Infection - Cardiomyopathy - Pericardial Effusion
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
40%
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
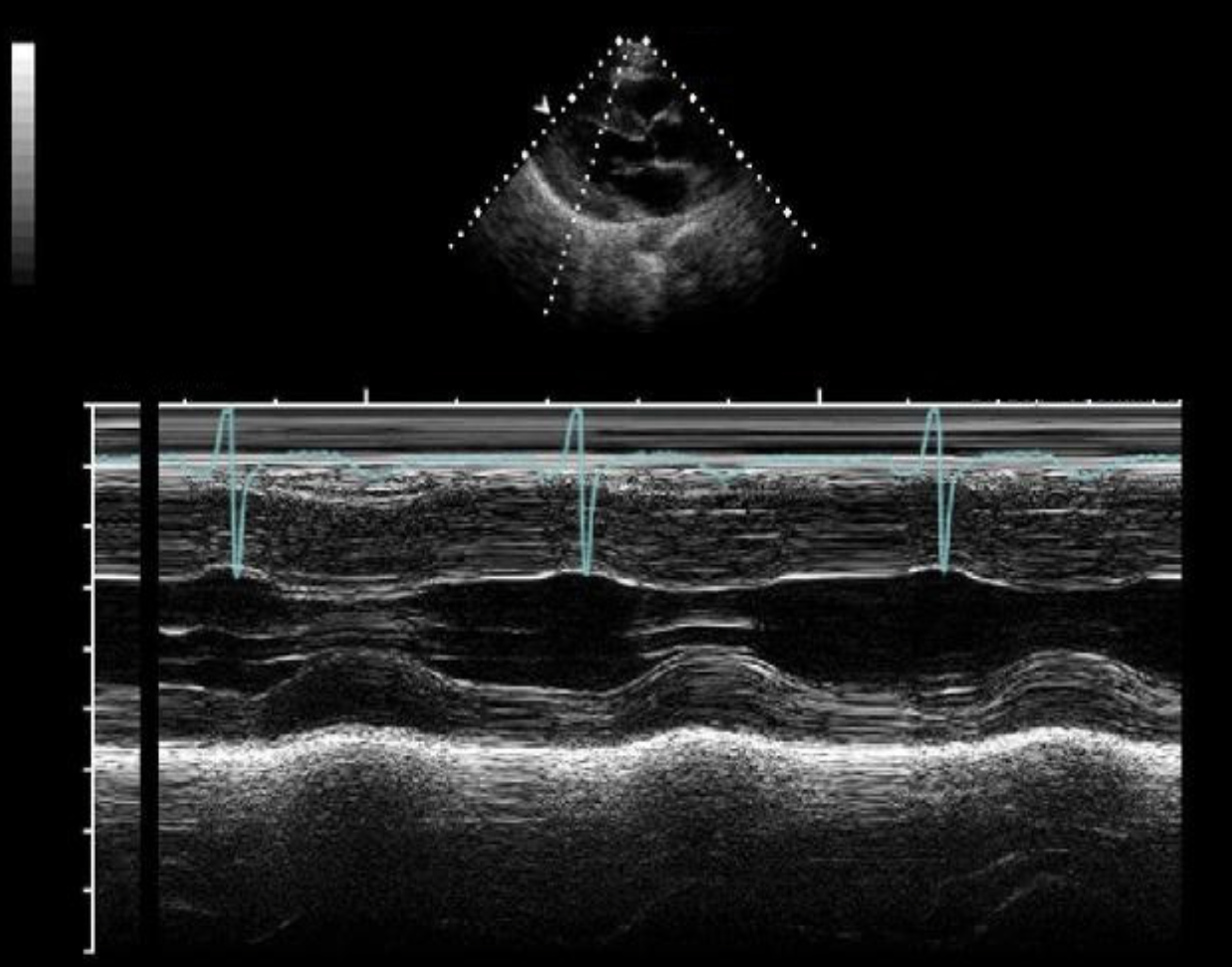
The m-mode tracing demonstrates which of the following?
HCM
The echo demonstrates endocardial thickening of the inflow tracts, fibrous tissue overgrowth in the apex of the left ventricle and diastolic dysfunction. These findings are most suggestive of?
Endomyocardial fibrosis
Pulsus paradoxus is defined as a > 10 mmHg decrease in systolic BP during inspiration and is commonly seen with which of the following abnormalities?
Cardiac tamponade
_____ is usually present in patients with HOCM because of the pressure changes caused by obstruction to flow leaving the left ventricle through the LVOT
MR
Which of the following would cause you to suspect cardiac tamponade?
Becks triad
Cardiac tamponade causes?
Restrictive diastolic filling
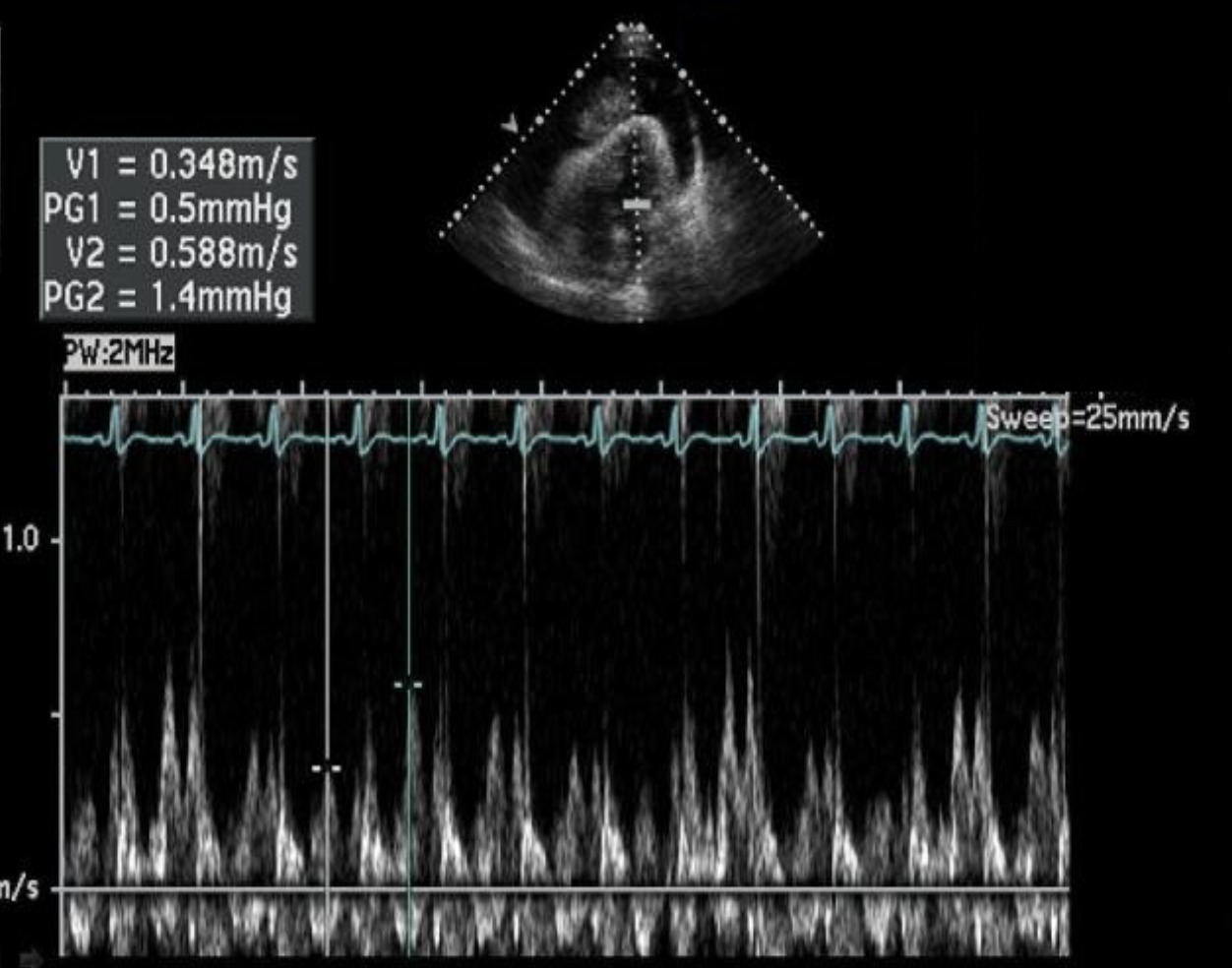
The calipers on the image are measuring?
Abnormal respiratory variation of the E velocities of the mitral valve due to cardiac tamponade
Annulus reversus is best documented using _____ and if present indicates _____
Tissue Doppler and constrictive pericarditis
In cardiac tamponade the RV free wall will collapse in diastole except in patients with significant?
Pulmonary HTN
Endocarditis affects the _____ and cardiomyopathy affects the _____
Endocardium and myocardium
Greater than 2 cm of pericardial fluid surrounding the heart indicates?
Severe pericardial effusion
A patient presents for an echo because they have been experiencing positional and respiratory variation in chest pain. You expect to find which of the following on the exam?
Pericarditis
A patient is referred to the echo lab with a 6 week history of chemotherapy treatment for hepatoma and a new onset of SOB. Which of the following is the most likely finding that will be identified on the exam?
Pericardial effusion
Which of the following is the most likely finding with radiation therapy of the left breast?
Pericardial thickening
Which of the following is not a sonographic characteristic of cardiac tamponade?
Mid systolic collapse of the RA
What is the most common complication seen with a septal myectomy that is performed to correct ASH?
VSD
Which of the following sonographic signs of HCM is not usually demonstrated in patients with isolated focal thickening in the mid cavity of the LV?
SAM of the MV
Pheochromocytomas, Friedreich ataxia and Fabry disease commonly demonstrate what echo finding?
LVH
Which of the following statements best describes the characteristics of the left ventricle with DCM?
LV dilated with decreased contractility
Which of the following is the most common type of infiltrative cardiomyopathy to develop restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Amyloidosis
A valve ring abscess is usually a sign of what cardiac disorder?
Infective endocarditis
A prominent A wave and reduction in amplitude of the systolic wave on pulmonary vein Doppler indicates?
Elevated LVEDP
Which of the following can be used to differentiate HCM from LVH caused by systemic HTN?
Pattern of LVH
Which of the following types of infiltrative disease commonly presents with a dilated LV with normal wall thickness and reduced function?
Hemochromatosis
Which of the following describes findings associated with ASH seen with HCM?
Septal to posterior wall ratio of 1.3:1 or greater
LVH and a longitudinal strain measurement of -8 indicates?
HCM or amyloidosis
The most important cardiac structure that should be evaluated in patients with suspected tamponade is?
RV free wall
A patient with conduction abnormalities, asymmetric LV hypertrophy, prominent papillary muscles and hyperechoic endocardial layer most likely suffers from?
Fabry disease
In a patient with cardiac tamponade, the IVC will?
Remain dilated with no respiratory changes in diameter
Which of the following is associated with equal diastolic pressures in the right and left ventricles
Constrictive pericarditis
A patient presents for an echo complaining of trouble sleeping because certain positions cause chest pain. The EKG report indicates widespread ST elevation. The echo demonstrates trivial mitral and tricuspid regurgitation and a mild pericardial effusion. These findings are most suggestive of?
Pericarditis
Which of the following best describes the valvular flow abnormalities seen in a heart with DCM?
Due to volume overload caused by the hypocontractile LV, the presence of multivalvular regurgitation is common
This form of cardiomyopathy typically demonstrates normal LV size, biventricular hypertrophy and significant biatrial enlargement
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
What is the most common form of infiltrative cardiomyopathy?
Amyloidosis
Which of the following is an autosomal recessive disease that involves abnormal storage of glycogen in the muscle tissues?
Pompe disease
Which type of cardiomyopathy is most strongly associated with diabetes?
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Which of the following is a way to differentiate an athletic heart from HCM?
LV wall thickness measurements
The early stages of infiltrative cardiomyopathy are commonly associated with which type of diastolic dysfunction?
Grade 1
Which of the following m-mode measurements will increase in patients with DCM?
EPSS
Asking a patient with constrictive pericarditis to take in a deep breath will cause?
Decrease in expiration of the mitral E velocity > 25%
Which of the following patients would benefit from the placement of an intra-aortic balloon pump?
Patients with DCM
The double diamond sign on a m-mode tracing of the MV is indicative of mid diastolic closure caused by?
DCM
What effect does DCM have on HR?
Increased
An intra-aortic balloon pump or a heart transplant are recommended for patients with advanced?
DCM
How does DCM affect the Doppler waveform of the pulmonary veins?
Elevated D wave with blunted S wave
Dilated IVC and HPVs are commonly associated with?
Constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade
The tissue Doppler velocities of the mitral annulus cannot be used when evaluating a patient for diastolic dysfunction if _____ is present
Annulus reversus
Which of the following describes HOCM?
Peak pressure gradient in the LVOT is 30 mmHg at rest
Tachycardia, dyspnea, orthopnea and lower extremity edema are clinical findings that are most suggestive of?
DCM
Which type of cardiomyopathy is related to fatty and fibrous tissue replacement of the myocardium of the RV?
Arrhythmogenic RV cardiomyopathy
A 52 year old male enters the ER with a fever of 103 degrees and admitted history of IV drug use. He also demonstrates a recent onset of extreme dyspnea. A VQ scan of the lungs demonstrates an emboli lodged in the right bronchial artery. Which of the following is the most likely source of the emboli?
Vegetation on the TV
Which of the following causes the AV to close mid systole?
LVOT obstruction
Propranolol can be used to treat?
Subaortic stenosis caused by HCM
What is an acute, transient, stress induced cardiomyopathy?
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
Which of the following correctly describes how to differentiate a vegetation from a papillary fibroelastoma on the MV?
Locate the point of attachment for the mass
Hemochromatosis involves excess _____ deposits in the _____
Iron and myocardium
Which of the following will lead to a decrease in dp/dt ratio?
DCM
Which of the following is an autosomal dominant disorder?
HCM
The pattern of wall hypertrophy in hypertensive heart disease is _____ and in HCM the pattern is usually _____
Symmetric and asymmetric
Which layer of the heart wall is most affected by Staphylococcus Aureus infection?
Endocardium

Which left heart abnormality will cause the aortic CW Doppler flow pattern demonstrated in the image?
HCM
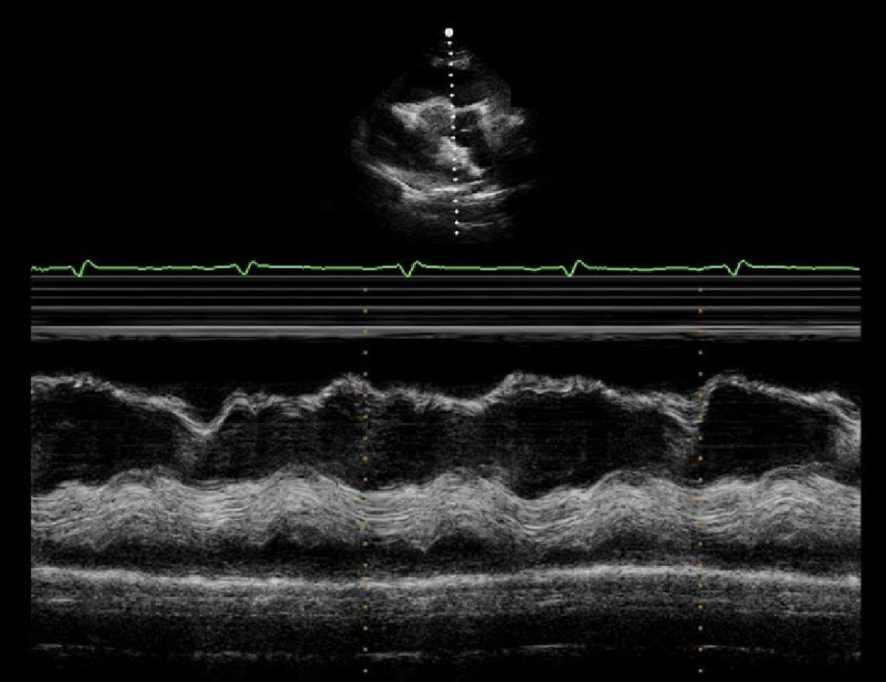
The m-mode tracing is consistent with which of the following cardiac abnormalities?
Cardiac tamponade
A left ventricular myectomy is most commonly used to treat with of the following disorders?
HOCM
DCM demonstrates _____ diastolic dysfunction early on and _____ diastolic dysfunction in advanced stages
Grade 1 and 3
What m-mode changes will be identified with increased LVEDP?
B-notch on the MV tracing
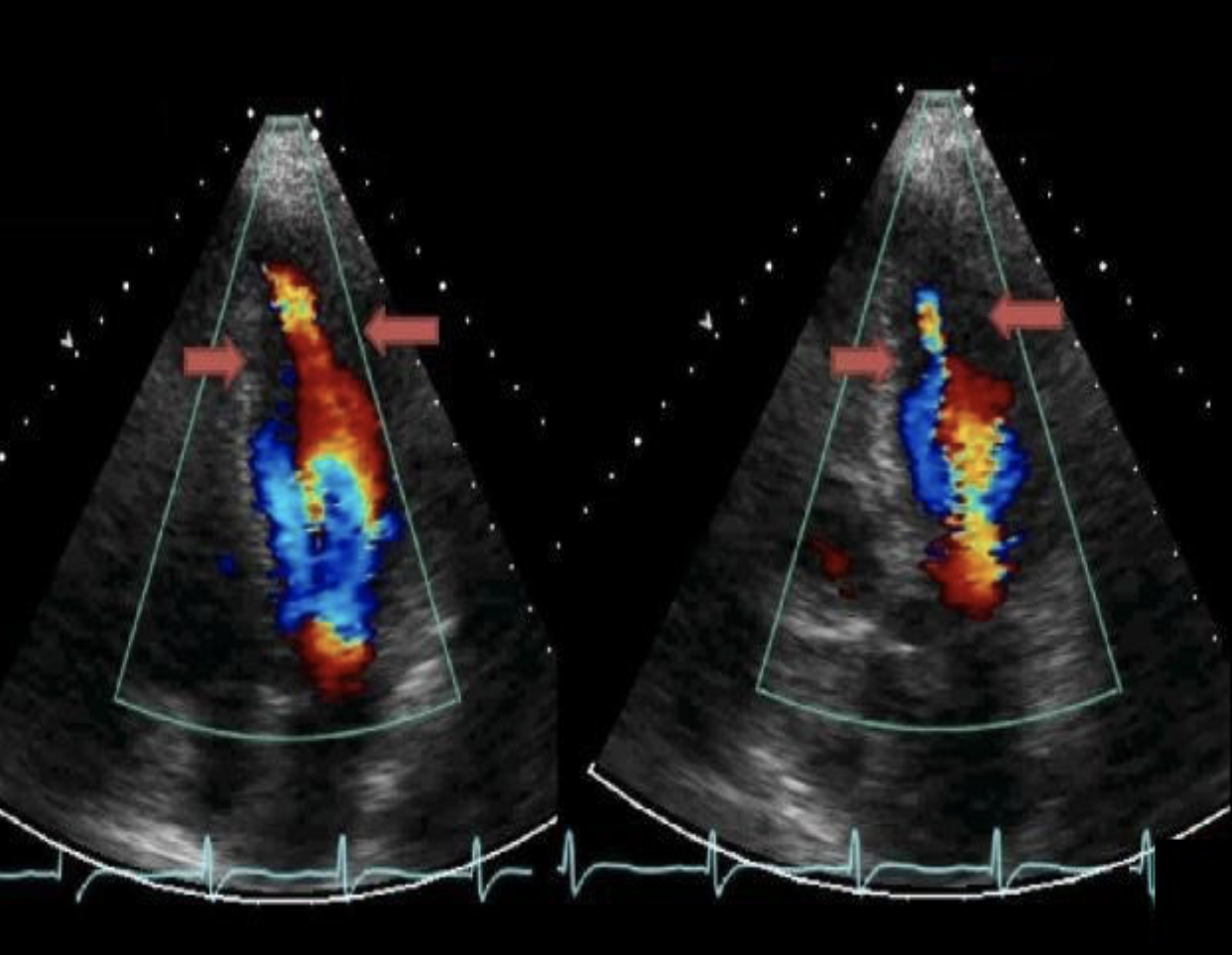
The image displays a focal wall structure and motion abnormality caused by?
Focal HCM
The echo findings below are most suggestive of:
Non-dilated thick walled LV with EF 63%
E/A ratio 2.1
E/E 19
Moderate biatrial enlargement and pulmonary HTN
RVH and dilated IVC
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
A 22 year old patient presents for an echo and you identify biventricular wall thickening, mild pericardial effusion and thickening of the leaflets of all four valves. Which of the following is the most likely cause for these findings?
Amyloidosis
Which of the following describes the appearance of a mild pericardial effusion?
< 1 cm fluid located posterior to the heart
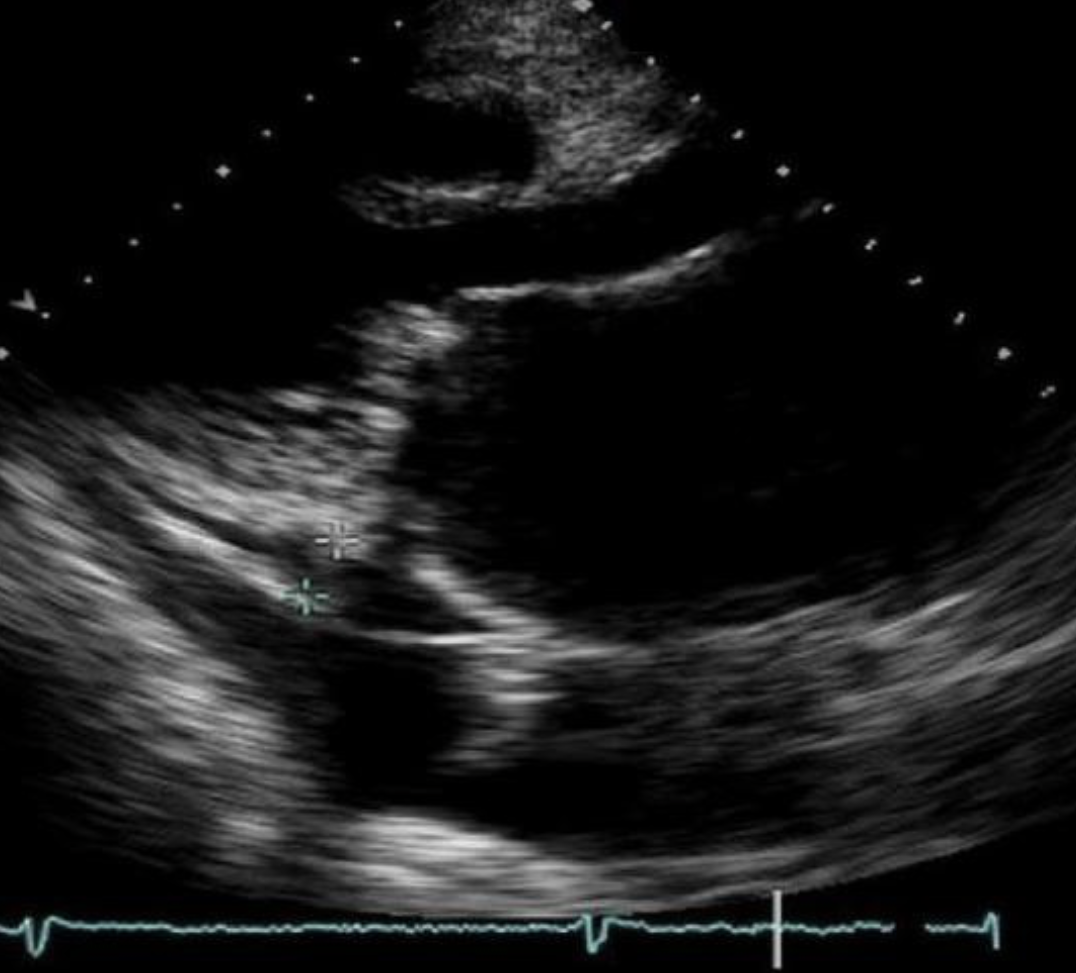
Which of the following is present not he image?
Mild pericardial effusion and moderate pleural effusion
HCM will usually cause what change in brachial blood pressures during treadmill testing?
Decrease in systolic nad diastolic pressure
Which of the following is the typical treatment for advanced pericarditis?
Pericardectomy
Respiratory variation in the isovolumic relaxation time is usually a sign of?
Constrictive pericarditis
Which of the following will cause an increase in the murmur associated with hypertrophic subaortic stenosis?
Amyl nitrite administration
A 42 year old male presents for an echocardiogram 2 weeks post pericardectomy due to constrictive pericarditis. What is an expected finding on the exam?
Increased cardiac motion at rest
On the parasternal views, you identify an isolated 1.5 cm nearly echo free space anterior to the RV that does not change dimension with cardiac motion. Which of the following describes this finding?
Epicardial fat pad
Mid diastolic closure of the MV may be seen with which of the following abnormalities?
DCM
A patient presents for an echo after a recent diagnosis of Chugs disease. What are you looking for on the exam?
DCM and apical aneurysm
Electrical alternans is a common finding in which of the following abnormalities?
Cardiac tamponade
Which of the following lists an expected finding on tissue Doppler evaluation of the septal annulus in a patient with constrictive pericarditis?
E’ = 10 cm/s
An m-mode tracing of the MV records normal motion with a shaggy appearance of the anterior leaflet in all phases of the cardiac cycle. Which of the following is the most likely cause for this?
Vegetation formation
Which of the following presents as heart failure with a preserved EF% and significant diastolic dysfunction?
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
_____ is the preferred method of diagnosis of constrictive pericarditis
Cardiac catheterization
The Doppler tracing of the LVOT seen with HOCM is said to resemble?
Dagger
What type of infection only affects the cardiac valves with no involvement of myocardium or other cardiac structures?
Marantic endocarditis
Which of the following is the most likely EF% on a patient with DCM?
15%
Which of the following describes the appearance of the Doppler tracing of the MV in a patient with restrictive cardiomyopathy due to amyloidosis?
Higher peak velocity of the E wave and a very low peak velocity of the A wave
A cardiac murmur is auscultated with the patient supine. The murmur gets louder when the patient stands next to the table. These findings are most suggestive of?
HCM
Chest pain increasing at night and dyspnea accompanied by a “knocking” sound with auscultation are clinical findings that are most consistent with?
Pericarditis
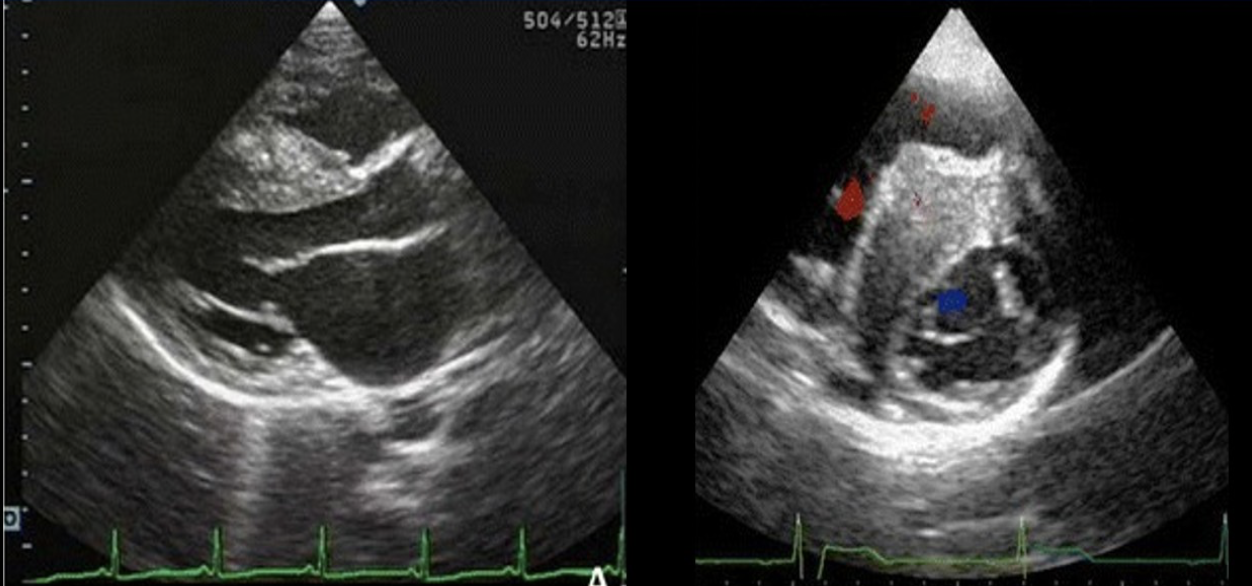
Which of the following valvular abnormalities is commonly associated with the abnormality on the image?
SAM
The most commonly identified cause of DCM
Alcoholism
Refers to an arterial pulse waveform with alternating strong and weak beats
Pulsus alternans
Diastolic flow reversal in the HPVs, diminished S velocity and prominent. A wave on the pulmonary venous tracing with a mitral E/A ratio of 1.9 correlates with which of the following?
Constrictive pericarditis
Which of the following types of regurgitation is usually the first to develop with DCM?
Mitral
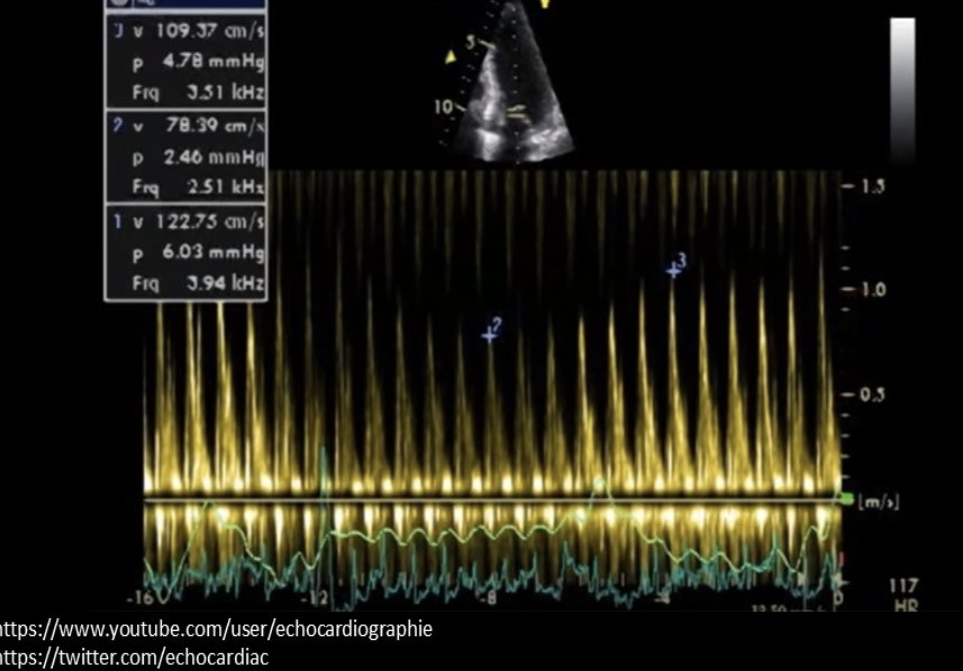
The Doppler tracing is consistent with which of the following cardiac abnormalities?
Constrictive pericarditis
An alcohol induced septal ablation is used to treat which of the following cardiac abnormalities?
HOCM
Which of the following is an expected EF% on a 25 year old patient with HCM?
85%
Which of the following is the most common method of treatment for a patient with cardiac tamponade?
Pericardiocentesis
Which of the following will demonstrate a below normal EPSS measurement?
HCM
How does restrictive cardiomyopathy affect pulmonary venous flow?
Blunted systolic velocity and increased diastolic velocity