Forensic Bio Exam 3
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
The structure of DNA can be described as a
Double Helix
DNA is packaged tightly, helped by proteins called
Histones
The key difference in DNA that determines if an organism is going to be a human or a flower is the
genetic instructions
What is the Nucleus
a large membrane bound organelle that contains the cells genetic material in the form of dna
What is one characteristic of YSTR
Y chromosome short tandem repeat, extends range of cases accessible to obtaining probative dna results, technical simplicity due to allele profile can recover dna from smaller samples and courts have widely accepted strs,
Is YSTR through the maternal or paternal line
Paternal, father to son
PCR name
Polymerase Chain Reaction
What happens to DNA during PCR
DNA is amplified (copies are made) of a specific loci
What are the names of DNAs nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
What is a polymer
a polymer is a large molecule that is made up of smaller monomers
What is a monomer
a small basic molecular unit that can form polymers
Anti parallel dna
strands are parallel but run in opposite direction,
5’ end to 3’ end then 3’ end to 5’ end
How many nucleotide base pairs do humans have according to The Innocence Project?
3 billion nucleotide base pairs
Who were the contributing scientists, in the 1950’s who pioneered the work on DNA structure?
James Watson, Francis Crick who based their work on Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
Who are Watson, Crick, Wilkins and Franklin in relation to DNA structure research?
Watson and Crick discovered DNA structure and Fraklin used Xray crystallogy to visualizes the molecular structure which w and c used to create the model of DNA structure
What does the Innocence Project’s work focus on?
Cases that have DNA as an option to clarify innocence or guilt in a case
At what institution was the Innocence project first established?
Benjamin Cardozo School of Law
The work of the Innocence Project primarily focuses on what as an option for to clarify innocence or guilt in a case?
DNA
What is recidivism?
A person’s relapse into criminal behavior, often after the person has received sanctions or undergoes intervention for a previous crime.
What is the 3-year recidivism rate in NYC?
43%
Was there an existing law that allowed for justice involved persons to apply for their criminal history to be sealed? What was it? Was it an easy process?
The 2017 Sealing Law but it is very burdensome and a long process. Individuals convicted of up to two crimes can have their convictions sealed after a ten year waiting period
Is the Clean Slate Act accessible to every type of criminal history?
no, only misdemeanor with no sex offense and some felonies
What are the 3 major tenets of the Innocence Projects’ work?
Restore Freedom, Support Post Incarceration and Transform the system
What does the innocence project’s “transforming the system” look like? What do they describe doing?
They shine a light on factors to consider that lead to a wrongful conviction Identify & share recommended reforms to combat wrongful convictions
What are the key factors that can lead to wrongful conviction
Eyewitness misidentification, misapplication of forensic science, false confessions, unreliable, unregulated jailhouse informants, inadequate defense, official misconduct, coerced pleas, harmful surveillance and investigative techniques,
Is suspect misidentification a significant contributing factor to wrongful conviction?
yes, 63 % of cases involve this
When thinking about how eyewitness misidentification can contribute to wrongful conviction, what are estimator variables?
1.Gaps in witness memory
2.witnesses’ ability to actually clearly see the crime
3, stress or trauma the witness experienced
4.visibility conditions
5.challenged with cross racial identity
What are the system variables that contribute to wrongful convictions?
Variables that are controlled by
the criminal legal system
⧫ Law enforcement procedures for
eye witnesses
⧫ How lineups & photo arrays are
given
Key concept: The connection between the suspect and the crime may have been,…
over exaggerated OR the limitations of the techniques that were used were underplayed.
What are 4 techniques that the Innocence projects specifically call out as problematic?
Bite Mark Analysis
⧫ Tool Mark Analysis
⧫ Arson Investigation
⧫ Hair Analysis
⧫ Dog Scent Evidence
⧫ Comparative Bullet Analysis
⧫ Shaken Baby Syndrome
Analysis
What is prosecutorial misconduct
This occurs when a prosecutor violates the law or code of ethics while they’re prosecuting a case
⧫ An example is withholding evidence of innocence or favorable evidence (Brady
Violation)
Who was the first person to be exonerated as a result of new DNA findings?
Kirk Bloodworth, e was convicted, in 1984, of the rape of a
convicted in 1984 of the rape of a 9-year old girl.
⧫ He was 22 at the time and sentenced to death
in Maryland.
⧫ There was no physical evidence linking him.
He was convicted based on eye witnesses.
How are DNA findings advantageous in forensic science?
high accuracy and reliability individualization identification, linking crimes to suspects, exonerating innocents DNA databases and solving coldcases
What is a short tandem repeat
repeat sequences of non-coding dna that are found between genes that code for proteins, they greatly vary between individuals and the number of repeats is inherited
What did James Watson contribute to discovering
double helix structure of dna
What is the name of Watson’s scientific colleague who contributed to his historic discovery
Francis Crick
Did Watson participate in the Human Genome Project?
yes he was a director from 1988 to 1992
Who was the female scientist who worked on X-ray diffraction images of the DNA molecule that was key research in Watson’s later discovery?
Rosalind franklin
Was Watson’s “shady” ethical practices ignored or did he eventually experience justice
they were ignored until he spoke a racist remark in a newspaper and was removed from his chancellors position in a lab and his public image was never the same
What is a key advantage of using SNP versus STR
provides a vastly richer dataset of hundreds of thousands of markers, which expands capabilities to analyze forensic biological evidence to provide investigative leads far beyond those of STR typing. The power of SNPs lies in their stability, genome-wide distribution, and ability to be detected in smaller DNA fragments, making them particularly useful for analyzing degraded forensic samples. This latter feature allows for the recovery of genetic information from evidence that would otherwise yield incomplete or no STR data.
Singles nucleotide polymorphism
SNPs provide hundreds of thousands of markers, are more stable, and can be detected in very small or degraded DNA fragments, allowing useful genetic information to be recovered even when STRs fail.
Can SNP support forensic genotyping
yes by providing information about an individuals ancestry, physical traits and the ability to analyze degraded samples.
Based on article two what can forensic genotyping include the predictions of
ancestry, physical features and sex and age
What are FGGs
forensic genetic genealogy
Combines
• SNP-based DNA profiles
• Genealogical databases
• Family-tree building
• Kinship matching across multiple generations
FGGs help identify unknown individuals and solve cases even when there is no direct STR match or no suspect in CODIS.
Who won the Nobel prize in medicine for the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA?
Watson Crick and Wilkins
What kind of bond do nucleotide base pairs have?
Hydrogen
Who is Erwin Chargaff?
a biochemist from Austria
What was one of Chargaff’s findings that relates to the structure of DNA.
1. A, T. C & G nucleotide bases are NOT found in equal
amounts
2. The number of nucleotide bases varied in different
species but not very much within the same species
3. The amount of A always equaled the number of T bases
& the amount of C always equaled the number of G
Are DNA replication and cell division the exact same thing?
NO, replication happens in the S phase of Cell division and SNA is synthesized in the 5’; to 4’ direction only. cell division occurs after dna replication
When does DNA replication occur during the cell cycle?
s phase of cell division
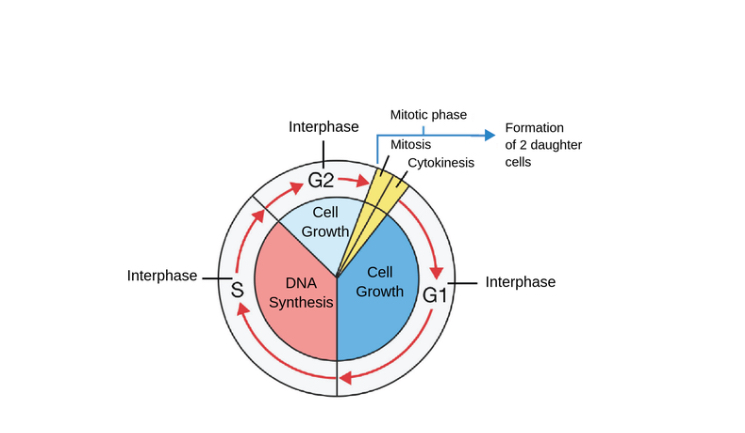
How does DNA replication support survival of a species?
allows for transfer of genetic info to the next generation
What are 4 ways in which DNA can be damaged?
cellular metabolism, uv light exposure, ionizing radiation. chemical radiation, replication errors, shaken roughly,
What are 3 environmental factors that can impact the integrity (quality) of DNA?
temperature, humidity and contaminats
What are 3 examples of what DNA samples can be collected from at a crime scene
blood, semen,saliva, urine, feces, hair, teeth, bone, tissue, cells
What is Touch DNA?
DNA samples that are present in very small amounts.
Can be found in bruises, on the skin of a person, on surfaces that came in
contact with the person
Where can touch dna be collected?
masks, hats, gloves, tools, clothes, toothbrush, eyeglases, brush condoms, tape
What is elimination dna
Samples that are collected from relationship partners, sexual partners, first responders, etc. that may have come in contact with victim or crime scene
Why can elimination dna be useful in a criminal investigation
These samples are taken to eliminate them from suspicion
What is the M vac
a piece of equipment that uses we vacuum technology to spray a buffer(made with solutions that help preserve the DNA) on the area DNA is being collected from.
That same buffer is then effectively sucked back up into the device efficiently collecting all
particles.
Why is it an advantageous piece of equipment for a forensic scientist collecting DNA?
Thermal Cyclers for PCR or Mvac
When was DNA first used during a criminal case?
the 1980s.First case DNA evidence was used in,in England
Colin
Pitchfork
Who first discovered DNA fingerprinting?
alec jeffries
What does the Innocence Project’s work focus on?
Their work primarily focuses on
cases that have DNA as an
option to clarify innocence or
guilt in a case.
True or false: The combination of SNP’s, FGG’s and genealogical databases have significantly supported the advancement of forensic science and the resolution of unsolved violent crimes and unidentified remains
true
True or false: According to article 2, the trends in solved cases from 2018 to 2024 has
increased dramatically.
true
One of the major challenges in working with DNA is only having small amounts available or
degraded samples. What kind of advancements have helped get past this
PCR,STR typing, aDNA, FGG and WGS
What is WGS
whole genome sequencing
What is STR
short tandem repeats
What are the building block molecules of DNA?
Phosphate group, Deoxyribose sugar, nitrogenous bases (ATCG)