Purchasing_Chapter 13: Negotiation and Conflict Resolution
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Negotiation
A process of formal communication, either face-to-face or via electronic means, where two or more people, groups, or organizations come together to seek mutual agreement about issue or issues
Relationships between people, not just organizations
Negotiation skills can be learned and enhanced
Supports implementation of supply management strategies and plans
Bargaining Zone Example
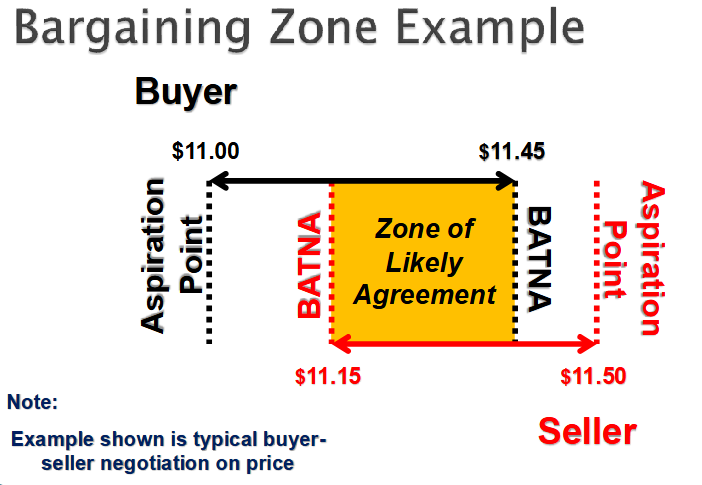
BATNA
That point where it is advantageous to walk away from the negotiation
◦ Best Alternative to a Negotiated Agreement
◦ Bottom line or reservation point
Position
Negotiator’s opening offer
◦ Represents the optimistic (or ideal) target value of issues being negotiatedStated demand at negotiation table
Interests
Learn to play detective
◦ Try to separate other party’s interests through series of open-ended, probing questions
◦ Then listen carefullyAlways focus on the other party’s underlying interests, not its stated positions
Need vs Want
Need
◦ Negotiated outcome that negotiator must achieveWant
◦ Negotiated outcome that a negotiator would like to have
◦ May often be exchanged as a concession
Triangle Talk
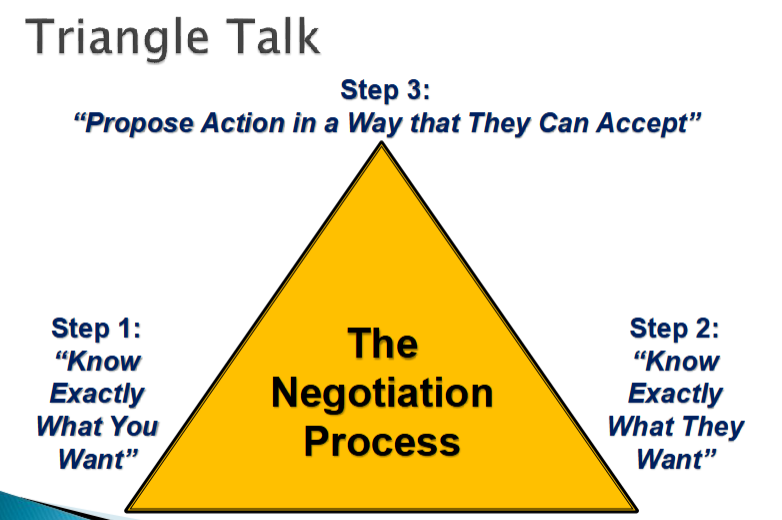
Know Exactly what you want
Determine and formalize specific goals and objectives
◦ Helps retain clear focus and minimize distraction
◦ When written, can be referred to readily during negotiation
◦ The more clearly defined, the more likely that priorities can be achievedAttempt to distinguish other party’s likely needs and wants
◦ Estimate underlying interests to other party’s stated positionsBeware of expecting other party to think in same way as you do
Ask probing, open-ended questions to confirm or counter assumptions
Propose Action in a Way that they can accept
Frame your own needs in terms of other party’s needs
Make it easy for other party to say “Yes”
Remain fair, flexible, and reasonable
Address their needs first
The Negotiation Framework
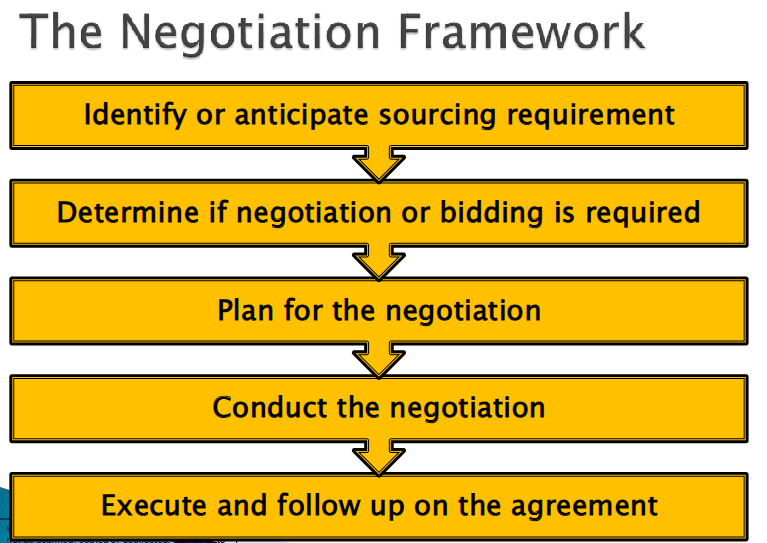
Identify or Anticipate the Sourcing Requirement
Purchase requisitions
New product development
New facilities
Develop Specific Objectives
Objective
◦ Aspiration or vision to work toward in futureTypical objectives
◦ Acceptable unit price
◦ Contract quantities
◦ Required delivery lead time
◦ Improved supplier qualityNot all objectives are equally important
◦ Need to prioritize
Must have (needs)
Would like to have (wants)
◦ Serves as basis for concession strategy
Gather Relevant Information
Previous experience with other party
◦ What happened between parties?
◦ Was negotiator satisfied with previous outcome?
◦ Are we negotiating with same people or with different negotiators?
◦ What were important issues to supplier? To buyer?Previous experience with other party
◦ What were areas of disagreement?
◦ Is there anything about previous conduct or protocols that should be changed?
◦ What is relative power between parties?
◦ Who has most to lose? To gain?
Determine if Negotiation or Competitive Bidding is Required
Is bid process inadequate?
Are many non-price issues involved?
Is contract large?
Are technical requirements complex?
Does contract involve plant and equipment?
Planning for the Negotiation
Better planning → better outcomes
Electronic communication tools vs. face-to-face negotiations
◦ Reduce expensive and time-consuming travel
Regcognize your counterpart’s needs
Must consider longer-term success
Issues critical to supplier may not be issues critical to buyer, and vice versa
Give-and-take must be considered
◦ Each party should not expect to prevail in all issues
◦ Setting priorities for concessions and issue tradeoffs
Phase of Negotiation
Phase I
◦ Fact finding and information sharing
◦ Clarify or confirm information
Phase II
◦ Recess to assess new information and findings
◦ Assess relative strengths and weaknesses
◦ Review and revise objectives and positions, if necessary
◦ Organize agendaPhase III
◦ Meet face-to-face or electronically
◦ Narrow differences on issues
◦ Offer proposals and counterproposals
◦ Exchange concessionsPhase IV
◦ Seek agreement
◦ Conclude negotiation
◦ Agree to follow-on activities
Execute and Follow Up on the Agreement
Provide performance feedback
Build on success of negotiation
Monitor contract provisions
Reaffirm commitment of parties
Negotiation Planning
Develop plan and overall strategy
Specific strategies
Research
Actions
Tactics
Power in Negotiation
Power
◦ Ability to influence another person or organization to do somethingPower by itself is neither good nor bad
◦ It is actual application or use of power that makes it good or badSources of negotiating power
Sources of Negotiating Power
Informational power
Reward power
Legitimate power
Expert power
Legitimate Power
Power based on official position held
◦ The higher the job position or title, the greater the power inferredMay be separate from reward power or coercive power
Buyer has legitimate power due to his/her ability to award contract
Win-win Negotiation
Understand each other’s needs and wants
Focus on common ground rather than personal interests
Conduct joint efforts to solve problems
Develop creative solutions that provide additional value
Engage in open information sharing
International Negotiation
Added complexity and challenge with different …
◦ Customs
◦ Laws
◦ CulturesExtra time and effort required
Culture shock