Topic 1 - The drug discovery process: general principles and some case histories
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
drug discovery - from therapeutic concept to molecule
drug development - from molecule to registered product
commercialization - from product to therapeutic application to sales
3 main phases of creating a new drug
Target selection
Target validation
Lead finding
Lead optimization
The discovery phase includes these stages
Preclinical development
Clinical development
Regulatory approval
The development phase includes these stages
Targets (receptors or enzymes)
Disease
Molecules (compound library
Target selection is the finding of a perfect molecule. It could start with
Target validation
Means to validate target; undergoes screening/assays
Lead finding
Means finding lead compound; uses softwares or technology
Lead optimization
Discovery phase where there already is a candidate drug
true
Development phase is not a linear process, it takes about 10 years
True or false
Branded drugs = discovery, development, commercialization
Generic drugs = development, commercialization
Branded drugs are expensive since it undergoes stages from ____, while generic drugs only undergo _____
HTS
SAR
Molecular docking
Softwares used in screening
HTS
This software used in screening is used to fine tune a drug. It is a special computer equipment
SAR (structural activity relationships)
This software used in screening has something to do with structure of molecules and how it acts
Molecular docking
This software used in screening finds receptors where molecules highly fit. Molecules in 3D are being docked
Distribution, metabolism, pharmacokinetic
DMPK means
Small molecules
Biopharmaceuticals
Natural products
Sources of drugs
Small molecules
compact, synthetic compounds refined through the classic synthetic-drug workflow
Workflow:
Select a disease/target
Validate the target
Screen compound libraries (HTS)
Confirm hits
Progress hit-to-lead and optimize leads
Nominate a preclinical candudate
E.g., imatinib
biopharmaceuticals
Source of drugthat includes endogenous substances (comes from humans, within the body) optimized and made better. E.g., trastuzumab
Natural products
Source of drug that are therapeutic agents originating from nature (plants, microbes, and animals). Historically much of the pharmacopoeia are from these
E.g.,
Paclitaxel
Artemisinin
Ciclosporin
Antibiotics
speedups
Refers to the time from project start to the compound shrank (often less than or equal to 3 years post target selection via HTS, automated synthesis and modeling)
Front loading
Earlier DMPK/tox screens reduce late attrition
1960 to 1980
This period was actually highly productive in terms of drug discovery, representing a return on R and D investment
Defined molecular targets
This is the necessary starting point for drug discovery, and turn automatically to molecular technologies to provide the necessary tools
Biopharmaceutical agents
Are very diverse, including endogenous mediaters, monoclonal antibodies and vaccines, and in the future, no doubt, products for siRNA and gene therapy application
Natural products
Therapeutic agents, particularly anti-infective and anti-tumour drugs originate from these products rather than synthetic molecules
1950
This period is when synthetic chemistrry really came into its own as a source of new drugs, most of the pharmacopoeia consisted of natural products, and they continue to be important
artemesinin
Anti-malarial drug
Ciclosporin fujimycin (FK506)
rapamycin
paclitaxel
Immunosuppressant
epothilones
Anticancer drugs
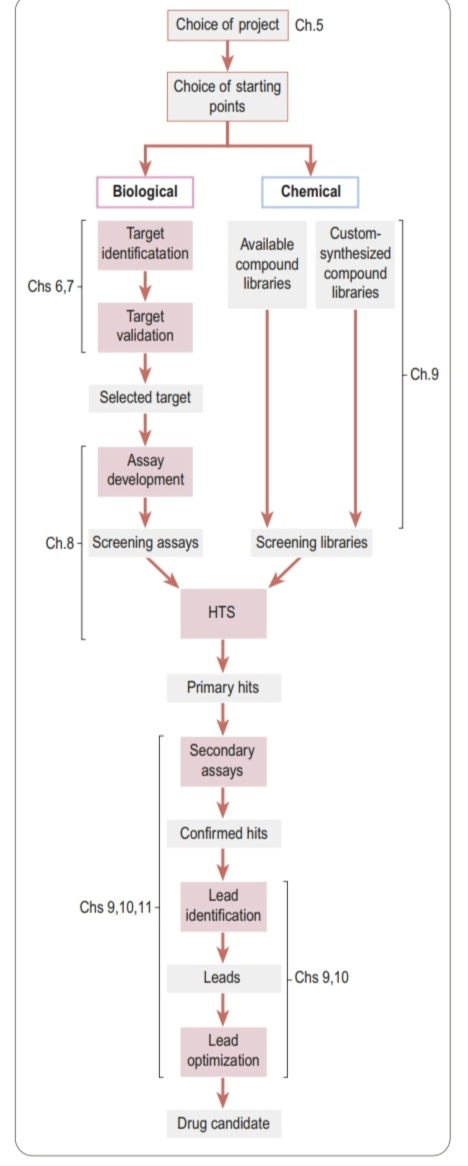
Drug discovery phase of a typical project aimed at producing a new synthetic drug
warfarin
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Anticoagulant. Synthetic compound derived from dicoumarol, found in spoiled sweet clover
dicoumarol
Warfarin is a synthetic compound derived from this which is found in spoiled sweet clover
heparin
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Anticoagulant, occurring naturally in mammalian tissues
Hirudin
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Anticoagulant from leech, now produced by genetic engineering
Warfarin
Heparin
Hirudin
Examples of therapeutic drugs derived from natural products that are anticoagulants
opiates
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Analgesic compound from poppies
Methylxanthines (caffeine, theophylline)
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors and adenosine receptor antagonists. Produced by tea, coffee and coca plants
statins
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors used to reduce plasma cholesterol
Lovastatin (statins)
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Is a fungal metabolite
(statins)
Mevastatin
pravastatin
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Compounds synthesized from lovastatin
cromoglycate
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Asthma prophylaxis. Synthetic compound based on khellin, a plant product used as a herbal medicine
Vinca alkaloids (vincristine, vinblastine)
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Anticancer drugs produced by plants of the periwinkle family
paclitaxel
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Anticancer drug from yew tree
etoposide
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Anticancer drug synthesized from podophyllotoxin, produced by mandrake plant; used in folk medicine
Artemether
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Antimalarial drug, semisynthetic derivative of artemesin, produced by Chinese herb
Ivermectin
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Antihelminthic drug semisynthetic derivative of avermectin, a fungal metabolite
antibiotics
Example of therapeutic drug derived from natural product
Too numerous to list. The majority of current ___ are derived from fungal metabolites
Opiates
Atropine
Ephedrine
Ergot alkaloids
Strychnine
Tubocurarine
Digoxin
Quinine
Veratidine
Reserpine
In earlier times the pharmacopoeia consisted very largely of plant-derived compounds, many of which remain in therapeutic use or provide valuable research tools
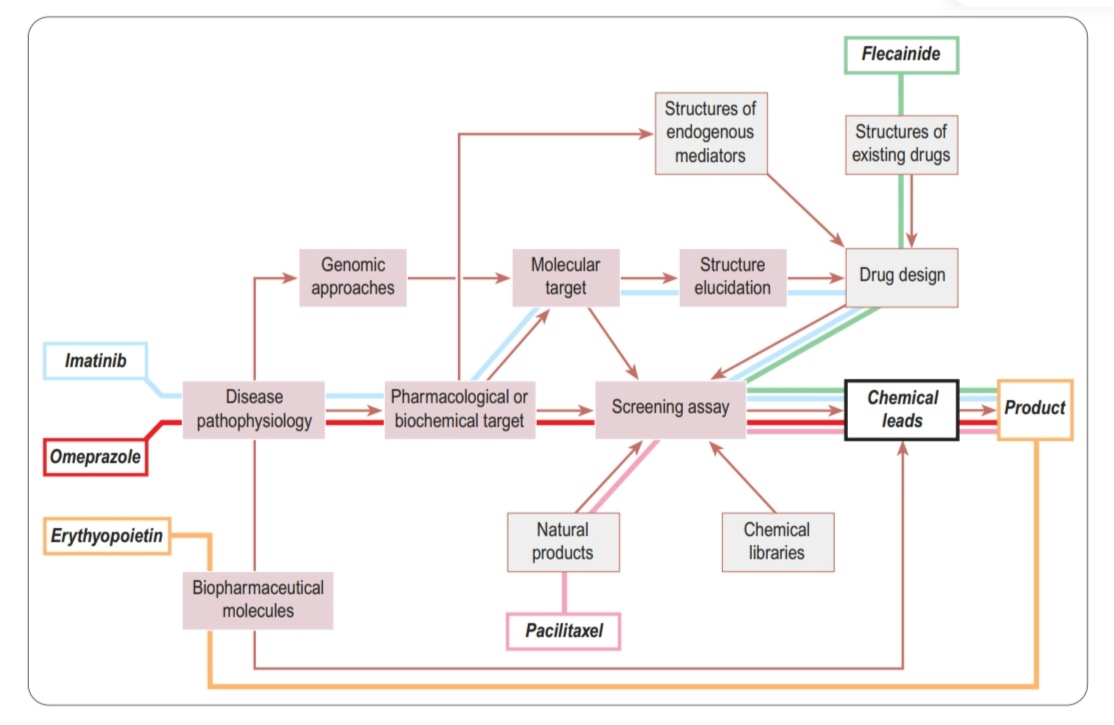
Discovery pathways of some successful projects
Natural product inhibitor of tubulin depolymerization
Paclitaxel (Taxol) MOA
US National Cancer Institute/Bristol Myers Squibb
Paclitaxel (Taxol) was developed by the company
Ovarian cancer
Paclitaxel (Taxol) indication
1964
Paclitaxel (Taxol) project started in
1971 (7 years from when the project started)
The year Paclitaxel (Taxol)’s compound was synthesized or its structure determined
1983 (19 years)
Paclitaxel (Taxol) phase 1 started in
1992 (28 years)
Year Paclitaxel (Taxol) was registered
1962
1969
To create Paclitaxel (Taxol), the sample bark from the Pacific Yew was collected in ___ and found to have modest activity against various tumour cell lines. The active substance was isolated in ___
Paclitaxel is insoluble in water and early formulations for injections used in Phase 1 trials contained high proportion of the solubilizing agent Cremophor EL (causes severe allergic reactions when given as a bolus IV)
Supply material for clinical trials and the uncertainty that it could ever be produced on a commercial basis
Development of Paclitaxel (Taxol) was difficult for 2 main reasons
baccatin
Commercialization of the material (Paclitaxel) extracted from the Pacific Yew bark was seen as a major problem, but it was solved when the needles of many yew species contain this, from which paclitaxel can be produced
1999
Synthetic Paclitaxel was officially approved in
Failure of the primary screen to reveal the compound as anything out of the ordinary
Appearance of serious side effects resulting from the properties of the excipient
Supply problem
Obstacles to progress in Paclitaxel include
Antidysrhythmic drug. Blocks cardiac Na+ channels
Flecainide (Tambocor) MOA
3M
Flecainide (Tambocor) was developed by the company
Cardiac dysarhythmias
Flecainide (Tambocor) indication
1965
Flecainide (Tambocor) project started in
1974 (9 years from when the project started)
Flecainide (Tambocor)’s compound was synthesized or its structure determined in
1976 (11 years)
Flecainide (Tambocor) phase 1 started in
1984 (19 years)
Flecainide (Tambocor) was registed in
Quinidine
Procainamide
Digoxin (for supraventricular tachyarhythmias)
lidocaine (given i.v. for ventricular dysarhythmias)
In the early 1960s, the drugs used to treat cardiac dysarhythmias were mainly
true
In Flecainide (Tambocor) project,
primary screening assay was based on the ability of compounds to prevent ventricular fibrillation induced by chloroform inhalation in mice
Secondary assays on selected compounds were carried out on anesthesized dogs
True or false
Flecainide (Tambocor)
Was the first deliberate effort to develop an improved antidysrhythmic drug and proved highly successful in the clinic, now accepted as the standard Class 1c antidysrhythmic agent according to the current classification
Slow chemistry
The main delaying factor in the flecainide project was simply
Inhibitor of gastric acid secretion. Blocks proton pump
Omeprazole (Losec) MOA
Astra
Omeprazole (Losec) was developed by the company
Peptic ulcer
Omeprazole (Losec) indication
1966
Omeprazole (Losec) project started in
1978 (12 years from when the project started)
Omeprazole (Losec)’s compound was synthesized and its structure determined in
1981 (15 years)
Omeprazole (Losec) phase 1 started in
1988 (22 years)
Omeprazole (Losec) was registered in
Omeprazole (Losec)
Developed by Astra and was the first proton pump inhibitor, and transformed the treatment of peptic ulcers when it was launched in 1988, quickly becoming the company’s best selling drug
carbamates
Astra started a project aimed at developing inhibitors of gastric acid secretion. They started a chemistry programme based on ___, and collaborated with an academic group to develop a suitable in vivo screening assay in rats
Compounds with weak activity were identified
Hepatotoxicity problems
In developing inhibitors of gastric acid secretion using carbamates, Astra encountered issues while doing so
Smith, Kline, and French
Developed histamine H2 anatagonists to inhibit gastric acid secretion
benzimidazoles
Searle reported a new class of gastric acid inhibitory compounds ____ which were active but toxic
picoprazole
The forrerunner of omeprazole synthesized in 1976
picoprazole
Was tested in human patients suffering from Zolinger-Ellison syndrome and was found tobe highly effective in reducing acid secretion
omeprazole
An analogue of picoprazole, was synthesized in 1979, and was chosen for development instead of picoprazole
Poor stability
Sensitivity to light
The chemical development of omeprazole was complicated by the compound’s
1981
Phase II/III clinical trials of omeprazole began in __, but were halted for 2 years as a result of yet another toxicology scare - carcinogenicity
Inhibits Abl kinase
Imatinib (Gleevec/Glivec) MOA
Novartis
Imatinib (Gleevec/Glivec) was developed by the company
Chronic myeloid leukemia
Imatinib (Gleevec/Glivec) indication
1983
Imatinib (Gleevec/Glivec) project started in
1990 (7 years)
Imatinib (Gleevec/Glivec)’s compound was synthesized or its structure determined in
2001 (18 years)
Imatinib (Gleevec/Glivec) was registered in
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
In the mid-1980s, it was discovered that a rare form of cancer ____, was almost invariably associated with the expression of a specific oncogene product Bcr-Abl kinase. The enhanced tyrosine kinsase activity of this mutated protein was shown to underlie the malignant transformation of the white blood cells
Ciba-Geigy
This oncology team began a project seeking inhibitors of Abl kinase
2-phenylaminopyramidine class
Compounds of the ____ showed selectivity in blocking Abl and PDGF-receptor kinases, and systematic chemical derivatization led to the synthesis of imatinib in 1992, roughly 8 years after starting the project
Imatinib
Proved to have no major shortcomings in relation to pharmacokinetics or toxicology, and was highly effective in suppressing the growth of cells engineered to express Bcr-Abl, and of human tumour cells transplanted into mice. It also inhibited the growth in culture of peripheral blood or bone marrow cells from CML patients
May 2001
Specifically, the imatinib was registered in ___ just 3 years after being tested for the first time in humans
imatinib
Is the first designer kinase inhibitor to be registered (other drugs, such as rapamycin, probably act by kinase inhibition, but this was not known at the time)