Anatomy and Physiology Lab 11: Cranial Nerves, Eye, and Ear
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
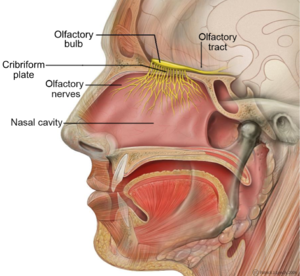
CN I
Olfactory nerve
SENSORY
olfactory bulb on the end
sits on cribiform plate
When we are sick, CN I can become compressed which is why we can loose our sense of smell
CN II
Optic nerve
SENSORY
passes through optic canal
connects to eye
one optic nerve per eye
the two optic nerves are connected by the optic chiasm
CN III
Oculomotor
MOVEMENT
passes through superior orbital fissure
eye movement
constrict pupil (parasympathetic)
CN IV
Trochlear
MOTOR
passes through superior orbital fissure
1 specific eye muscle
can cause double vision or eye misalignment if damaged
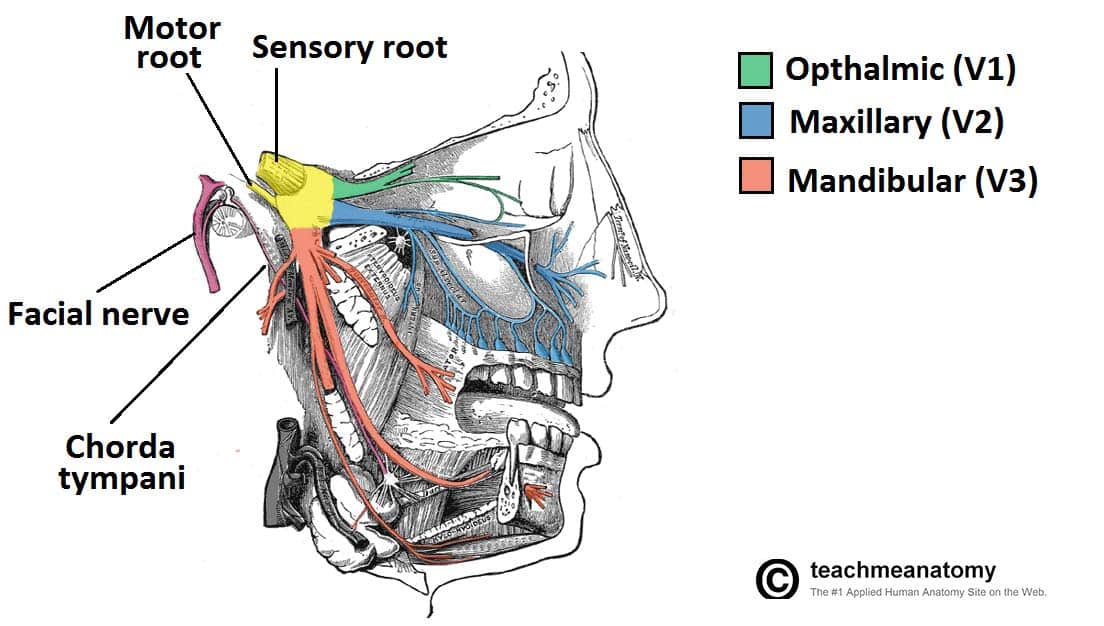
CN V
Trigeminal
3 branches
Ophthalmic: SENSORY to superior face; passes thru superior orbital fissure
Maxillary: SENSORY to middle face; passes through foramen rotundum
Mandibular: MOTOR and SENSORY to inferior face/jawline (opens and closes jaw); passes through foramen ovale
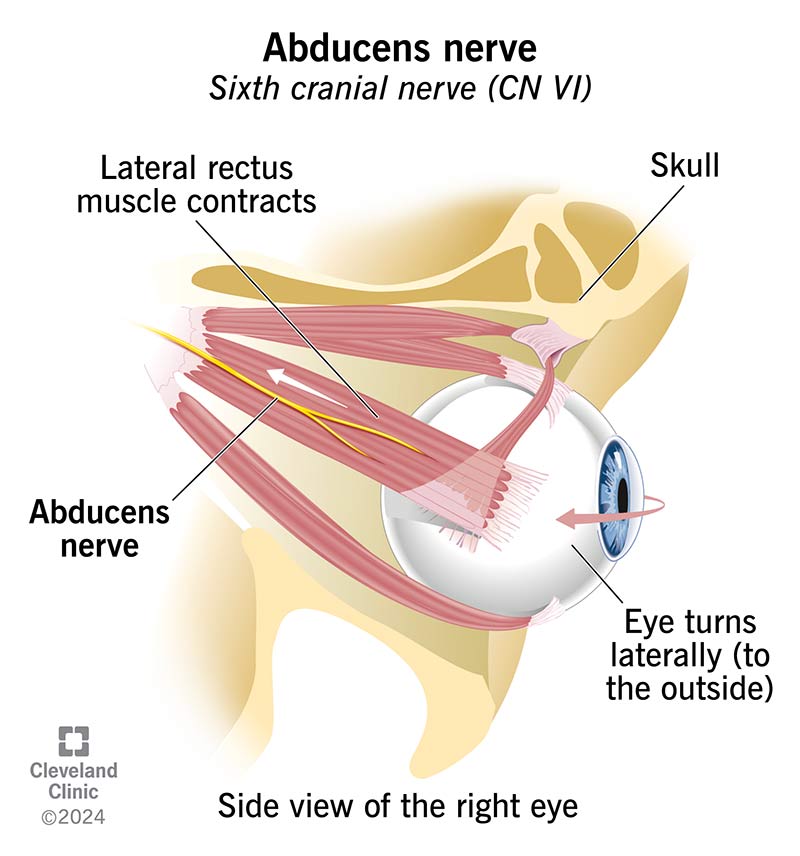
CN VI
Abducens
MOTOR
passes through Superior orbital fissure
abducts eye (move one specific eye muscle)
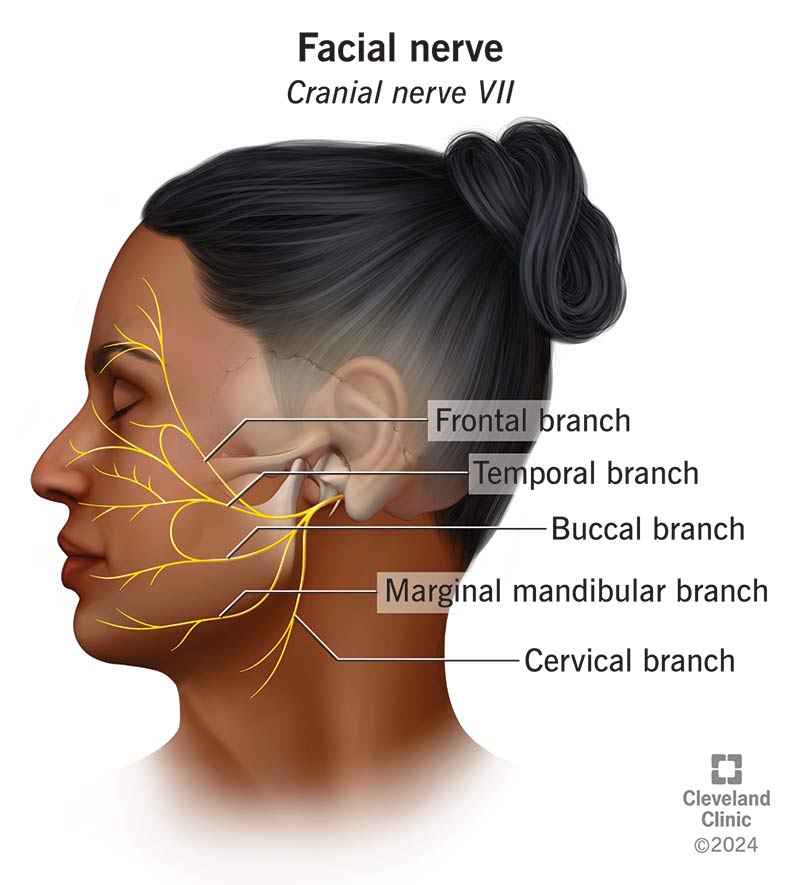
CN VII
Facial
MOTOR and SENSORY
passes through internal acuoustic meatus
facial expressions and blinking
salivation
taste to front 2/3 of tongue
sensory to ear
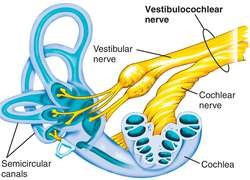
CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear
SENSORY (Balance and Hearing)
passes through internal acoustic meatus
stays in inner ear
1 branch attaches to cochlea
1 branch attaches to semicircular canals
CN IX
Glossopharyngeal
MOTOR and SENSORY
passes through jugular foramen
swallowing, salivation
taste of back 1/3 of tongue
sensory to middle ear, auditory tube, oralpharynx
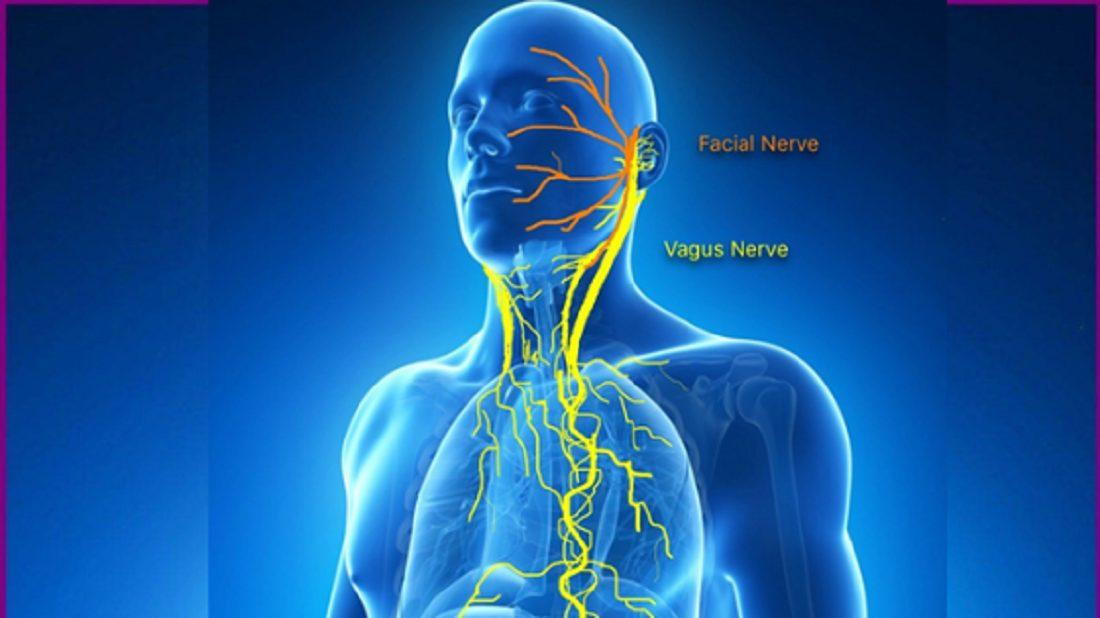
CN X
Vagus
MOTOR and SENSORY
passes through jugular foramen
Motor: swallowing, decrease heart rate and respiration
General sensory: ear, thoracic, and abdominal organs
Special sensory: taste of epiglottis (back of throat)
CN XI
Accessory
MOTOR
passes through jugular foramen
neck and shoulder movement
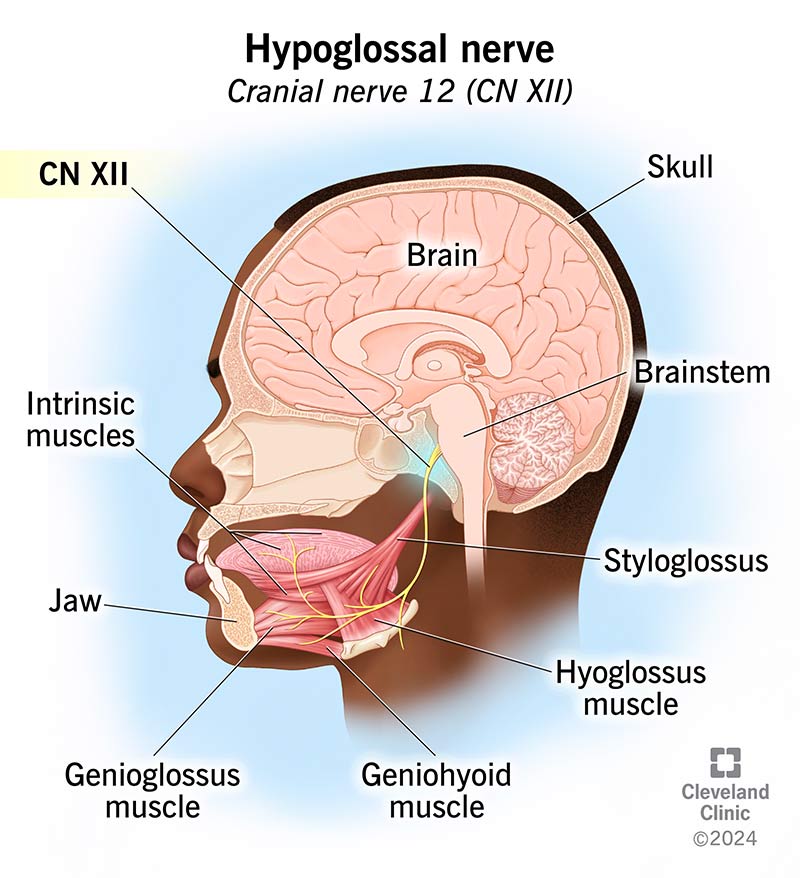
CN XII
Hypoglossal
MOTOR
passes through hypoglossal canal
tongue movement
O.O.O.T.T.A.F.V.G.V.A.H
Some say marry money, but my brother says big brain matter more.
***figure out a way to remember order of cranial nerves
What are these?
orbits/ eye sockets
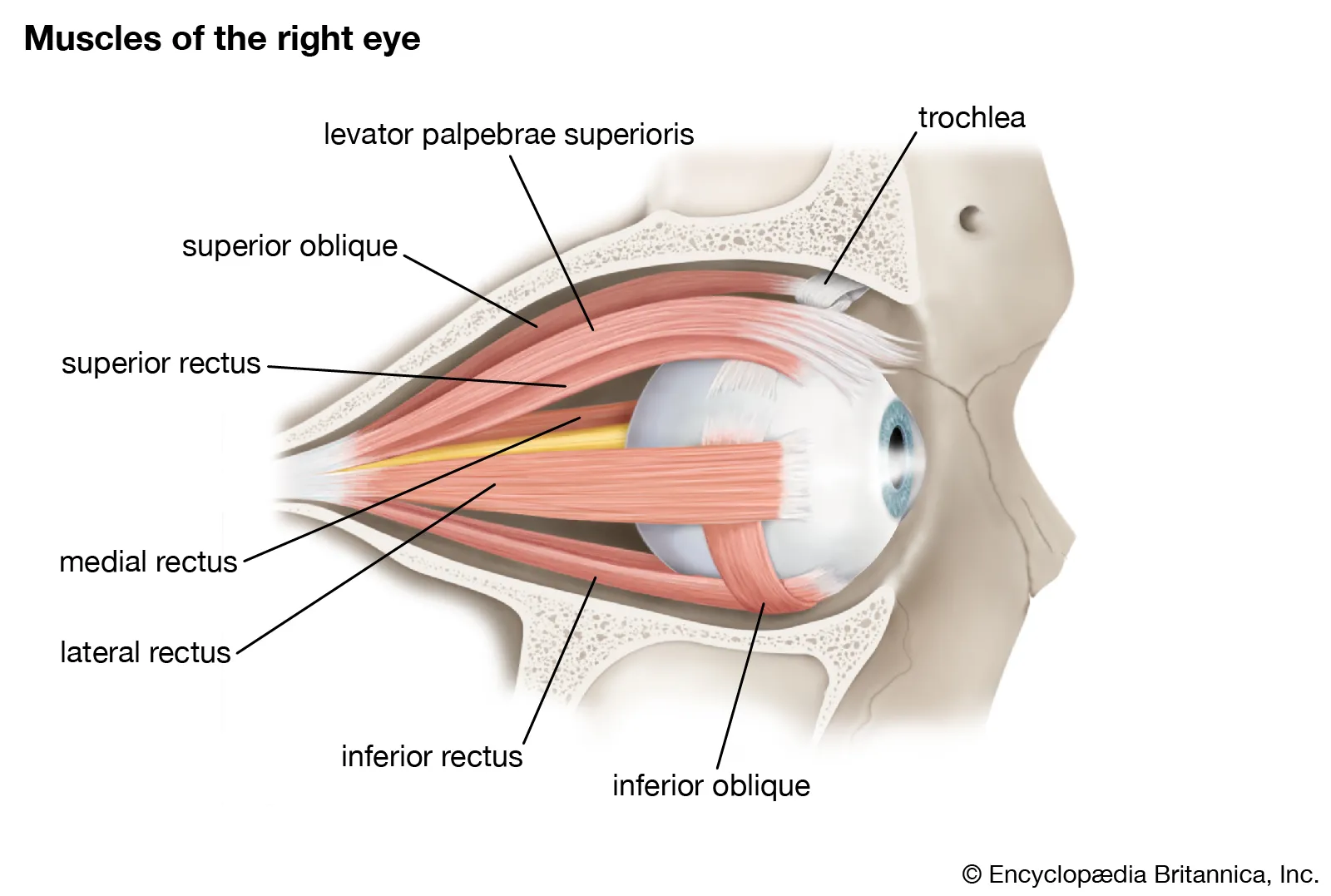
What are these?
extraocular muscles
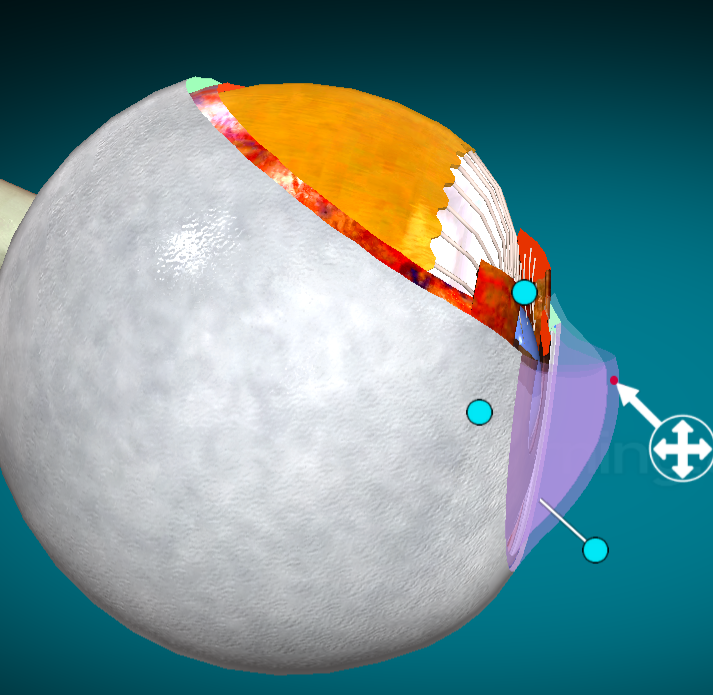
What layer of the eye is this?
Cornea
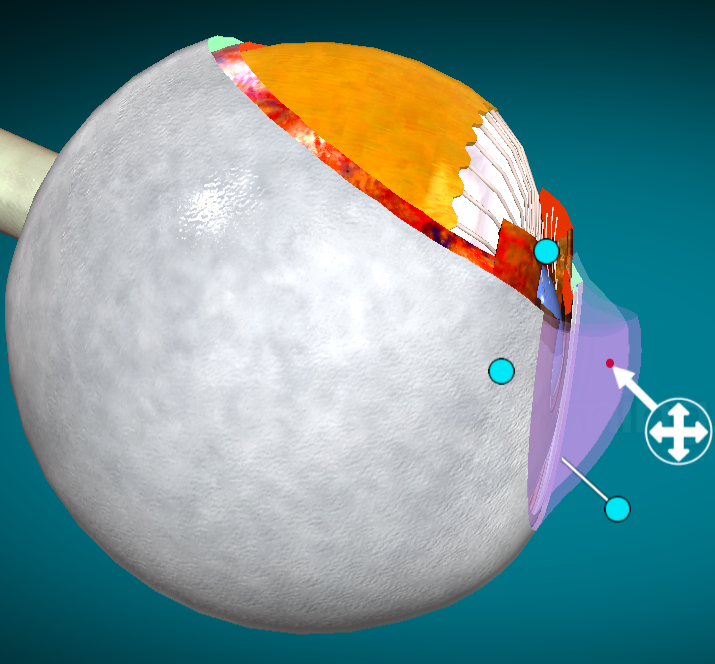
Where is the aqueous humor?
Right under the cornea and on top of the iris (?). It helps keep the shape of the cornea.
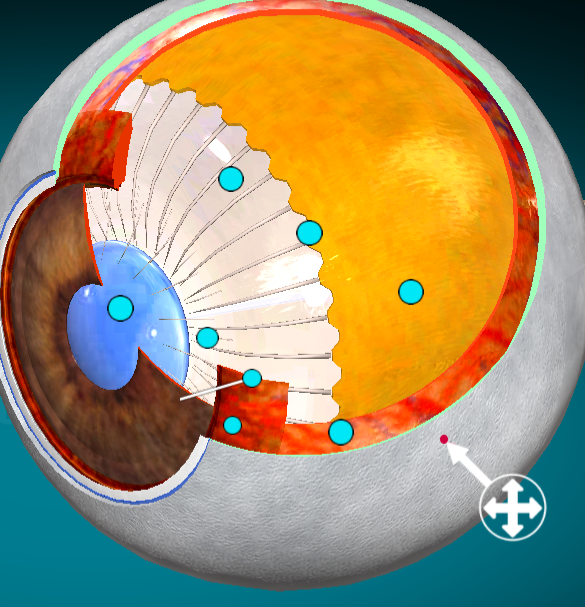
What layer of the eye is this?
Sclera (whites of the eye)
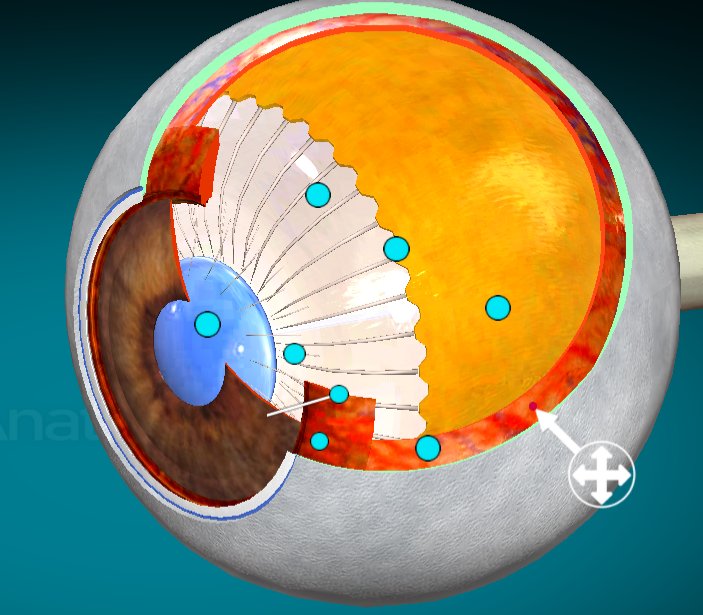
What layer of the eyes is this?
Choroid
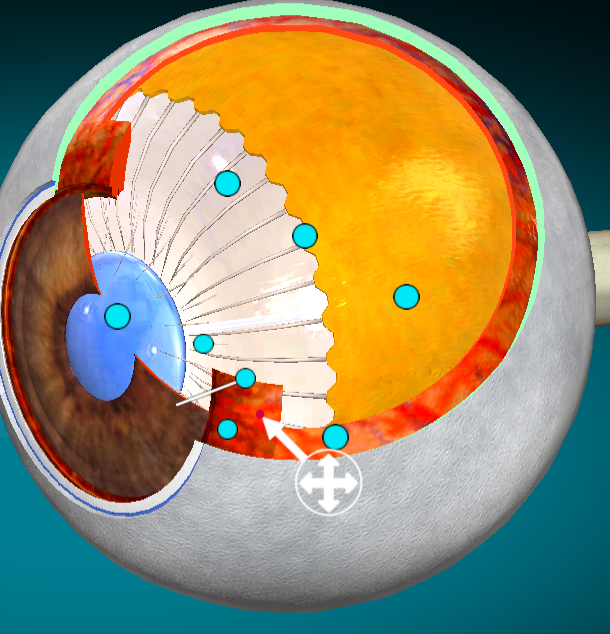
What layer of the eye is this?
Ciliary body (sits on top of the iris)
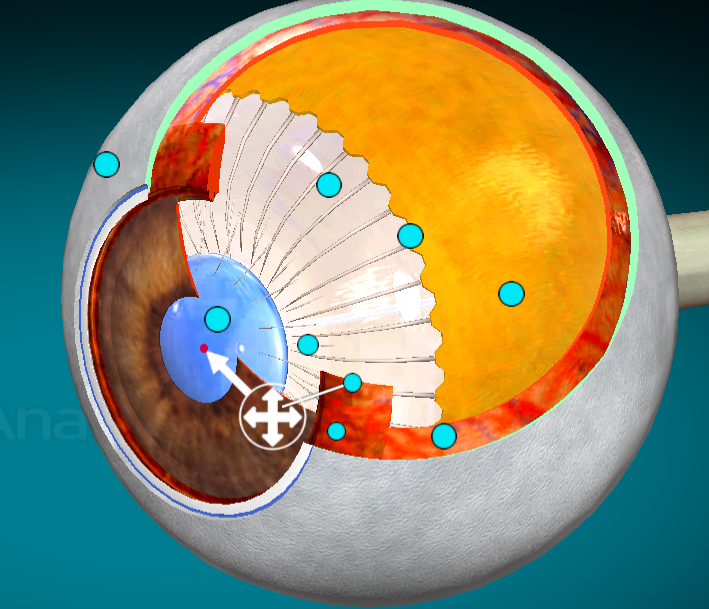
What is this?
Lens
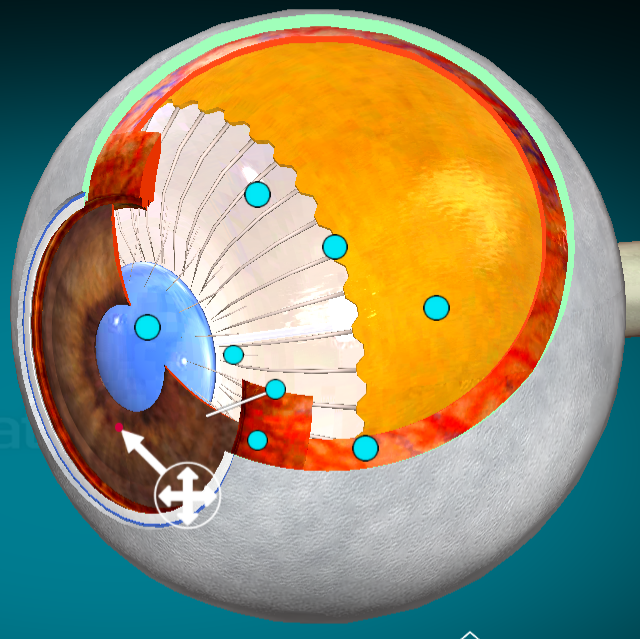
What layer of the eye is this?
Iris
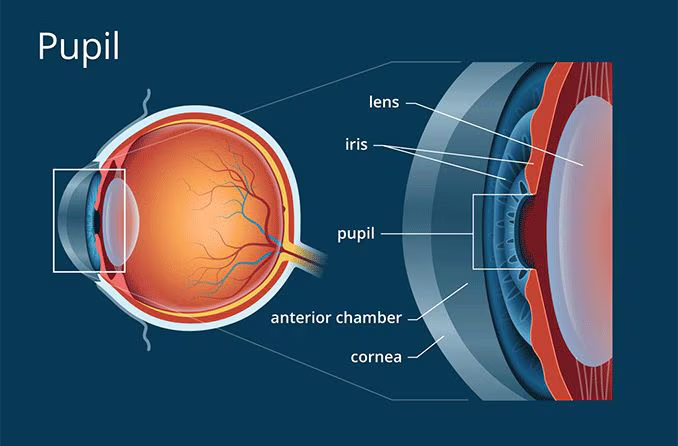
what part of the eye is this?
pupil
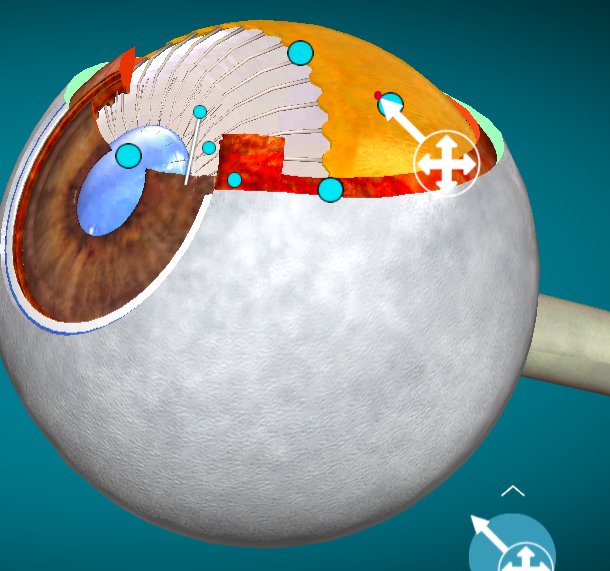
What layer of the eye is this?
Retina
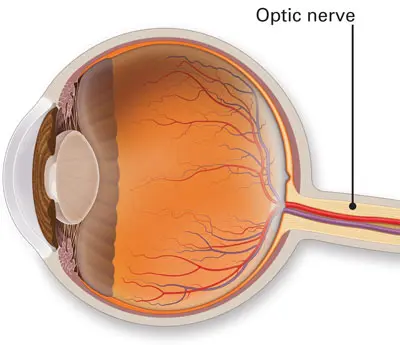
Where is the optic disk?
In the back of the eye, on the inside. It is where the optic nerve connects to the eye. There is a blind spot in that location because the optic disk has no rods or cones to detect light.
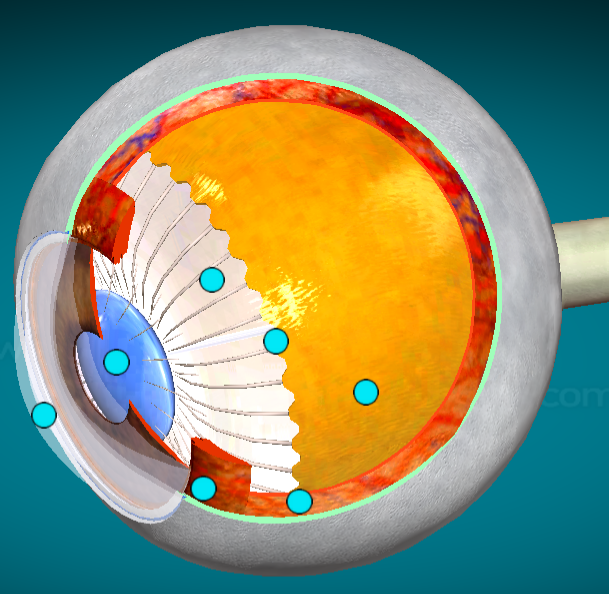
What is the order of the layers of the eye from superficial to deep?
1.) cornea
2.) aqueous humor
3.) sclera
4.) iris/ciliary body (surrounds iris)
5.) choroid
6.) retina
7.) lens
8.) vitreous humor
Anterior segment
Posterior segment
Middle ear
Inner ear
Auricle
External auditory canal
Tympanic membrane
aka ear drum
Malleolus
Incus
Stapes
Auditory tube
Vestibule
Cochlea
Semicircular canal