AP Human Geography Final/Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/303
Earn XP
Last updated 6:38 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
304 Terms
1
New cards
Reference map
For trivia, you need to *reference* **names**, **boundaries**, and **features**
2
New cards
Thematic map
Emphasizes a particular **theme**
3
New cards
cartogram
Distorts land area to show changes in value
* This type of map **looks distorted** and that it got hit by a shopping *cart*
* This type of map **looks distorted** and that it got hit by a shopping *cart*
4
New cards
Choropleth map
Map that uses multiple different shades
* **COLORS** THINK *CHORO*
* **COLORS** THINK *CHORO*
5
New cards
Dot Map
Uses **dots** to show different values
6
New cards
Graduated Symbol map
Uses a symbol to represent a certain value
* your brain is **bigger** and **holds more value** after you *graduate* than before you did
* your brain is **bigger** and **holds more value** after you *graduate* than before you did
7
New cards
Isoline maps
Maps with **lines** drawn to link different places that share a common value
8
New cards
relative space
Space that’s created and defined by how humans interact with the environment
9
New cards
Absolute distance
I am *absolutely* sure that the lake is at **74°N**
* numerical value
* numerical value
10
New cards
Relative distance
compares object to a known geographical feature
* At the family reunion, I stood on the left of my relative.
* At the family reunion, I stood on the left of my relative.
11
New cards
Uniform
Evenly spaced
12
New cards
Clustered/clumped
grouped together
* think how on nerds clusters all the nerds stick to one gummy and cluster together
* think how on nerds clusters all the nerds stick to one gummy and cluster together
13
New cards
Dispersed/scattered
Distributed over a wide area
14
New cards
Agglomeration
Grouped together Purposefully
* companies of similar industries near each other in order to decrease infrastructure costs and increases cost efficency
* companies of similar industries near each other in order to decrease infrastructure costs and increases cost efficency
15
New cards
Map projection
* all map projections distort the surface
16
New cards
Robinson projection
* in meet the *Robinsons*, they had to **accurately know the size, distance, and shape** to travel to the future
* The problem with this map is that it’s less accurate at the poles and can’t be used for navigation
* The problem with this map is that it’s less accurate at the poles and can’t be used for navigation
17
New cards
Mercator projection
* *Gators* have to Have **good navigation and direction around nautical areas**, it helps them to try and swim on a **straight line of longitude and latitude**
* The problem with this is that it __distorts area__
* The problem with this is that it __distorts area__
18
New cards
Gall-Peters projection
* Mrs. *Peters* helps VIC’s go in the **right direction** and her senses are **accurate** on if a girl will go in this **area**. She also keeps a tidy office and **doesn’t distort** it.
19
New cards
Polar Projections (azimuthal)
* shown from pole and preserves direction and distances from the center
* Distorts latitude, shape, area, and only shows top half of earth
* Distorts latitude, shape, area, and only shows top half of earth
20
New cards
Geographic Information Systems
I wanted to get the *gis*t of the geographic area, so I **compiled data in layers**
* helps visualize spatial patterns and relationships
* helps visualize spatial patterns and relationships
21
New cards
Remote Sensing Systems
The **aircraft** *sensed* the physical characteristics of the area.
* helps collect info about large areas of land
* Helps monitor areas of the world that are hard to explore
* helps collect info about large areas of land
* Helps monitor areas of the world that are hard to explore
22
New cards
Satellite Navigation systems
The satellite provided geospatial positioning on Earth’s surface by using longitude and latitude
23
New cards
Geographic data
Any data with a geographic (location/refers to a location on Earth) aspect
* helps people understand problems and make decisions and can be layered
* Some methods are census data, remote sensing, openstreetmap
* helps people understand problems and make decisions and can be layered
* Some methods are census data, remote sensing, openstreetmap
24
New cards
Place
That place has frigid (**weather**) mountains (**landforms**) with no trees (**vegetation**). There they speak English (**language**), and believe in a higher power (**religion**).
25
New cards
Site
A place’s absolute location and surroundings
* EX: Louisville Kentucky is located at 38.2527° N, 85.7585° W and is situated near the Falls of the Ohio and is located between the karst plateau of Southern Indiana and the Bluegrass plateau of Kentucky
* EX: Louisville Kentucky is located at 38.2527° N, 85.7585° W and is situated near the Falls of the Ohio and is located between the karst plateau of Southern Indiana and the Bluegrass plateau of Kentucky
26
New cards
Situation
How one place interacts with other places
* EX: Louisville is one of the largest cities in Kentucky with major highway systems connecting it to neighboring states as well as a relationship to the Ohio River
* EX: Louisville is one of the largest cities in Kentucky with major highway systems connecting it to neighboring states as well as a relationship to the Ohio River
27
New cards
Distance decay
Farther places are from one another, the less they will interact
* the further you drive from a radio tower, the less strong the signal is
* the farther a strawberry is away from the fridge, the more it will decay
* the further you drive from a radio tower, the less strong the signal is
* the farther a strawberry is away from the fridge, the more it will decay
28
New cards
Time-space compression
Space between places seems smaller as technology/communication improves
29
New cards
Density
number of people or things in a space
30
New cards
Sustainability
Focused on providing for society in the future
* two issues are natural resources (human societies use Earth’s resources) and land use (human societies determine how they use land in terms of purpose along with level of use
* two issues are natural resources (human societies use Earth’s resources) and land use (human societies determine how they use land in terms of purpose along with level of use
31
New cards
Environmental determinism
**Environment** **determines** characteristics of human society and even the success of failure of the society
32
New cards
Environmental possibilism
With people anything is **possible**
* human societies are influenced by their natural environment, but not controlled by it
* human societies are influenced by their natural environment, but not controlled by it
33
New cards
Large map scale
Shows less area in greater detail
* Things look bigger because you move in
* Things look bigger because you move in
34
New cards
Small map scale
Shows larger area in less detail
* things look smaller because you move out
* things look smaller because you move out
35
New cards
Scale of analysis
The level at which the data is displayed
36
New cards
Formal region
The group was dressed in *formal* wear, all wearing a **common attribute**.
* common religion, ethnicity, climate, political boundaries
* common religion, ethnicity, climate, political boundaries
37
New cards
Functional (nodal) region
Grouped around a central point or node
38
New cards
Vernacular region
Grouped by how the people feel is a region
* I **feel** like *vernacular* is a weird word.
* I **feel** like *vernacular* is a weird word.
39
New cards
Arithmetic density
Number of people living in a given unit of land
* population/total land area
* population/total land area
40
New cards
Agricultural density
\# of farmers per unit of arable (land used for agriculture) land
41
New cards
Physiological density
Number of people per unit of arable land
* Egypt has a high one of these
* Egypt has a high one of these
42
New cards
Malthusian
Thomas Malthus was an English economist who proposed the ____________ theory, which suggests that __**population growth will eventually outpace the food supply,**__ leading to famine, disease, and other catastrophic events.
43
New cards
Crude birth rate
Number of births per year per 1000 people
44
New cards
Crude death rate
Number of deaths per year per 1000 people
45
New cards
Migration
The movement of people from one area to another
46
New cards
Total fertility rate
The average number of children a woman will have in her lifetime
47
New cards
Infant mortality rate
Number of deaths of children under the age of 1 per 1000 people
48
New cards
Immigration
Movement of people into an area
49
New cards
Rate of natural increase
Percentage of natural population growth in an area
* CBR-CDR/10
* includes **birth And death**, not migration
* High this means rapid growth
* CBR-CDR/10
* includes **birth And death**, not migration
* High this means rapid growth
50
New cards
Doubling time
70/RNI
* the lower the rate of natural increase, the higher the number of years it takes for the population to double
* the lower the rate of natural increase, the higher the number of years it takes for the population to double
51
New cards
Stage 1 DTM
High CBR, CDR - steady/low population
* No examples
* No examples
52
New cards
Stage 2 DTM
* **Death drop** due to improved living conditions
* Lots of babies + less people dying = rapid pop. Growth
* EX: most peripheral countries Niger, Afghanistan
* Lots of babies + less people dying = rapid pop. Growth
* EX: most peripheral countries Niger, Afghanistan
53
New cards
Stage 3 DTM
* Low birth rate + less death = increasing population
* Women’s education
* EX: most semi-peri./peripheral, Colombia, Mexico, India, South Africa
* Women’s education
* EX: most semi-peri./peripheral, Colombia, Mexico, India, South Africa
54
New cards
Stage 4 DTM
* births/deaths decrease due to good healthcare, women’s employment, rural-urban migration, strong economies
* EX: US, China, Australia
* EX: US, China, Australia
55
New cards
Stage 5 DTM
* fewer babies than people dying so lower population
* EX: Germany, Japan, Greece
* EX: Germany, Japan, Greece
56
New cards
Thomas Malthus positive checks
Reduce population; famine, disease
57
New cards
Thomas Malthus preventative checks
Actions to prevent population growth; postponing
58
New cards
Neomalthusians
Believe that the world space and resources were limited, but the environment was not determinant
59
New cards
Cornucopian Theory
Humans can innovate ways to expand the food supply
60
New cards
Anti-natalist policies
When a country’s birth rate and TFR is high, so people are **discouraged** from having children
* EX: paying extra taxes whenever you have a child, increased education of women
* Goal is to lessen risk of overusing resources, schooling jobs/services
* Typically in 2-3 LDC’s
* EX: paying extra taxes whenever you have a child, increased education of women
* Goal is to lessen risk of overusing resources, schooling jobs/services
* Typically in 2-3 LDC’s
61
New cards
Pro-natalist policies
When a country has low birth rates and fertility rates, so people are **encouraged** to have children
* EX: free childcare, paid maternity leave
* Typically found in 4-5 LDCs
* EX: free childcare, paid maternity leave
* Typically found in 4-5 LDCs
62
New cards
Immigration policies
Government policies that determine if people can migrate into the
* a country may encourage this to balance out a negative rate of natural increase
* a country may encourage this to balance out a negative rate of natural increase
63
New cards
Cultural landscape
Combination of cultural features such as **language and religion, economic features, physical features**
64
New cards
Migration for women
Women tend to migrate for economic/marriage reasons
* More migratory than men within their area of birt, but outside zone men are more migratory
* More migratory than men within their area of birt, but outside zone men are more migratory
65
New cards
Scale of analysis
The level at which the data is displayed
* global, regional, national, local
* global, regional, national, local
66
New cards
Dependency ratio
The # of people in the population age group (under 15 - older 64)/ people between
67
New cards
Push factors
**Negative** cause that compels one to **leave a place**
68
New cards
Pull factors
Positive cause that attracts someone to a place
69
New cards
Intervening opportunity
* positive factor that interrupts someone during migration and makes them choose some other place than that they were going
* EX: job/economic opportunities
* EX: job/economic opportunities
70
New cards
Intervening obstacle
Negative factor that hinders a person’s migration process
* EX: mountains that don’t allow someone to pass
* EX: mountains that don’t allow someone to pass
71
New cards
Forced migration
Migrants must leave because they are in life-threatening situations
* EX: refugees, asylum seekers, and internally displaced persons
* EX: refugees, asylum seekers, and internally displaced persons
72
New cards
Refugee
Crosses international borders due to fear and is granted **refugee status before** they enter where they are allowed to stay in the country
73
New cards
Asylum seeker
Cross international boundaries but **enter the country without refugee status**
74
New cards
Internally displaced persons
Flee their home due to safety but they flee **within** their home country
75
New cards
Voluntary migration
Migrants must leave because they feel like they can better their situation (economically, socially, personally)
* some cross international boundaries (transnational migration)
* Chain migration, step migration, guest workers
* Some are internal where they stay in the country
* Most common type of this is rural-urban
* Transhumance migration involves farming and moving with livestock herding
* some cross international boundaries (transnational migration)
* Chain migration, step migration, guest workers
* Some are internal where they stay in the country
* Most common type of this is rural-urban
* Transhumance migration involves farming and moving with livestock herding
76
New cards
Culture
Comprised of the shared practices, attitudes, behaviors, and technology that are transmitted by society
* EX: food preferences, architecture, land use, clothing
* EX: food preferences, architecture, land use, clothing
77
New cards
Culture relativism
The judgement of another culture based on its unique characteristics
* EX: person wanting to try crickets to understand this perspective of food
* EX: person wanting to try crickets to understand this perspective of food
78
New cards
Ethnocentrism
The judgement of another culture based on its preconceived notions or ideas of that culture
* calling someone who eats crickets gross
* calling someone who eats crickets gross
79
New cards
Sense of place
Personal attachments people have to a specific geographic location
* language (dialects), religion (place of worship and architecture), ethnicity (ethnic neighborhoods)
* language (dialects), religion (place of worship and architecture), ethnicity (ethnic neighborhoods)
80
New cards
Centripetal forces
One common language, ethnicity, religion
* EX: 91% of China is Han Chinese, meaning they can all relate to one another based on a unified ethnicity.
* EX: 91% of China is Han Chinese, meaning they can all relate to one another based on a unified ethnicity.
81
New cards
Centrifugal forces
Multiple languages, religions, religious branches
* EX: Balkanization, the breakup of Yugoslavia based on differences in religion, culture, etc, in dominant religion different ethnic groups
* EX: Balkanization, the breakup of Yugoslavia based on differences in religion, culture, etc, in dominant religion different ethnic groups
82
New cards
Relocation diffusion
Phenomena is spread across space
* population of people = same
* Not expansion diffusion
* population of people = same
* Not expansion diffusion
83
New cards
Stimulus diffusion
Spreading of idea prompts new ideas
* ideas change based on the culture of an area
* EX: McDonald’s in India changes menu to suit the population’s taste like having McCurry pan
* ideas change based on the culture of an area
* EX: McDonald’s in India changes menu to suit the population’s taste like having McCurry pan
84
New cards
Expansion diffusion
* includes all diffusion except relocation
* Diffusion which results in a change of numbers (increasing)
* Diffusion which results in a change of numbers (increasing)
85
New cards
Hierarchical diffusion
Spreads from rank order
* how popular culture spreads
* EX: fashion brands start in Paris, skips over smaller cities, goes to NYC, then eventually arrives in Louisville
* how popular culture spreads
* EX: fashion brands start in Paris, skips over smaller cities, goes to NYC, then eventually arrives in Louisville
86
New cards
Contagious diffusion
Spreads randomly based on proximity
* EX: epidemics
* EX: epidemics
87
New cards
Causes of diffusion
**Imperialism** (one state’s direct or indirect control over the affairs of another political society), **colonialism** (form of imperialism in which a state takes possession of a foreign government and occupies it), **trade**
88
New cards
Effect of diffusion
* Rise of the British empire across diff. Countries in the world influenced the spread of the English language
* Through trade, many new ideas and innovations diffused into another culture
* Diffusion of religion also happened all over the world
* Through trade, many new ideas and innovations diffused into another culture
* Diffusion of religion also happened all over the world
89
New cards
The Columbia’s exchange
Type of spatial diffusion and the widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the Americas, West Africa, and the Old World
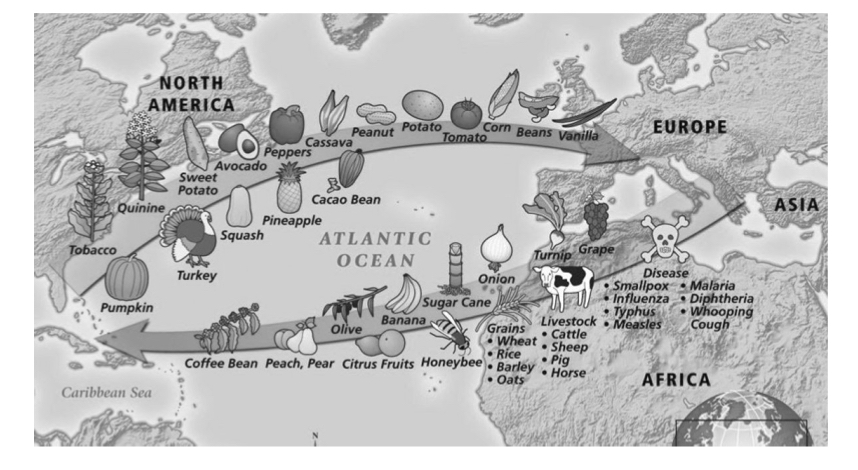
90
New cards
Lingua franca
A language used by people who don’t speak the same language to communicate for trade or business
91
New cards
Globalization
Greater interconnectedness among the world’s people, places, and institution
92
New cards
Supranationalism
Supranational organizations such as the EU allow for ideas within it to spread to the organization’s members and others
93
New cards
Urbanization
New technology/transportation allows cities to expand
* MNCs in developing countries can aid urbanization through providing jobs
* MNCs in developing countries can aid urbanization through providing jobs
94
New cards
Cultural convergence
Cultures become more alike as their interactions increase
* increasing use of English language
* Loss of indigenous languages
* Placelessness
* increasing use of English language
* Loss of indigenous languages
* Placelessness
95
New cards
Cultural Divergence
A group/ society separates usually due to being unsimilar
* EX: different dialects within a language represent cultural divergence
* EX: different dialects within a language represent cultural divergence
96
New cards
Indo-European
Largest language family with the widest distribution
* originated in Asia and Europe
* Diffused through colonization
* EX: English, German, the Romance languages.
* originated in Asia and Europe
* Diffused through colonization
* EX: English, German, the Romance languages.
97
New cards
Sino-Tibetan
Originated in Asia
* diffused contagiously
* EX: Mandarin, Burmese, Tibetan
* diffused contagiously
* EX: Mandarin, Burmese, Tibetan
98
New cards
Niger-Congo
* Originated in Africa
* spread through contagious and relocation diffusion
* EX: Swahili, Igbo, Fula
* spread through contagious and relocation diffusion
* EX: Swahili, Igbo, Fula
99
New cards
Afro-Asiatic
* Originated in Africa and Asia
* EX: Arabic, Herbu
* EX: Arabic, Herbu
100
New cards
Universalizing religion
Have universal appeal and seek converts
* typically grows faster and spreads more geographically through a combination of relocation and expansion diffusion
* typically grows faster and spreads more geographically through a combination of relocation and expansion diffusion