Distortion
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
distortion
when accuracy is affected by the misrepresentation of the true shape and size of the anatomy being examined
always will exists but can be minimized
distortion with size (aka magnification)
causes image to appear larger than object being radiographed
magnification is the only possible size distortion
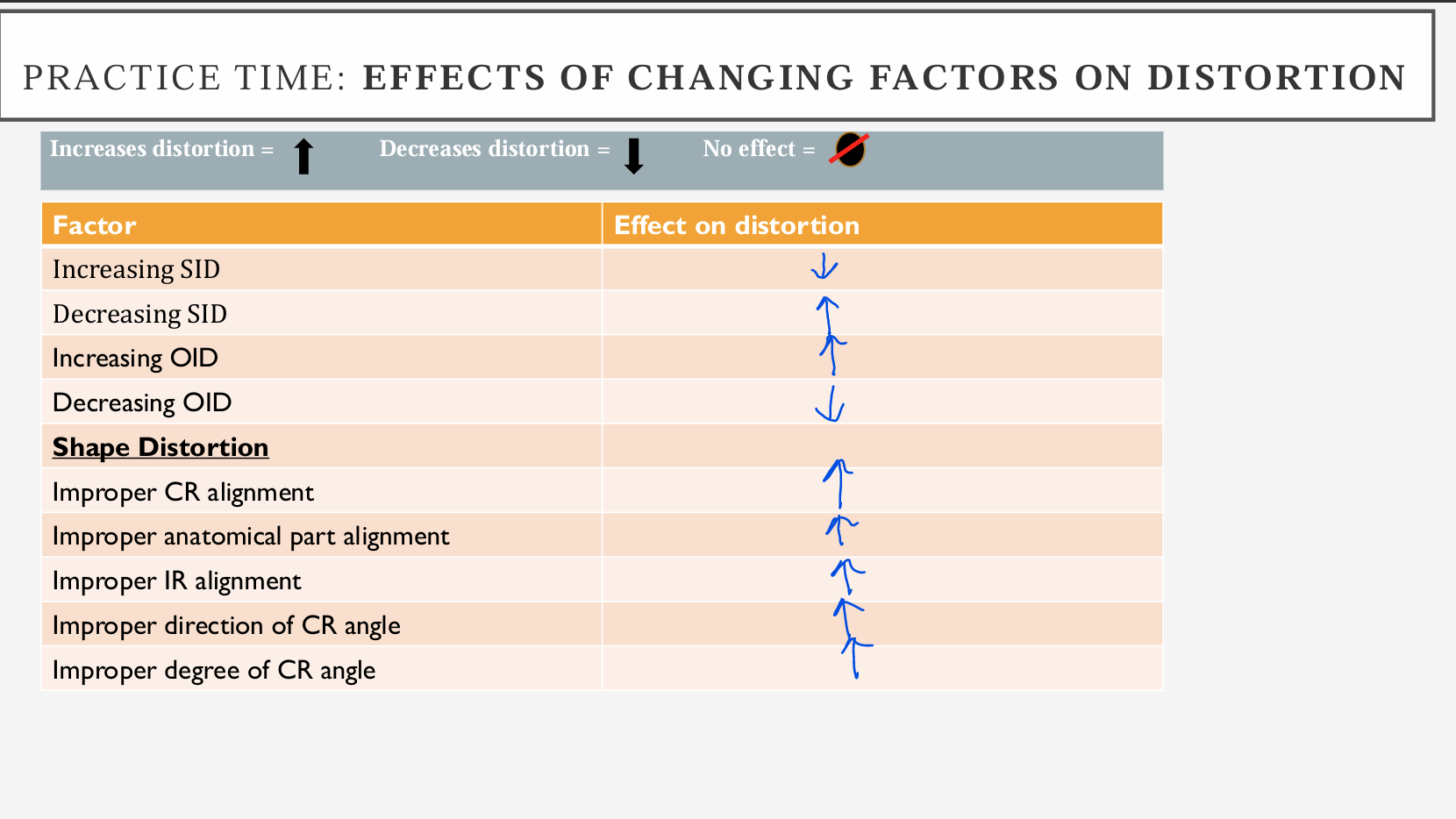
controlled by distance only (SID or OID)
digital post processing can resize
when size distortion decrease, resolution increase
SID with size distortion
when SID increase, size distortion decrease
makes up the OID
OID with size distortion
when OID increase, size distortion increase
AP vs PA: which is closer to the IR to reduce OID bw the IR and anatomy needed
OID and dosimetry
important bc establishes SOD
when OID is larger, skin is closer to the tube, ESE will increase
ex: AP less ESE than LAT bc OID is larger in a LAT than AP
large patients get more radiation bc they’re skin is closer to the xray tube naturally, causing more OID, smaller SOD, and more ESE
calculating magnification (formula)
M= SID/SOD
tells you how much longer and wider the image is compared to the original object
calculating actual object size (formula)
O= I/M
I: image size
M: magnification factor
O: object size
shape distortion
misrepresentation of the true shape of the object
either elongated (longer and thinner) or foreshorten (shorter and thicker)
elongation
occurs when tube or IR isn’t properly aligned
tube: when tube is angled and object parallel to IR
IR: when IR and object not parallel but CR is perpendicular
image appears stretched out
can be used as an advantage (open joint space, remove superimpose, show hidden anatomy, etc.)
foreshortening
occurs only when the object isn’t properly aligned when CR is perpendicular to the IR
image appears squashed together and produces unequal magnification
factors affecting shape distortion
structures at different levels/depths within the body (think OID within the body based on the part) causes beam divergence
lengths vary based on the angle bw the object and the diverging beam
Alignment
proper alignment of the CR, IR and object insures minimal distortion
achieved by CR being perpendicular to the parallel object and IR
when alignments are hard, creativity needed
When the CR is further
beam divergence increases and distortion increases
cases of creativity to avoid distortion
sometimes needs multiple projections (like casted elbow) to get entire elbow with less distortion
Angulation
direction and degree of the tube
used to avoid superimprovision
changes the SID so unless new SID used, IR exposure decreases and changes in magnification
almost always longitudinal (cephalad and caudad)
sometimes uses transverse angulation (roll)
Effects of changing factors on distortion chart