Middle Ages Quiz
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Medieval Europe or Middle Ages
• The period of European history between the collapse of Rome and the Renaissance, lasting roughly from 500 CE to 1450 CE.
Feudalism
• A political and social system in which lords gave land to vassals in exchange for service and loyalty
Manor
• The estate of a feudal lord, usually including a fortified building or castle
Lords
A powerful landholding noble
Vassals
• A lesser noble who received land and protection from a lord in return for loyalty
Knight
A man who fights on horseback
Oath of loyalty
A pledge or a promise of support or allegiance
Fief
A feudal estate or piece of land belonging to a vassal
Chivalry
A code of conduct of medieval knights, focusing on bravery, honor, towards women and the weak
Serf
A member of the peasant class who works for a lord and is tied to the land in exchange for protection and certain rights
Who split the Roman Empire in two
Diocletian
What was the two split parts of the Roman Empire called
The west and the east
When _____ became emperor he moved the capital from failing Rome to _______ an Ancient Greek city
Constantine, Byzantium
Constantine eventually renames the capital to what
Constantinople (Present day Istanbul, Turkey)
Cities in the west were what
Less successful
Why were cities in the west less successful
They were located farther away from trade routes
When was the last emperor removed from power
476 CE (symbolizing the fall of the western Roman Empire)
What happened after the last emperor was removed from power (3 things)
Roads and public structures fell apart, trade declined, and nomadic tribes attacked and claimed the land
Constantinople was considered a what
Crossroad between the east and the west
Constantinople was busy with traders from where
Asia, Africa, and Europe
The east thrived for how much longer
1000 years
The eastern half of Rome became known as what
The Byzantine empire
What happened in Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire
It was divided into different kingdoms
Did citizens live peaceful lives after the Germanic tribes took control of the land (if not why)
No, because they were constantly at war
What was the only thing that united the Germanic kingdoms during the Middle Ages
Christianity
What led to feudalism
An unstable and violent period
In feudalism everyone owed their loyalty to whom
The king
Below the king were
Powerful landholding nobles or lords
The lords gave fiefs to whom
Vassals or knights
The vassal gave what to the lord in return for the land
Military service and protection
At the bottom of the feudalistic pyramid were who
The peasants or serfs
What did the serfs do
Tasks around the manor
What did the serfs get in return for working the land
Protection
Who fought in the Hundred Years’ War and when did it take place
England and France, and 1337 to 1453
What were the causes of this war (2 causes)
England Claimed territory in southern France and France wanted it back, and the king of England declared himself the king of France
What were the two weapons that helped England to be successful in the war
Longbow and gunpowder
Why was the longbow powerful
Used steel tip arrows that penetrate knights armor, and could fly farther
Why was gunpowder powerful
It was used to “make” cannons
Who is Joan of arc
A peasant girl who believes heavenly voices called to her to save France; she eventually led an army against England
What happened to Joan in the end
She was captured by a French traitor and sold to England where she was tried as a witch and burned at the stake when she was 18
What were the effects of the war for France
Everyone in France was ruled by one king and they had an increased sense of nationalism
What were the effects of the war for England
Can’t achieve their goal of being a continental empire and everyone in England was ruled under one king
What were the effects of the war in the medieval world
The longbow and cannon gave soldiers more purpose, castles and knights will not survive due to the use of firepower of cannons, and monarchs had large armies instead of Vassals
What were the Crusades
Religious wars or holy wars
Who took part in the crusades
Muslim Turks and Christian’s
Where did the crusades take place
Jerusalem
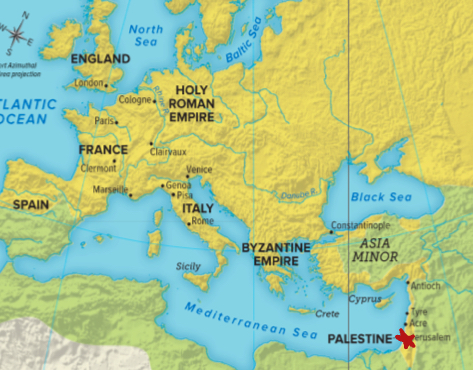
Why were the Crusades fought
Control of the holy land (Jerusalem)
What is the name of the disease that led to Black Death
The bubonic plague
Where do we believe Black Death first began
Central Asia
How did the plague make its way to Europe
Trade routes-the fleas on the rats and mice were on merchant ships
How did the plague effect the economy
Trade decreased and people did not perform jobs
How did the bubonic plague influence the actions of people in society
People did not go to public gatherings like church
What happened to Europes population during the plague
30%-50% of the population died
How did hygiene impact the spread of Black Death (2 ways)
No sanitation system (people would drop their filth and leftovers into the street), and no running water (Washing hands and cleaning did not happen
What happened to the laws and rules of society during Black Death
They disappeared
Who was Justinian I
Ruler of the Byzantine empire for 35 years, and he was a strong ruler
What was one of the most famous churches and what did the name mean
Hagia Sophia means holy wisdom
What was Justinian most remembered for
The Justinian code
What was the Justinian code
Revised and organized laws of Ancient Rome, and it served as the basis for the legal systems of almost every country in the western world (innocent until proven guilty)
Who was Justinians wife
Theodore
What were the 4 geographic features that helped the kingdoms of Western Europe survive

What did Theodore do
Participated in government and helped women get more legal rights
What did Justinian I do to increase land in the Byzantine empire
Conquered
Why was the land that Justinian I conquered lost
A plague killed many in his army as well as Justinian I himself
Why did the laws and rules of society disappear during the Black Death
There was no one there to enforce them
In the first crusade the crusaders did not have the knowledge of what of the holy land
Geography, climate, or culture
The third crusade was known as what
“The crusade of the kings”
King Richard led troops what was King Richard I of England also known as
Richard the lion-hearted
What increased as a result in the crusades
Trade between Europe and Asia (improved the economy and helped towns and cities grow)
What did they start to exchange because of the crusades and what is it called
Food, medicine, literature, clothing, technology and this is known as cultural diffusion
What was a negative impact of the crusades
Many people think that the tensions between the west and Middle East today was rooted from the crusades