Water Quality Unit 1
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SciConnect flashcards based on the 2026 SciOly Seasaon
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
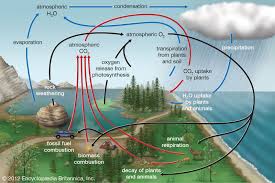
biogeochemical cycles
movement of certain chemical elements through various forms (living AND nonliving)
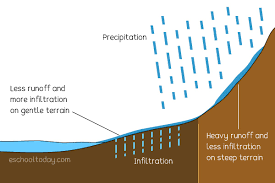
runoff
water from precipitate and snow melt that doesn’t melt into the ground
transpiration
plants absorb water via roots, some evaporate into the atmosphere through stomata
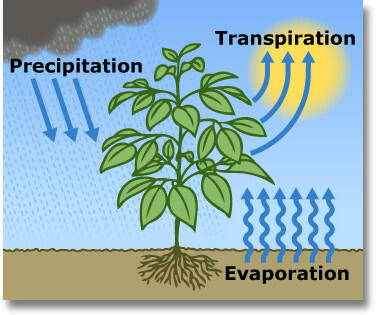
evapotranspiration (ET)
total liquid water loss from surface to the atmosphere (evaporation + transpiration)

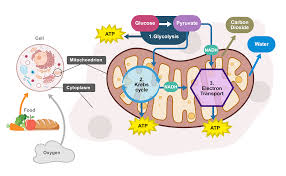
cellular respiration
living organisms convert glucose and oxygen in energy (ATP), H2O, CO2
Equation: C6H12O6 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
infiltration
water on the surface soaks into the ground

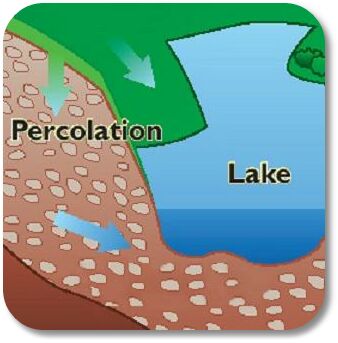
percolation
movement of water through porous material
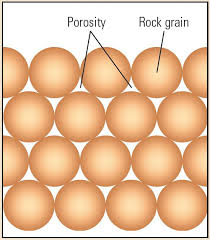
porosity
measure of empty spaces within a material. indicates how much liquid a material holds
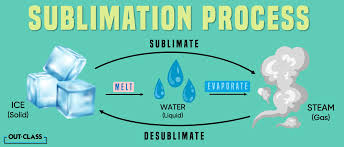
sublimation (rare)
ice —> water vapor, can occur w/ unique conditions like some dry winds
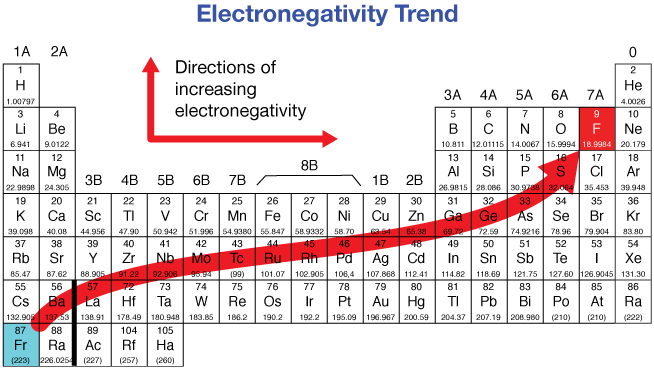
electronegativity
measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons
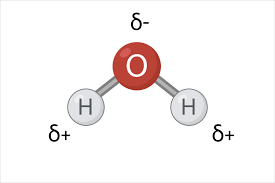
polarity
when one part of the molecule has a slightly negative charge and another part has a slightly positive charge
don’t share their electrons evenly
hydrogen bond
a strong type of bond between molecules that can occur when the polar molecules contain hydrogen atoms
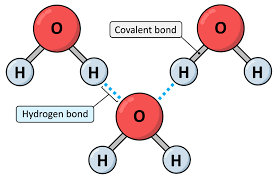
cohesion
water’s tendency to stick to itself (caused by H2O’s polar and hydrogen bonding & causes water tension)

adhesion
tendency to stick to other substances (caused by H2O’s polar and hydrogen bonding)

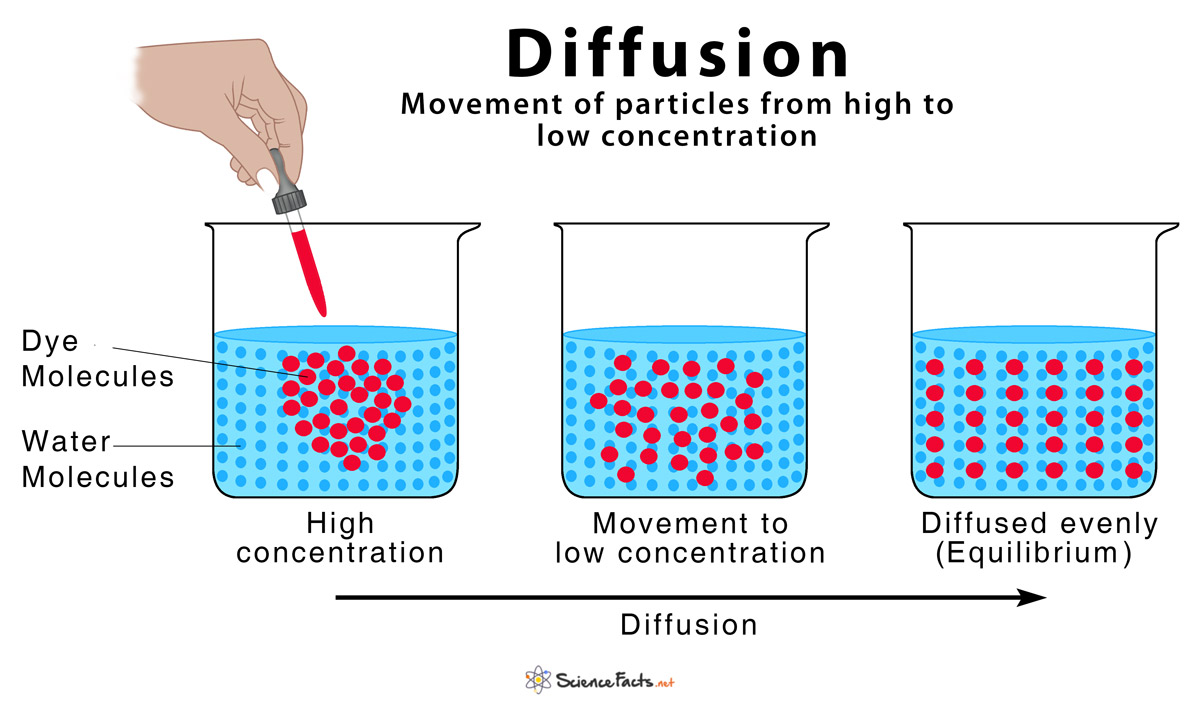
diffusion
molecules move from high to low concentrations
sources of carbon
atmosphere (CO2 & CH4 (methane))
land
earth’s interior (fossil fuels & volcano)
ocean (carbonic acid)
human (burning & deforestation) and organisms (photosynthesis & cell respiration)
nitrogen cycle
the process by which nitrogen moves through the atmosphere, soil, and living organisms; driven by bacteria, limiting nutrient
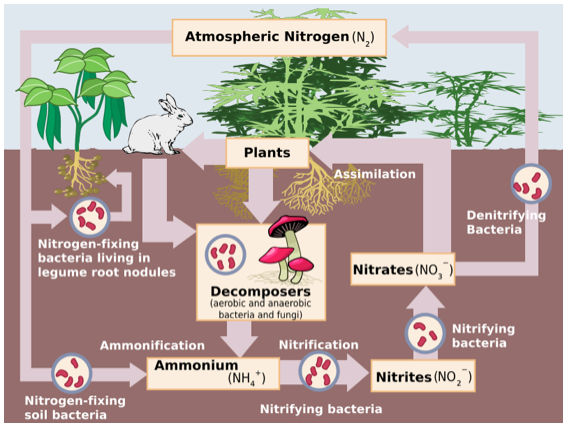
non usable forms
nitrogen gas (N2), nitrites (NO2)
usable forms of nitrogen
ammonia (NH3), ammonium (NH4+), & nitrates (NO3)
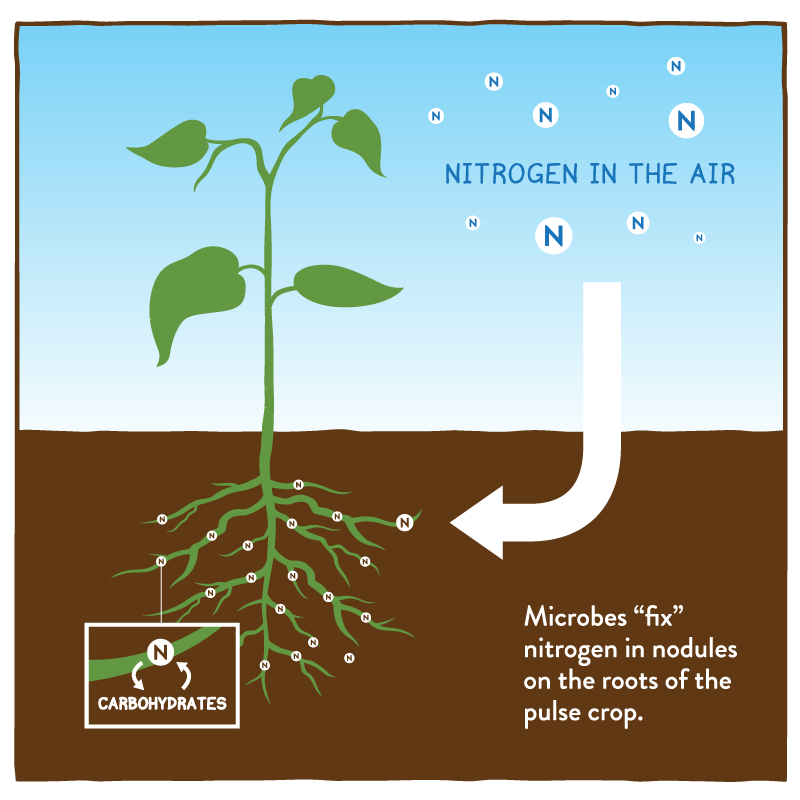
nitrogen fixation
atmospheric nitrogen can’t be used by plants —> ammonia (by bacteria) and sometimes nitrates; lightning heats air very hot & allows it to react —> nitrogen oxides (add water) —> nitrates
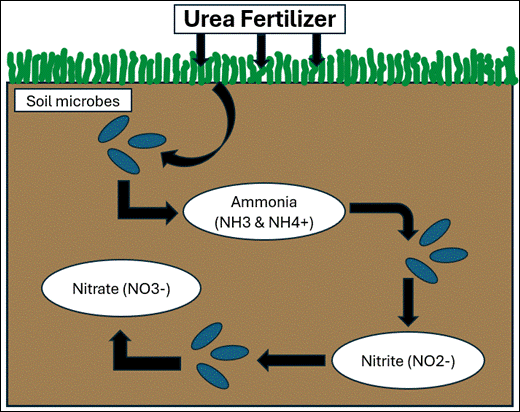
nitrification
ammonia —> nitrite —> nitrate
assimilation
inorganic nitrogen —> organic molecules (adding carbon)
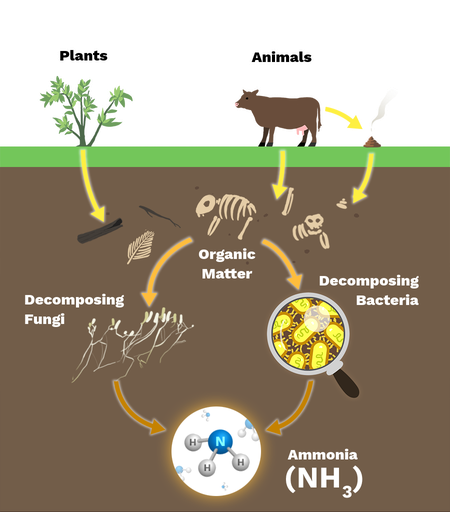
ammonification
decomposes convert org. waste to ammonia (NH3) or ammonium (NH4+)
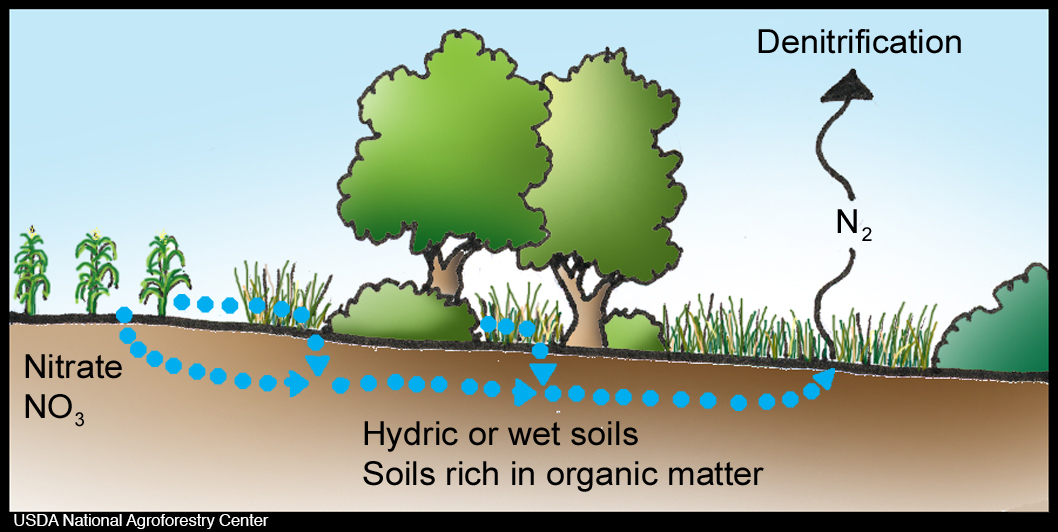
denitrification
bacteria convert nitrate or nitrite to atmospheric nitrogen (N2)
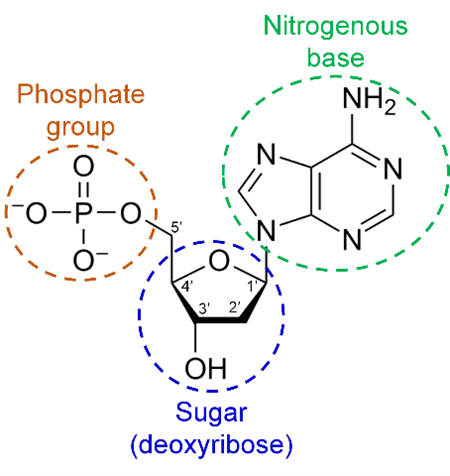
phosphorus
not found in gas form

sedimentary rocks
most common source of phosphorus
inorganic phosphate
rocks

organic phosphate
DNA components
biological assimilation
plants and microorganisms take up inorganic sulfates and convert them into organic sulfur compounds
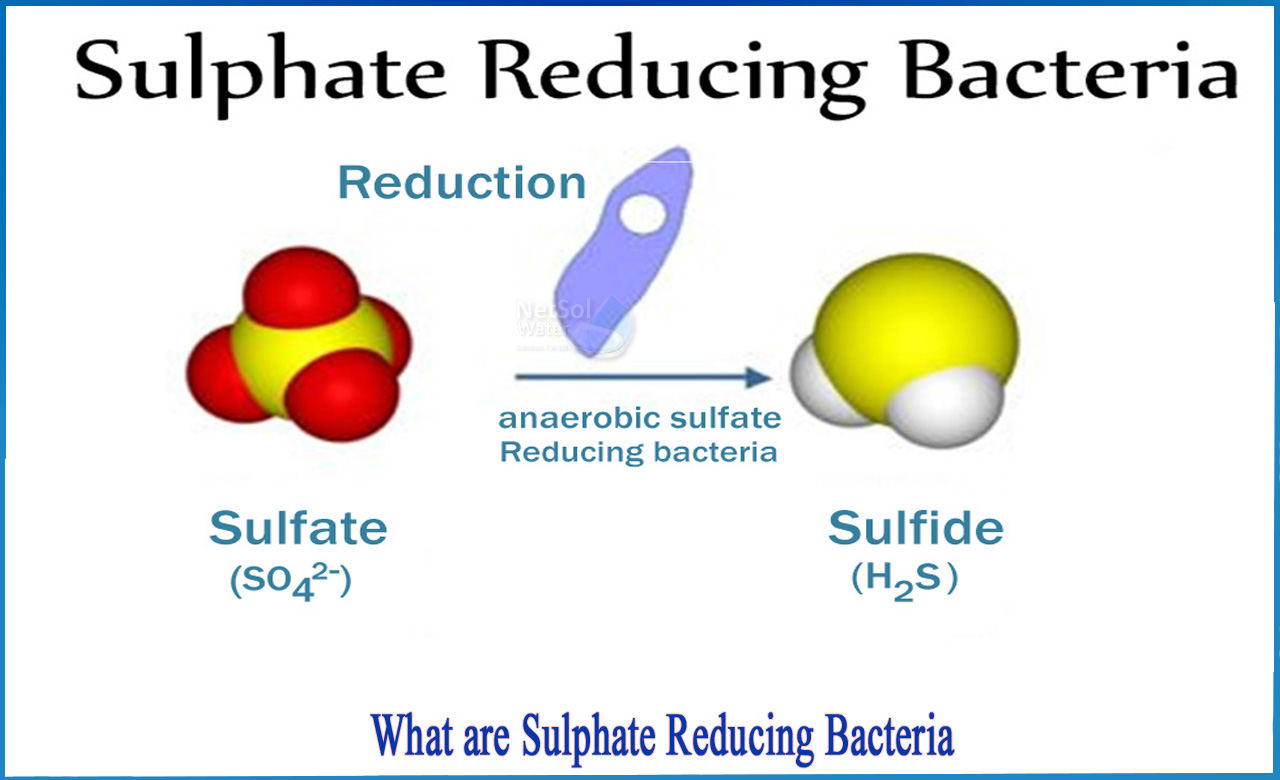
sulfate reduction
anaerobic microorganisms reduce sulfates to sulfides, marine sediments
decomposition
decomposers break down organic matter releasing hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
sulfide oxidation
chemoautotrophs and sulfur-oxidizing microbes use hydrogen sulfide or elemental sulfur as energy source, converting it back to sulfates