Chapter 14 - Gycolysis
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biochemistry - Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
glucose
only fuel used by all cells in our body
glycolysis
metabolic pathway where glucose is oxidized to produce energy in the form of ATP
glycolysis importance
universal pathway
occurs in cytoplasm
does NOT required oxygen
glycolysis in anaerobes
only significant source of ATP from CHOs
glycolysis in aerobes
significantly more ATP can be produced from subsequent steps such as Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
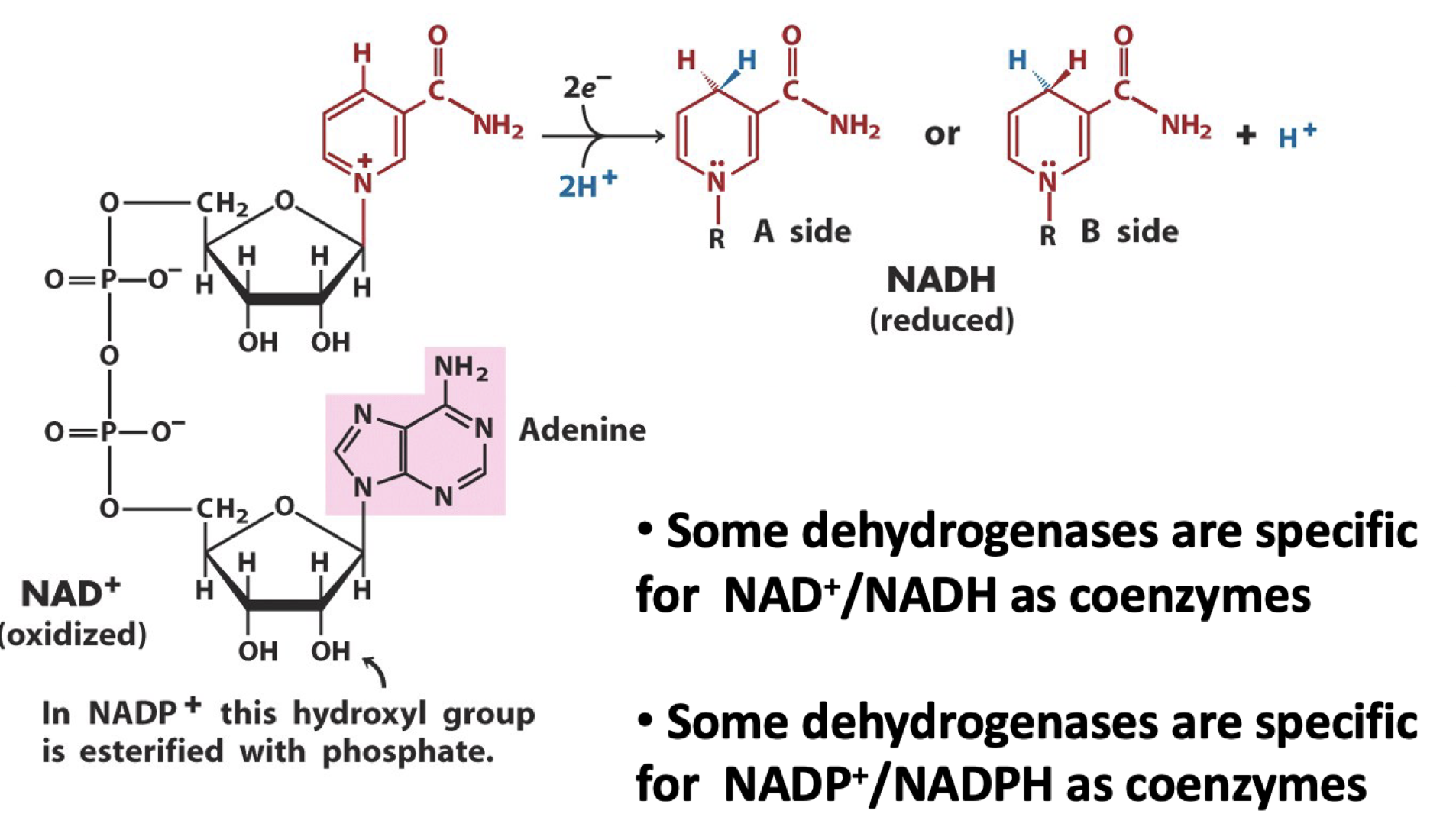
structures of NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH
glycolysis - phase one
preparatory phase
preparatory phase

phase one reactions
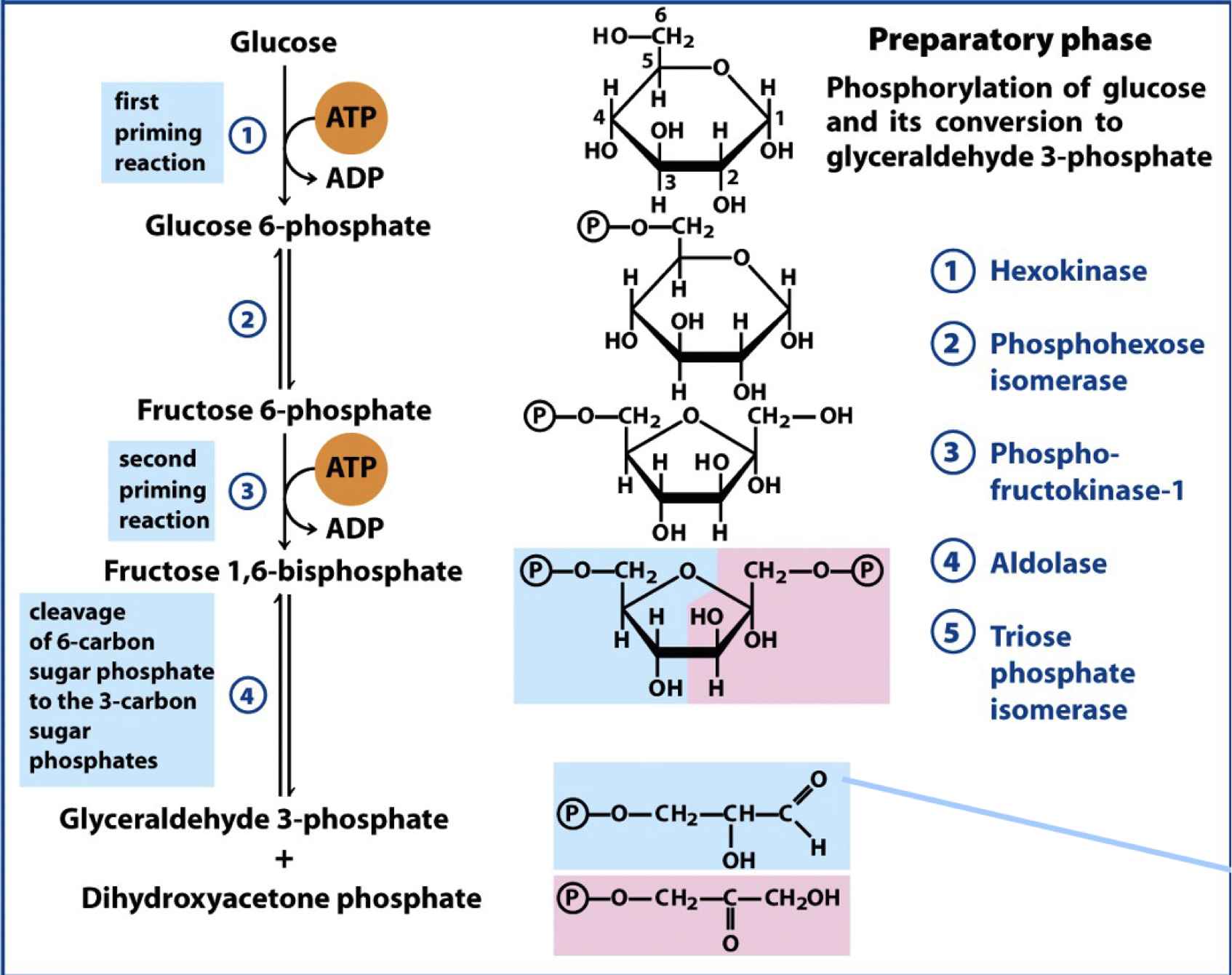
glycolysis step one
glucose is phosphorylated at the hydroxyl group on C6 to d-glucose 6-phosphate
enzyme: hexokinase
glycolysis step two
d-glucose 6-phosphate is converted to d-fructose 6-phosphate
enzyme: phosphohexose isomerase
glycolysis step three
d-fructose 6-phosphate is phosphorylated at C1 to to yield d-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
enzyme: phosphofructose kinase
glycolysis step four
d-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is split in half to yield two three carbon molecules: dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
enzyme: aldolase
glycolysis step five
dihydroxyacetone phosphate is isomerized into a second glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
enzyme: triose phosphate isomerase
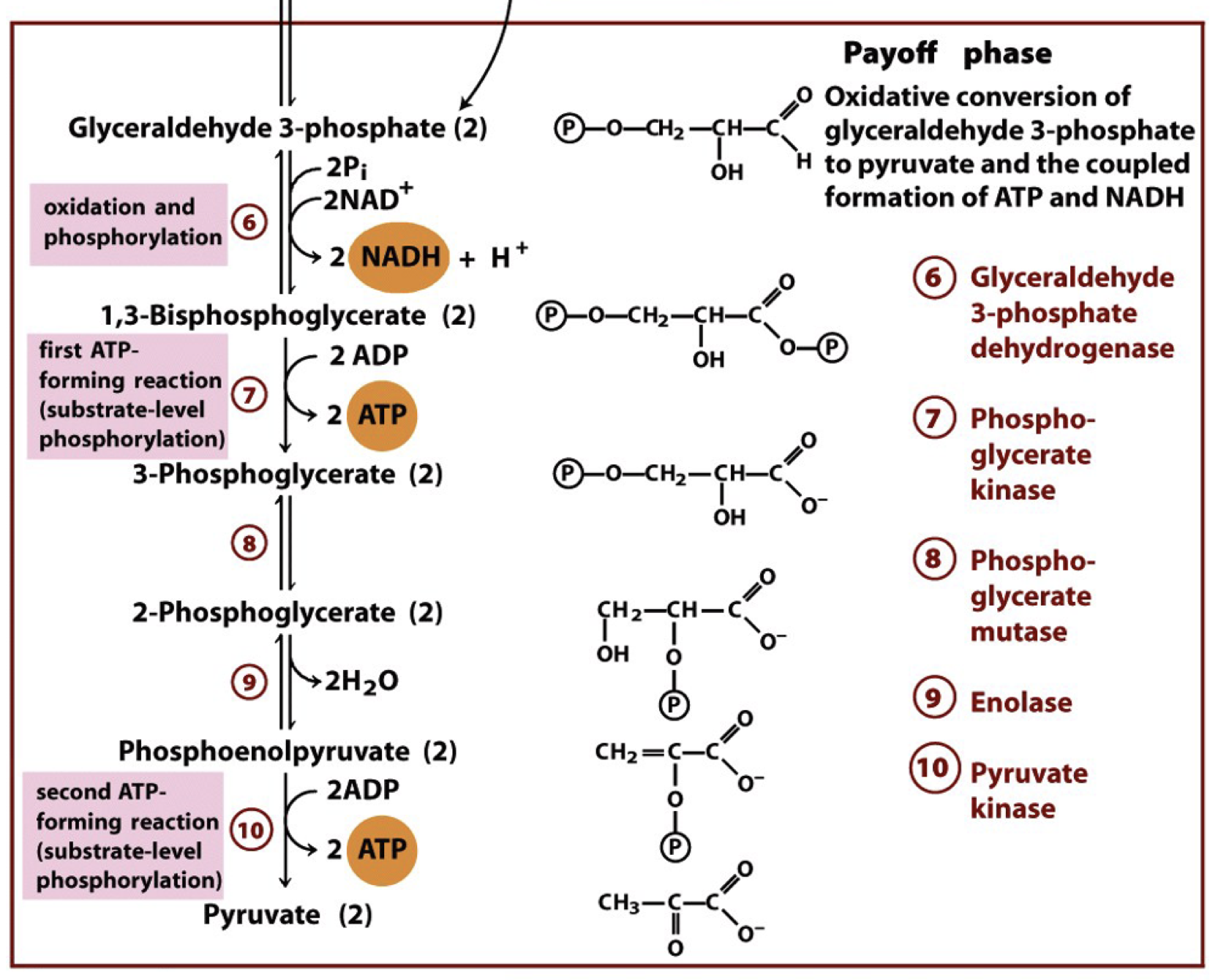
glycolysis - phase two
payoff phase
glycolysis step six
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is oxidized and phosphorylated to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
enzyme: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
glycolysis step seven
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is converted to 3-phosphoglycerate and generates ATP
enzyme: phosphoglycerate kinase
glycolysis step eight
3-phosphoglycerate is converted to 2-phosphoglycerate
enzyme: phosphoglycerate mutase
glycolysis step nine
2-phosphoglycerate in converted into phosphoenolpyruvate and generates H2O
enzyme: enolase
glycolysis step ten
phosphoenolpyruvate is converted into pyruvate and generates ATP
enzyme: pyruvate kinase
payoff phase

phase two reactions
hypoxic conditions
pyruvate is fermented into ethanol and carbon dioxide in yeast
hypoxic condition products
ethanol, 2NAD+ and 2ATP
anaerobic conditions
pyruvate is fermented into lactate in vigorously contracting muscles
anaerobic condition products
lactate, 2NAD+ and 2ATP
aerobic conditions
pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA and then subsequently processed through the citric acid cycle to produce carbon dioxide and water
aerobic condition products
CO2/H2O, 10NAD+/2FAD+ and 28-30ATP
pyruvate metabolism summary
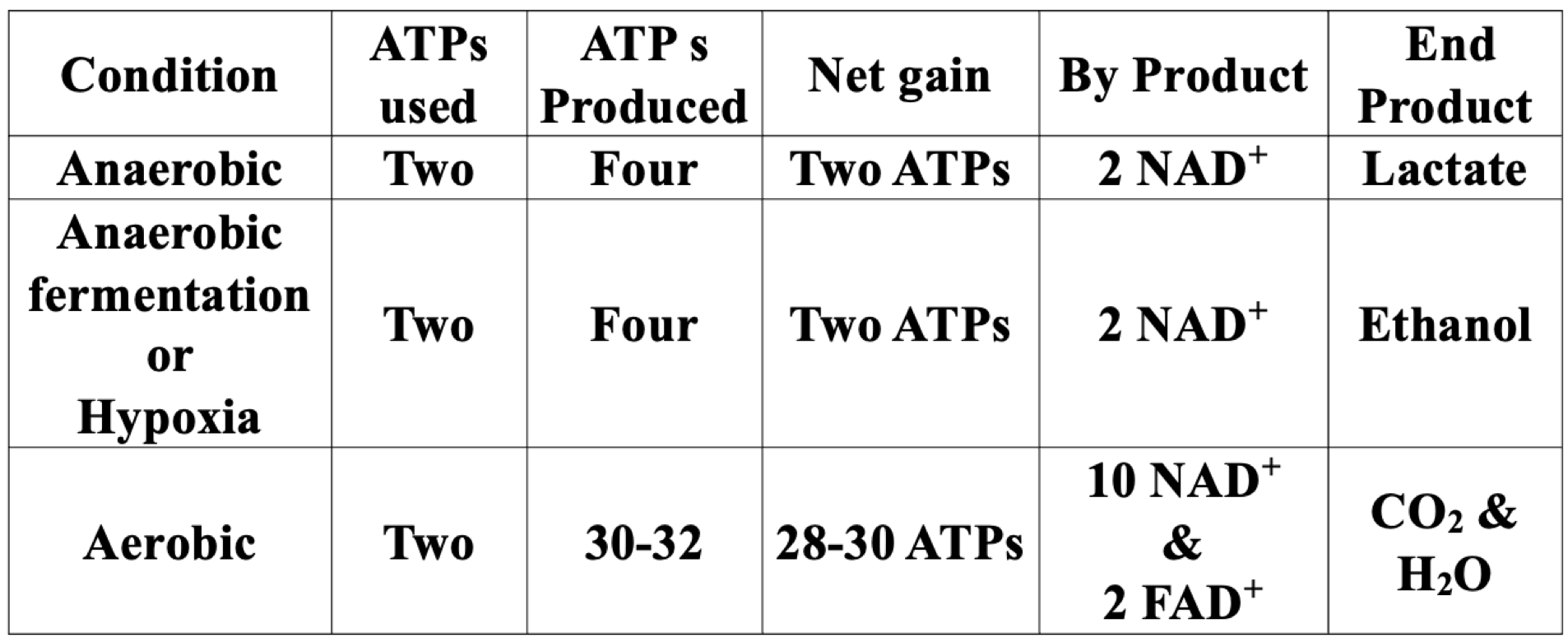
glycolysis energetics
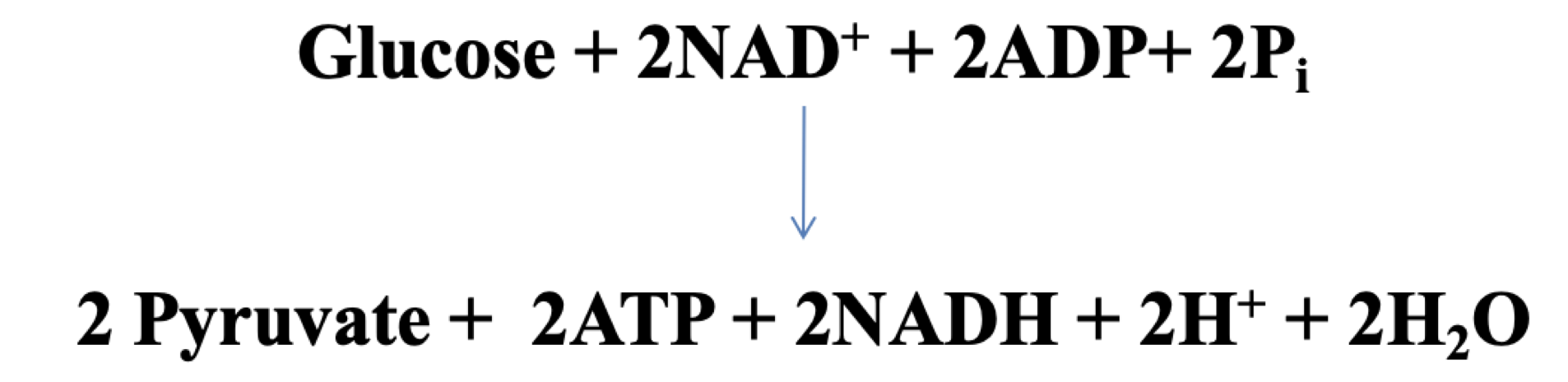
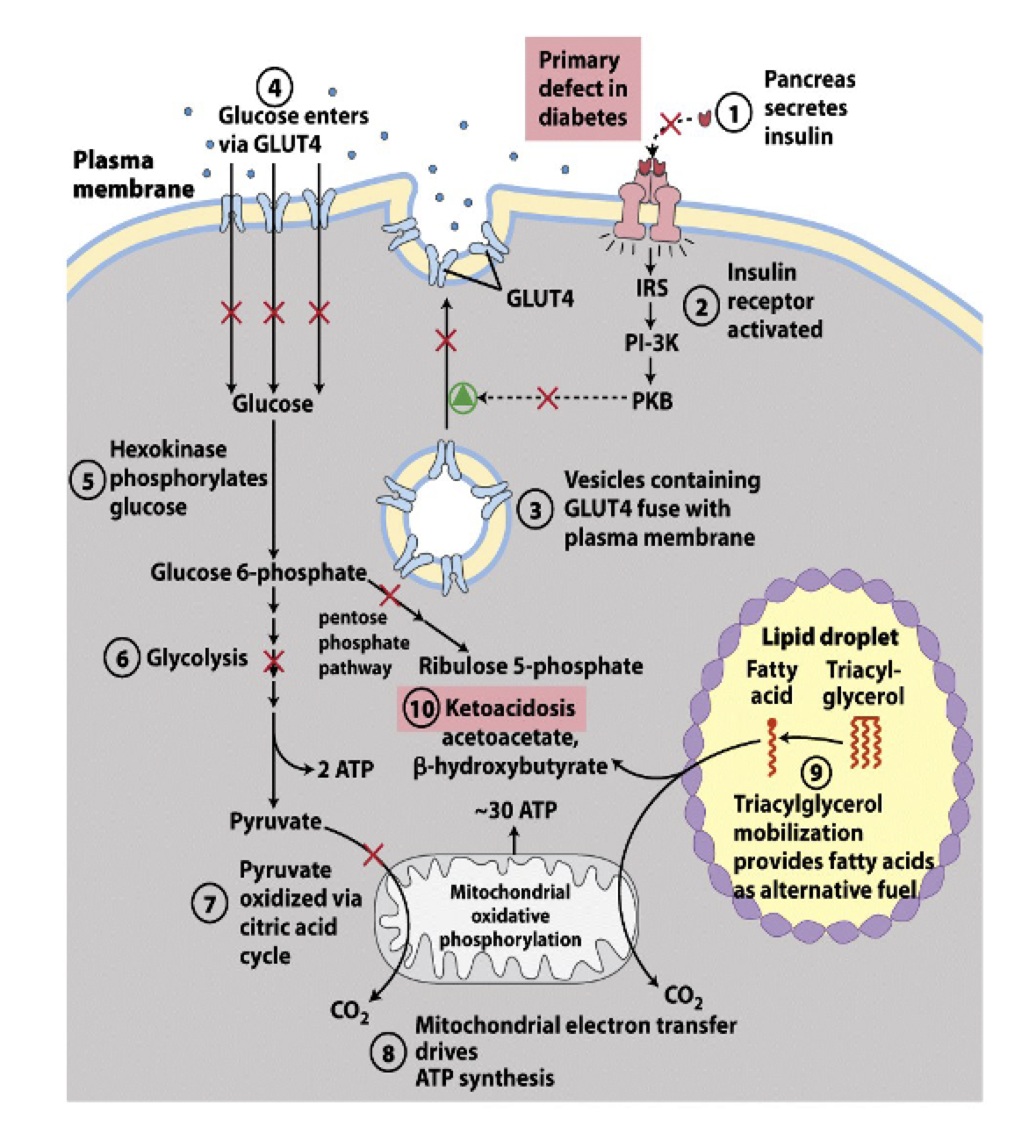
fat and glucose metabolism in type 1 diabetes
feeder pathways for glycolysis
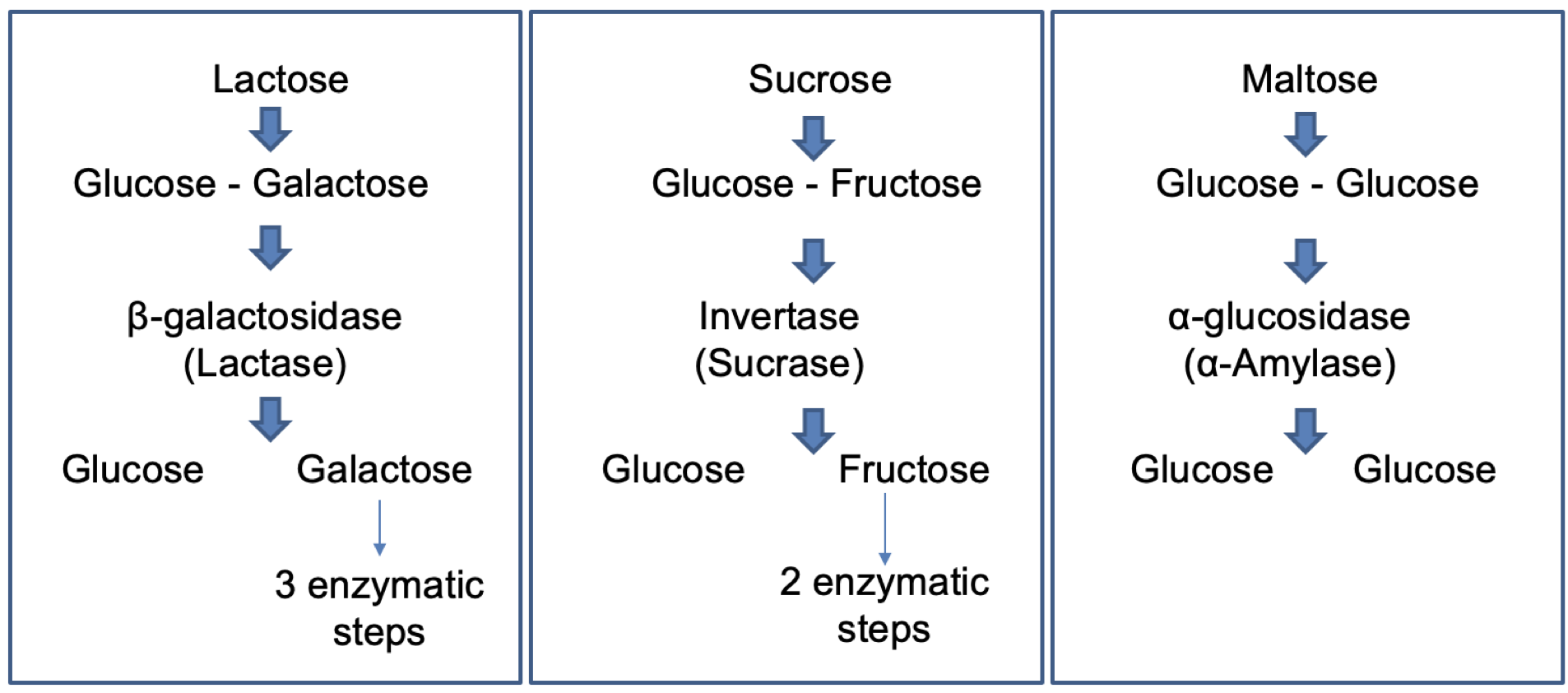
lactose feeder pathway products
glucose and galactose
enzyme: B-galactosidase (lactase)
sucrose feeder pathway products
glucose and fructose
enzyme: invertase (sucrase)
maltose feeder pathway products
two glucose
enzyme: a-glucosidase (a-amylase)
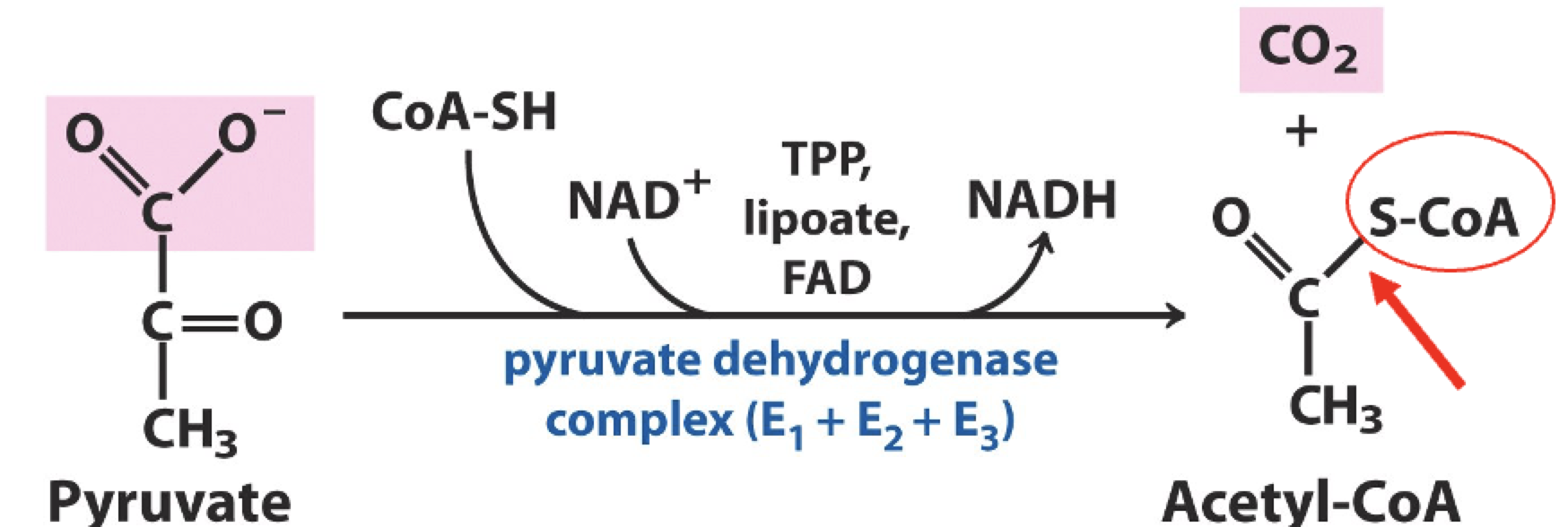
acetyl-CoA production
gluconeogenesis
synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates such as oxcaloacetate and pyruvate
gluconeogenesis
pathway is identical in all organisms
in humans, mainly occurs in liver and kidneys
gluconeogenesis pathway
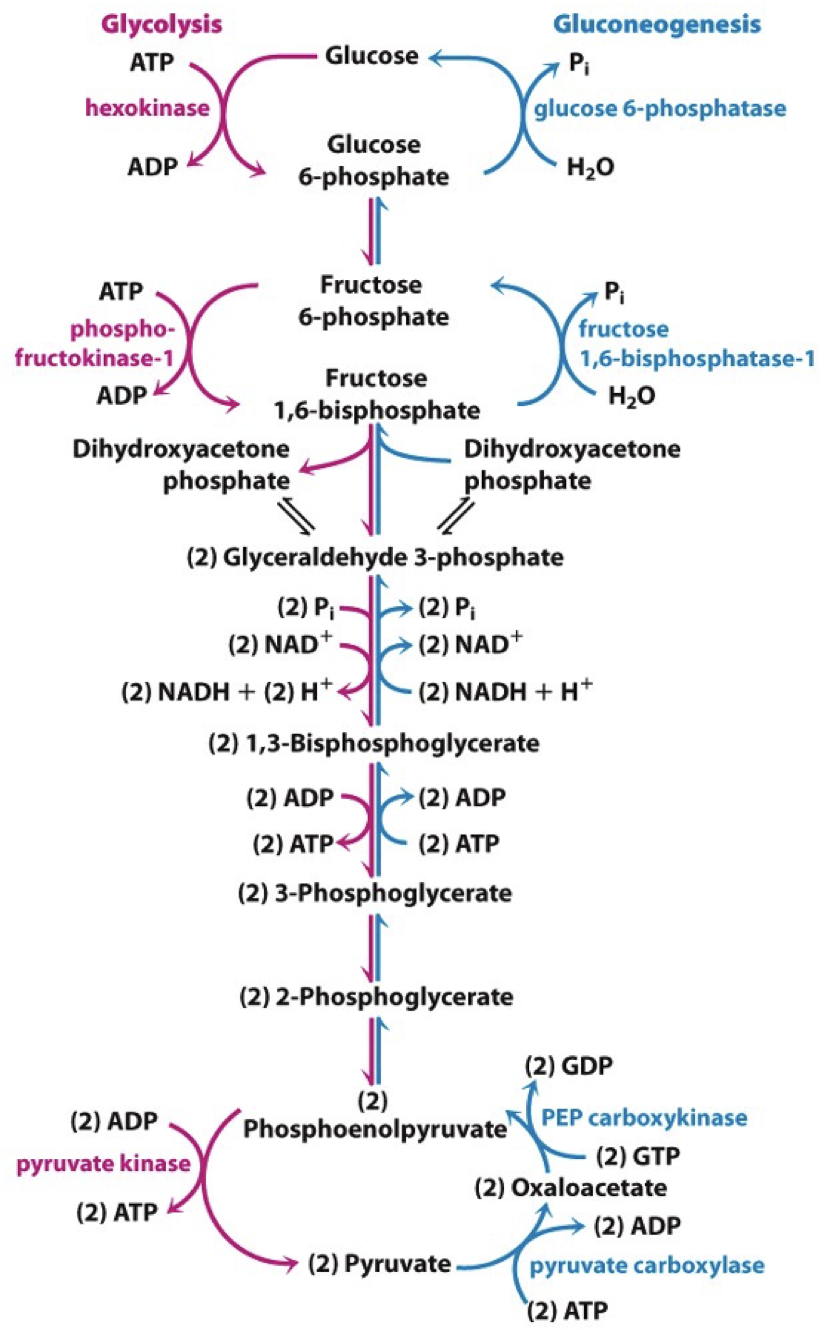
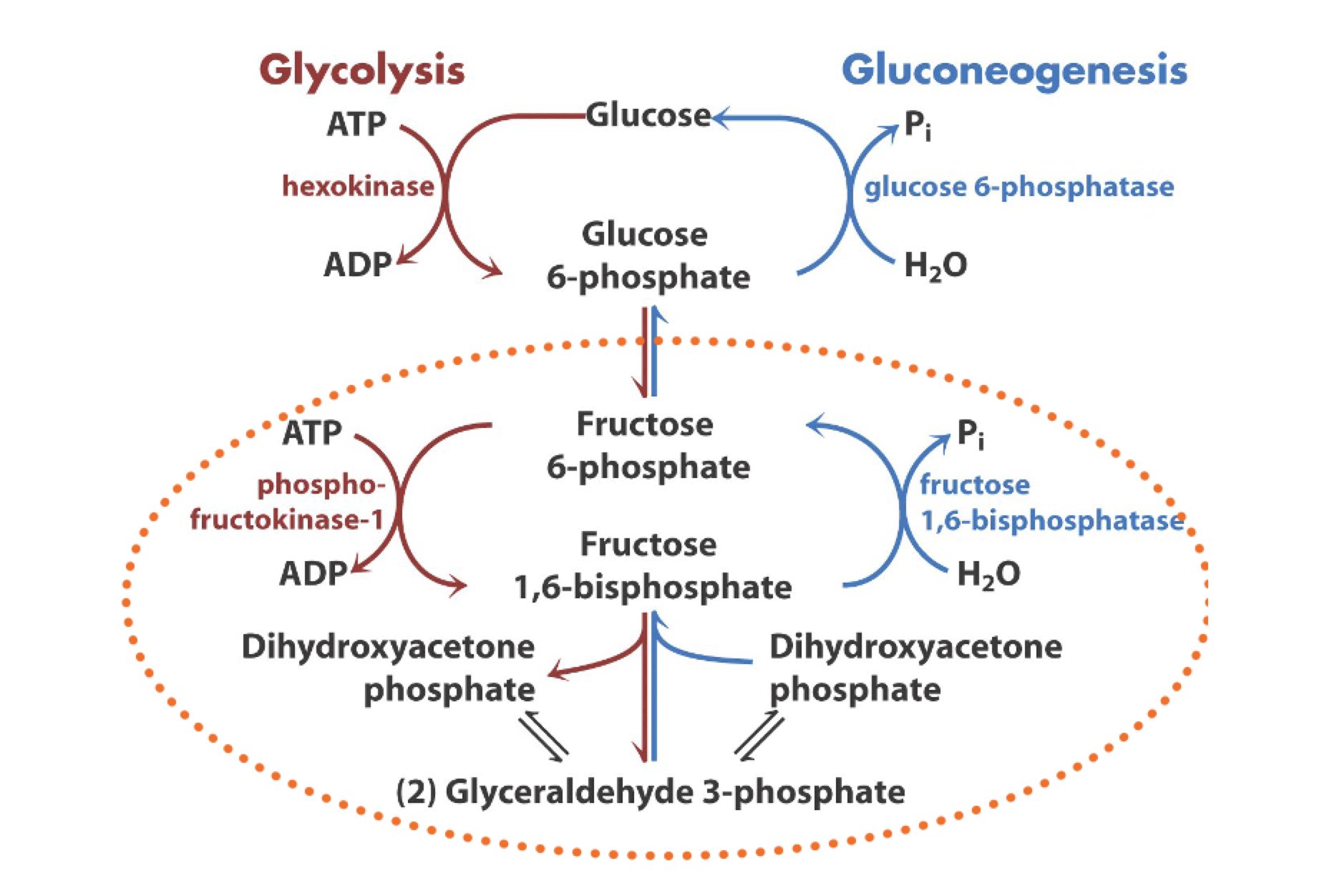
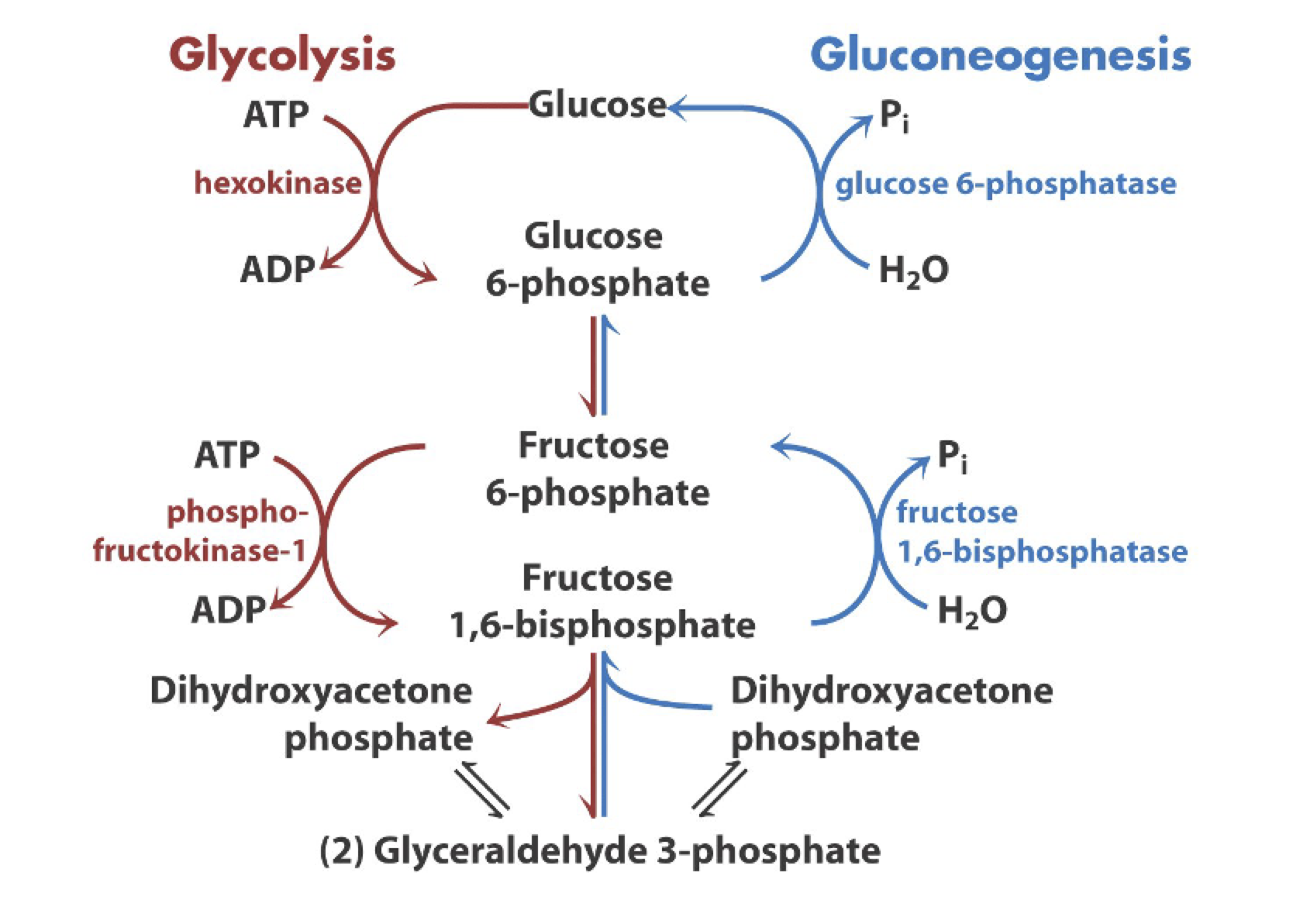
gluconeogenesis: first bypass reaction
very expensive
gluconeogenesis: second bypass reaction
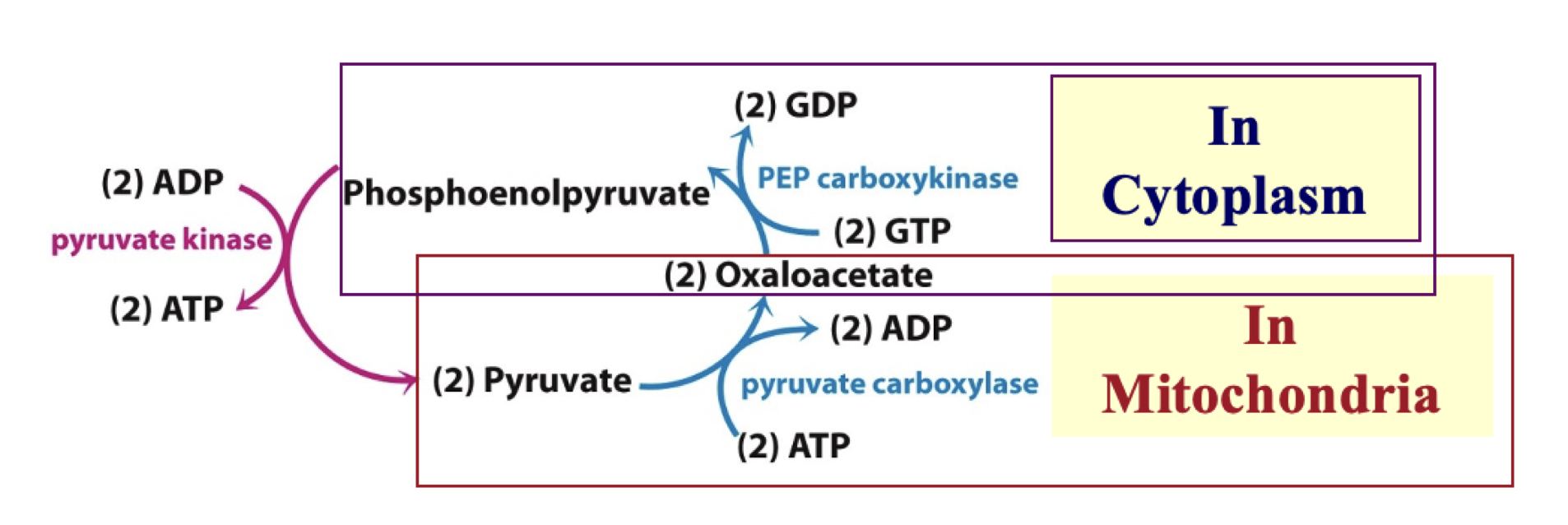
point of control
gluconeogenesis: third bypass reaction
pentose phosphate pathway
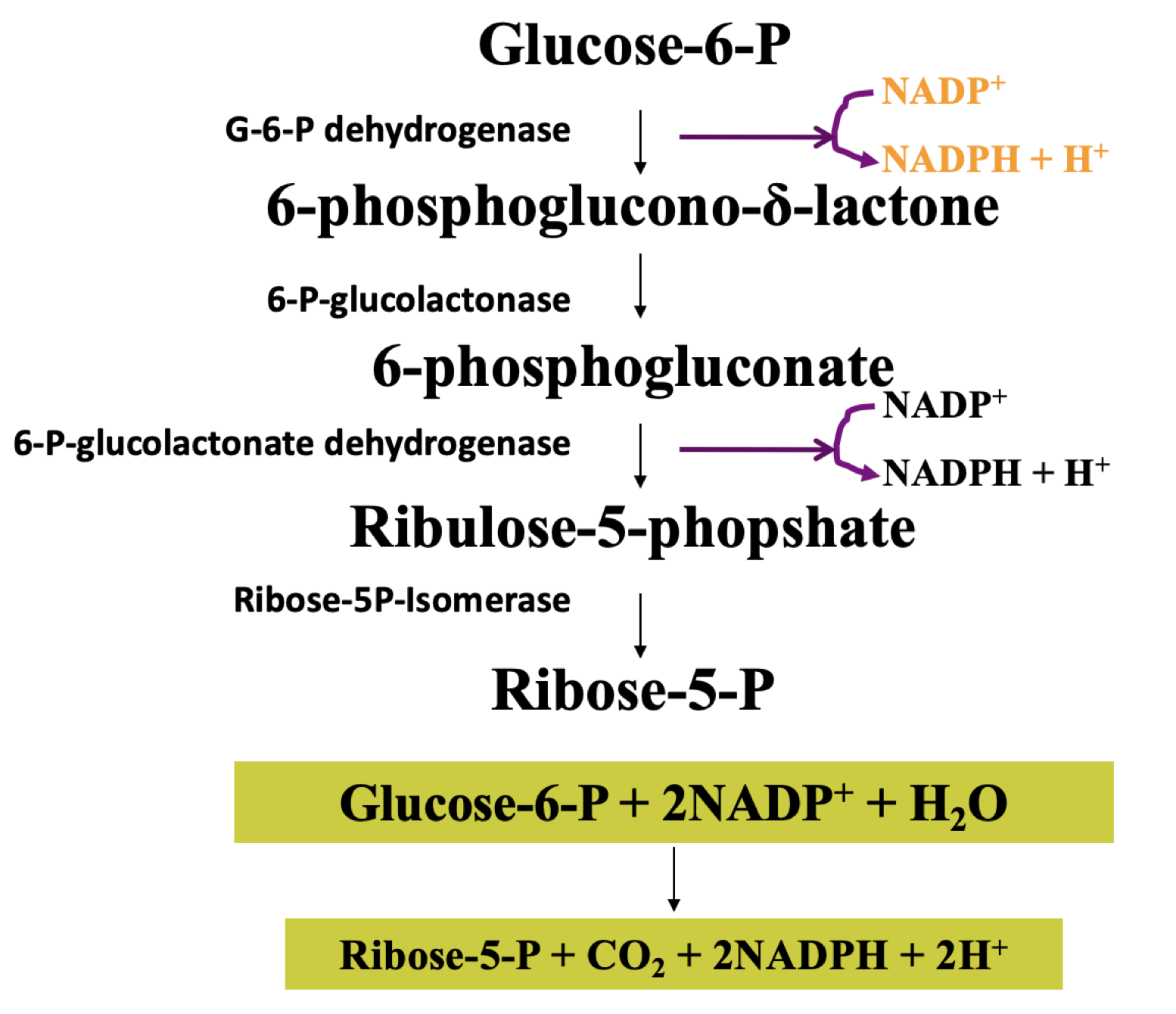
pentose phosphate pathway functions
generate ribose-5-p
(re) generate NADPH
pentose phosphate pathway defects
