PSYC 200 Chapter 3
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Materialism
Behavior and cognition can be explained by the working of the brain and rest of nervous system
Mind is part of physical world
Materialists believe that mental phenomena can be explained through physical processes
Consciousness arises from complex interaction within brain
Mind is an emergent property of brains physical structures
Dualism
Mind and body are distinct entities
mind is not completely reducible to material body or brain
Mind is partially independent of the body
Mind functions in a way that cannot be fully explained by physical processes
How are the brain and behavior related
The brain affects behavior
Hyperactivity in the dopamine system causes schizophrenia
Behavior affects the brain
Learning can bring about long lasting changes in the brain
Evidence of Materialism
fMRI and EEG allow observations of brain activity in real time, correlating between specific mental states and pattern. Brain chemistry can alter mood, memory, and perception, and that physical processes in the brain are linked to consciousness
Neurons
Basic structural and functional units of the nervous systemG
Glial cells
Outnumber neurons by 10-1
make up 50% of the brain volume
Support, nourish neurons and remove waste
Unipolar Neuron
has 1 axon which extends into dendrites
Primary afferents of spinal and some cranial nerves in vertebrates
Most common neurons in the CNS of invertebrates
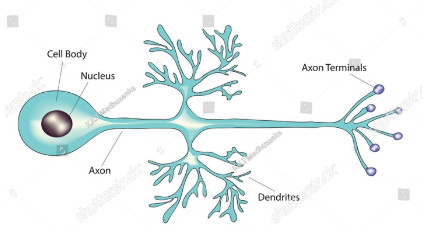
Pseudo unipolar neuron
1 axon that projects from the cell body for a short distance before splitting into 2 branches
Most sensory neurons are pseudo unipolar, dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves
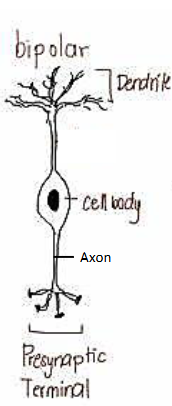
Bi polar neuron
2 independent structures extending from the cell body, 1 is an axon, other is a dendrite
IE: Rod and cone cells of retina olfactory system
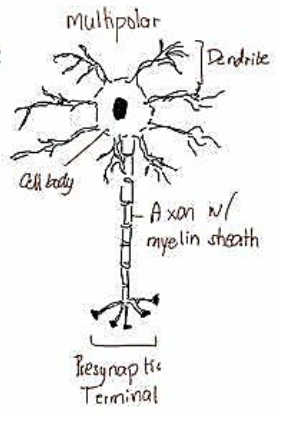
Multipolar neuron
only has 1 axon, but multiple dendrites, making transmitting information easier
Most common with multiple extensions from soma
A motor neuron
Majority of neurons of CNS and PNS as well as majority of interneurons
3 types of neurons
Sensory neurons
Interneuron
Motor neuron
Function of a neuron is to receive, integrate and transmit information
All neurons have:
A cell body/soma
Tree like dendrites to specialized to receive information
an axon
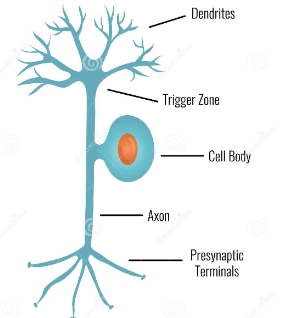
Axon
Long thin fiber that transmits signals away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles or glands
Direction of impulse in a sensory neuron
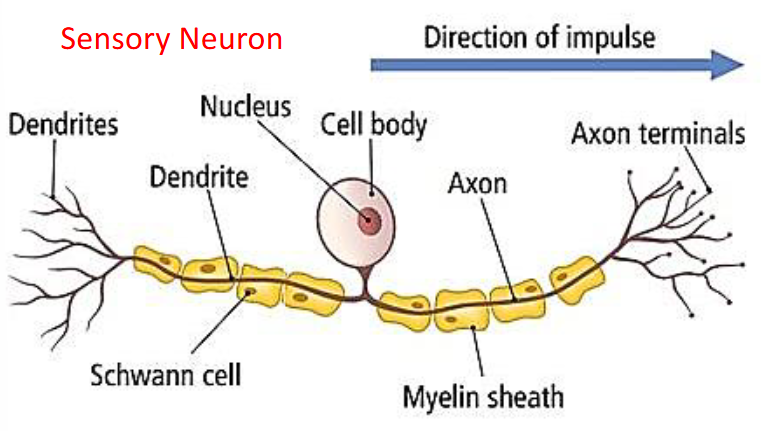
Direction of impulse in motor neuron
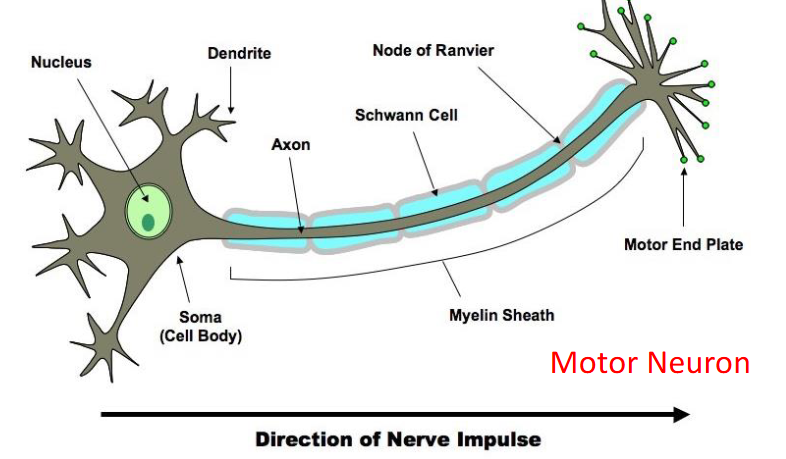
Interneuron signal direction
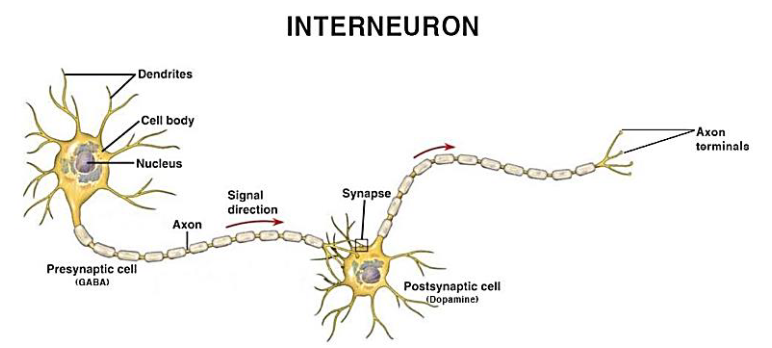
Myelin sheath
Many axons are wrapped in a myelin sheath
is derived from glial cells
speeds up signal transmission along an axon
Degeneration of myelin sheath
Leads to
ineffective signal transmission
in MS
Loss of muscle control
Weakness and paralysis
Vision difficulties
End of an axon
Connection between 2 neurons or neuron and effector is called a synapse
(filled with neurotransmitters)
Neuron at rest
Cell membrane is semipermeable
Na and K are pumped back and forth across the membrane at different rates
Difference in flow rates leads to a significantly higher concentration of negatively charged ions inside
Resting potential at -70mV
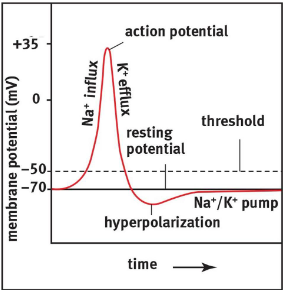
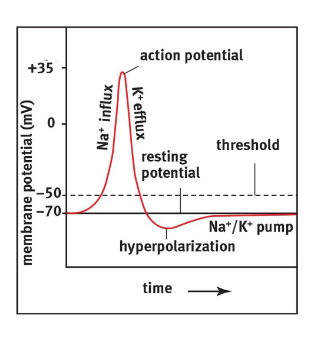
Action potential
When a neuron is stimulated, brief jump occurs in the neurons voltage
change is called an action potential
AP travels along the axon like a spark along a trail of gunpowder
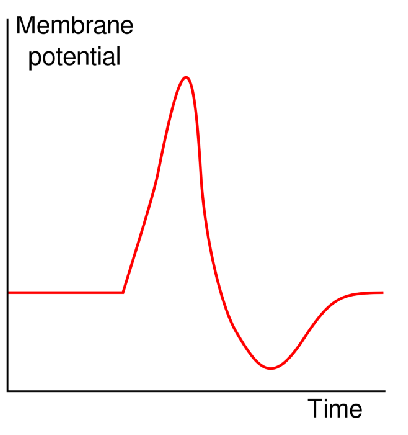
Action potential steps
Resting potential
Na+/K+ pump
Depolarization
Voltage gated Na+ channel
Repolarization
Voltage gated K+ channel
Resting potential
Na+/K+ pump
Depolarization
In myelinated neurons, AP occur only in nodes of Ranvier
When neuron is stimulated, voltage gated Na+ channels in its cell membrane open briefly, allowing Na+ to rush in
The negativity of the membrane potential is reduced
Depolarization between -70 and 55 mV has no effect
When membrane potential is reduced to less than -55, AP occurs
Repolarizartion
When transmembrane potential reaches 35+mV, the voltage gated Na+ channels close, and K+ channels open, allowing K+ to rush out of membrane
This causes the negativity of the cell membrane potential increases
Membrane is repolarized and membrane potential overshoots to -90 mV
Causes the K+ channels to close
Na/K pumps bring back to resting potential of -70mV
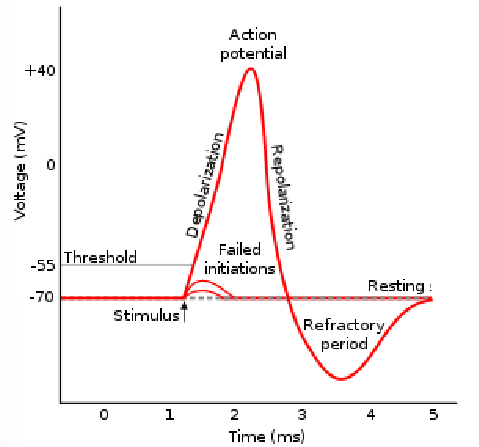
Absolute refractory period
After firing of an action potential, some time is needed to before firing another AP
Called the absolute refractory period
lasts 1-2 milliseconds
Relative refractory period
Neuron can fire but threshold for firing is elevated
more intense stimulation is required to initiate AP
All or None law
Neural impulse either fires or does not fire
when it fires, AP are all the same size
Weaker stimuli does not equal smaller AP
Stronger stimulus will cause faster rate of firing than weaker stimulus
Thicker axons transmit neural impulse faster than thinner ones
3 possibilities of NTS during transmitters
Some are successful in making it to receptor
Some are destroyed in the synaptic cleft
Some are pumped back in via re-uptake pump
excitatory transmitters
Cause depolarization
inside of receiving neuron becomes more positive
Increases likelihood of AP
inhibitory transmitters
Cause hyperpolarization
inside of receiving neuron becomes more negative
decreases likelihood of an AP
Convergent/divergent synaptic transmission
Convergent = summation
will produce a graded post synaptic potential
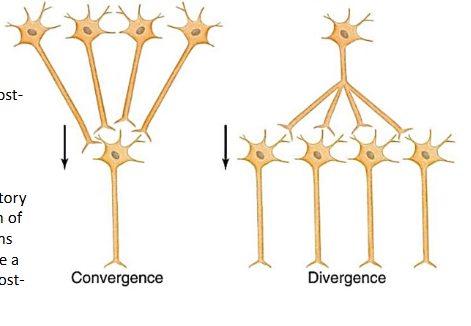
Post synaptic potential
When NT and a receptor molecule combine, reactions in the cell membrane cause a post synaptic potential (a voltage change at a receptor site on a post synaptic cell membrane)
PSP are graded because it is a summation of many signals from the presynaptic neurons
Size and direction of PSP will increase or decrease the probability of a neural impulse in the receiving cell
Excitatory PSP
Positive voltage shift
Increases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will fire action potential
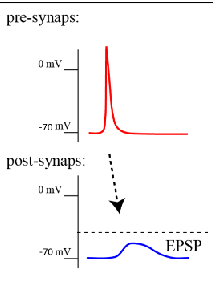
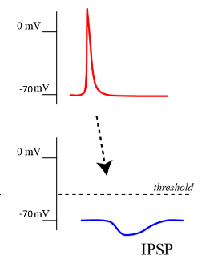
Inhibitory PSP
Negative voltage shift
Decreases the likelihood that the post synaptic neuron will fire action potentials
Dopamine
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
Malfunctions:
Excess dopamine = schizophrenia
starved of dopamine = parkinson’s disease
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal
Malfunctions:
Undersupply linked to depression
Agonist drugs
Mimics a neurotransmitter, binding to NTs receptor and activating/increasing NT’s effects
Can also block reuptake sites of neurotransmitter or stimulate production
Antagonist drugs
Displace a particular NT, binding to the Nts receptor site to block neurotransmitter binding
Can destroy NT in synapse or block production
Dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia
Some forms of schizophrenia caused by excessive dopamine activity
Amphetamine and cocaine create schizo symptoms by increasing dopamine activity at the dopamine synapses
Agonist:
Drug that mimics or enhances effect of NT
Amphetamine and cocaine
Antagonist
Drug that blocks effect of NT
Chlorpromazine (used to reduce symptoms of schizophrenia)
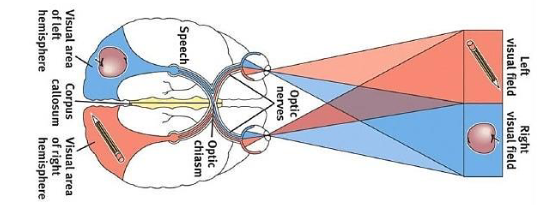
Corpus Callosum
Nerve fibers that enable communication between the 2 hemispheres
Michael Gazziniga
With teh corpus callosum severed, objects presented in the right visual field can be named but not the objects in the left
Transduction
Process by which sensory stimuli are converted to neural signals the brain can interpret
Sensation
Stimulation of sense organs
Involves absorption of energy by sensory organs
Perception
Selection, organization and interpretation of sensory information
Involves organization and translation of sensory information into something meaningful
Saturation
Purity of color
Brightness/value
Amplitude
Concentration of light energy
Hue/color
Wavelength/frequency
Timbre
Purity of sound: a pure tone that has only 1 frequency and 1 amplitude (sine wave produced by a tuning fork)
Timbre sets apart sound of piano from sound of flute
Loudness
Amplitude/ concentrationP
Pitch
Wavelength/frequency
Receptive field of ganglion cell
Responsible for seeing light/dark contrast
Has a property known as center-surround antagonism
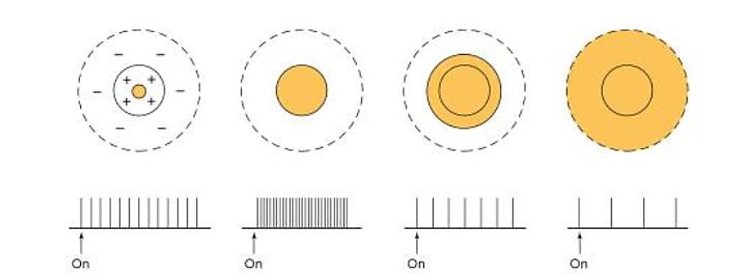
Rate of firing decreases when light falls in the center of a receptive field
Shading indicates area stimulated with light. Largest response occurs when the entire center is illuminated
Visual information processing
Thalamus
perception of brightness
Primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe
Perception of orientation
Inferior temporal lobe
Perception of form and color
Parietal lobe
perception of motion and depth
Cat experiment

Ventral stream
Leads to temporal lobe
Processes details of what objects are

Dorsal stream
Leads to the parietal lobe

Color sensation

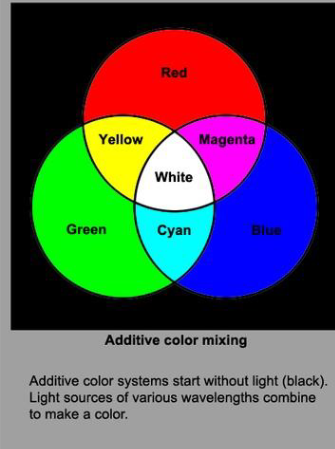
Additive color mixing
Mixing light
adding light so light gets lighter
Subtractive color mixing
Mixing pigments
subtracting light so light gets darker
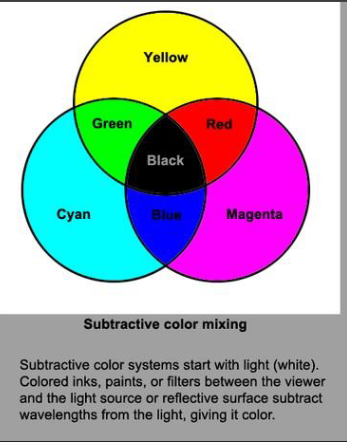
Color absorption
Yellow absorbs blue
Magenta absorbs green
Cyan absorbs red
Additive vs subtractive color mixing

Theories of color vision

Color blindness
Color-blind = born with only 1 or 2 cone receptors
Common deficiency is red or green receptor
If person is missing 2 types of receptors, person cannot create any colors
Opponent process theory
Trichromatic theory fails to explain complementary afterimage
Stimulus triggers excitatory reaction from 1 neuron, inhibitory from another
After repeated exposure to the same stimulus, both reactions weaken
When the stimulus is removed, inhibited neuron is released from the inhibition and becomes more active than its baseline
Blind spot
nerves that run from the retina to the brain coverage at a spot
There are no receptor cells on this spot
Each eye has a blindspot that is compensated for by the other eye
Receptor cells/photoreceptors
Are in the innermost layer to the retina
only 10% of light arriving at the cornea reaches the receptors
Rod to cone ratio
100-125million rods
5-6.4million cones
Fovea
Tiny spot in the center of retina that only contains cones
Cones
Responsible for color vision
Daylight vision
Visual acuity
Rods
Peripheral vision
Night vision
Convergent synaptic transmission
Multiple rod cells converge to one ganglion cell
allows for low light conditions compared to cones
Rods vs cones
Both rods and cones have light absorbing pigments
Rods have the same pigment
Cones have three different pigments
Psychophysics
study of how physical stimuli are related or translated into psychological experience
Absolute threshold
minimum amount of stimulation that an organism can detect
No single stimulus intensity at which the subject jumps from no detection to accurate detection
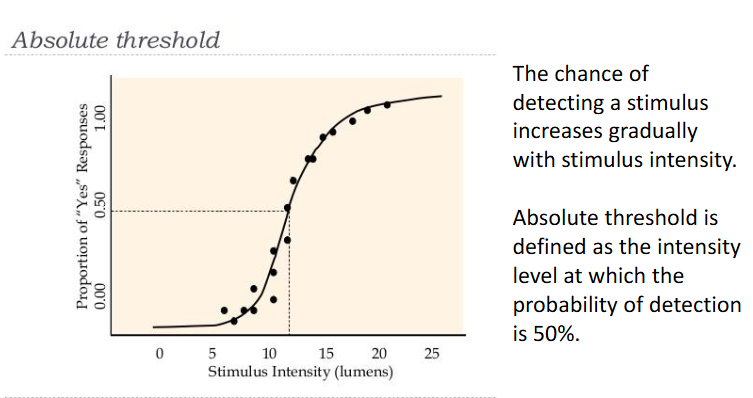
Signal detection theory
Depends on the
intensity of stimulus
If intensity of stimulus is low/ambiguous, decision outcome is affected by other factors
psychological state of individual or context of situation
2 processes involved
sensory process
decision making process
4 possible decision outcomes
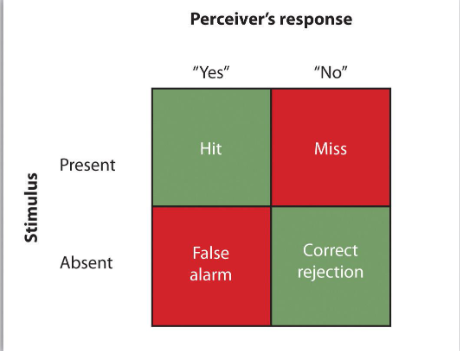
just noticeable difference
Smallest difference in the amount of stimulation that a specific sense can detect
Webers law
Size of a just noticeable difference is a constant proportion of the size of the initial stimulus
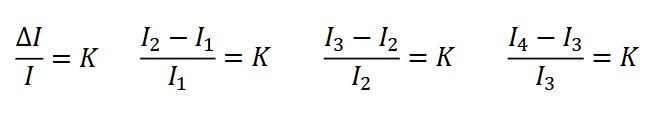
Fechner’s Law
Subjective sensation proportional to the logarithm of the intensity of the stimulation
S = K Log R
k=constant
S=sensation
R=Reiz(stimulus)
Sensation
Stimulation of sense organs
Involves absorption of energy by sensory organs
Perception
Selection, organization and interpretation of sensory information
Involves organization and translation of sensory information into something meaningful
Word superiority effect
People have better recognition of letters within words compared to isolated letters and to letters presented in nonword strings
Bottom up processing
Perception is based on the physical features of the stimulus
Data-driven processing
Identify letters isolated from words or words isolated from sentences complete the stroop task without being affected by the meanings of the words
Top down processing
Interpretation of sensory information based on knowledge, expectations and past experience
Concept driven processing
Context effect, word superiority effect, Stroop effect
Structuralism
Breaks down the whole into its parts/ a compound into its elements
Method: introspection
(experimental: systematically varied the stimulus and then recorded the subjects subjective feelings about the change)
Gestalt psychology
The whole is more than the sum of its parts
Integrating elementary components to form a whole - the opposite of structuralism
Humans have tendency to organize into a coherent whole
Organization is guided by general principles