AP Biology Unit 2
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Terms for AP Biology Unit 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Eukaryotic Cell
Nucleus
Membrane-Bound Organelles
Plants & Animals
Large (10-100um)
Multi. & Uni. Cellular
Linear DNA
Prokaryotic Cells
No nucleus
No membrane-bound organelles
Bacteria
Small (0.1-0.5um)
Only unicellular
Circular DNA
Div. by Binary Fission
No cytoskeleton
Cytoplasm
Both Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
Cell Membrane
Div. by Mitosis
Has DNA
Has ribosomes
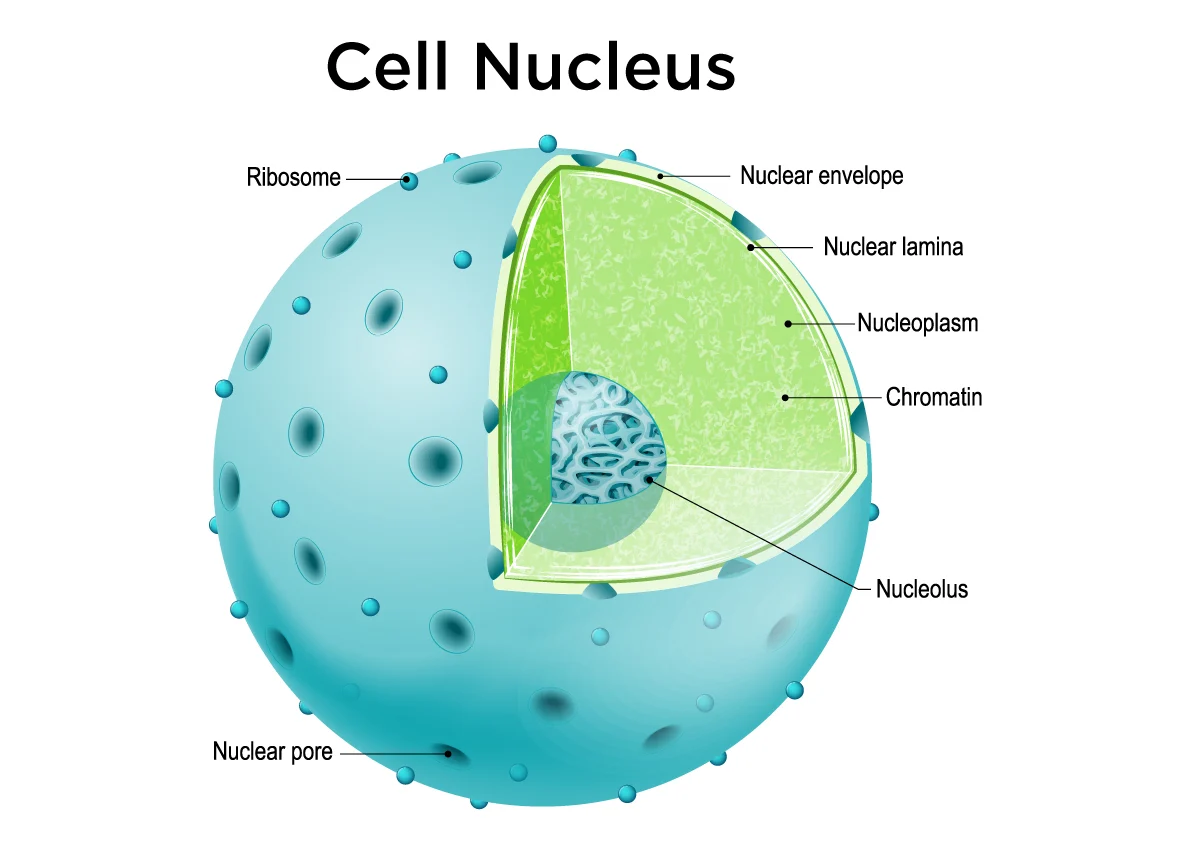
Nucleus
Contains genetic information
Eukaryotic
Plants & animals
Ribosomes
Synthesizes proteins
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic
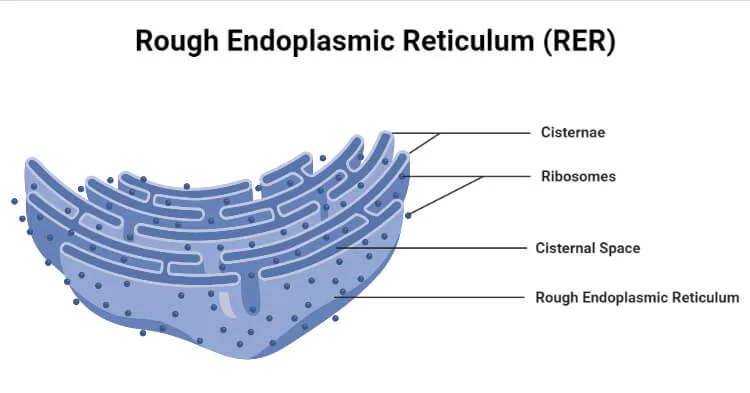
Rough ER
Produces proteins; important to detoxify foreign bodies in cell
Eukaryotic
Plants & Animals
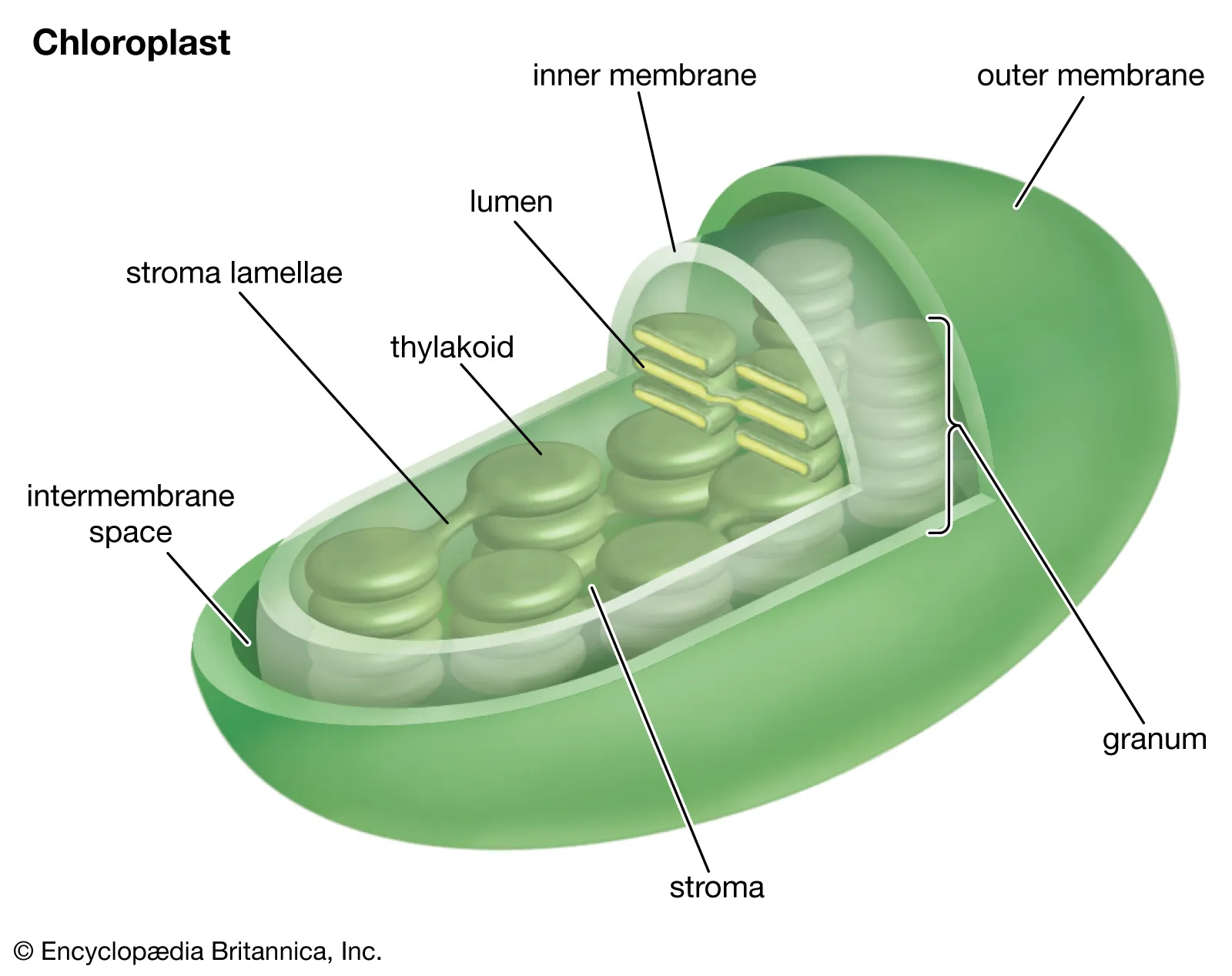
Smooth ER
Synthesizes lipids and steroids; helps detoxification
Eukaryotic
Plants & Animals
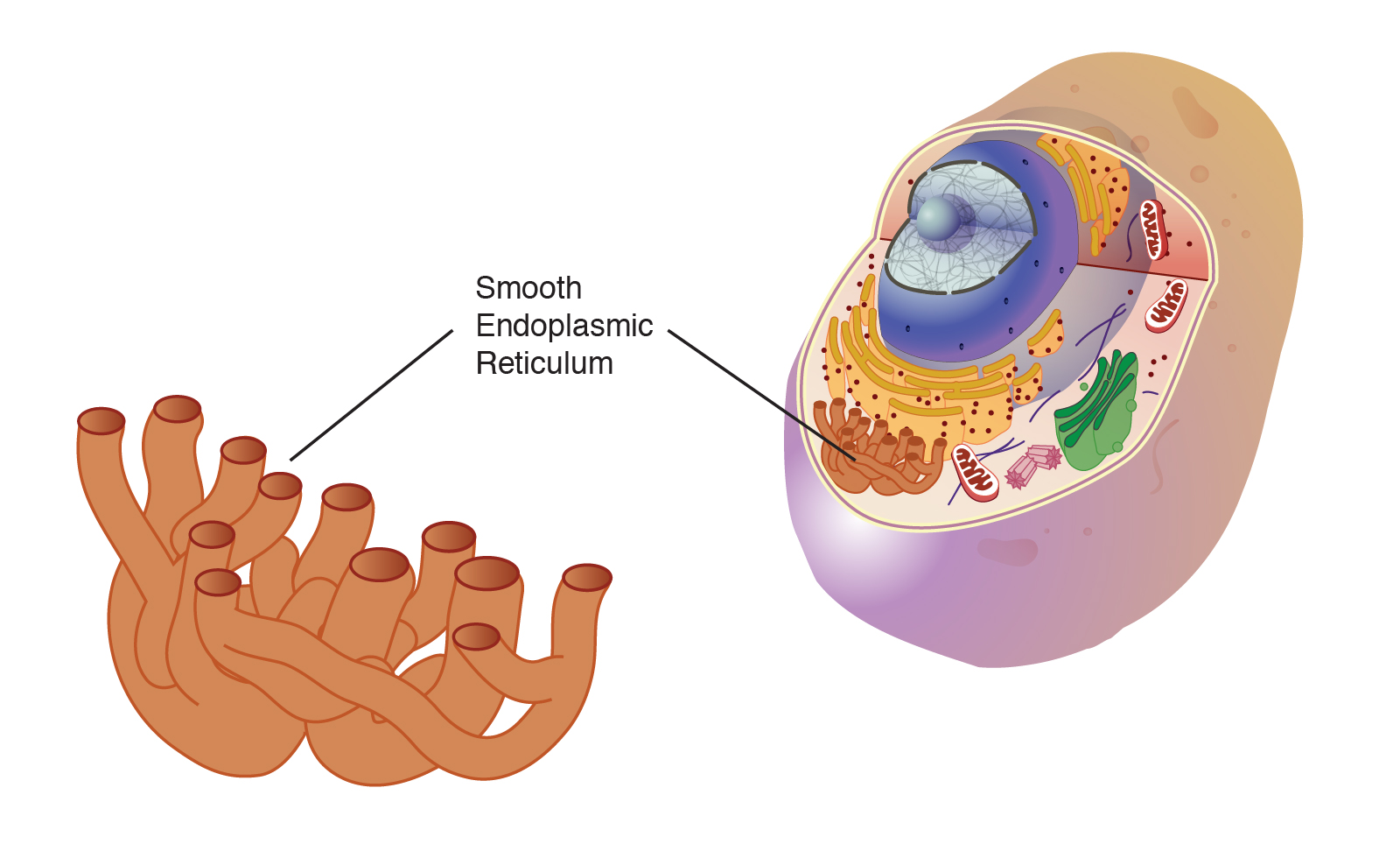
Golgi Apparatus
Proteins go from the ER to be packaged, then sent to other parts of the cell; modifies proteins and lipids
Eukaryotic
Plants & Animals
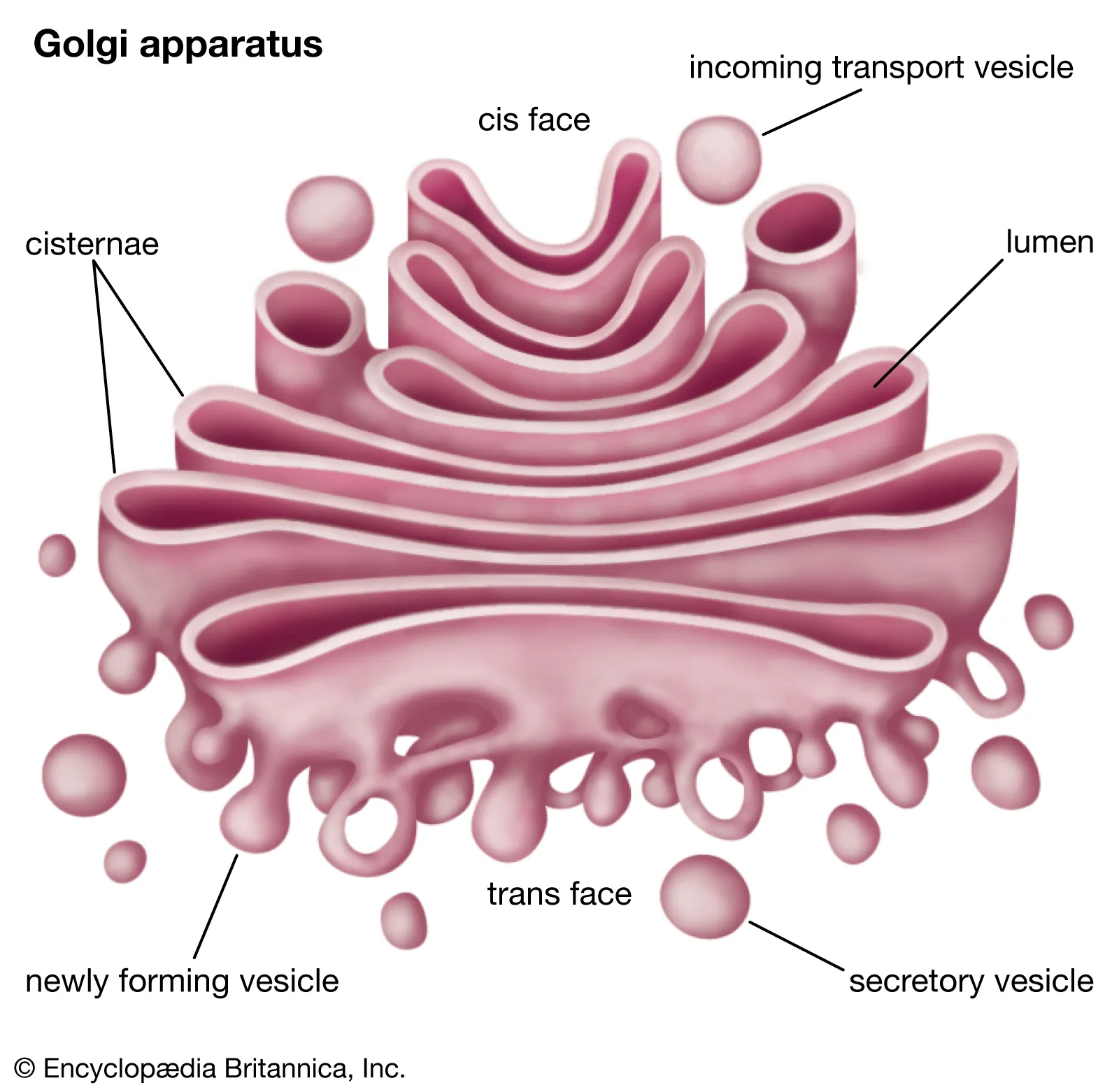
Lysosome
Breaks down/digests macromolecules, repairs the cell membrane, and responds to foreign substances within the cell
Eukaryotic
Plants & Animals
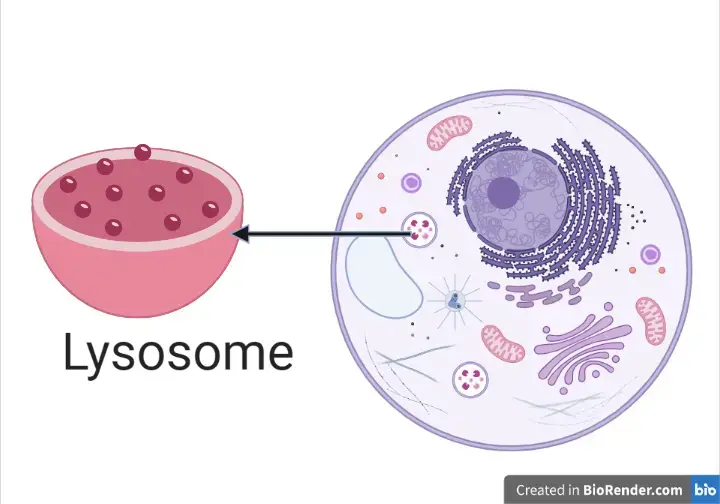
Chloroplast
Converts sun energy into oxygen and carbohydrates; carries out photosynthesis
Eukaryotic
Plants & Algae
Mitochondria
Converting glucose into ATP as energy for the cell
Eukaryotic
Plants & Animals
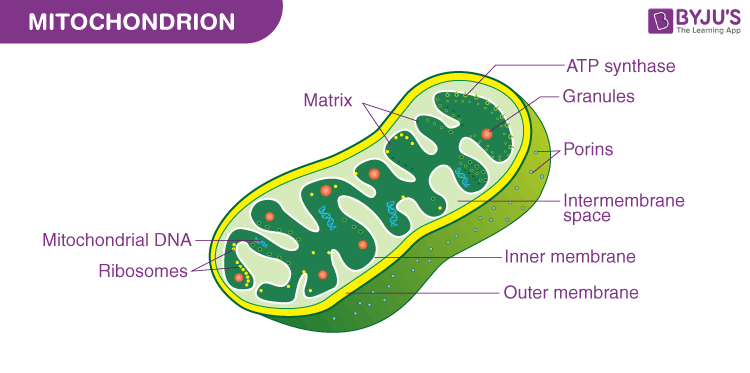
Cell Membrane
Controls what enters and exits the cell
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic
Cell Wall
Structure and protection of cell
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic
Vacuole
Stores food, water, and waste; helps remove waste
Eukaryotic
Flagellum
Bacterial locomotion, makes cell move
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic
Animals
Compartmentalization
Allows cells to locate metabolic processes (create separate mini-environment within cells)
Imagine a house with rooms, dividing each process into sections so that they don’t interact and interfere with one another
Compartmentalization Ex. Lysosome
Lysosome membrane allows inside to become acidic and break things down without harming the rest of the cell
Compartmentalization Ex. Mitochondria
Mitochondria’s double membrane allows for 2 different environments; allows for ATP to be made on inner membrane
Endosymbiotic Theory
Organelles (mitochondria & chloroplasts) were once free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by other cells
Origin of organelles
Enydosymbiotic Theory Evidence
Double membranes
Own circular DNA
Makes own ribosomes
Only made by other organelles
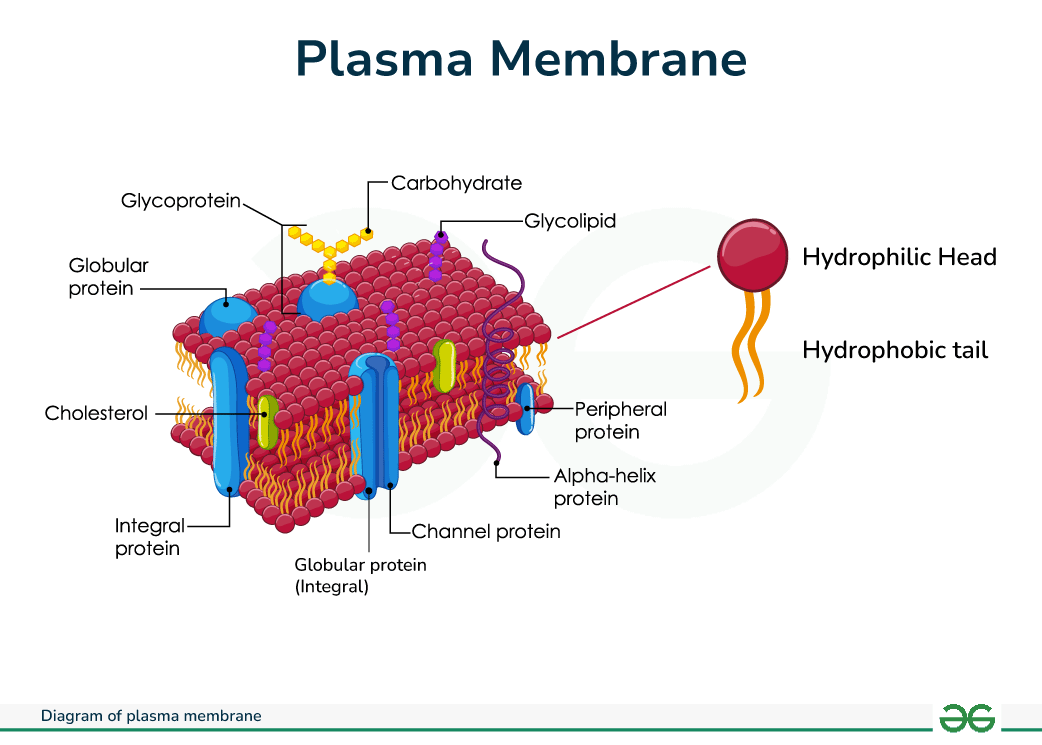
Plasma Membrane
Peripheral Proteins
Integral Proteins
Channel Proteins
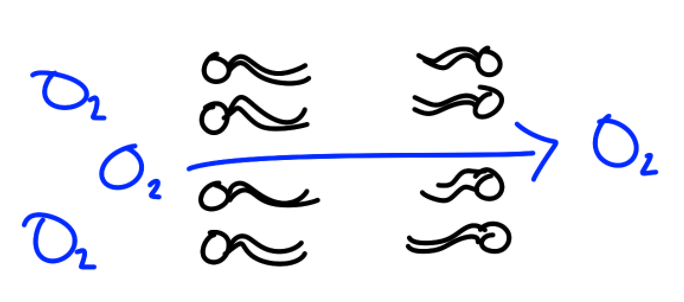
Passive Transport
Doesn’t need energy
High to Low Concentration
Down the gradient
Simple Diffusion
Doesn’t need transport/channel proteins
Particles go straight through the membrane
Small, non-polar (CO2 & O2)
Medium non-polar and small polar; sometimes very slowly
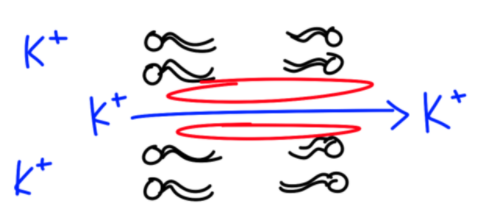
Facilitated Diffusion
Do need transport proteins
Large, non-polar
Polar (H2O or glucose)
Charged ions (Na+ K+ Cl-)
Aquaporin - H2O transport protein
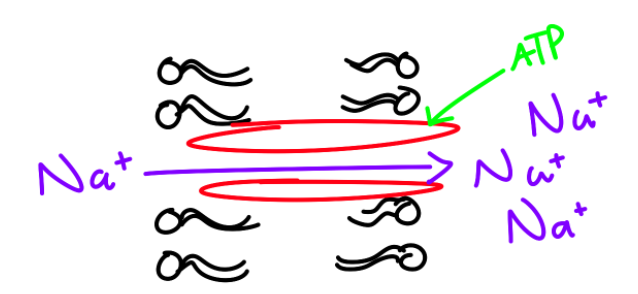
Active Transport
Needs energy
Low to High Concentration
Up the gradient
General Transport
ATP’s energy source
Needs transport proteins
Large, non=polar
Polar
Charged
Bulk Transport
ATP’s energy source
Move large solids or liquids
Endocytosis & Exocytosis
Endocytosis
Phagocytosis: large solids
Pinocytosis: large amounts of liquid with nutrients
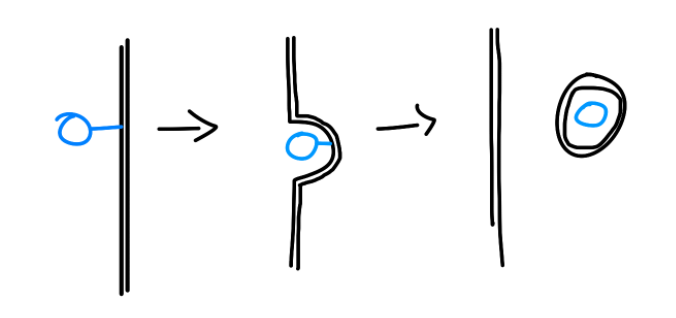
Exocytosis
Macromolecules and waste
Reverse of Endocytosis
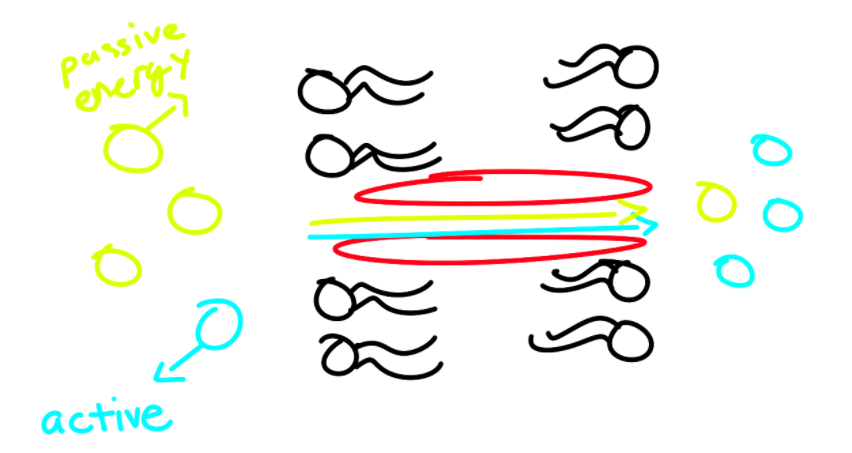
Symport Transport
No ATP
2 particles that move in same direction
1 particle moves passively down gradient
Energy source
Other particle moves actively
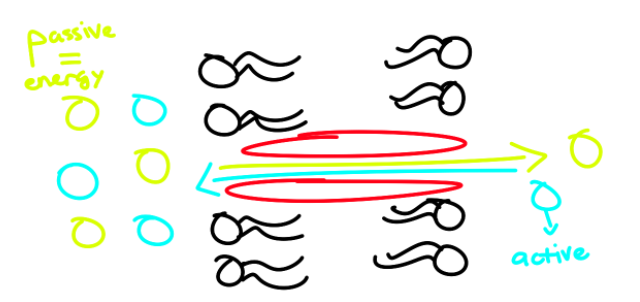
Antiport Transport
2 particles that move in opposite direction
1 particle moves passively
Energy source
Other particle moves actively
Small Non-Polar Molecules
O2, CO2, N2
Small Uncharged Non-Polar Molecules
H2O, NH3, Glycerol
Large Uncharged Polar Molecules
Glucose, Sucrose
Ions
Na+, K+, Cl-
Osmoregulation and Water Potential
Water moves from…
Low to high solute concentration
High to low water potential
Low to high osmolarity
Tonicity
The capability of a solution to modify the volume of cells by altering their water content
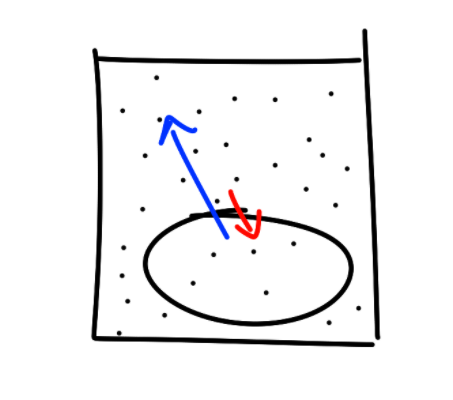
Hypotonic Cell
Cell has lower solute concentration
Net H2O moves out
Animal cell shrivels
Plant cell plasmolysis
Contraction
Isotonic Cell
Equal solute concentration in & out of cell
No net H2O movement
Cell remains the same
Hypertonic
Cell has higher solute concentration
Net H2O into cell
Animal cell swells
Plant cell turgid