Nuclear Chemistry
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Mixture
combination of two or more substances
Homogenous Mixture
Mixture that looks uniform all through out
Looks “properly mixed”
Ex. Salt water, air
Heterogenous Mixture
Mixture where different parts are not evenly mixed
You can see the different components
Ex. Oil and water, sand and water
Solutions
Appearance: Homogenous
Particle Size: Small, < 1nm
Settling: NO
Separation: Cannot be separated by filtration
Tyndall Effect: Do not scatter light
Colloid
Appearance: Homogenous
Particle Size: Larger, 1nm - 1μm
Settling: NO
Separation: Cannot be separated through common filtration techniques
Tyndall Effect: Scatter light or can be opaque
Suspension
Appearance: Heterogenous
Particle Size: Large, > 1 μm
Settling: Yes
Separation; can be separated by filtration or centrifugation
Tyndall Effect: Scatters light
Types of Solution - Undersaturated
Solution that contains less than the maximum amount of solute that it can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature.
Types of Solution - Saturated
Solution that contains the maximum amount of solute that it can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature.
Types of Solution - Supersaturated
Solution that contains more than the maximum amount of solute that it can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature.
Polar Solvent dissolution
Polar and Ionic Compounds are soluble in this type of solvent
Non Polar Solvent Dissolution
Non Polar Compounds are soluble in this type of solvent
Dissolving NaCl in Water
When ionic NaCl dissolves in water, the Na+ and Cl− interactions of the crystal are replaced by new interactions with the solvent.
Each ion is surrounded by water molecules, which arrange so that opposite charges are near each other.
Dissolving and Energy Changes
Dissolving a solute in a solvent is a physical process with energy change.
Breaking solute particles → requires energy
(endothermic)
Forming new forces between solute and solvent
→ releases energy (exothermic)
Applications of Hot & Cold Packs
Breaking the seal lets salt and water mix, causing
the salt to dissolve.
Hot packs (CaCl2 or MgSO4) - Salt dissolves →
releases heat → muscle pain relief (exothermic)
Cold packs (NH4NO3) - Salt dissolves → absorbs
heat → reduce swelling (endothermic)
Henry’s Law
The solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to its partial pressure above the liquid.
Concentrated Solution
Relatively large amount of dissolved solute
Diluted Solution
Relatively small amount of dissolved solute
Percent weight per volume (%w/v)
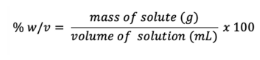
Percent of volume per volume (%v/v)
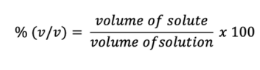
Molarity (M)
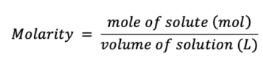
Parts per million (ppm)
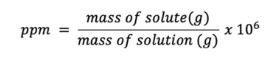
Dissolving Sodium Chloride in Water
When NaCl meet with H2O
Water molecules surround the Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions
Negative end of the water (oxygen) is attracted Na⁺
Positive end of water (Sodium) is attracted to Cl⁻
Separation:
bonds are strong enough to pull Na⁺ and Cl⁻ apart from the salt crystal
each ion is now surrounded by water molecules (hydration)
Dissolving and energy changes - “Like-Like” Bond
Requires energy
Endothermic
Solute-solute bonds
solvent-solvent bonds
Dissolving and energy changes - “Opposite” Bond
Doesn’t require energy
Exothermic
Solute-Solvent bond
Application of hot packs and cold packs - Hot Pack
Pack releases heat, Patient Absorbs heat
Contain a solid like calcium chloride (CaCl₂) or magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄).
When Pack is activated, salt dissolves in water inside
Energy is released and pack becomes hot
Applications of hot packs and cold packs - Cold Pack
Pack Absorbs heat, Patient releases heat
Contain a salt like ammonium nitrate (NH₄NO₃) or potassium chloride (KCl).
When Pack is activated, salt dissolves in water inside
It absorbs heat from surroundings → the pack feels cold.
EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE ON
SOLUBILITY
The solubility of solids in liquids generally increases with
temperature
Colligative Properties
Properties of a solution that depends on the concentration
or number of particles dissolved in a solution, but not its
identity
Common colligative properties include:
○ Boiling Point elevation
○ Freezing Point Depression
○ Osmotic Pressure