Cells/Metabolism Exam 2
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What cellular functions are provided by the cytoskeleton?
cellular movement
cellular structure
what are microtubules?
globular proteins
composed of heterogeneous protein subunits
largest cytoskeleton subtype
what are microfilaments?
smallest cytoskeleton subtype
globular proteins
composed of homogeneous protein subunits
what are intermediate filaments?
composed of many types of proteins
fibrous proteins
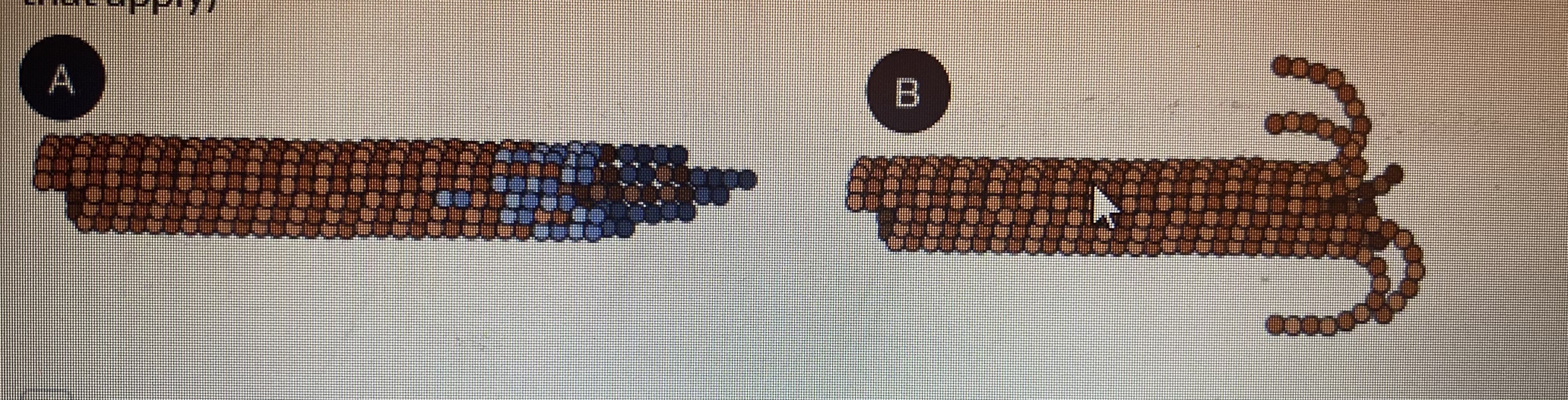
what is true of microtubule phase A?
rescue
GTP- associated
growth phase
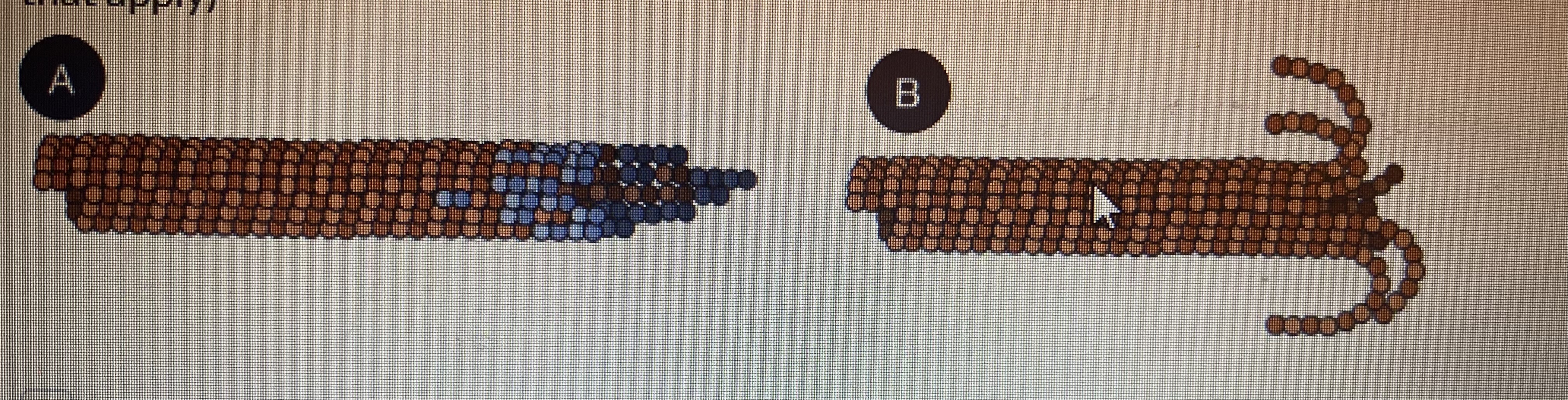
what is true of microtubule phase B?
catastrophe
GDP-associated
shrinkage phase
microfilaments
supports microvilli of enterocytes
intermediate filaments
holds organelles in place
microtubules
highway for neurotransmitter-containing vesicles in neurons
Terms related to the roles of microtubules in cellular motility
dynein
centrioles
cilia
terms related to microfilaments role in cellular motility
myosin
sarcomeres
pseudopods
which cellular structures are linked together across cells by the extracellular matrix?
cytoskeleton
cell membrane
glycoprotein
protein-carbohydrate macromolecule with more protein monomers than carbohydrate
proteoglycan
protein-carbohydrate macromolecule with more carbohydrate monomers than protein
integral protein
protein embedded in the cell membrane
peripheral protein
protein associated with the edge of the cell membrane
transporter
protein that facilitates movement of mlcls across the cell membrane
Which of the following terms is associated with the MAJOR glycoprotein in the extracellular matrix?
collagen
fibrous protein
glycine
fibroblasts
what protein accounts for nearly 40% of mammalian protein
collagen
proteoglycans
provides function in the extracellular matrix
glycoproteins
provides structure to the extracellular matrix
fibronectin
anchors collagen to integral proteins
integrin
anchors peripheral proteins to the cytoskeleton
Properties of tight junctions?
water tight
integral proteins
interact with microfilaments
properties of desmosomes
not water tight
interact with intermediate filaments
integral proteins
catabolic
metabolic pathway in which degradation of molecules occurs
amphibolic
metabolic pathway in which both degradation and synthesis occur
anabolic
metabolic pathway in which synthesis of molecules occurs
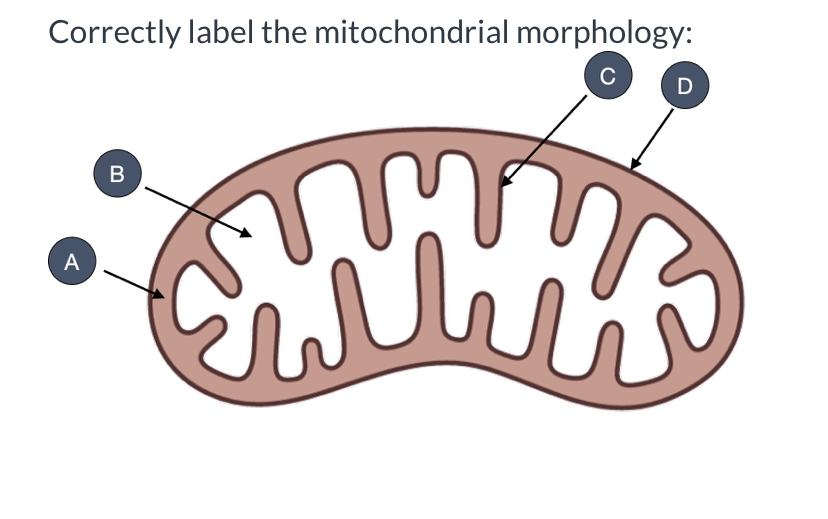
what is A?
intermembrane space
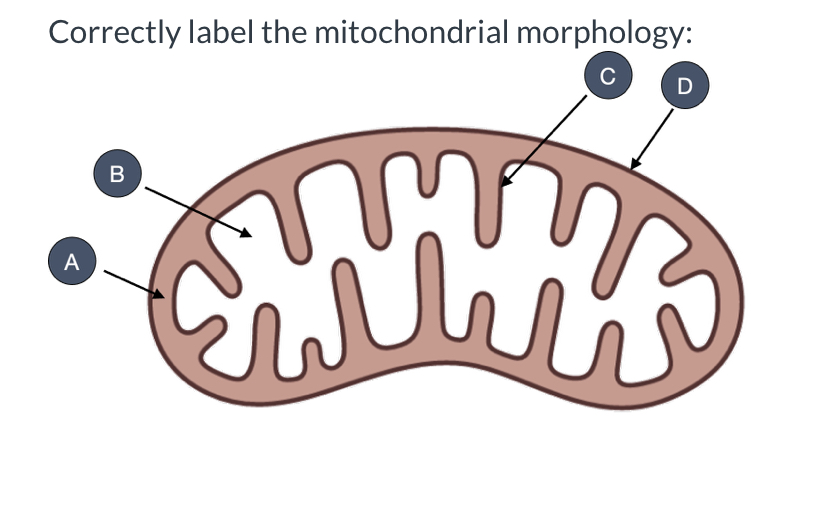
what is B?
mitochondrial matrix
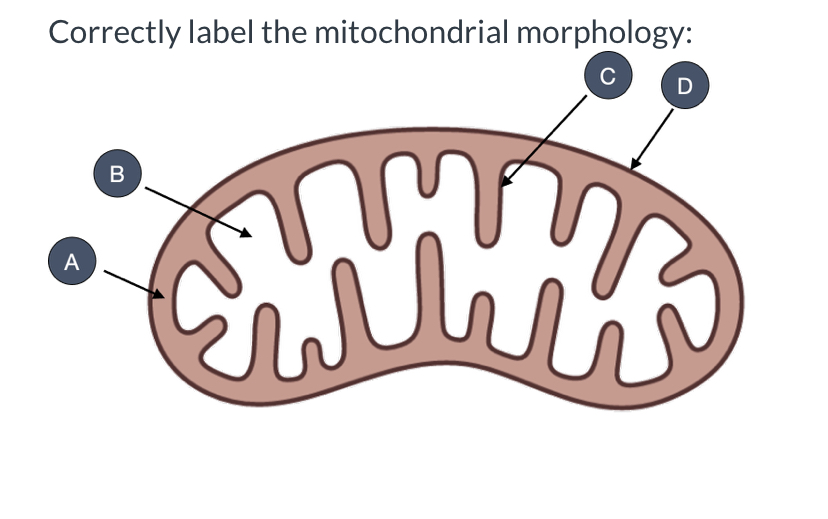
what is C?
inner membrane
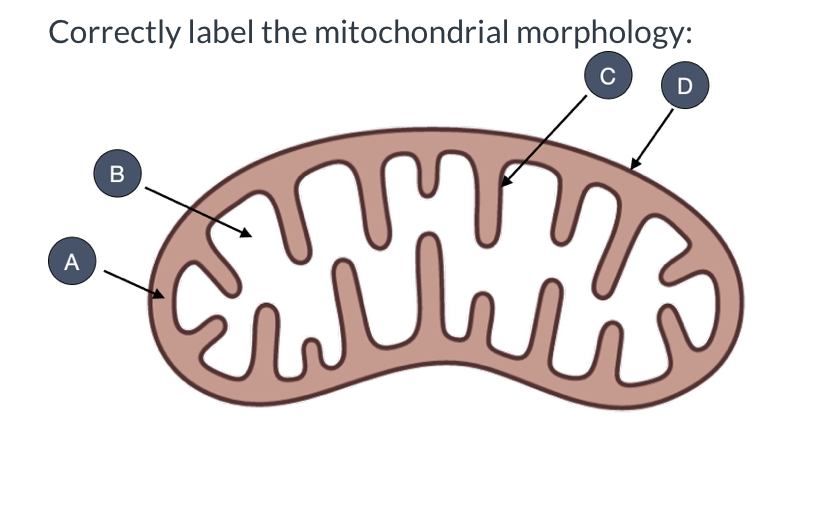
what is D?
outer membrane
examples of REDUCED reducing equivalents
NADH
FADH2
examples of anabolic pathways?
glycogenesis
gluconeogenesis
what enzyme determines whether glucose liberated from glycogen enters circulation to supply other organs or enters glycolysis?
glucose-6-phosphatase
what enzyme adds the second phosphate group to what used to be glucose, committing it to glycolysis?
phosphofructokinase
what enzyme in glycolysis produces reducing equivalents(NADH) that can be utilized in the electron transport chain?
triose phosphate dehydrogenase
which nucleotide triphosphate is involved in glycogenesis?
UTP
what type of cells do not rely on the oxidation of glucose to derive most of their energy?
hepatocytes
examples of gluconeogenic metabolites?
lactate( from glucose metabolism)
glycerol(from triglycerides)
propionate(a 3-carbon fatty acid)
what type of reaction does the enzyme kinase perform?
move phosphate groups to and from high energy mlcls
What is the net ATP yield from one round of glycolysis?
2
how does phosphorylation of glucose-6-phosphate keep glucose from leaving the cell?
G6P can no longer be transported by glucose transporters
what compound if formed via substrate-level phosphorylation?
ATP
possible products of pyruvate
glucose
lactate
acetyl-CoA
production of which metabolite from pyruvate is the most important to allowing glycolysis to continue?
NAD+
what is a product of oxidation reactions in the TCA cycle?
FADH2
what is a reactant of condensation reactions in TCA?
water
what is a product of substrate level phosphorylation reactions in TCA?
GTP
what is a product of isomerization reactions in TCA?
a product with the same chemical formula as the reactant
what metabolite entering the TCA cycle is the product of carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism?
acetyl-CoA
in what complex of the ETC does NADH enter
complex I
in what complex of the ETC does cytochrome C enter
complex IV
in what complex of the ETC does coenzyme Q enter
complex III
in what complex of the ETC does FADH2 enter
complex II
how many electrons are pumped into the mitochondrial membrane space in complex I of ETC?
4 electrons
how many electrons are pumped into the mitochondrial membrane space in complex II of ETC?
0 electrons
how many electrons are pumped into the mitochondrial membrane space in complex III of ETC?
4 electrons
how many electrons are pumped into the mitochondrial membrane space in complex IV of ETC?
2 electrons
what helps facilitate the transfer of electrons between complex I and complex III via Coenzyme Q?
complex I and III can associate in lipid rafts
coenzyme Q is hydrophobic
if glucose goes though glycolysis and one mlcl of pyruvate enters the TCA while the other is converted to lactate, how many net ATP equivalents will be produced by the end of ETC?
17
hydrolysis
water reacts with a larger mlcl to break it down
transamination
movement of amine groups
methylation
movement of methyl groups
oxidation
removal of electrons from the target compound
what amino acid does 3-phosphoglycerate react with?
serine
what amino acid does alpha-ketoglutarate react with?
glutamine
what amino acid does phosphoenolpyruvate + erythrose-4-phosphate react with?
phenylalanine
what amino acid does pyruvate react with?
alanine
what amino acid does oxaloacetate react with?
asparate
what amino acid does ribose-5-phosphate react with?
histidine
what amino acids contribute to nitrogen catabolism(urea cycle)?
aspartate
arginine
what amino acids contribute to methylation(urea cycle)?
cysteine
methionine
serine
where does the urea cycle take place?
mitochondria
cytosol
what energy-yielding metabolite can alpha-ketoglutarate be transformed into?
glutamate
what energy-yielding metabolite can leucine be transformed into?
acetyl-CoA
what energy-yielding metabolite can methionine be transformed into?
succinyl-CoA
what energy-yielding metabolite can cysteine be transformed into?
pyruvate
what energy-yielding metabolite can phenylalanine be transformed into?
fumarate
what energy-yielding metabolite can asparagine be transformed into?
oxaloacetate
which metabolites connect the urea cycle and the TCA cycle?
fumarate
aspartate
what are the reactants of Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase?
fatty acyl-CoA
FAD
what are the reactants of acetyl transferase?
acetyl-CoA
Acyl carrier protein
what are the reactants of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase?
acetyl-CoA
bicarbonate
ATP
what are the reactants of MAG lipase?
monoacylglycerol
what are the reactants of acyl-CoA synthetase?
fatty acid
ATP
CoA
what are the reactants of carnitine palmitoyl-transferase I?
fatty acyl-CoA
carnitine
what are the products of MAG lipase?
fatty acid
glycerol
what are the products of acyl-CoA synthetase?
fatty acyl-CoA
AMP
diphosphate
what are the products of acetyl transferase?
acetyl-CoA
acyl carrier protein
what are the products of carnitine palmitoyl-transferase I?
acylcarnitine
CoA
what are the products of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase?
trans unsaturated fatty acyl-CoA
FADH2
what are the products of acetyl-CoA carboxylase?
malonyl-CoA
ADP
Phosphate
H+
thiolase can be involved in both beta oxidation and ketogenesis?
true
How much ATP must be invested to get a diacylglycerol into fatty acid catabolism?
2
How many ATP equivalents would be produced from a diacylglycerol composed of glycerol and two molecules of palmitate (16 carbon fatty acid)? Assume that lipids complete beta-oxidation, all metabolites produced enter the TCA cycle, and all reducing equivalents produced enter the electron transport chain.
232.5
addition of each malonyl-CoA to the growing fatty acid in fatty acid synthesis requires how many ATP equivalents?
3
which enzymes perform their reactions in the cytosol?
MAG Lipase
Acyl-CoA synthetase
Acyl-CoA carboxylase
what enzymes perform their reactions in the mitochondria?
carnitine palmitoyl-transferase I
Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
thiolase
what are hormones?
signaling mlcls that are produced in one part of the body, act in another to stimulate a reaction