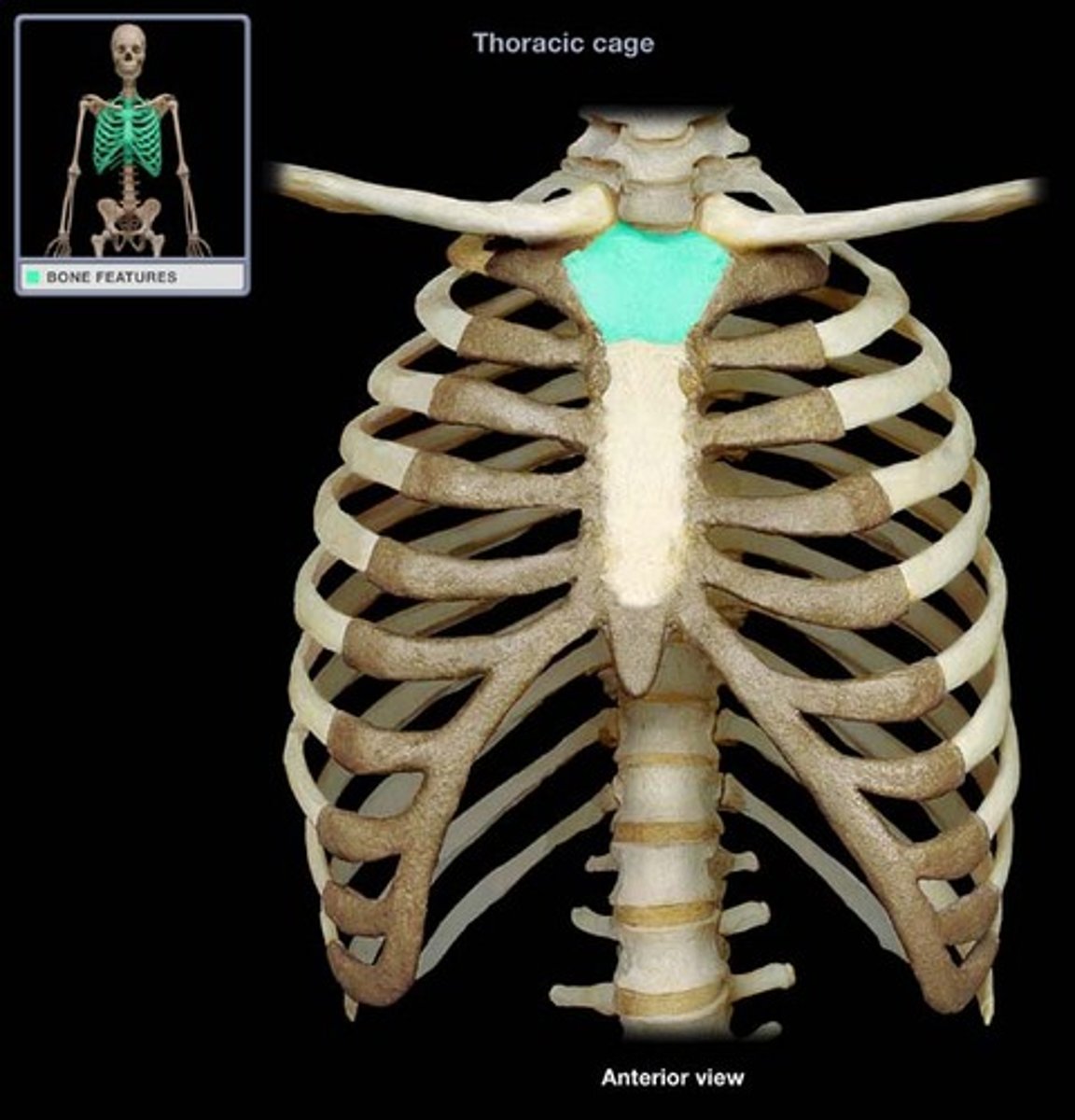
Anatomy Practical 1
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
209 Terms
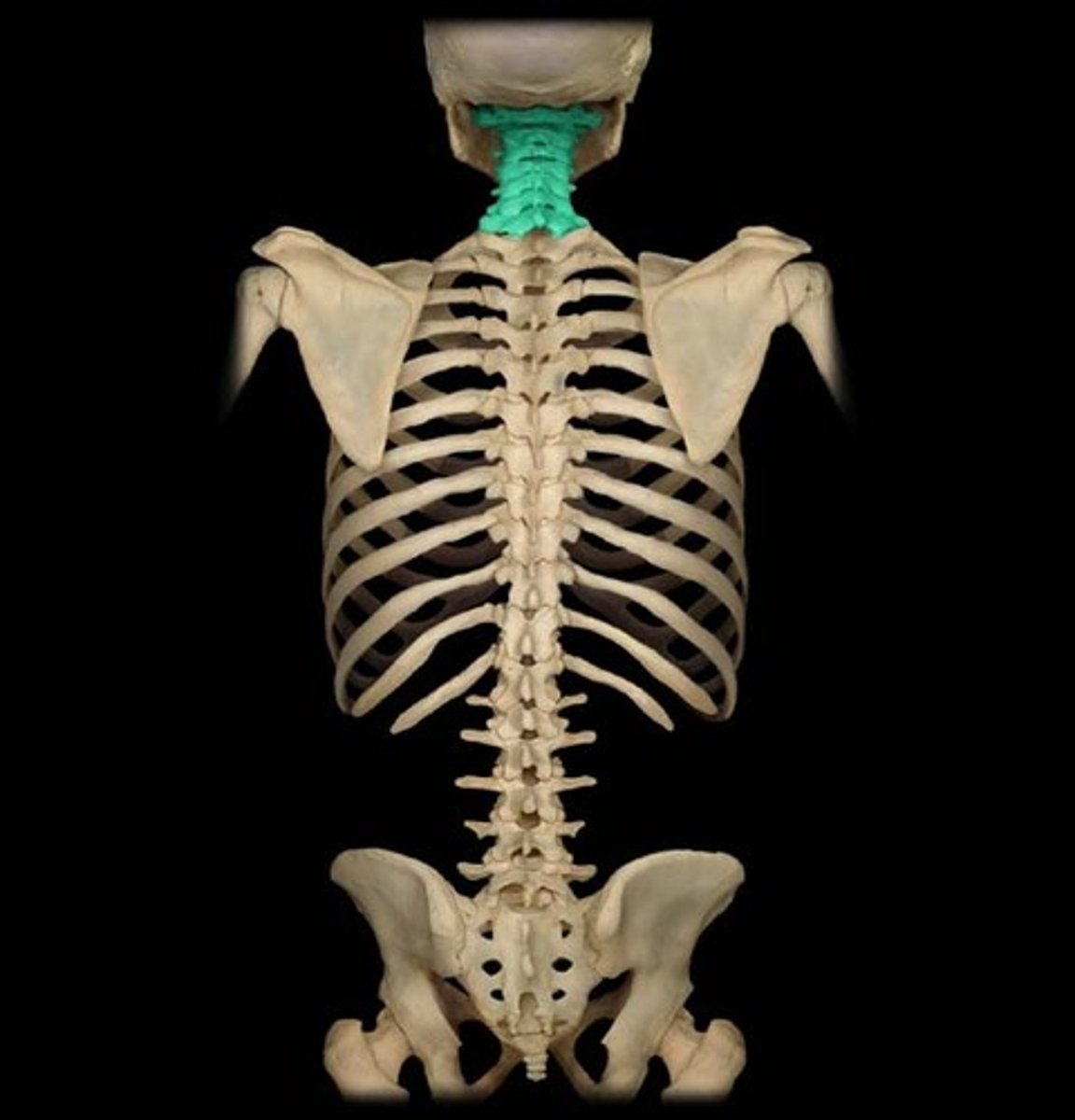
Cervical vertebrae (C1-C7)
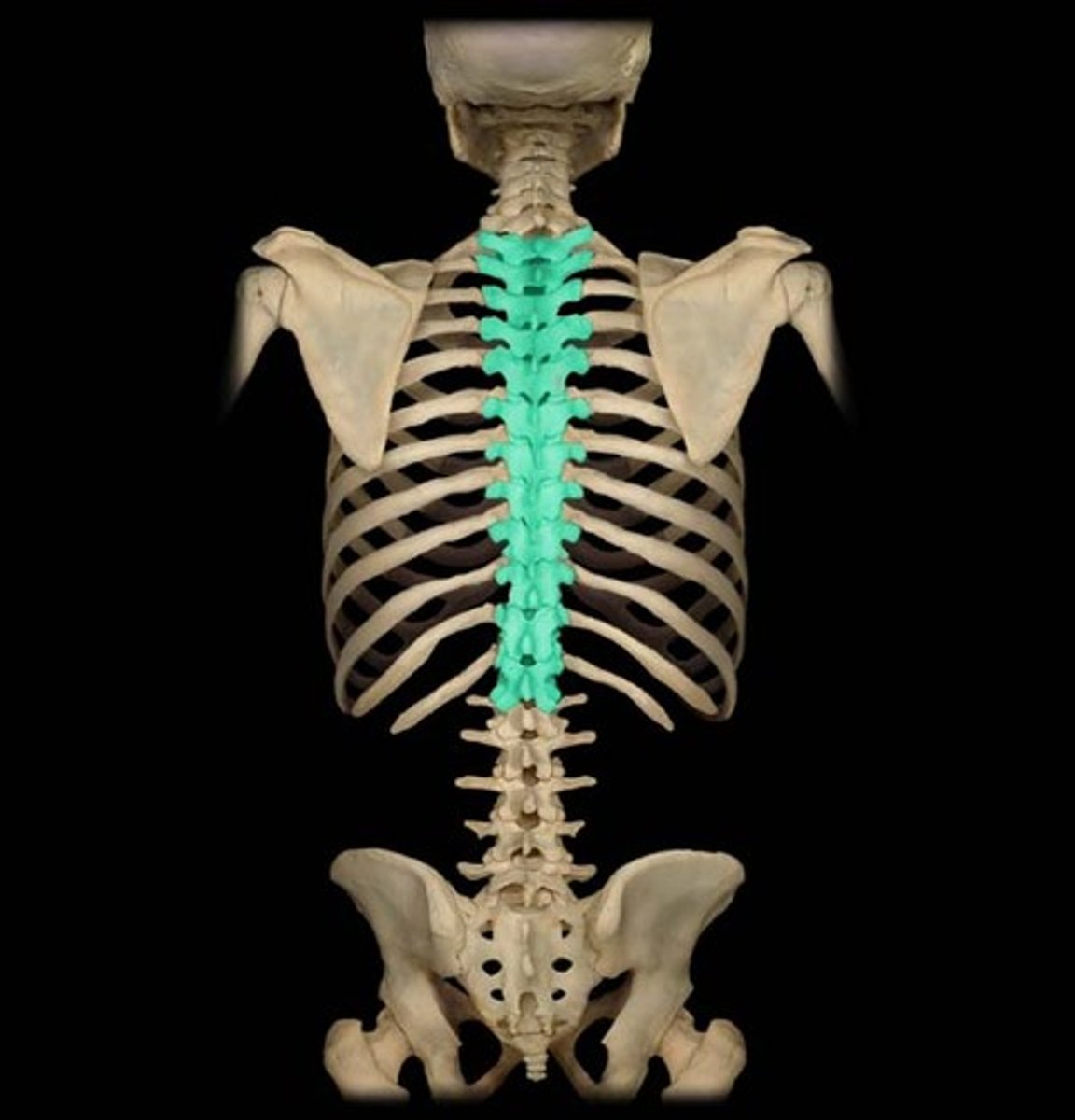
Thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12)
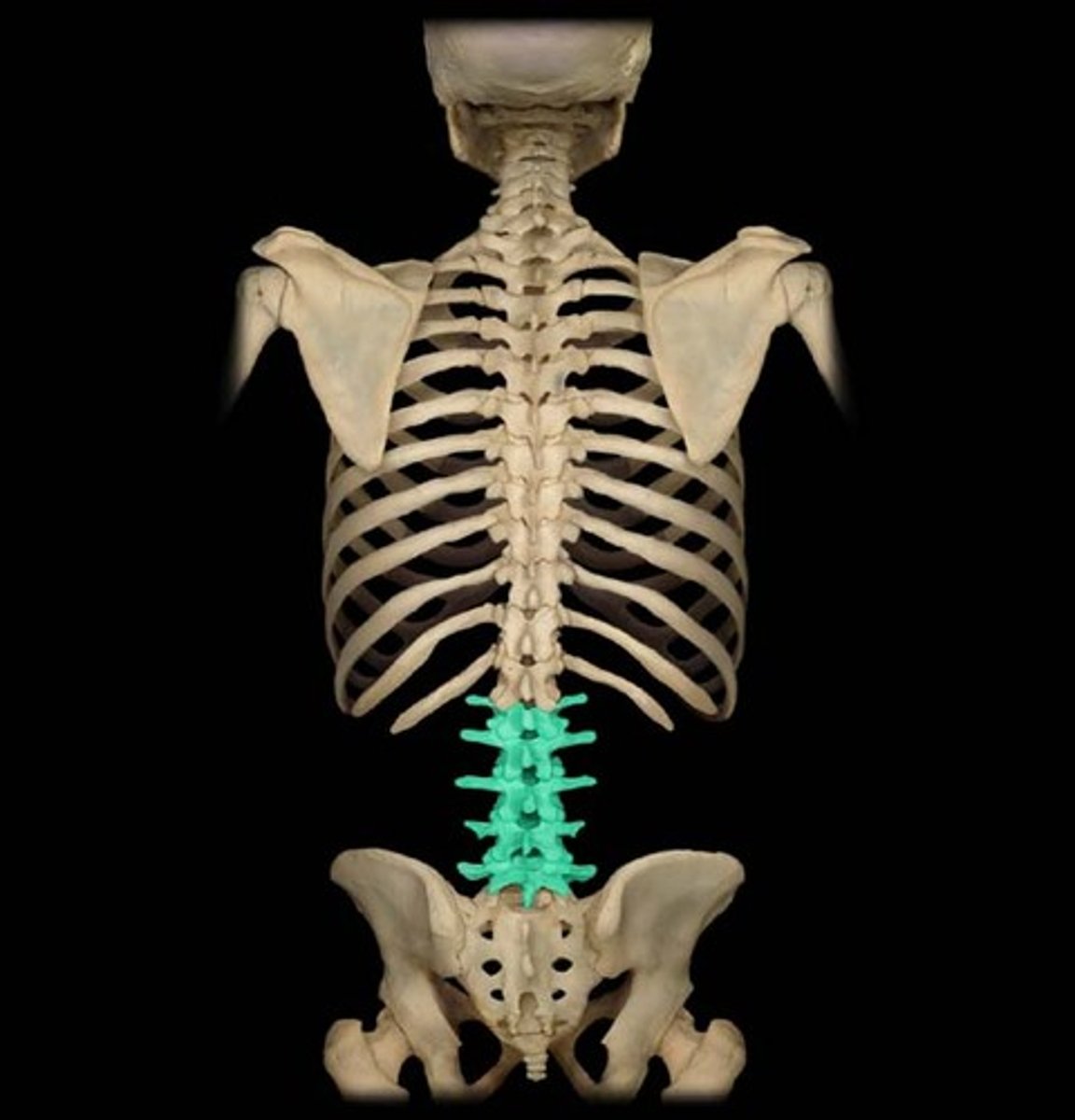
Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L5)
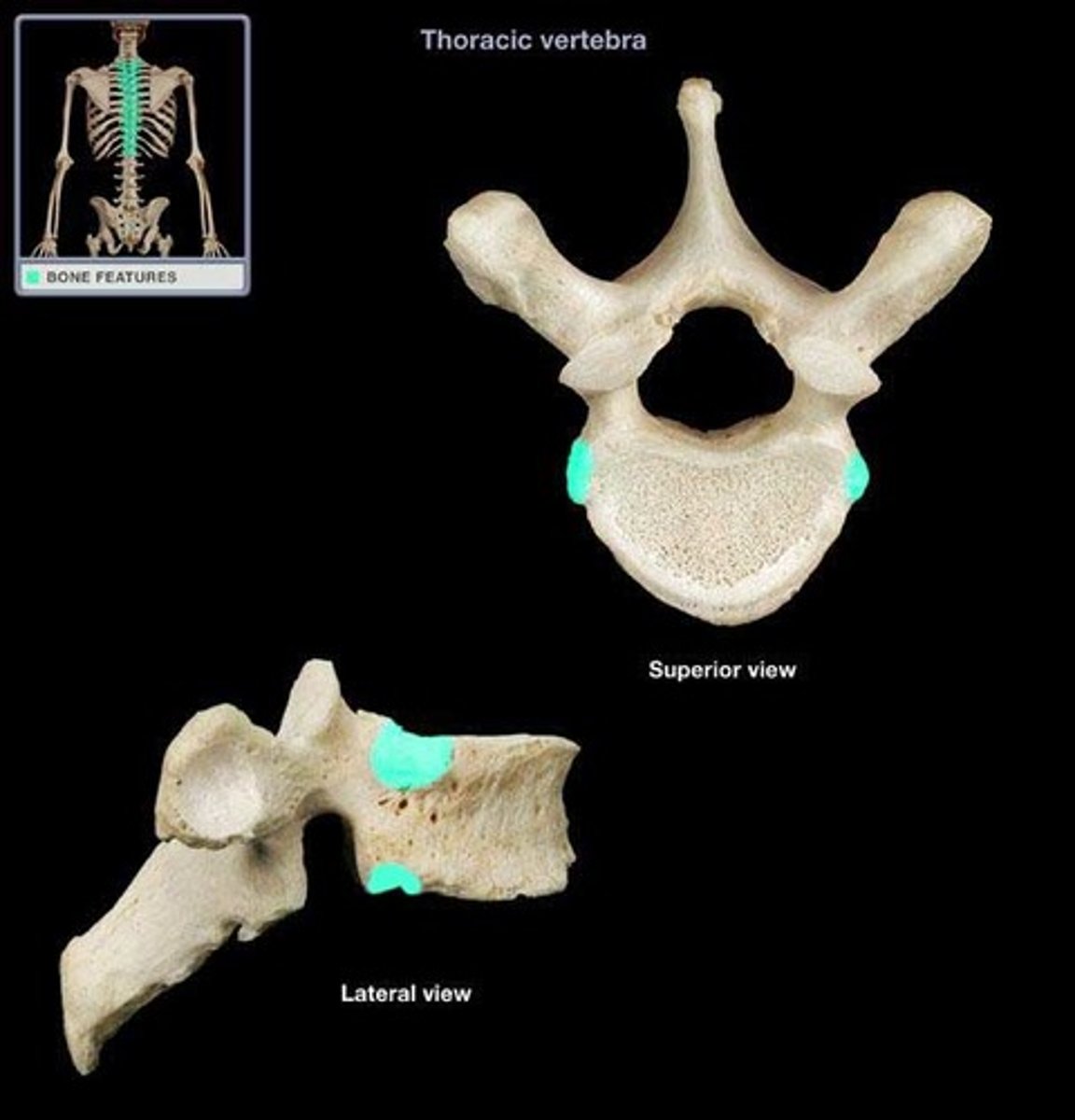
thoracic
- long inferiorly positioned spinous process
- has costal facets
- long transverse processes
What type of vertebra is this?
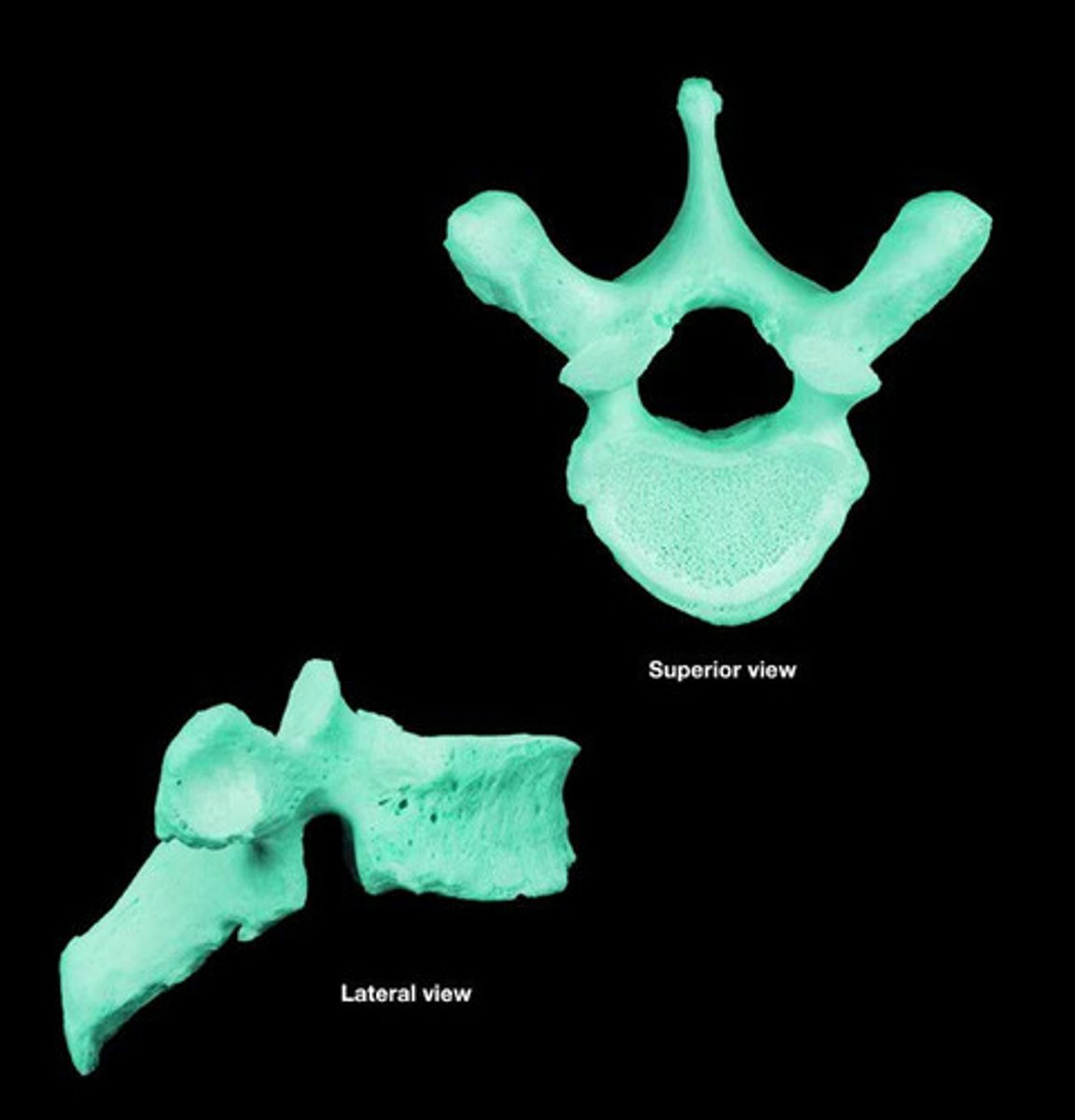
lumbar
- large vertebra body
- short, wide spinous process
What type of vertebra is this?
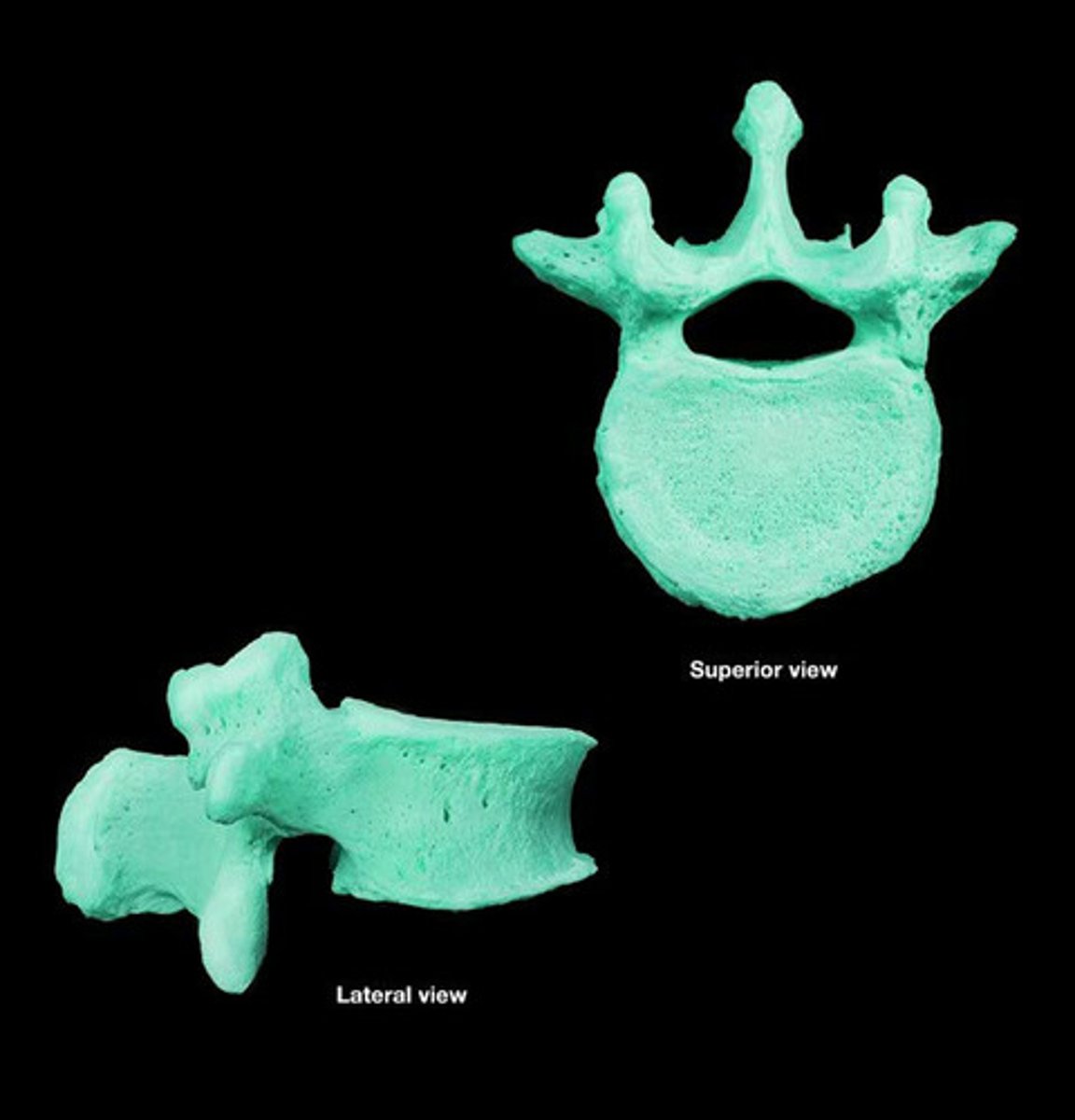
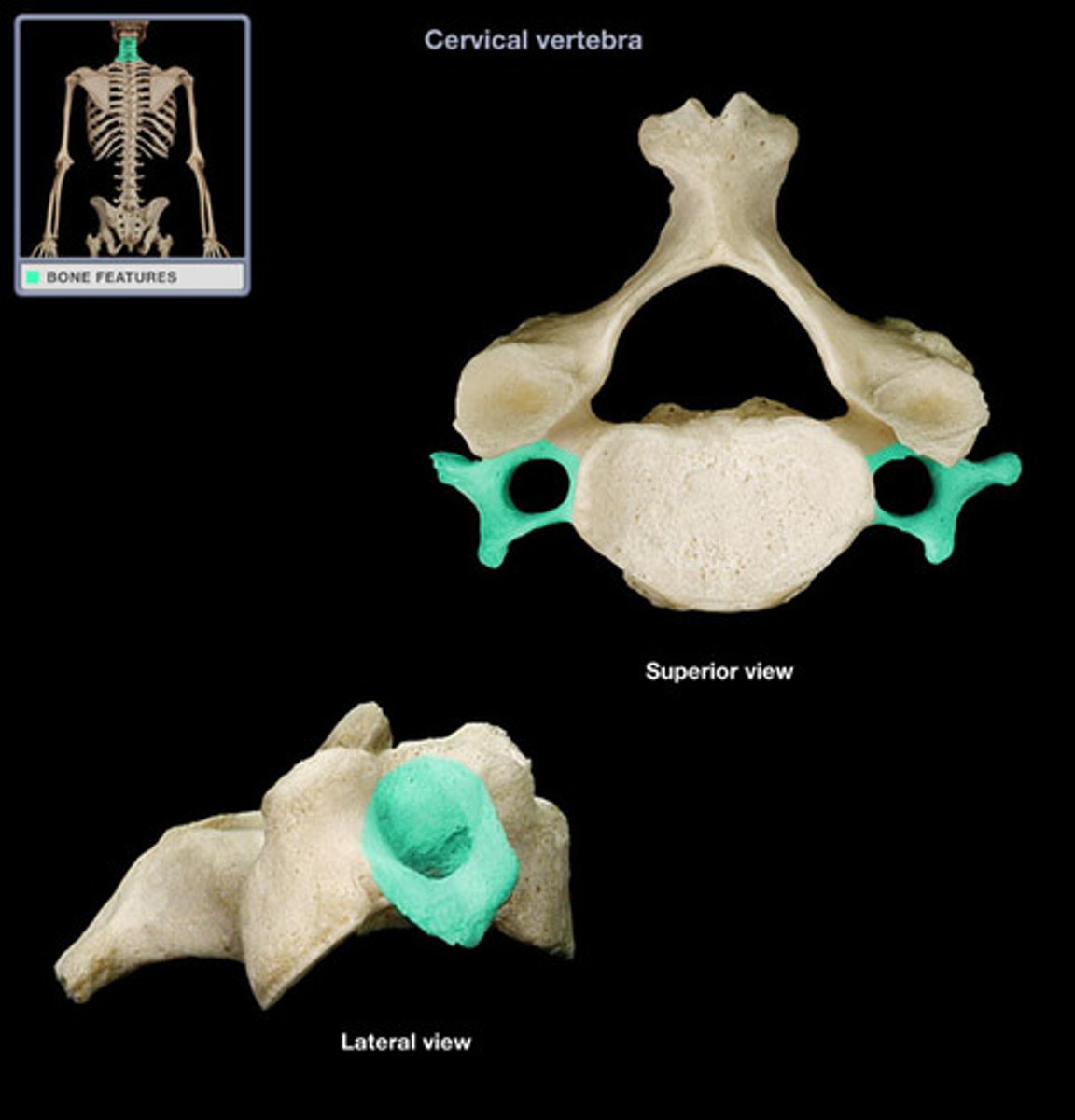
cervical
- has transverse foramen
- bifid spinous process
What type of vertebra is this?
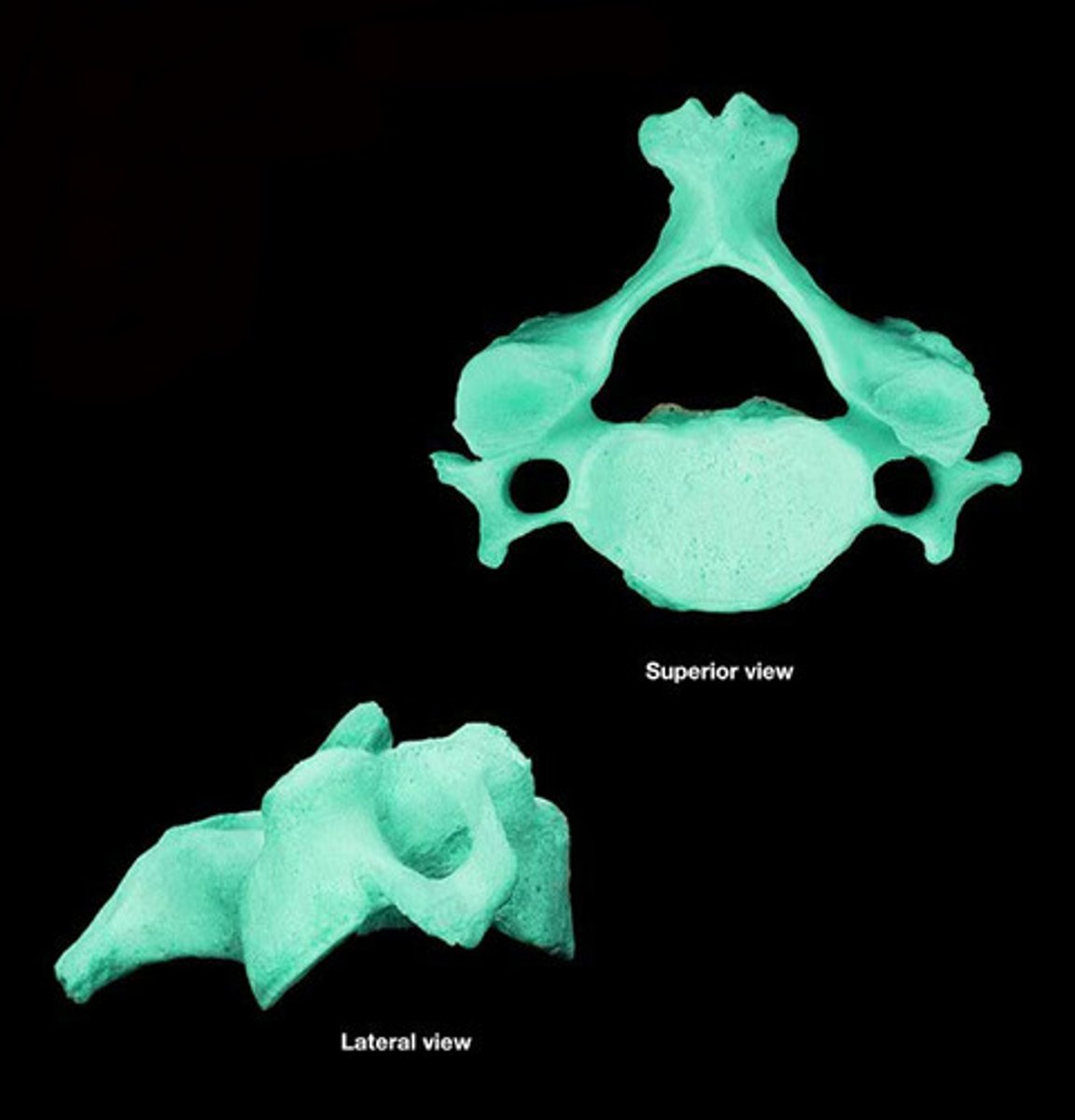
Atlas (C1)
- no vertebral body or spinous process
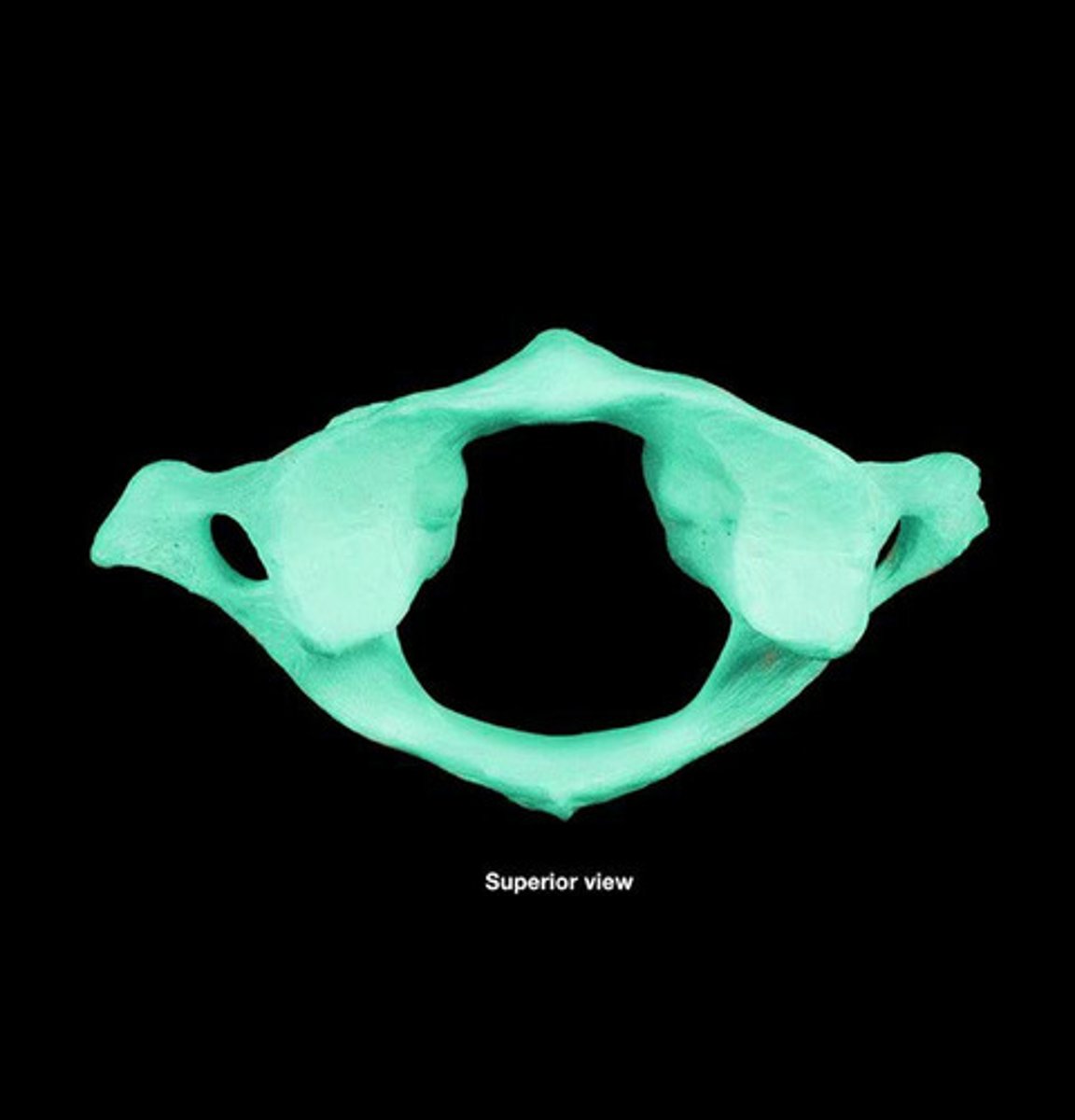
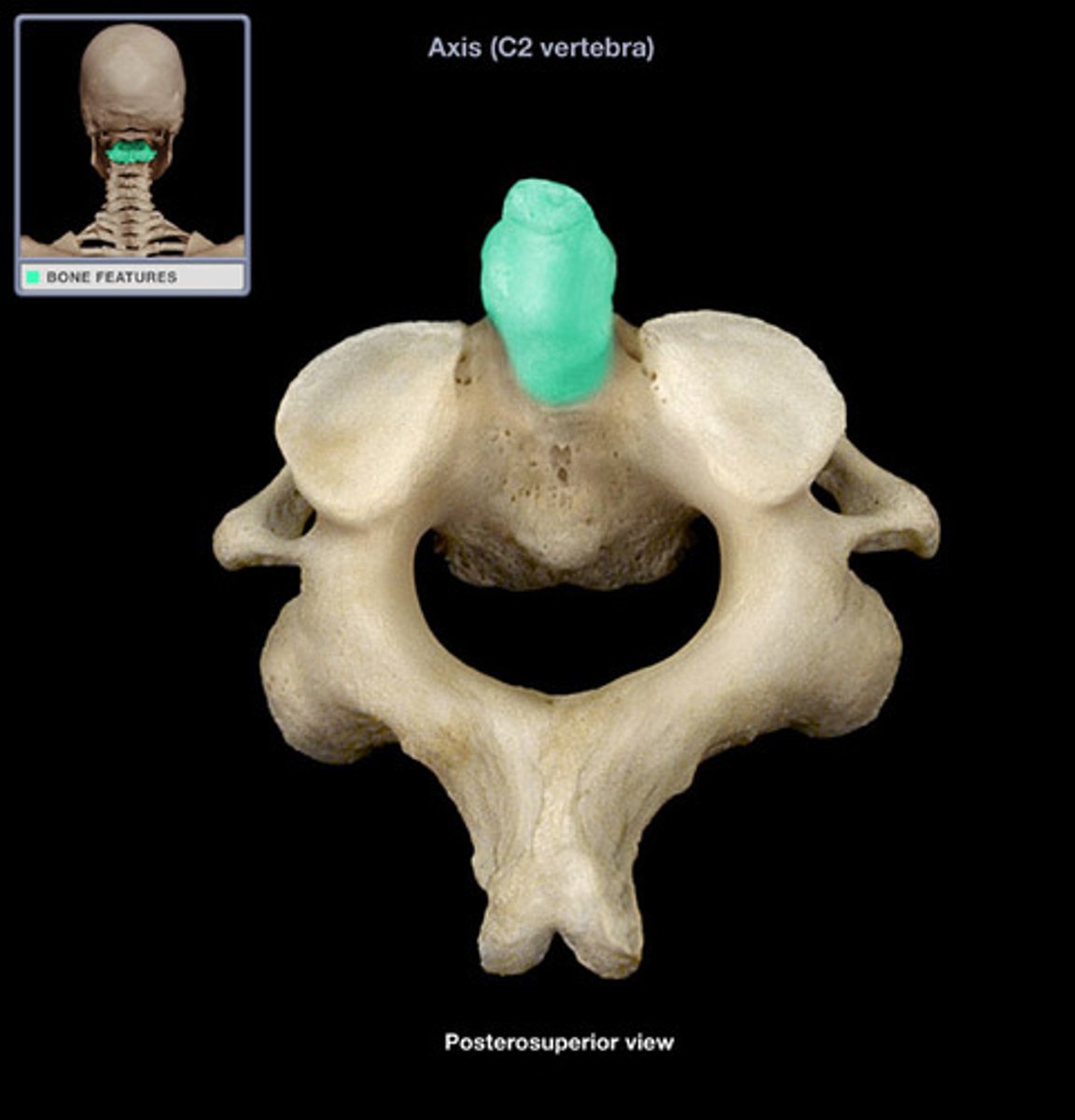
odontoid process (dens) on Axis (C2)
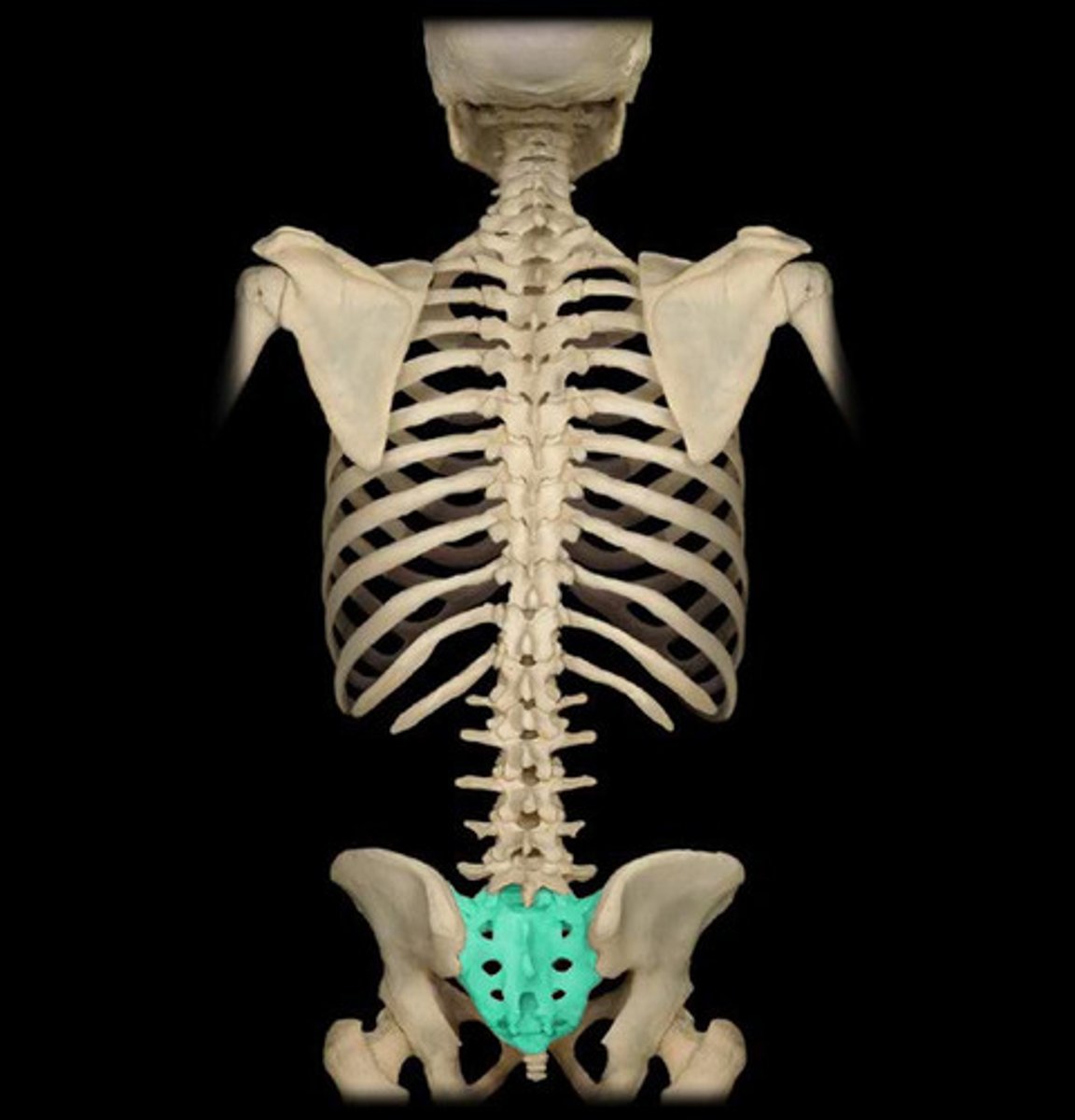
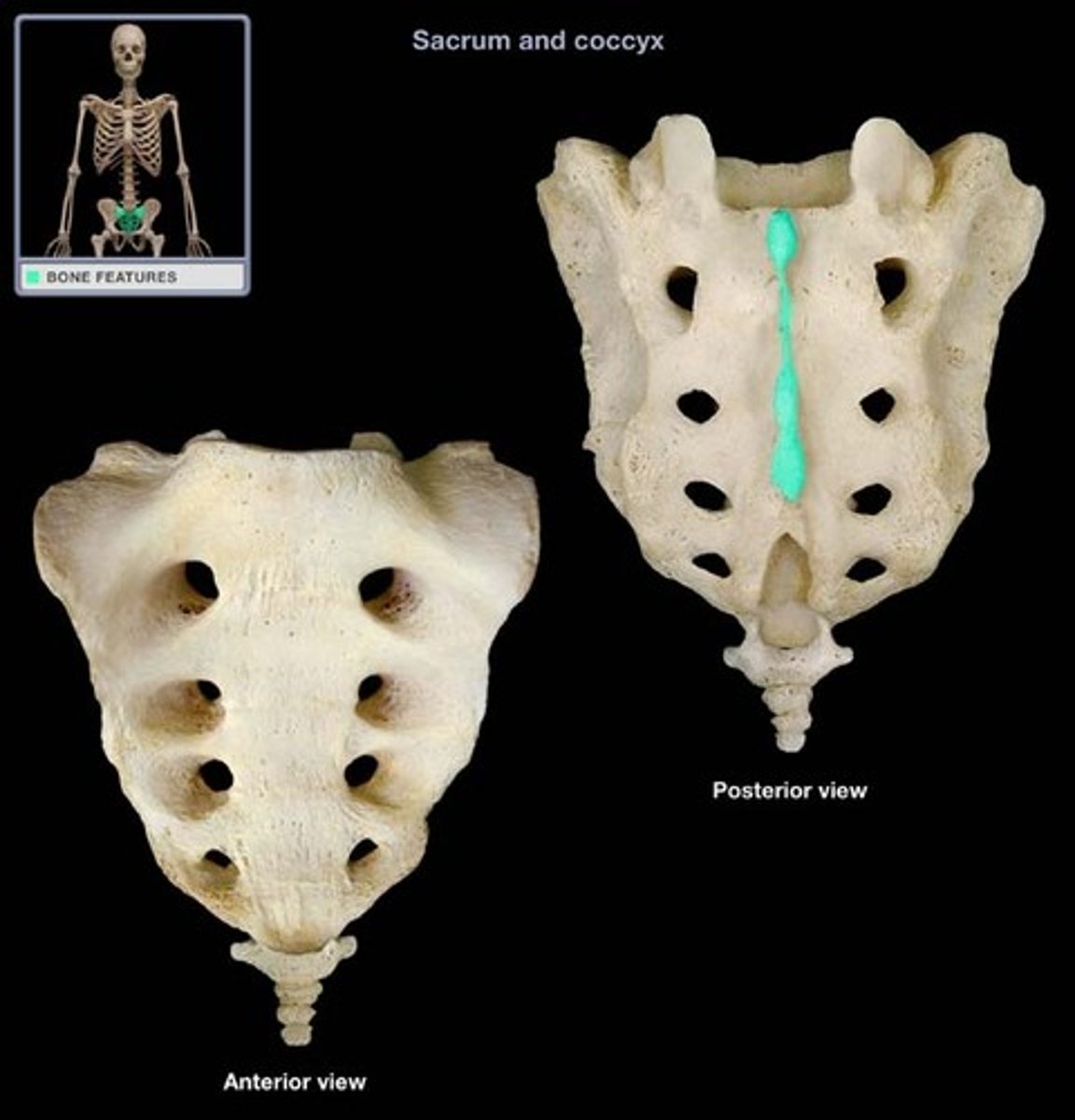
sacrum (5 fused vertebrae)
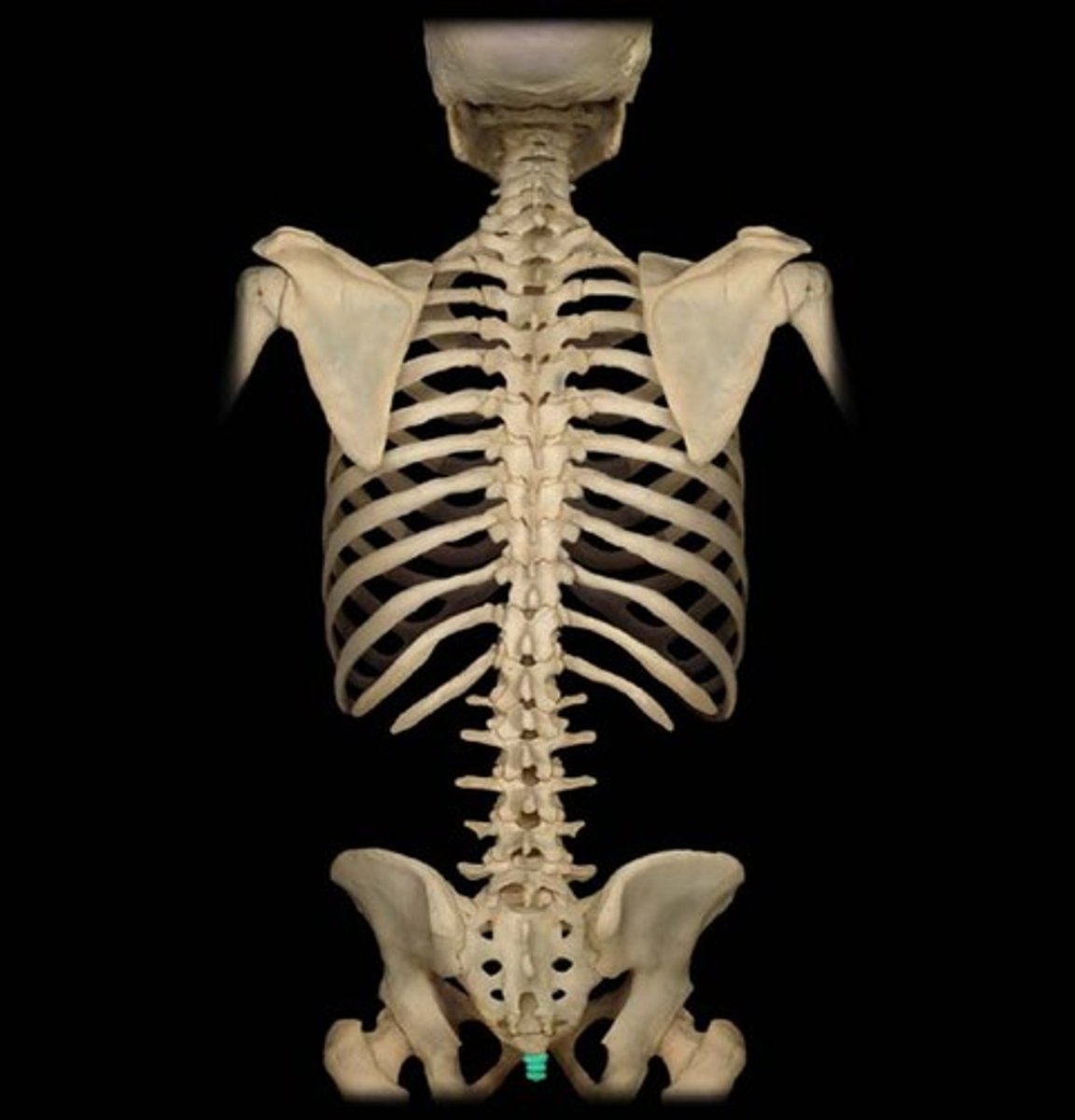
Coccyx (3-5 fused vertebrae)
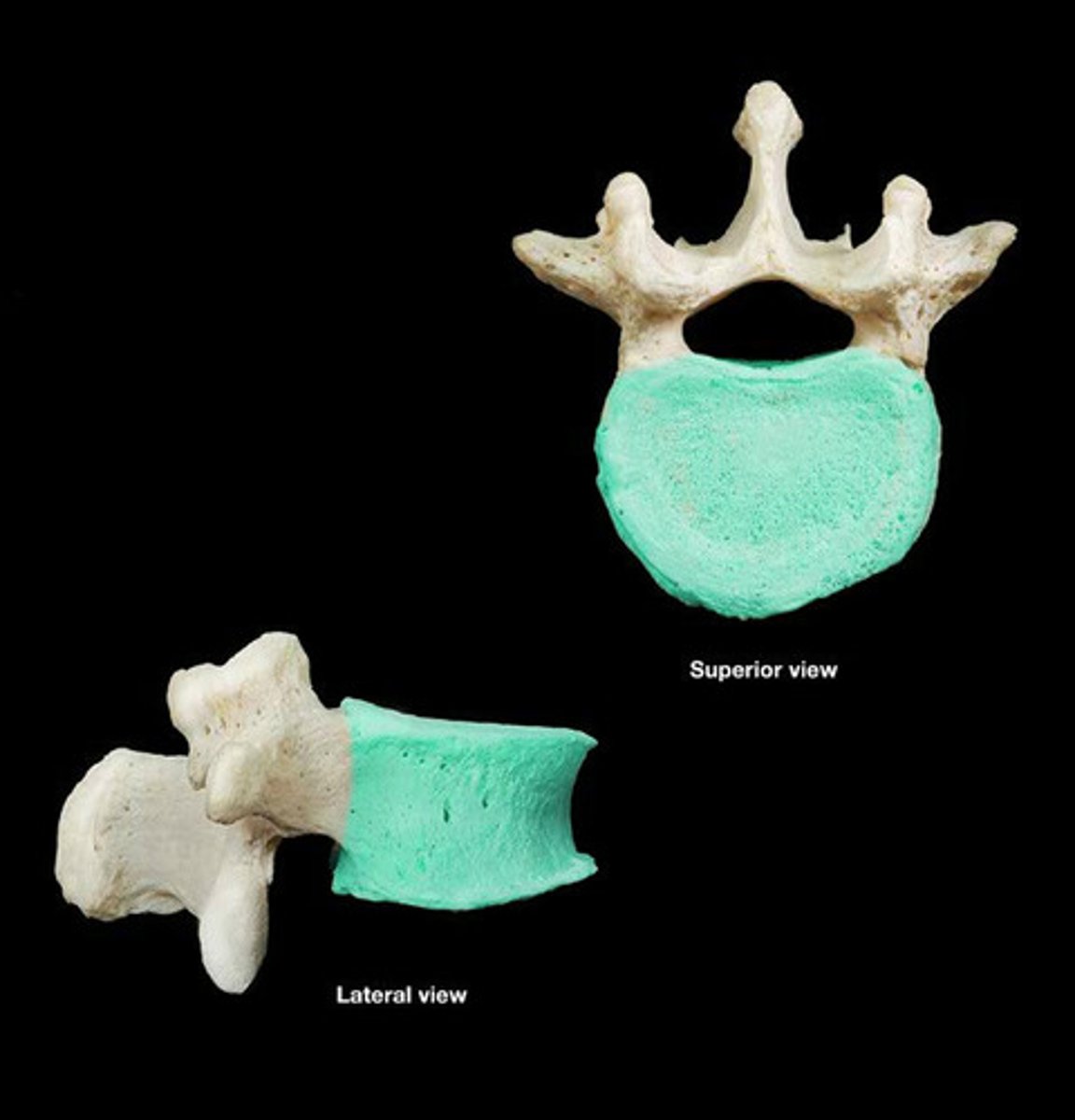
vertebral body
vertebral arch (formed by pedicles and laminae)
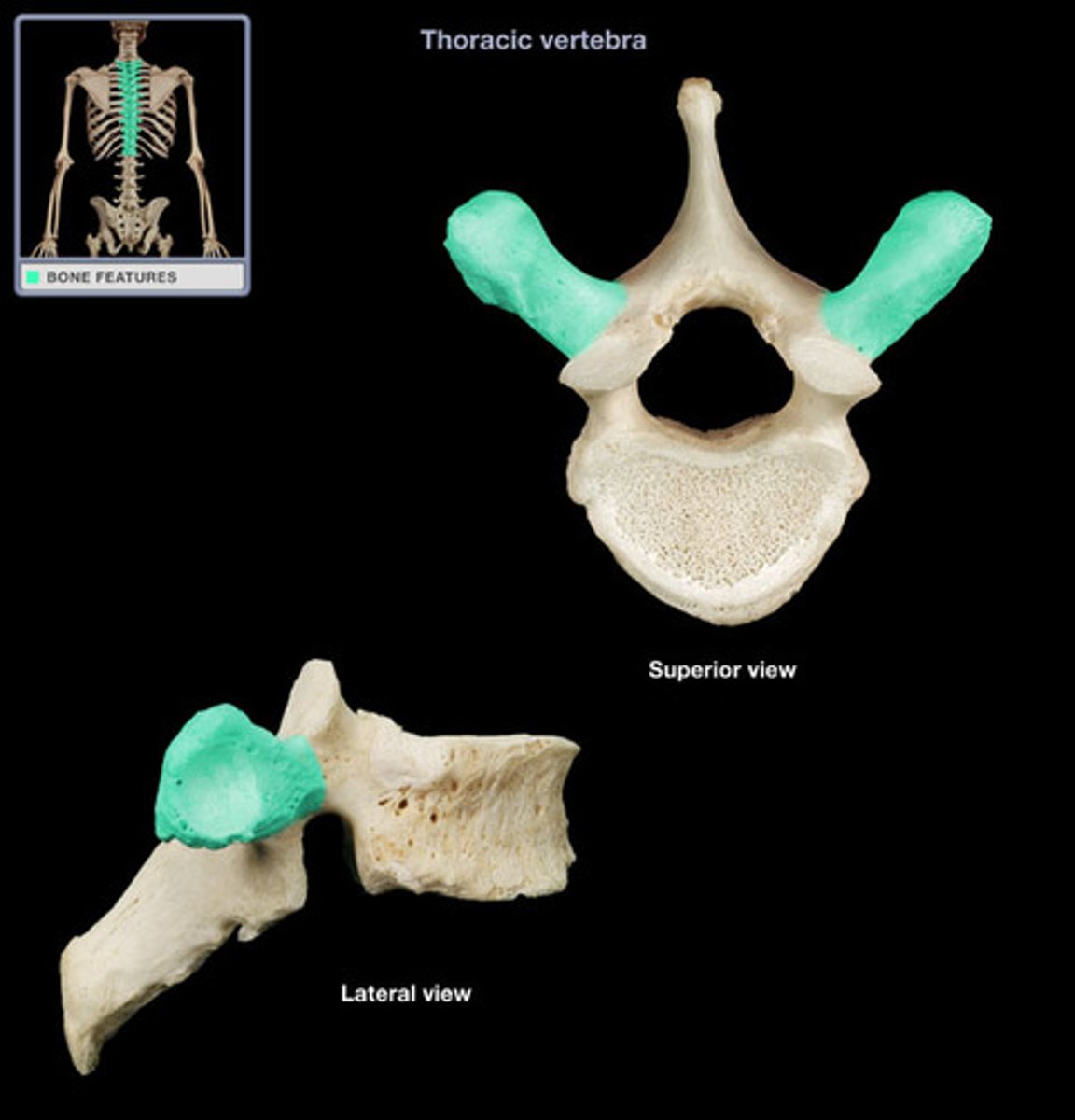
transverse processes
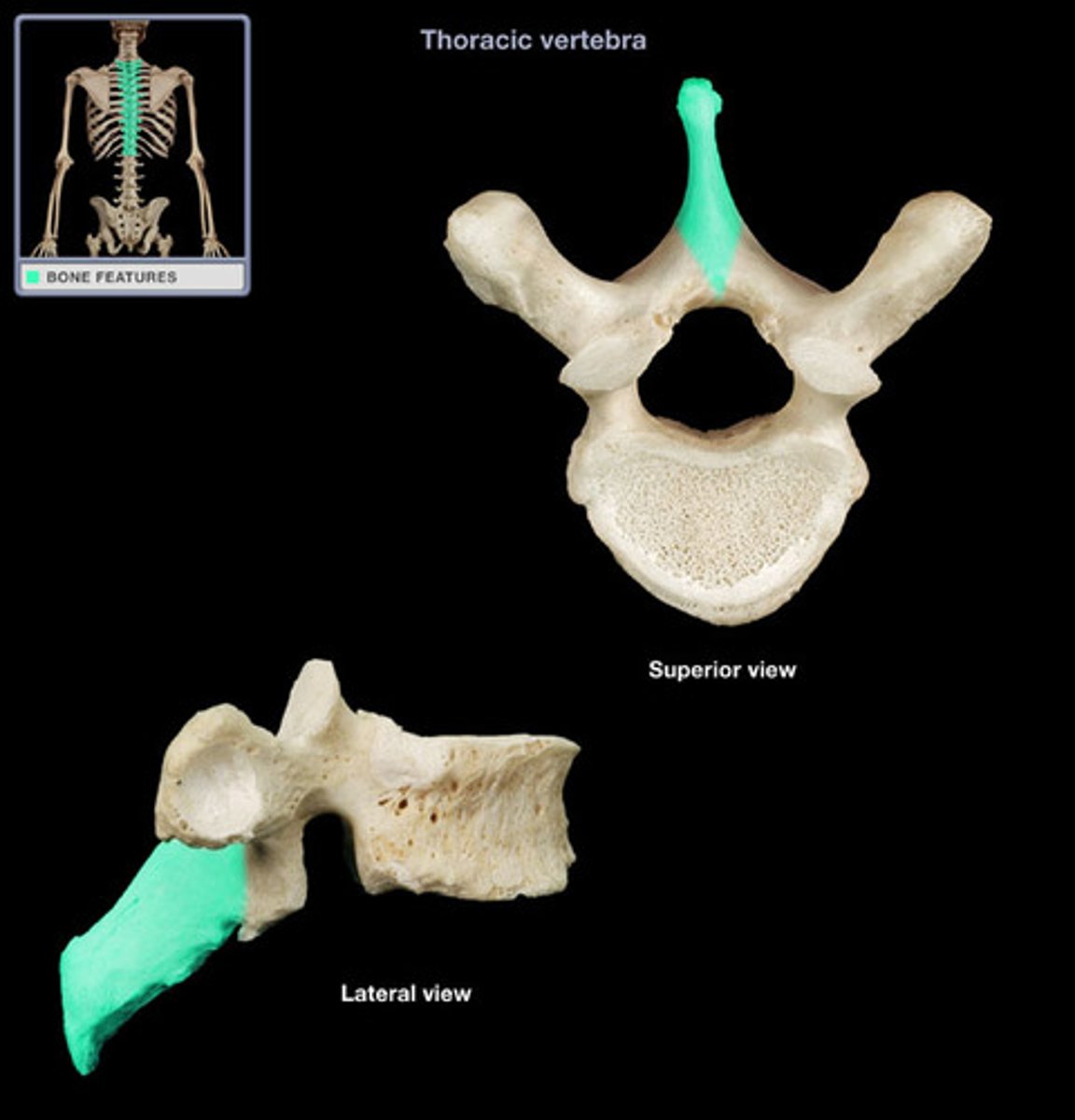
spinous process
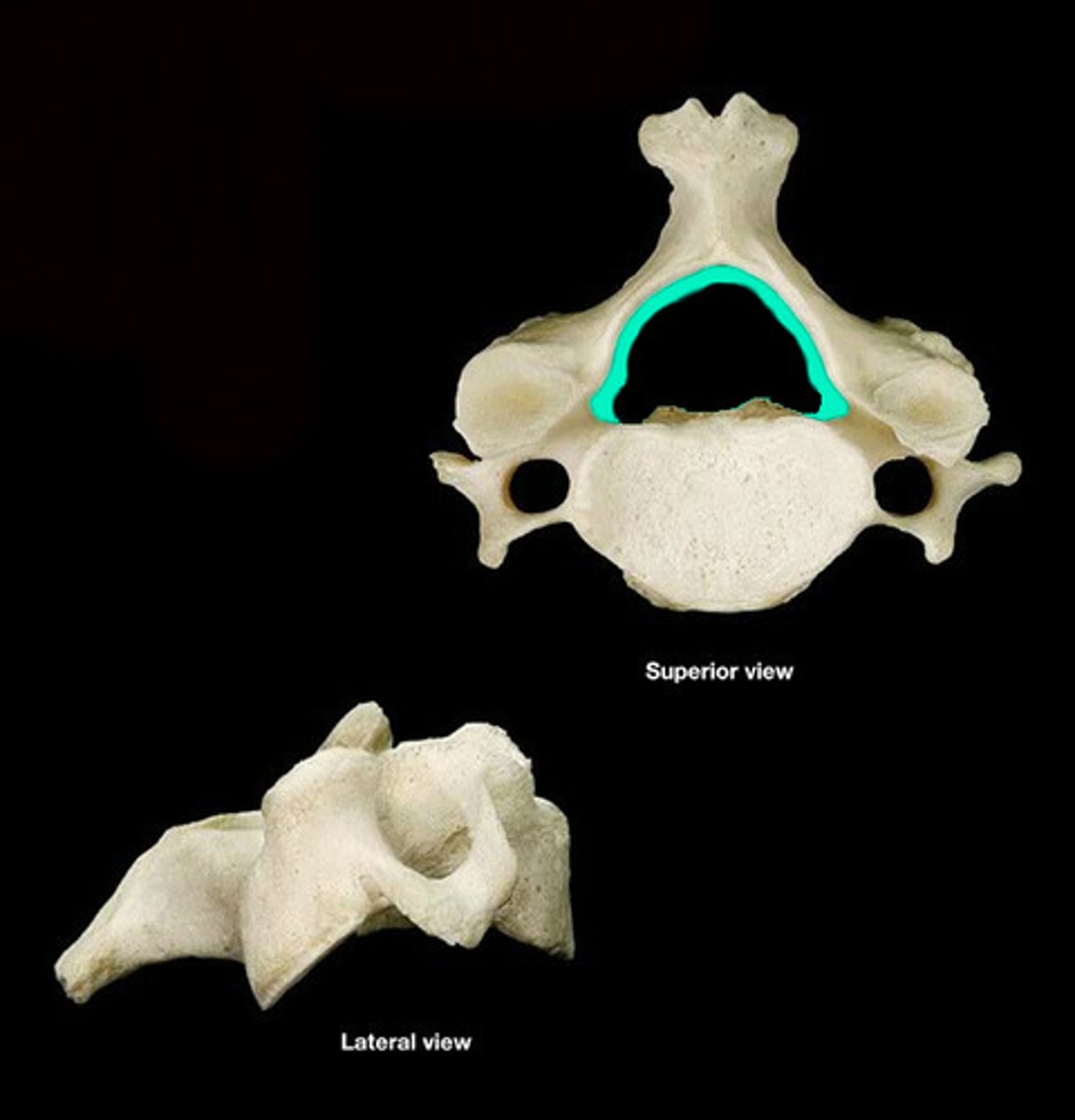
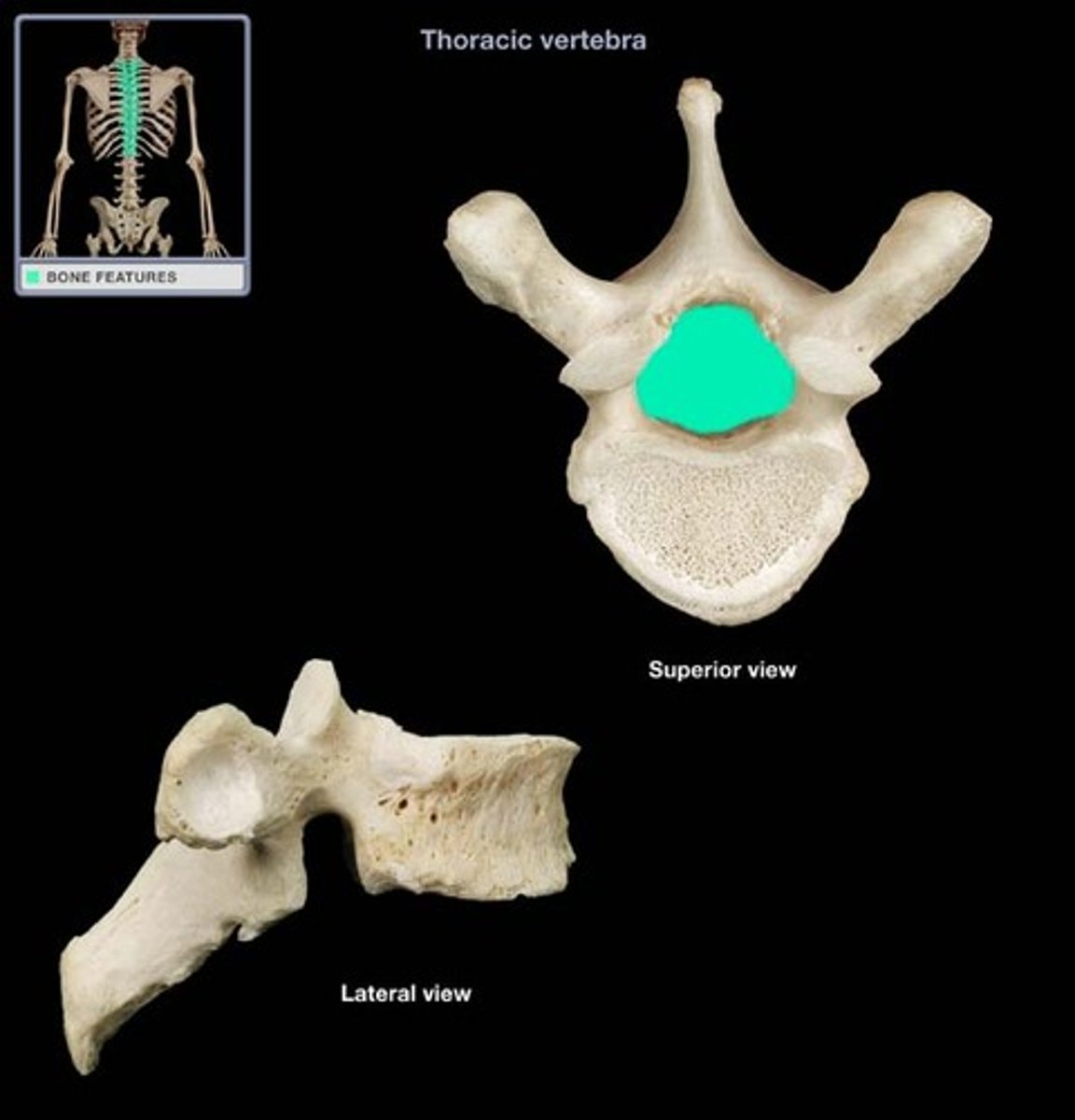
vertebral neural foramen
- holds the spinal cord
transverse foramen (cervical vertebrae only)
- holds vertebral arteries
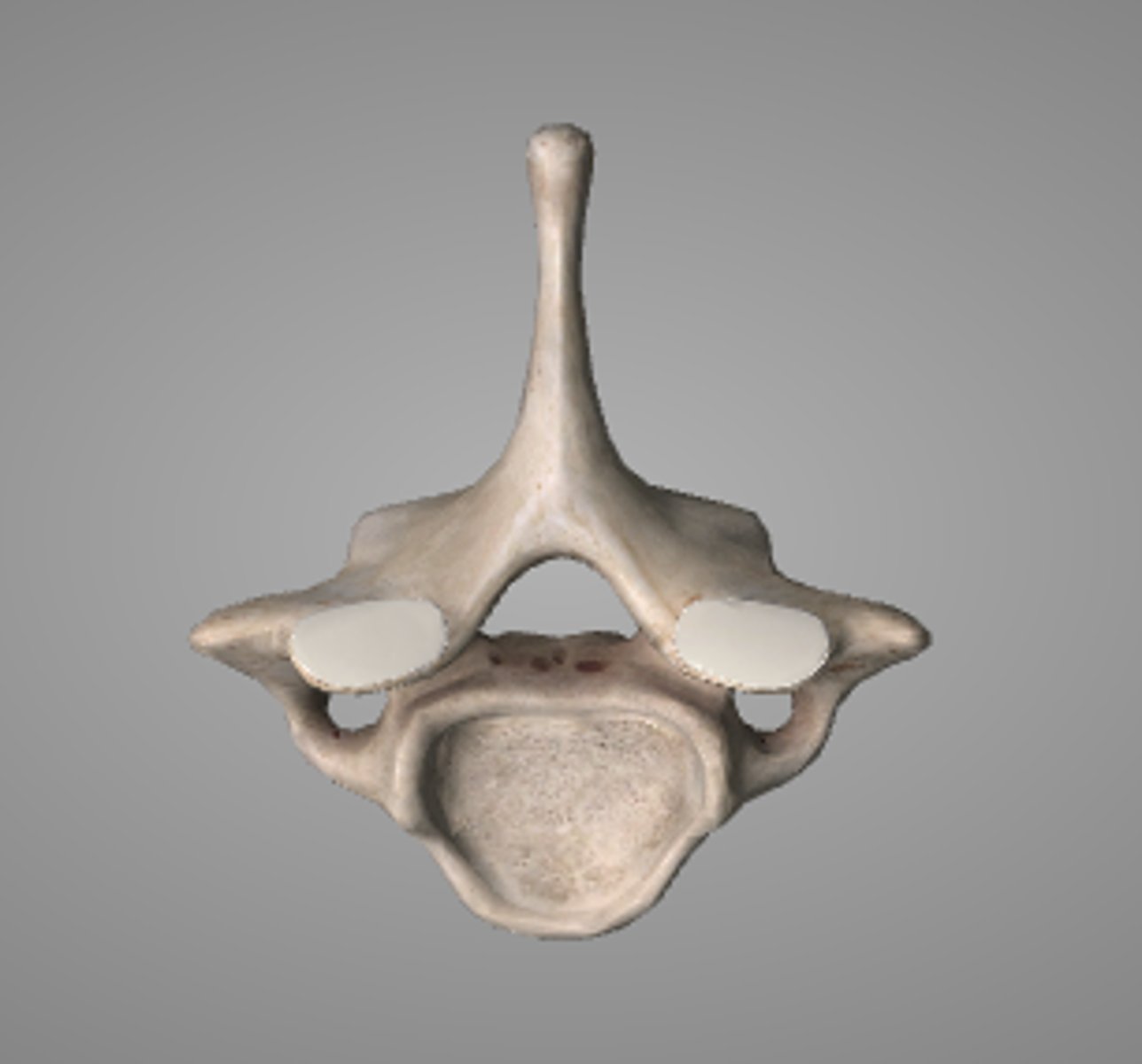
Vertebra prominens (C7)
- spinous process is NOT forked
- transverse foramen so still cervical
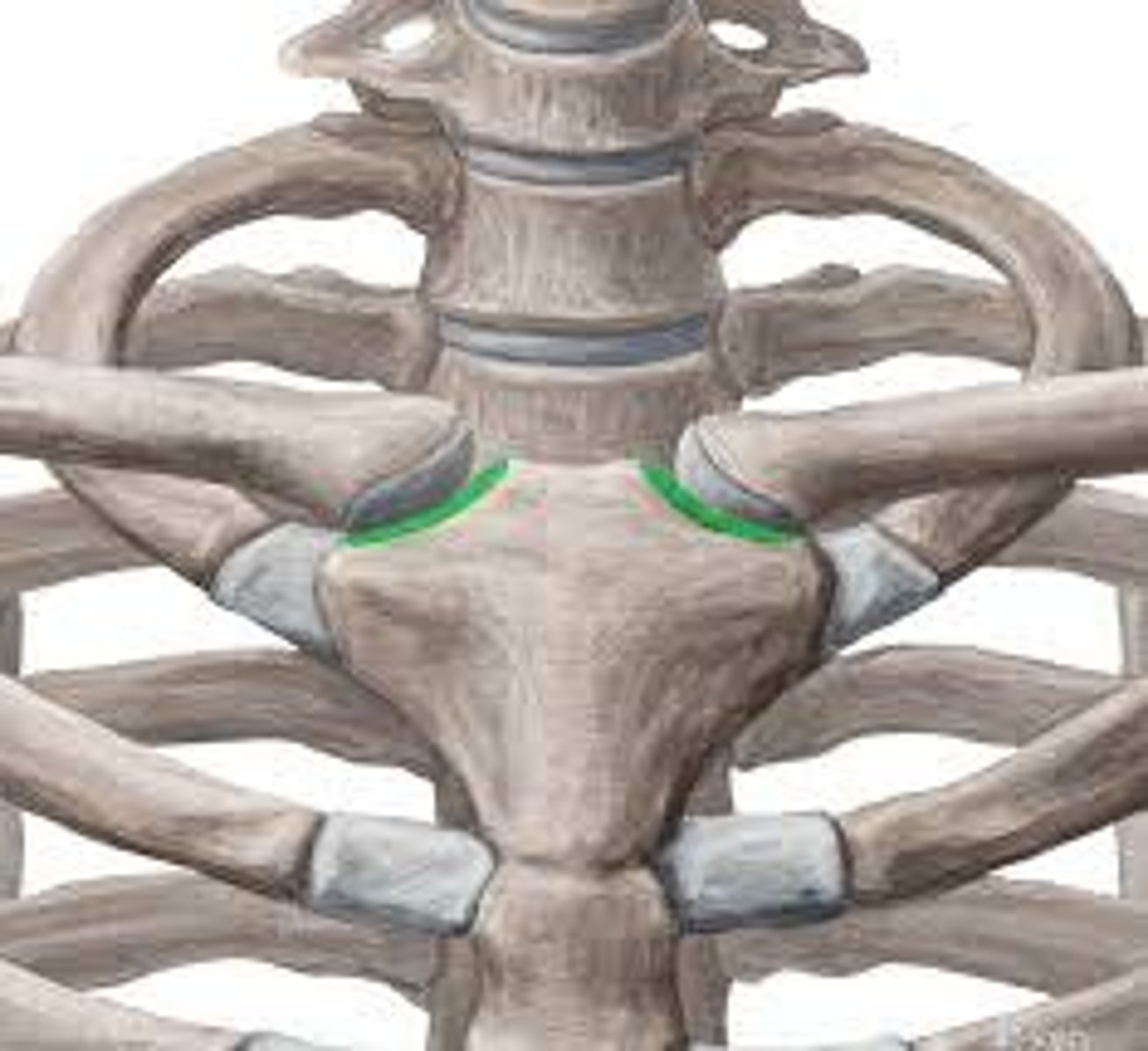
superior and inferior costal facets (thoracic)
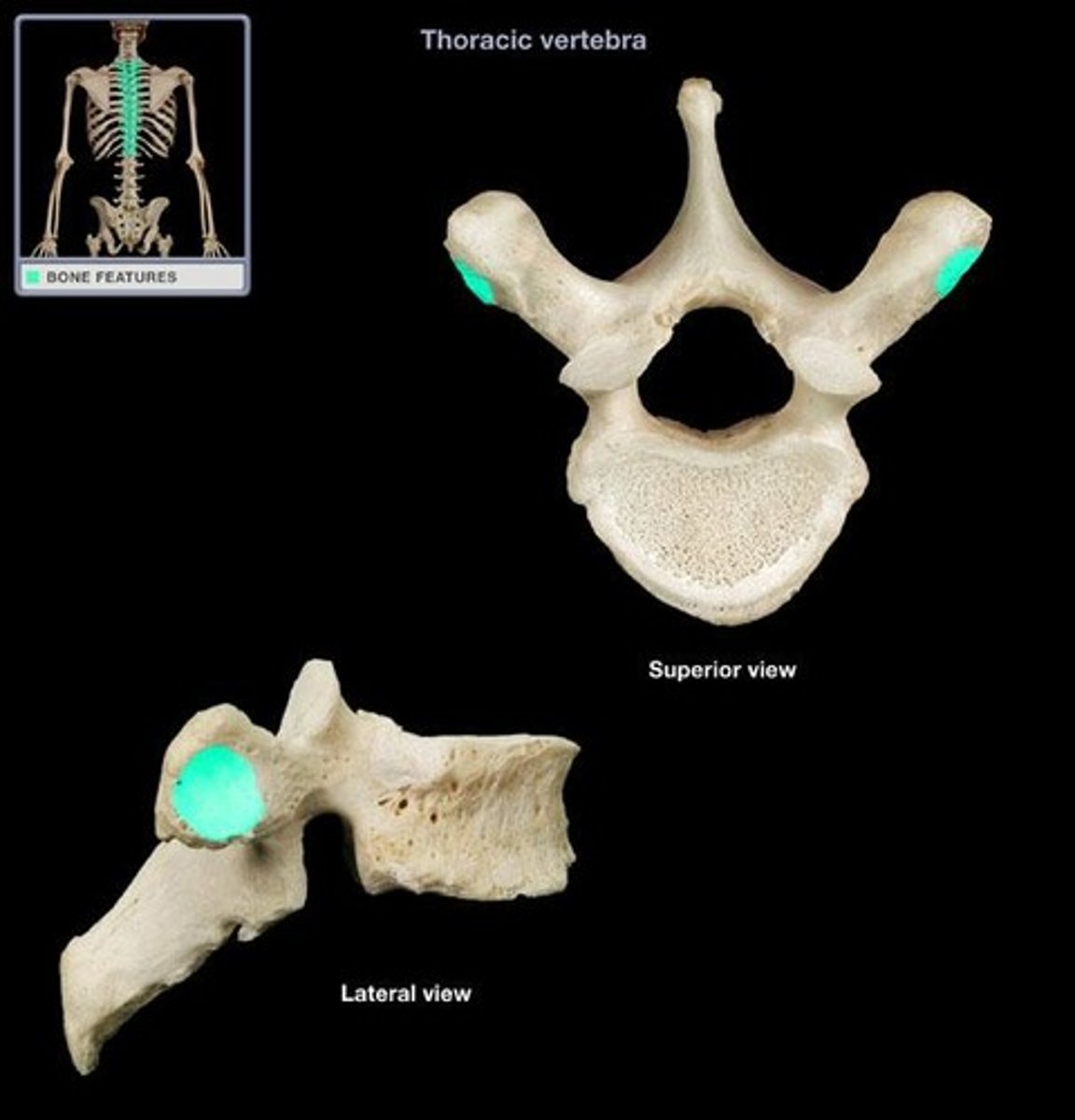
Transverse costal facet (T1-T10 only)
- articulates the tubercles of ribs
Spinous process
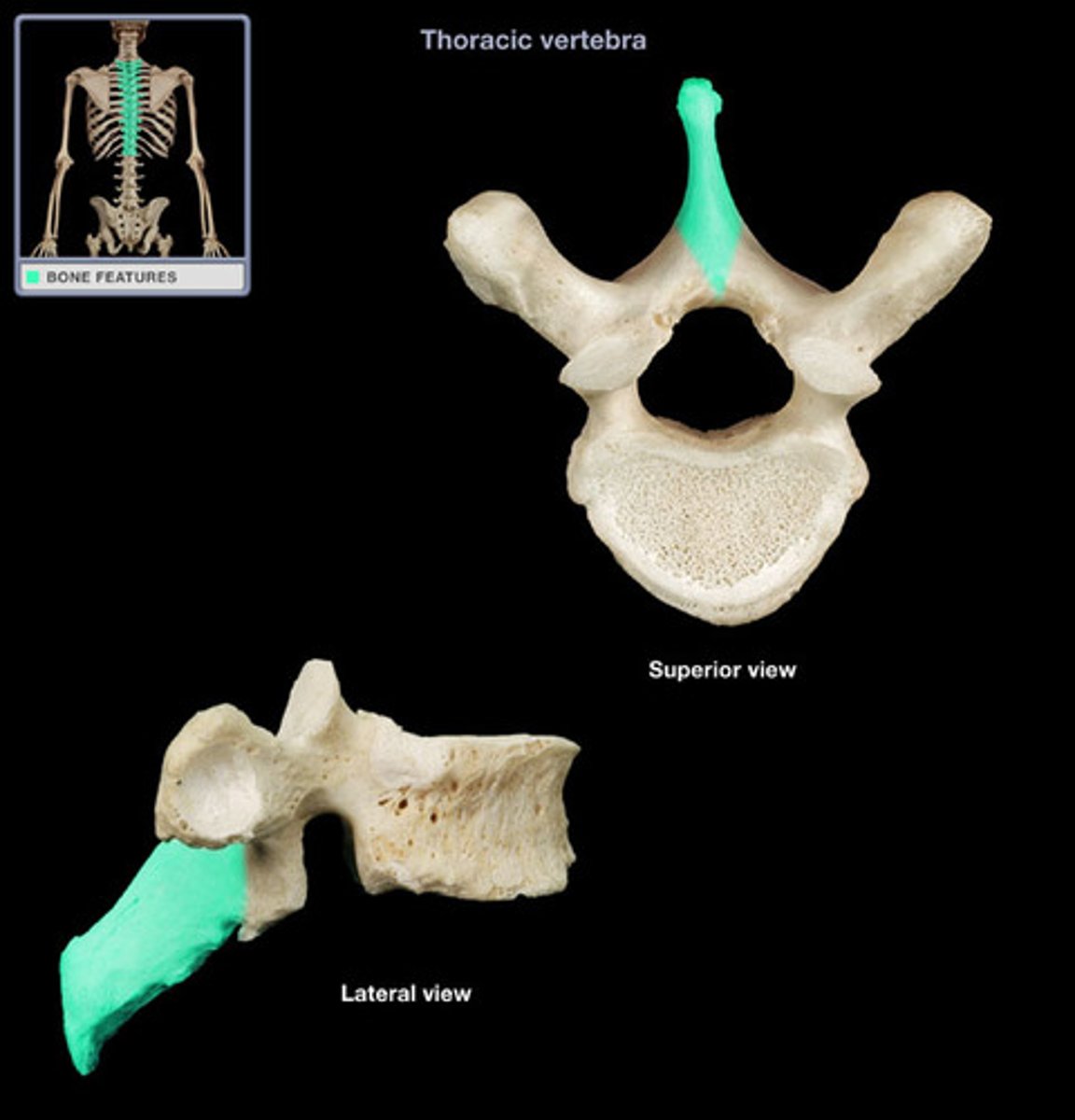
Lamina
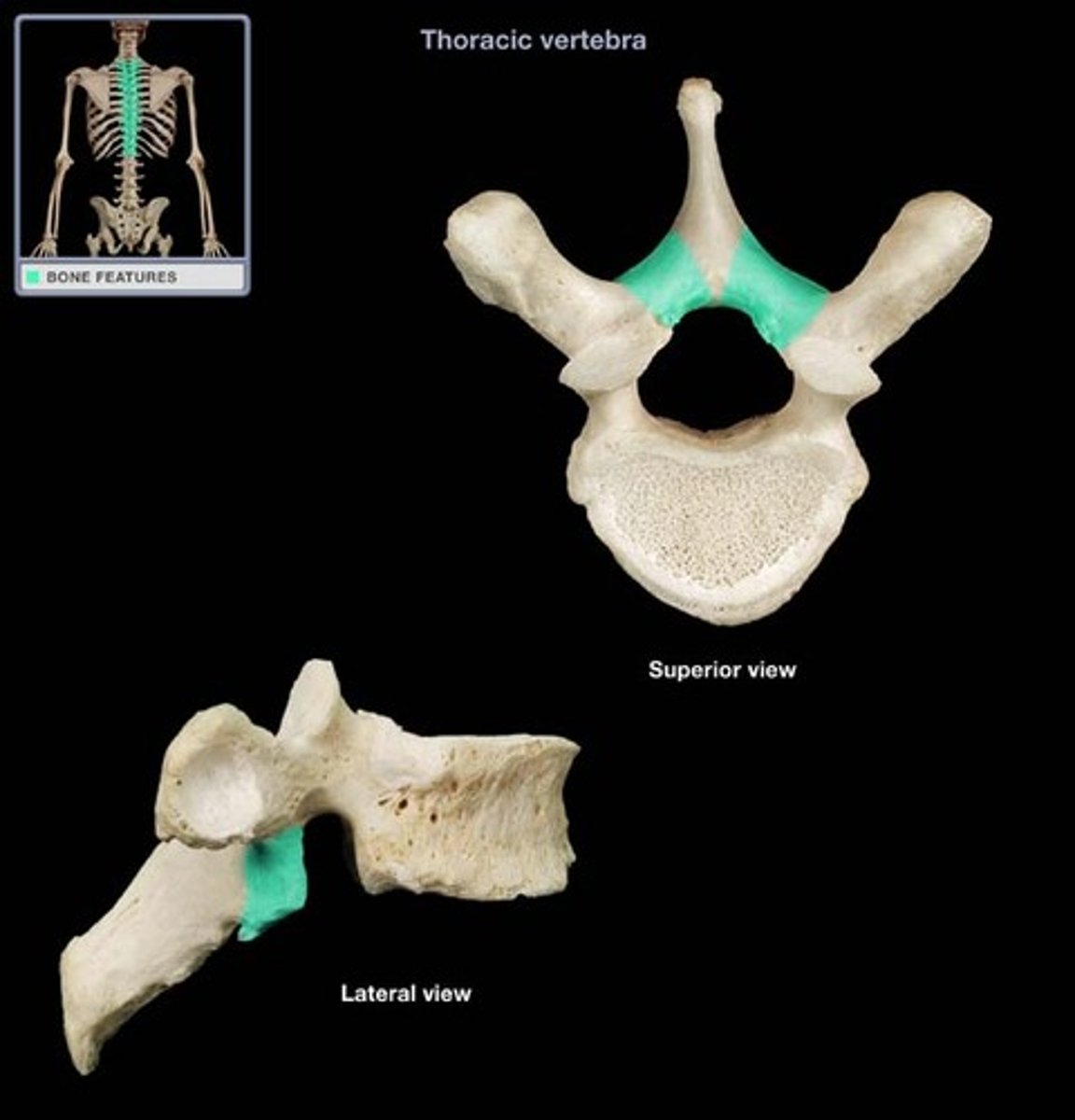
pedicle
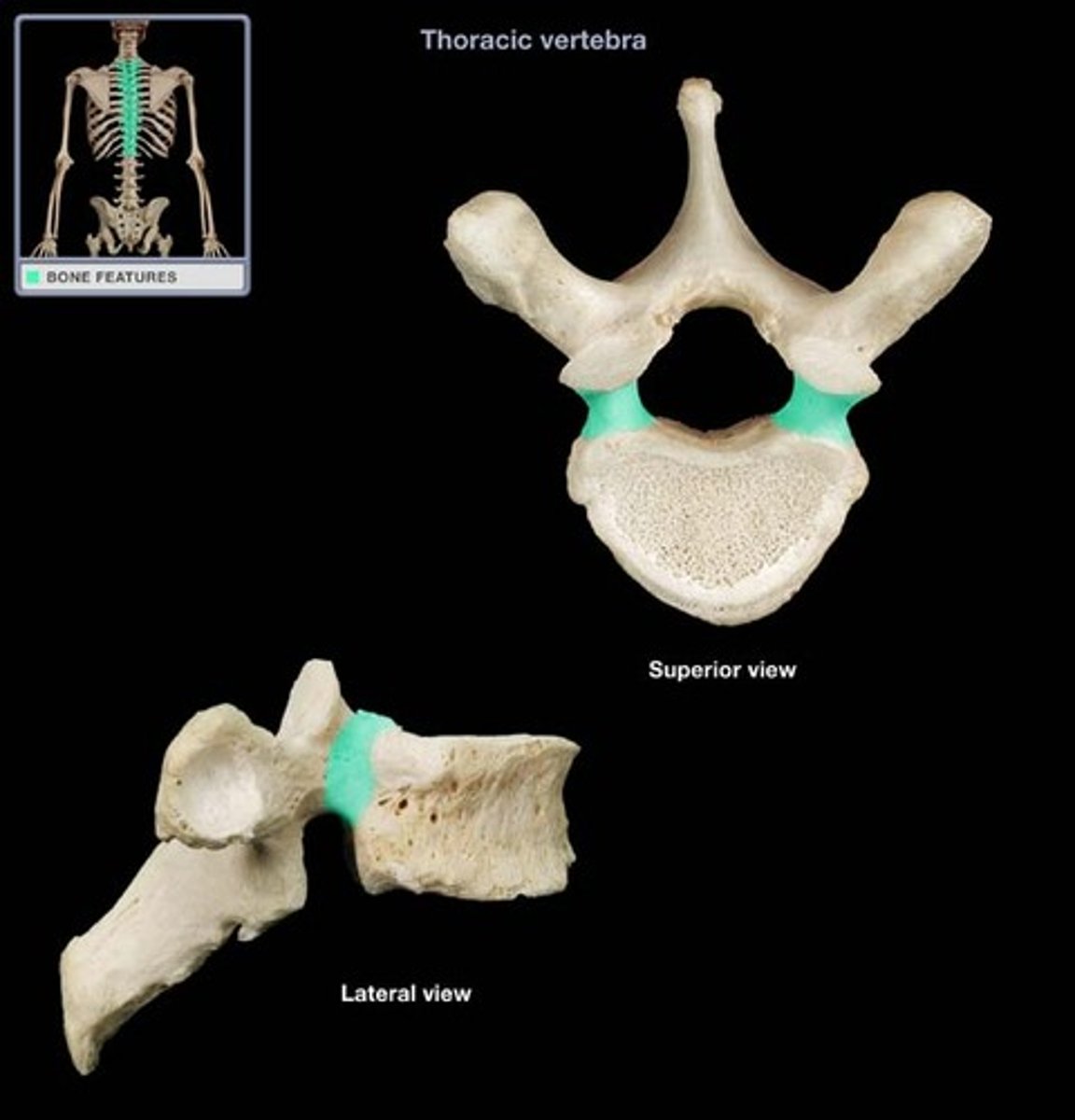
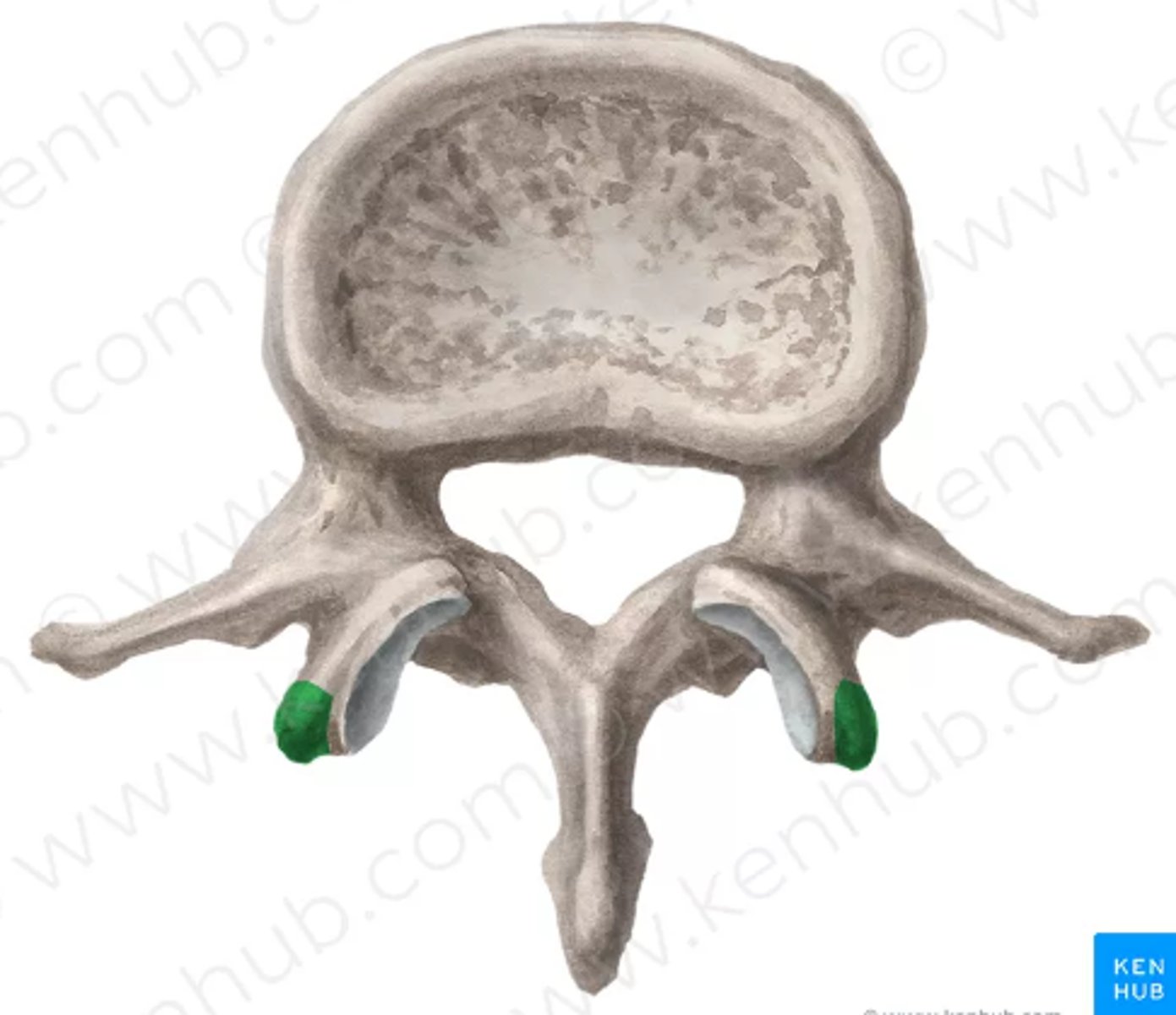
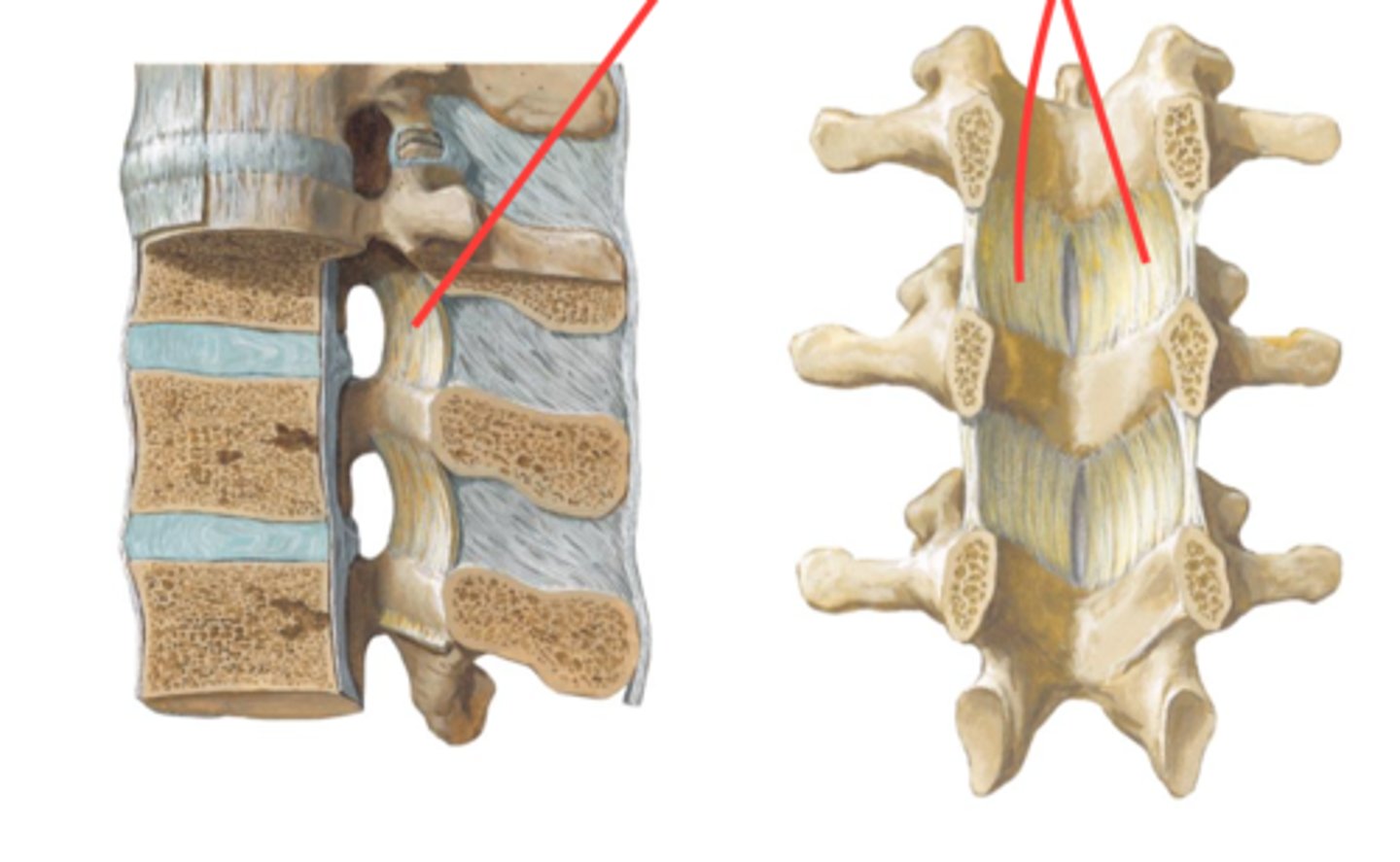
red: superior vertebral notch
green: inferior vertebral notch
What is red and green?
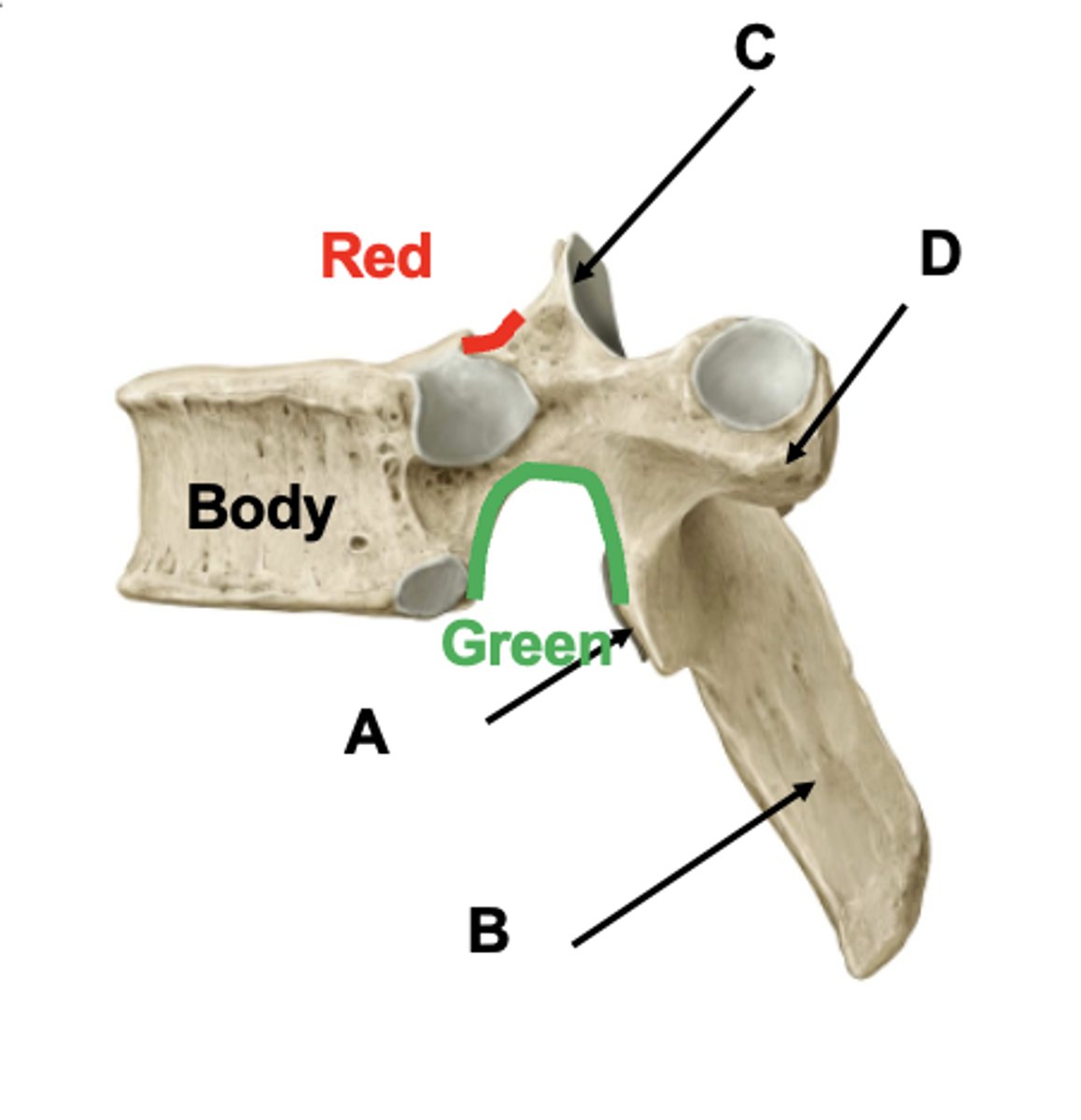
Intervertebral foramen
- holds spinal nerves
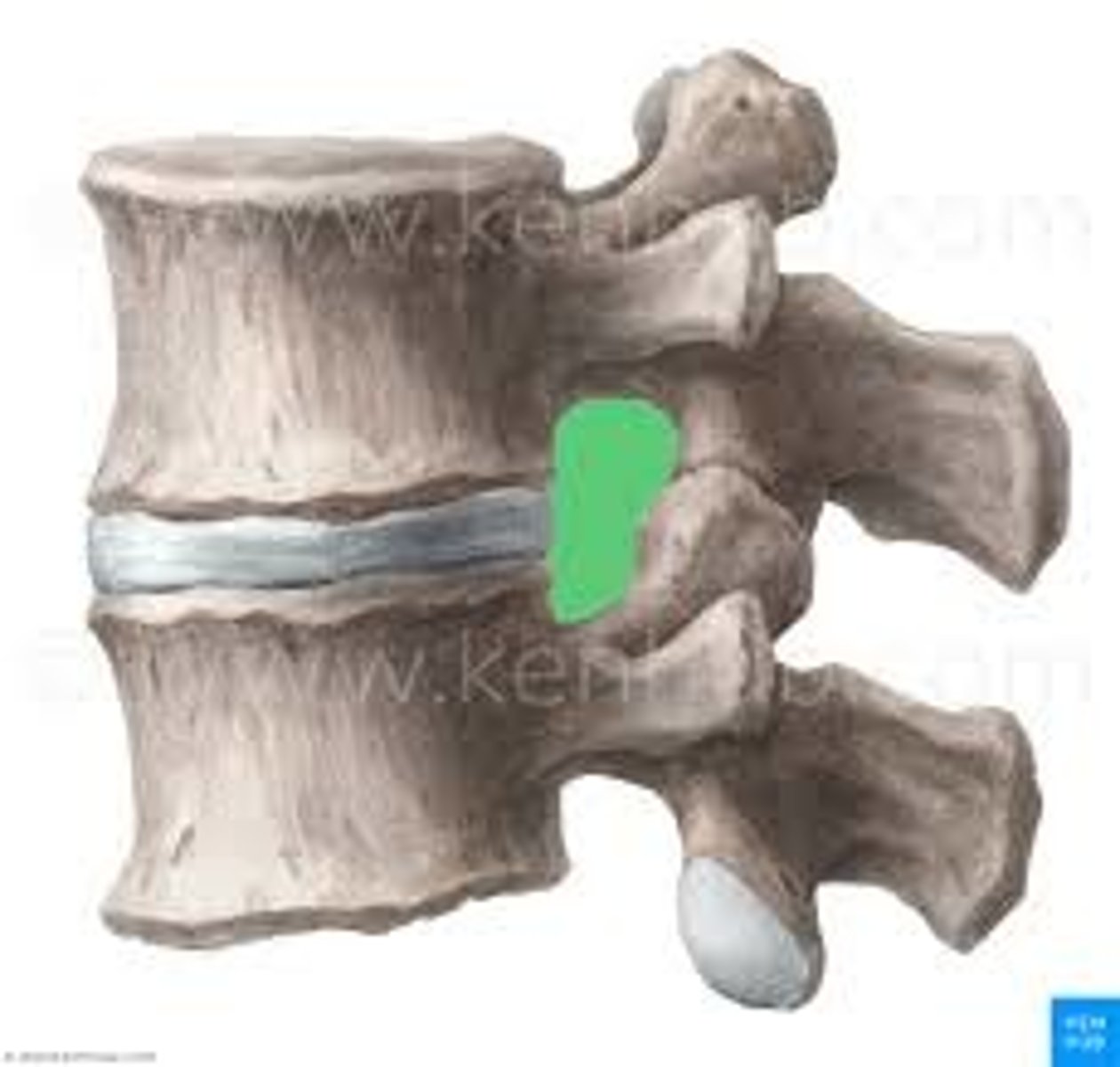
superior articular facet
- joints with inferior articular facet of adjacent vertebrae to form facet (Z) joints
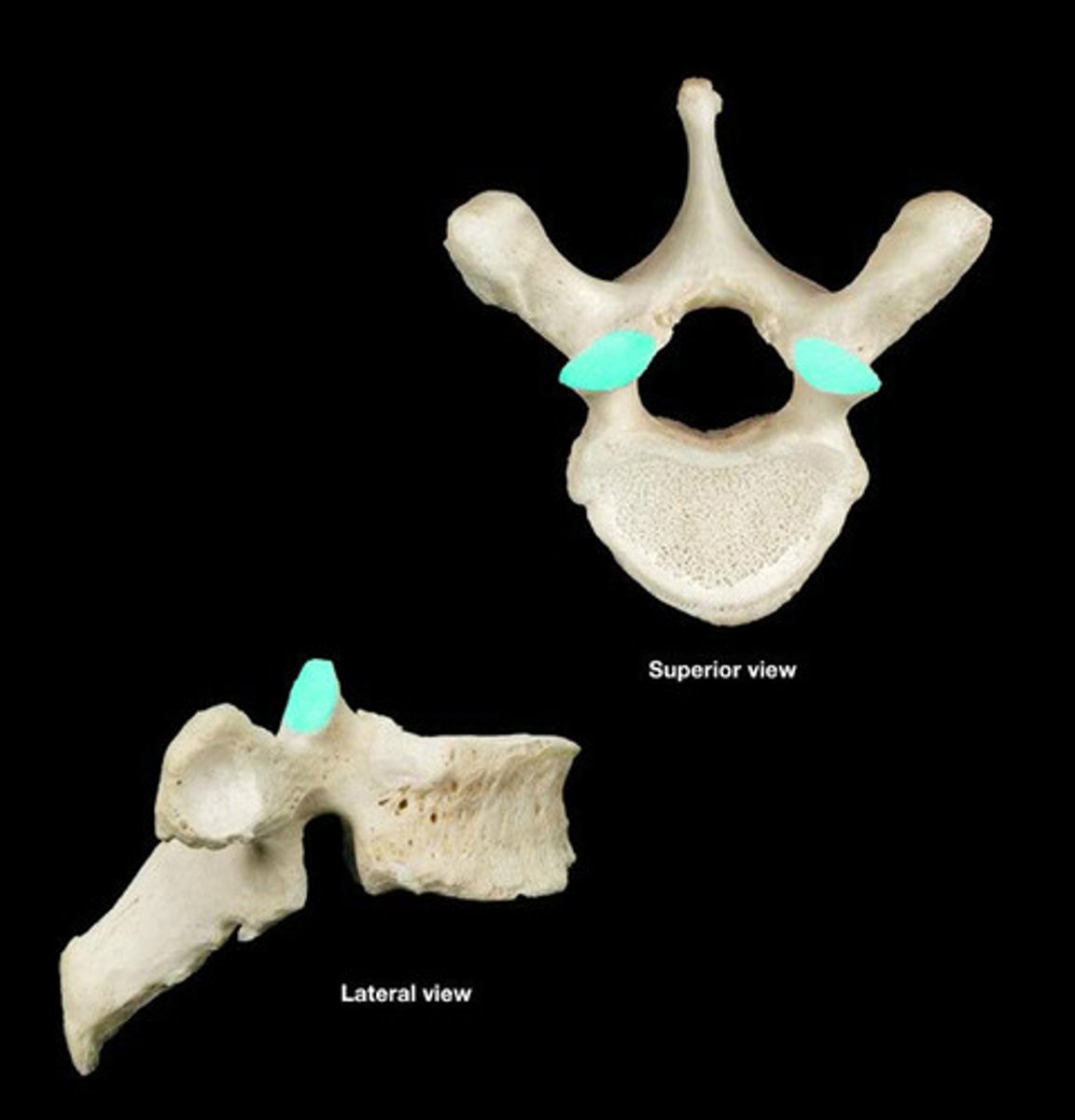
inferior articular facet
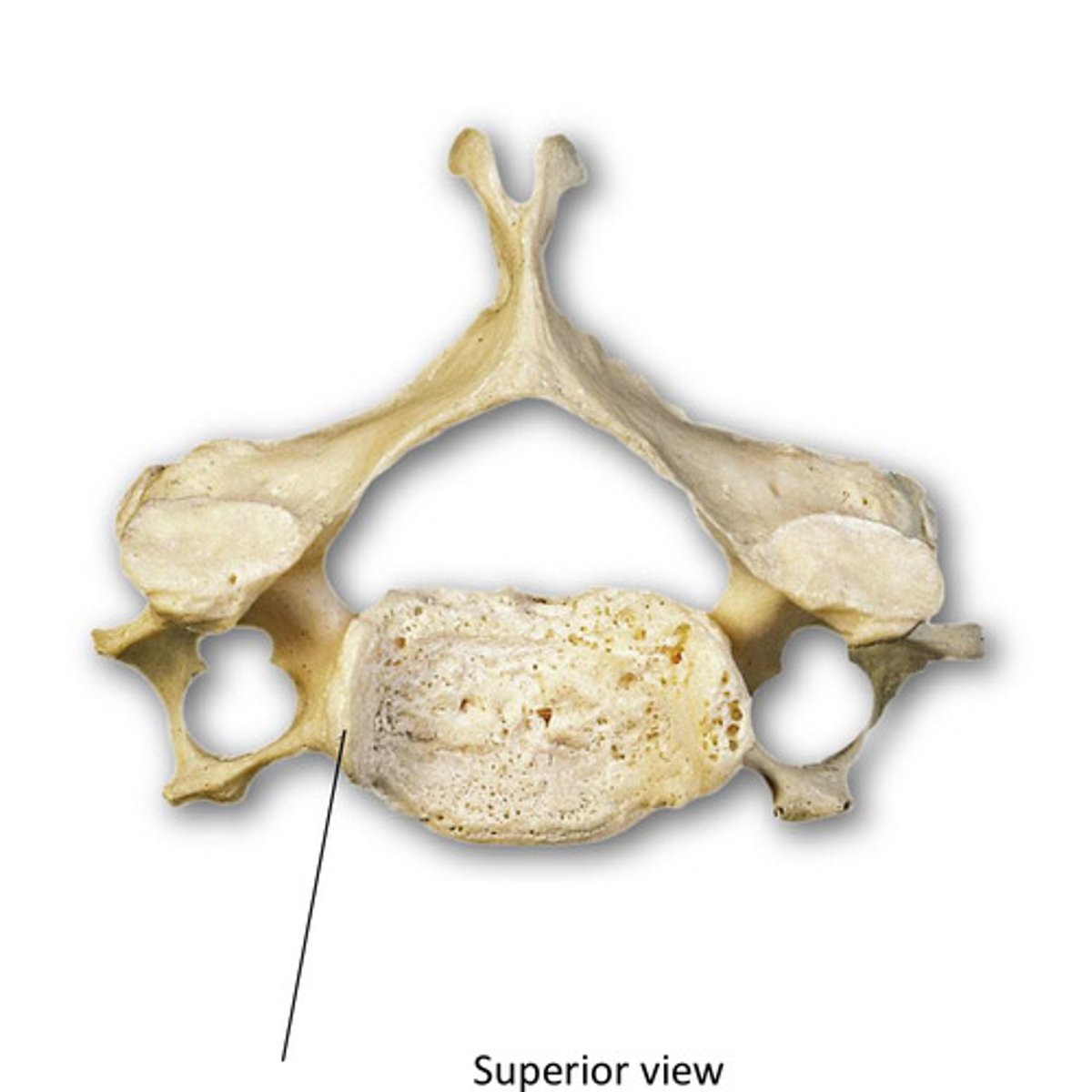
uncinate processes (cervical vertebrae)
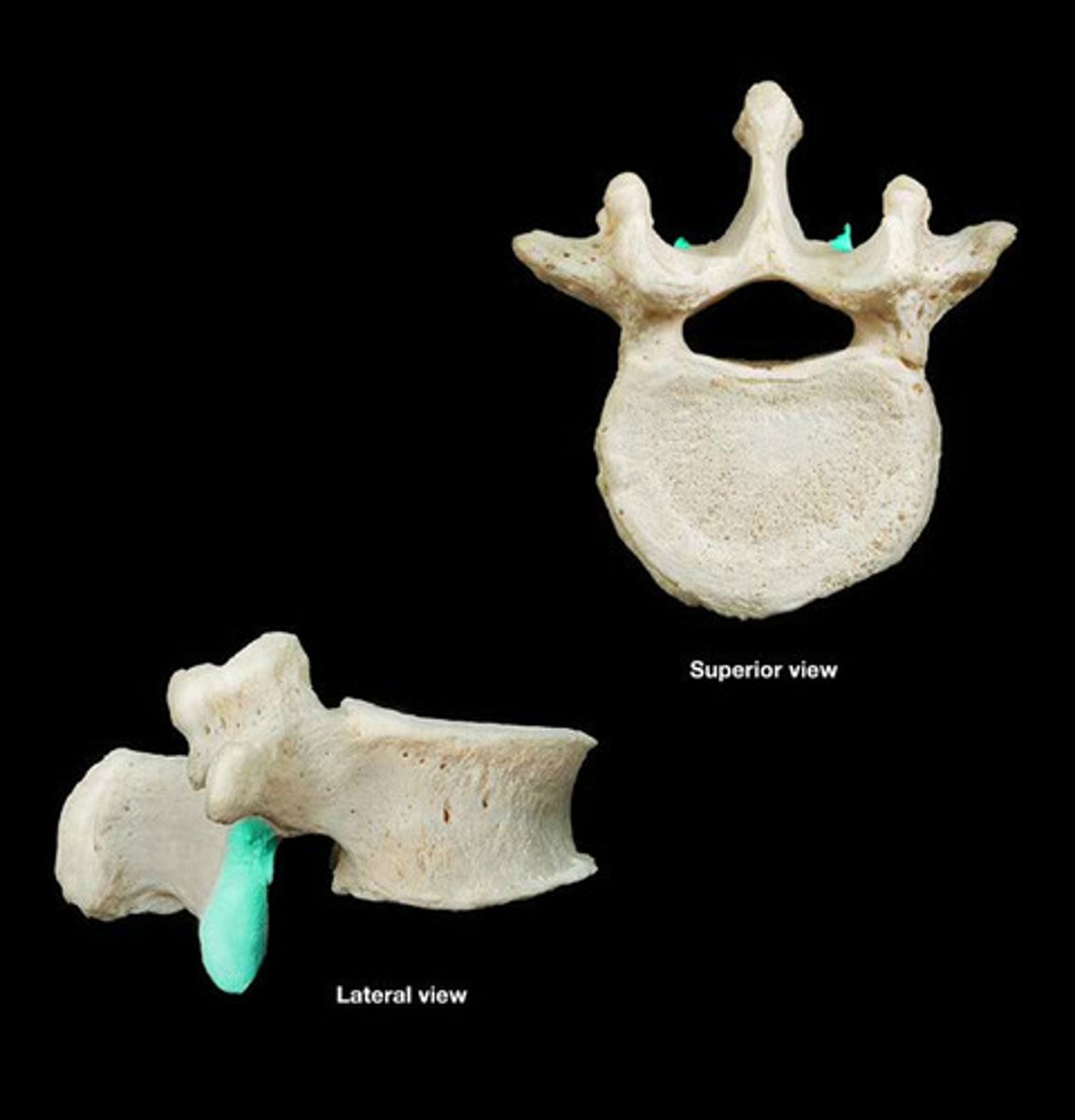
mammillary process (lumbar vertebrae)
- small tubercles on posterior part of superior articular process
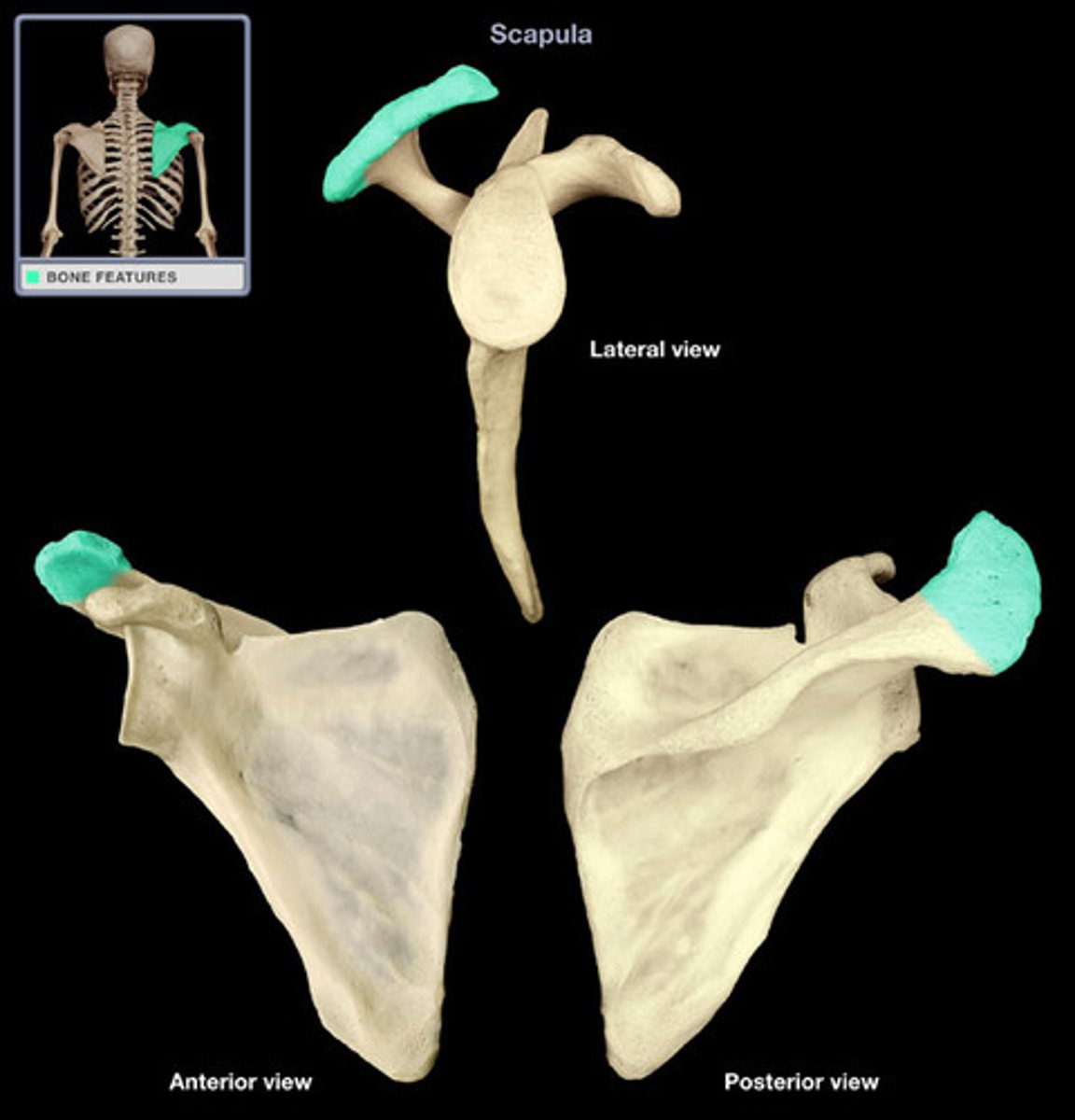
Acromion
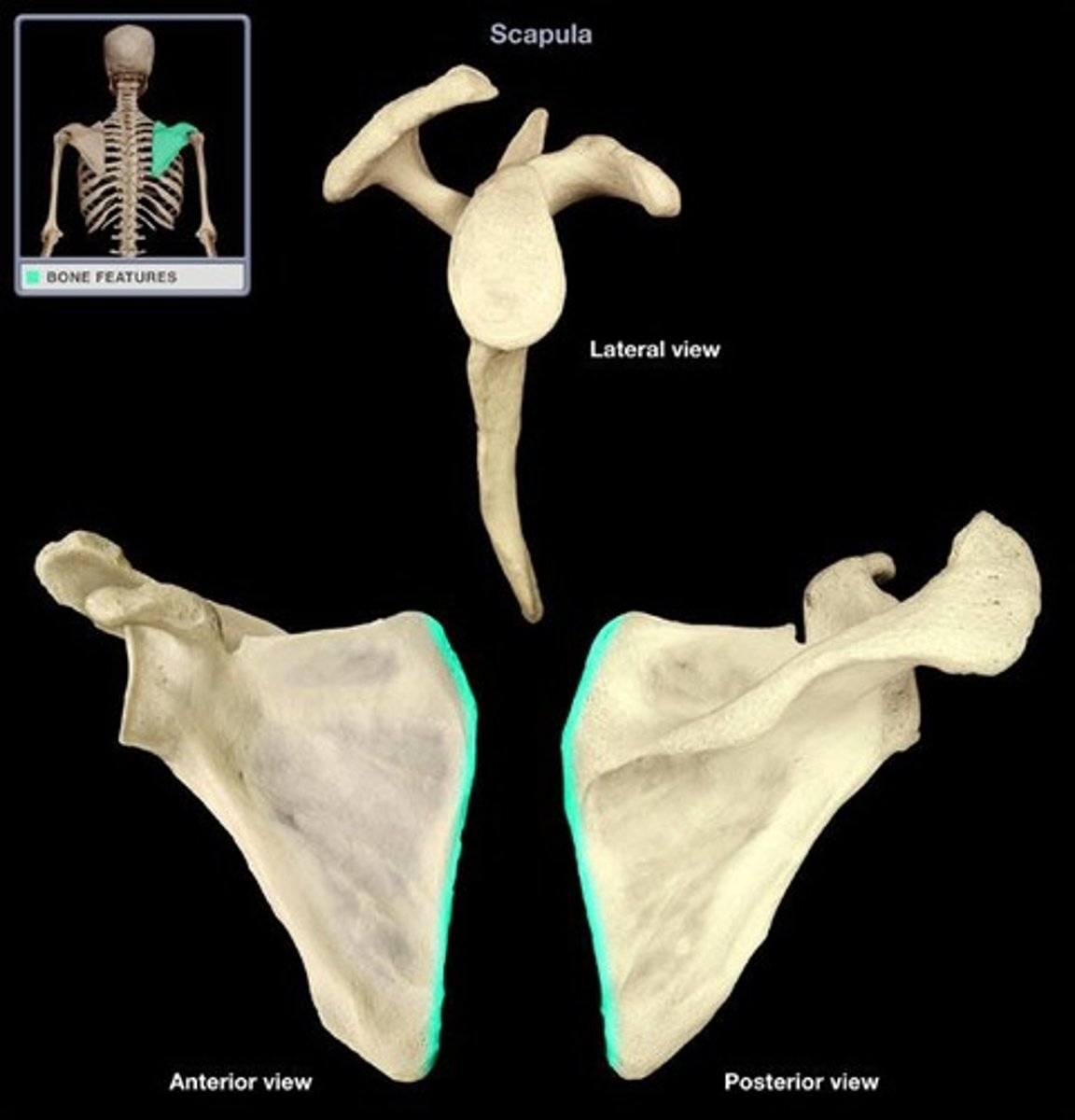
medial (vertebral) border
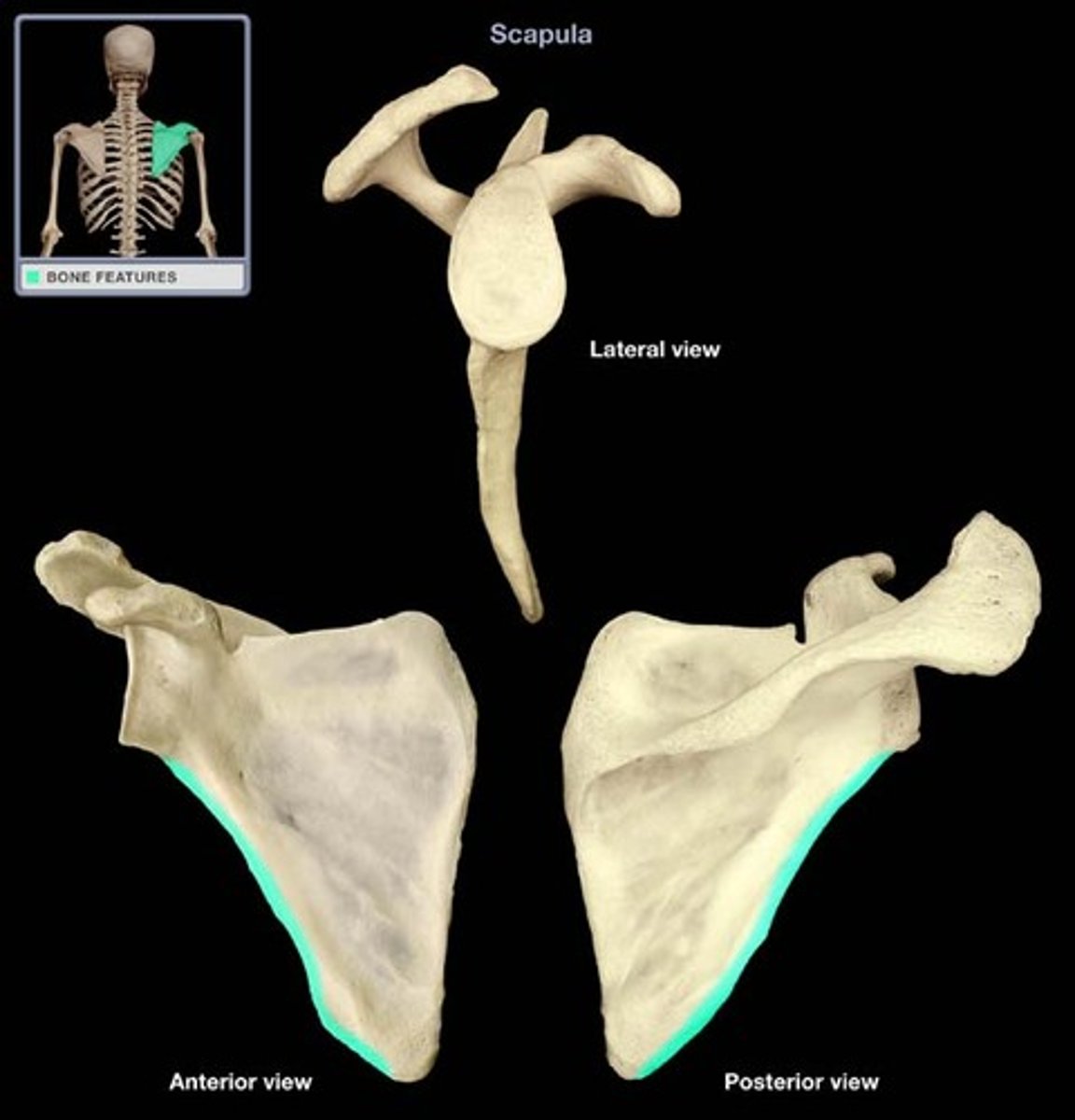
lateral (axillary) border
superior border
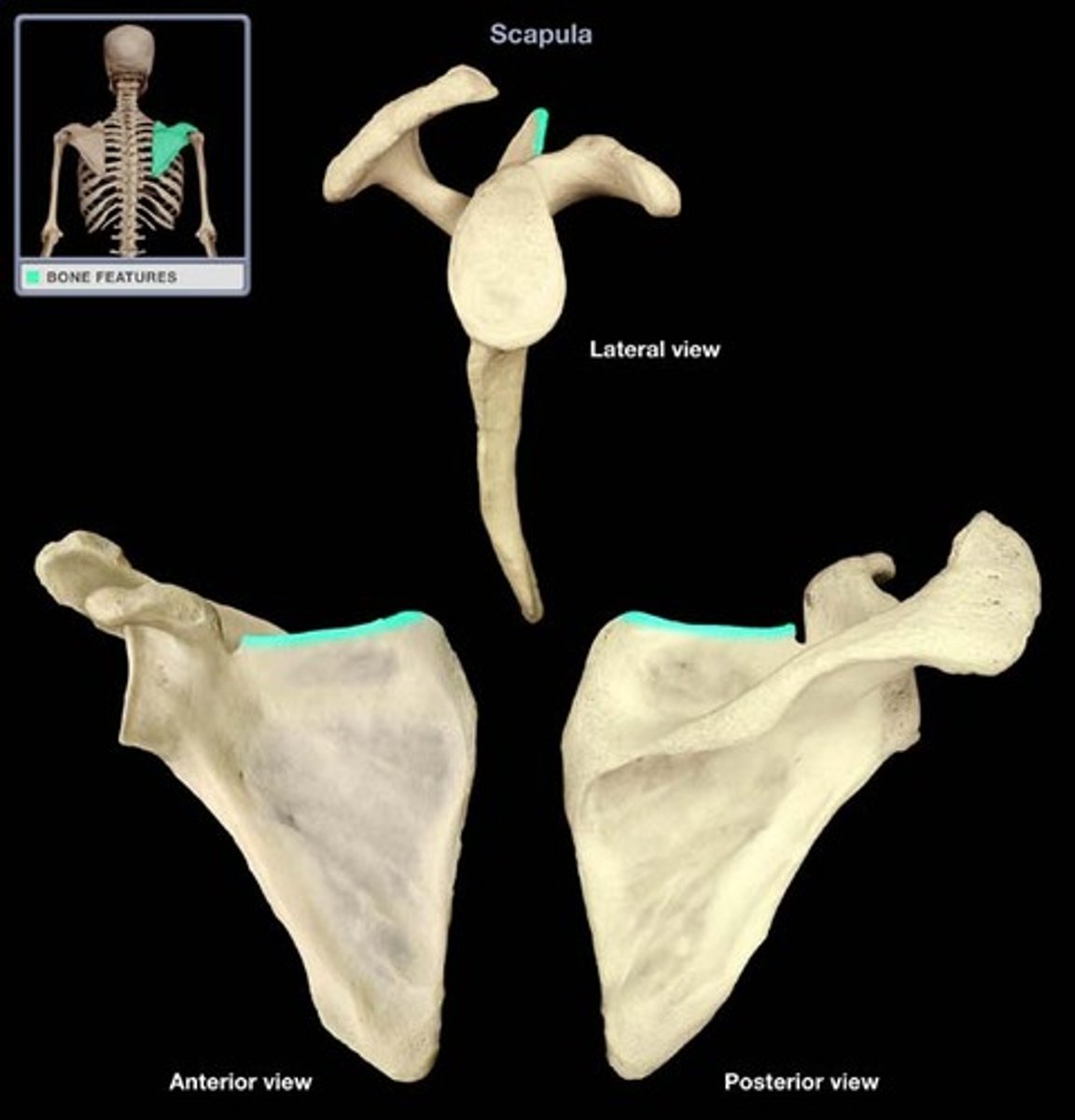
superior angle
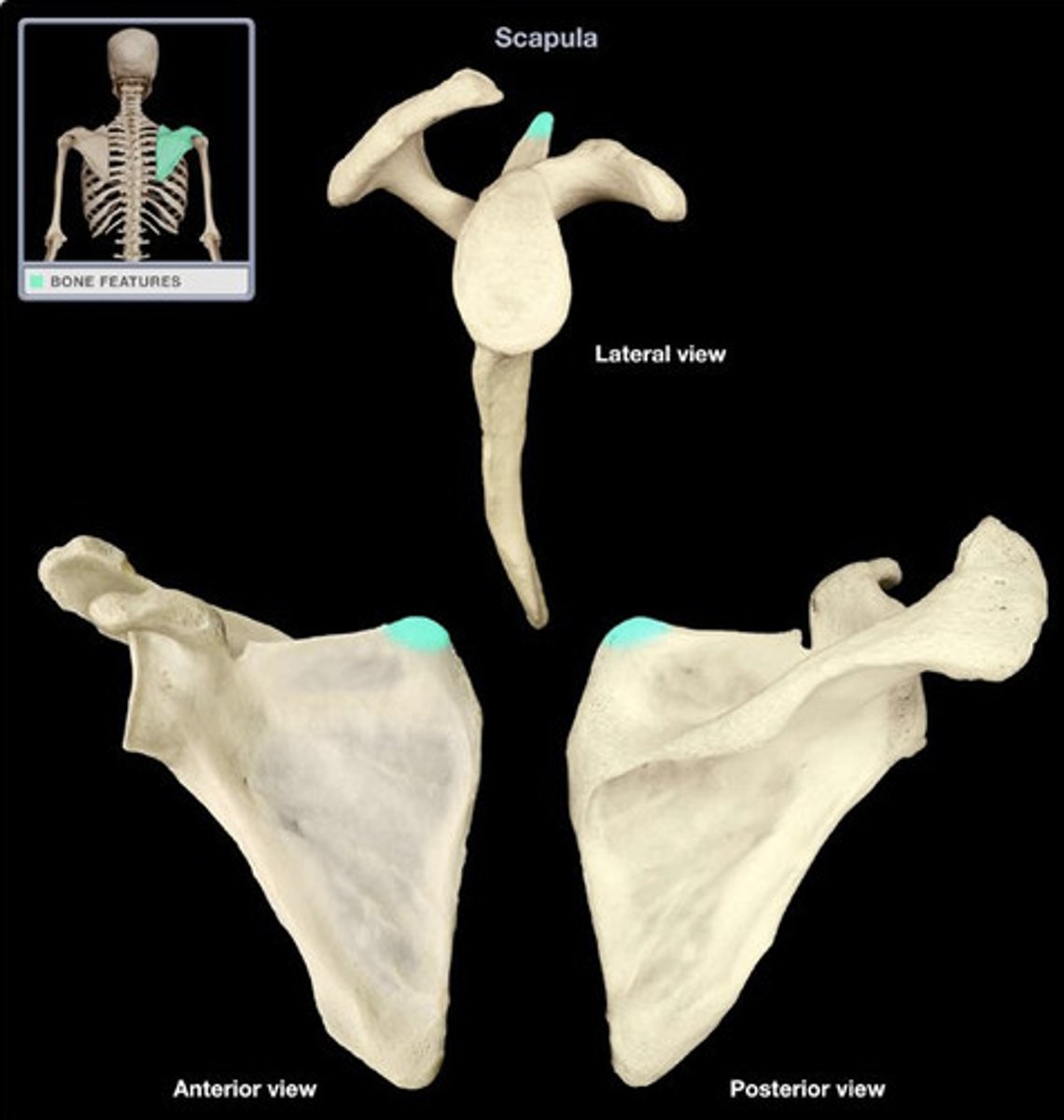
inferior angle
- T7 transverse plane
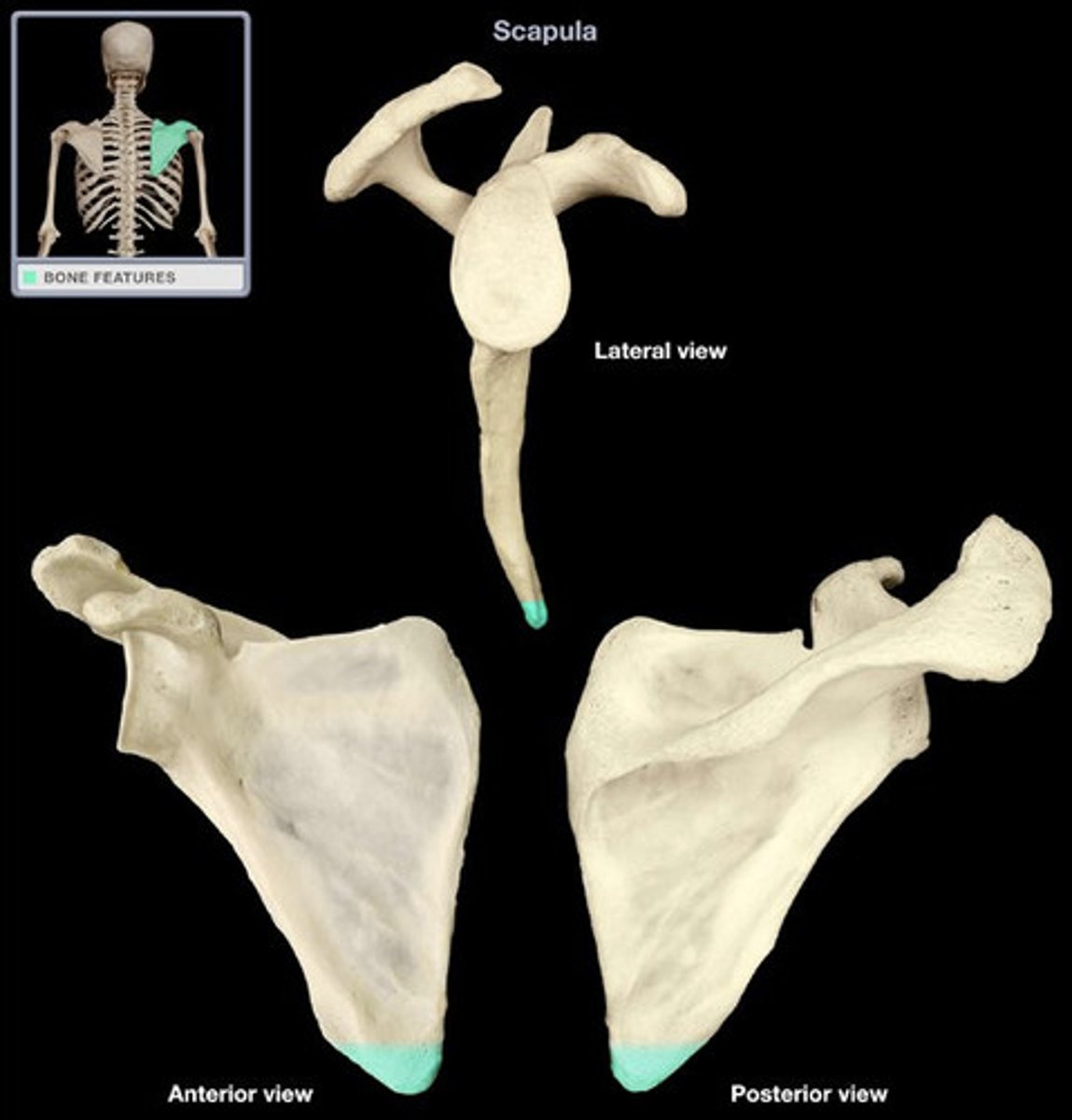
lateral angle (glenoid fossa)
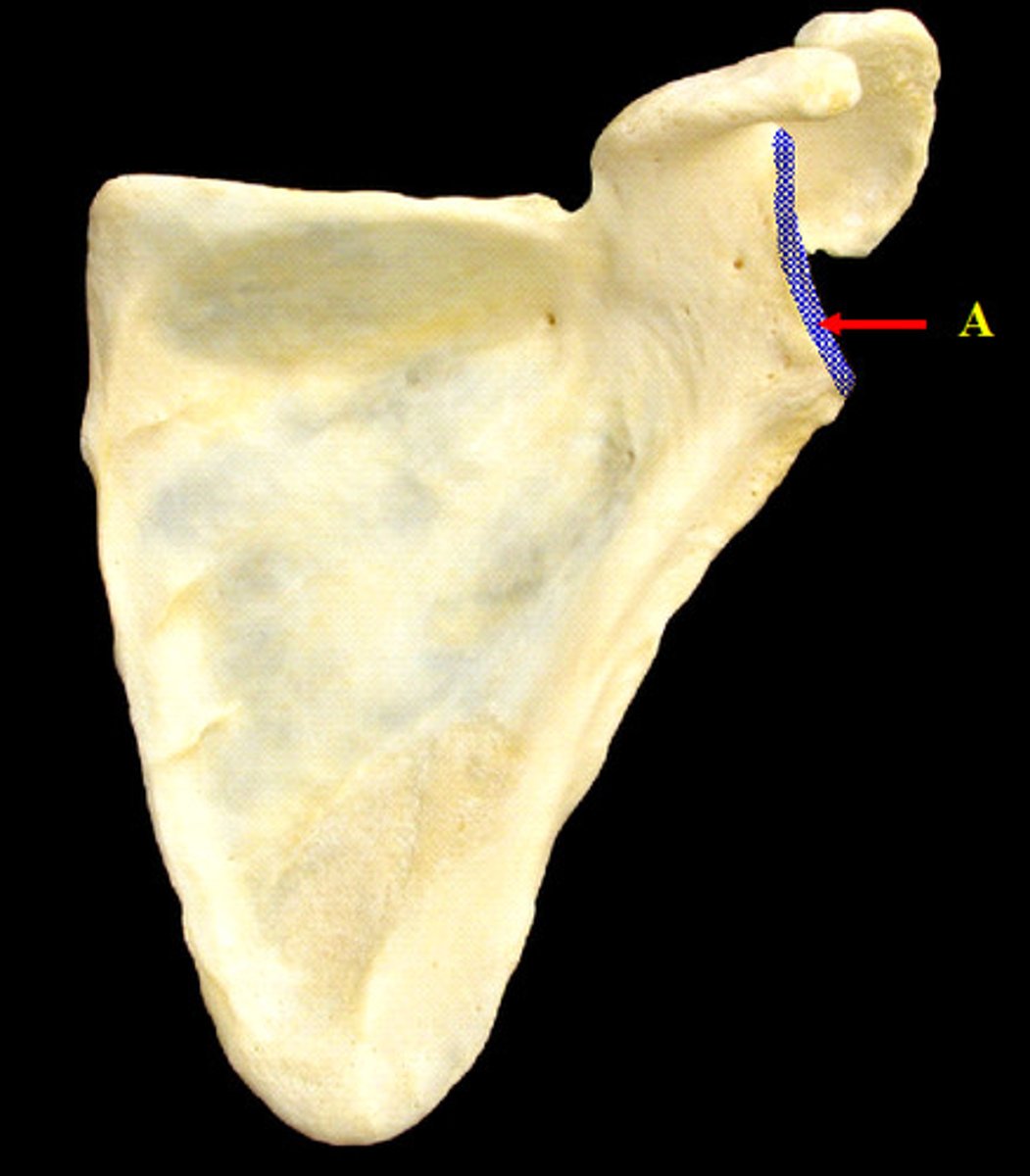
scapular spine
- lies in T3 plane
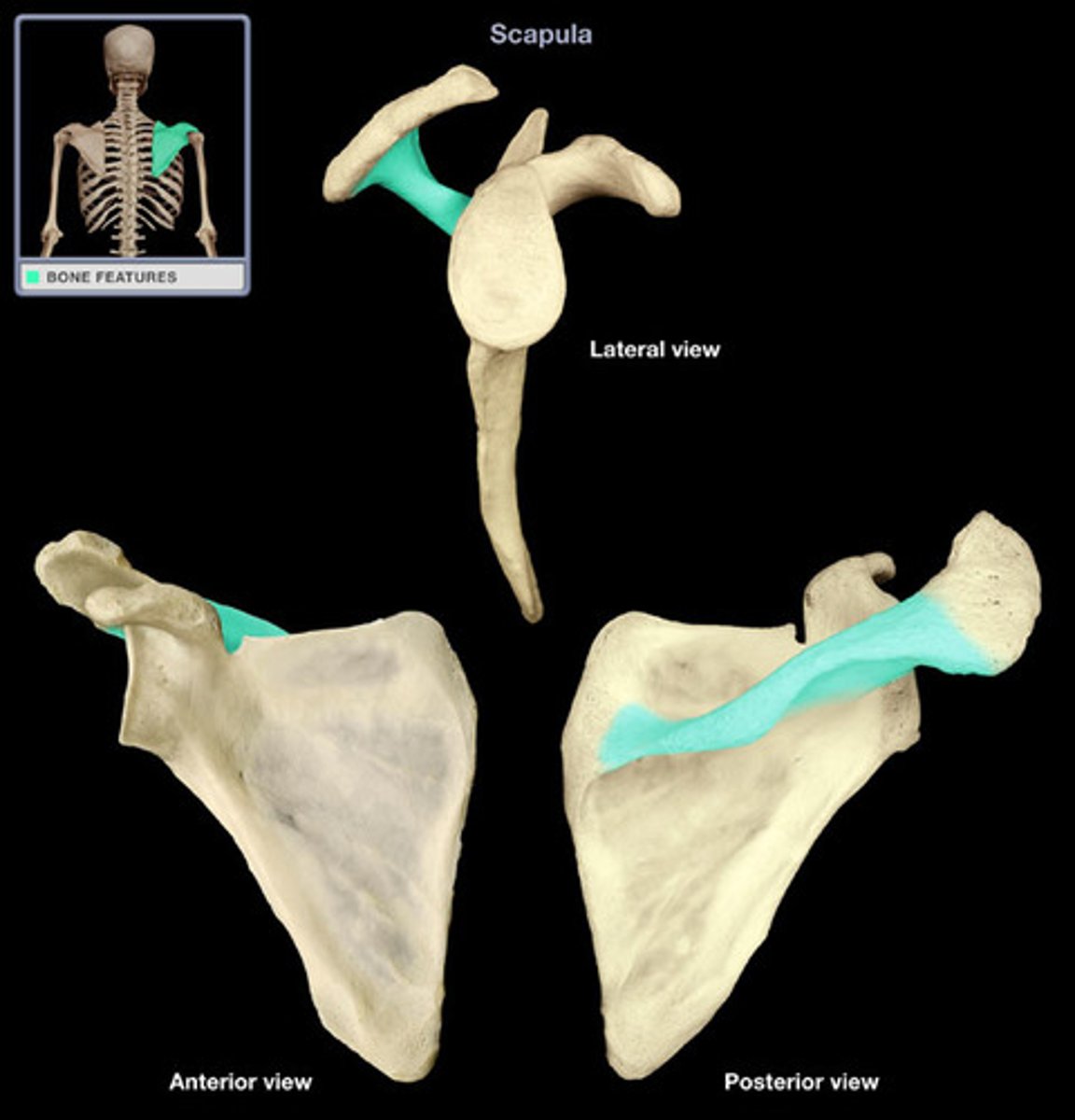
scapular notch
true ribs (1-7)
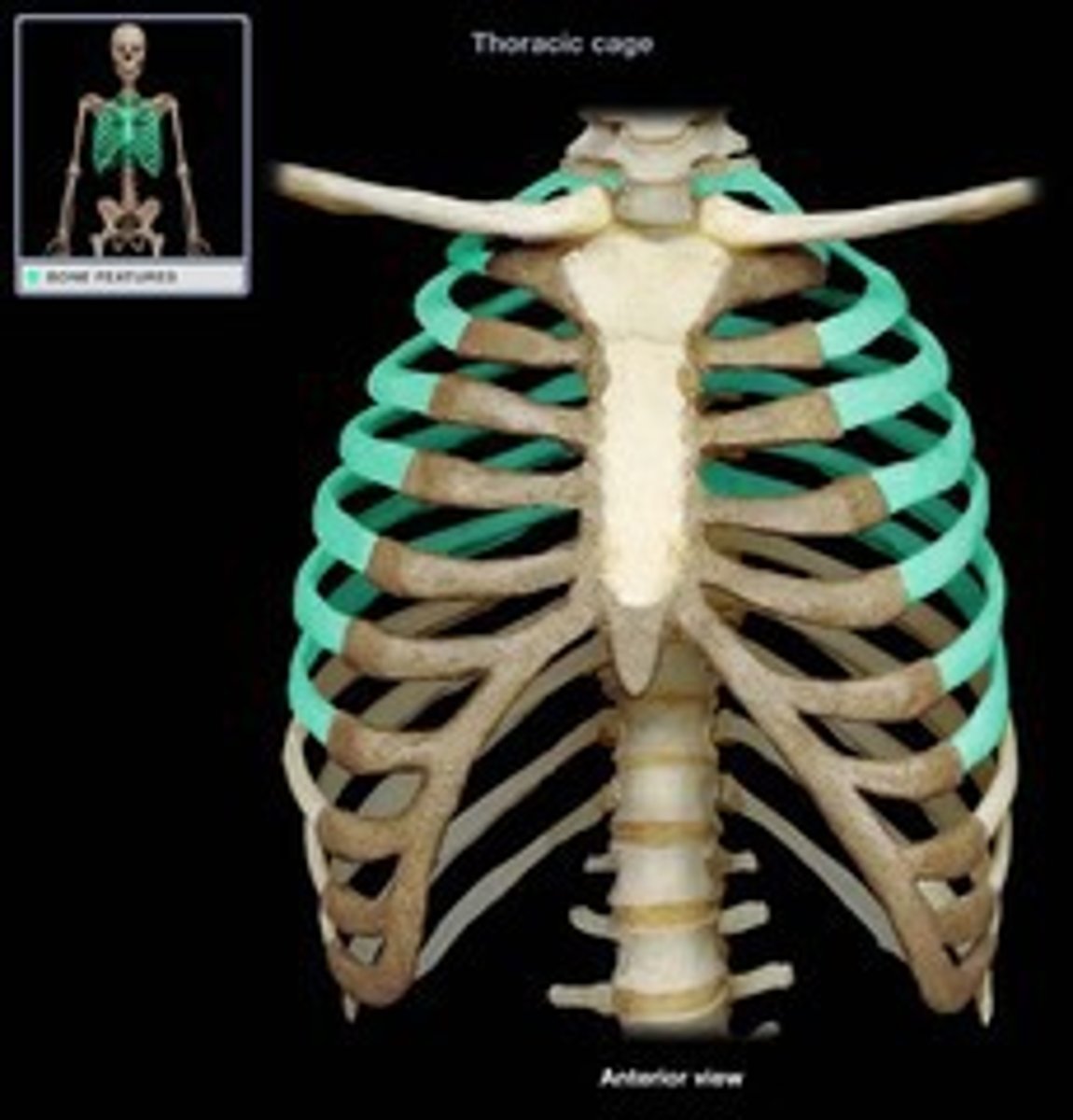
false ribs (8-10)
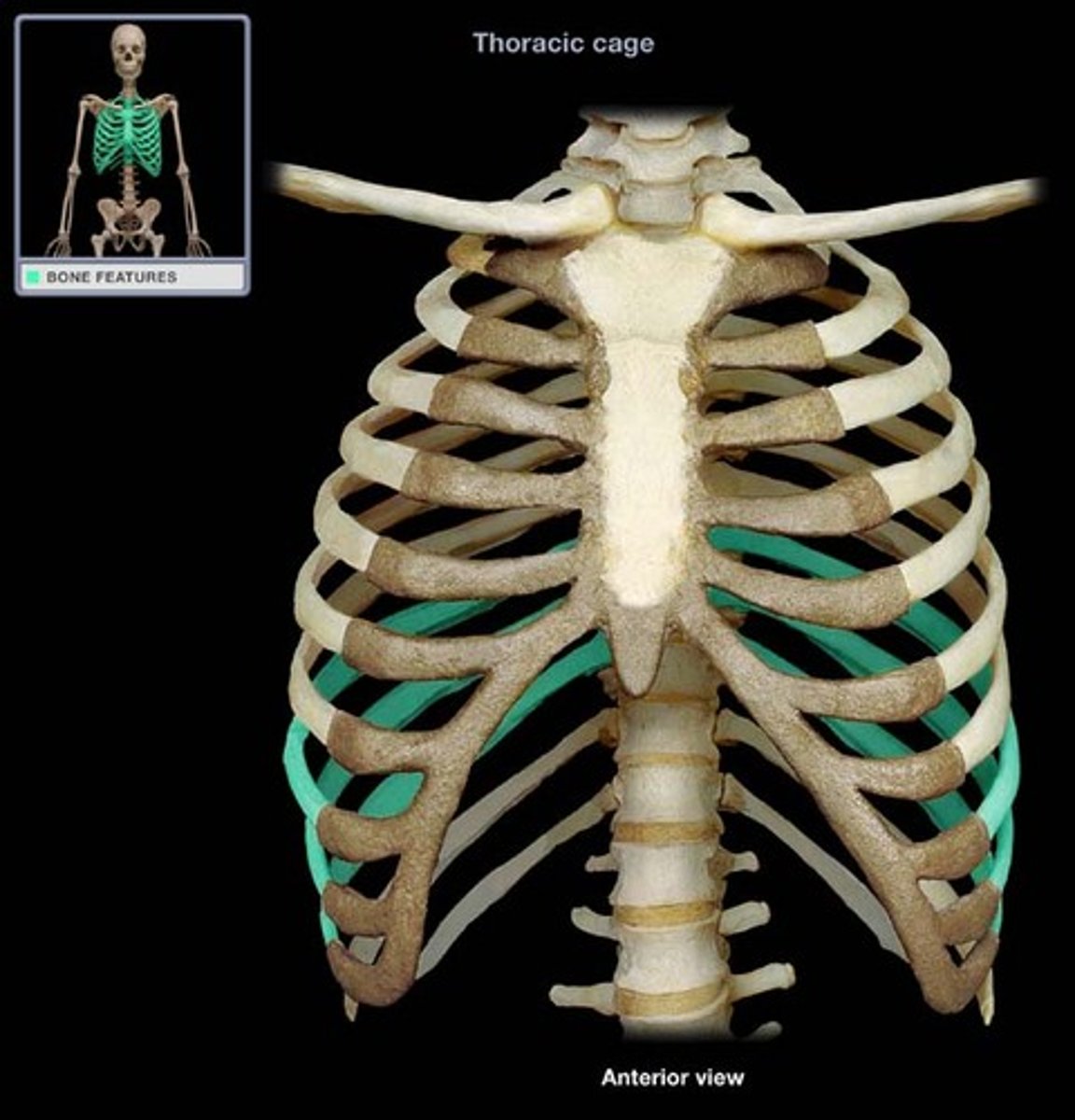
floating ribs (11-12)
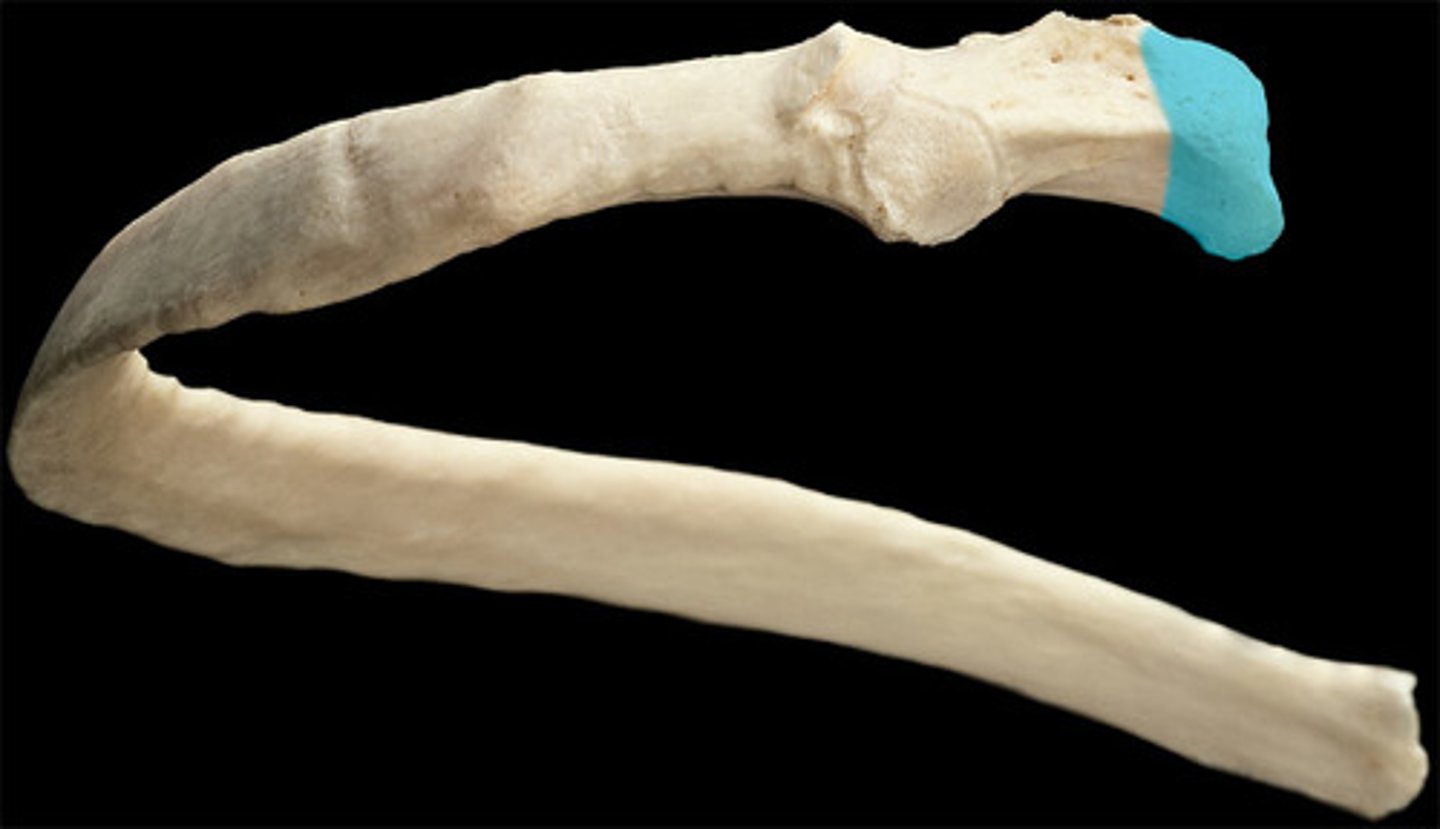
head of rib
- posterior end of a rib that articulates with the bodies of thoracic vertebrae
neck of rib
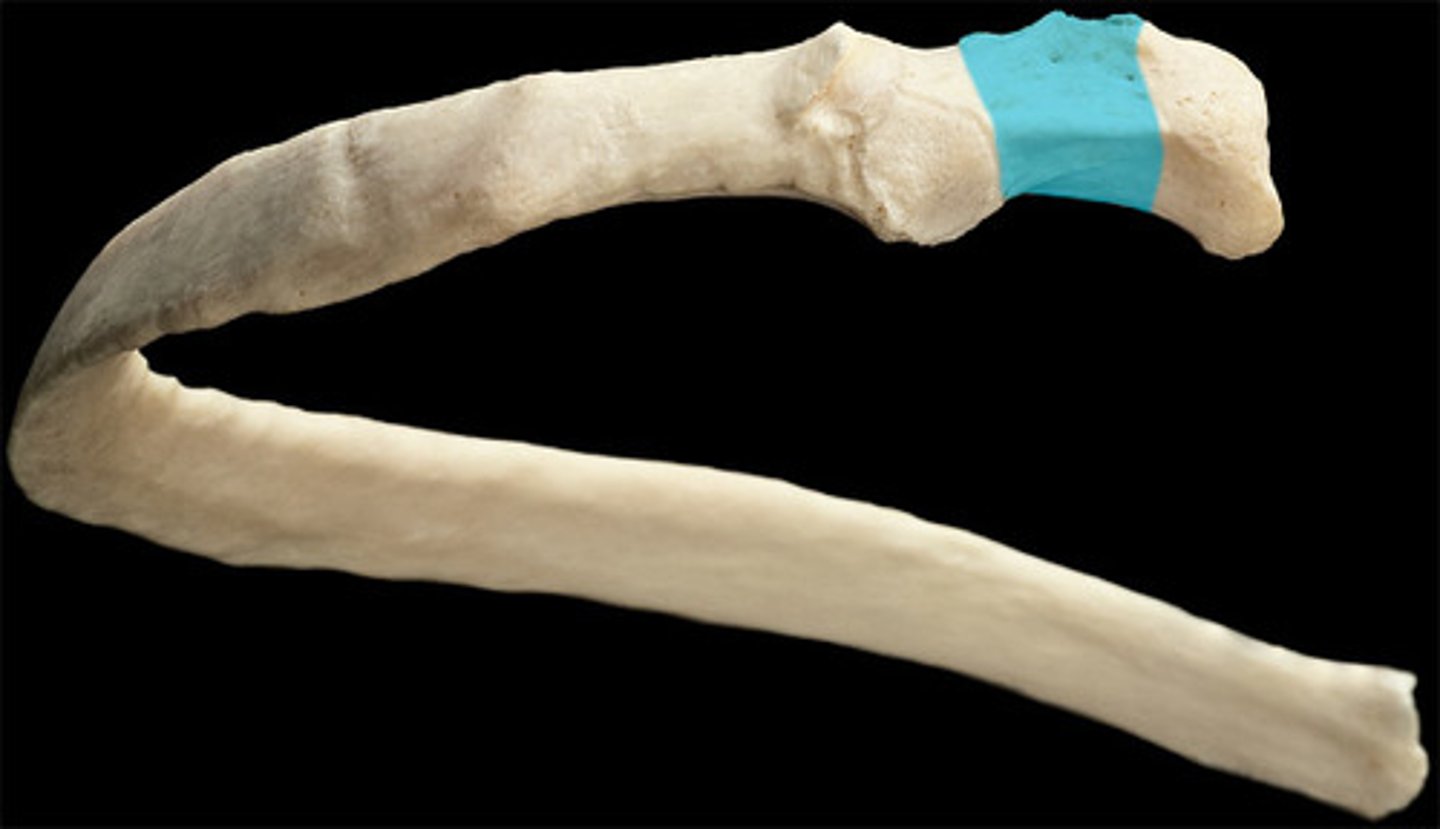
tubercle of rib
- articulates with the costal facet of thoracic vertebra's transverse process.
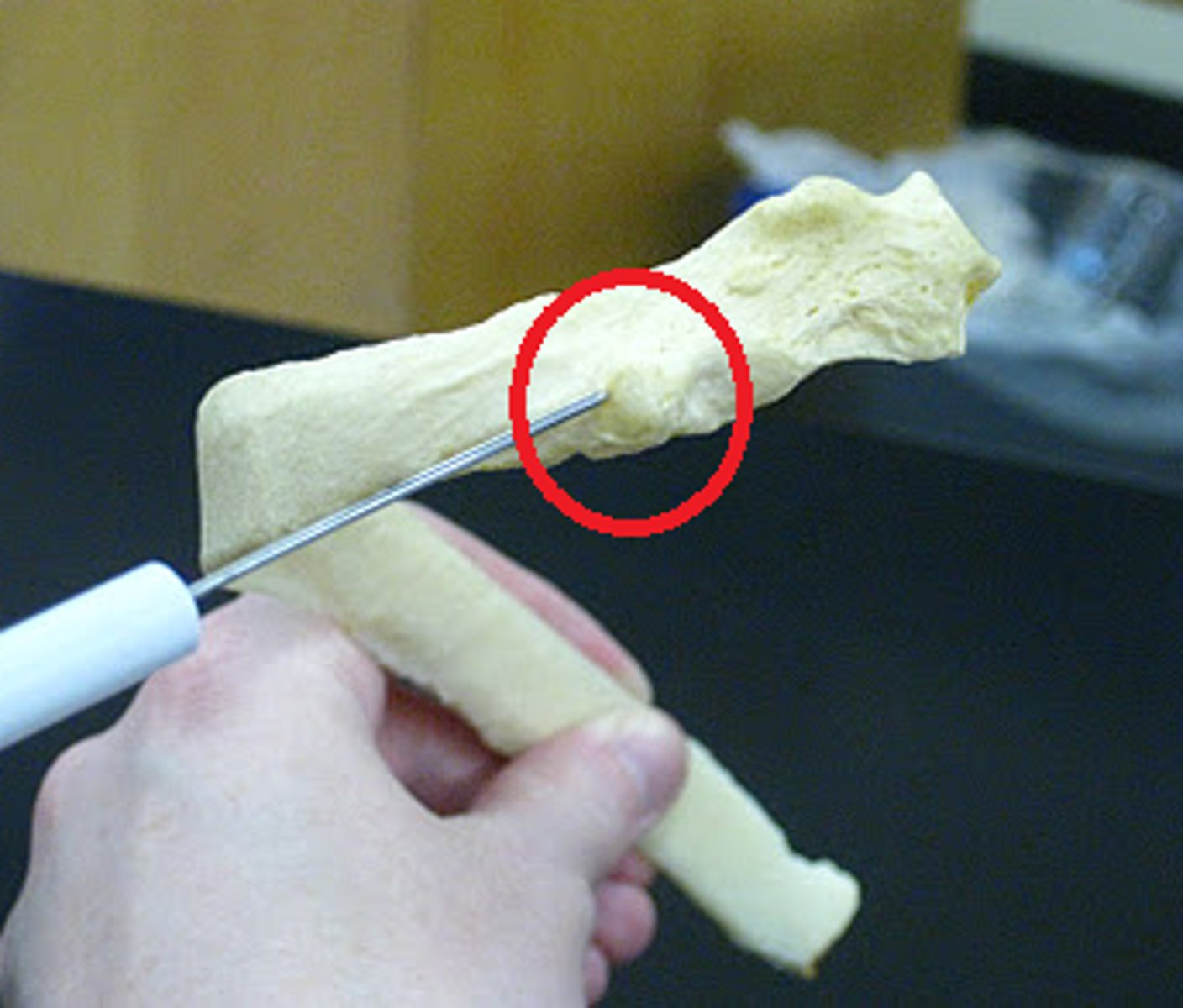
costal groove
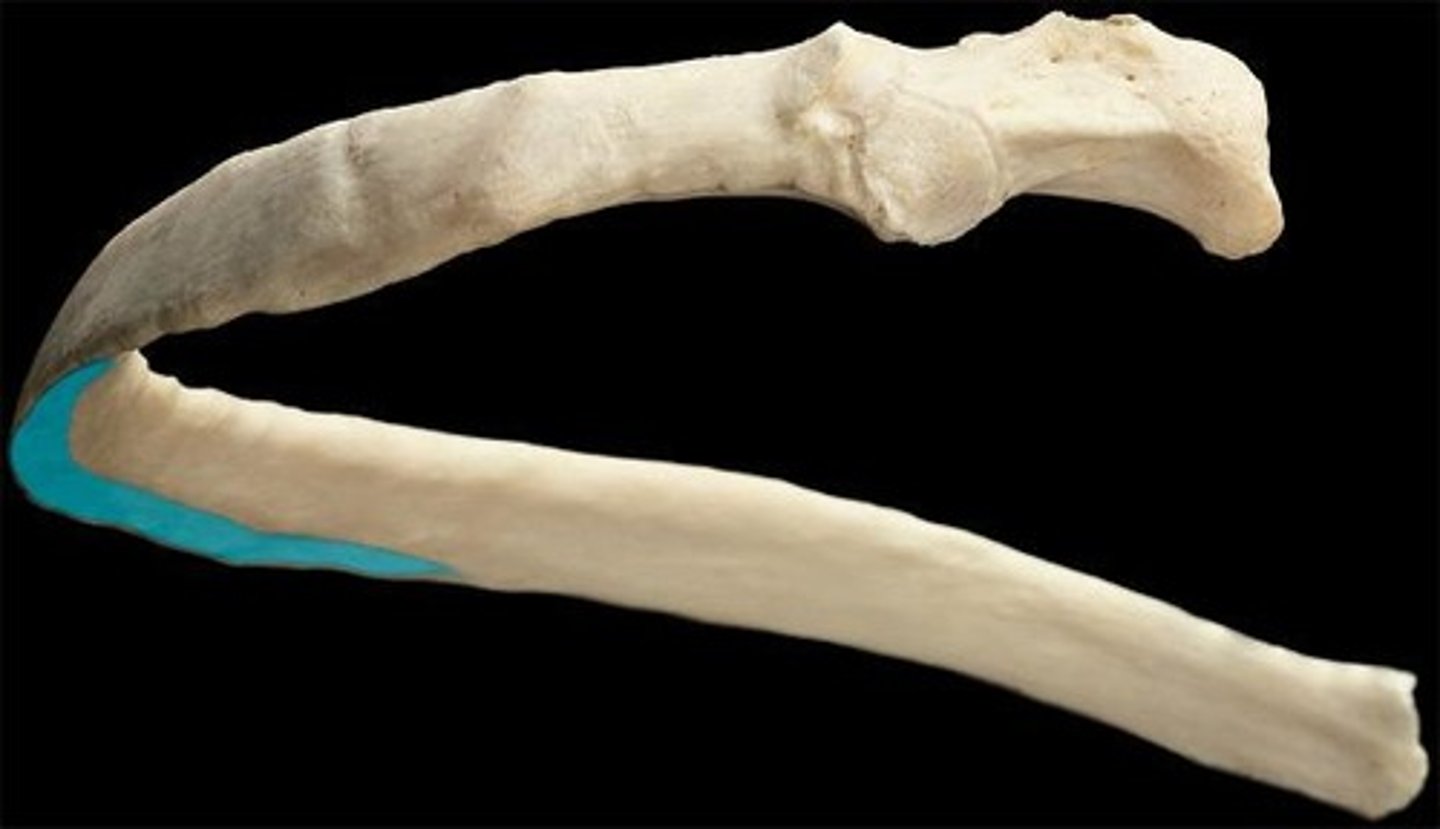
shaft of rib
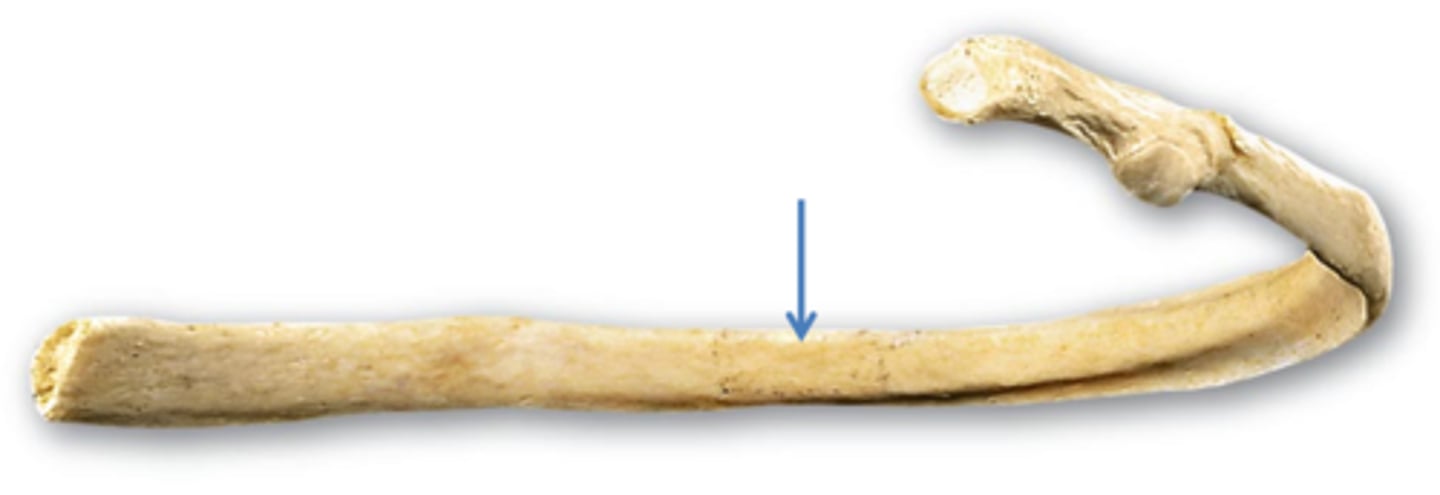
angle of rib (curve of rib)
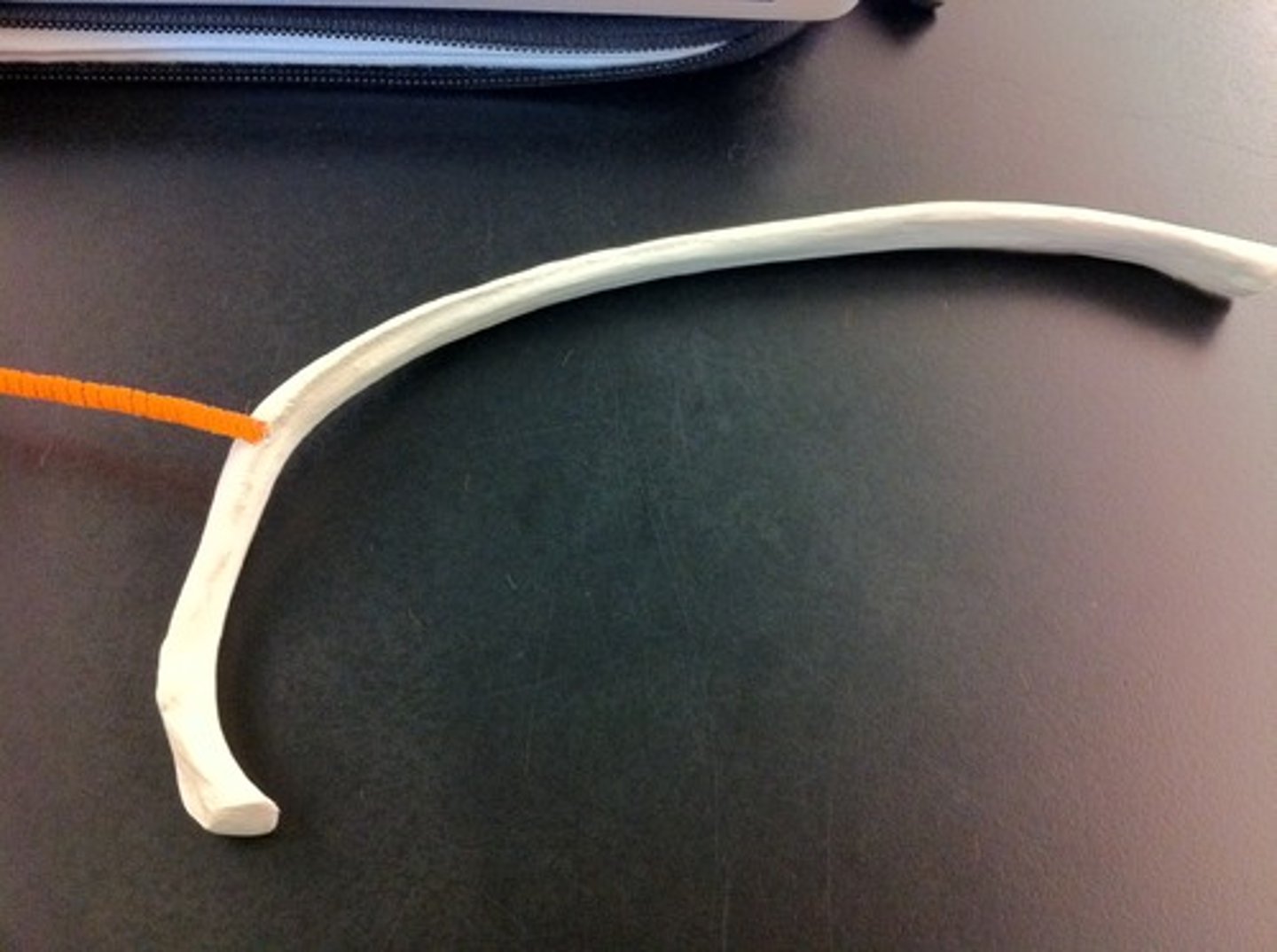

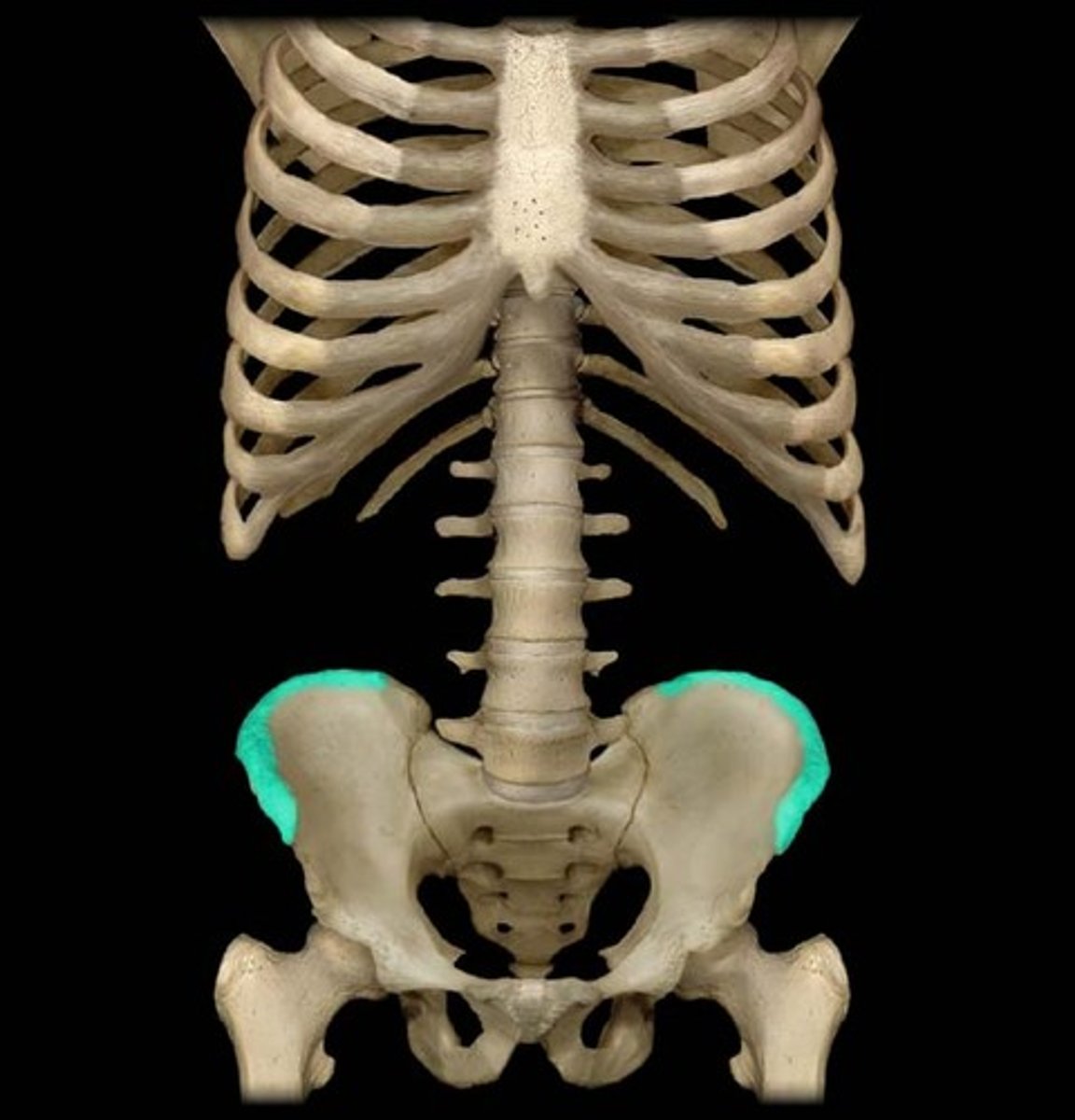
iliac crest
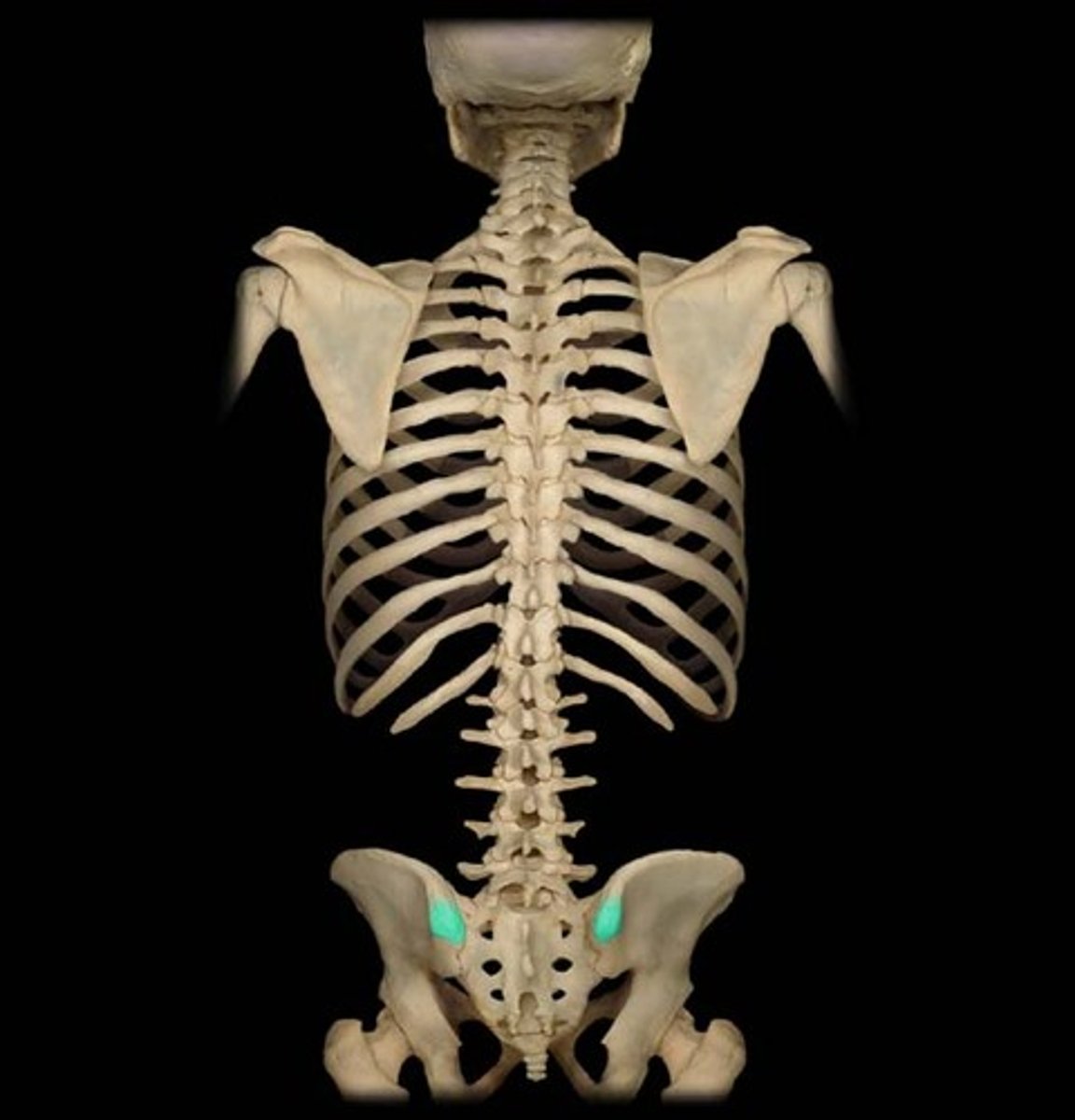
posterior superior iliac spine
median sacral crest
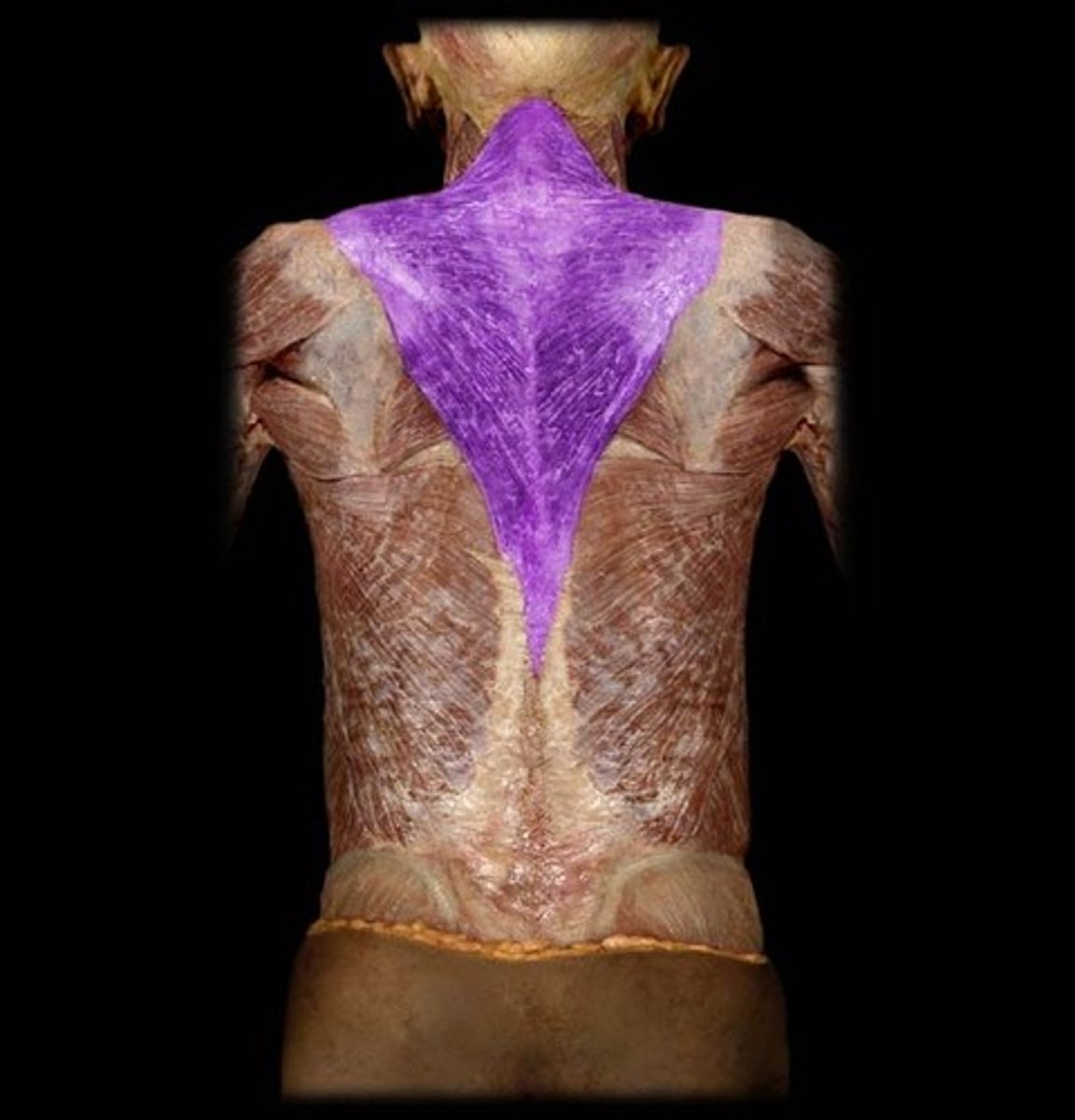
trapezius
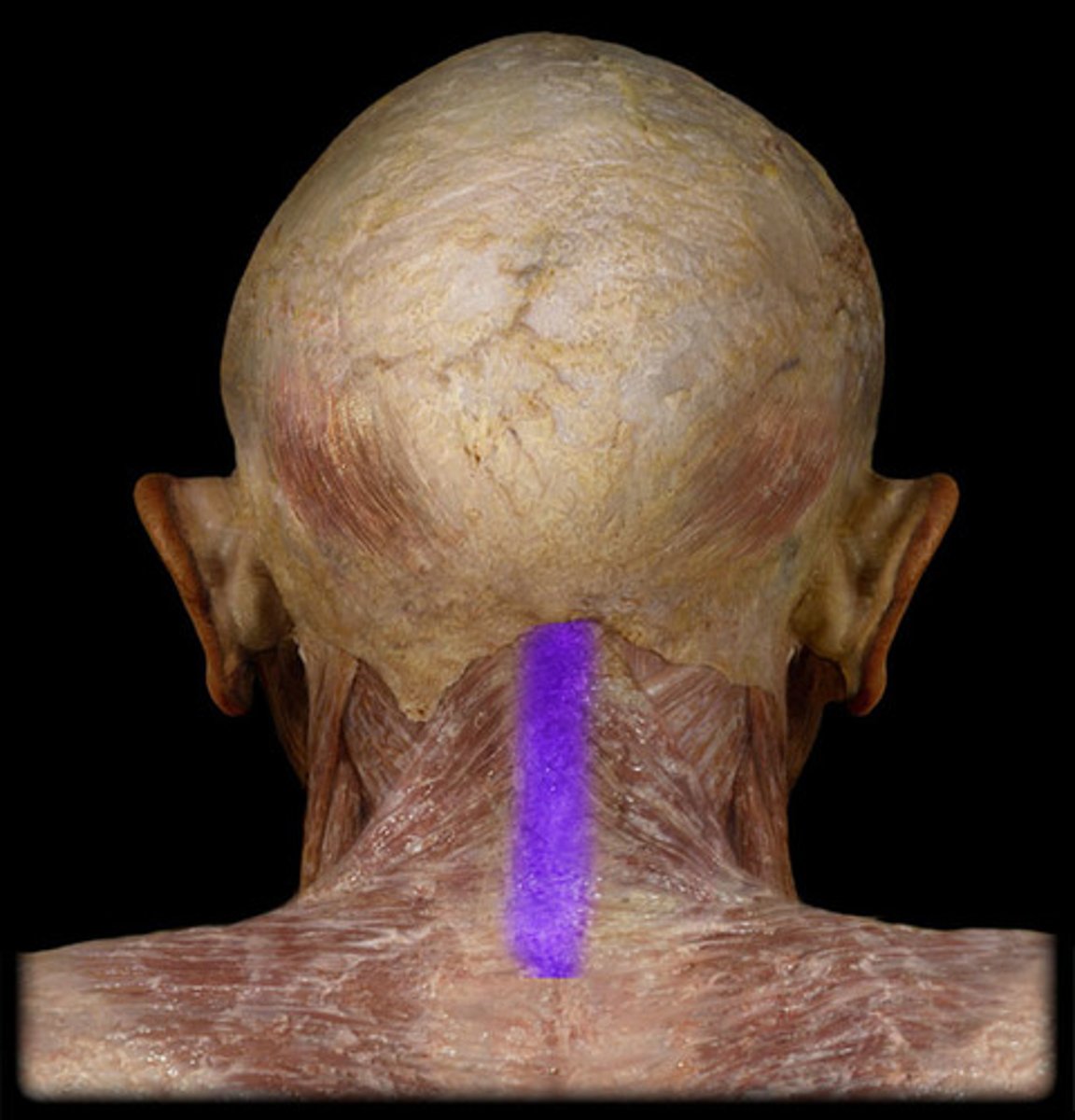
ligamentum nuchae (nuchal ligament)
spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
transverse cervical artery
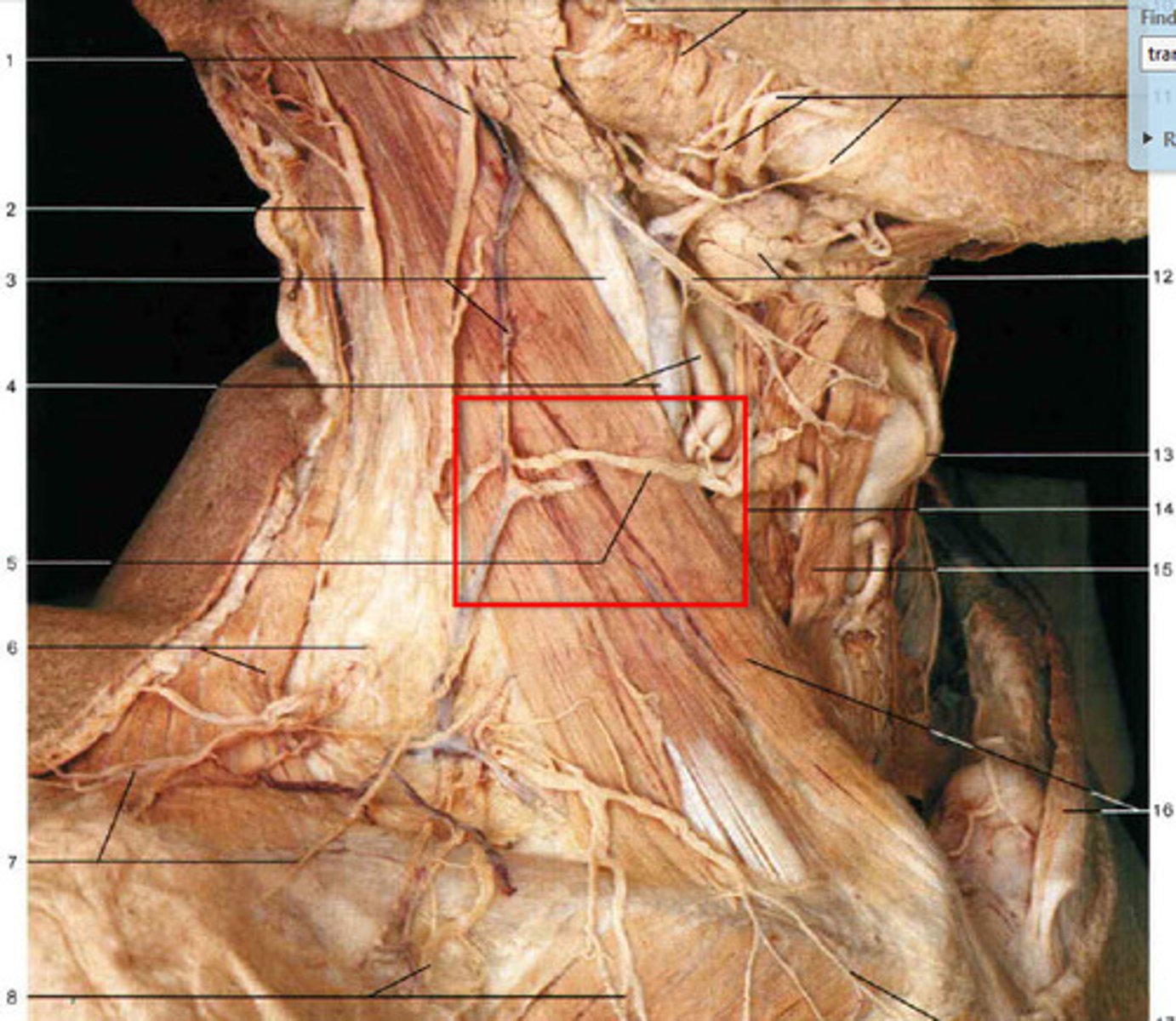
latissimus dorsi
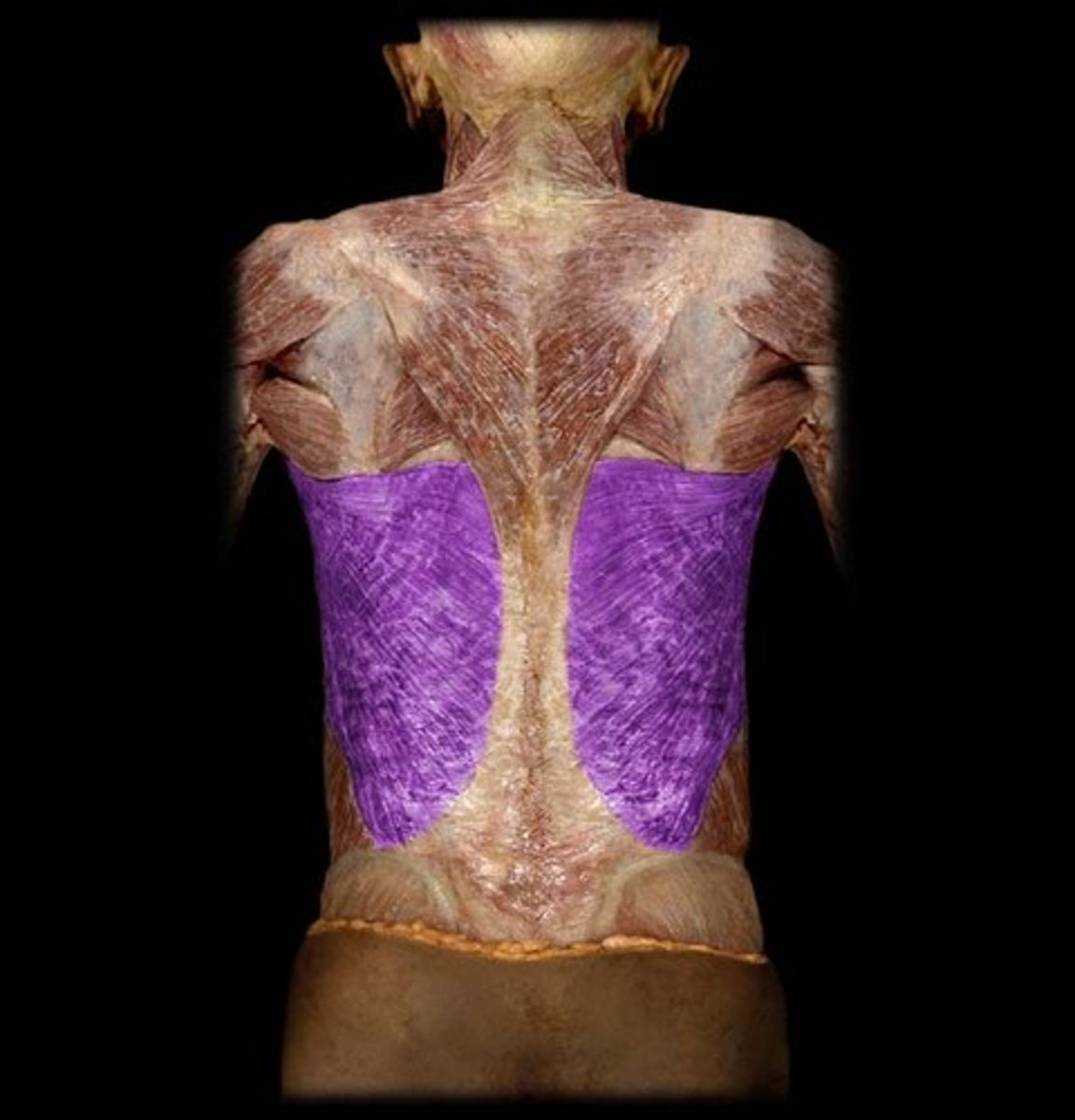
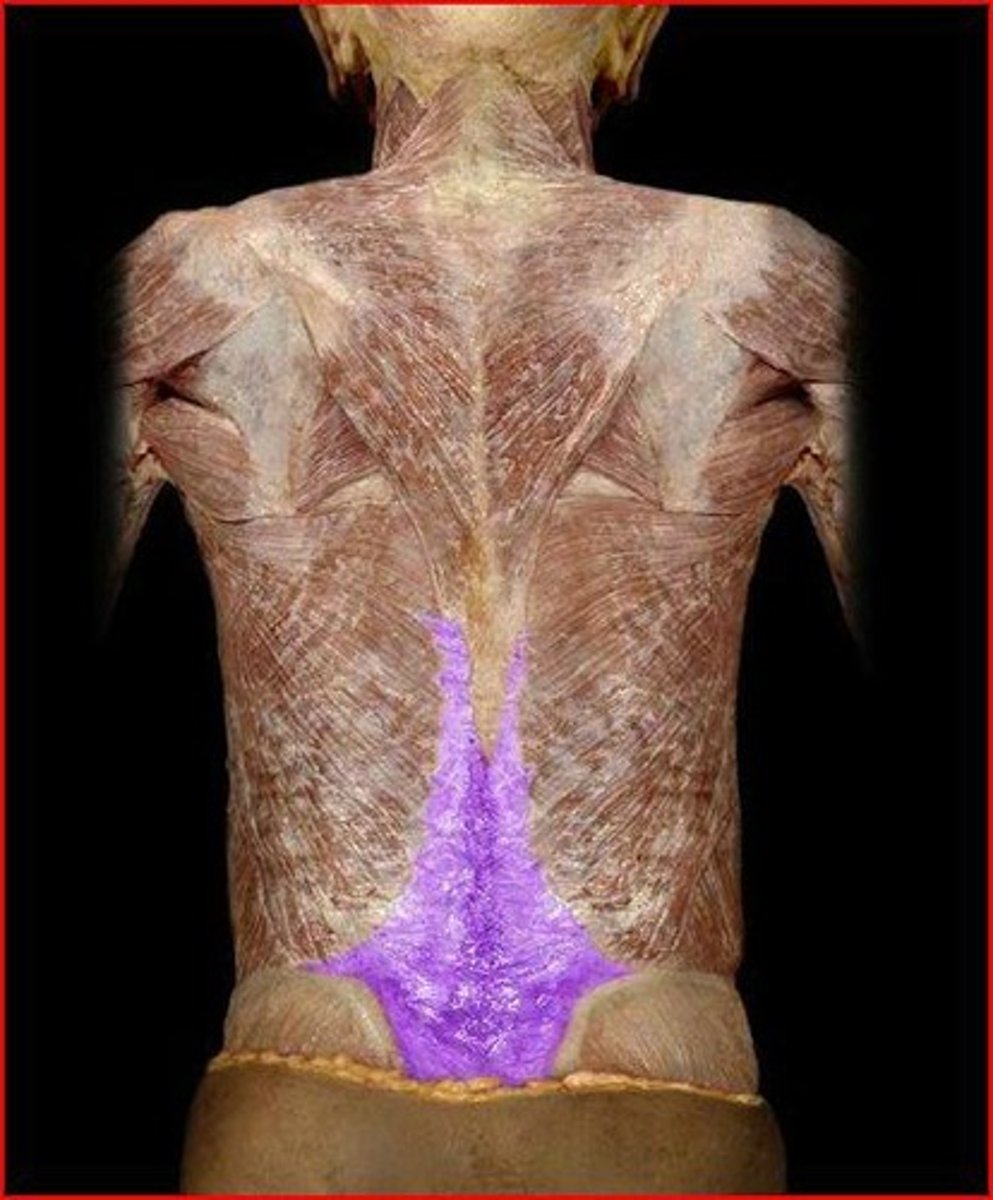
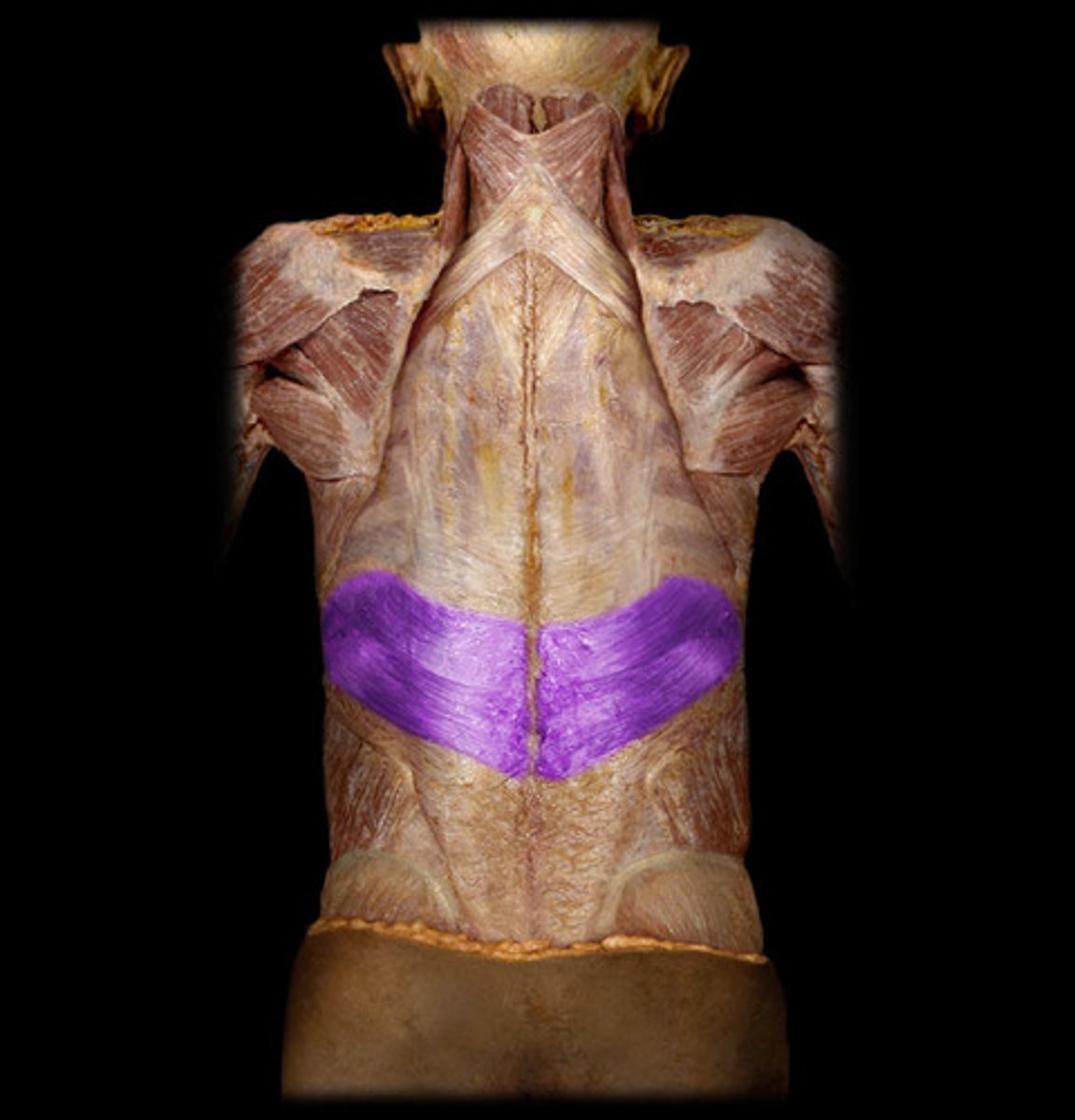
thoracolumbar fascia
Serratus Posterior Inferior
dorsal scapular nerve
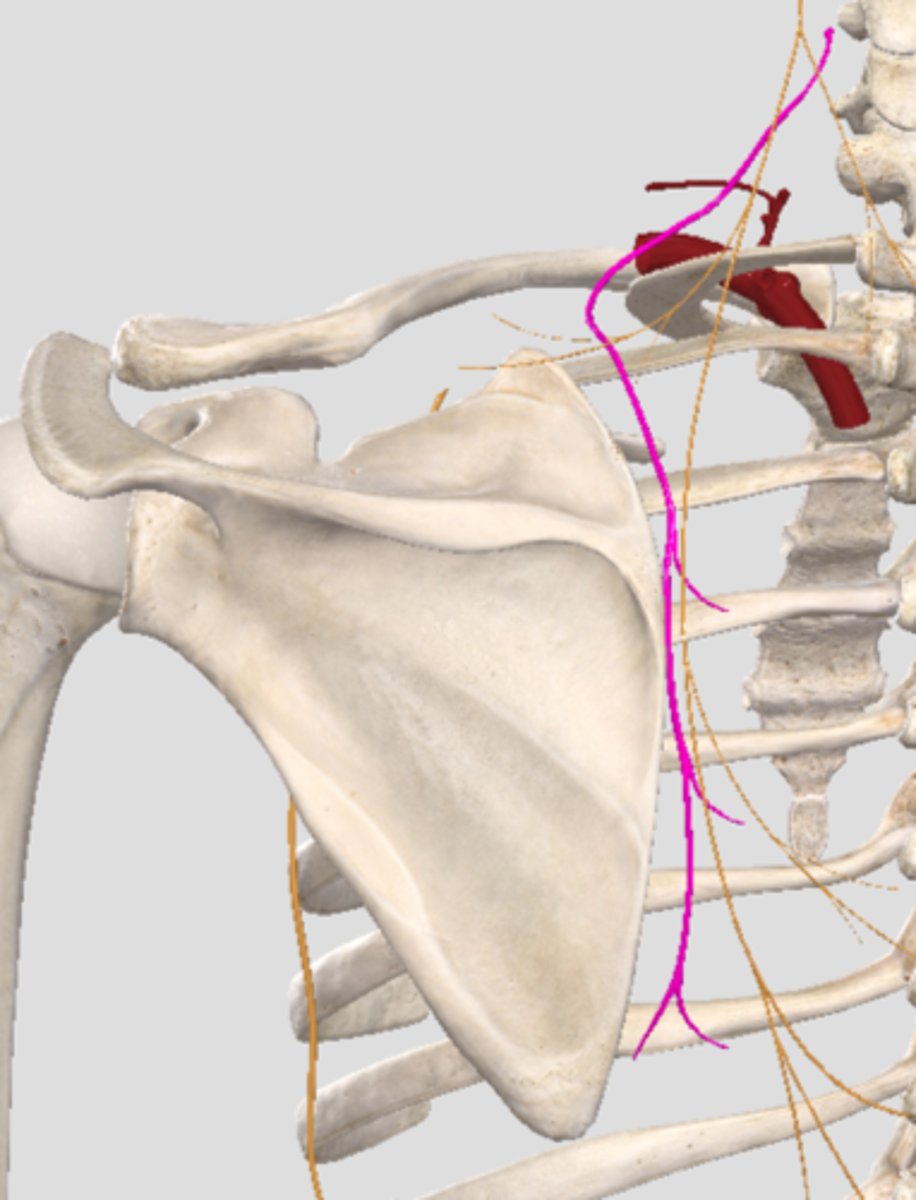
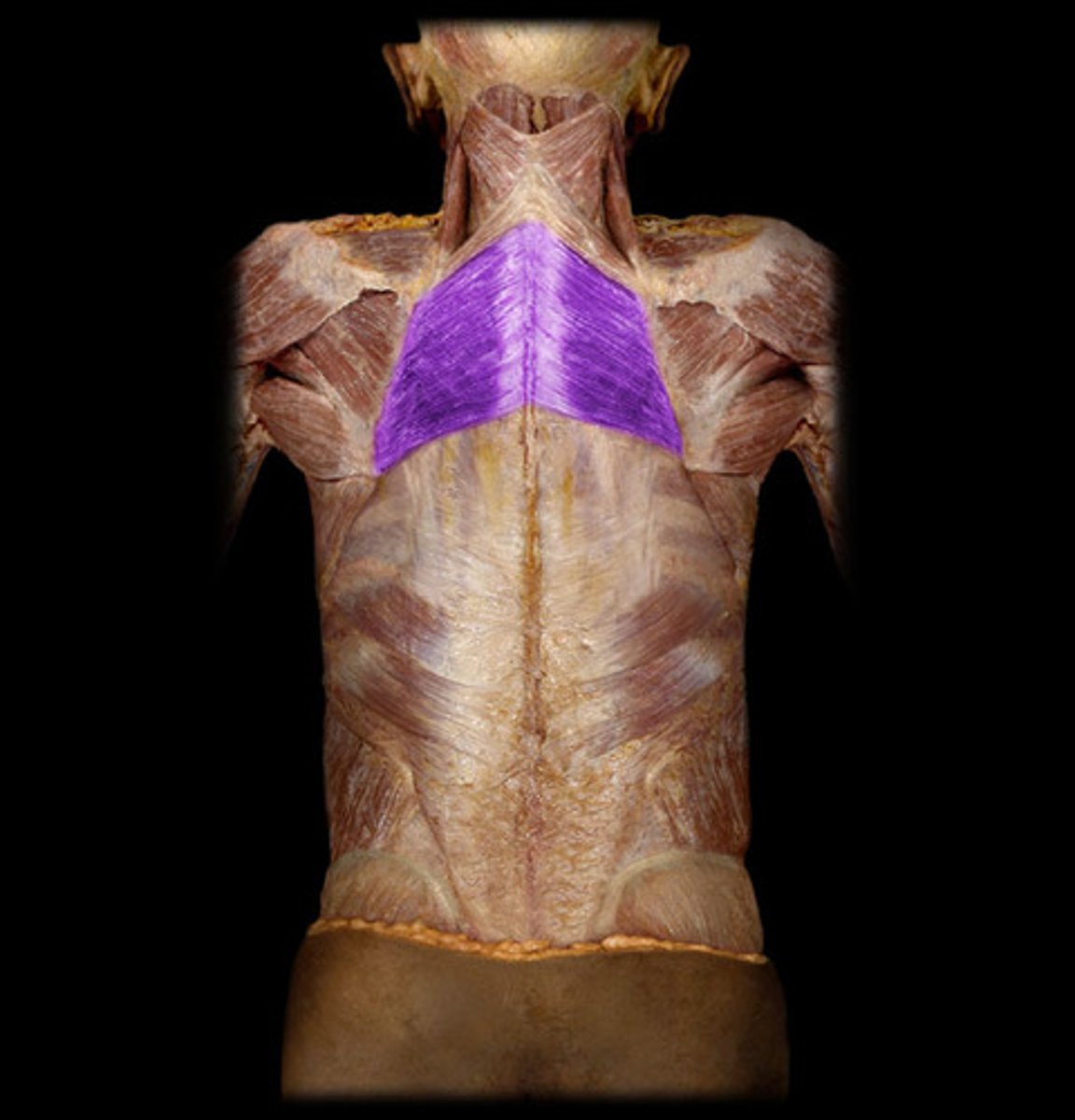
rhomboid major
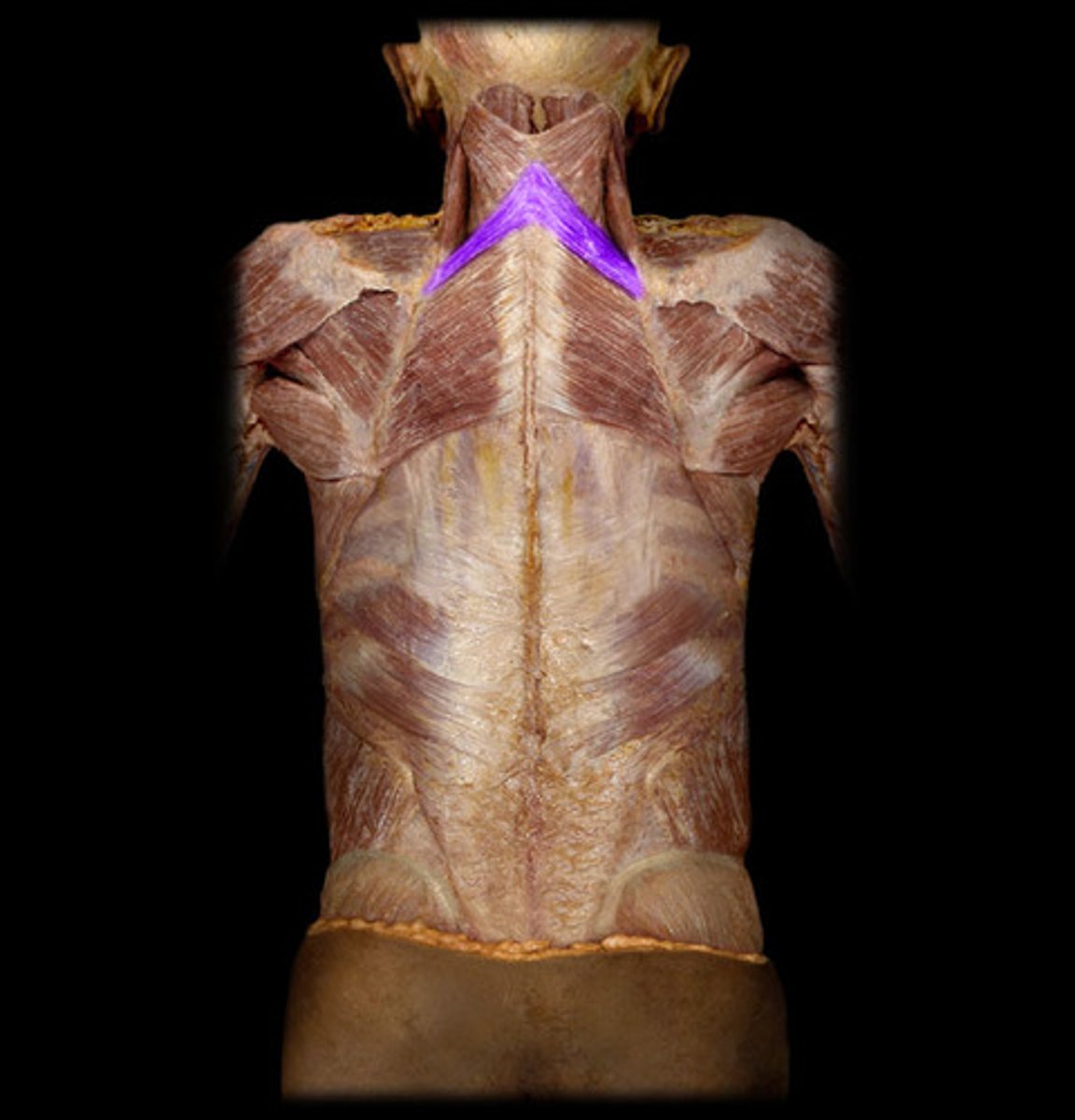
rhomboid minor
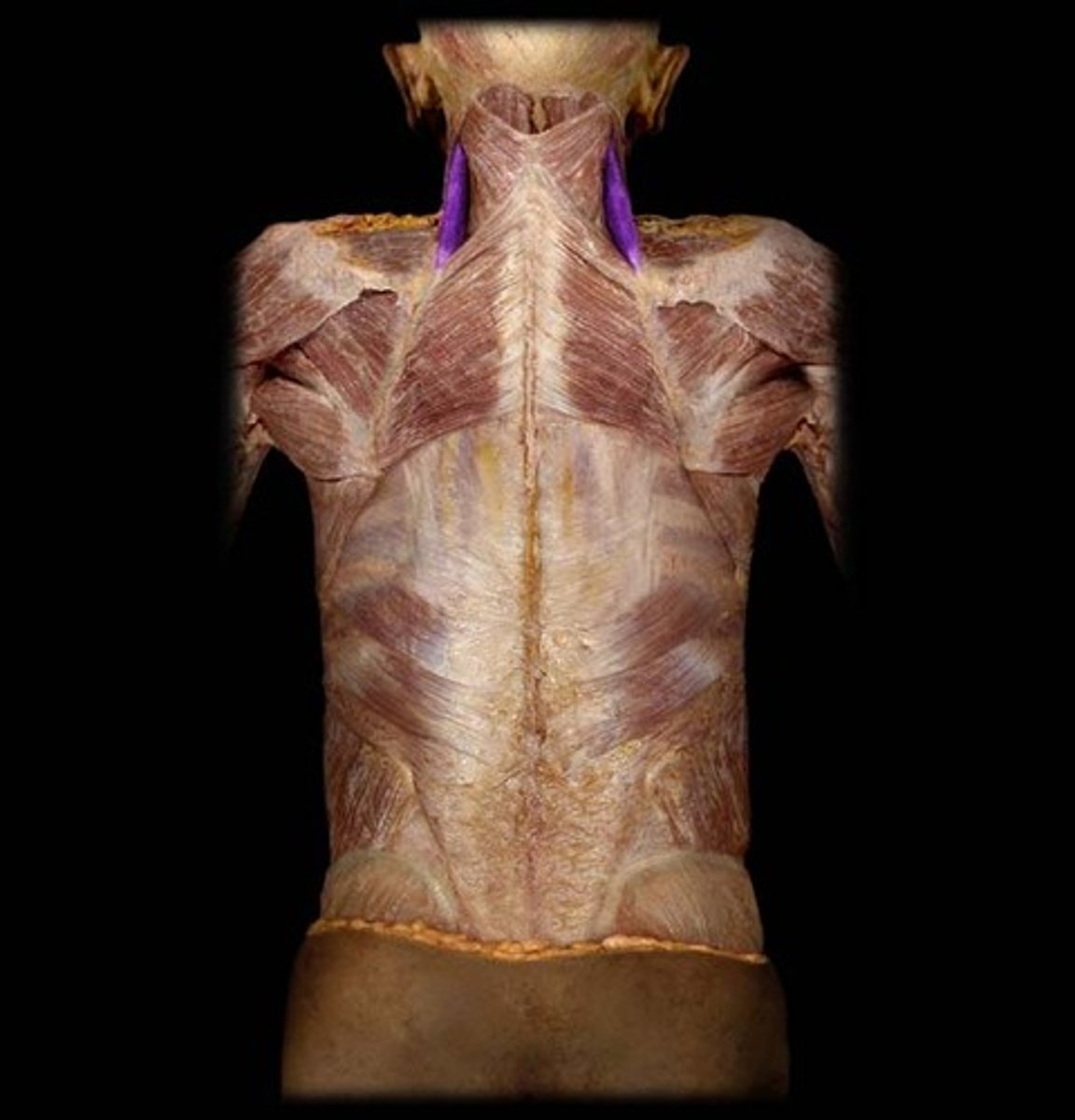
levator scapulae
Multifidus lumborum
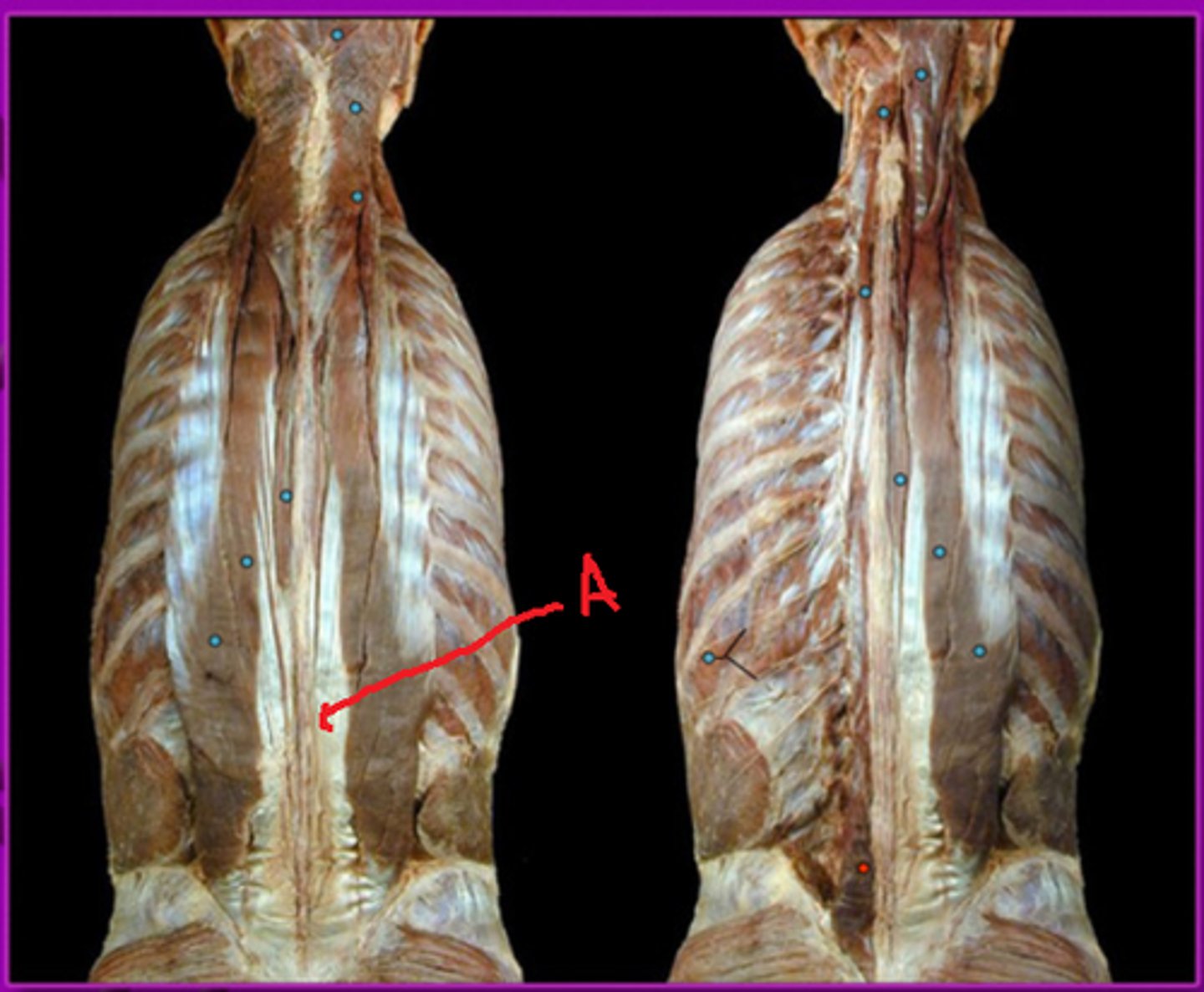
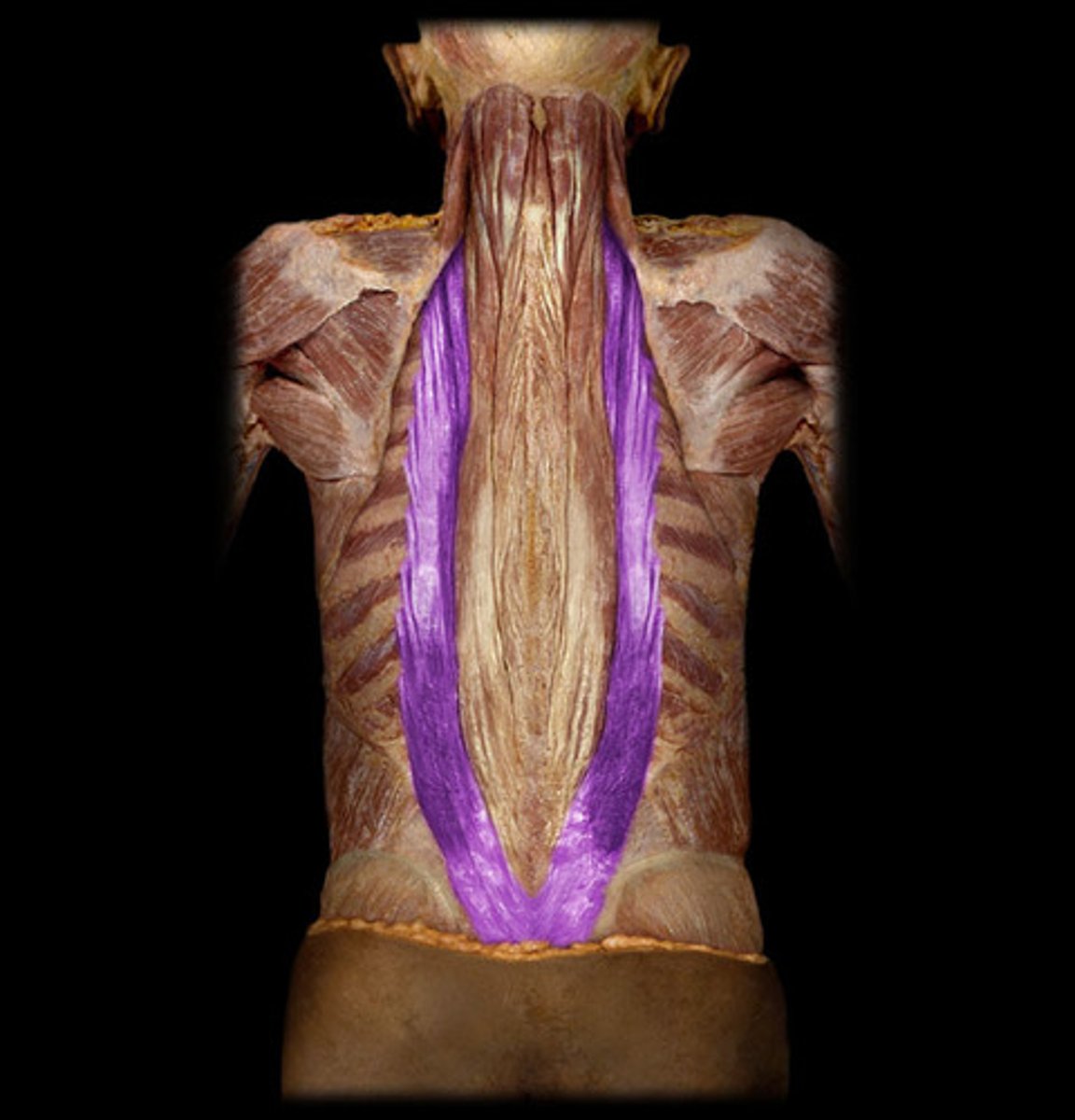
iliocostalis
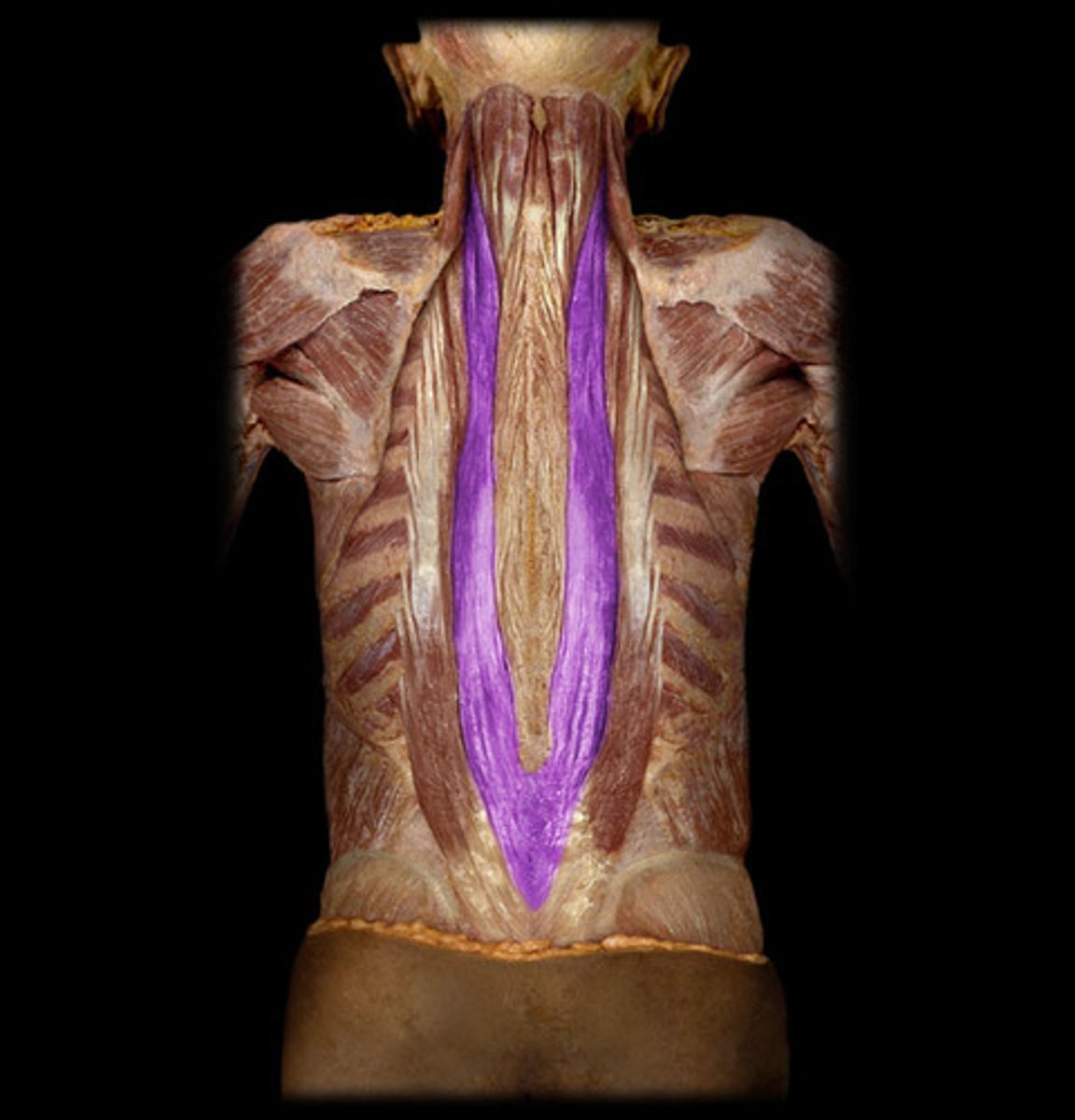
Longissimus
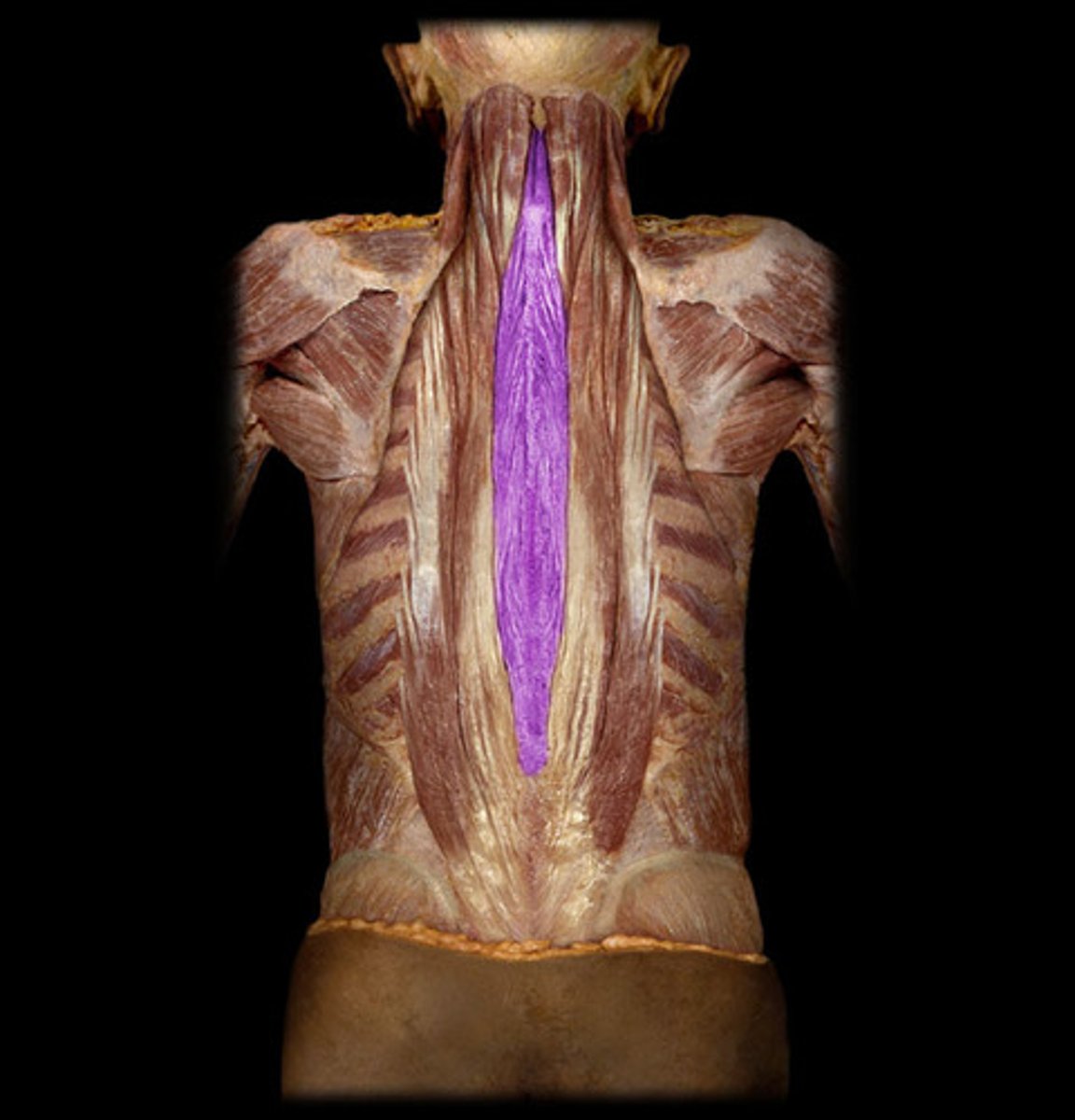
Spinalis
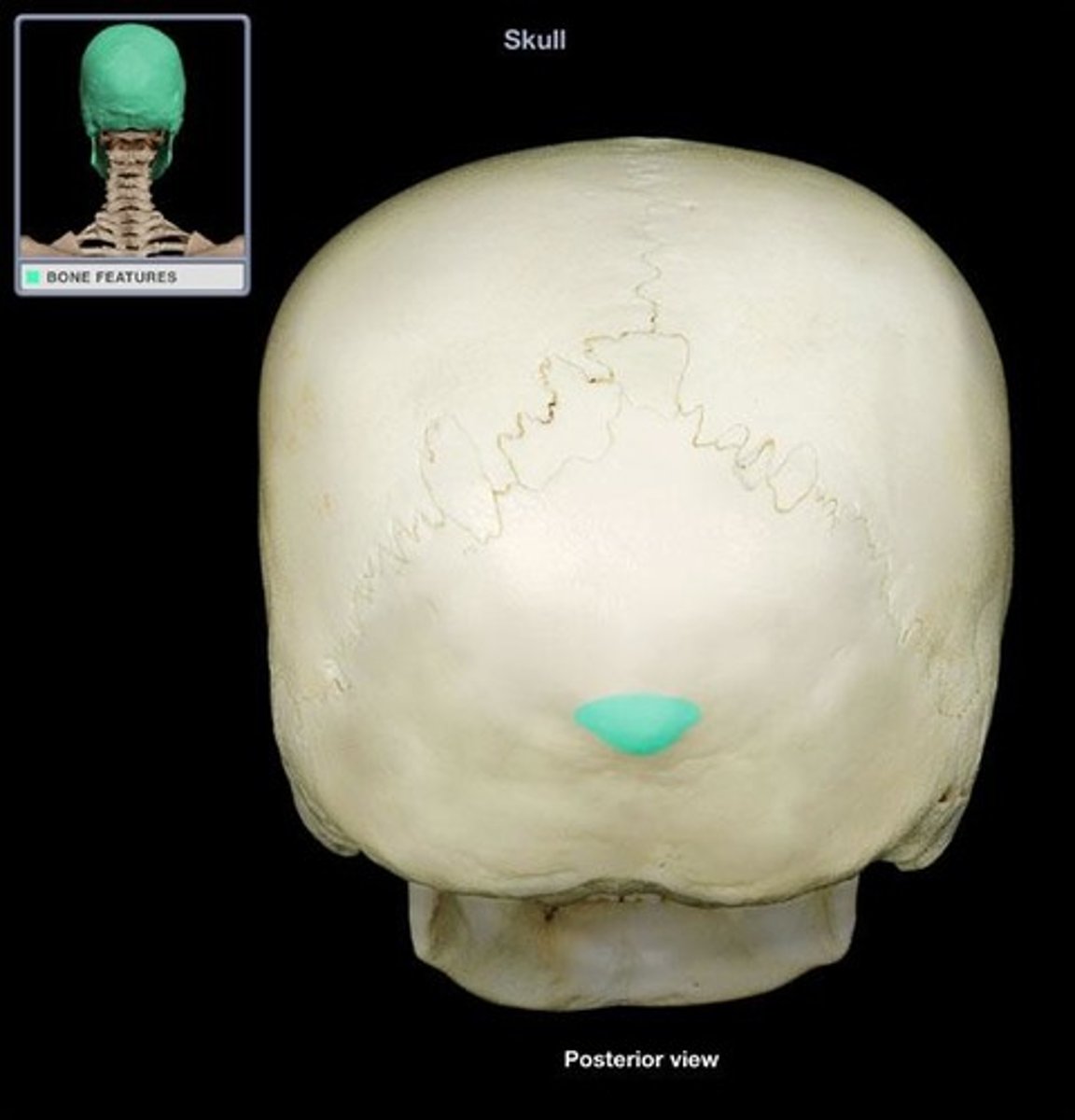
external occipital protuberance
- most posterior projection of cranium
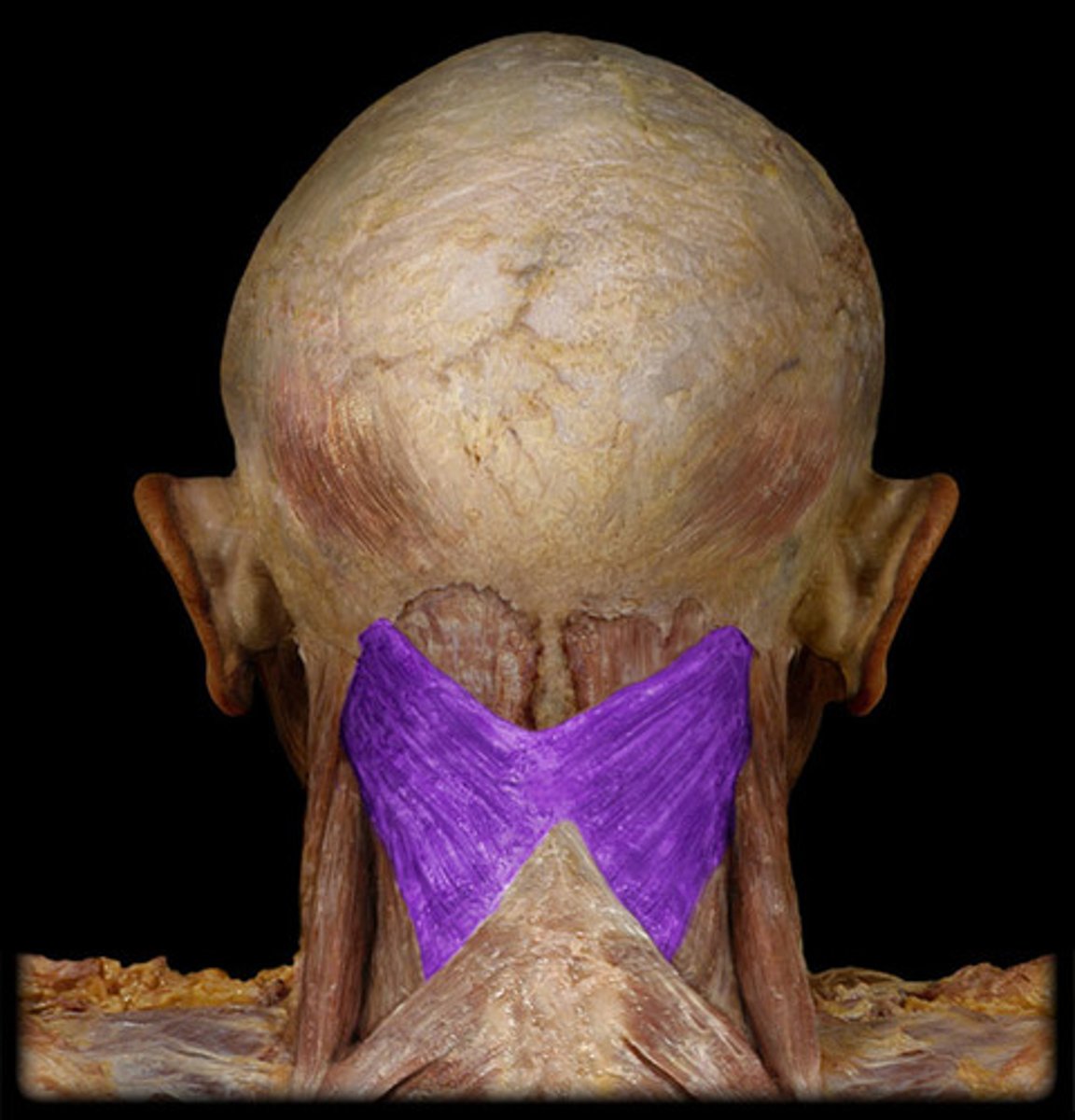
Serratus posterior superior
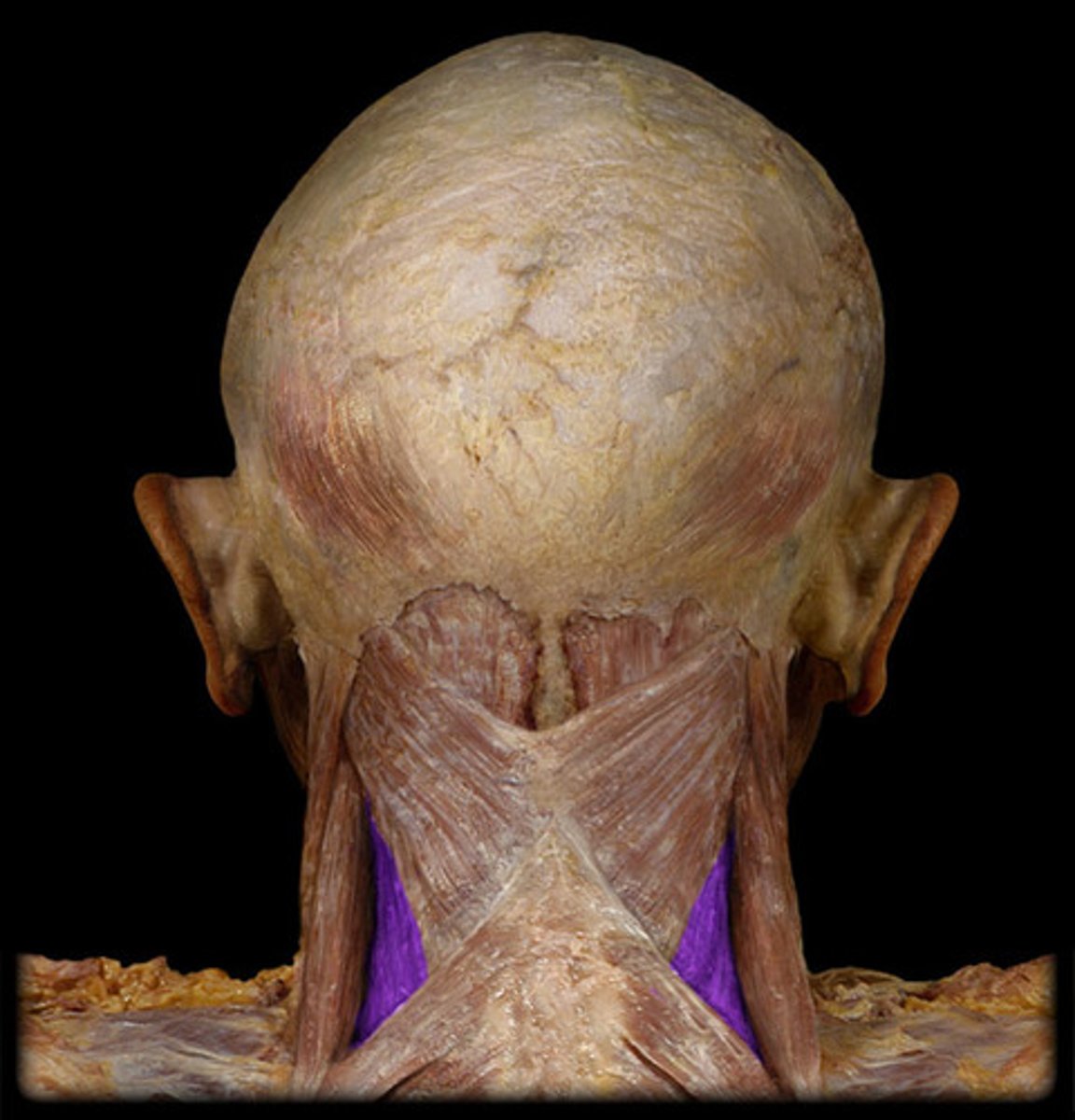
Splenius capitis
splenius cervicis
Semispinalis capitis
vertebral canal
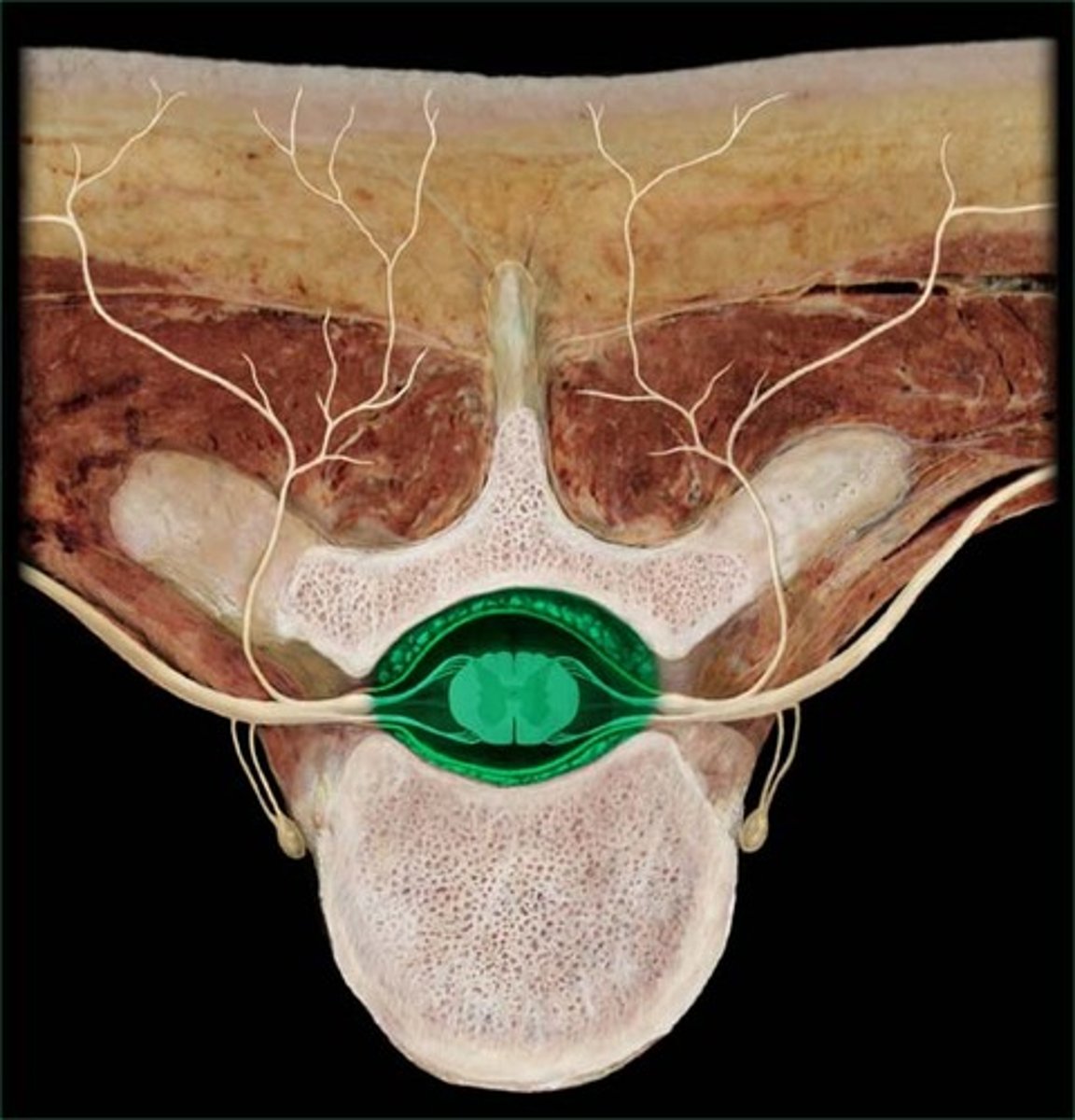
ligamentum flavum
- thick and yellowish
- connects adjacent laminae
epidural space
- between dura mater and bone
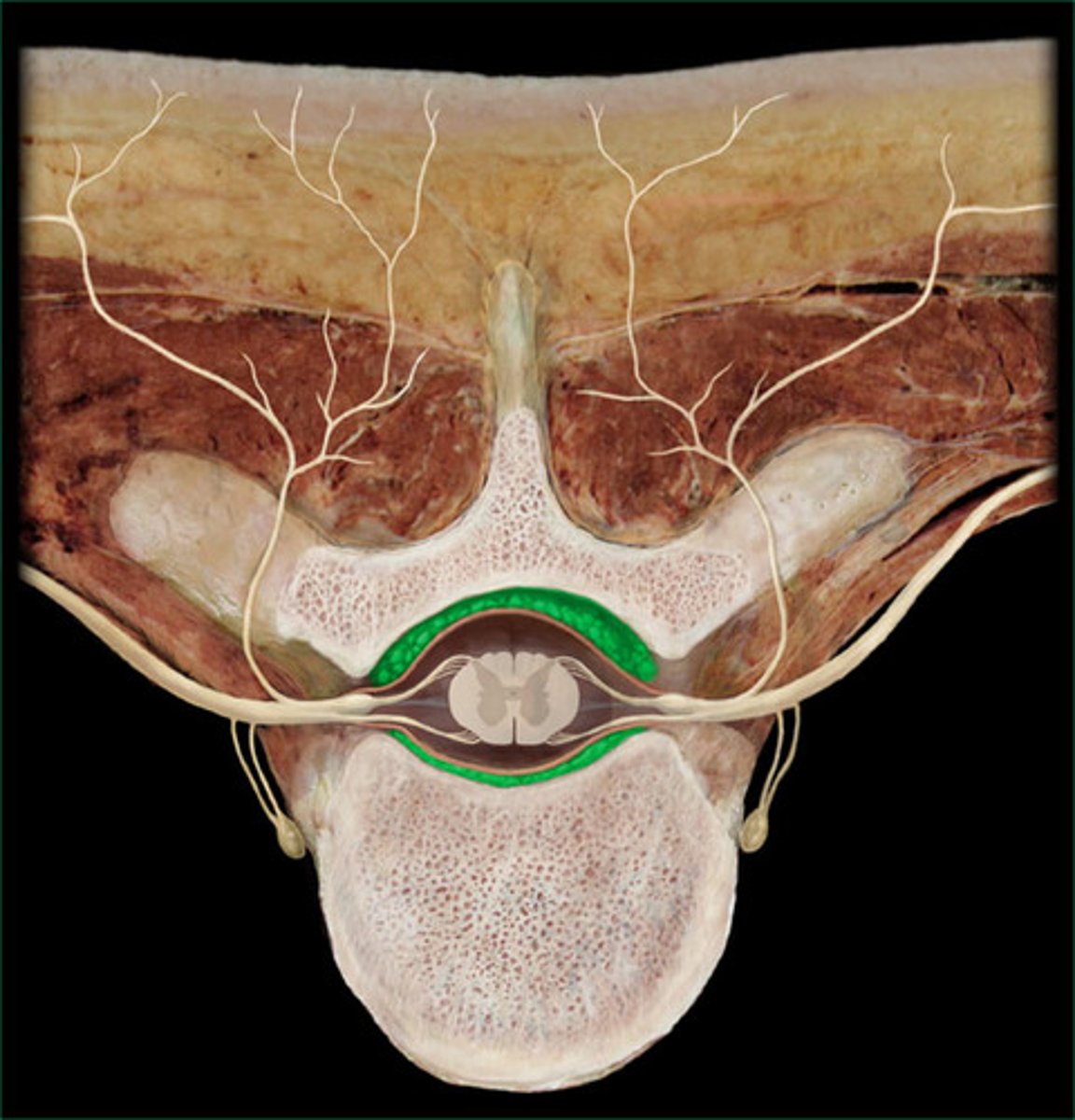
epidural fat
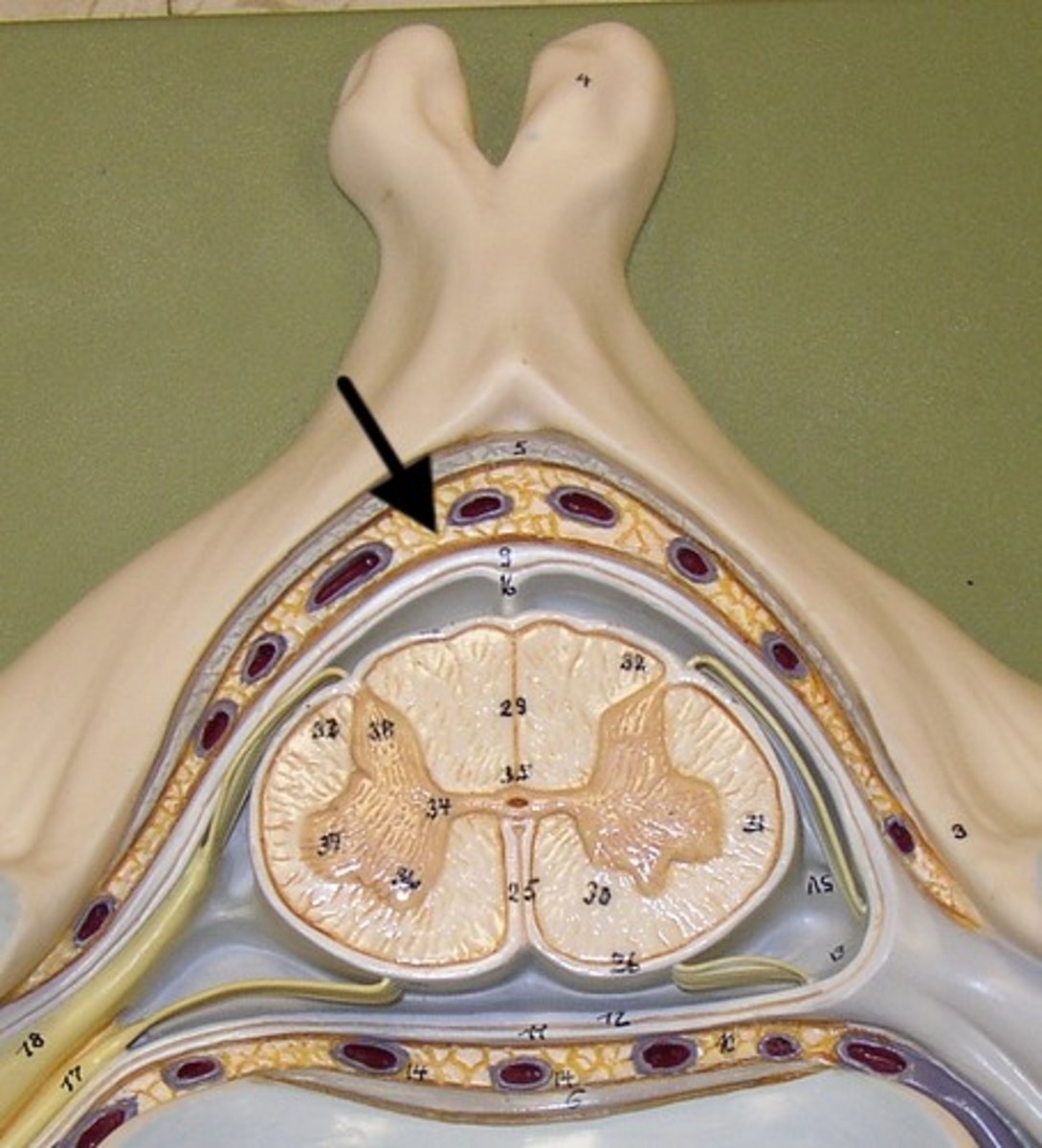
internal vertebral venous plexus
- located in epidural space
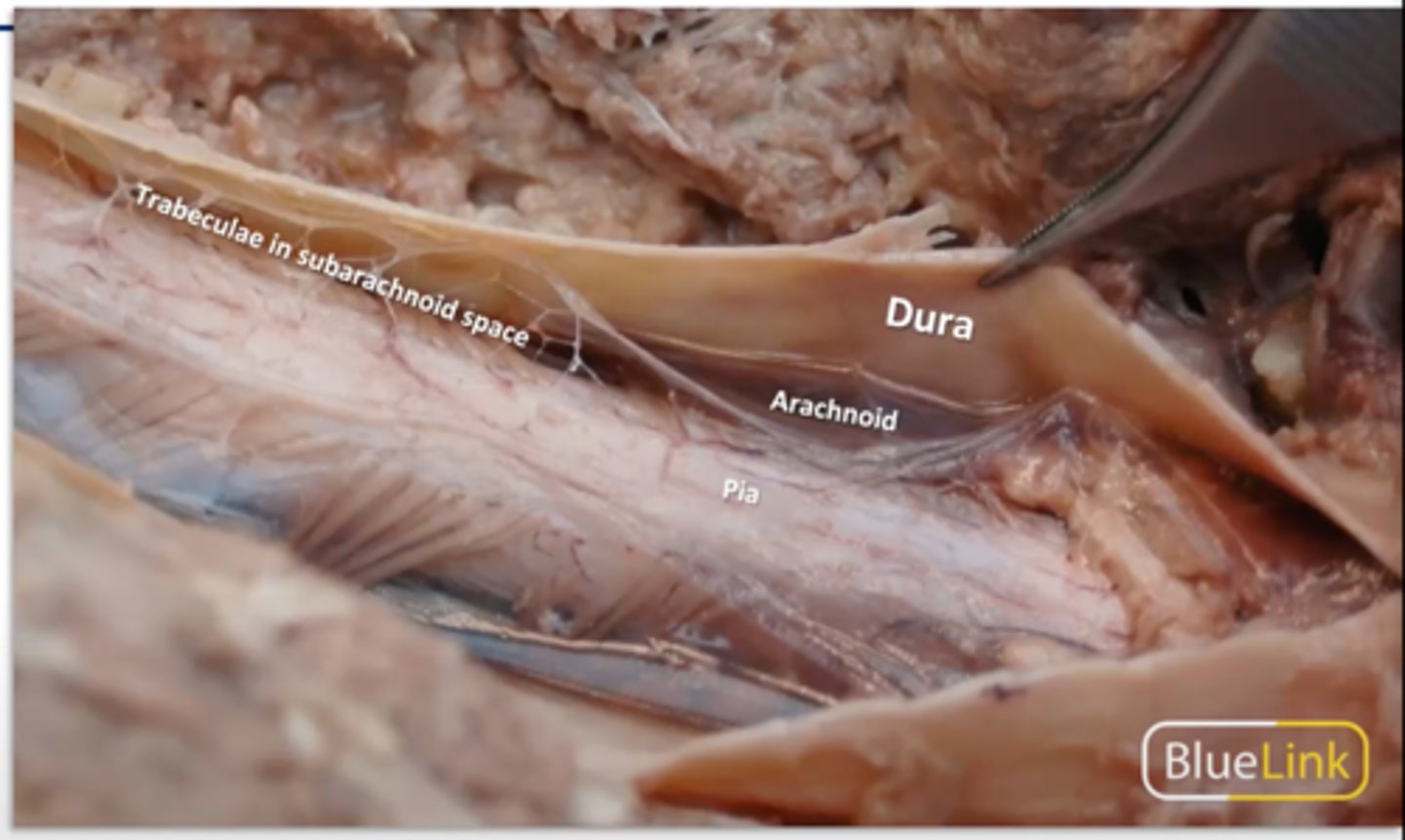
meninges
- dura mater (outermost, thickest)
- arachnoid (subarachnoid space has CSF)
- pia mater
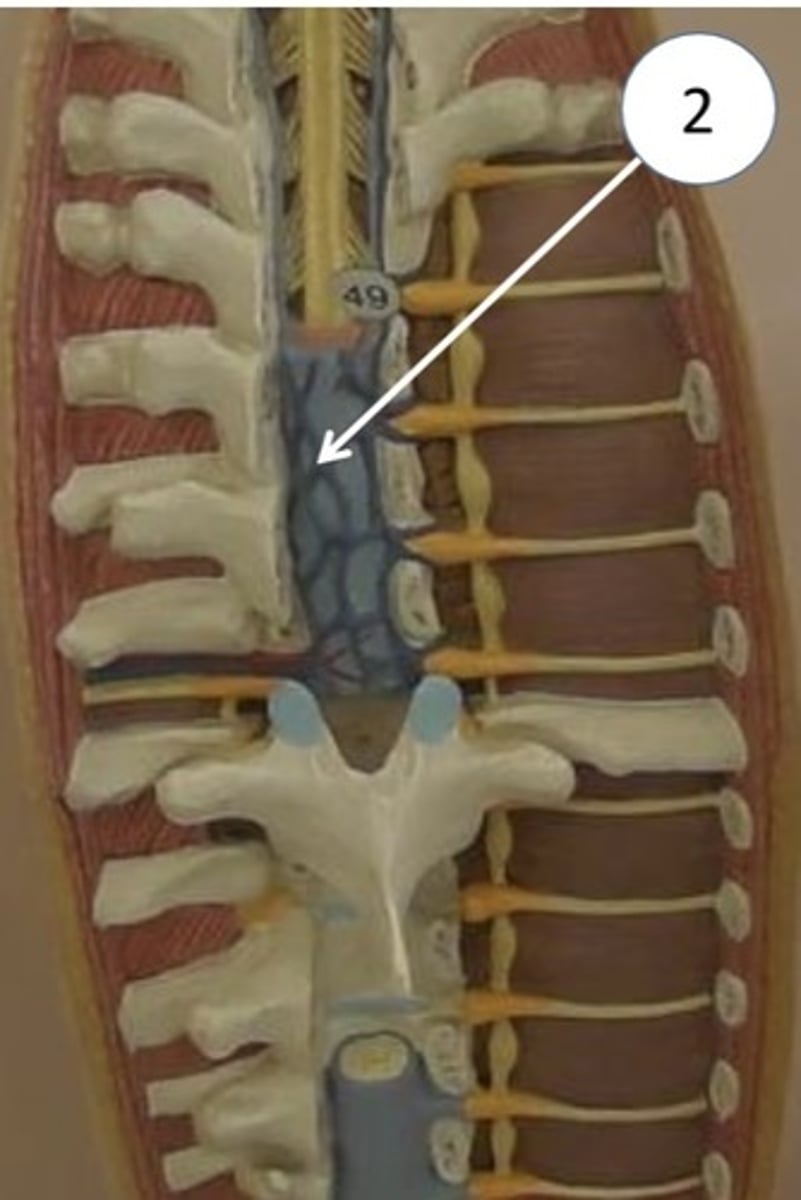
dural (thecal) sac
- ends at S2
?
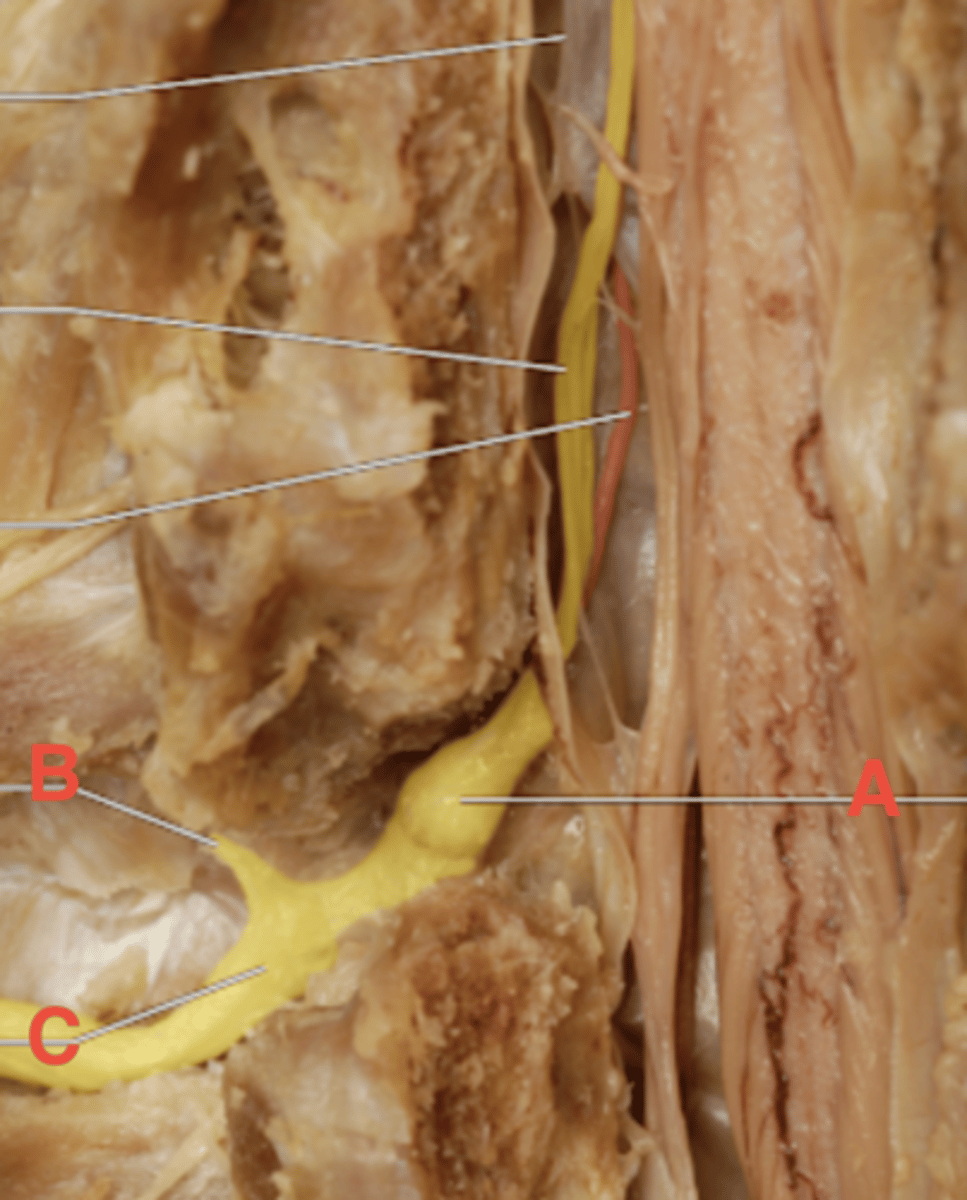
spinal (dorsal root) ganglion
What is 8?
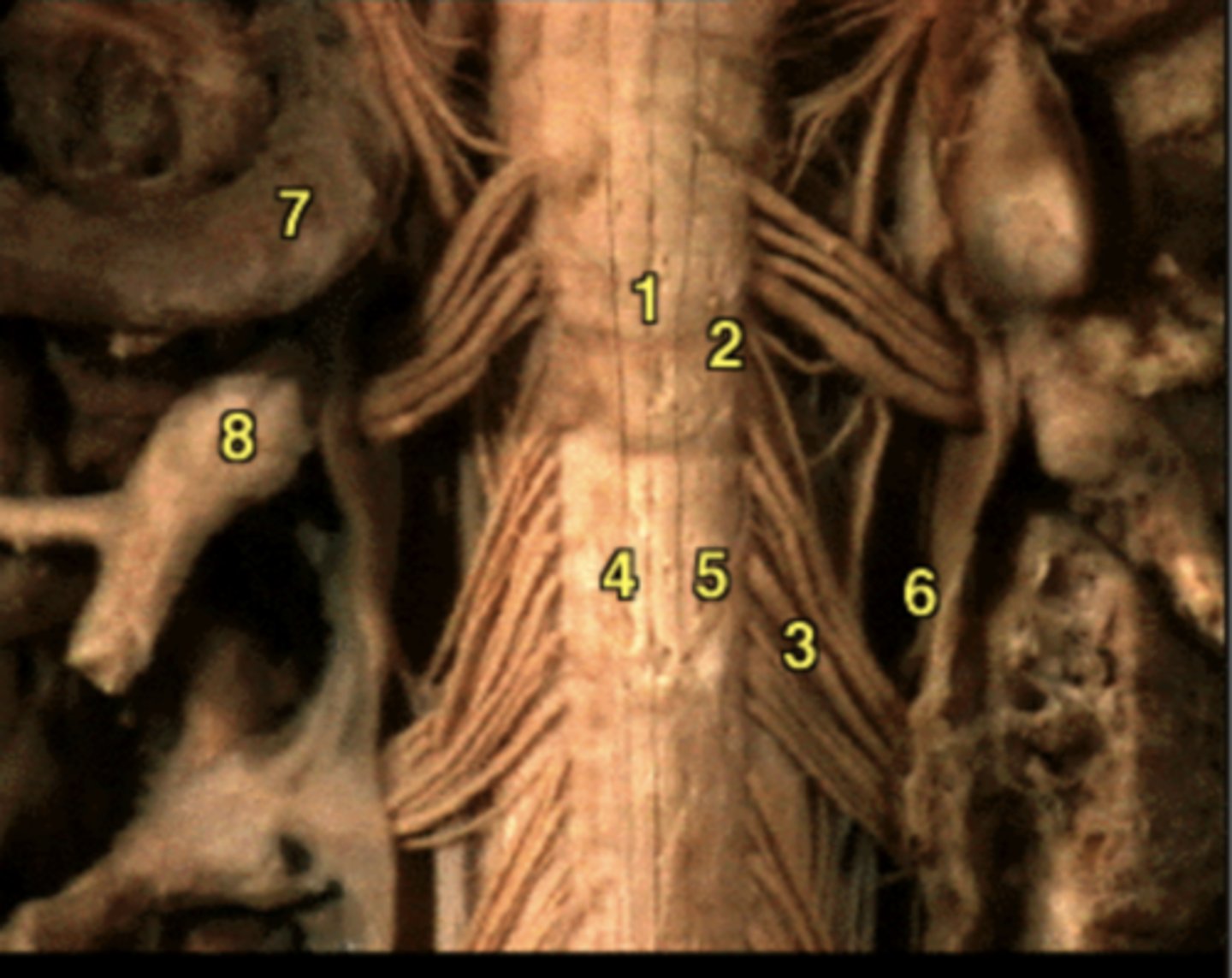
A: dorsal root ganglion
B: dorsal rami
C: ventral rami
cervical enlargement of spinal cord
lumbosacral enlargement of spinal cord
conus medullaris
- tapered end of the spinal cord at L1 and L2
red line
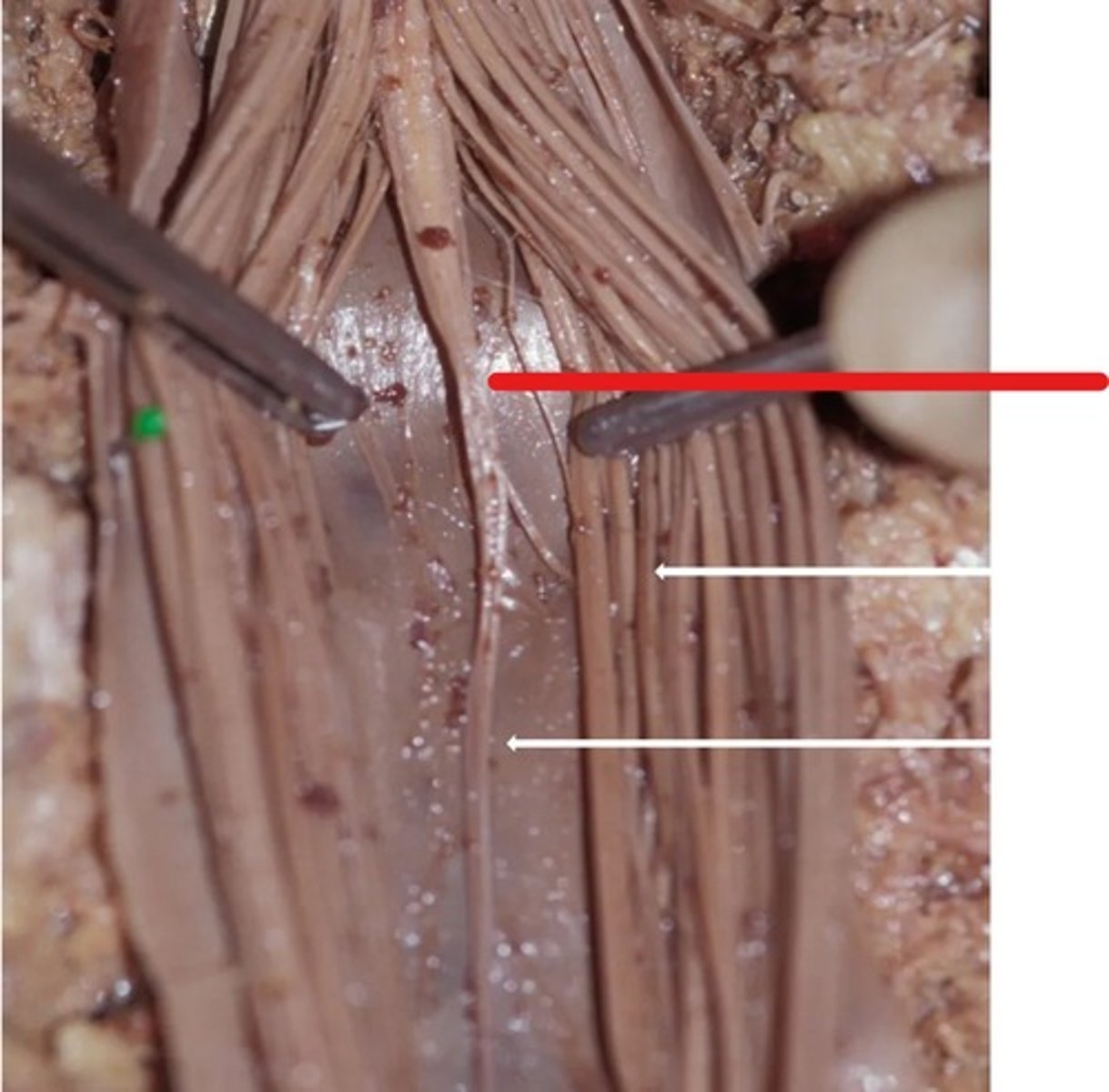

filum terminale
red line
cauda equina
- collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
(looks like horse tail)
denticulate ligaments
- extensions of pia mater that secure cord to dura mater
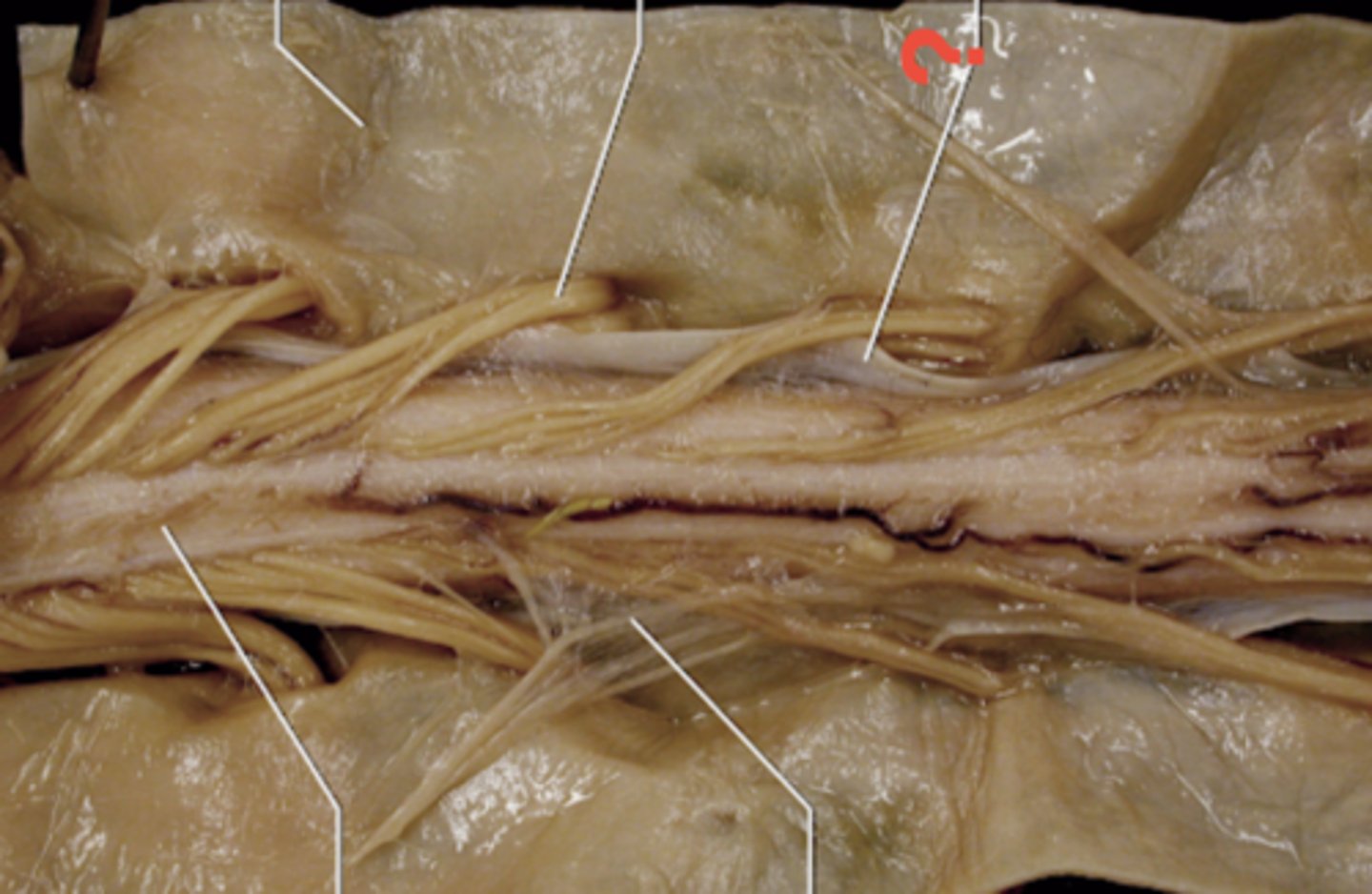
posterior spinal arteries
F
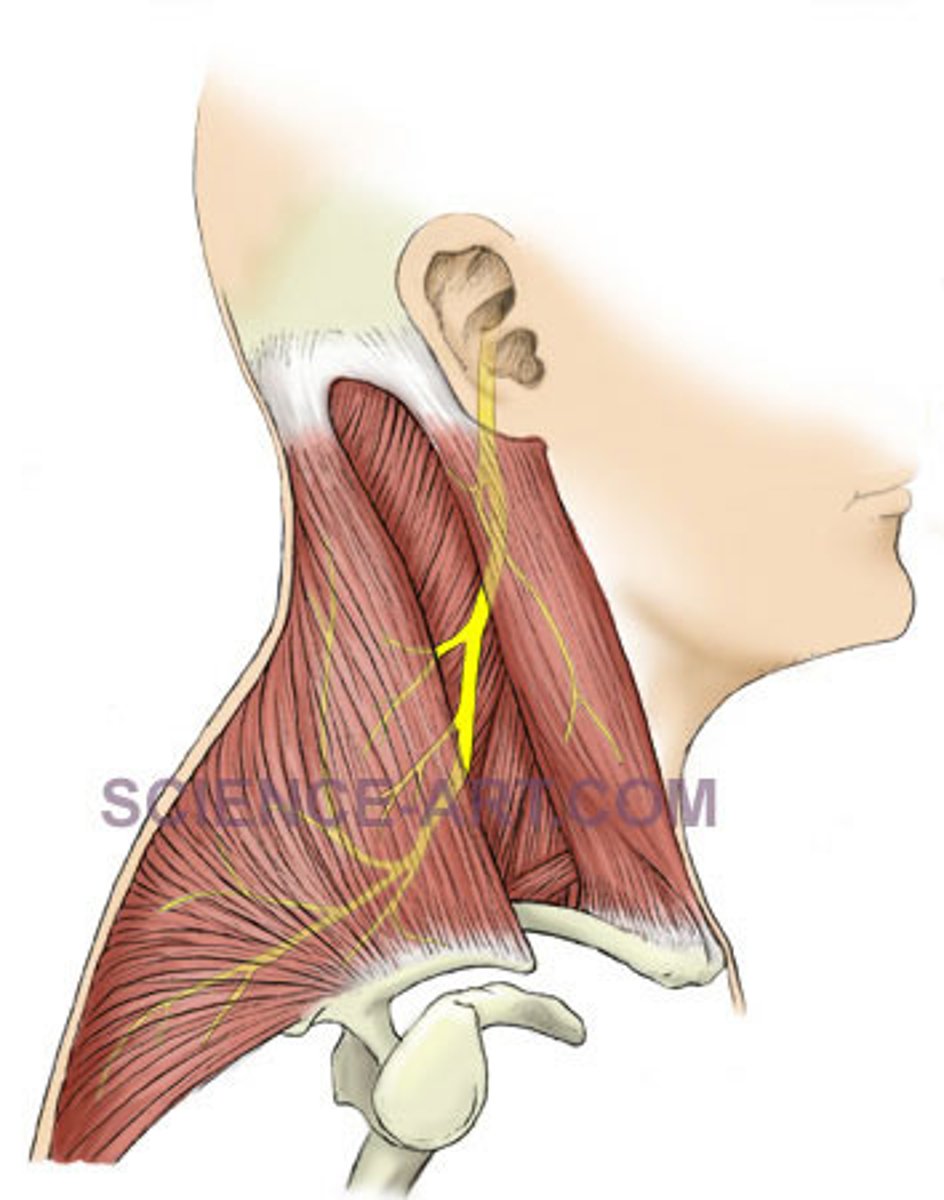
Greater occipital nerve
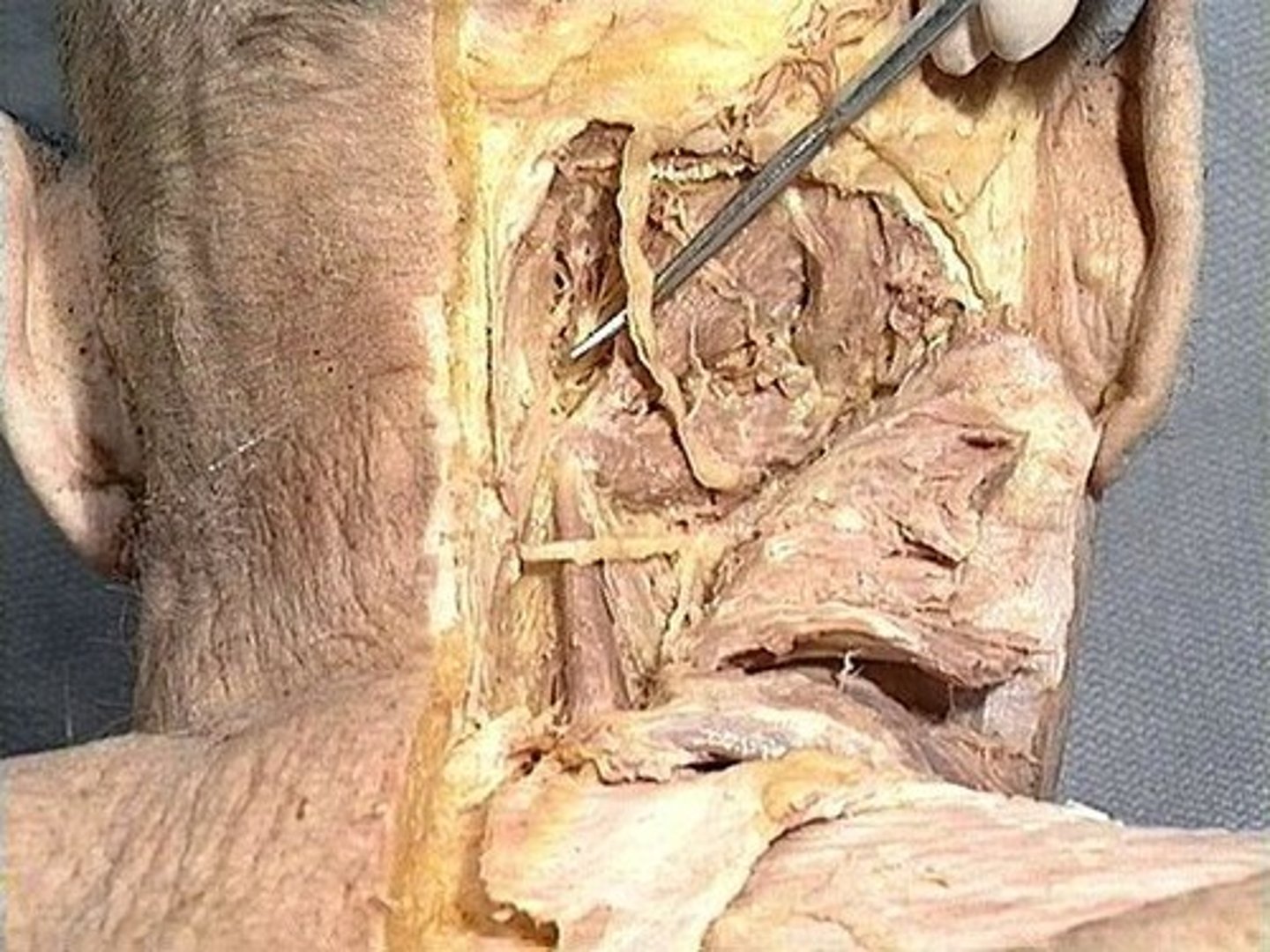
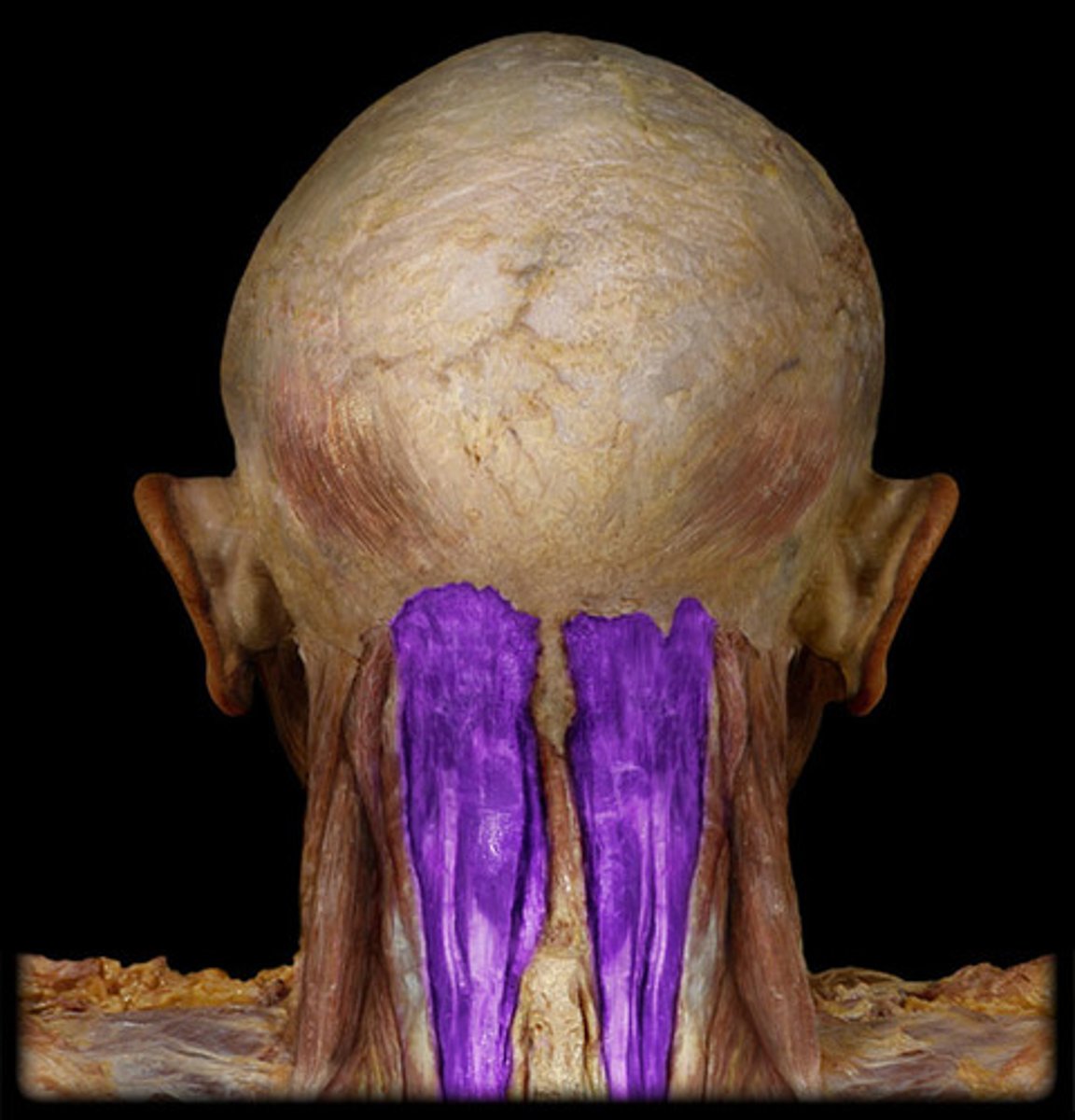
Rectus capitis posterior major
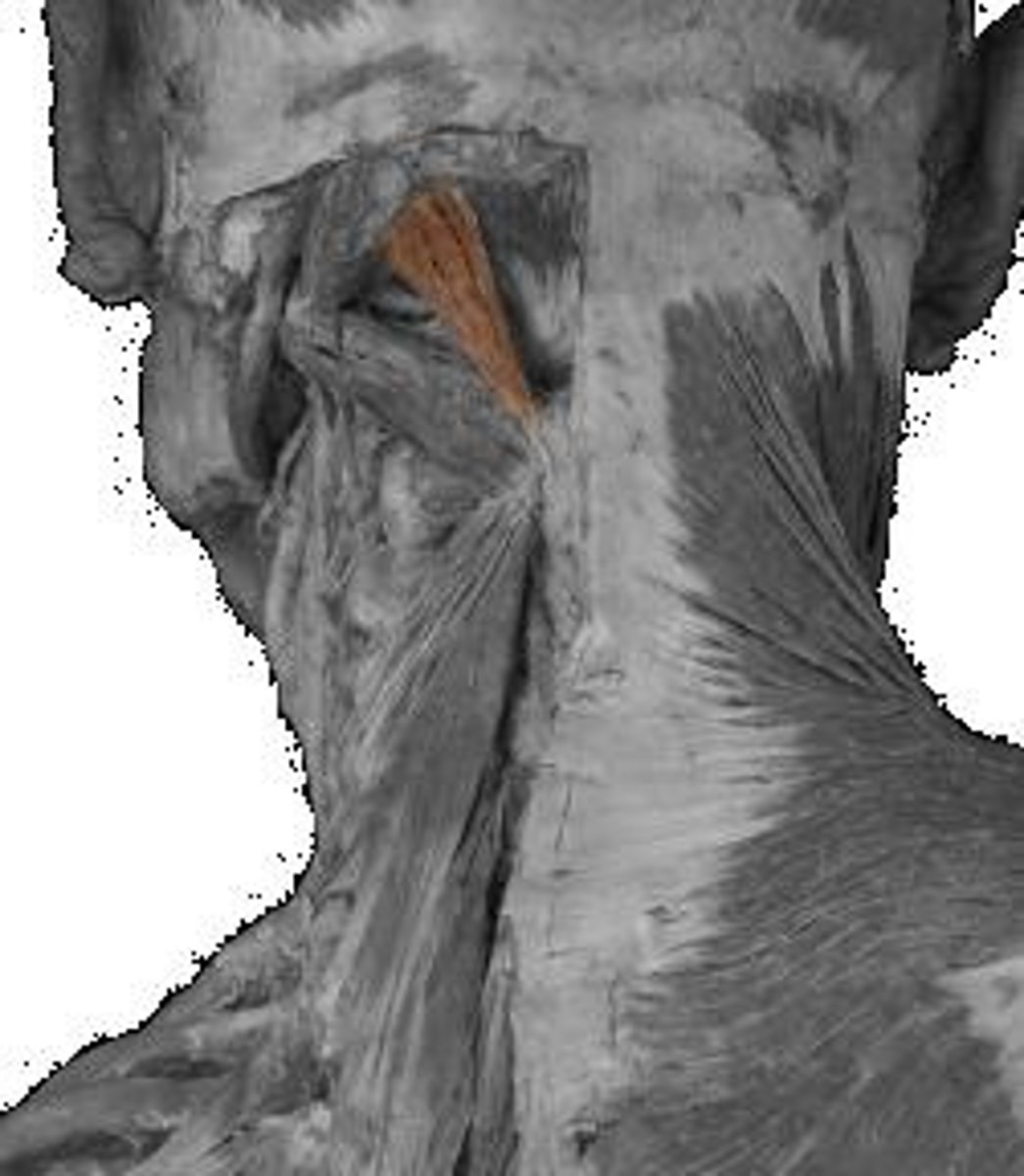
Obliquus capitis inferior
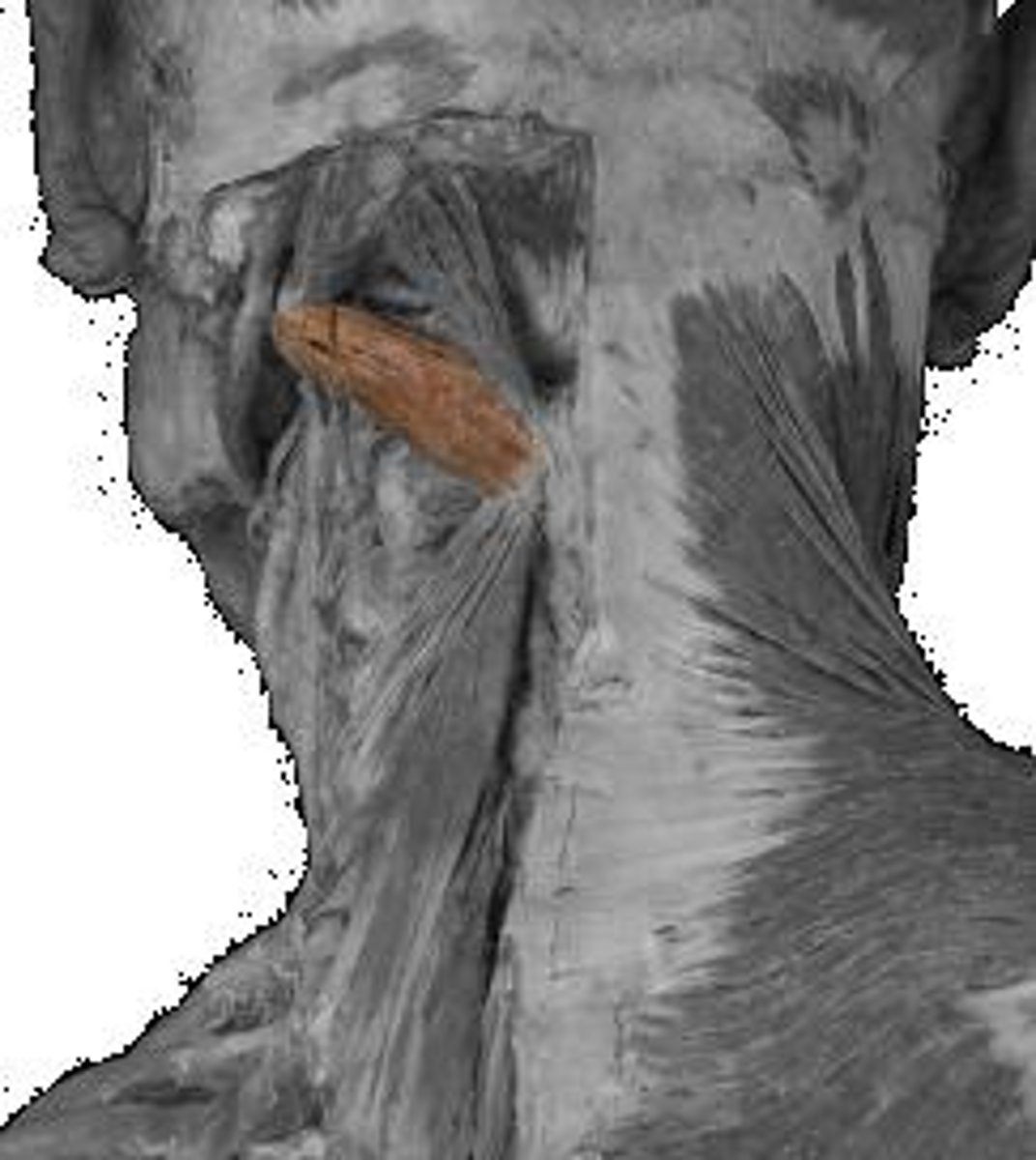
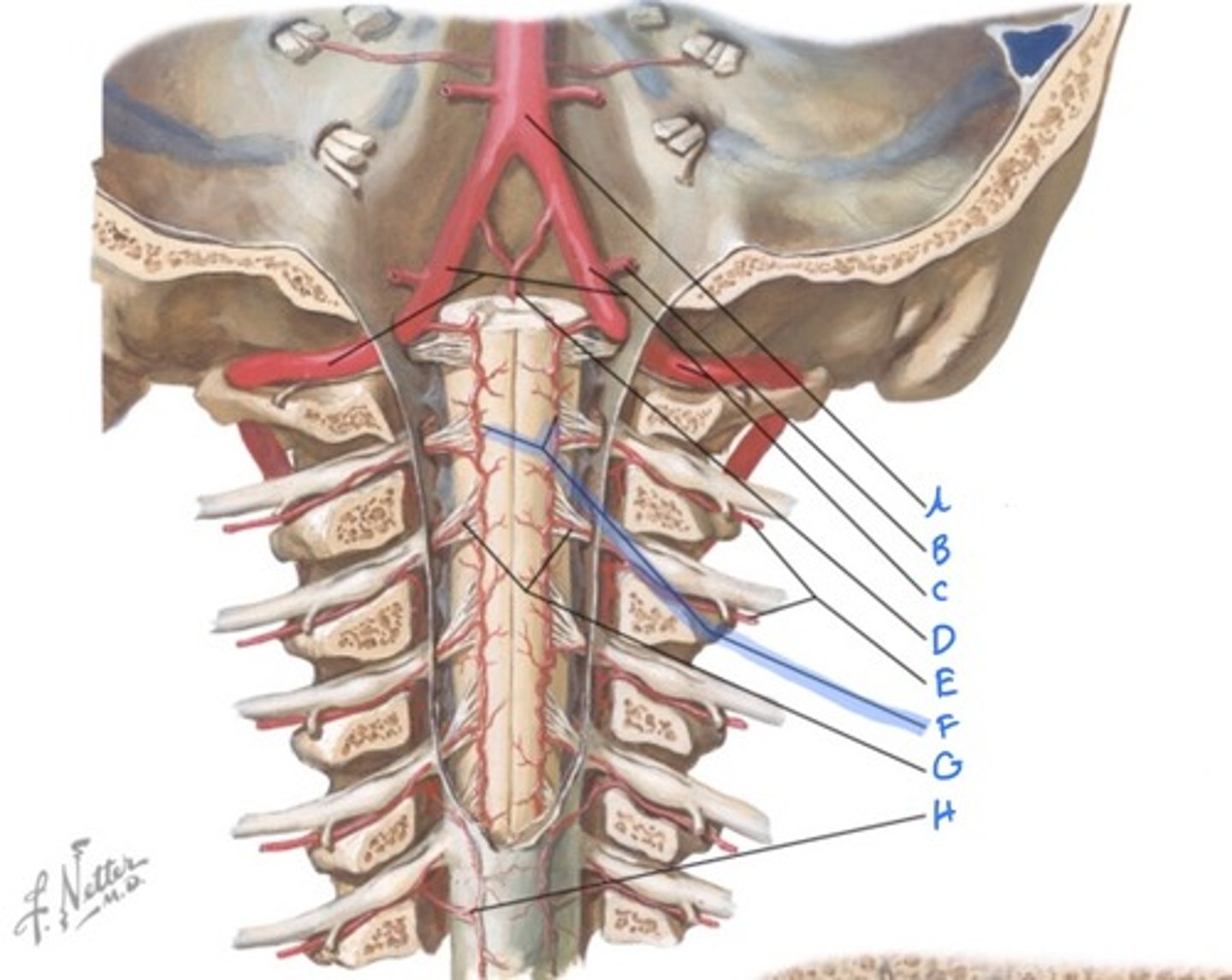
vertebral artery
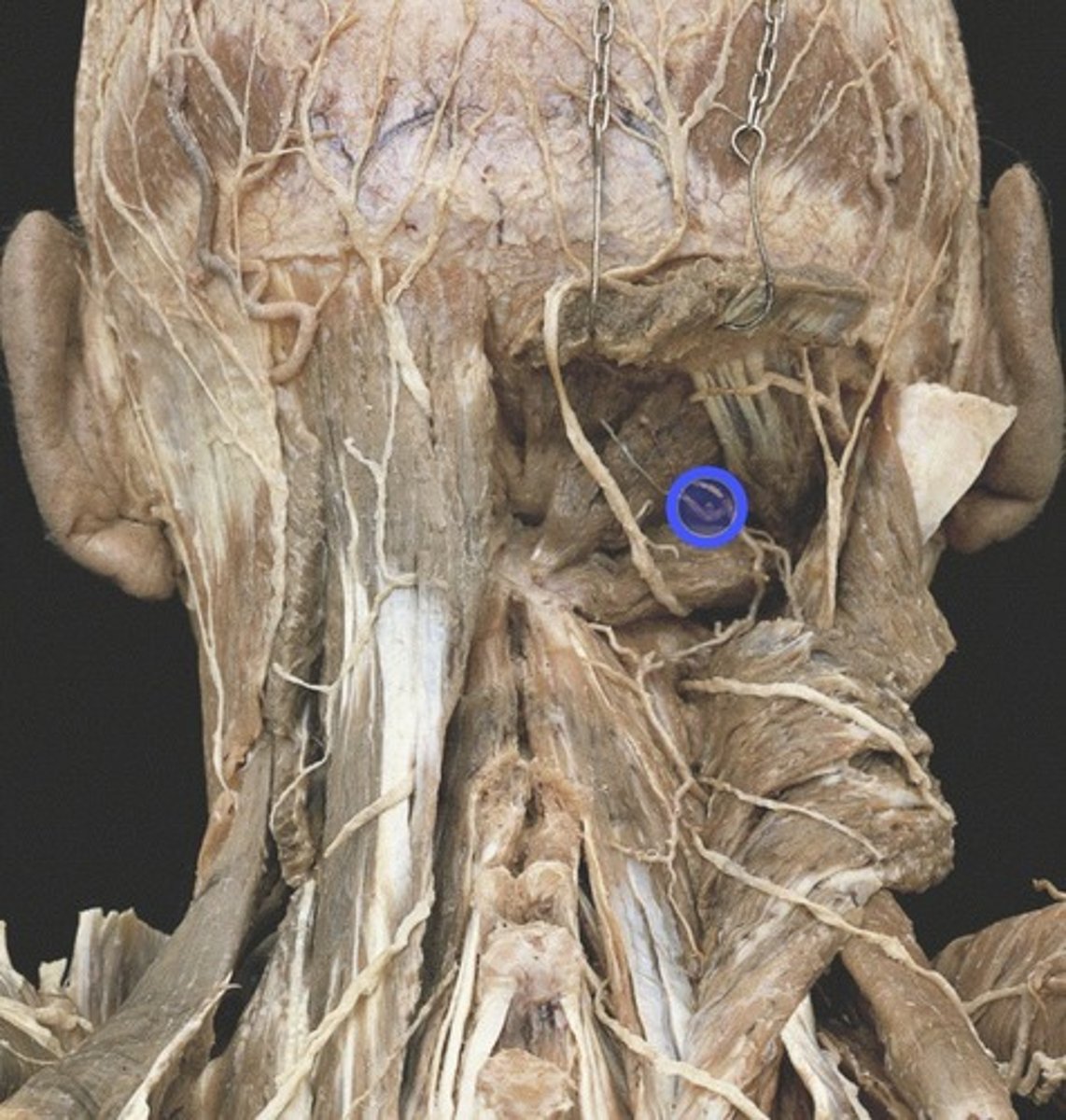
suboccipital nerve
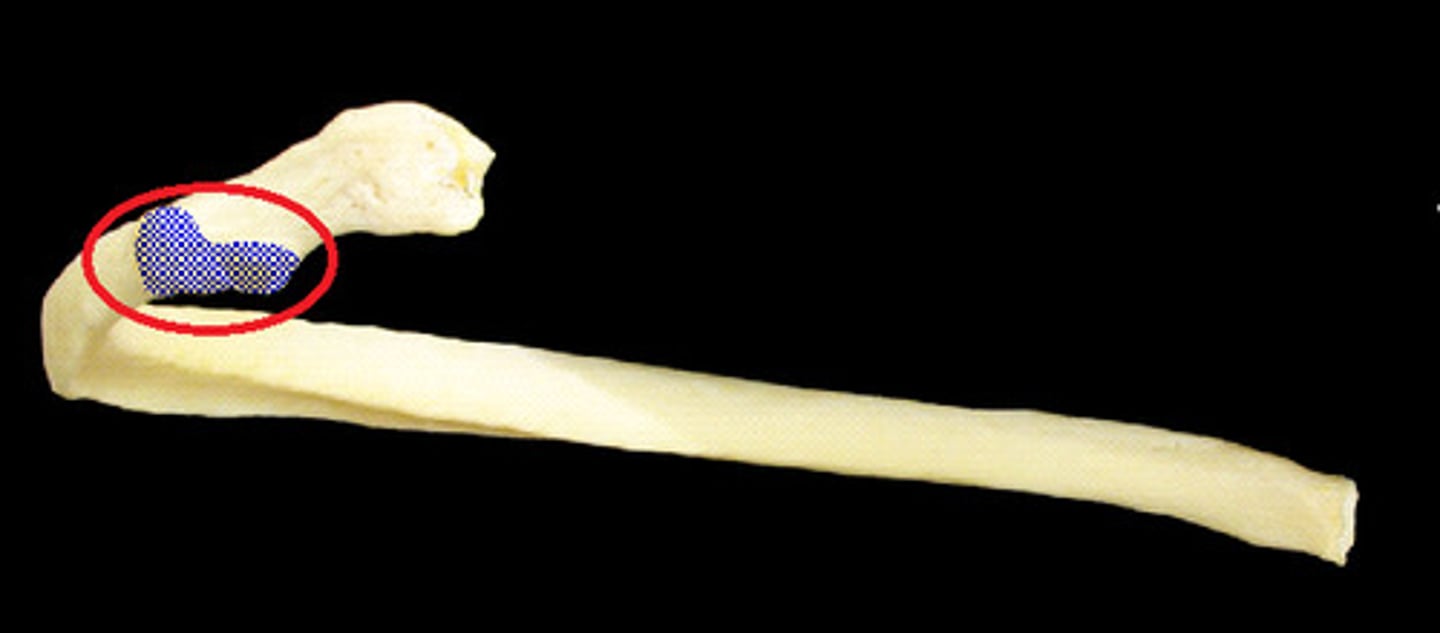
tubercle of a rib

jugular notch
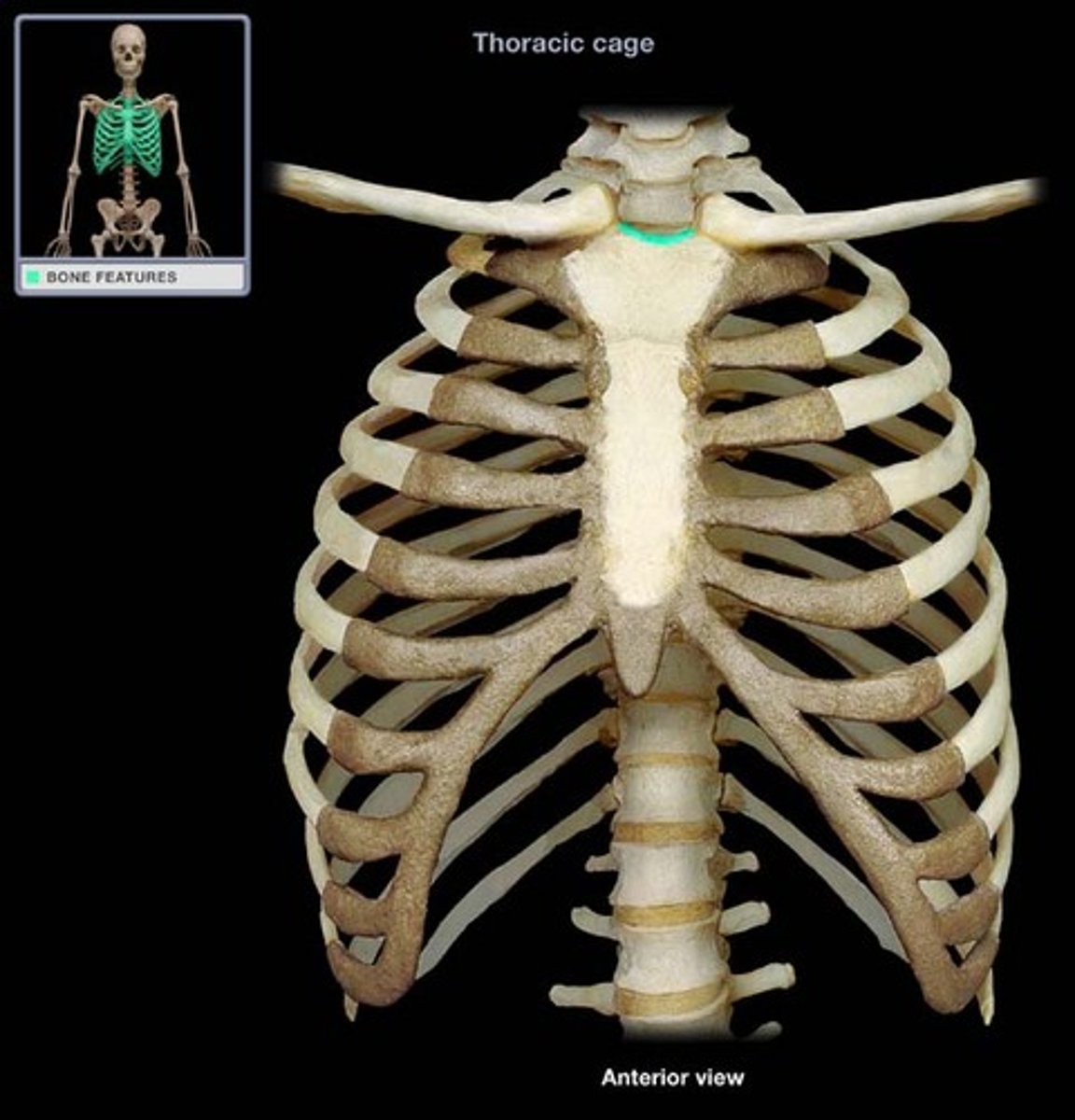
clavicular notch (sternoclavicular joint)
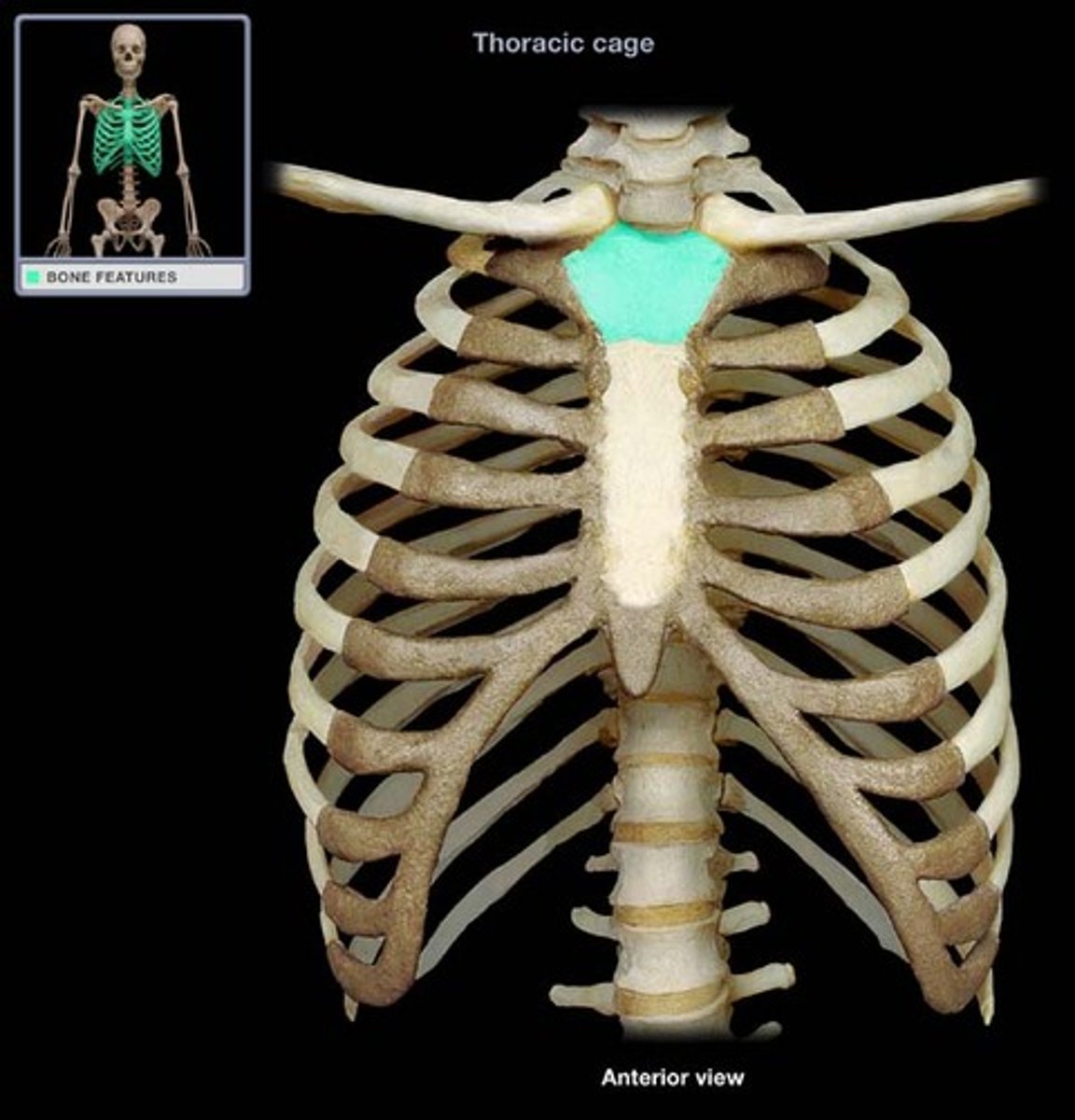
manubrium
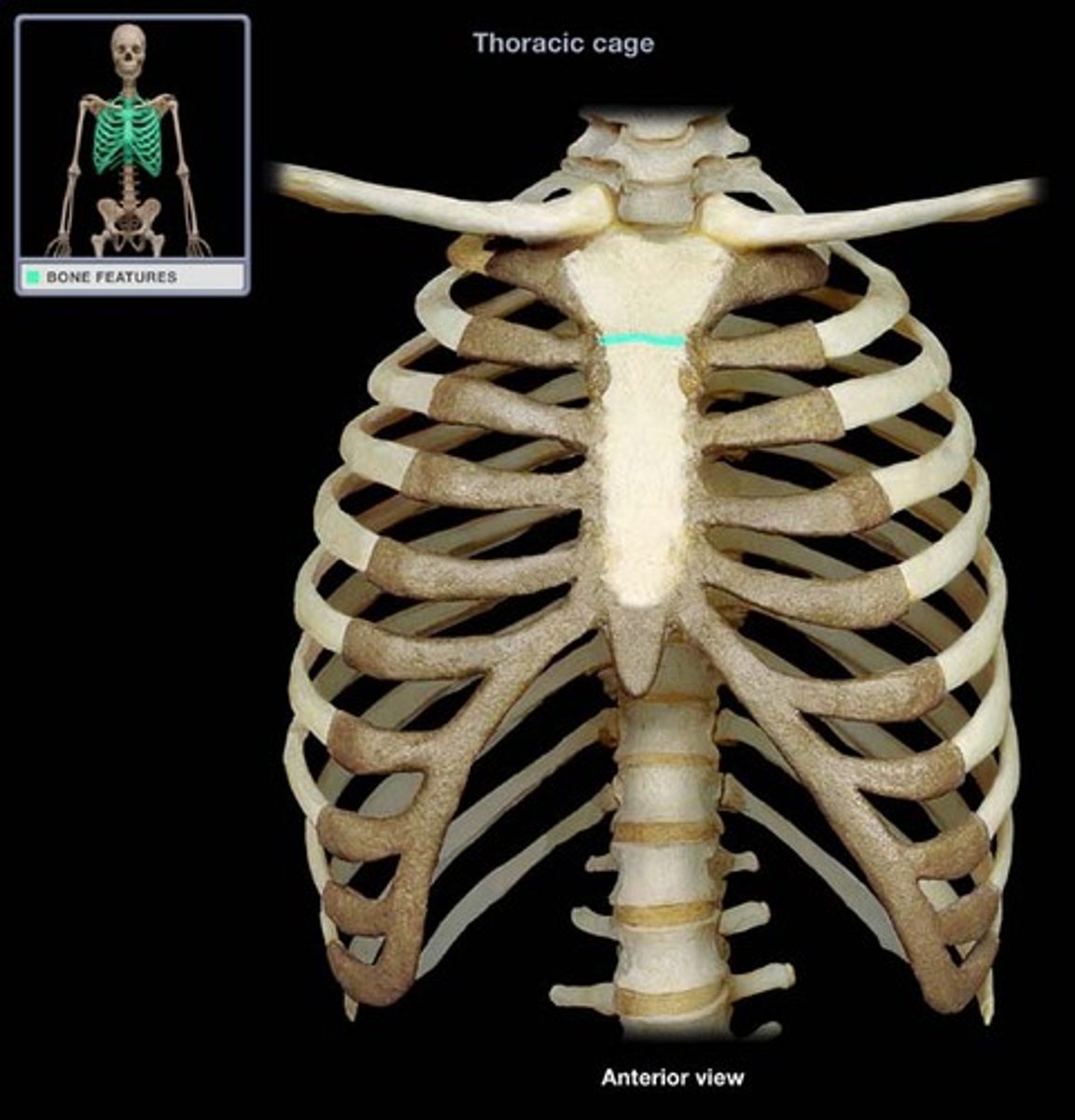
sternal angle
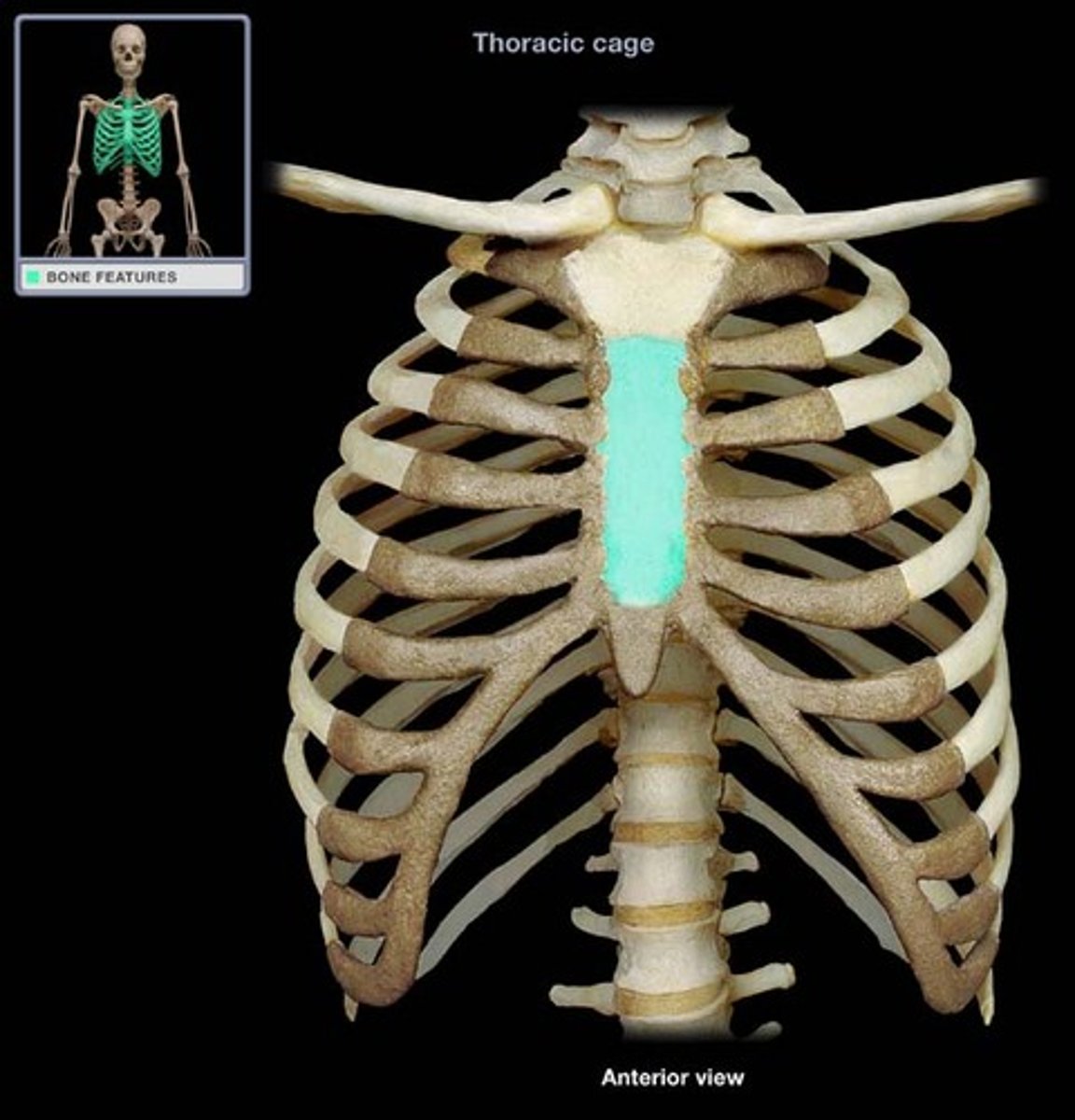
body of sternum (gladiolus)
xiphoid process
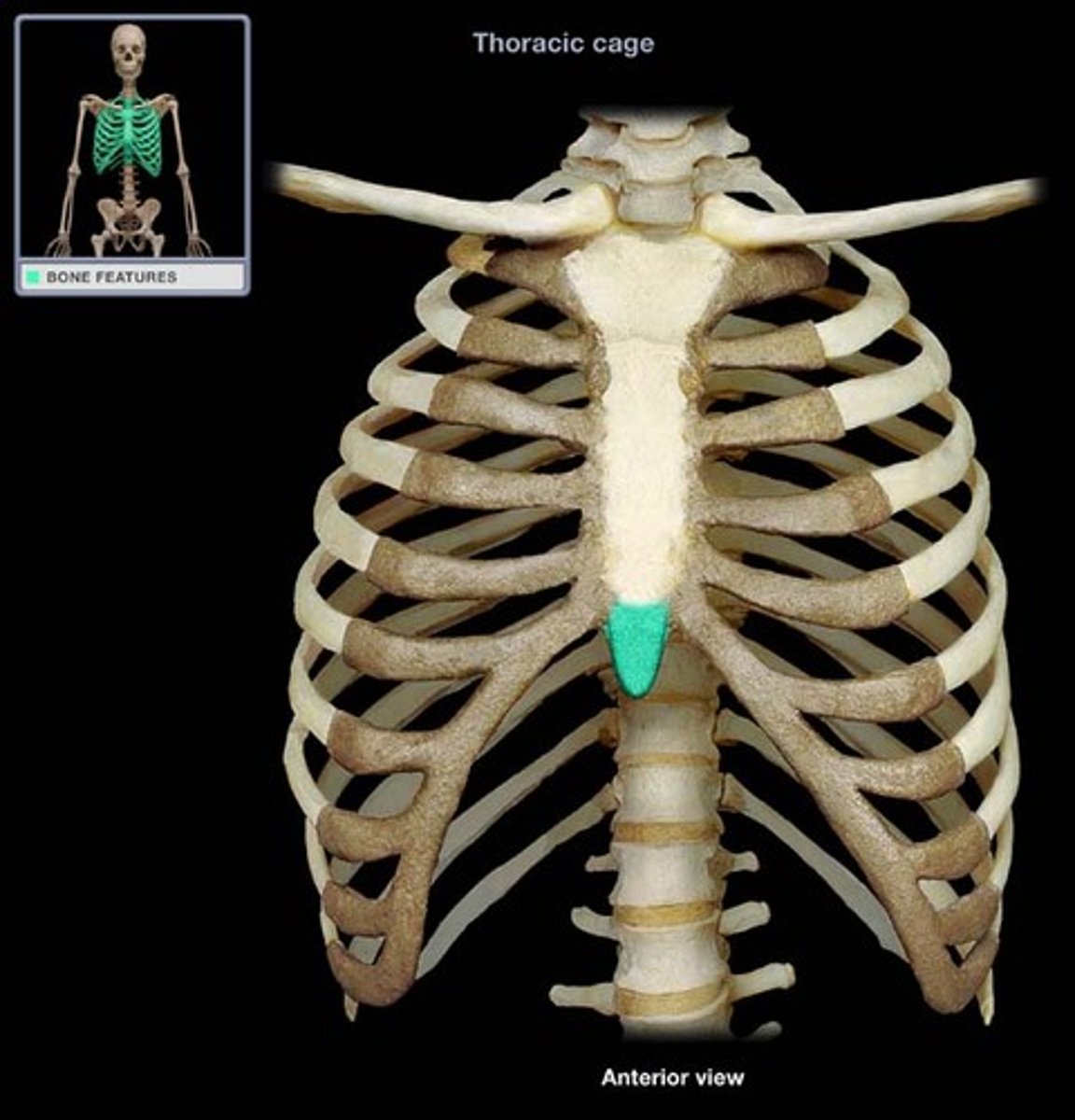
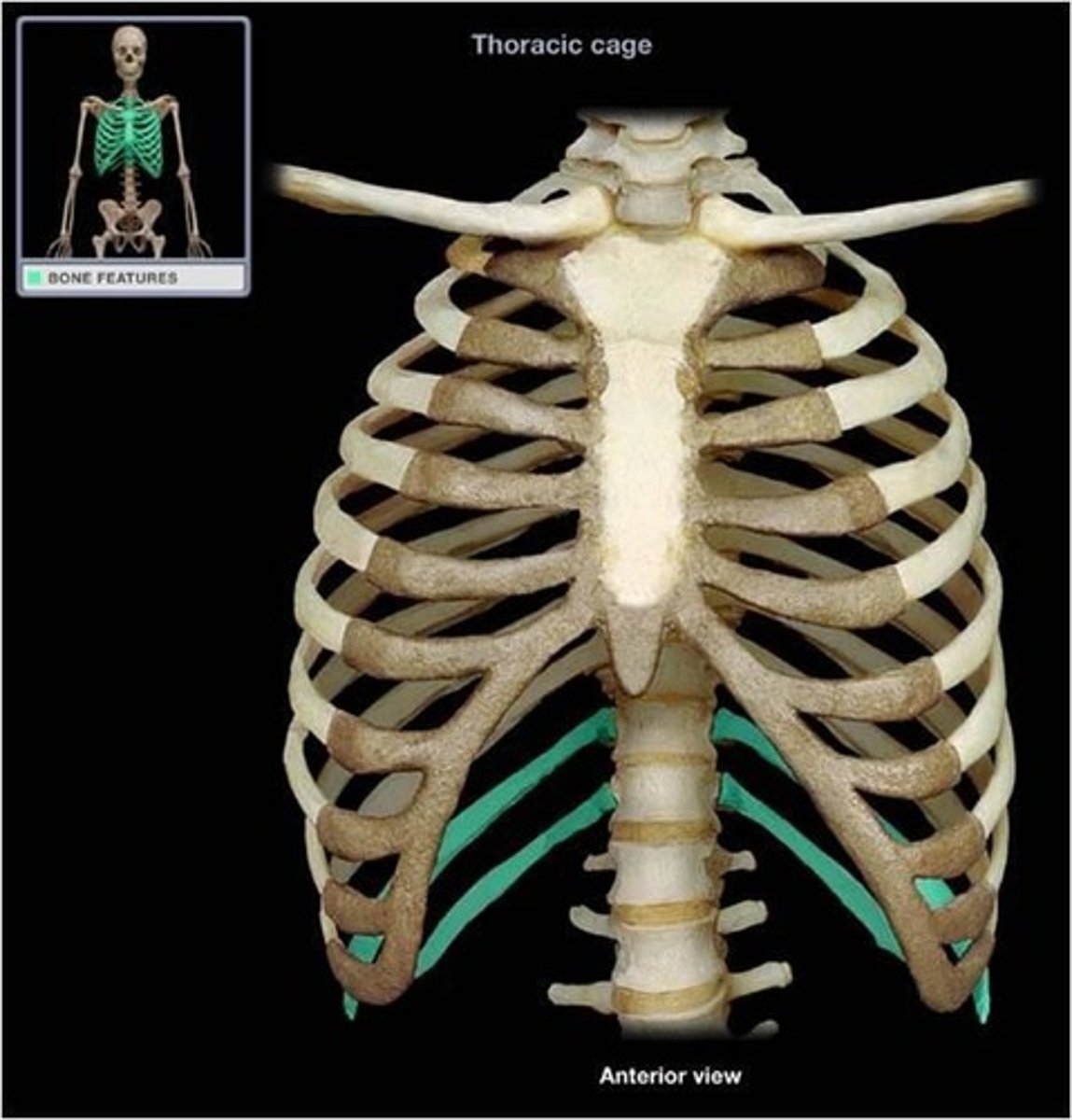
costal margin
- inferior border of thoracic cage formed by downward arc of ribsinferior border of thoracic cage formed by downward arc of ribs
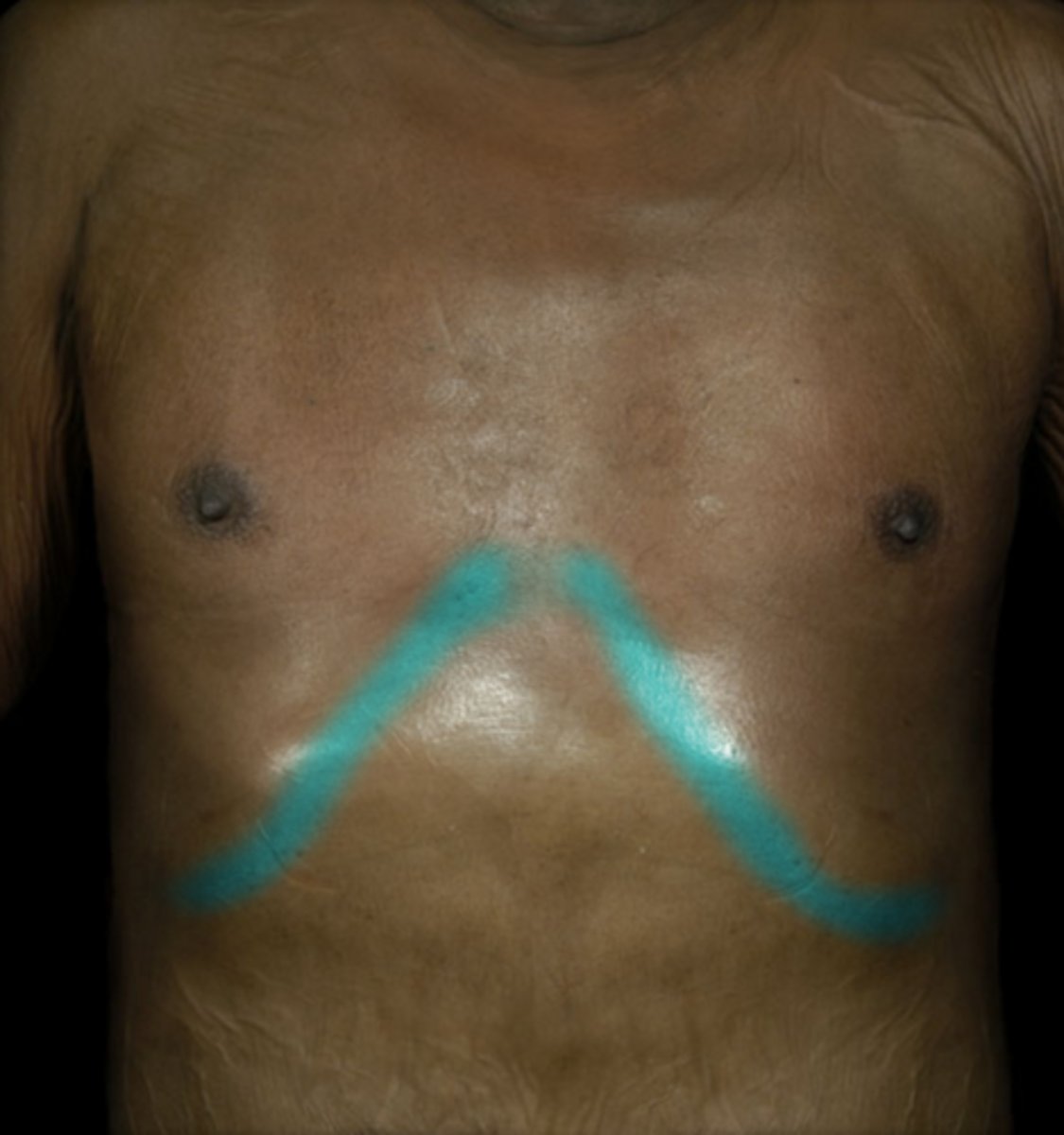
first rib
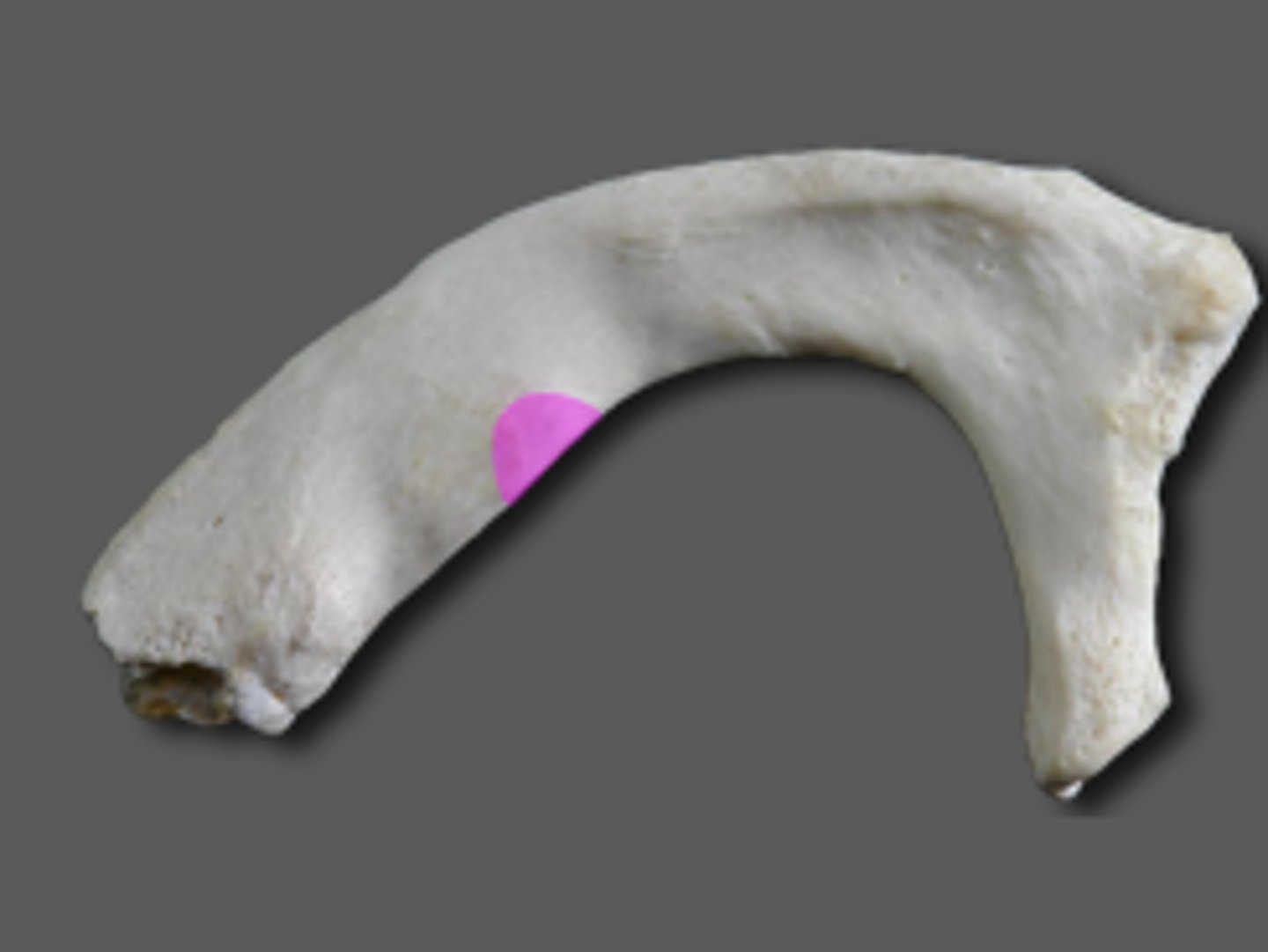
Manubrium