(3+4) Small Organic Molecules
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Small organic molecules are less than _ in size
1000 daltons
There is at least different types of small organic molecules found primarily in the of a cell
1000; cytoplasm
4 families of small organic molecules
sugars, fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides
Simple sugar
monosaccharides or disaccharides
Monosaccharides (structure and function)
carbon based compound that follows the basic formula of (CH2O)n, n=3-7. May be oxidized to release energy (energy source). May be combined into di-,tri-, or polysaccharides which have different functions.
Monosaccharides contain groups as well as or ____ groups
hydroxyl; ketone or aldehyde
Oligosaccharide
a group of monosaccharides (usually 3-15 or 20) chained together. May be linear or branched. Important when bound to lipids or proteins
Glycolipid
formed when a lipid has a oligosaccharide bound to it
Glycoprotein
formed when a protein has a oligosaccharide bound to it
Fatty acid (structure and function)
carboxyl group on one end attached to a hydrocarbon tail with a methyl group on the terminal end. Usually an even number of carbons. May be oxidized to produce energy (energy source).May form into triglycerides or phospholipids to perform other functions
Fatty acids may vary in or
saturation or length
Saturated fatty acid
highly reduced fatty acid in which carbons of the hydrocarbon tail have the maximum amount of hydrogens attached to them
Unsaturated fatty acid
fatty acid in which there are one or more double bonds in the hydrocarbon tail
Difference in mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids
mono- means there is only one double bond in the hydrocarbon tail of the fatty acid whereas poly- has multiple
When counting carbons on fatty acids, from which carbon do you start counting? (aka which carbon is considered carbon 1?)
the methyl carbon is considered carbon 1
Draw an 8 carbon saturated fatty acid
Fatty acids may be oxidized via in order to
beta oxidation; release energy
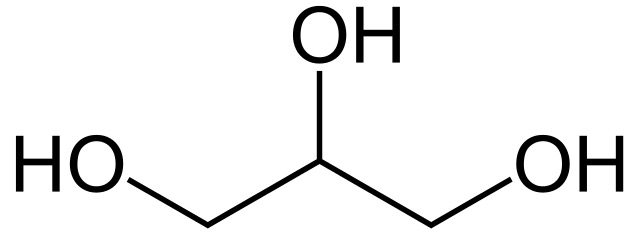
Glycerol
alcohol sugar composed of 3 bonded carbons with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
Triglyceride (structure and function)
formed by 3 fatty acids attaching a glycerol via ester linkages at the carboxyl group of the fatty acid. Used for energy storage in blood and other organs.
Phospholipid (structure and function)
formed by two fatty acids and a phosphate group connected to a R-group attaching to a sugar alcohol. makes up the bulk of the lipid component of a membrane. The R-group example used was choline.
Amino acids (structure and function)
composed of an alpha carbon attached to a hydrogen, carboxyl group, R group, and amino group (clockwise order). Function is determined by the R group. May be oxidized to release energy (energy source). Building blocks for proteins.
Draw the basic structure of an amino acid
Draw two amino acids linked by a peptide bond
Peptide bond
bond formed between the carboxylic carbon and amino nitrogen of two amino acids when forming a protein
Nucleotides (structure and function)
Nitrogen containing rings, 5 carbon sugars and one or more phosphates attached to the sugar. May be oxidized for energy. Other functions in reactions/energy (ATP and GTP). building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Nucleic acid
two or more nucleotides linked together
5 basic nucleotides
adenine, gunanie, thymine, cytosine, uracil
Nucleoside vs nucleotide
nucleoside contains only sugar and nitrogenous ring (no phosphate)
Pyrimidine (how many rings, associated nucleotides, draw an example)
nucleotide containing 1 ring (C, T, U)
Purine (how many rings, associated nucleotides, draw an example)
nucleotide containing two rings (A, G)
Difference in ribose and deoxyribose sugar (draw ribose and label it with numbers)
ribose has a hydroxyl group at the #2 carbon while deoxyribose does not (ribose sugar is shown)
Adenosine triphosphate
adenine nucleotide with three phosphates attached, hugely important for energy (may be ribose or deoxyribose for the sugar)
Does ATP have ribose or deoxyribose in the cell?
it can use both
How many phosphates may be attached to a nucleotide
1-3
Cyclic AMP (adenosine monophosphate
adenine nucleotide with one phosphate attached to the 5 and 3 carbons of the sugar. Powerful cell signaling molecule.