Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease-Non-endocrine
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
4/30
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is another word for Jaundice?
Icterus
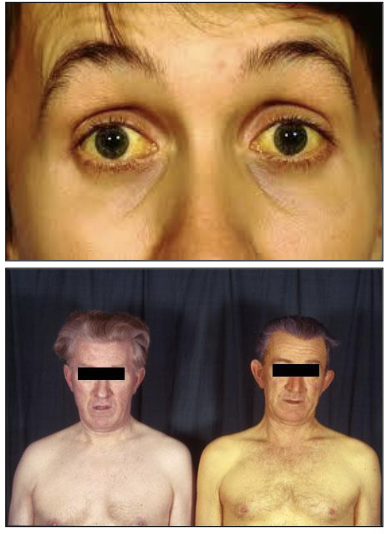
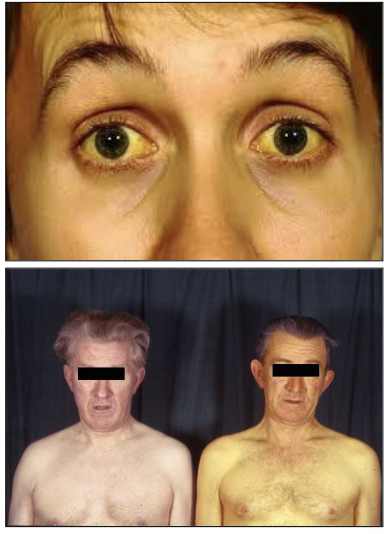
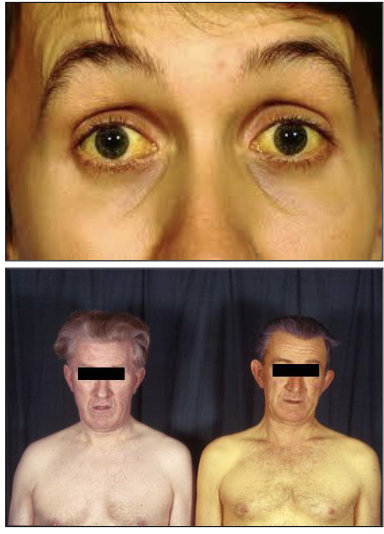
What is Jaundice?
Excess bilirubin in the bloodstream accumulates in yellowish discoloration of the skin and mucosa
What are the causes of bilirubin?
Hemolytic anemia/Sickle cell anemia
Liver disease
Bile duct obstruction
Cancer
Gilbert syndrome (glucuronosyltransferase)
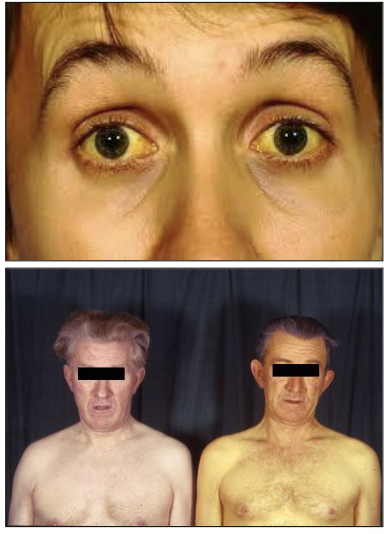
What are bilirubin levels?
Levels exceeds 2mg/dl
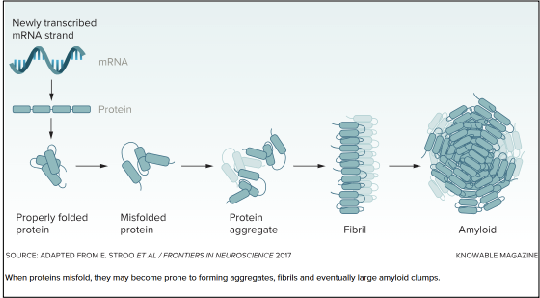
What is amyloidosis?
A group of conditions characterized by the deposition of an extracellular, proteinaceous substance termed amyloid
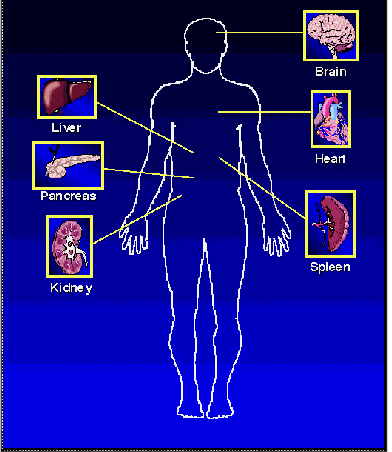
What are the systemic manifestations of amyloidosis?
Death within a few years due to cardiac or renal failure
If amyloidosis is organ limited, what kind of protein is affected
AL
What are the features of organ limited amyloidosis?
Limited to one organ
Infrequent oral features
If amyloidosis is primary and myeloma associated amyloidosis, what kind of protein is affected?
AL- light chain
What are some features of primary and myeloma associated amyloidosis?
Older males
15-20% are due to multiple myeloma
location: eyelid, neck, and lips
Oral: thick lips and macroglossia
Skin: smooth-surfaced, firm, waxy papules and plaques
What type of protein is affected in secondary amyloidosis?
AA- Acute phase reactant protein
What are the features of secondary amyloisosis?
Result of chronic inflammatory process, such as TB, sarcoidosis or osteomyelitis
Spares the heart but affects the liver, kidney, spleen
What protein is affected in hemodialysis-associated amyloidosis?
ABeta-2 Microglobin protein
What features do you see in hemodialysis associated amyloidosis?
Protein isn’t removed by dialysis
Eventually deposits in the bones & joints
What are some features associated with heredofamilial?
Uncommon
Autosomal dominant in Swedish, portuguese, japanese population
Autosomal recessive in mediterranean
May develop congestive heart failure, and renal failure
What protein is affected in heredofamilial amyloidosis?
None
Fissured tongue due to enlargement
Amyloidosis
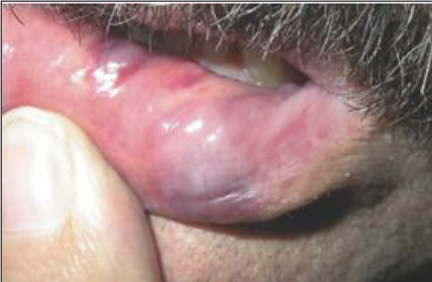
Nodule on lip
Amyloidosis
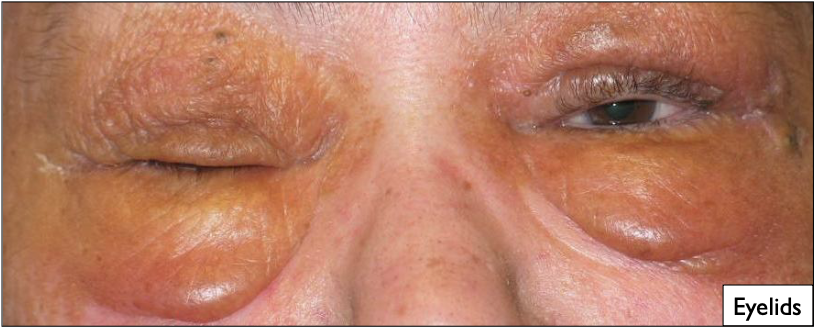
Swelling on eyelids
Amyloidosis
What is Crohn’s Disease
Inflammatory and immunologically mediated condition of unknown cause
What age group do you see those affected by Crohn’s Disease
Teenagers
Where does Crohn’s Disease manifest?
Anywhere along the GI tract
What are the oral implications of Crohn’s Disease?
Oral lesions are significant because they precede the GI lesions 30% of the time
What are some symptoms people that have GI issues in Crohn’s Disease experience?
Abdominal cramping
Diarrhea
Pain
Nausea
Fever
What may develop from Crohn’s Disease?
Weight loss and malnutrition
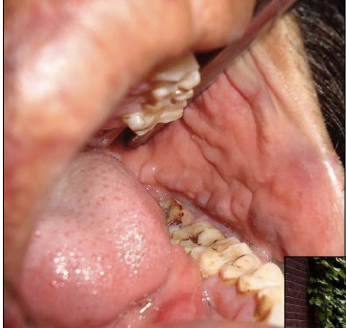
What kind of oral lesions do you see in Crohn’s Disease?
Diffuse, nodular swellings
“Cobblestone appearance” of the oral mucosa
Linear ulcerations of the buccal vestible
Treatment: sulfa drug/ prednisome
Oral lesions clear with treatment of GI disease
What is hypophosphatasia?
Rare metabolic disease
Autosomal recessive
How can you get hypophosphastasia?
A decrease in alkaline phosphatase enzyme

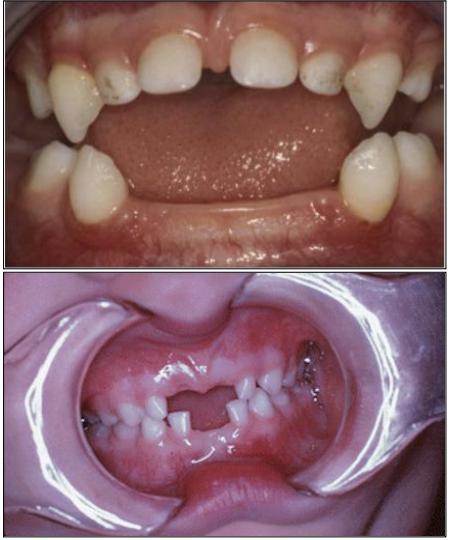
What oral manifestations do you see in hypophosphatasia?
Lack of cementum and bone abnormalities
Premature loss of teeth (especially in lower incisors)
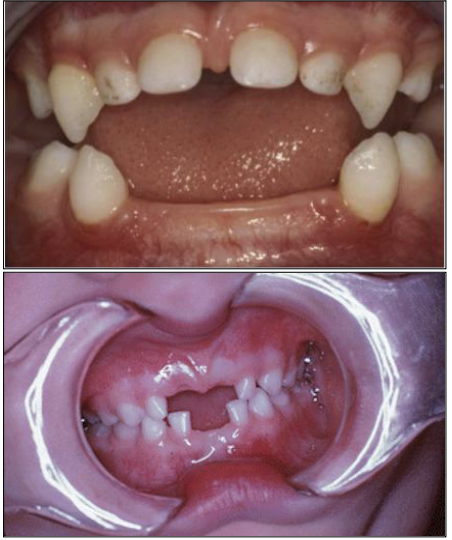
What is another name for Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets?
Hereditary Hypophosphatemia
What is Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets?
X-linked dominant (M>F)
Early age (infancy/ childhood)
Normal vit D
Low serum phosphate (hypophosphatemia)
Low calcium
Clinical: Short bowing lower limbs
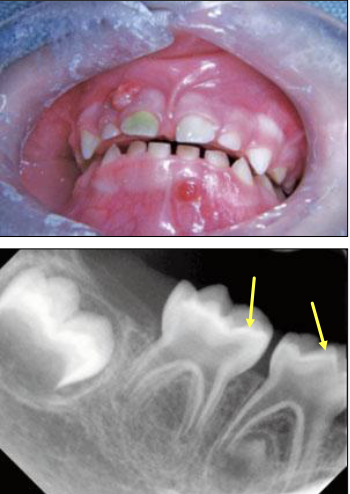
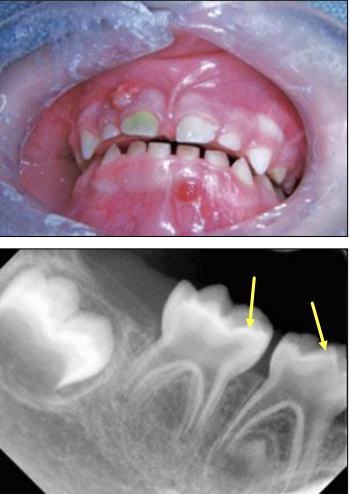
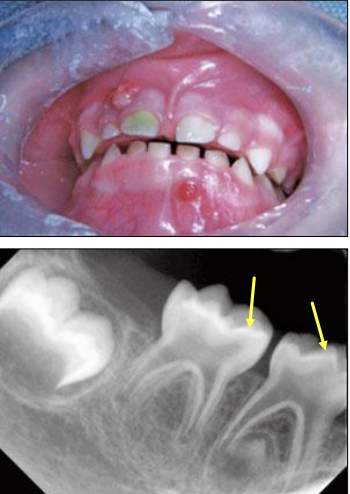
What are some oral manifestations seen in Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets
Large pulp horns extending to DEJ
Multiple non-vital teeth
Absence of caries or trauma
What is Iron Deficiency Anemia?
The most common cause of anemia
What are some clinical features of Iron Deficiency Anemia?
Fatigue, tired, lightheaded, lack of energy
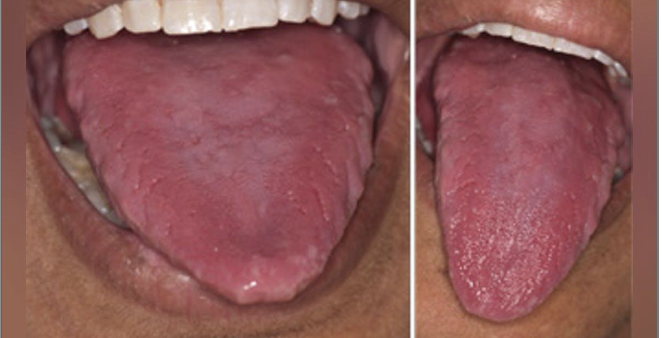
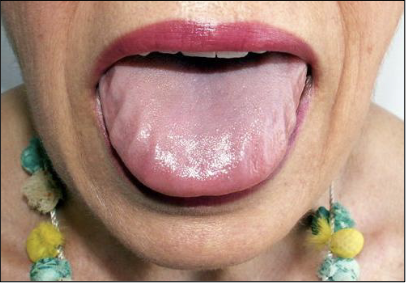
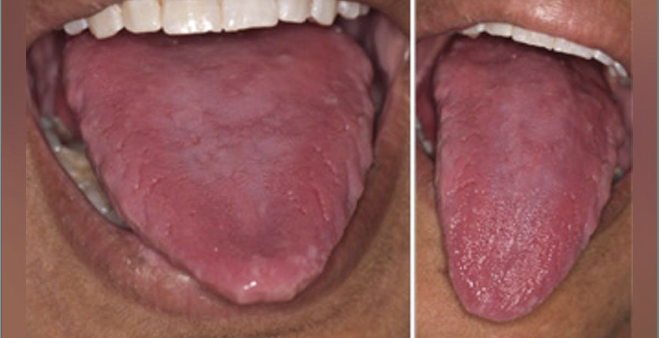
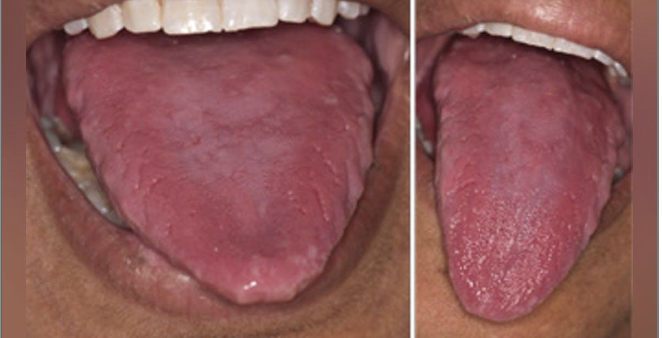
What are some oral features of Iron Deficiency Anemia?
Angular cheilitis
Atrophic tongue
Glossitis
Burning sensation maybe due to candidiasis
What is another name for Plummer-Vinson Syndrome?
Paterson-Kelly syndrome
What is Plummer-Vinson Syndrome (Paterson-Kelly syndrome)?
A rare condition reported in women of Scandinavian or North European background and characterized by:
Iron deficiency anemia
Dysphagia
Atrophic glossitis
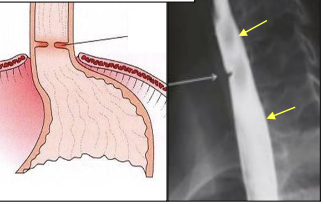
Esophageal webs
Koilonychia (spoon like nails)
Premalignant and associated with oral and esophageal SCC
What is Koilonycha
Spoon like nails
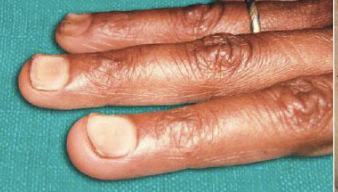
Glossitis
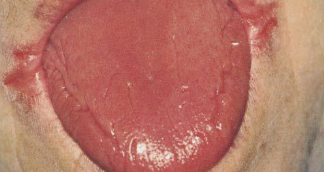
Esophageal webs