Chapter 23: Understanding Diversity: Systematics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Genus
a noun and the first part of the binomial designation
Species
an adjective and the second part of the binomial designation
Ancestral Characteristics
a characteristic that is present in an ancestor and all of its descendants
Derived Characteristics
a characteristic that appears in a recent common ancestor and is not present
earlier in that ancestral line
Clade
all the organisms in the taxa being considered together
Node
a branching point on a cladogram [a change in characteristics occurs at a node]
Root
base point and common ancestor of a cladogram
Ingroup
all the organisms in the taxa being considered together
Outgroup
a taxon that branched off before the ingroup
Mononphyletic
includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants
Paraphyletic
includes a common ancestor but not all of its descendants
Polyphyletic
a group that has evolved from more than one ancestor and does no share a common ancestor
Convergent evolution
evolution in similar environments results in similar characteristics [e.g. flight in birds and insects]
Homologous gene
genes that are related due to sharing a common ancestor
Homologous structure
similarities in structures due to sharing a common ancestor
Homoplasy
apparent similarity in traits due to convergent evolution or the reversal of a trait back to its ancestral state
Parsimony
selecting the simplest explanation for interpreting taxa
Systematics
constructing cladograms [phylogenetic trees]
Phenetics [numerical taxonomy]
uses the number of shared features to form taxa
Evolutionay taxonomy
uses the degree of evolutionary change and phylogenetic
relationships to form taxa
Phylgenetic systematics [cladistics]
uses most recent common ancestor and shared and
derived characteristics to form taxa
Taxonomy
naming, describing, classifying organisms
Taxon
a formal grouping of organisms [e.g. kingdom, phylum, family, etc.]
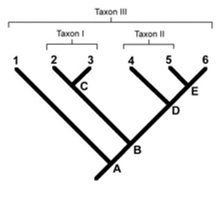
In this figure, taxon II is
A.) monophyletic
B.) Paraphyletic
C.)Polyphyletic
D.) a clade
E.) an outgroup
B.) Paraphyletic
Explain the Movement Toward Clades (4)
-Classical phylogenetic trees have lines of unequal length that represent a period of time (branching (tree) represents hypothesized evolutionary relationships among organisms)
-All lines within a clade are equal of length (phylogenetic relationships based upon a common ancestor and its descendants)
-Classification becoming more reliant on molecular data (DNA sequences, RNA data, Protein sequencing)
-Currently a combination of classical and “modern” approaches
Explain Cladograms
a type of phylogenetic tree (forces a common ancestor as the base), but monophyletic
-represent a monophyletic clade (contains all descendants from a common ancestor)

Define Node
base of branching point
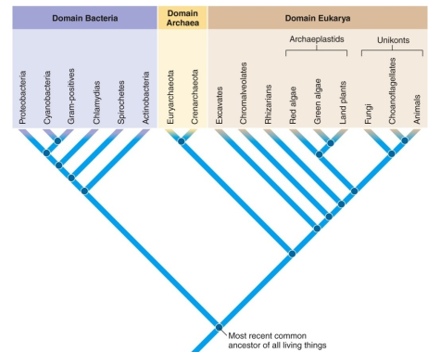
Define Root
a organism at base of cladogram under consideration (most recent common ancestor of all clades show)
Explain plesiomorphies
(shared ancestral cahracters)
-in ancestral (original) species and alll descendants (do not distinguish from another within the clade)
Ex: vertebral column in subphylum Vertebrata
Explain synapomorphies
( a “recent” development not in ancestors up to that point)
-point of divergence between groups but clade s share derived characters
Choosing taxonomic criteria (vertebrate ear bones)
-Ancestral feature: all vertebrates have ear bones
-Derived feature: reptiles have 1 but mammals have 3 (node)
Choosing Taxonomic criteria (egg laying)
-ancestral feature: birds and reptiles lay eggs
-derived feature: birds have feathers and reptiles have scales
Cladogram grouping: outgroup
taxon that branches off earlier than taxa under investigation
Cladogram groupings: ingroup
Ingroup: all taxa starting at derived character and sharing common features
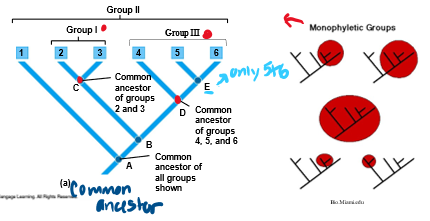
Explain Monophyletic Grouping
Common ancestor and all descendants must share at least one derived character
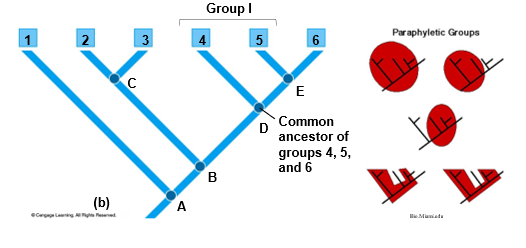
Explain Paraphyletic grouping
Only some descendants of a common ancestor will share ancestral characters (subset of the whole)
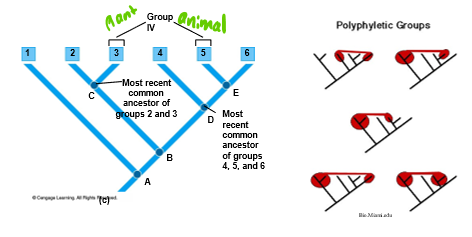
Explain Polyphyletic grouping
Do not share common ancestor
-Unnatural grouping-misrepresents evolutionary relationships