Lab Practical #1 Exam prep
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Hypothesis
A tentative answer to a question; an explanation on trial
Independent variable
Factor that scientists manipulate or put into categories (the ¨cause¨)
Control group
a category of the independent variable : a group that does not receive treatment -this serves as a basis for comparison
dependent variable
Part of the experiment that gets measured (the ¨effect¨)
Controlled variables
Part of the experiment that stays the same
A researcher conducts an experiment to assess the effects of alcohol on people’s sense of balance. The test subjects are all between the ages of 5-30. He divides his subjects into three groups: in one group the participants drink one ounce of alcohol. In another they drink two ounces of alcohol and in a third group the participants drink soda (no alcohol). He then watches as each participant tries to walk on a straight line from one corner of the room to the next and counts how many times they stumble outside of the line. What is the independent variable of this experiment? (The cause, or categories people are being put into)
The three groups with different amounts of alcohol
A researcher conducts an experiment to assess the effects of alcohol on people’s sense of balance. The test subjects are all between the ages of 5-30. He divides his subjects into three groups: in one group the participants drink one ounce of alcohol. In another they drink two ounces of alcohol and in a third group the participants drink soda (no alcohol). He then watches as each participant tries to walk on a straight line from one corner of the room to the next and counts how many times they stumble outside of the line. What is the control group of this experiment? (a group that does not receive treatment - this serves as a basis for comparison)
The group that is given soda (no alcohol)
A researcher conducts an experiment to assess the effects of alcohol on people’s sense of balance. The test subjects are all between the ages of 5-30. He divides his subjects into three groups: in one group the participants drink one ounce of alcohol. In another they drink two ounces of alcohol and in a third group the participants drink soda (no alcohol). He then watches as each participant tries to walk on a straight line from one corner of the room to the next and counts how many times they stumble outside of the line. What is the dependent variable of this experiment? (What is the effect being measured)
The count of how many times they stumble outside the line
A researcher conducts an experiment to assess the effects of alcohol on people’s sense of balance. The test subjects are all between the ages of 5-30. He divides his subjects into three groups: in one group the participants drink one ounce of alcohol. In another they drink two ounces of alcohol and in a third group the participants drink soda (no alcohol). He then watches as each participant tries to walk on a straight line from one corner of the room to the next and counts how many times they stumble outside of the line.What is the controlled variable of this experiment? (What is the same between all 3 groups)
The age range
The task
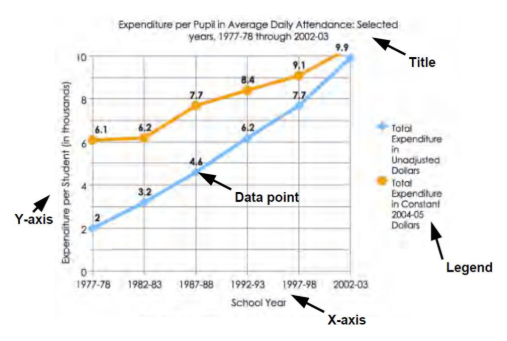
What is the title of a graph meant to represent?
Offers a short explanation of what is in your graph
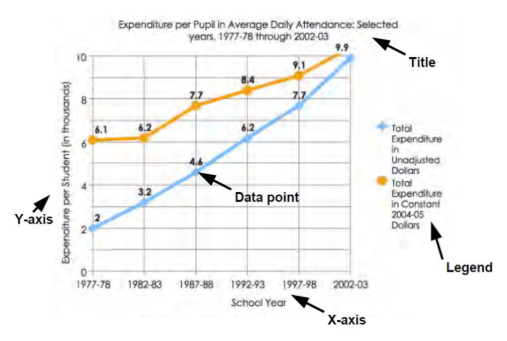
What is the legend of a graph meant to represent?
Tells what each line represents
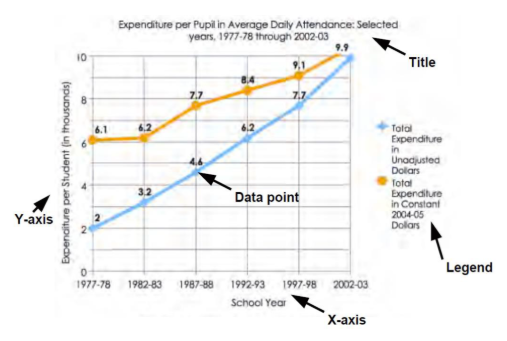
What is the y-axis of a graph meant to represent?
Typically, it has numbers for the amount of stuff being measured by your experiment.
What is the x-axis of a graph meant to represent?
Typically, it has numbers representing different time periods or other continuous variables that are not affected by the experiment.
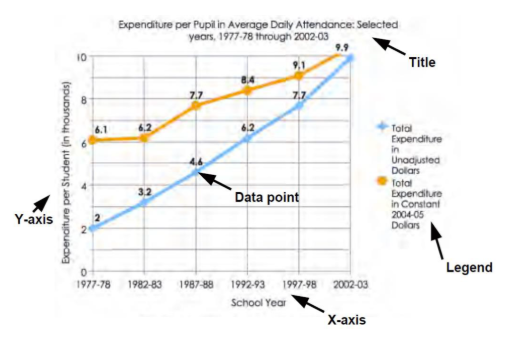
What is the data of a graph meant to represent?
the information
What is a scientific theory?
A much broader in scope than a hypothesis
How can a scientific theory become widely accepted in science?
if they are supported by an accumulation of extensive and varied evidence
What units do we use in science?
Meters, grams, liters, celsius
what tools do we use to measure units?
(mm,cm), (mg,kg), (ml), (C)
Where is the atomic number in a periodic table ?
The top number in the square
Where is the element symbol in a periodic table?
above the element name
Where is the element name in a periodic table?
above the atomic mass
where is the atomic mass in a periodic table?
The number below the element name
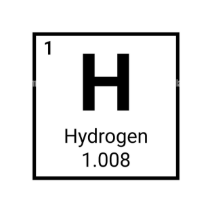
What is the atomic number of this element
1
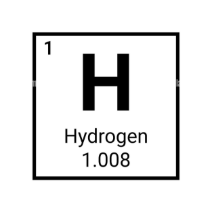
What is the symbol of this element ?
H
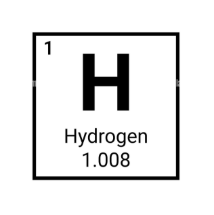
What is the name of this element?
Hydrogen
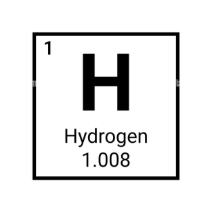
What is the atomic mass of this element?
1.008
What color does I2KI turn into with the presence of starch?
blue-black
What color does I2KI turn into without starch ?
yellow-brown
Why does I2KI turn into those colors ?
forms a complex with starch, producing the blue-black color. In the absence of starch, it remains dissolved, appearing yellow-brown.
what color does Phenolphthalein turn into when a liquid is acidic?
Colorless
what color does Phenolphthalein turn into when a liquid is basic?
Pink
What color does Phenolphthalein turn into a a very high base ?
Colorless
Why does Phenolphthalein change colors that way
It is a pH indicator that remains colorless in acidic conditions. When in a basic solution, it deprotonates, forming a pink-colored structure.
What color does Bromothymol Blue turn into when a liquid is acidic?
yellow
What color does Bromothymol Blue turn into when a liquid is neutral ?
Green
What color does Bromothymol Blue turn into when a liquid is basic ?
Blue
Why does Bromothymol Blue turn into those colors?
It is a pH-sensitive dye that changes color depending on protonation: In acidic conditions, it takes up H⁺ ions, turning yellow. At neutral pH, it appears green due to a mix of acidic and basic forms. In basic conditions, it loses H⁺ ions and turns blue.
what is the fatty acid chemical formula ?
CnH2n+100H
What is the glycerol chemical formula?
C3H8O3
What is the Amino Acid chemical formula?
R-Cn(NH2)-COOH
What is the monosaccharide chemical formula
CnH2nOn
Nucleic Acid
C10H14N5O7P
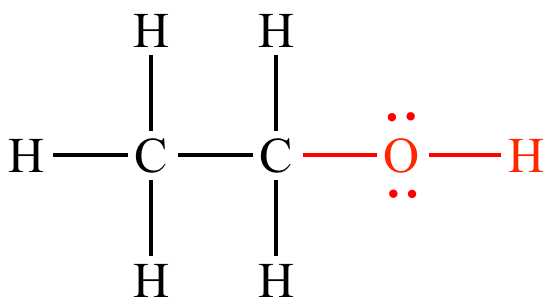
What Functional group is this
Hydroxyl (-OH)
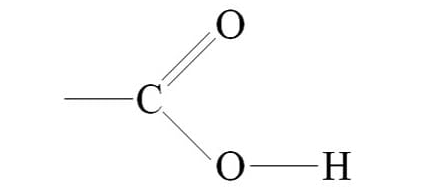
What functional group is this ?
Carboxyl (-COOH)
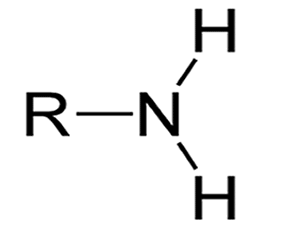
What functional groups is this?
Amine (-NH2)
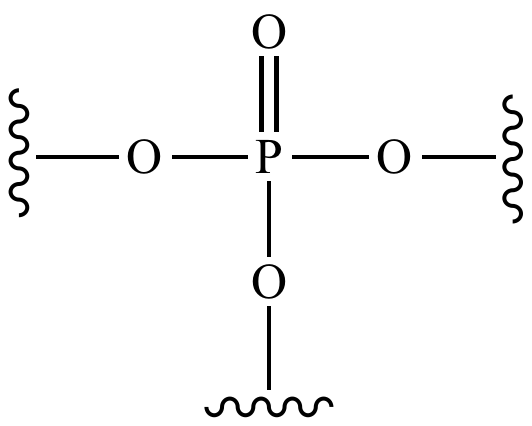
What functional groups is this?
Phosphate (-PO4)
What is hydroxyl found in ?
It is found in Lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and alcohol
What is carboxyl found in?
It is found in lipids and proteins
What is amine found in
It is found in proteins and nucleic acids
What is phosphate found in
Nucleic acids and phospholipids
Hydroxyl characteristics
Polar, Hydrophilic, and forms Hydrogen bonds
Carboxyl characteristics
Polar, - charge, hydrophilic, forms ionic bonds
Amine characteristics
Polar, + charge, hydrophilic, forms ionic bonds
Phosphate characteristics
Polar, - charge, hydrophilic, forms ionic bonds
Dehydration synthesis
When two molecules are joined by removing a water molecule
Hydrolysis
When molecules are broken apart by adding water
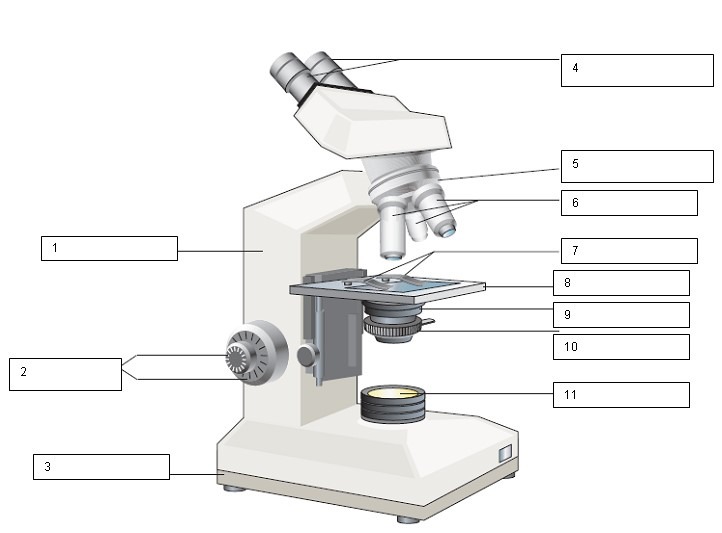
What is the name of the number 4?
Ocular lens and Diopter adjustment
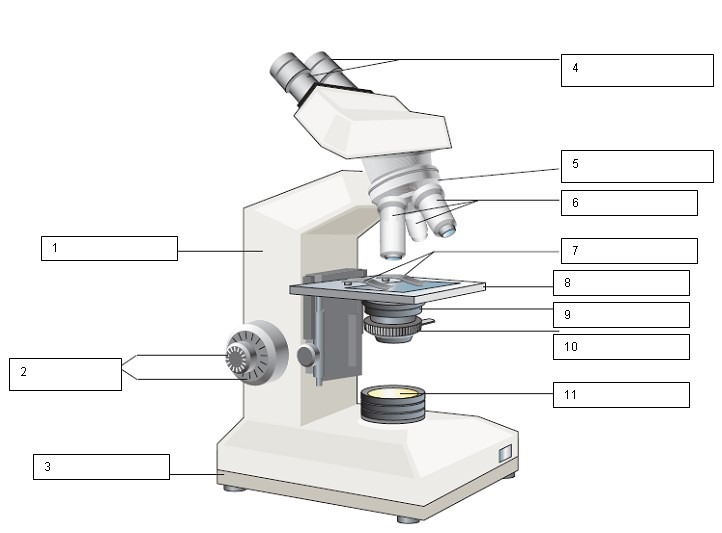
What is the name of number 1?
Arm
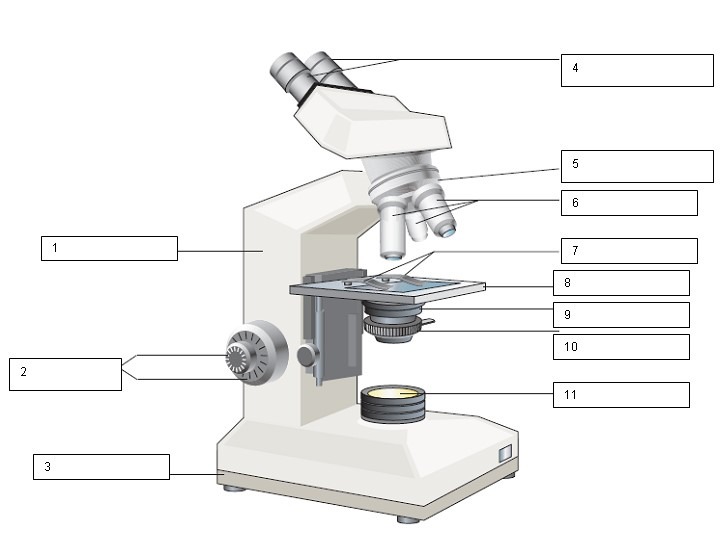
What is the name of number 2?
Coarse and Fine focus
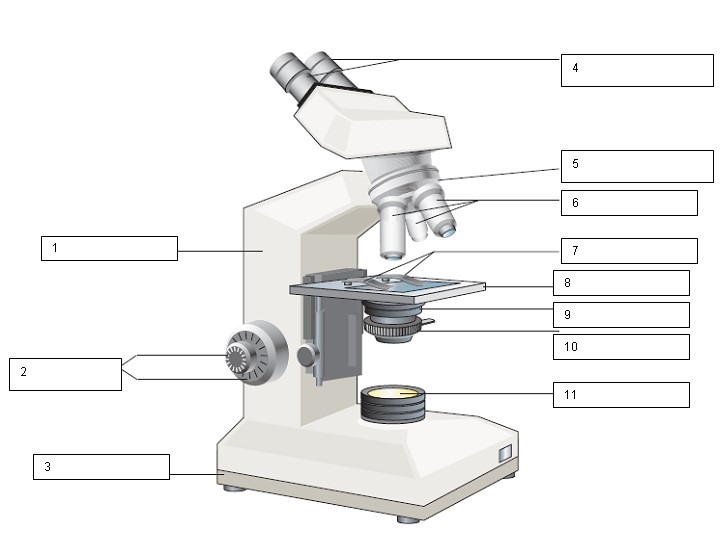
What is the name of number 3?
Base
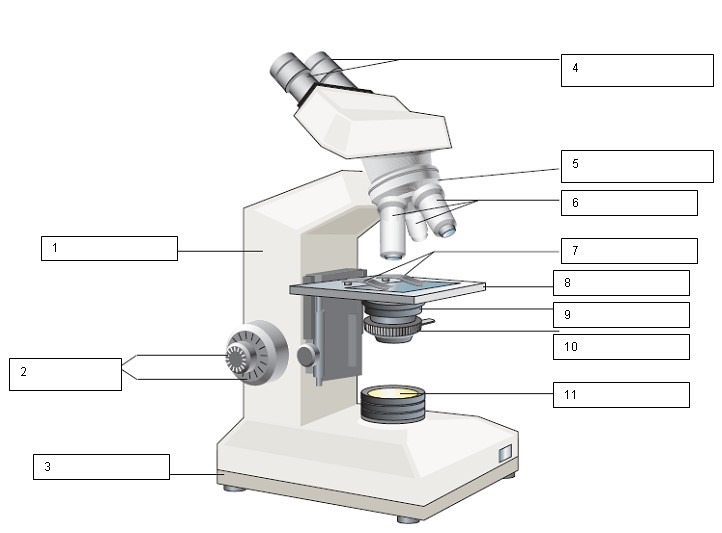
What is the name of number 5?
Nose Piece
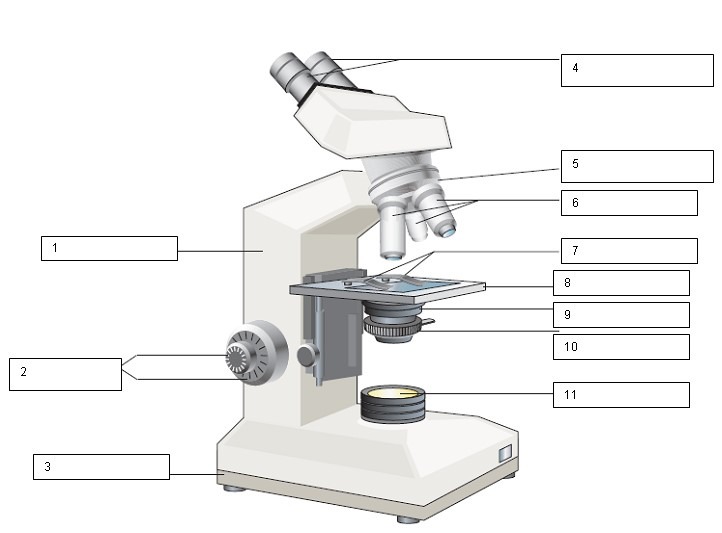
What is the name for number 6?
Objective lens
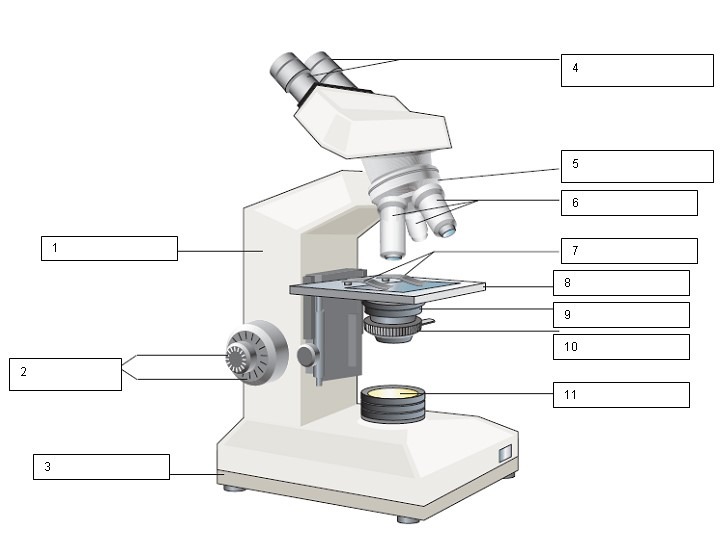
What is the name for number 7?
Slide holder
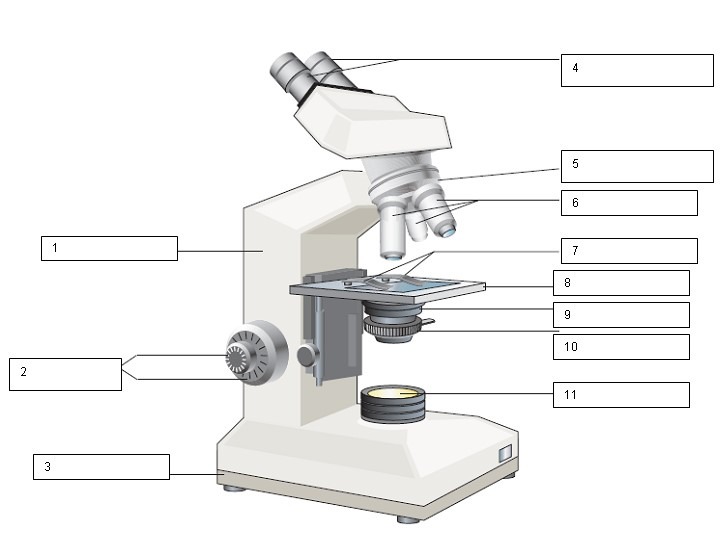
What is the name for number 8?
Stage
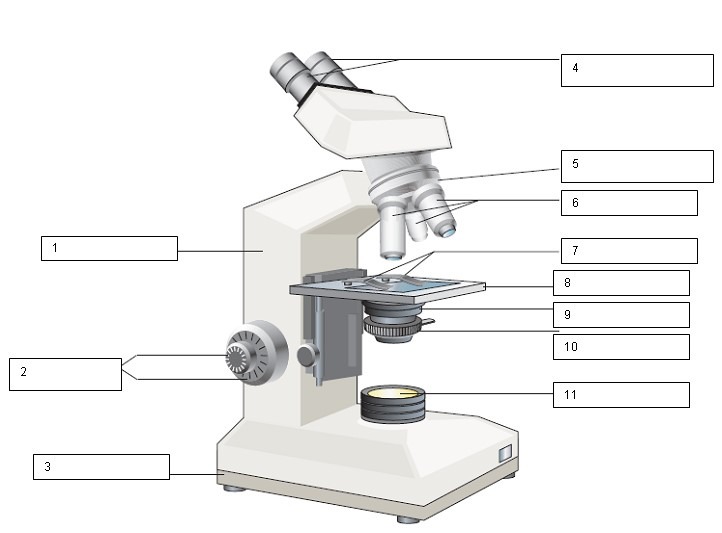
what is the name for number 9?
Condenser
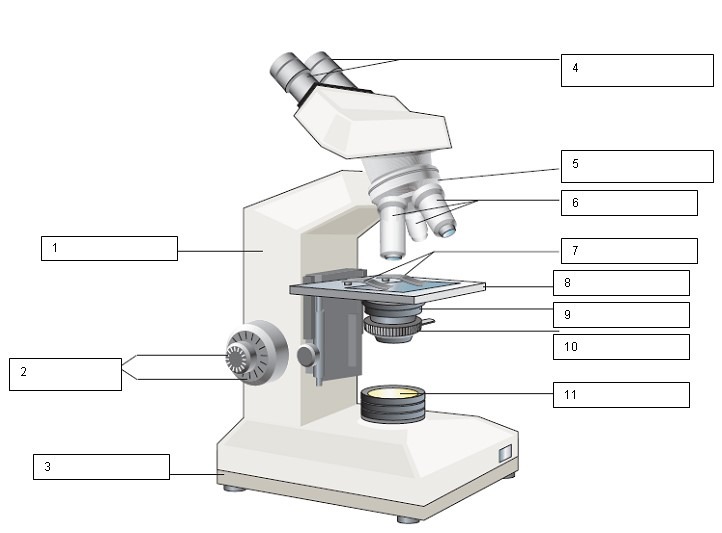
What is the name for number 10?
Iris diaphragm
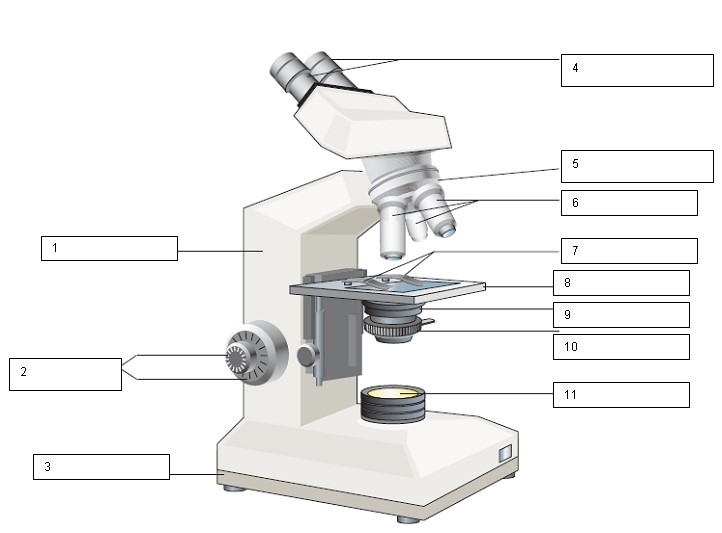
What is the name for number 11?
Light source
How do you use a microscope?
Set Up the Microscope, Prepare Your Slide, Prepare your slid, adjust the objective lens, focus the image, increase magnification (if needed), adjust lighting and diaphragm, observe and record, clean up
How do you put away your microscope?
Lower the stage and switch to the lowest power lens, remove the slide and clean the lenses with with lens parer, turn off the microscope and cover it with protection
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water across a selectively pereable membrane
What is diffusion
The net movement of molecules from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration until the concentration everywhere is equal