Chapter 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/122
Last updated 4:04 AM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
1
New cards
What are almost all molecules in a cell composed of ?
Carbon
2
New cards
What can carbon form?
Large and complex molecules
3
New cards
Organic molecules
Molecules with carbon
4
New cards
How do carbon skeletons vary?
Length, double bonds, branching, rings
5
New cards
Why are isomers with four different partners important in the pharmaceutical industry?
Using 2 different isomers of a drug can be harmful
6
New cards
Hydrocarbons
Molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
7
New cards
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structural formulas
8
New cards
How can isomers be created?
From differences in spatial arrangements
9
New cards
How do testosterone and estrogen differ?
In their groups of atoms
10
New cards
Function groups
Affect a molecule's function by participating in chemical reactionsWha
11
New cards
What are two properties of functional groups?
Polar and hydrophyllicW
12
New cards
What are the function groups?
Hydroxyl, Carbonyl, Carboxyl, Amino group, phosphate, methyl group
13
New cards
Hydroxyl group
Contain hydrogen bonding to oxygen, ie ethanol and other alcohols
14
New cards
Hydroxyl formula
-OH
15
New cards
Carbonyl
Carbon double bonded to oxygen
16
New cards
What are simple sugars made of
Hydroxyl and Carbonyl groups
17
New cards
Carbonyl formula
>C=O
18
New cards
Carboxyl
Carbon double bonded to oxygen and hydroxyl, and can act like an acidCarb
19
New cards
Carboxyl formula
-COOH
20
New cards
Amino group
Nitrogen bonded with two hydrogens and can act like a base after being ionized
21
New cards
What do amino acids contain?
Amino and carboxyl groups
22
New cards
Amino formula
-NH2
23
New cards
Phosphate
Phosphorous atoms bonded to four oxygen atoms and unequally ionizedW
24
New cards
What is phosphate involved in?
The transfer of energy
25
New cards
Phosphate formula
-OPO32-
26
New cards
Methyl group
Carbon bonded to three hydrgen
27
New cards
What composes DNA?
Methyl groups
28
New cards
Methyl formula
-CH3C
29
New cards
Classes of molecules
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid
30
New cards
Macromolecules
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids
31
New cards
How do cells make macromolecules?
By joining smaller molecules into chains called polymers
32
New cards
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many identical building blocks strung together
33
New cards
Monomers
Building blocks of polymers
34
New cards
How do cells link monomers together?
Using dehydration reaction
35
New cards
Dehydration reaction
A reaction that moves a molecule of water as two molecules bond together
36
New cards
Hydrolysis
Reverse dehydration process
37
New cards
What to dehydration and hydrolysis reactions require to make or break bonds?
Enzymes
38
New cards
Enzymes
Specialized macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions in cells
39
New cards
How many components make up cells?
40-50
40
New cards
How many components makeup proteins?
20 kinds of amino acids
41
New cards
What composes DNA?
4 kinds of monomers called nucleotides
42
New cards
Carbohydrates
A class of molecules ranging from small sugar molecules to large polysaccharides
43
New cards
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars and the monomers of carbohydrates
44
New cards
What are glucose and fructose
Single unit sugars that use dehydration to form polysaccharides
45
New cards
Formula for monosaccharides
CH2O
46
New cards
Two trademarks of a sugar
Hydroxyl + Carbonyl group
47
New cards
How long can monosaccharides carbon structures be?
3-7 carbons long
48
New cards
What are the most common sugars?
Pentose and hexoseM
49
New cards
What are the main fuel components for cellular molecules
Monosaccharides, mainly glucose
50
New cards
What happens when cells break down glucose
They release energy
51
New cards
How do cells use the carbon skeletons of monosaccharides?
They make other kinds of organic molecules like amino and fatty acids
52
New cards
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides bonded by dehydration reactions
53
New cards
What is the most common disaccharide
Sucrose composed of a glucose monomer and fructose
54
New cards
Polysaccharides
Macromolecules composed of polymers made of hundreds of thousands of monosaccharides linked by dehydration reactions
55
New cards
Lipid
Neither huge macromolecules or polymers built from similar monomers
56
New cards
Fat
Large lipids made from two kinds of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids
57
New cards
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
Contains one or more double bond and have kinks in their tails which prevent them from packing tightly together
58
New cards
Saturated Fatty Acid
Tails lack double bonds so they compact closely together
59
New cards
Polysaccharides
Starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
60
New cards
Starch
Unbranched storage molecules for plant cells
61
New cards
Glycogen
Highly branched molecules used for energy storage in liver and muscle cells
62
New cards
Cellulose
Polymer made of glucose made to structure plant cell walls
63
New cards
What is the most abundant organic compound?
Cellulose
64
New cards
Chitin
Structural polysaccharide used by insect and crustaceans for exoskeletons, and fungi for their cell walls
65
New cards
Fats
Lipids that are mostly energy storage molecules made from glycerol and fatty acids, and has 3 carbons and a hydroxyl and a hydrocarbon
66
New cards
What are polysaccharides
Hydrophillic because they contain storage groups
67
New cards
Types of lipids
Fats, phosophlids, steroids
68
New cards
What is the main function of fat
Energy storage
69
New cards
Composition of fat
3 fatty acids + glycerol
70
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acid
Hydrocarbon chain containing double bonds, which create kinks and bends, mostly fish and plant fats
71
New cards
Saturated fatty acids
No double bond in hydrogen, mostly animal fats
72
New cards
Phospholipids
Structurally similar to fats, except that they contain only two fatty acids attached to glycerol instead of three
73
New cards
Phospholipid structure
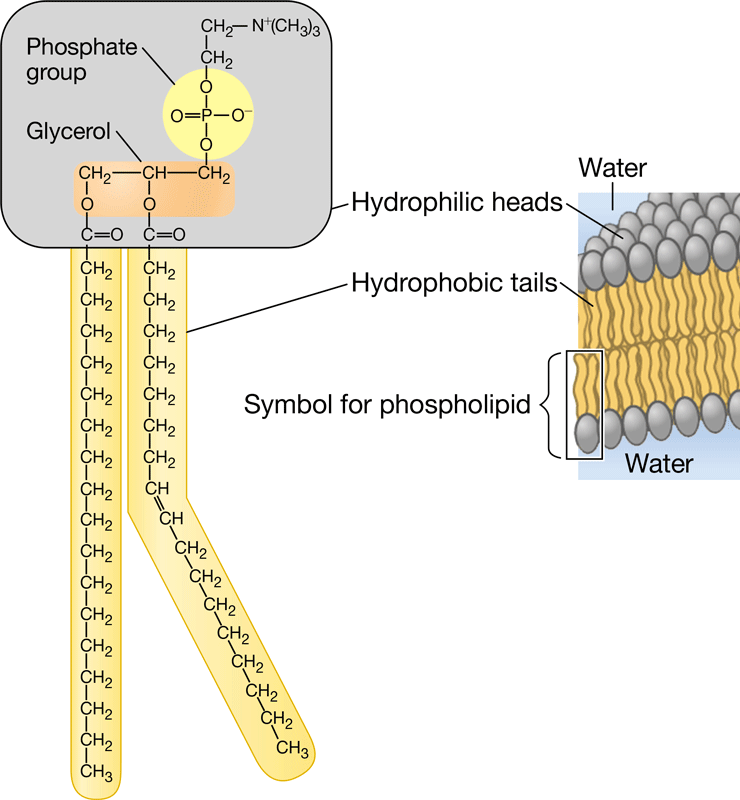
74
New cards
Phospholipid head
Polar and hydrophillic
75
New cards
Phospholipid tail
Nonpolar and hydrophobic
76
New cards
How are phospholipids in water structured?
In a double layered sheet, where the tails cluster together in the center of the sheet, excluded from water, and the heads face the watery environment on either side of the resulting membrane
77
New cards
Steroids
Lipids in which the carbon skeleton contains four fused rings
78
New cards
Steroids structure
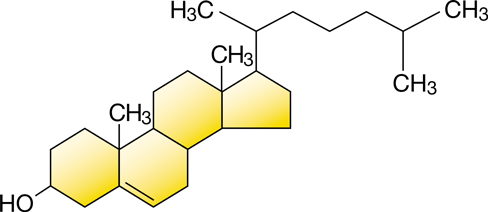
79
New cards
Cholesterol
A steroid that is a common component in animal cell membranes and is also the precursor for making other steroids, including sex hormones
80
New cards
Composition of phospholipids
Two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to glycerol
81
New cards
What do amino acids contain?
Amino and carboxyl group, hydrogen atom, and variable group covalently bonded to carbon atom
82
New cards
General structure of amino acid
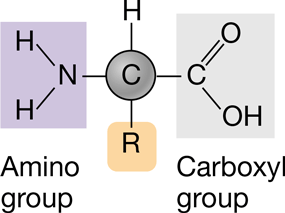
83
New cards
R/Variable group
Consists of one or more carbon atoms with various functional groups attached.
84
New cards
Hydrophobic amino acids
Nonpolar R group
85
New cards
Hydrophilic amino acids
Charged R groups
86
New cards
Peptide bonds
Cells join amino acids together in a dehydration reaction that links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next amino acid as a water molecule is removed
87
New cards
Dipeptide
Two amino acids
88
New cards
Peptide bond formation
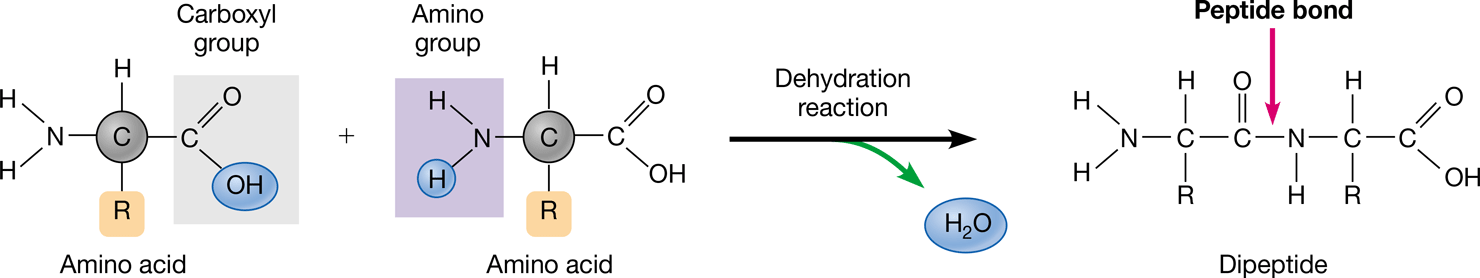
89
New cards
What are the stitches that coil and fold a polypeptide chain into its unique three-dimensional shape?
Hydrophobic amino acids may cluster together in the center of a globular protein, while hydrophilic amino acids face the outside, helping proteins dissolve in the aqueous solution of a cell.
90
New cards
What helps determine a protein's shape?
Hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds between hydrophilic R groups and covalent bonds called disulfide bridges between sulfur atoms in some R groups.
91
New cards
What generally determines a protein's shape?
The unique sequence of the various types of amino acids in a polypeptide
92
New cards
Primary structure of protein
The precise sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
93
New cards
Secondary structure of a protein
Segments of the chain coil or fold into local patterns
94
New cards
Tertiary structure
The overall three-dimensional shape of a protein
95
New cards
Quaternary structure
Proteins with more than one polypeptide chain
96
New cards
Protein shape
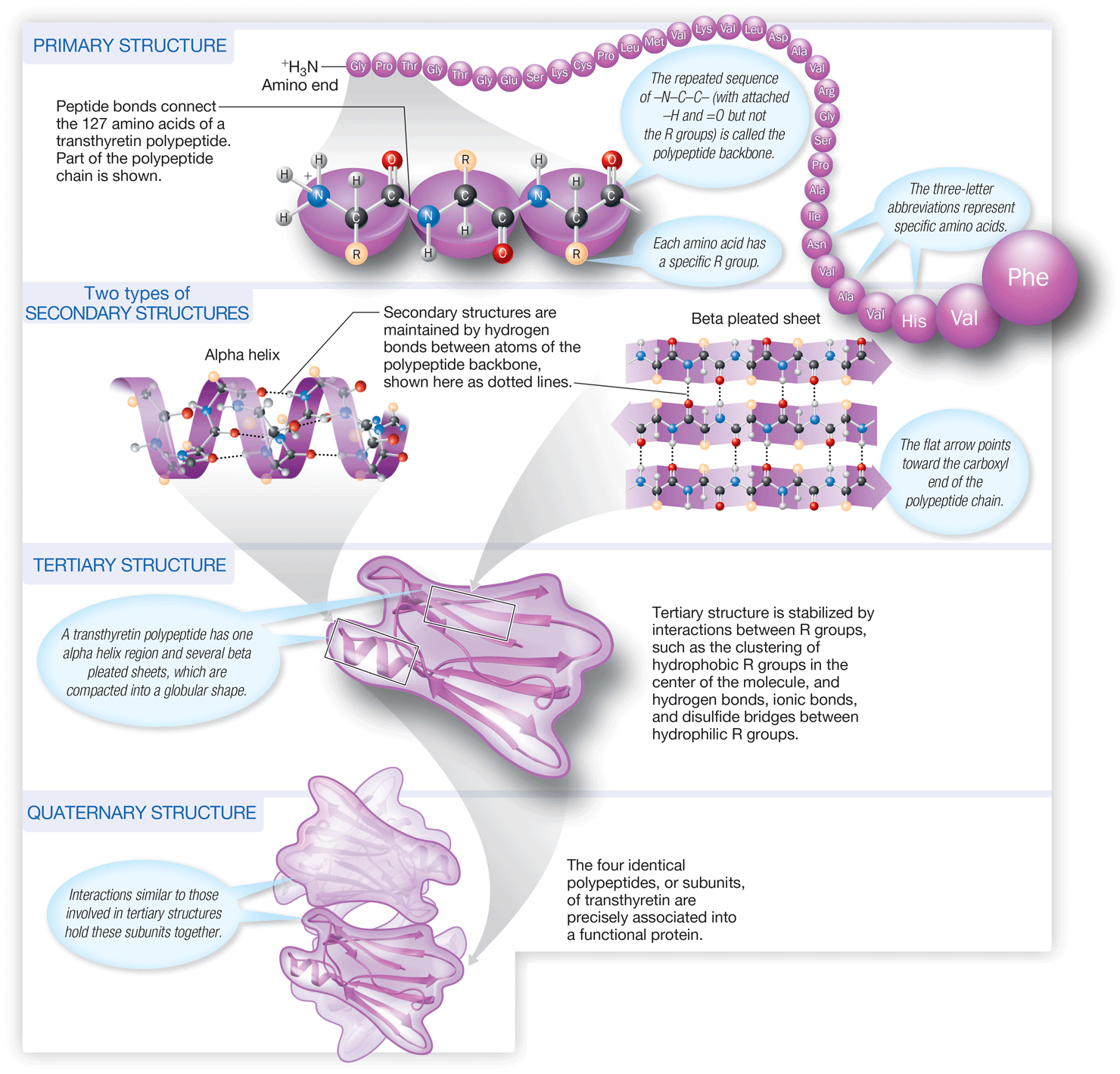
97
New cards
Gene
The discrete unit of inheritance that programs the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
98
New cards
DNA
Deoxyribose nucleic acid
99
New cards
RNA
Ribonucleic acid
100
New cards
What nucleic acids are in genes?
RNA and DNA