Chem Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons: an introduction to organic molecules
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
two properties that make carbon unique
carbon atoms can form strong, stable chains, lined by covalent bonds
carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds, allows each carbon atom in a chain to form bonds to additional atoms
bonding patterns for carbon atoms
has 4 valence electrons and four empty spaces in its valence shell
four single bonds
one double bond + two single bonds
two double bonds
one triple bond + one single bond
valence shell electron pair repulsion model
the principle that valence electrons around an atom arrange themselves to be as far apart as possible (VSEPR)
tetrahedral arrangement
an arrangement in which four bonded atoms are equally spaced around a central atom
the four atoms around a carbon atom always form a tetrahedral arrangement
solid wedge
represents a bond that is coming toward you (out of paper)
dashed wedge
represents a bond that is going away from you (into paper)
hydrocarbons
compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms (simplest of all organic compounds bc only contains 2 elements)
alkane
an organic compound / hydrocarbon that contains only single bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms
alkene
contain at least one carbon to carbon double bond
alkyne
contains at least one carbon to carbon triple bond
aromatic compound (arene)
contains a six membered ring of carbon atoms linked by alternating single and double bonds (has 3 extra electrons that float freely within the ring of carbon atoms)
linear alkanes
an alkane in which the carbon atoms form a single continuous chain with single bonds
smallest linear alkane is methane
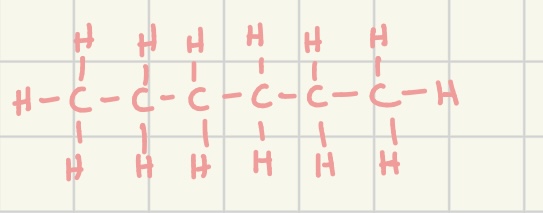
full structured formula
a way to represent an organic molecule in which all atoms and chemical bonds are drawn out
does not shown non bonding electrons
condensed structural formula
an abbreviated way to write structural formula, represents an organic molecule that lists the # of hydrogen atoms beside the atom to which they are bonded
ex. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3
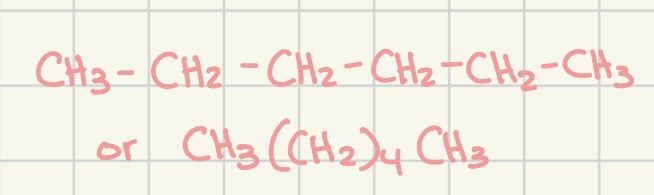
common ways to represent an organic molecule
wedged dash structure
full structural formula
condensed structural formula
line structure
molecular formula
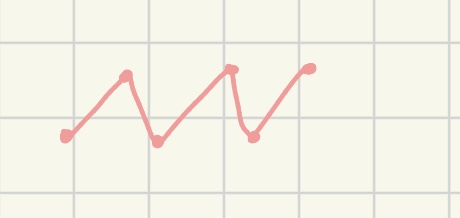
line structure
structure of organic compound using zigzag lines to represent hydrocarbon chains, no C labels / omit H all together
molecular formula
useful for writing balanced equations (C6H14)
branched alkane
an alkane in which the carbon atoms do not form a single continuous chain (ex. isobutane)
isomers
compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures
different arrangement of atoms will often produce a molecule with dramatically different physiological properties
constitutional isomers
molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in the order in which the atoms are connected to one another
have different shapes = different physical and chemical properties
cycloalkane
an alkane in which the carbon atoms form a ring
methane
CH4
ethane
C2H6
propane
C3H8
butane
C4H10
pentane
C5H12
hexane
C6H14
heptane
C7H16
octane
C8H18
nonane
C9H20
decane
C10H22
cycloalkanes and alkanes
are not isomers, cycloalkanes don’t have hydrogen ends, so cycloalkanes always have 2 fewer hydrogens
saturated hydrocarbons
a hydrocarbon that does not contain any double or triple bonds, contains more hydrogen atoms then hydrocarbons with double, triple bonds
To name a branched alkane
start with identifying the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule (principal carbon chain)
identify the branches that are attached to the principal chain (alkyl groups)
name alkyl groups by replacing “ane” ending of the corresponding alkane with “yl”
for chains that contain 3 or more carbon atoms, there is more than one possible alkyl group depending on where we remove the hydrogen atom
propyl, butyl, and so forth are reserved for the alkyl groups that are missing a hydrogen from the end of the chain
principal carbon chain
longest continuous carbon chain
alkyl groups
fragment of an organic compound consisting of an alkane that is lacking / one hydrogen atom has been removed, which allows alkane to be attached to a larger molecule
methyl
number of carbon atoms = 1
condensed structure = CH3
ethyl
number of carbon atoms = 2
condensed structure = CH2-CH3
propyl
number of carbon atoms = 3
condensed structure = CH2-CH3-CH3
isopropyl
number of carbon atoms = 3
condensed structure = CH3-CH-CH3 (missing the hydrogen in the middle instead of the end
butyl
number of carbon atoms = 4
condensed structure = CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
naming an alkane with only one branch
focus on carbon chain and ignore hydrogen atoms
identify and name the principal carbon chain and the alkyl group
# the carbon atoms in the principal chain, starting from the end that is closest to the alkyl group
write the name of the branch in front of the name of the principal chain
naming a cycloalkane that is attached to an alkyl group
rules are similar, we do not write # to show location of alkyl group
name one branch step 1
identify and name the principal carbon chain and the alkyl group

name one branch step 2
# the carbon atoms in the principal chain, starting from the end that is closest to the alkyl group
use #’s to tell where the alkyl group is attached to the principal chain

name one branch step 3
write the name of the branch in front of the name of the principal chain
rules are designed to give every organic molecule a unique name that does not depend on how we draw the structure of the molecule

same IUPAC name
if 2 structural formulas have the same IUPAC name, they represent the same chemical compound
different IUPAC name
if 2 structural formulas have different IUPAC names but the same chemical formula, they must be isomers
naming an alkane with more than 1 branch
the alkane has 2 or more identical branches - use prefixes di, tri, tetra, etc to show # of identical alkyl groups
the molecules contain 2 or more different branches - molecules that have alkyl groups that are different sizes, list the alkyl groups alphabetically
the molecule contains both identical and different branches - if we have 2 or more identical branches ignore the prefixes when alphabetizing names
both ends of the principal chain are the same distance from a branch - if this happens we simply proceed to next branch thats closest
naming more than one branch (2 or more identical branches)
the alkane has 2 or more identical branches - use prefixes di, tri, tetra, etc to show # of identical alkyl groups
each alkyl group gets a #, separate the # using commas

naming more than one branch (contain 2 or more different branches)
the molecules contain 2 or more different branches - molecules that have alkyl groups that are different sizes, list the alkyl groups alphabetically

naming more than one branch (contain both identical and different branches)
the molecule contains both identical and different branches - if we have 2 or more identical branches ignore the prefixes when alphabetizing names

naming more than one branch (both ends are same distance)
both ends of the principal chain are the same distance from a branch - if this happens we simply proceed to next branch thats closest

organic compounds are classified by
functional groups
functional groups
any bond or group of atoms that is not present in alkane and that gives a compound the ability to undergo specific chemical reactions
unsaturated hydrocarbon
any hydrocarbon that contains at least one double or triple bond
alkenes
molecules that contain a carbon-carbon double bond, double bond is referred to as the “alkene functional group”
contain a trigonal planar arrangement of atoms
alkynes
molecules that contain a carbon-carbon triple bond, bond known as alkyne functional group
triple bond and neighboring bonds line up
trigonal planar arrangement
an arrangement in which 3 bonded atoms are equally spaced around a central atom
alkenes and alkynes can be named using IUPAC rules
name must describe hydrocarbon framework of molecule, identify the functional group, and tell where the functional group is located
alkenes and alkynes naming rules
name the compound as if it were an alkane, ignoring the functional group
change the “ane” ending of the alkane name to “ene” for an alkene or “yl” for alkyne
# of carbon-carbon bonds starting from the end closest to the functional group and use these #’s to identify the position of the multiple bond
assemble the name by writing the # from step 3 followed by the name, use hyphen to seperate #’s from words
cycloalkenes
when a hydrocarbon contains an alkene group within a ring of carbon atoms
contain double bond within a ring of carbon atoms
name cycloalkenes
change ending of corresponding cycloalkane from “-ane” to “-ene”
in branched alkene or alkyne
the functional group determines the principal chain
naming branched alkene or alkyne
2 additional rules
the principal chain is the longest chain that includes the functional group
the principal chain is numbered from the side closest to the functional group, regardless of the positions of the branches
list the alkyl groups
trivial names
a traditional name for a chemical substance that is not part of the IUPAC system
flexible molecules
alkanes are flexible, able to adapt to a range of shapes while retaining the tetrahedral arrangement around each carbon atom
non flexible molecules
carbon-carbon double bonds do not permit free rotation
cis and trans isomeric forms
linear alkenes have cis and trans isomeric forms, if number is 2 or larger the alkene can either be cis or trans
cis
has 2 of the same atom / group on the same side
trans
has 2 of the same atom / group on opposite sides (one up, one down)
stereoisomers
molecules that have the same chemical formula but differ in the relative positions of the groups surrounding a single atom
benzene
C6H6
has 3 extra electron pairs that flow freely around ring
aromatic compounds
compounds that contain the benzene ring, alkyl groups can be added to benzene rings
large molecules have
higher melting and boiling points