Chapters 6: Arousal and Performance Dynamics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Arousal
Activation of energy for behavior preparation.
Two types of arousal
physiological and psychological arousal
Physiological Arousal
Bodily changes indicating readiness for action.
Example of physiological arousal
increased heart rate, faster breathing, sweaty palms
what controls physiological arousal?
autonomic nervous system
What are the two parts of the autonomic nervous system?
sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
What does the sympathetic nervous system do?
Prepares body for action and movement. Activating behavior and movement.
What does the parasympathetic nervous system do?
Conserves energy and deactivates behavior. Deactivating and de escalating behavior.
Psychological Arousal
Subjective feelings of being aroused.
Example of psychological arousal
excited, scared, anxious
What are the two dimensions of psychological arousal?
Energetic and tense arousal
Energetic arousal
positively felt arousal, ranges from sleepiness to alert
Tense arousal
negatively felt arousal, ranges from calm to anxious
What is a type of tense arousal?
anxiety
Two types of anxiety
state and trait
State Anxiety
feelings of apprehension and worry that are evoked by threatening situations; response to a threatening situation
Trait Anxiety
disposition to perceive the environment as threatening and to respond to anxiety; tendency to view more situations are threatening
our level of arousal can be influenced by...
time of day, caffeine, evaluation collative variables
Novelty
something new and that you haven't encountered increases arousal
Complexity
more complex stimuli increase our arousal more than less complex
Congruity
lack of consistency and congruity increases arousal (something different from what you expect)
Zone of Optimal Functioning Hypothesis
Some arousal enhances performance, too much hinders. Arousal affects performance depends on the task.
Yerkes-Dodson Law
low arousal best for difficult tasks and high arousal is best for easier tasks. Task difficulty determines what level for arousal is best for performance.
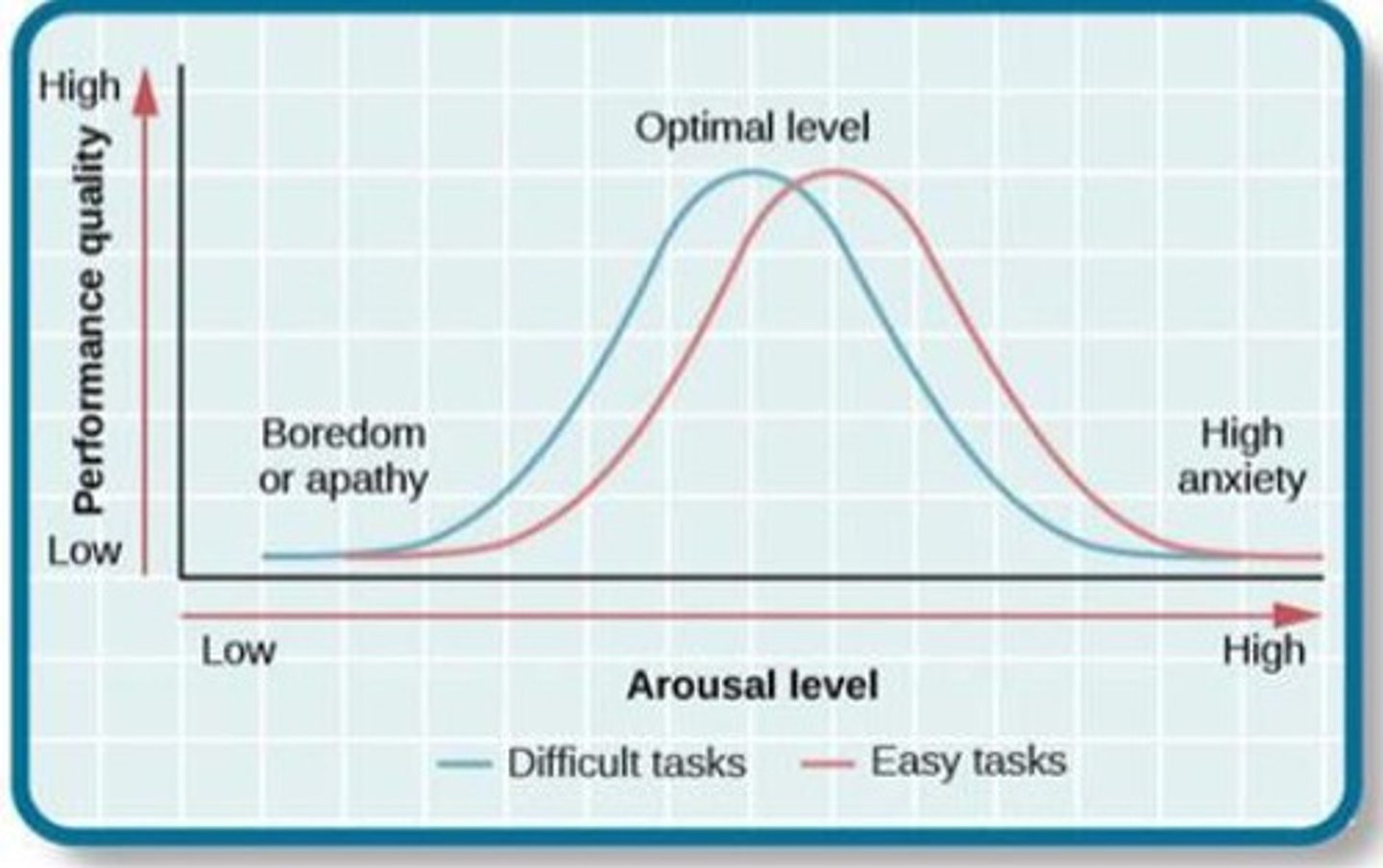
Hull-Spence Drive Theory
Drive creates arousal that increases likelihood of dominant responses.
According to Hull-Spence, what happens to the dominant response in an easy task?
Dominant response is successful
According to Hull-Spence, what happens to the dominant response in a difficult task?
Dominant response is failure
What is the only theory that divides physiological and psychological arousal?
Cusp Catastrophe Model
Cusp Catastrophe Model
Performance drops after peak arousal levels.
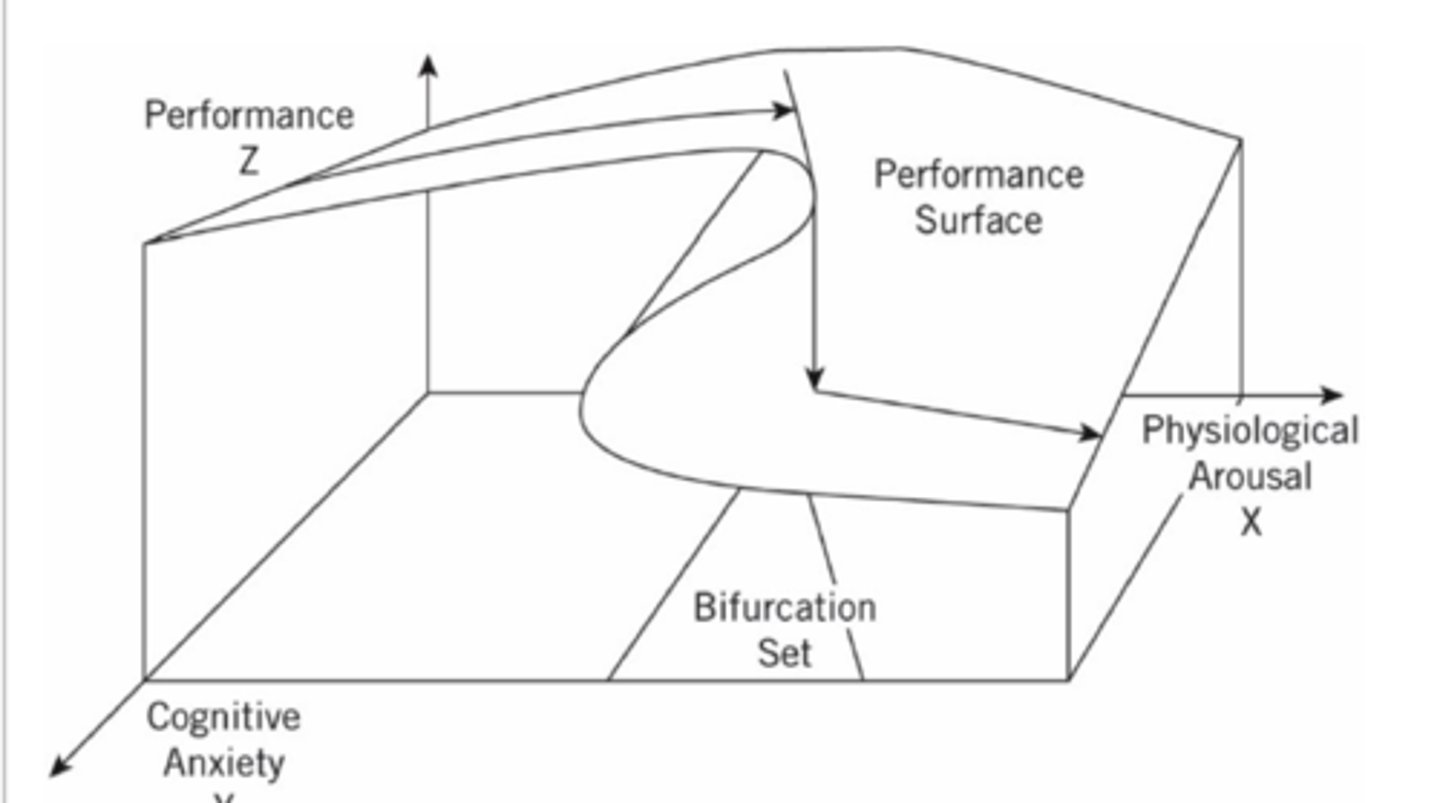
According to Cusp Catastrophe Model, what happens at low levels of psychological arousal/anxiety?
Arousal-performance relationship is a flattened inverted-U
According to Cusp Catastrophe Model, what happens at moderate levels of psychological arousal/anxiety?
arousal-performance increases to a "cusp"
According to Cusp Catastrophe Model, what happens at high levels (beyond the cusp) of psychological arousal/anxiety?
increases in arousal and leads to sharp drop-off in performance (backwards S)
Tonic Immobility
Behavioral paralysis due to extreme stress.
Arousal-Biased Competition Theory
Arousal increases attention to threatening stimuli/high priority stimuli. Ex: experiment with snake and chipmunk
Memory Systems
Addressing memory performance (examines arousal vs. recall)
location of cool memory systems
hippocampus
Cool Memory System
-memory of things in space and time
-best at intermediate levels of arousal but drops off at high levels
- where inverted-U is
location of hot memory systems
amygdala
Hot Memory System
- Memory of events that occur under high arousal
- Most efficient at high levels of arousal
- Addresses the reality that we can form memories under high levels of arousal but our recall is not as good
what happens when the cool system drops off?
Hot system takes over
Processing Efficiency Theory
Anxiety consumes working memory space.
Attentional Control Theory
- Extension of processing efficiency theory
- Adds that anxiety decreases cognitive capacity by inhibiting attention
- Theory says that worry takes up space because you're focusing on things you don't want to focus on
Optimal Level of Stimulation Theory
describes the relationship between the level of stimulation (arousal) and associated affective valence (feelings)
Based on the optimal level of stimulation theory, what is the relationship with arousal and affect
as arousal increases, positive affect increases, levels off, and then decreases
what causes optimal level of stimulation to vary over time?
time, age, experience
Benign Masochism
Enjoying initially negative experiences perceived as threatening.
Discrepancy Hypothesis
Pleasure increases with moderate deviations from expectations.
Inverted U Relationship
Arousal-performance relationship resembles an inverted U shape.
Relationship with stimulus complexity and enjoyment of art/music
- Complexity of stimuli contributes to arousal
- Liking increases, then decreases with complexity