Organic Chemistry (Chapter 13: Alkynes)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Nomenclature of Alkynes
Number the carbons in a way that the carbon-carbon triple bond has the lowest priority numbers
Name the substituents and note their location
methyl group on carbon number 5
Name parent chain of the molecule including the location of the triple bond
hexane to hexyne
location of the triple bond starts on the first carbon
Special nomenclature example
for this example it has a cyclic and a straight chain component
when naming the longest carbon chain it is either EXCLUSIVELY the ring or the straight chain
NO mix and match
since we are prioritizing the alkyne you want to name the longest carbon chain down in the straight chain

Priority: Highest to Lowest
Numbering begins closest to the highest priority group
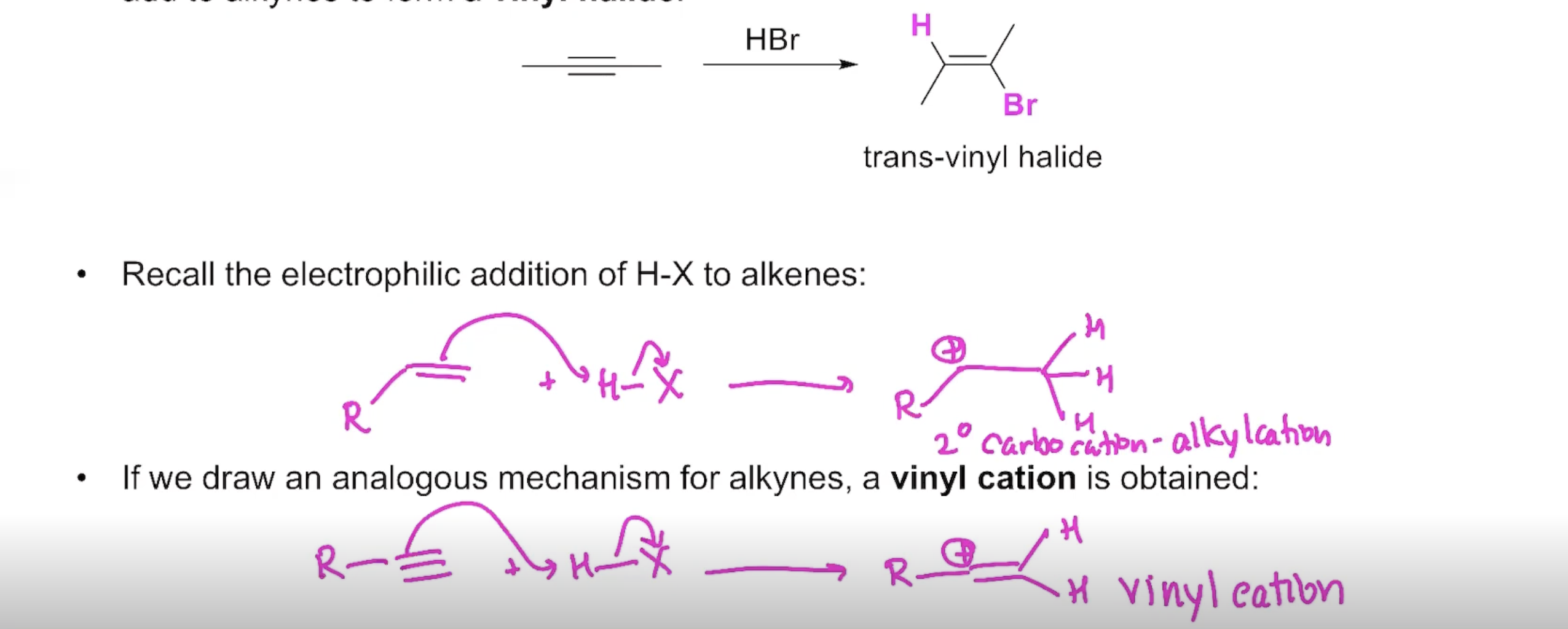
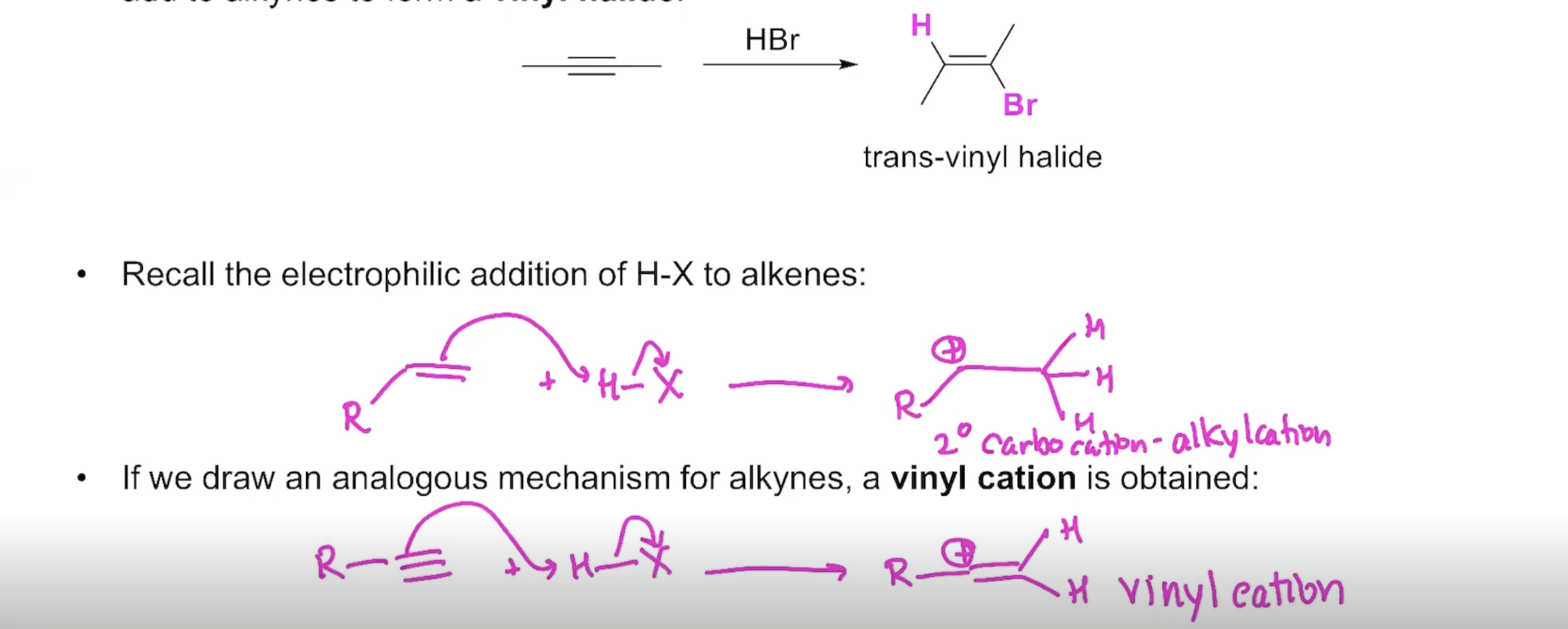
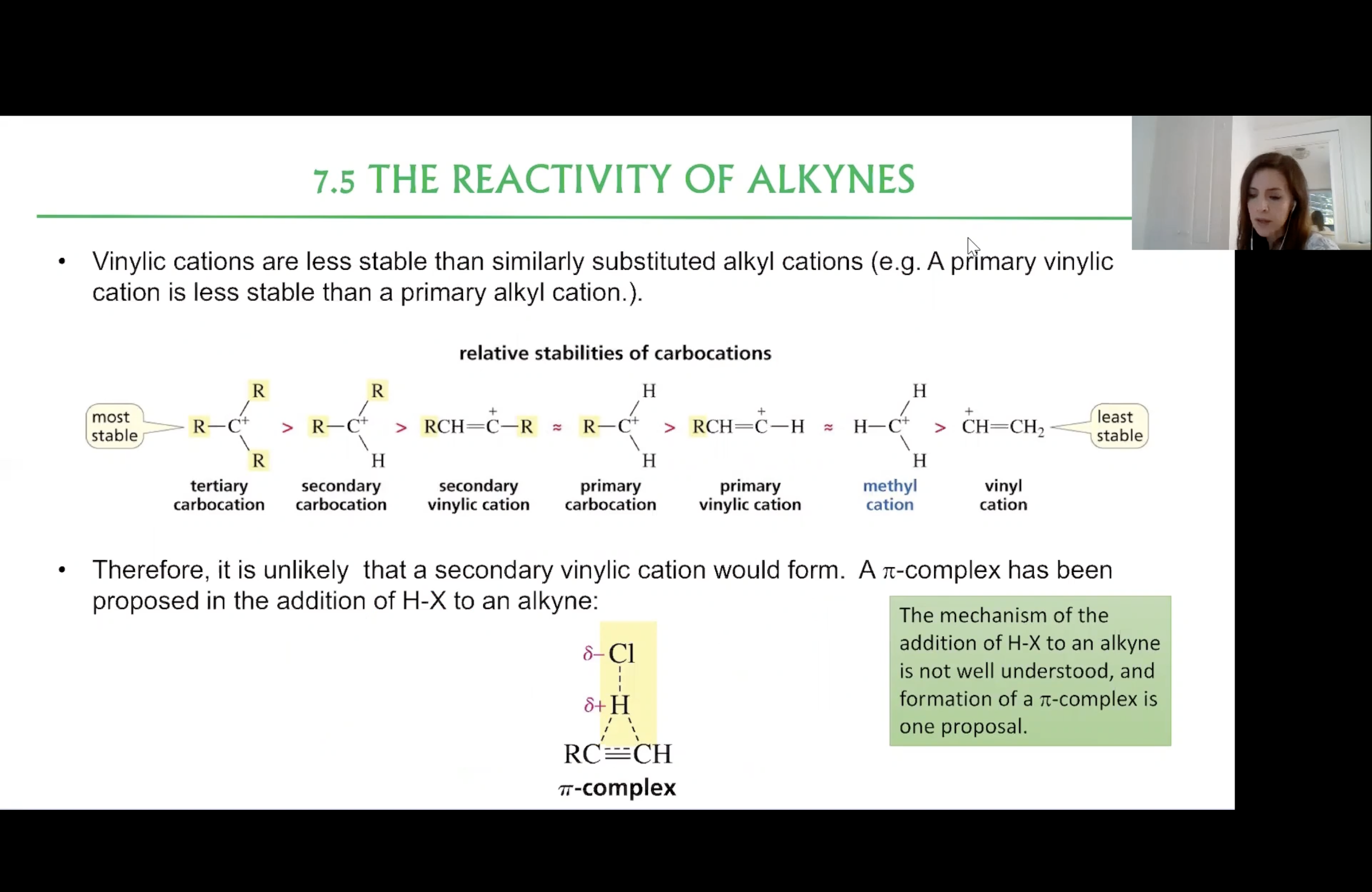
The Reactivity of Alkynes
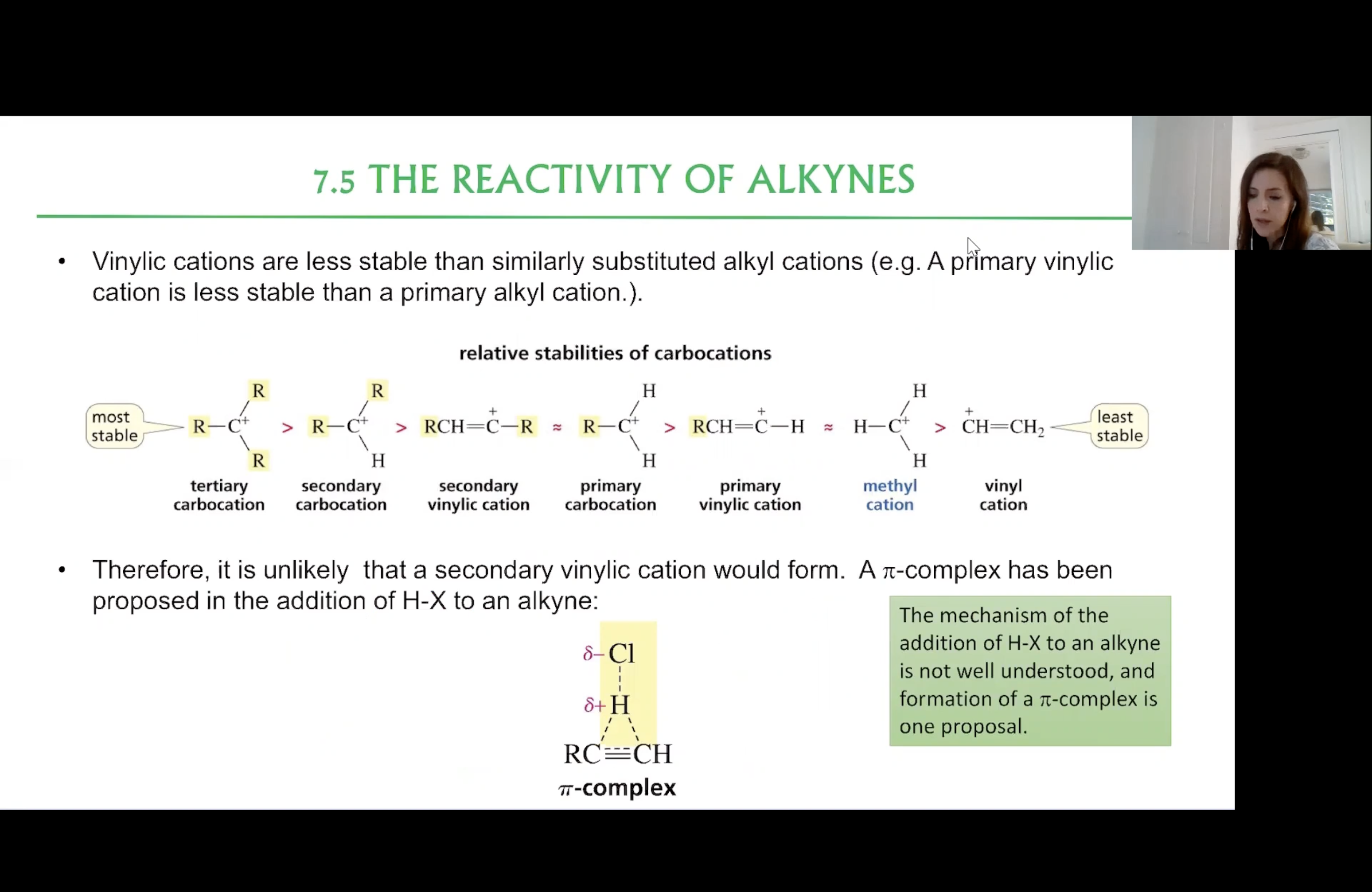
Relative Stabilities of Carbocations
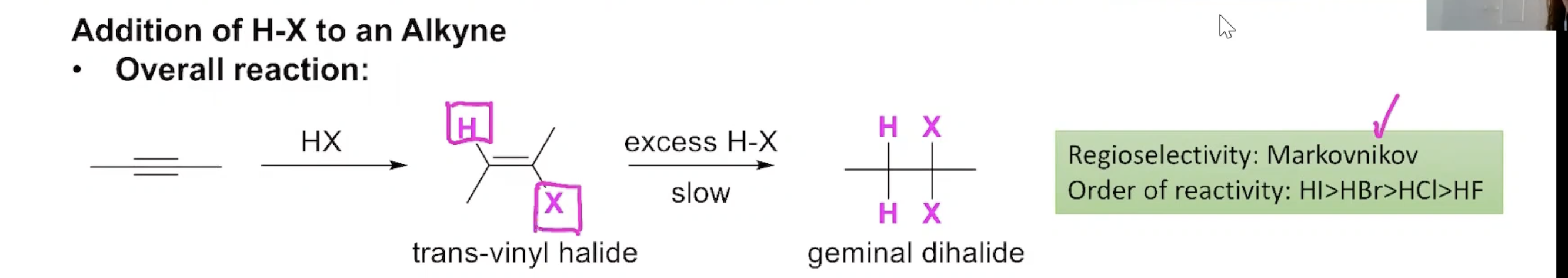
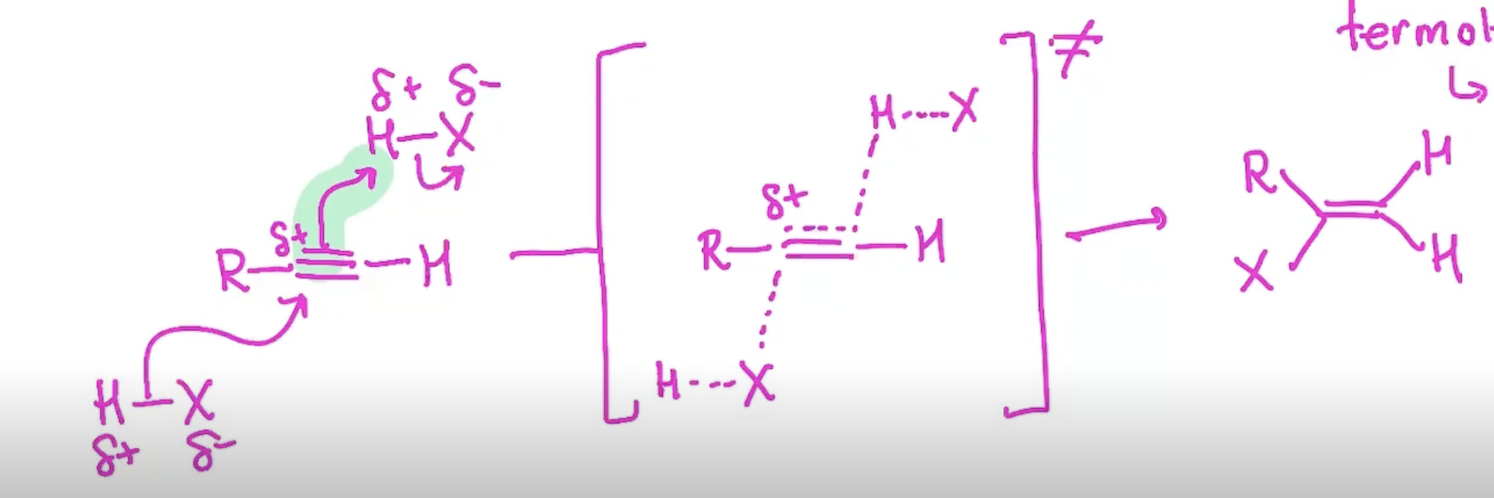
Addition of H-X to an Alkyne
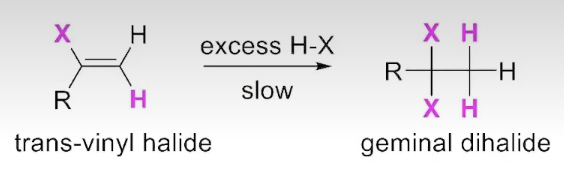
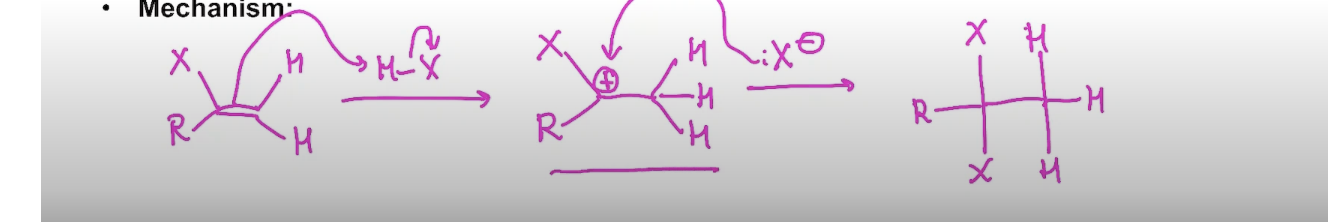
Addition of EXCESS H-X to an alkyne
In the presence of excess H-X the reaction proceeds to a geminal dihalide
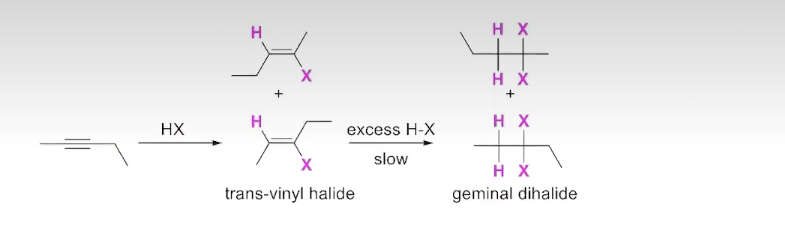
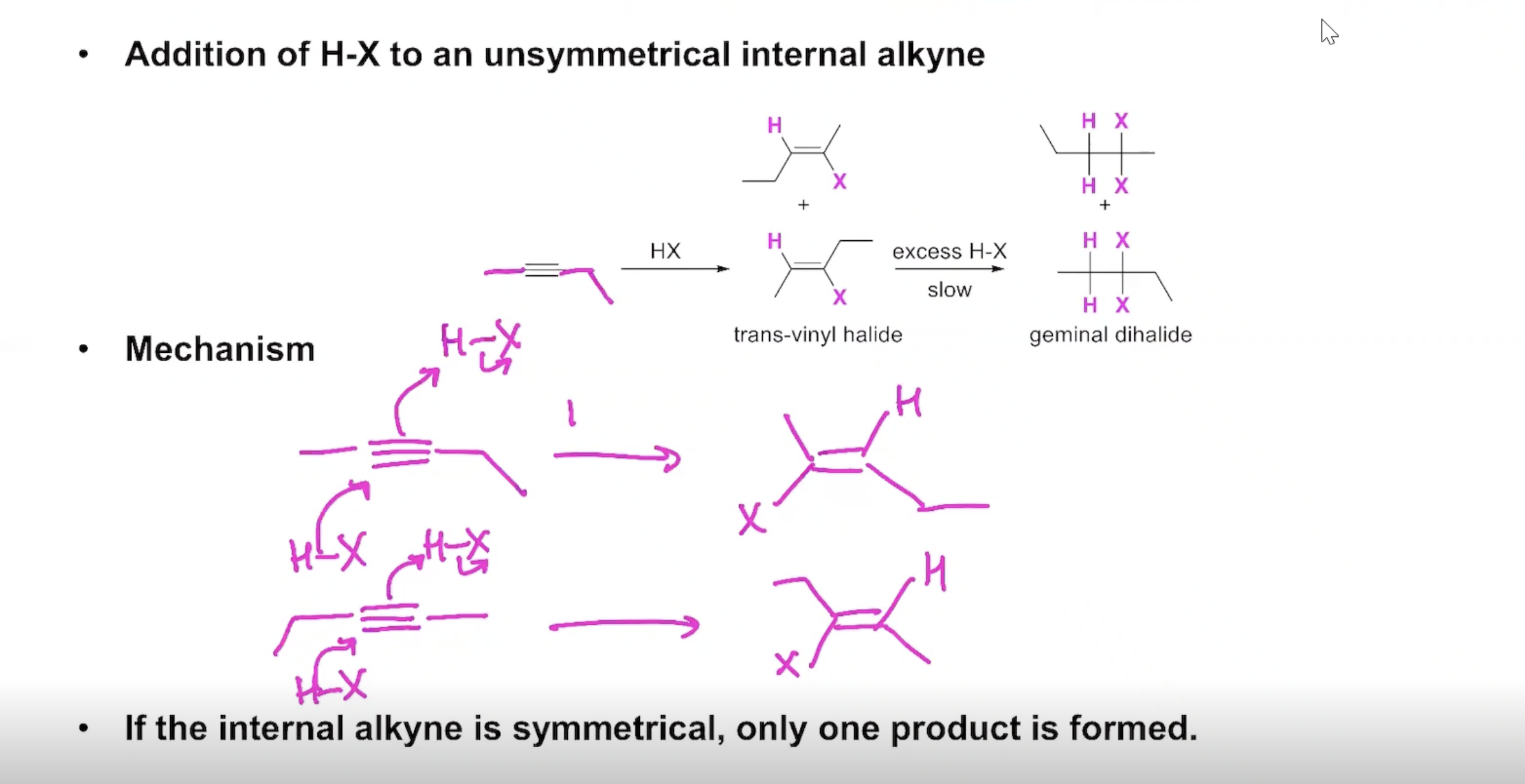
Addition of H-X to an unsymmetrical internal alkyne
If the internal alkyne is SYMMETRICAL only one product is formed
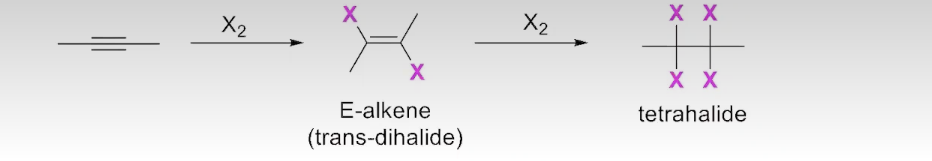
The Addition of X2 to Alkynes
Proposed mechanism: analogous to the addition of X2 to alkenes (X2=Cl2, Br2,I2)
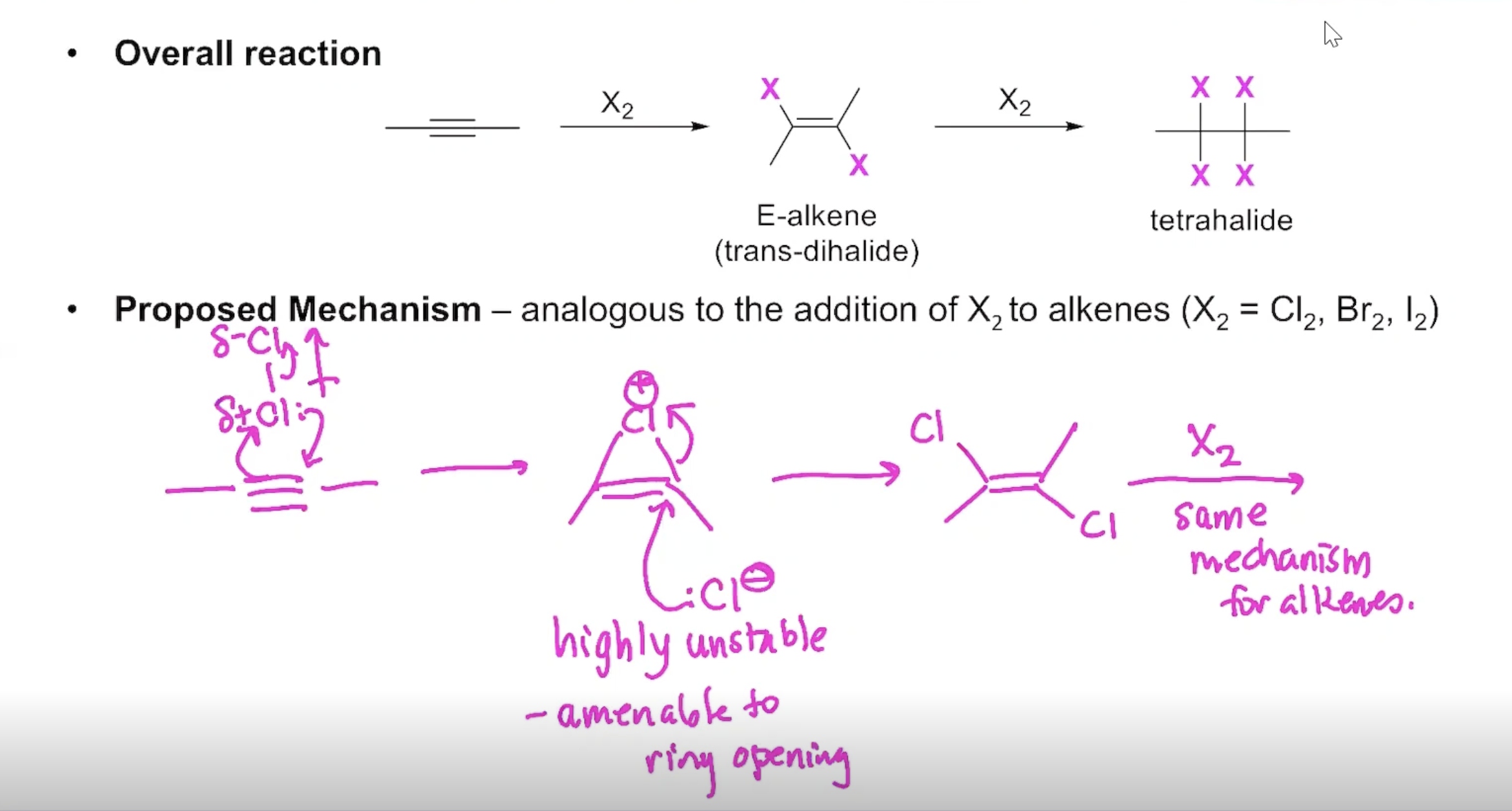
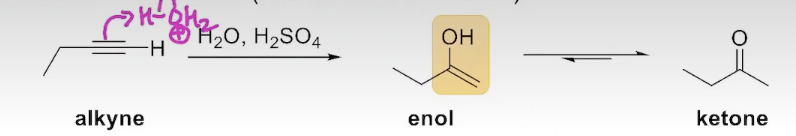
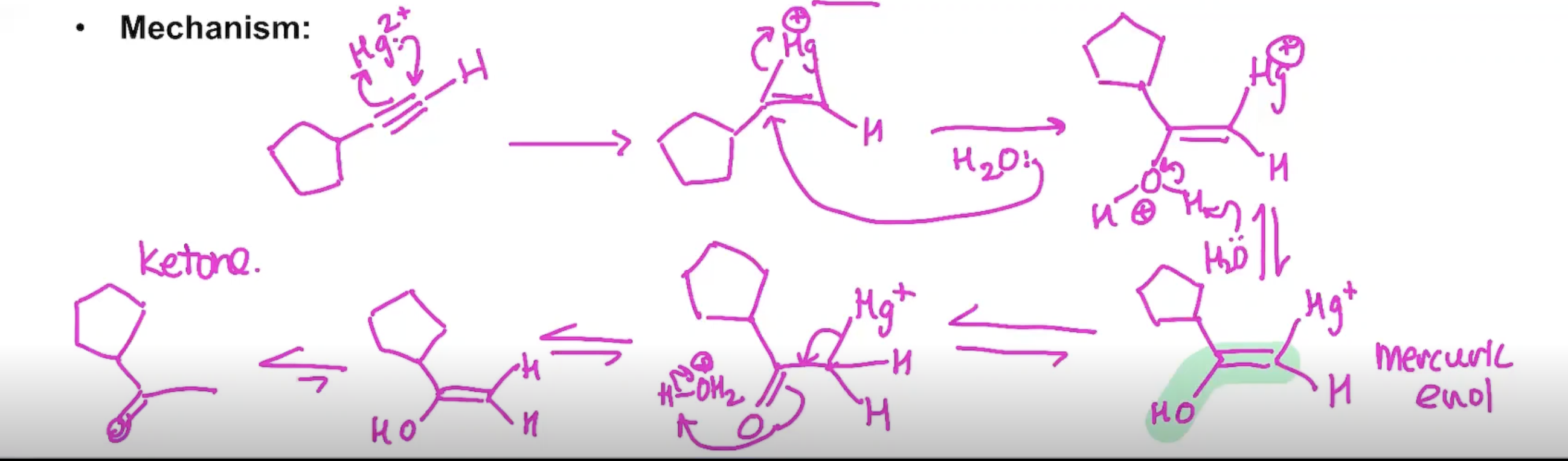
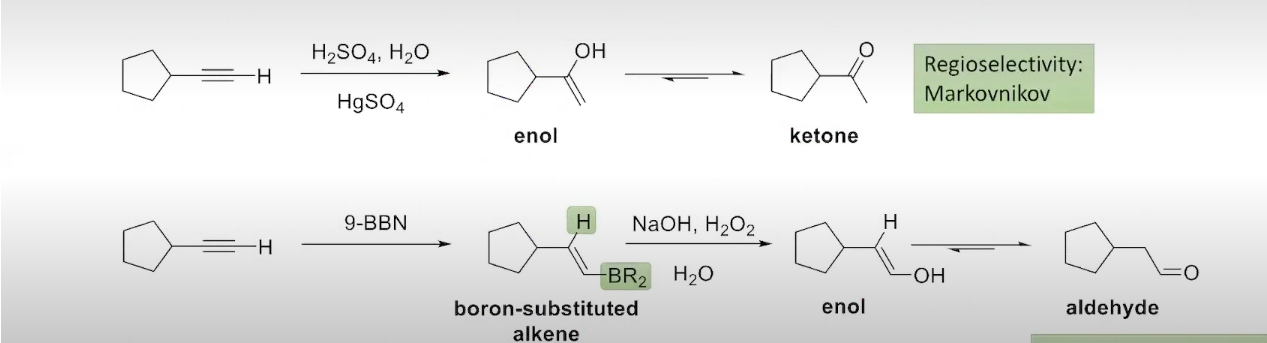
The Addition of water to an Alkyne
tautomerization is apart of the process
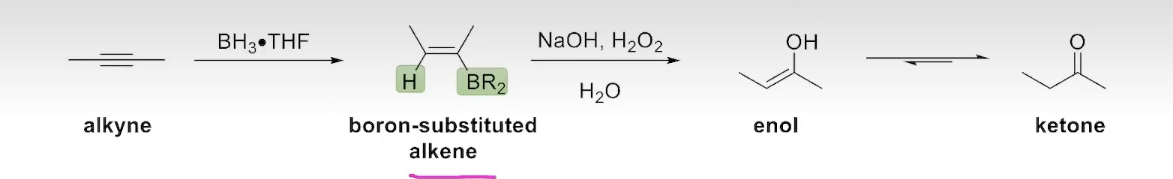
The Addition of Borane to an Alkyne (internal alkynes)
The hybridization-oxidation of internal alkynes occurs in an analogous way to the hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes:
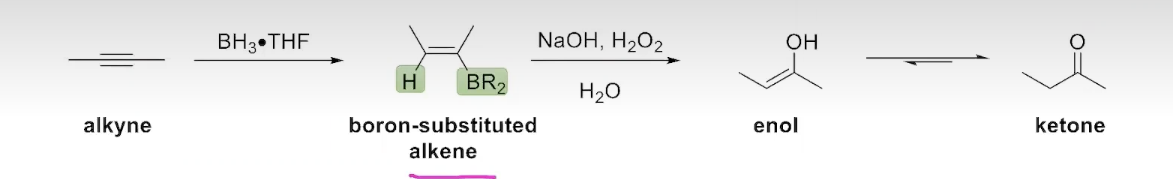
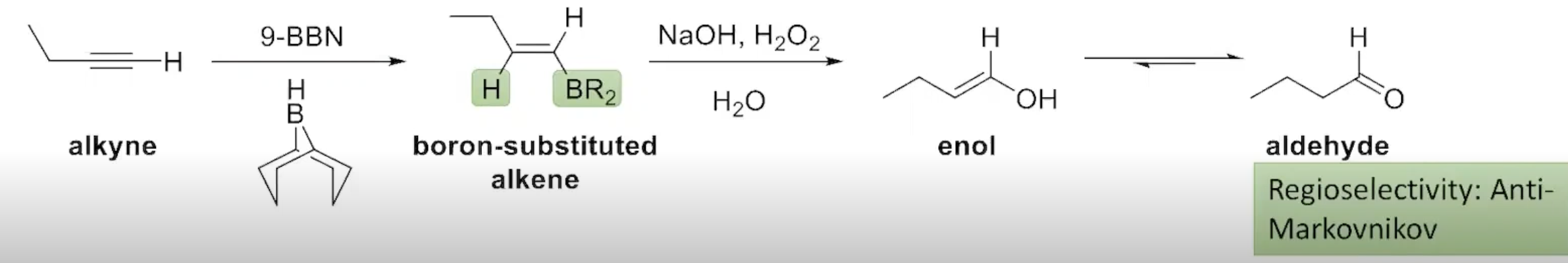
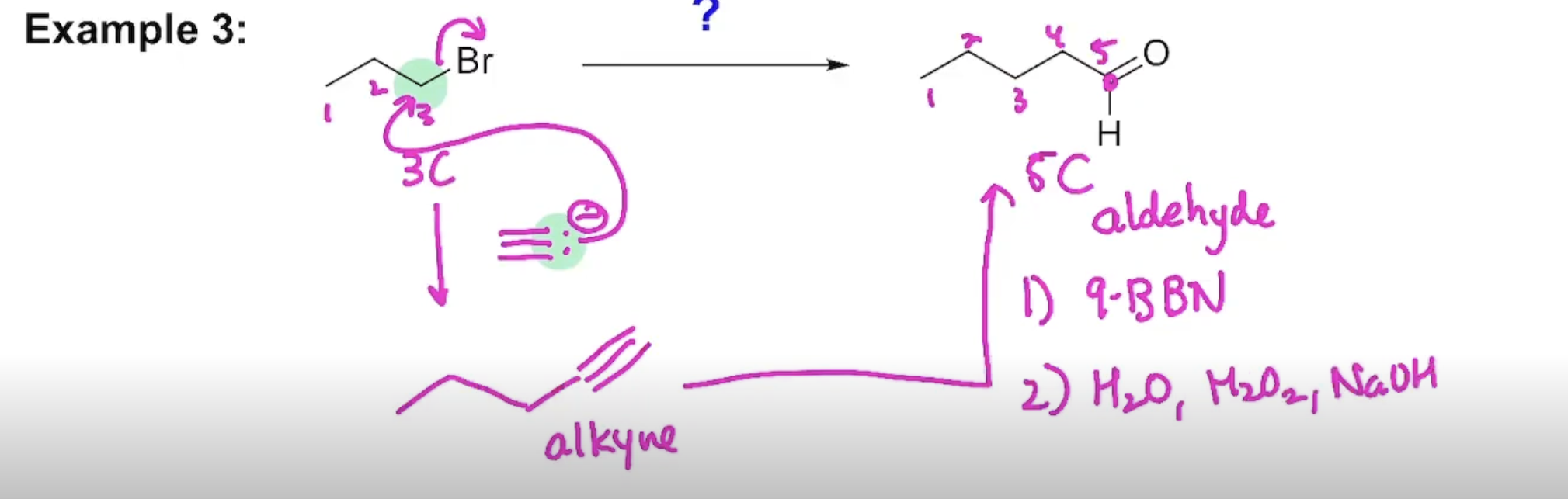
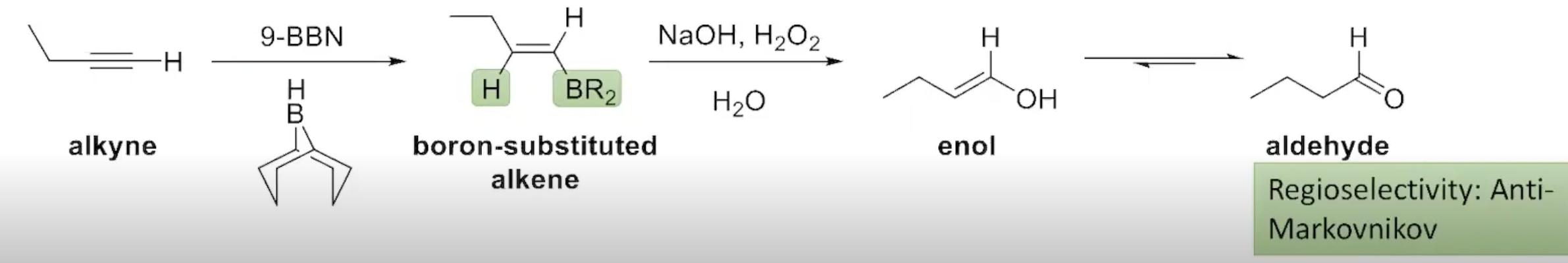
The Addition of Borane to an Alkyne (terminal alkynes)
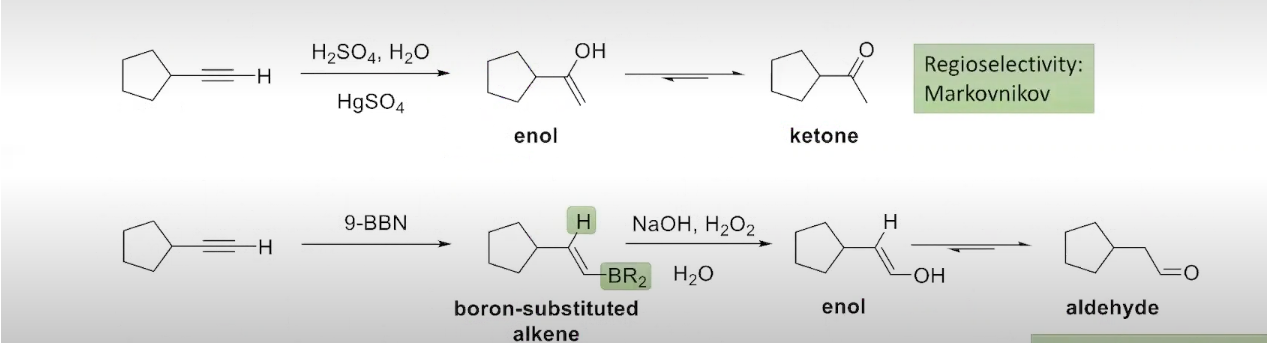
Two Methods to Hydrate an Alkyne
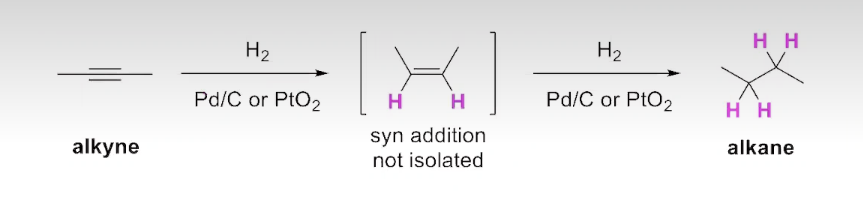
The Addition of Hydrogen to an Alkyne
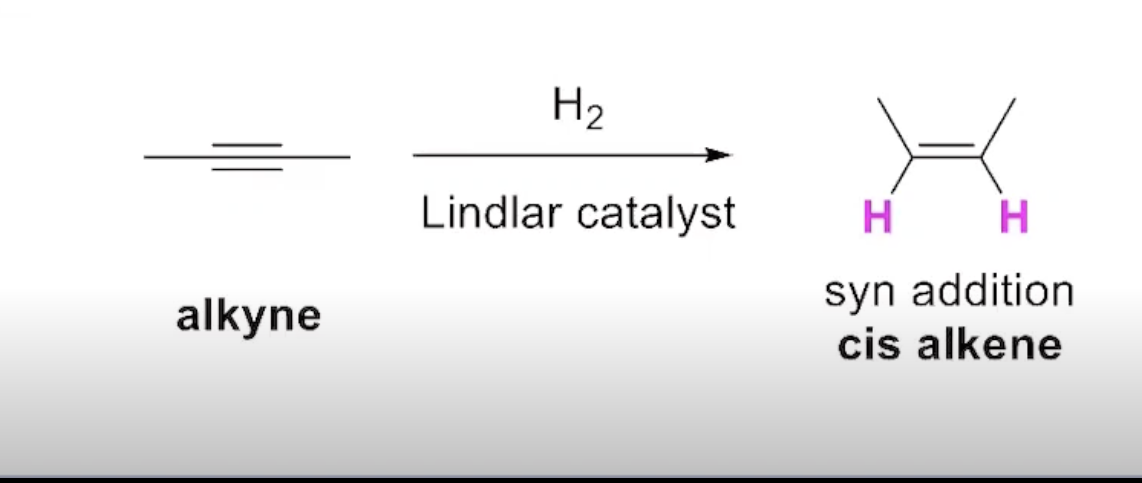
The Addition of Hydrogen to an Alkyne (Alternative=lindlar catalyst)
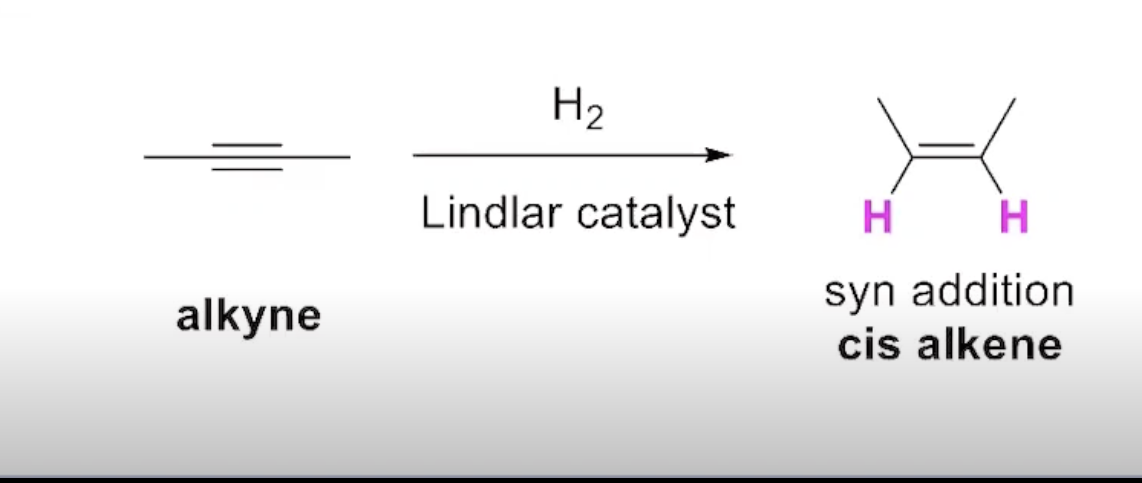
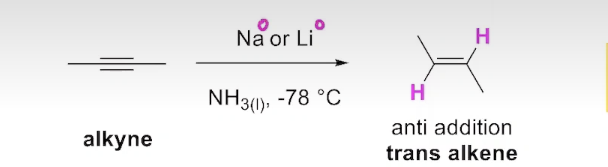
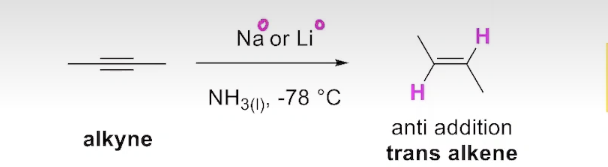
How can you obtain a trans alkene from partial reduction of alkynes
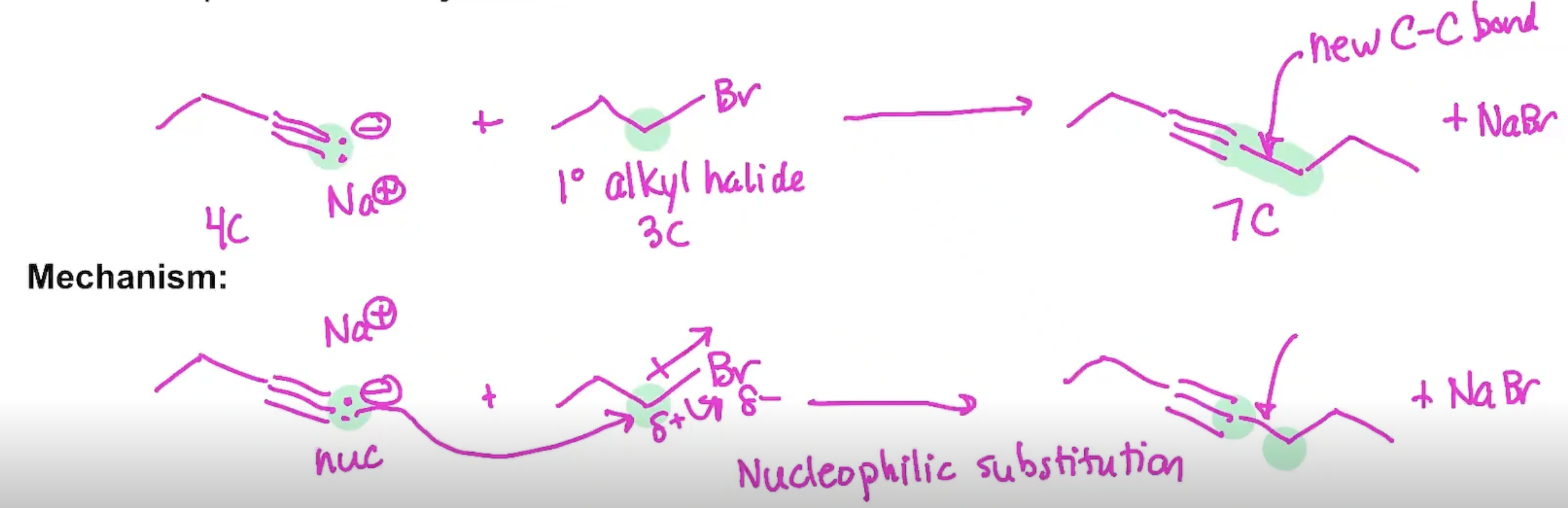
Synthesis using Acetylide Ions
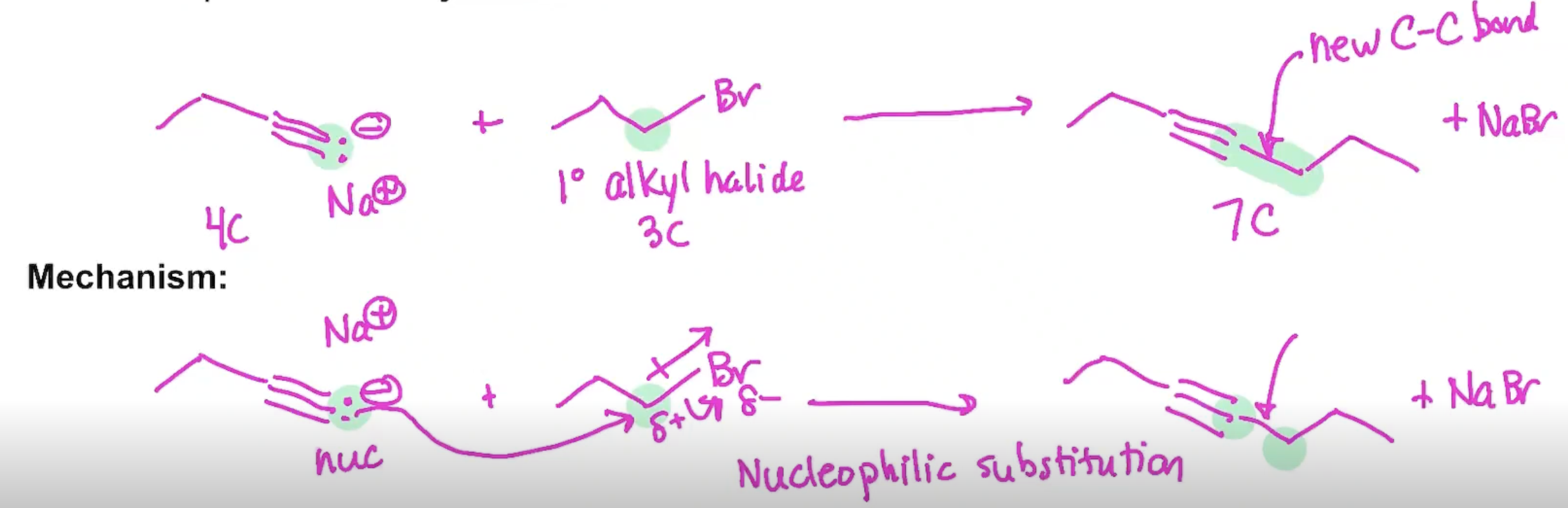
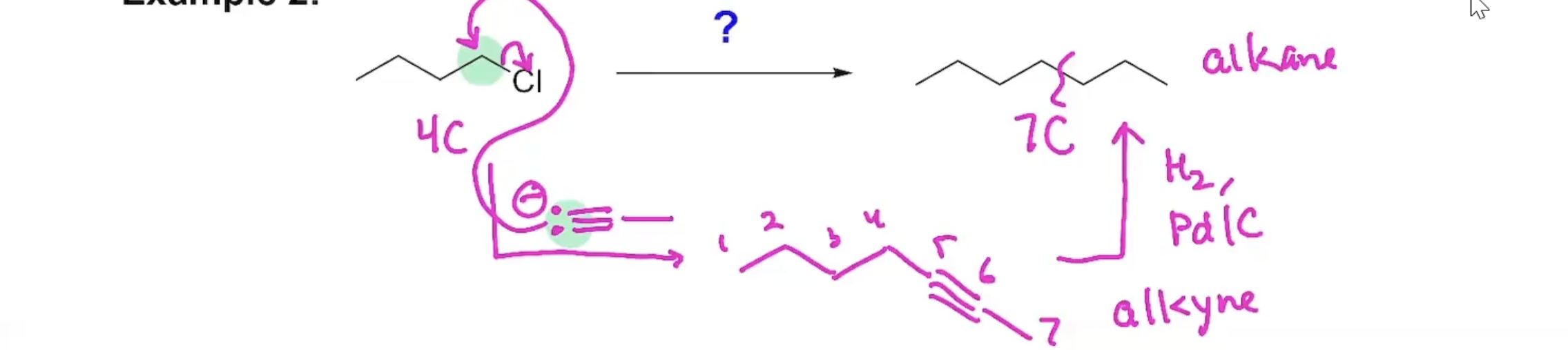
Synthesis (Example#1)
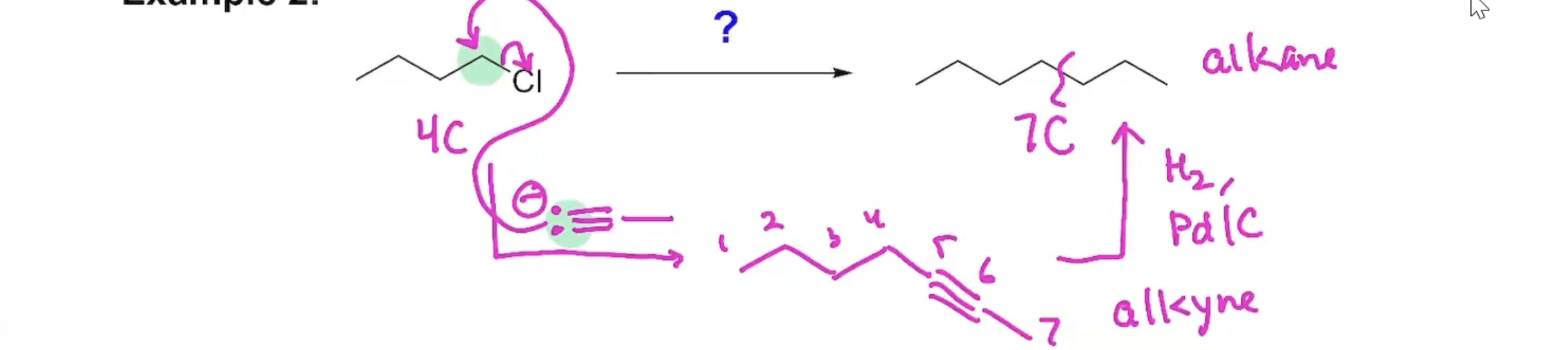
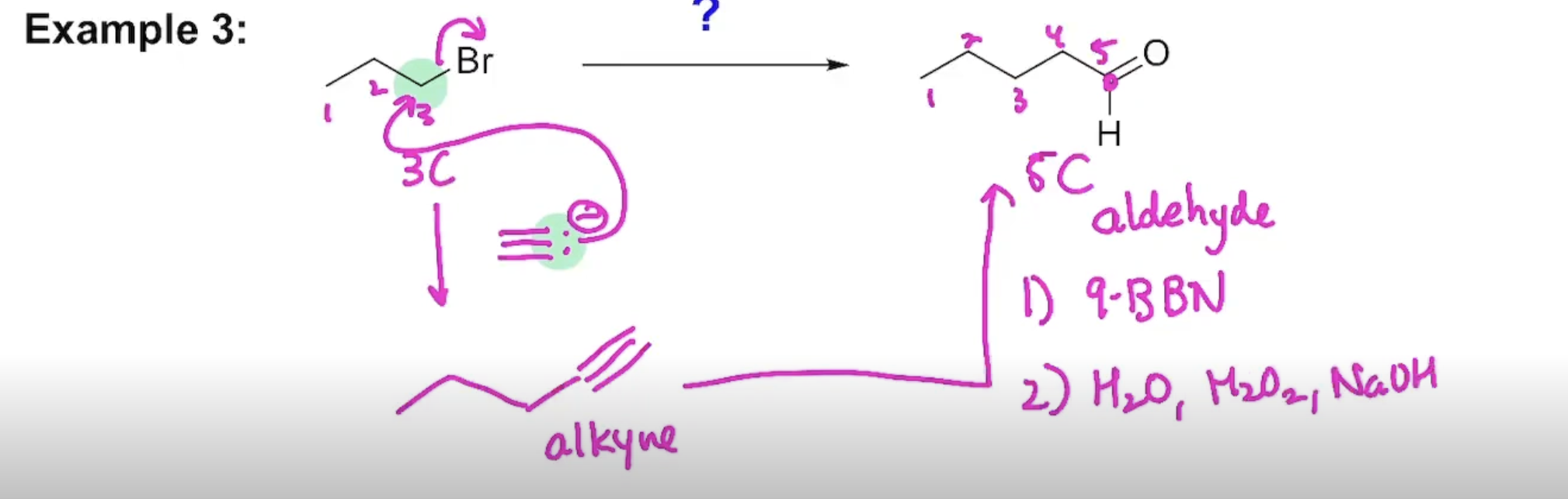
Synthesis (Example#2)