Lecture 1: Intro and Host-Pathogen Interactions
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What are the stages of a bacterial colonization?
Entry
Adherence
Invasion
Colonization
Growth
Health
The balance between normal microbiota and host
Disease
The imbalance between immune system and normal microbiota overwhelmed by pathogens
What are Koch’s Postulates?
The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease
Pathogen must be isolated in pure culture
Pathogen isolated from pure culture must cause the same disease in lab animal
Pathogen must be re-isolated from inoculated lab animal
Mutualism/Symbiosis
Bacteria and host are benefited (rumen bacteria)
Commensalism
Bacteria are benefited and host is unaffected (normal flora)
Parasitism
Bacteria are benefited and the host is harmed
Bacterial Antagonism
A protective function against pathogens by competing for attachment, nutrients, and producing substances that inhibit pathogens
Probiotics
Involved in competitive exclusion
Pathogenesis
Process/mechanisms of disease development (toxins, attacking immune system, etc.)
Pathogenicity
Capacity/potential of an organism to cause the disease
Virulence
Relative pathogenicity (LD50, ID50)
Invasiveness
Ability to enter, survive, multiply, and spread in the host
LD50
Number of microbes in a dose that will kill 50% of inoculated test animals
ID50
Dose required to produce demonstrable infection in 50% of test animals
Frank (True) Pathogen
Cause disease in normal hosts
Opportunistic Pathogen
Causes disease only when conditions are favorable (stress, vaccination, etc.)
Extracellular Pathogen
Grows and multiples in the space and fluids surrounding cells
Intracellular Pathogen
Grows and multiples inside the cells
Facultative
Grows/multiplies inside and outside cells; can be cultured in bacteriological media
Obligate
Grows/multiplies only inside cells; must be cultured in tissue culture media
Infection
Invasion or colonization by a pathogen; may or may not result in a disease
Disease
Change from a state of health
Primary Infection
Infection in a previously healthy host
Secondary infection
Occurs along with or immediately following another infection
Exogenous Infection
Bacteria originate outside the animal
Endogenous Infection
Bacteria originate from within the animal
Sporadic Disease
Occurs occasionally
Endemic Disease
Consistently present in a population
Epidemic Disease
Consistently present in a population
Pandemic Disease
Occurs worldwide
Acute
Rapid onset, usually severe, and lasts for a short period
Peracute
Higher degree of acute disease
Chronic
Slow onset, less severe, and lasts longer
Subclinical
Mild with no overt signs/symptoms
Localized
Confined to a relatively small area
Systemic
Spreads throughout the body. Bacteria enters lymph/circulation
Focal
Bacteria from a local infection enter lymph or blood to set up local infection in other parts of the body
Bacteremia
Bacteria circulating in the blood
Septicemia
Bacteria multiplying in the blood
Toxemia
Toxin is circulating in the blood
Incubation Period
Interval between the entry and the appearance of first symptoms
Illness
Signs and symptoms are evident
Symptoms
Effects of the disease experience by the patient (pain, nausea)
Signs
Effects of the disease (fever, swelling)
Convalescence
Period of recovery
What are the stages of an infection?
Incubation Period
Prodromal Stage
Period of Invasion
Convalescent Period
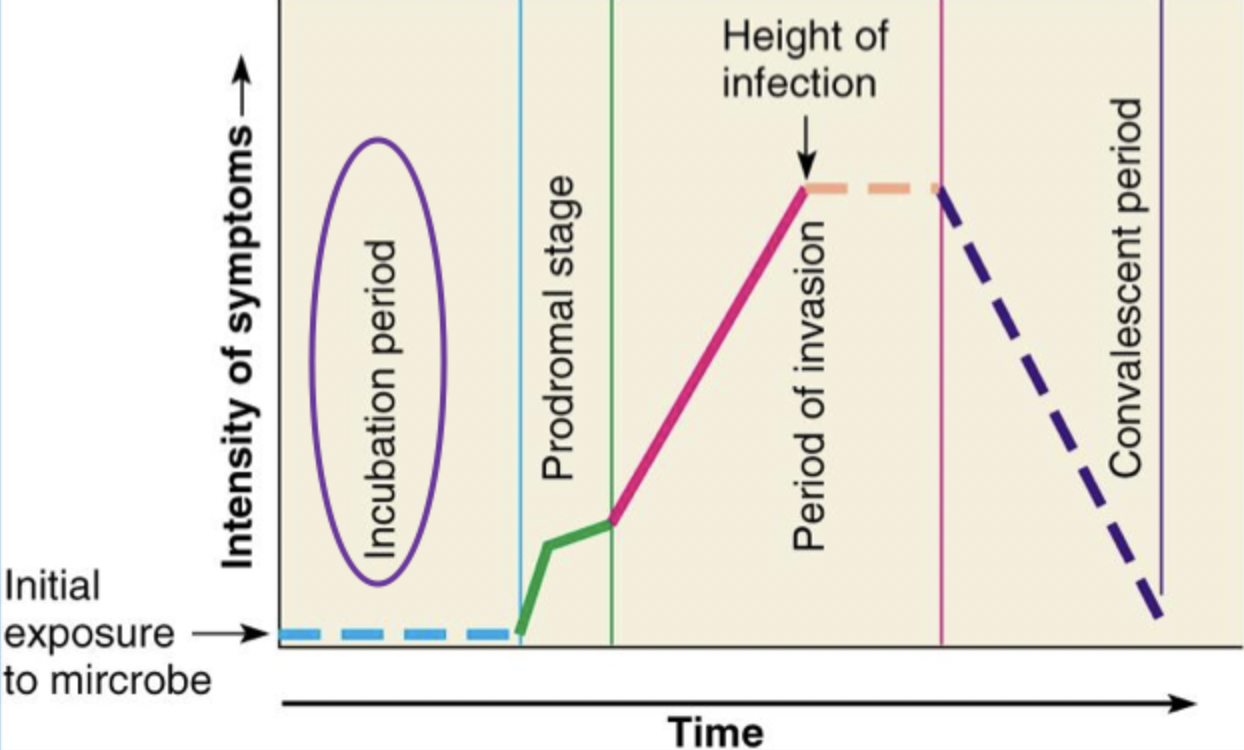
Incubation Period
From initial contact with the infectious agent to the appearance of first symptoms; agent is multiplying but damage is insufficient to cause clinical signs; can be several hours-years
Prodromal Stage
Vague feelings of discomfort; nonspecific
Period of Invasion
Multiplies at high levels and well-established; more specific signs/symptoms; height of infection
Convalescent Period
As host begins to respond to the infection, symptoms decline