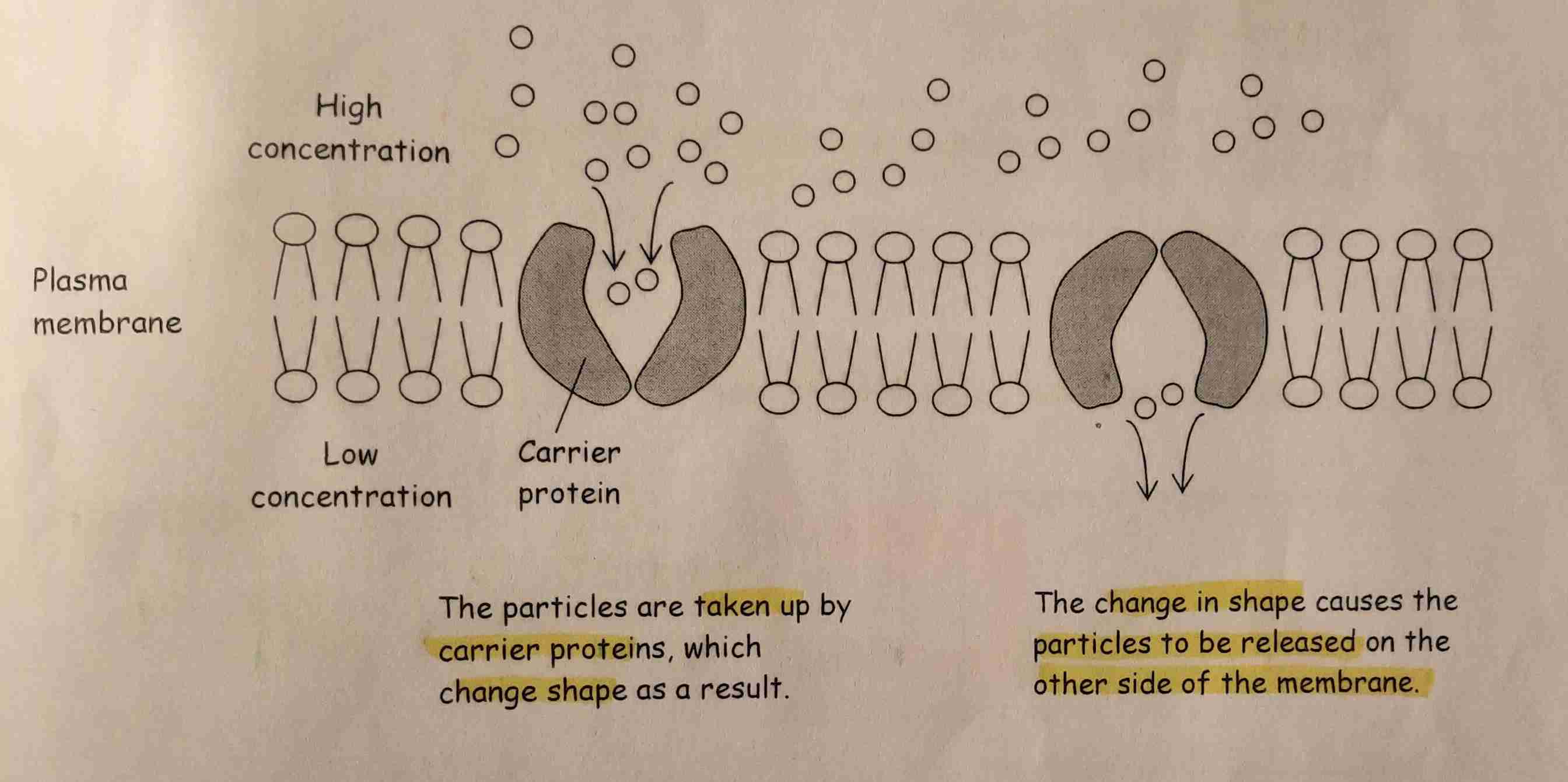
Facilitated Diffusion
Whenever large, water soluble molecules & charged ions can’t fit across the bilayer.
Proteins in the membrane help them move across.
-The proteins may act as channels. Allowing certain molecules to diffuse though.
- Channels are very selective
- Some permanently open
- Some gated (can open or close)
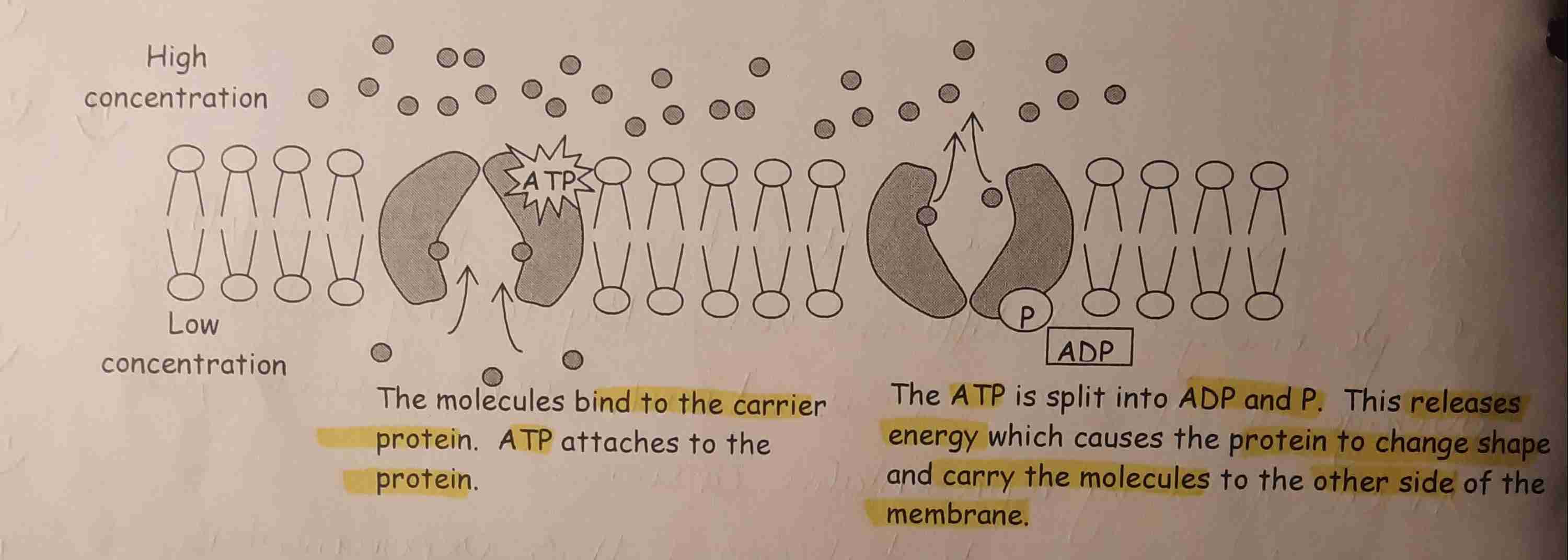
Active transport
The movement of molecules/ions from a region of lower conc. to a region of higher conc. Requiring an input of energy & carrier proteins.
Energy used to power carrier proteins- they change shape & carry the molecules across the membrane.
Cytosis
Substances being transported into or out of a cell without having to pass through the membrane
Transportation for particles too big for protein carriers
Bulk transport or smaller molecules (eg water)
Endocytosis
Cell surface membrane invaginates around the substance to be taken into the cell. Forming a vesicle, which pinched off on the inside of the cell surface membrane.
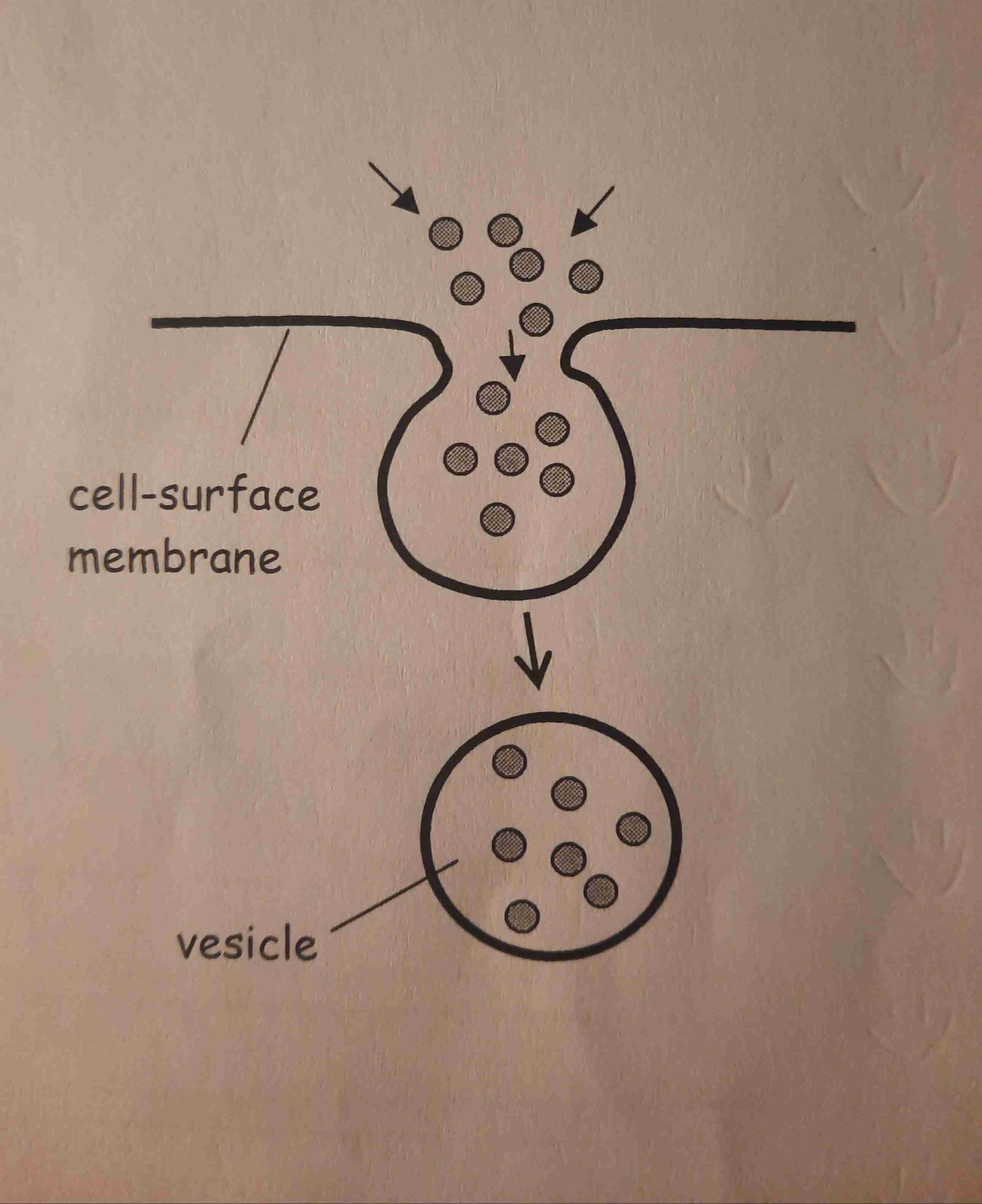
Phagocytosis
a type of endocytosis
The transport of solid material into a cell.
eg- phagocytosis WBCs engulfing bacteria
Pinocytosis
a type of endocytosis
Transport of fluid into a cell
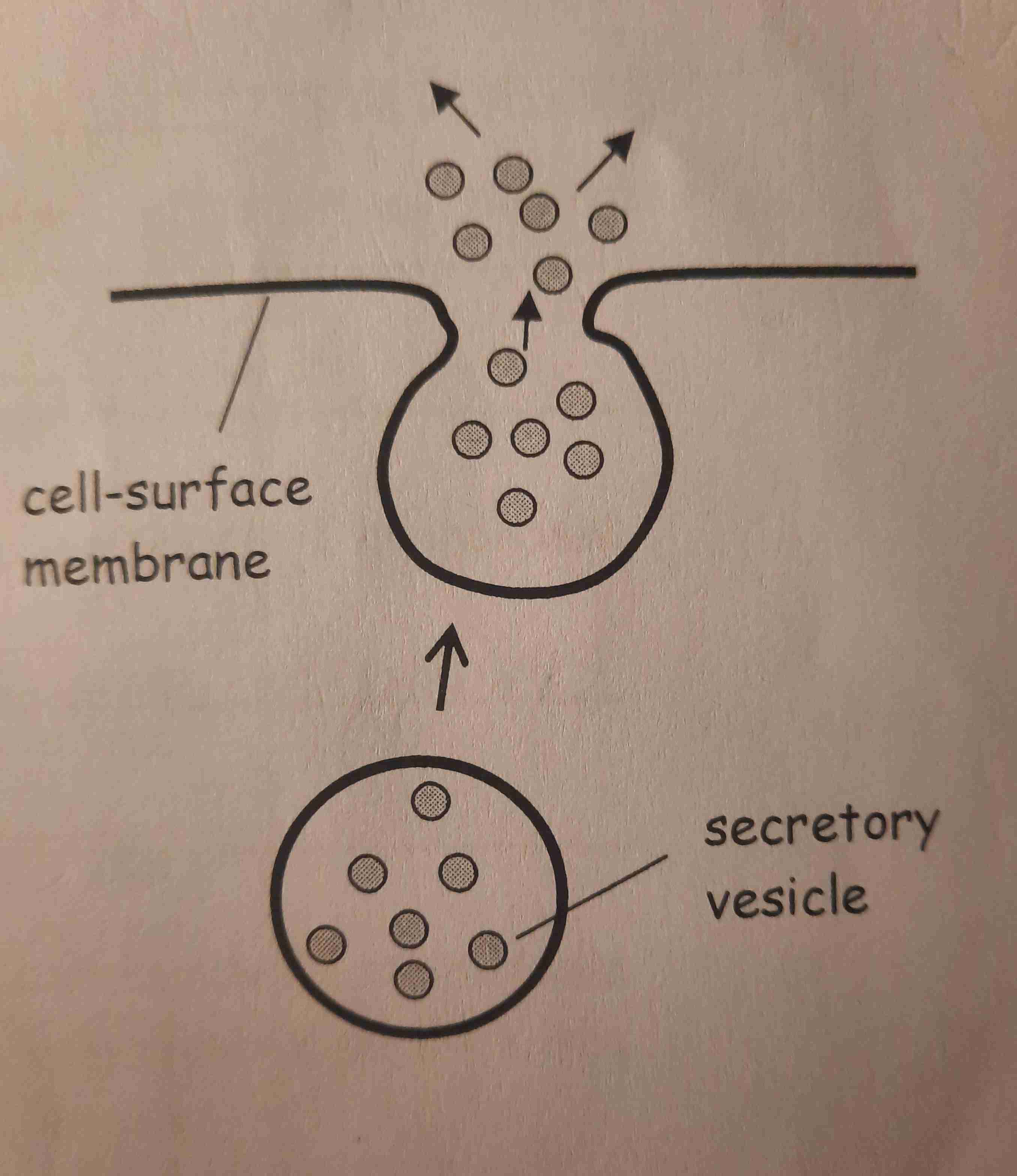
Exocytosis
Movement of substances out of a cell.
Secretory vesicles move to & fuse w/ the cell surface membrane. The contents of the vesicle are then released outside the cell.
Eg- secretion of proteins from cell- like digestive enzymes