Exam 2 SMC Policy Economics in one lesson
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
The art of economics
Consists in looking not merely at the immediate but at the longer effects of any act or policy.
The broken glass dilemma
A scenario illustrating the fallacy that destruction can benefit the economy by creating work.
Opportunity cost
The lost benefit that could have been gained from the next best alternative when a choice is made.
Public Works = Public Taxes
The concept that government spending must come from tax revenue, not from other sources.
Inflation
A more vicious form of taxation that decreases the purchasing power of money.
Economic fallacies
Misconceptions that arise from abstraction and overlook the impact on individual members of a community.
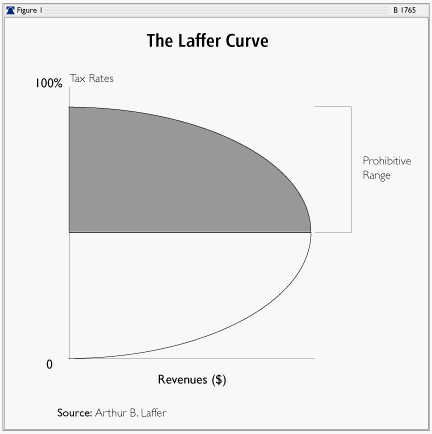
Laffer Curve
Illustrates a theoretical relationship between tax rates and tax revenue.
Net benefit
The overall gain or advantage after considering all effects and alternatives.
Manufacturing displacement
The shift in production focus due to external factors, such as war.
Government spending for employment
Often seen as wasteful when it does not result in net economic benefits.
T/F: Every dollar the government spends is taken away from tax payers.
True
T/F: Every job the government creates destroys a private sector job.
True
The Laffer Curve
The Laffer curve is a curve depicting the relationship between tax rates and revenue, based on a theory by economist Arthur Laffer.