M. 11 Weekly Quizzes
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
M.11, W.1-3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
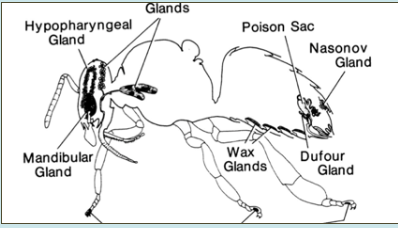
Which gland in honeybees produces brood food consisting of proteins, lipids and vitamins?
a. Dufour gland
b. Hypopharyngeal gland
c. Mandibular gland
d. Nasonov gland
e. Wax glands
Hypopharyngeal gland
What is the best diet type for Budgerigars?
a. Florivorous
b. Frugivorous
c. Granivorous
d. Nectivorous
e. Omnivorous
Granivorous
What are ferrets vaccinated against in the UK?
a. Calcivirus and Leptospirosis
b. Distemper and Rabies
c. Herpesvirus and Bordetella
d. Leukemia virus and Chlamydia
e. Parvovirus and Adenovirus
Distemper and Rabies
In relation to lizards, what is autotomy?
a. A fungal infection
b. Atrophy of scales
c. Increasing skin pigmentation
d. Proliferation of follicles
e. Tail shedding
Tail shedding
What is the function of the air sacs in the avian respiratory system?
a. Act as bellows to maintain unidirectional airflow through the lungs
b. Filter particulate matter before air enters the lungs
c. Increase the surface area for gas exchange
d. Store oxygen for use during flight
e. To protect organs from impact during landing
Act as bellows to maintain unidirectional airflow through the lungs
Which muscle is primarily responsible for the downstroke during avian flight?
a. Biceps brachii
b. Latissimus dorsi
c. Pectoralis major
d. Supracoracoideus
e. Trapezius
Pectoralis Major
A new ferret owner asks for advice on what to feed their pet ferret. What is your advice to this owner?
a. Ferrets are strict carnivores and should be fed a whole prey diet
b. Ferrets should be fed a commercially available complete dry biscuit diet
c. Ferrets should be fed a natural diet consisting of dead day old chicks
d. Ferrets should be fed dry dog biscuits mixed with tinned wet dog food
e. Ferrets should fed raw meat, scattered to provide enrichment
Ferrets should be fed a commercially available complete dry biscuit diet
An owner brings their 2 year old male Herman’s Tortoise to you for an annual health check. You notice that this animal’s upper beak is overgrown and the shell is soft when you apply gentle digital pressure. What is the likely husbandry related problem that has resulted in these clinical signs in this tortoise?
a. The ambient temperature within the enclosure is too low and should be increased by providing an additional focal heat source
b. The temperature gradient within the enclosure is not within the animal’s preferred optimal temperature zone
c. The tortoise is growing too rapidly and needs to be kept at a cooler environmental temperature
d. The tortoise is not being kept at a species appropriate humidity
e. The tortoise is not getting enough UVb light for vitamin D synthesis
The tortoise is not getting enough UVb light for vitamin D synthesis
Which aspect of avian renal function confers an advantage over the mammalian system for life on dry land?
a. Increased proportion of filtration due to portal vein involvement favours water conservation
b. Multilobular arrangement confers protection against glomerular damage and failure
c. Nitrogenous waste is secreted as uric acid which prevents its reabsorption and benefits water conservation
d. Smaller share of cardiac output favours muscular circulation
e.The central lobular vein allows secretion into the collecting ducts
Nitrogenous waste is secreted as uric acid which prevents its reabsorption and benefits water conservation
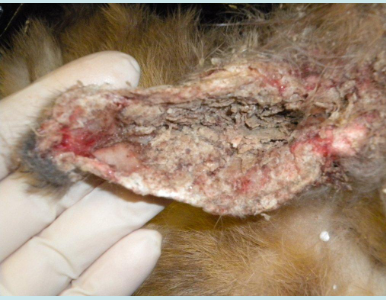
What is the cause of the skin lesion on the pinna of this rabbit?
a. Baylisascaris procyoni
b. Demodectic mange
c. Otitis interna
d. Psoroptes cuniculi
e. Sunburn damage
Psoroptes cuniculi (rabbit ear mite)
The purpose of the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 is to:
a. Protect animals used for experimental or other scientific purposes
b. Protect endangered species used for experimental or other scientific purposes
c. Protect people used for experimental or other scientific purposes
d. Protect scientists from animals used for experimental or other scientific purposes
e. Protect vertebrates and non-vertebrates from scientists
Protect animals used for experimental or other scientific purposes
What is a suitable brooding temperature for day-old chicks?
a. 15 degrees C
b. 21 degrees C
c. 27 degrees C
d. 32 degrees C
e. 37 degrees C
32 degrees C
In the UK who is legally allowed to diagnose, prescribe for and treat wild animals?
a. Any competent member of the public who finds a wild animal and becomes its 'owner'
b. Anyone working at a Licensed wildlife rehabilitation center
c. A RCVS Registered veterinary nurse
d. A RCVS Registered veterinary surgeon
e. A Registered wildlife rehabilitator
A RCVS Registered veterinary surgeon
Which egg production system(s) supplies the bulk of eggs consumed in the UK?
a. Battery cages
b. Colony / Furnished Cages
c. Free range
d. Organic free range
e. Perchery / Aviary / Barn
Free range
What is the major welfare concern that only applies to the rearing of broiler breeders?
a. Cannibalism
b. Feather pecking
c. Feed restriction
d. Heat Stress
e. High mortality
Feed restriction
At what age do commercial pullets typically start to produce eggs?
a. 8-12 weeks
b. 14-16 weeks
c. 18-20 weeks
d. 22-24 weeks
e. 26 - 30 weeks
18-20 weeks
Why is it important to record the location where an injured wild animal was found?
A. So that it be released in the same place
B. So that it can be given back to the member of the public
C. So that it can be taken to the nearest vet
D. To check if there are other injured animals
E. To isolate the area in case of zoonosis
so that it can be released in the same place
What action would violate the Wildlife and Countryside Act (WCA) 1981 in the UK?
a. Photographing a protected bird species from a distance
b. Planting native wildflowers in a designated conservation area
c. Possessing the body of a protected wild animal, even if found dead
d. Providing supplementary feeding to wild garden birds in winter
e. Relocating an abandoned domestic rabbit found in a public park
possessing the body of a protected wild animal, even if found dead
Under UK invasive species legislation (including the Destructive Imported Animals Act (1932) and Schedule 9 of the Wildlife and Countryside Act) what activity is unlawful for specified non-native species?
a. Conducting a population survey of non-native species
b. Housing a non-native species under a valid license
c. Humanely euthanizing a non-native species for welfare reasons
d. Releasing the non-native species back into the wild
e. Transporting an injured non-native species for treatment
releasing the non-native species back into the wild
In animal research and veterinary science, what is the primary purpose of the Replacement, Reduction and Refinement (3Rs) framework?
a. To eliminate the need for all biological research involving living systems
b. To ensure experimental animals are housed in identical environments
c. To improve the commercial efficiency of laboratory animal suppliers
d. To minimize animal use and suffering by improving experimental design and methods
e. To standardize the genetic background of all research animals
To minimize animal use and suffering by improving experimental design and methods
What is the ecological process that helps reduce disease transmission in animal populations?
a. Biodiversity acting as a disease buffer
b. Habitat shifts affecting wildlife movement
c. Land-use change altering host density
d. Seasonal migration changing contacts
e. Urban greenspace expanding coverage
Biodiversity acting as a disease buffer
What issue can follow a decline in insect-eating bird populations?
a. Fewer conflicts reported between wildlife species in shared areas
b. Insect changes increasing pet risks within community settings
c. Less pressure placed on clinics handling local wildlife casualties
d. Reduced opportunities for recording avian health observations
e. Slower regional spread of certain plant-associated pathogens
Insect changes increasing pet risks within community settings
Why is Mycobacterium marinum infection in ornamental fish important?
a. It is always fatal in 24 hours
b. It is a zoonotic disease
c. It is easily eradicated with common antibiotics
d. It is not transmissible to humans
e. It is primarily a fungal infection
It is a zoonotic disease
Which parasite is commonly known as “white spot”?
a. Argulus
b. Chilodonella
c. Dactylogyrus
d. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
e. Trichodina
Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
What is a typical health issue seen in UK dairy goats that requires close management?
a. Chronic diarrhoea caused solely by pasture contamination during late-season grazing
b. High incidence of congenital limb deformities related to intensive housing conditions
c. Persistent nasal discharge associated with structural defects in indoor ventilation systems
d. Pregnancy toxaemia and ketosis occurring around late gestation and peak lactation
e. Reproductive failure linked exclusively to inherited hormonal receptor mutations
Pregnancy toxemia and ketosis occurring around late gestation and peak lactation
Human–wildlife conflict often intensifies when animals are forced into smaller areas. What is one major consequence of this compression?
a. Decline in natural breeding activity across several wildlife groups due to altered social dynamics
b. Decrease in predator avoidance behaviors as animals adjust to reduced habitat ranges
c. Increase in contact between wildlife, humans, and livestock, raising overall disease risk
d. Reduction in vegetation quality across fragmented ecosystems affected by human expansion
e. Stabilization of feeding patterns in restricted habitats despite decreasing resource availability
Increase in contact between wildlife, humans, and livestock, raising overall disease risk
Feeding management during early gestation is critical for reproductive success. What is one recommended practice for this stage?
a. Feeding at high levels throughout gestation to maximize continuous fetal expansion
b. Increasing feed during the first weeks to support essential placental growth
c. Maintaining fixed feed levels from service until farrowing without adjustment
d. Reducing feed sharply from day one to limit early embryonic nutritional exposure
e. Sustaining a very low ration to avoid excessive gut fill during organ development
Increasing feed during the first weeks to support essential placental growth
During the weaning process, piglets face several immediate challenges. What is one common issue that arises at this time?
a. Continuous access to milk feeding while gradually transitioning to solid diets
b. Exposure to new infections as piglets shift rapidly from passive to active immunity
c. Immediate retention of passive immunity provided directly by the sow post-weaning
d. Minimal environmental change when piglets remain entirely in their birth accommodation
e. Stability of the social hierarchy maintained without changes in group behavior
Exposure to new infections as piglets shift rapidly from passive to active immunity
Under UK legislation, what is the definition of a “protected animal” in the context of scientific research?
a. Any animal bred within authorized facilities that meet established welfare certification standards
b. Any living vertebrate (other than humans) and any living cephalopod included within ASPA regulations
c. Any organism housed in licensed establishments and maintained for potential experimental purposes
d. Any species identified within designated Home Office licensing frameworks for controlled studies
e. Any vertebrate or cephalopod recognized as capable of sentience under statutory guidance documents
Any living vertebrate (other than humans) and any living cephalopod included within ASPA regulations
Which basic water quality parameter is most important for salmon respiration?
a. Ammonia
b. Carbon dioxide
c. Dissolved oxygen
d. Nitrate
e. pH
Dissolved Oxygen