Unit 5 - The Great Depression
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Bull Market
A period of increased stock trading and rising stock prices (most of 1920s)
Bear market
A steady drop in the stock market over a period of time (1929-1930s)
buying on margin
Purchasing stock with a little money down with the promise of paying the balance sometime in the future
margin call
demand by a broker that investors pay back loans made for stocks purchased on margin
Speculation
The practice of making high-risk investments in hopes of getting a big return
Black Tuesday
October 29, 1929; date of the worst stock-market crash in American history and beginning of the Great Depression.
Herbert Hoover
Republican candidate who assumed the presidency in March 1929 promising the American people prosperity and attempted to first deal with the Depression by trying to restore public faith in the community.

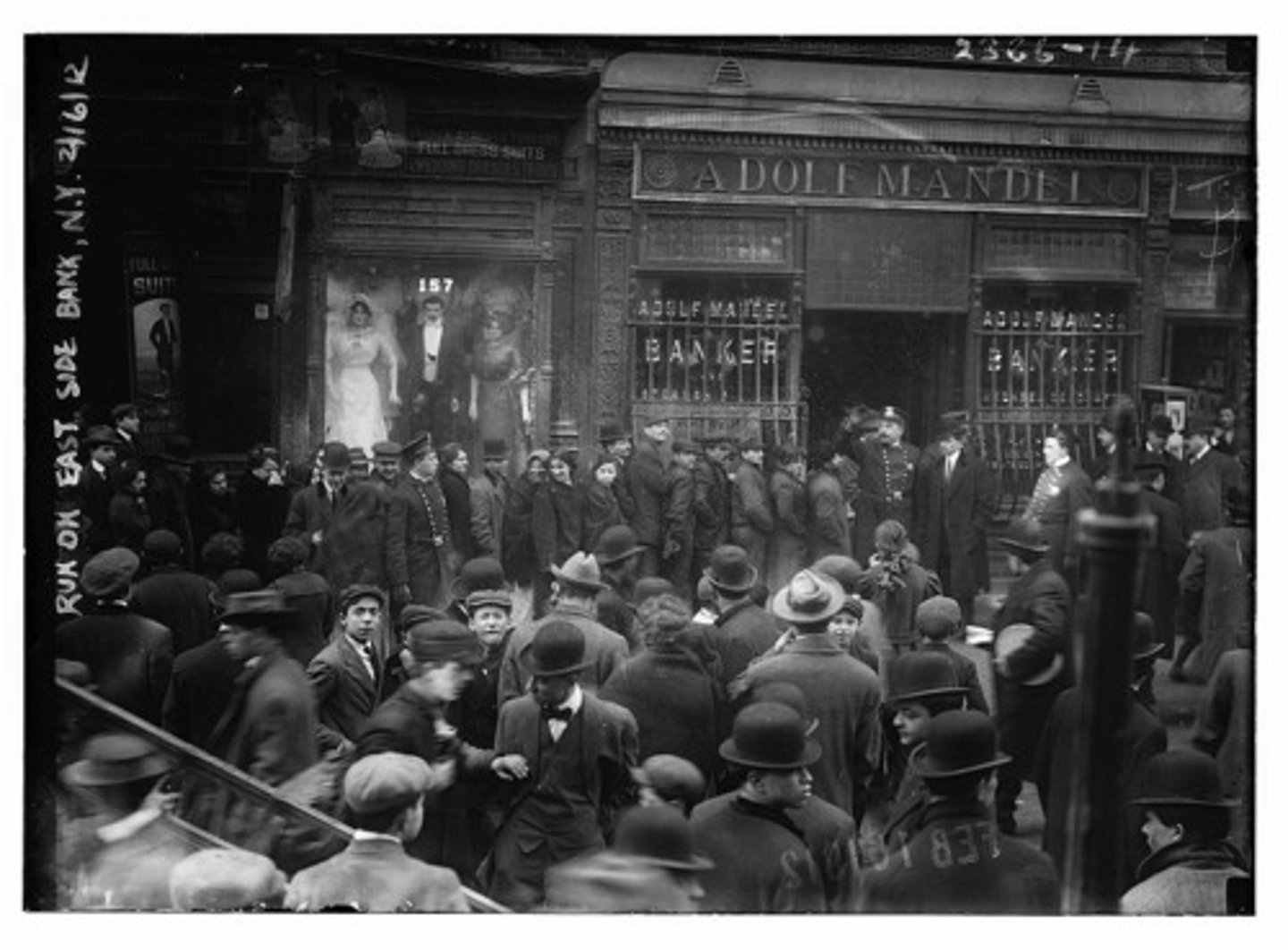
Bank run
A situation in which many of a bank's depositors try to withdraw their funds due to fears of a bank failure

Smoot-Hawley Tariff
A high tariff enacted in 1930 under Herbert Hoover. Sought to protect American manufacturing, but triggered retaliatory tariffs in other countries, which further hindered global trade and led to greater economic contraction.
Reconstruction Finance Corporation
Agency established under Hoover in 1932 to provide emergency relief to large businesses, insurance companies, and banks.
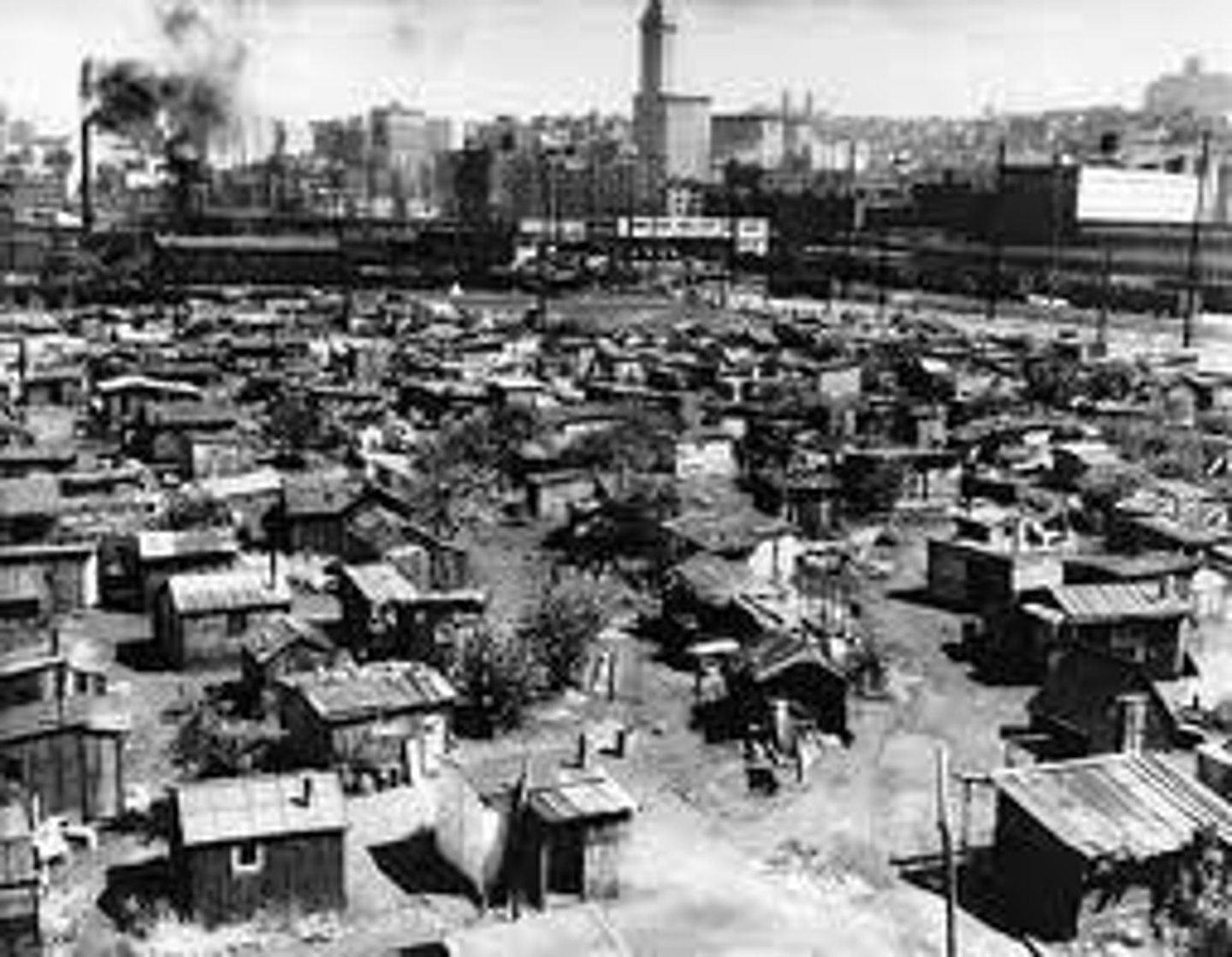
Hoovervilles
Depression-era shantytowns, named after the president whom many blamed for their financial distress

Gross National Product (GNP)
The total value of goods and services, including income received from abroad, produced by the residents of a country within a specific time period, usually one year.
Bonus Army
WWI veterans who marched on Washington in 1932 demanding their $1,000 bonus pay before the 1945 due date. Hoover called in the army to get the veterans out of there.

Breadline
line of people waiting for food handouts from charities or public agencies
soup kitchen
place where food is provided to the needy at little or no charge
John Steinbeck
American novelist who wrote novels that focused on the impact of the Great Depression on average Americans; famous for the Grapes of Wrath, which reflected the struggles of destitute farmers during the Depression

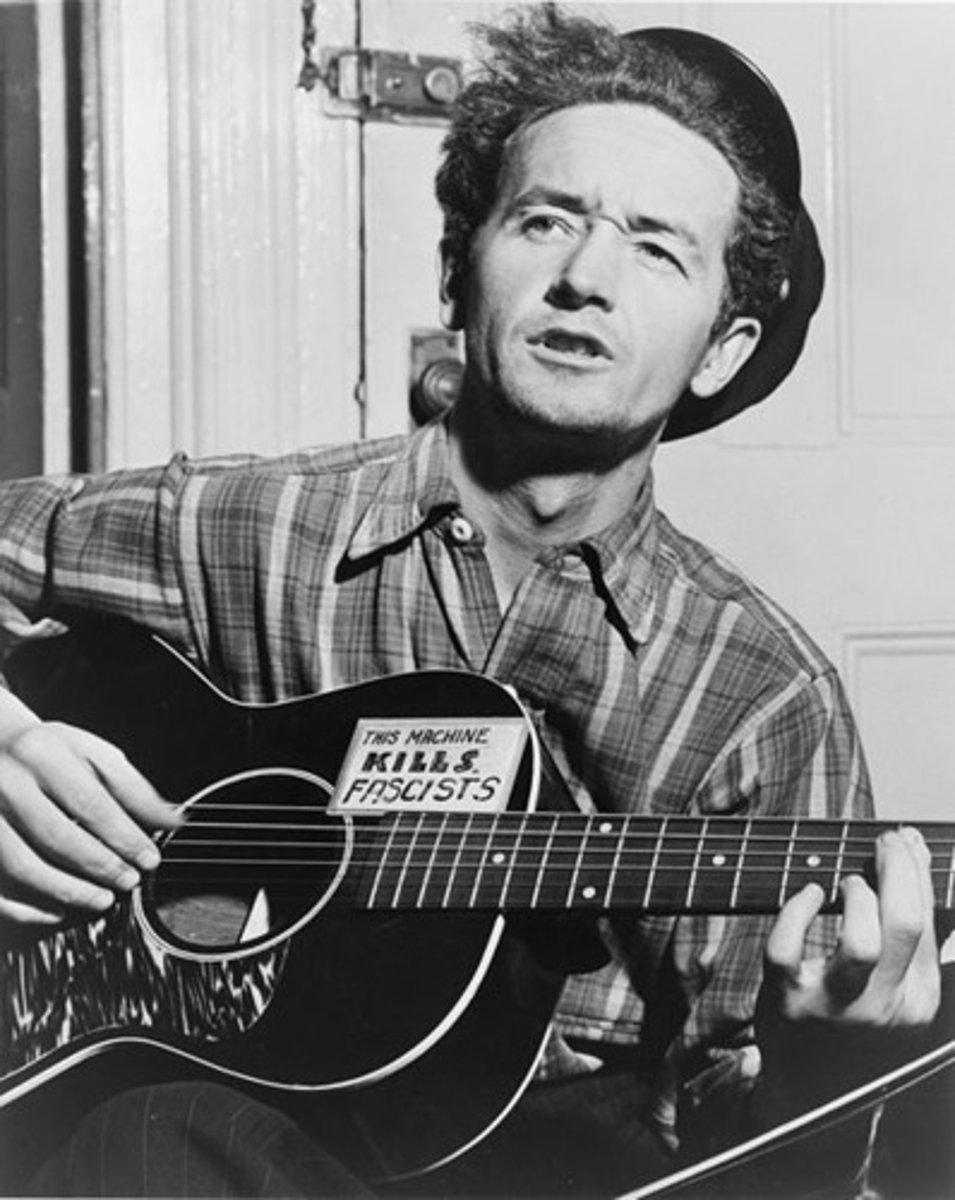
Woody Guthrie
American songwriter and folksinger who flourished in the 1930s, writing numerous songs about social injustice and the hardships of the Great Depression years; two of his best-remembered songs are "This Land is Your Land" and "So Long, It's Been Good to Know Yuh."

"Brother Can You Spare a Dime?"
Anthem of the Great Depression; reflected the boom to bust that affected so many Americans.
Hobos
Open-road wanderers who traveled the country by walking, hitchhiking or "riding the rails."
Dust Bowl
Region of the Great Plains that experienced a drought in 1930 lasting for a decade, leaving many farmers without work or substantial wages.
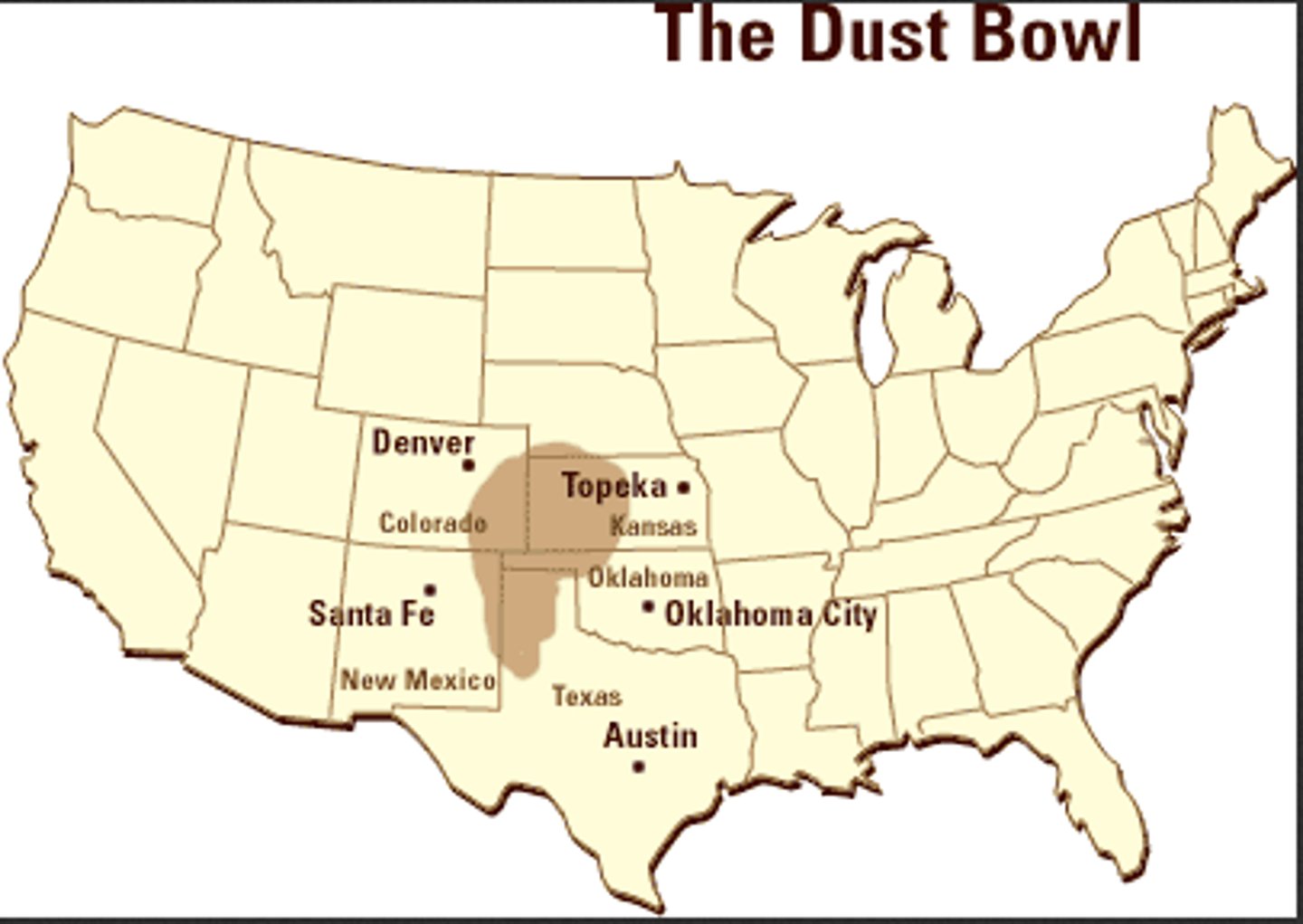
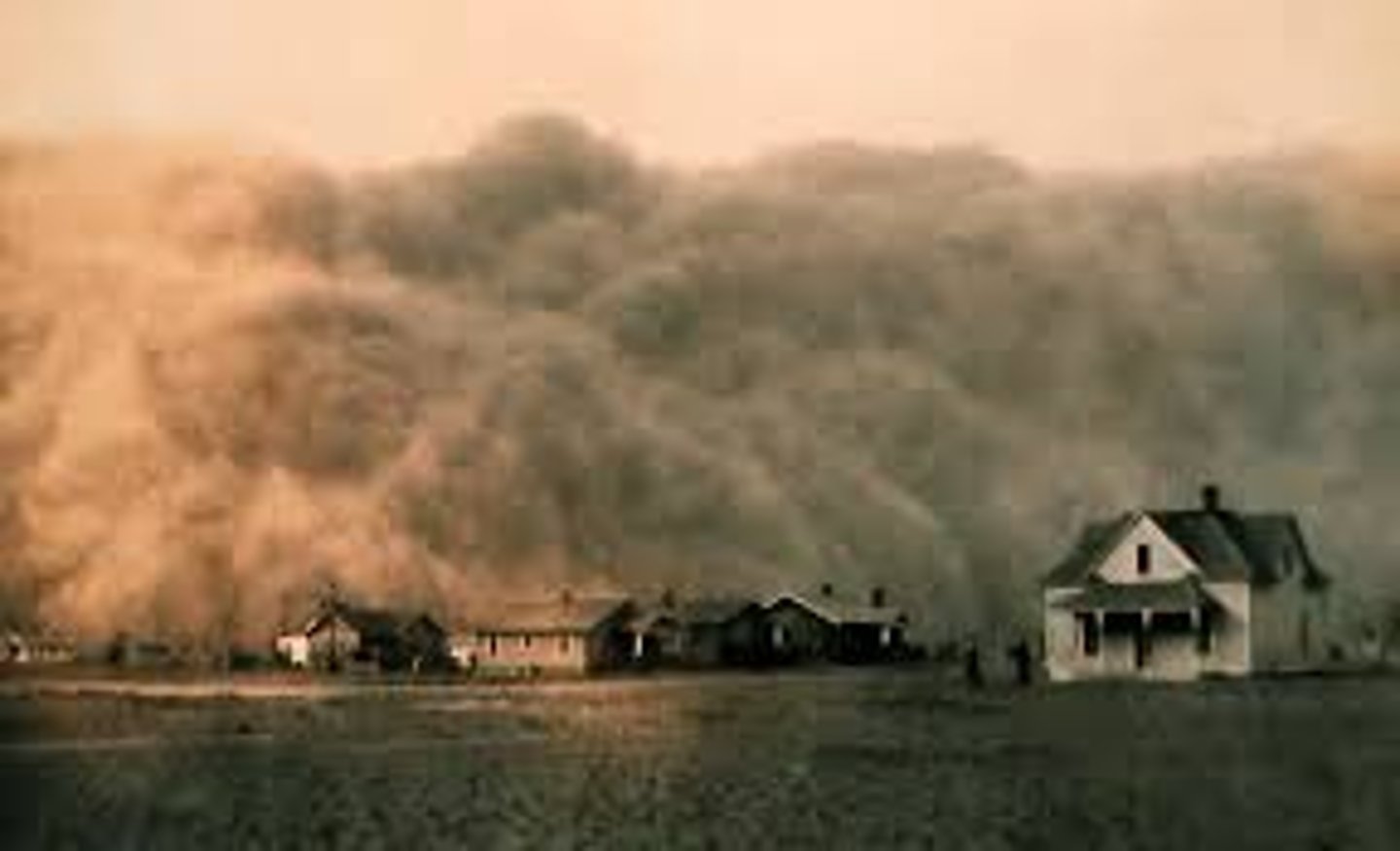
Black Sunday
A day in April 1935 in which massive storms of heavy black dirt swept across the Dust Bowl region, reaching as far as NYC.

Okies
Displaced farm families from the Oklahoma dust bowl who migrated to California during the 1930s in search of jobs.
Boulder Dam
a dam on the Colorado River—now called Hoover Dam—that was built during the Great Depression as part of a public-works program intended to stimulate business and provide jobs.
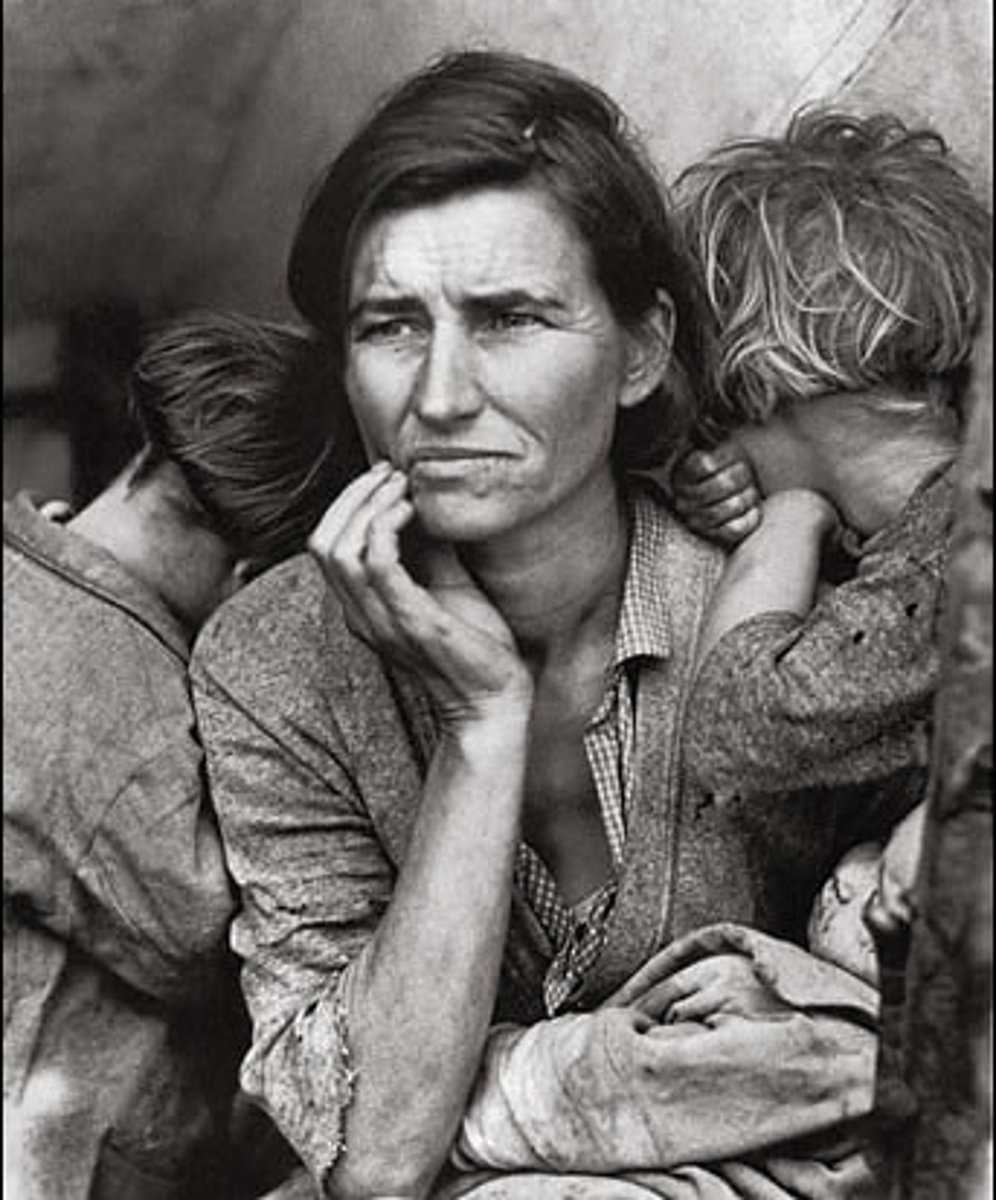
Migrant Mother
famous Dust Bowl image of mother and children taken by Dorothea Lange

"Anti-Okie Law"
Laws passed in California that made it a crime to bring "indigent" people into the state; really meant to prevent Okie migrants from coming to California
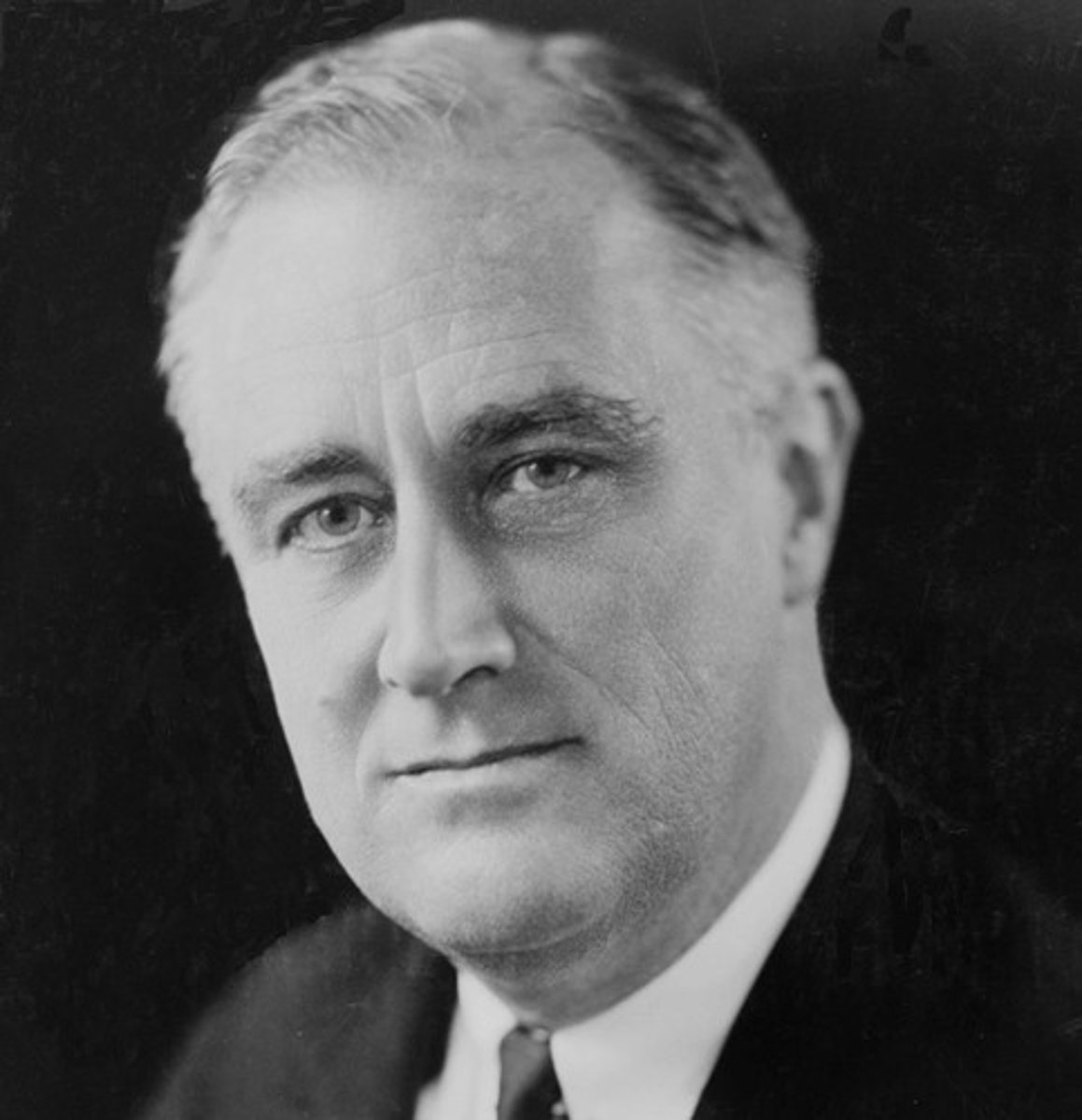
Franklin D. Roosevelt
President of the United States during most of the Depression and most of World War II.

First Hundred Days
This is the term applied to President Roosevelt's first three months in taking office. During this time, FDR had managed to get Congress to pass an unprecedented amount of new legislation that would revolutionize the role of the federal government from that point on.
Bank holiday
FDR closed all banks until government examiners could investigate their financial condition; only sound/solvent banks were allowed to reopen
Emergency Banking Relief Act
Gave the President power over the banking system and set up a system by which banks would be reorganized or reopened
Fireside chat
informal radio broadcast in which FDR explained issues and New Deal programs to average Americans
New Deal
A series of reforms enacted by the Franklin Roosevelt administration between 1933 and 1942 with the goal of ending the Great Depression.
Relief, recovery, reform
Three components of FDR's New Deal. Sought to provide immediate (though temporary) financial assistance, stimulate the economy through job growth, and allow greater government intervention to prevent future economic crises.
Keynesian economics
Theory based on the principles of John Maynard Keynes, stating that government spending should increase during business slumps and be curbed during booms.
Good Neighbor Policy
FDR's foreign policy of promoting better relations with Latin America by using economic influence rater than military force in the region
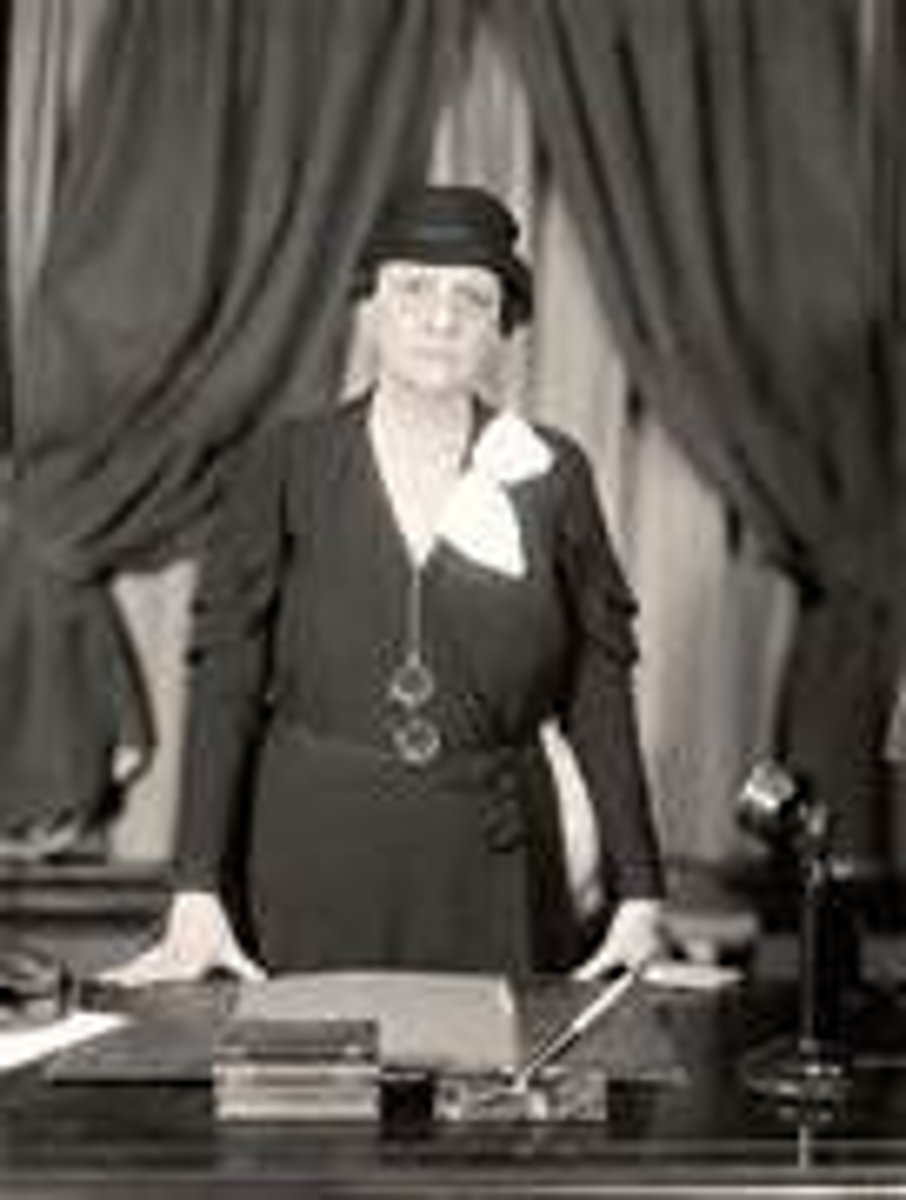
Frances Perkins
U.S. Secretary of Labor from 1933 to 1945, and the first woman ever appointed to the cabinet.

21st Amendment
Amendment which ended the Prohibition of alcohol in the US, repealing the 18th amendment
American Liberty League
A conservative anti-New Deal organization; criticized the "socialistic" policies of Roosevelt and what it perceived to be his attacks on the free enterprise system.
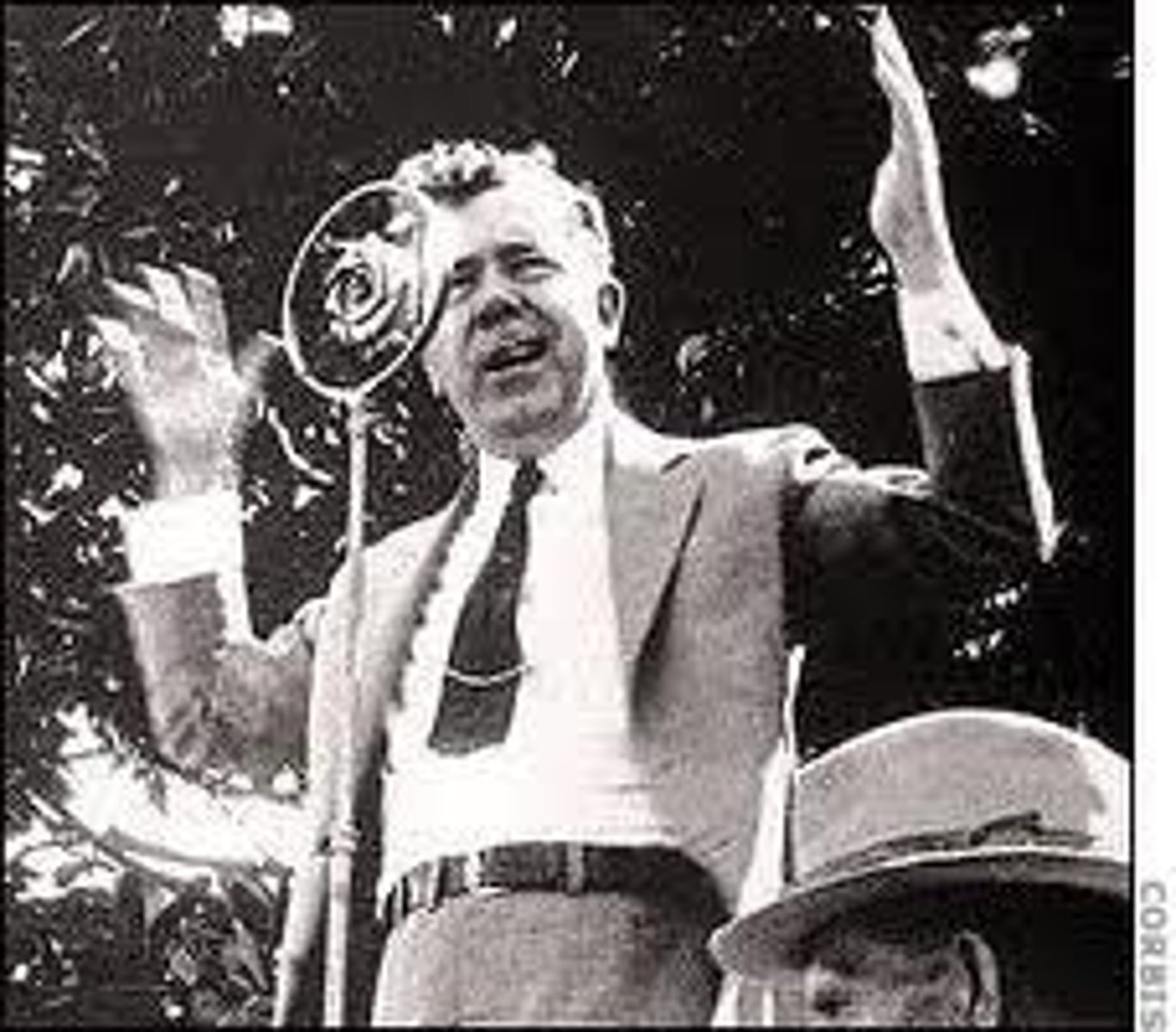
Huey P. Long
U.S. Senator known for his "Share Our Wealth" program that aimed to redistribute the nation's wealth and provide more direct aid to the nation's poor.

Schechter v. United States
SCOTUS declared the NRA/NIRA unconstitutional by stating that the President was regulating interstate commerce (a violation of the Constitution).
Court Packing Scheme
FDR's plan to "pack" the Supreme Court with supporters to keep his New Deal programs from being declared unconstitutional; failed.
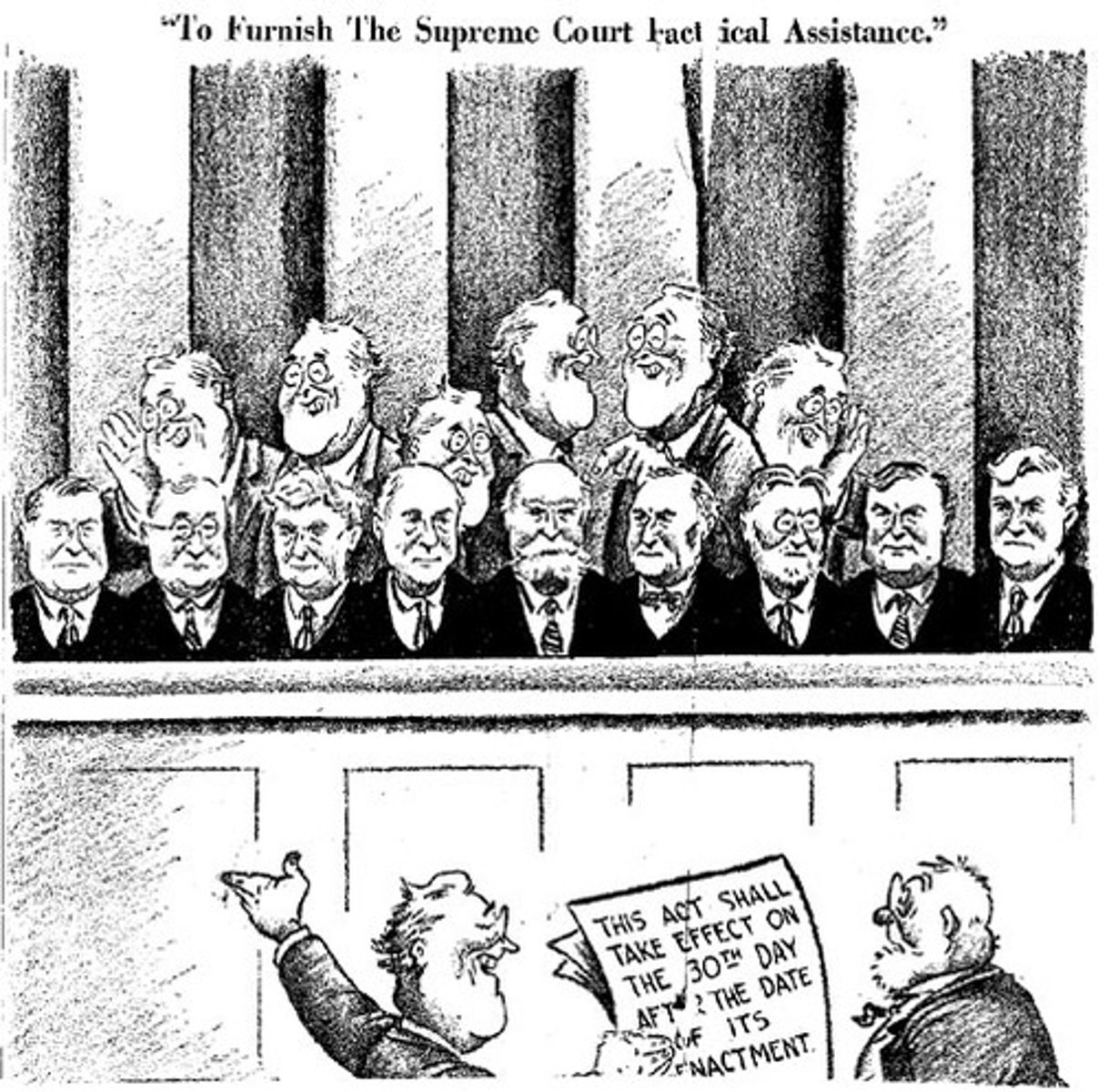
Roosevelt Recession
This terms refers to the period when FDR cut government spending to balance budget; this led to a recession
Wagner Act
Established National Labor Relations Board; protected the rights of workers unionize, to engage in collective bargaining, and to take part in strikes.