pulse sequence
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
mri scan principles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
A T2 weighted image will have an echo time (TE) in the range of:
A. 25 - 40 ms
B. 80 - 120 ms
C. 1600 - 2200 ms
D. 2000 - 6000 ms
B. 80 - 120 ms
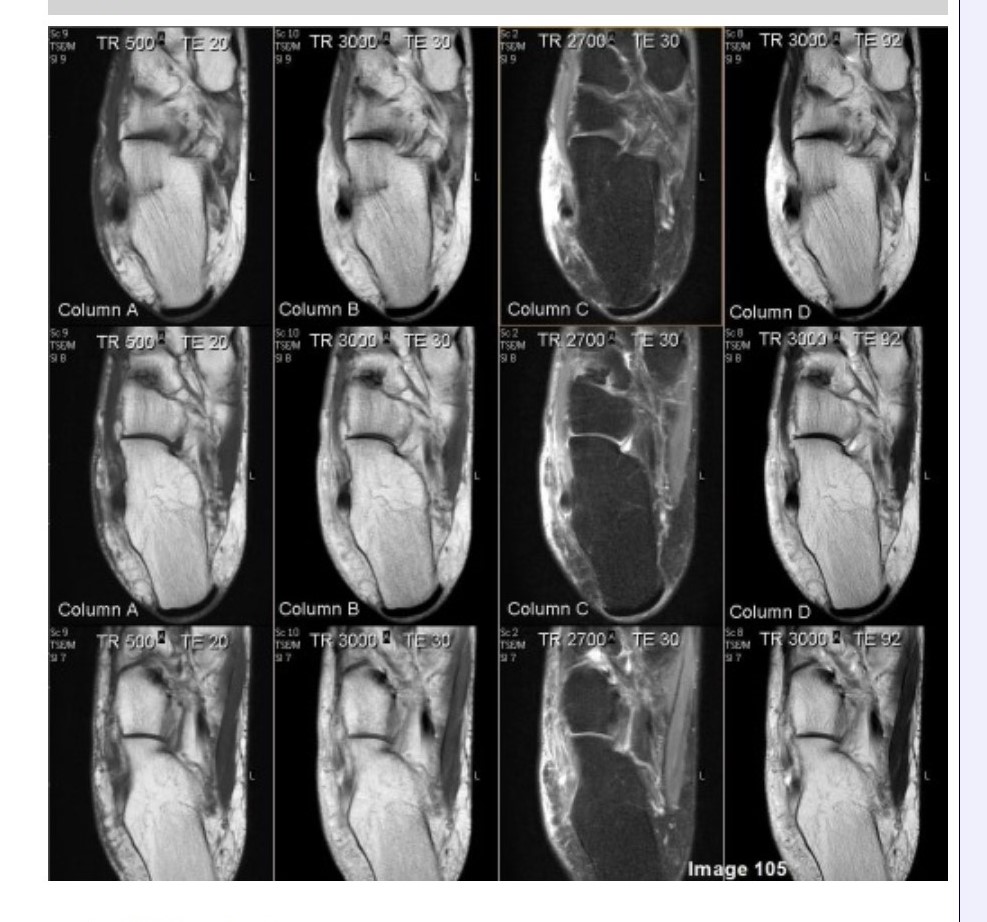
Column D in Image 105 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. Proton density with fat suppression
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
C. T2 weighted
Tissues with _______ are bright on T1 weighted spin echo scans and tissues with _________ are bright on T2 weighted spin echo scans.
A. short T1 times; short T2 times
B. short T1 times; long T2 times
C. long T1 times; short T2 times
D. long T1 times; long T2 times
B. short T1 times; long T2 times
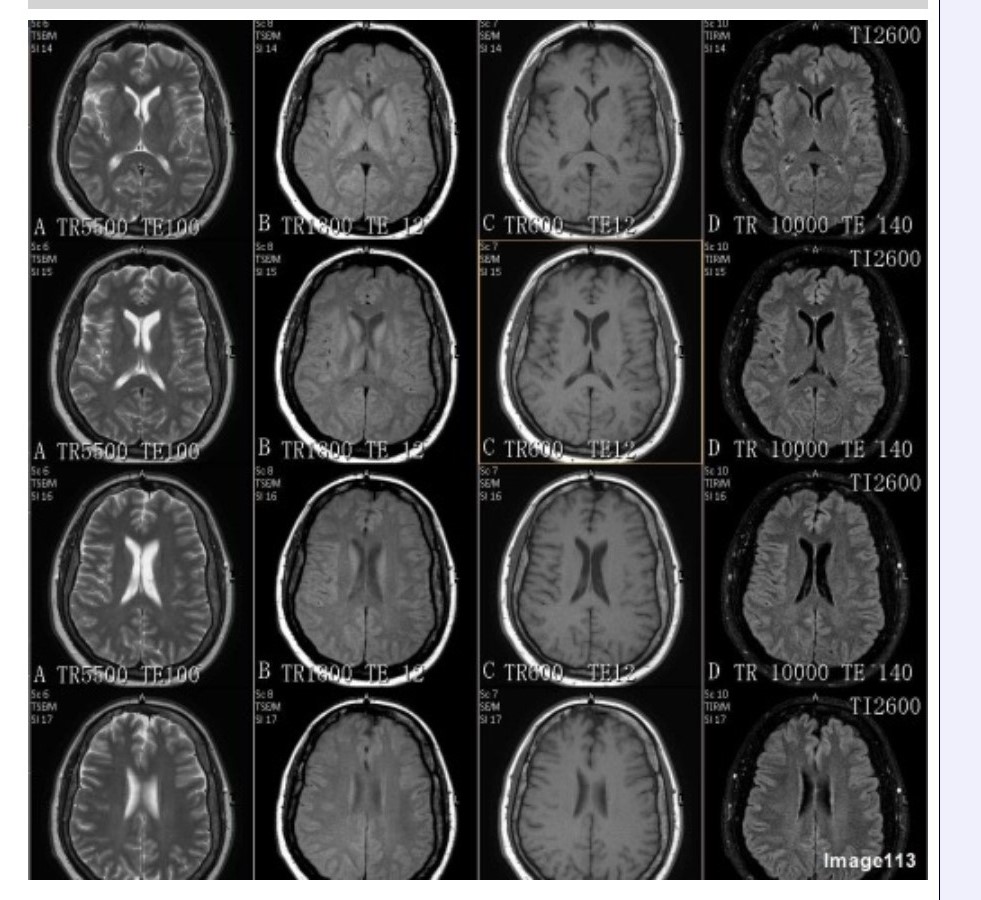
Which column in Image 113 would be best suited for evaluation of demyelinating disease?
A. Column A
B. Column B
C. Column C
D. Column D
D. Column D
A T2 FLAIR sequence is best utilized for evaluation of white matter lesions / demyelinating disease.
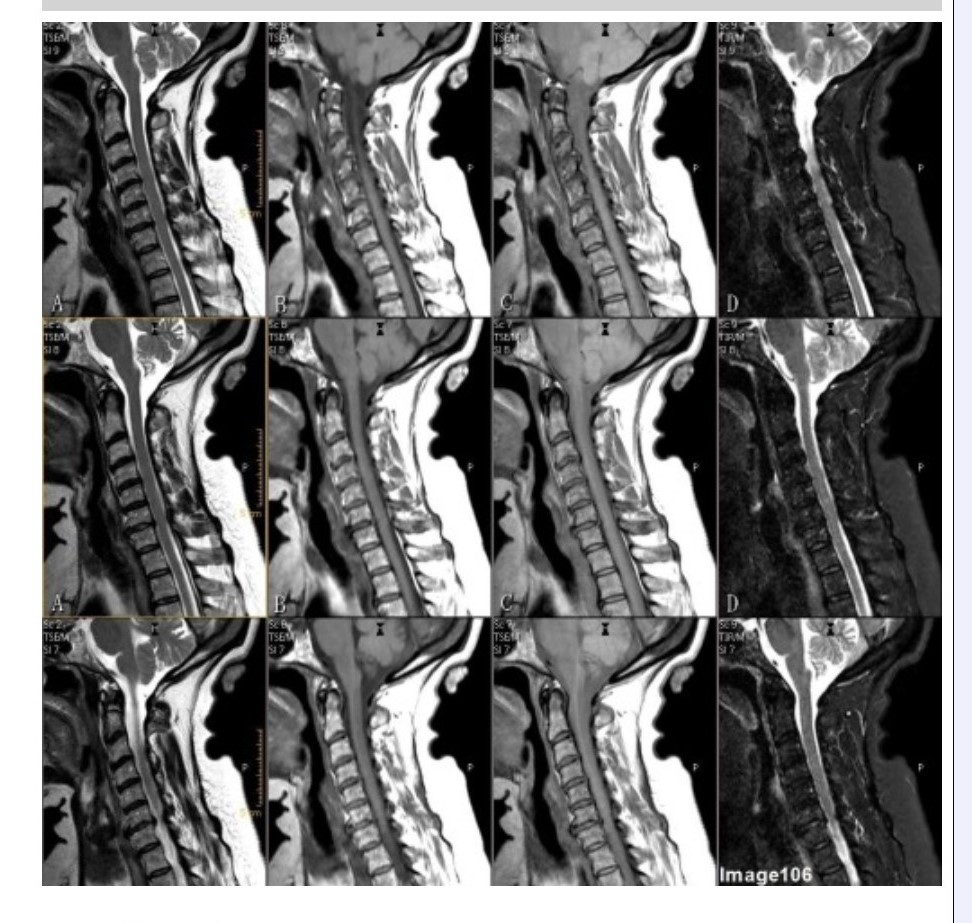
Column B in Image 106 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
B. T1 weighted
Water is dark and fat is bright in:
A. T1 weighted images
B. T2 weighted images
C. STIR
D. T2* gradient echo
A. T1 weighted images
As the TR increases the amount of T1 weighted contrast ___________.
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Is nulled
D. Is unchanged
B. Decreases
All of the following are true EXCEPT:
A. Inversion recovery --- 180° RF followed by 90°RF
B. Gradient echo --- 90° RF followed by 180° RF
C. Fast spin echo --- 90° RF followed by train of 180° RF pulses
D. Spin echo --- 90° RF followed by 180° RF
B. Gradient echo --- 90° RF followed by 180° RF
Gradient echo lacks 180° RF pulses
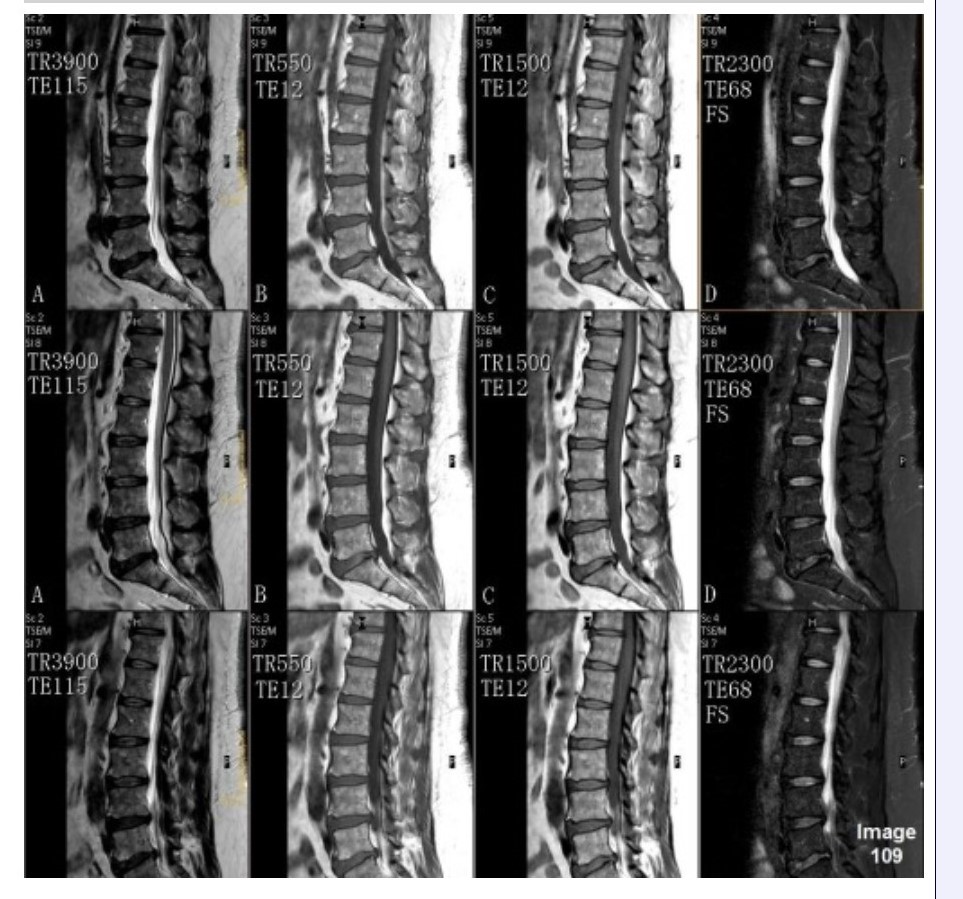
Column C in Image 109 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
A. Proton density
All of the following are examples of EXTRINSIC contrast parameters EXCEPT:
A. TR
B. TE
C. T1 time
D. Flip angle
E. TI
C. T1 time
Extrinsic contrast parameters are those that the MR technologist can adjust to alter the image.
What determines the amount of T2 weighting in an image?
A. TR
B. TE
C. Flip Angle
D. Matrix
B. TE
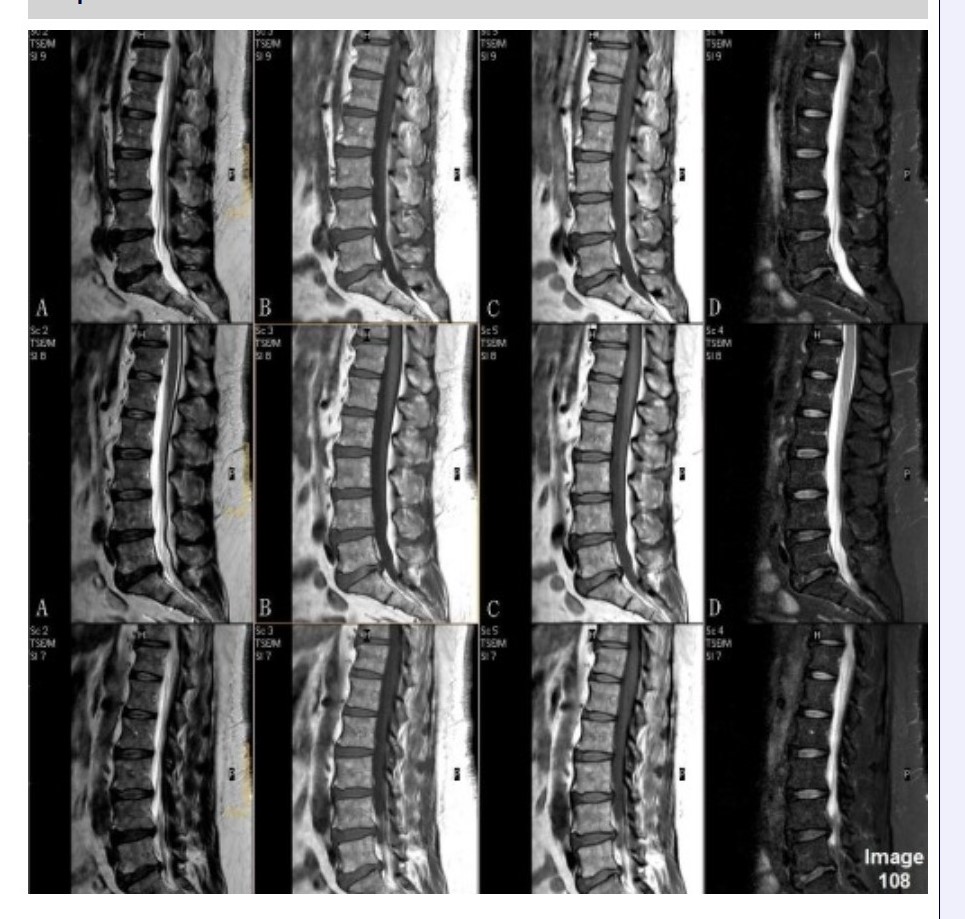
Column B in Image 108 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
B. T1 weighted
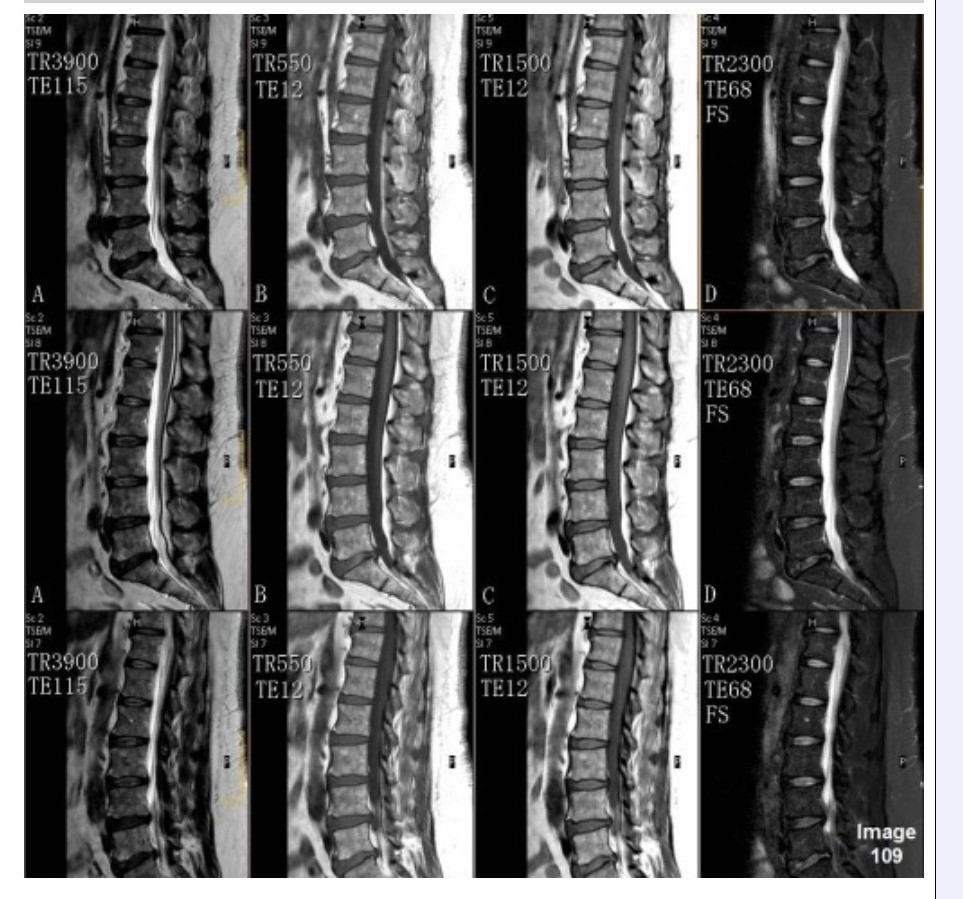
Column A in Image 109 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
C. T2 weighted
What determines the amount of T1 weighting in an image?
A. TR
B. TE
C. Flip Angle
D. Matrix
A. TR
Increasing the TE in a spin echo pulse sequence:
A. Has no effect on image contrast
B. Enables more T1 information in the image
C. Enables more T2 information in the image
D. Decreases the T2 information in the image
C.Enables more T2 information in the image
Enabling Driven Equilibrium will enable the operator to:
A. Utilize additional acquisitions/packages
B. Reduce TR and preserve contrast
C. Suppress the signal from fat
D. Eliminate wrap around (aliasing) artifacts
B. Reduce TR and preserve contrast
In an inversion recovery sequence, image contrast is controlled by:
A. TR
B. TE
C. TI
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
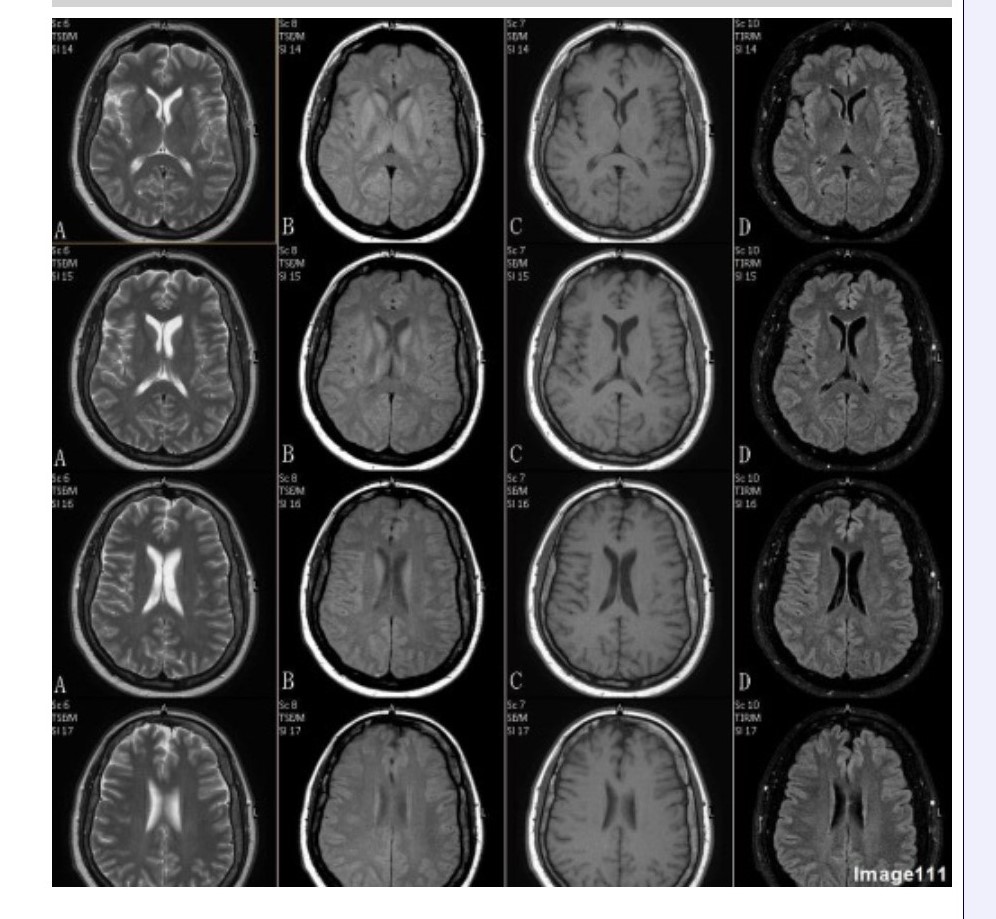
Column B in Image 111 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
F. T2* gradient echo
A. Proton density
A proton density weighted image will have a repetition time (TR) in the range of:
A. 25 - 40 ms
B. 80 - 120 ms
C. 350 - 700 ms
D. 1600 - 4000 ms
D. 1600 - 4000 ms
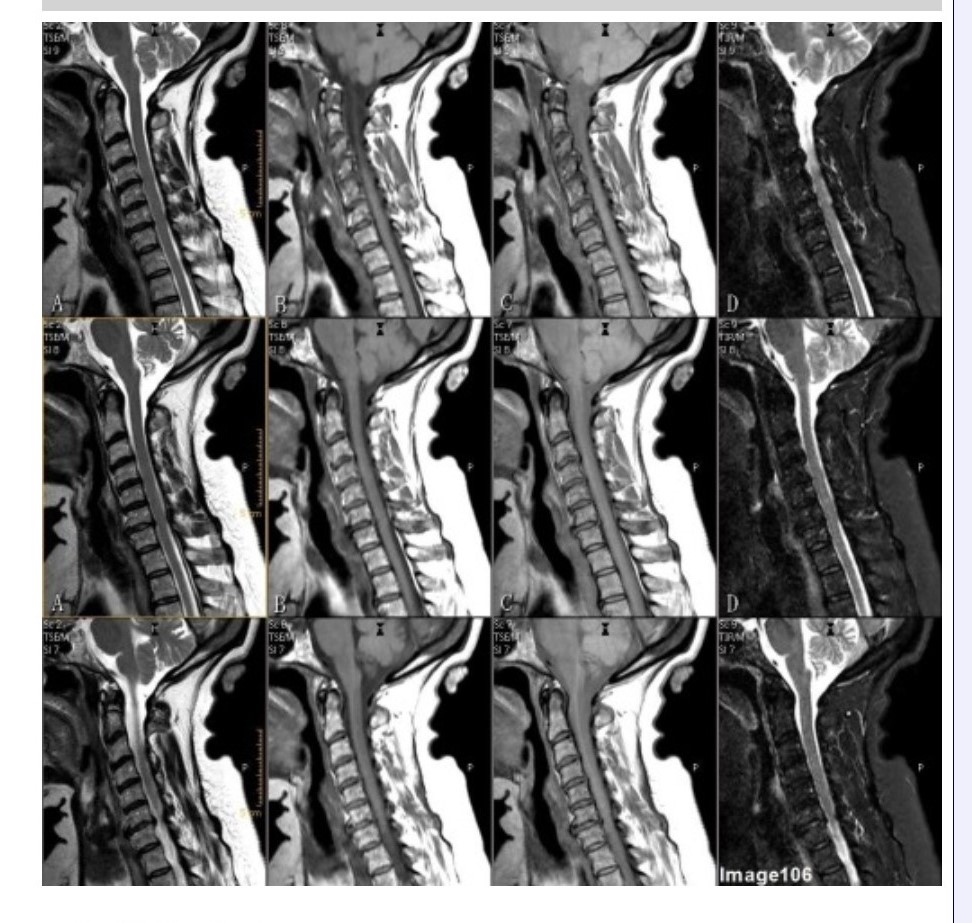
Column D in Image 106 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
E. STIR
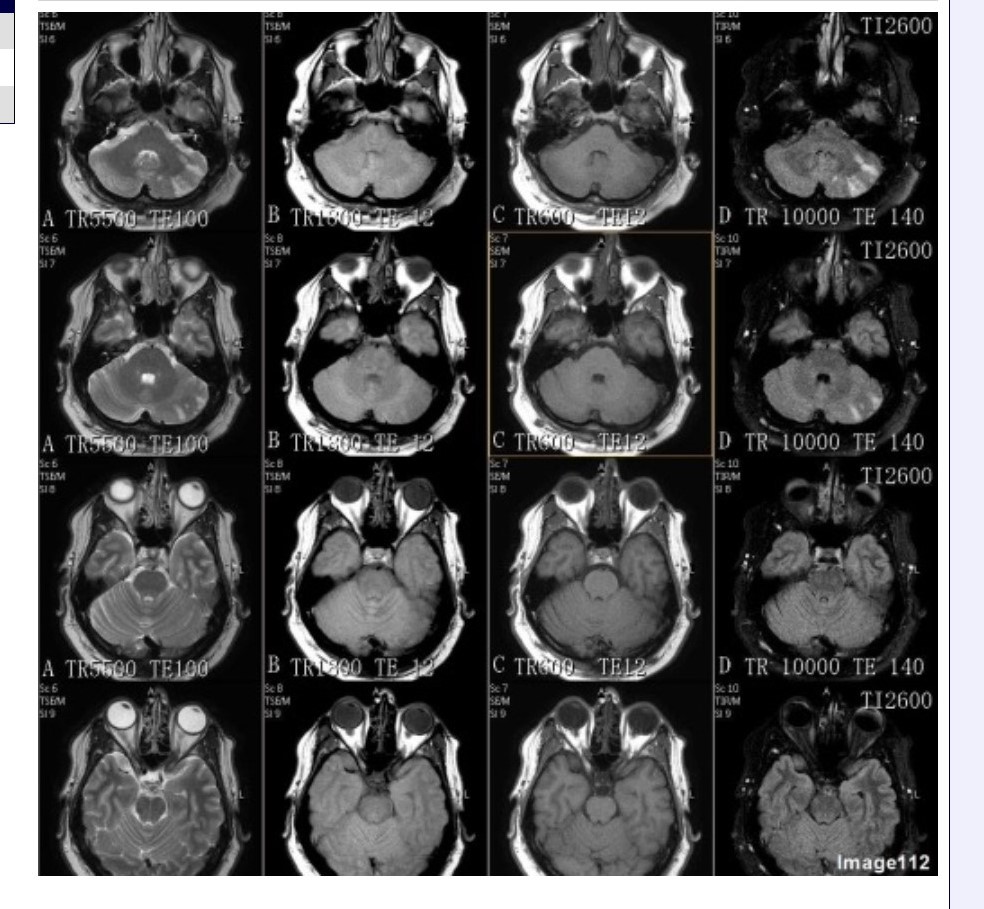
Column D in Image 112 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
F. T2* gradient echo
D. T2 FLAIR
Long TR + Long TE + Long TI = T2 FLAIR
A T2 weighted image will have a repetition time (TR) in the range of:
A. 25 - 40 ms
B. 80 - 120 ms
C. 350 - 700 ms
D. 2000 - 6000 ms
D. 2000 - 6000 ms
A sequence with a _________ TR and a _________ TE will exhibit T1 weighting.
A. short; short
B. short; long
C. long; short
D. long; long
A. short; short
T1 weighted images utilize a short TR and a short TE
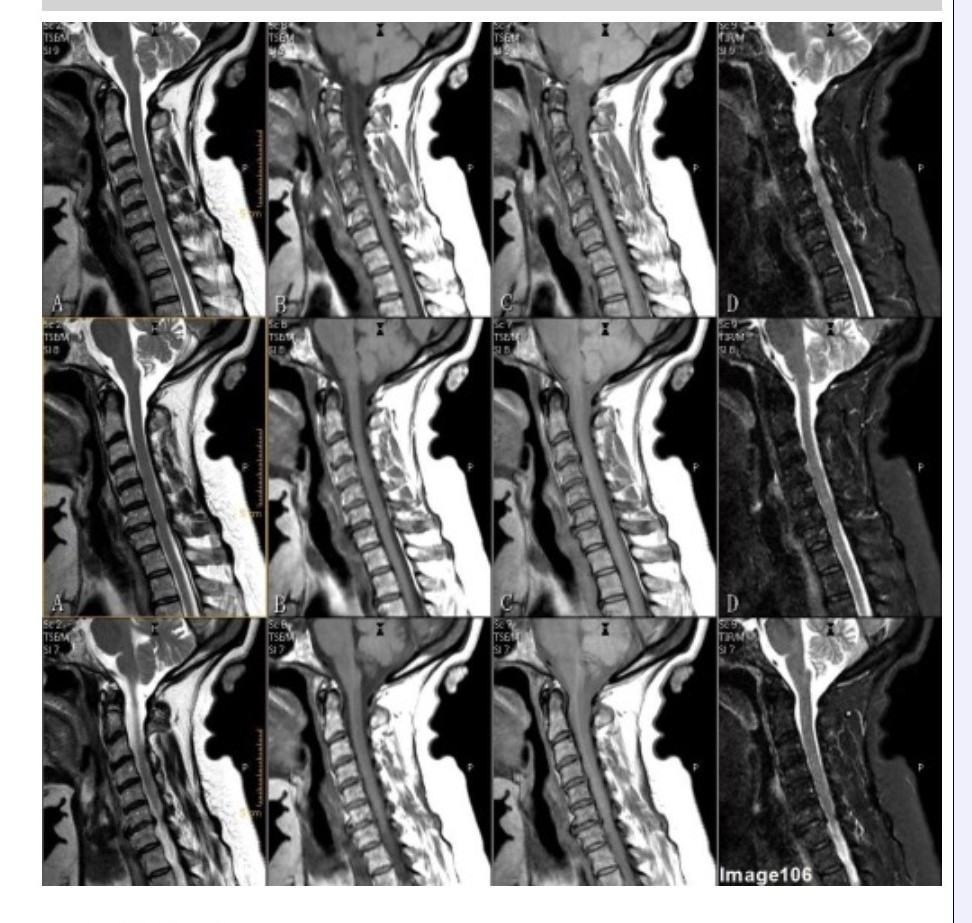
Column A in Image 106 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
C. T2 weighted
Which of the following parameter combinations would yield the most T2 weighted image?
A. 500 TR, 20 TE
B. 1600 TR, 30 TE
C. 2000 TR, 80 TE
D. 3500 TR, 120 TE
D. 3500 TR, 120 TE
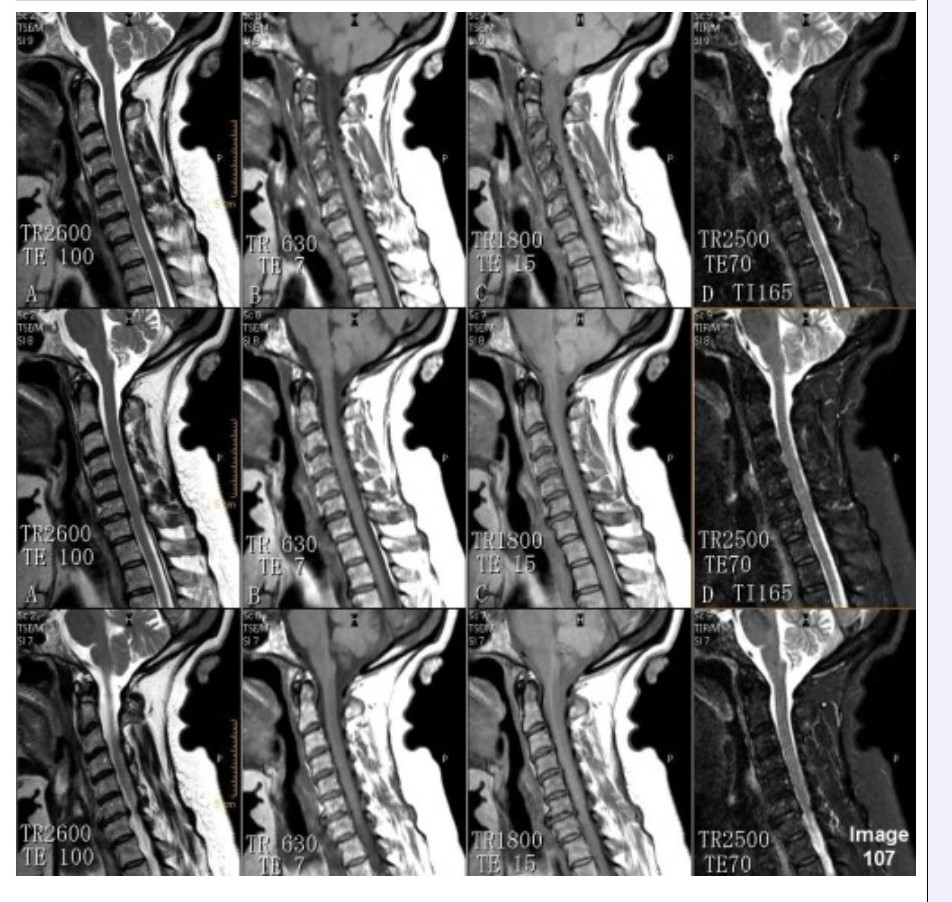
Column C in Image 107 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
A. Proton density
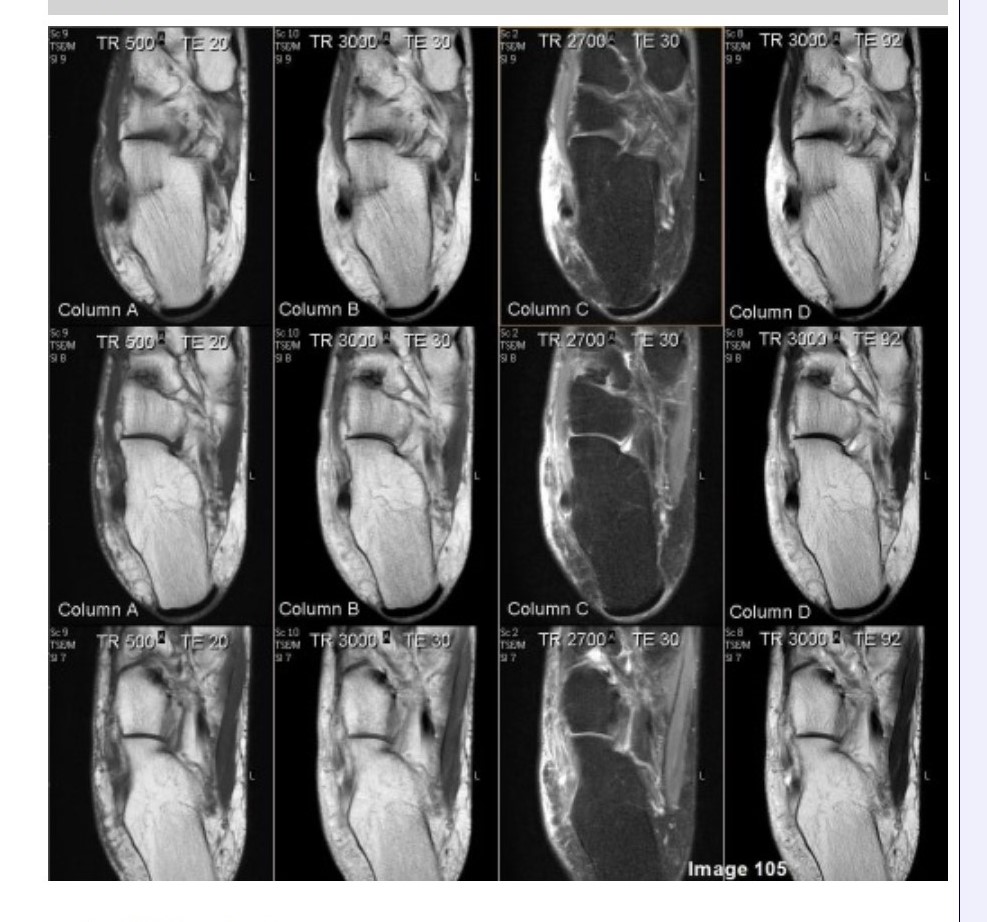
Column A in Image 105 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. Proton density with fat suppression
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
B. T1 weighted
To produce an image based on differences in T1, the time interval between 90° excitation pulses should be:
A. Short
B. Long
C. Inverted
D. Refocused with steady state
A. Short
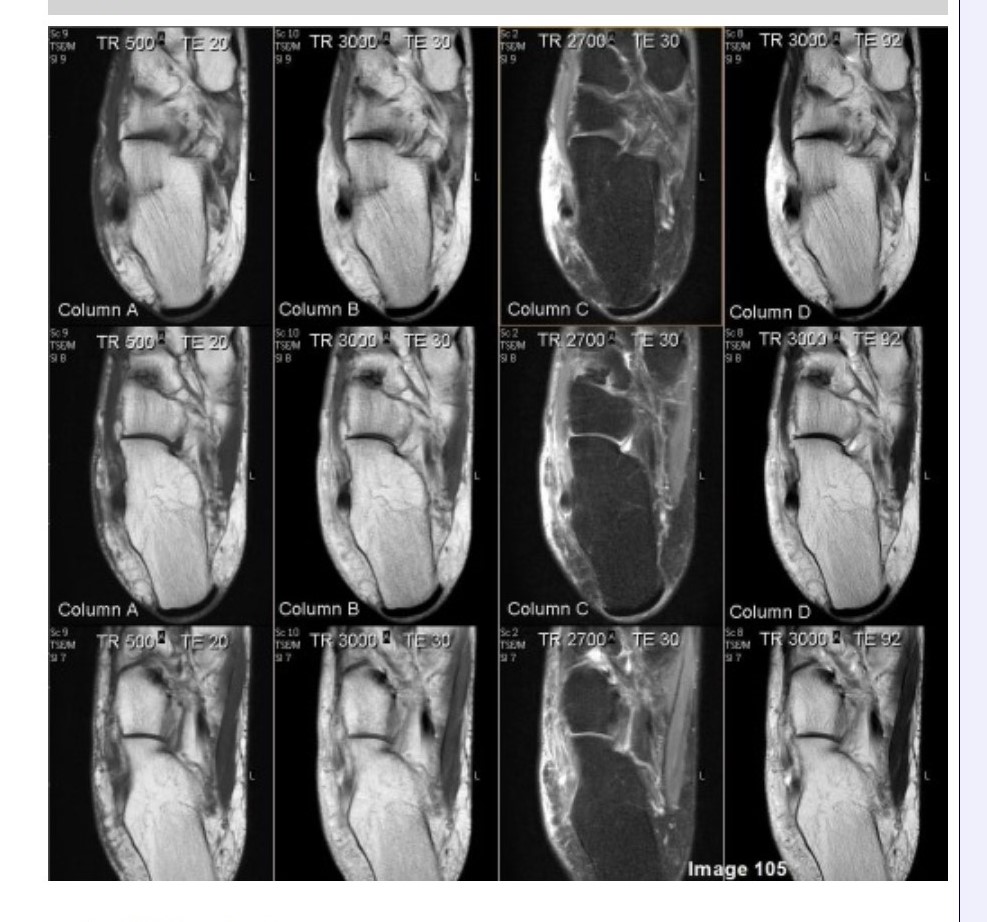
Column B in Image 105 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. Proton density with fat suppression
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
A. Proton density
A T1 weighted image will have an echo time (TE) in the range of:
A. 10 - 30 ms
B. 80 - 120 ms
C. 350 - 700 ms
D. 2000 - 6000 ms
A. 10 - 30 ms
A sequence with a _________ TR and a _________ TE will exhibit T2 weighting.
A. Short; short
B. Short; long
C. Long; short
D. Long; long
D. Long; long
Which of the following parameter combinations would yield the most T1 weighting?
A. 350 TR, 15 TE
B. 500 TR, 25 TE
C. 1600 TR, 30 TE
D. 3500 TR, 120 TE
A. 350 TR, 15 TE
Water is hyperintense and fat is typically dark in:
A. T1 weighted images
B. Proton density weighted images
C. T2 weighted images
D. FLAIR
C. T2 weighted images
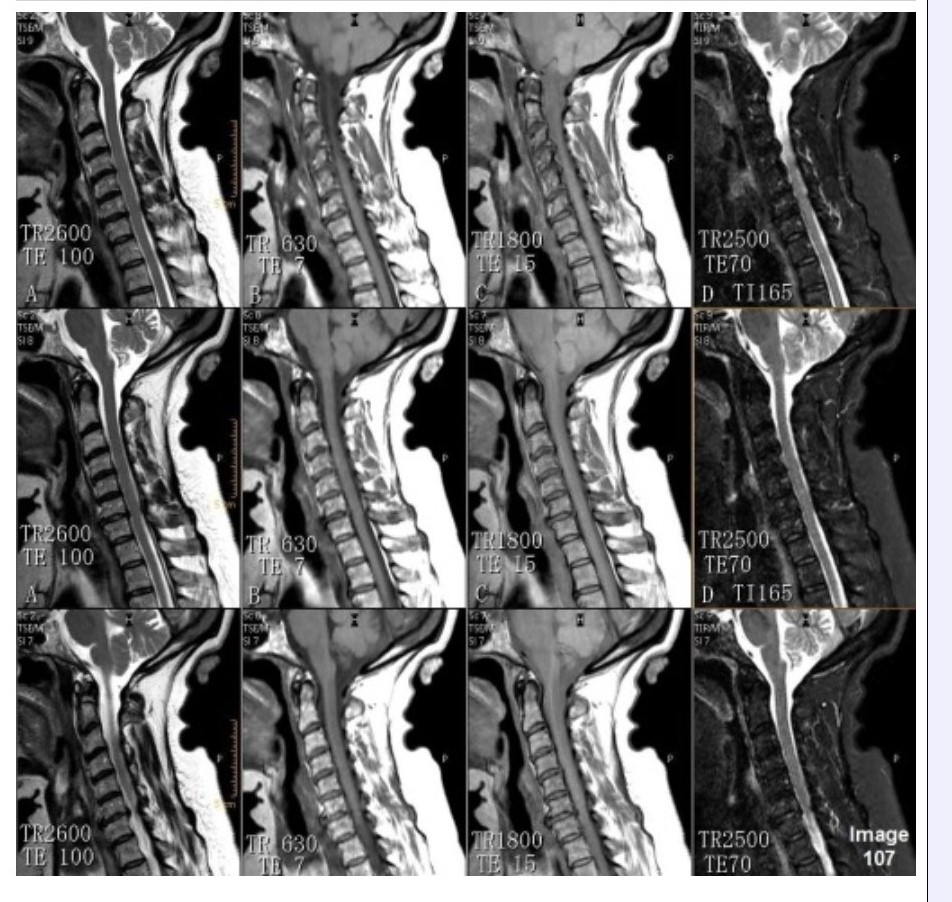
Column D in Image 107 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
E. STIR
A proton density weighted image will have an echo time (TE) in the range of:
A. 10 - 35 ms
B. 80 - 120 ms
C. 350 - 700 ms
D. 2000 - 6000 ms
A. 10 - 35 ms
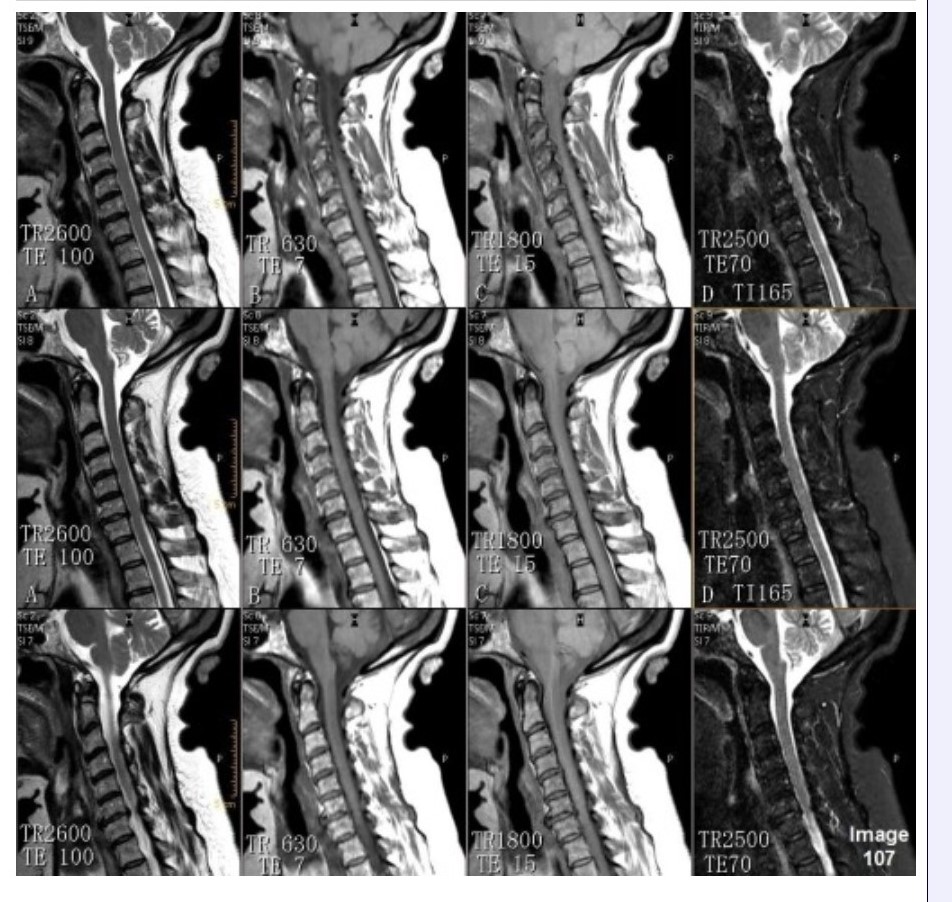
Column B in Image 107 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
B. T1 weighted
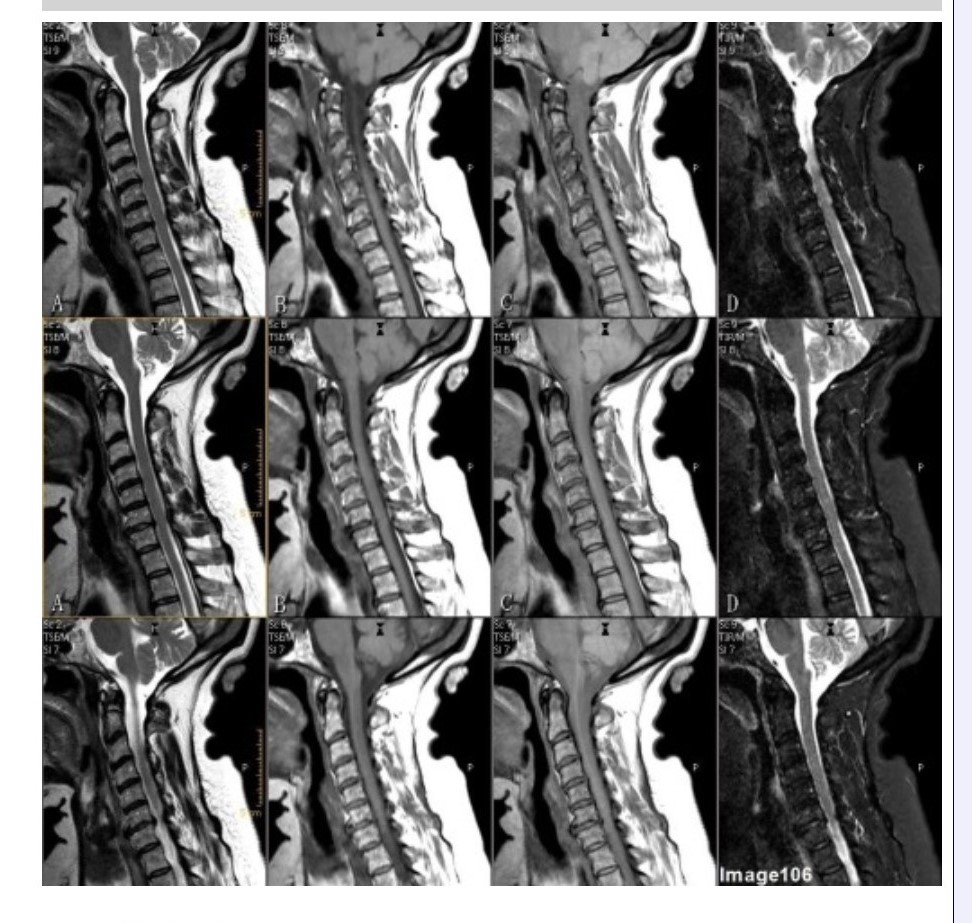
Column C in Image 106 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
A. Proton density
A sequence with a _________ TR and a _________ TE will exhibit PD weighting.
A. Short; short
B. Short; long
C. Long; short
D. Long; long
C. Long; short
A Proton Density weighted image has a TR that is long to _____________, and a TE that is short to _____________.
A. Maximize T1 contrast; minimize T2 contrast
B. Minimize T1 contrast; minimize T2 contrast
C. Maximize T1 contrast; maximize T2 contrast
D. Minimize T1 contrast; maximize T2 contrast
B. Minimize T1 contrast; minimize T2 contrast
All of the following are properties of T2 weighting EXCEPT:
A. Long TR, long TE are the parameter requirements
B. Spin spin
C. Transverse magnetization
D. 63% decay
E. Flip angle controls contrast
E. Flip angle controls contrast
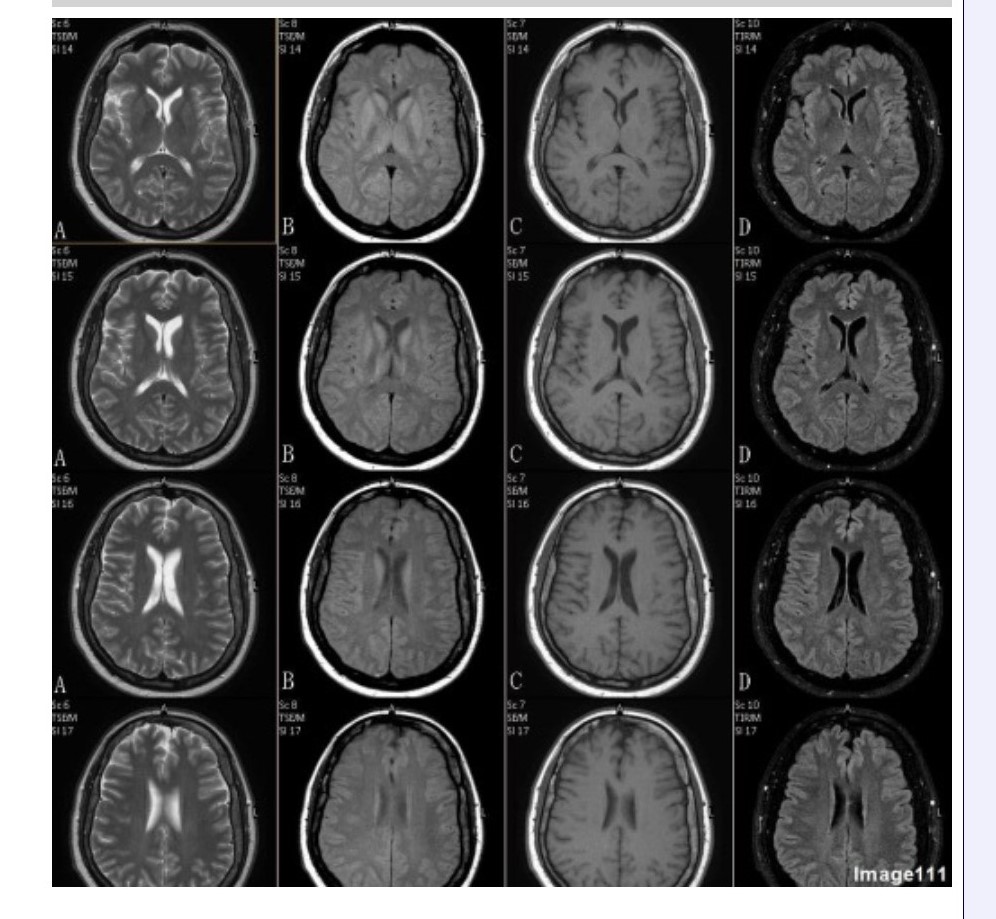
Column C in Image 111 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
F. T2* gradient echo
B. T1 weighted
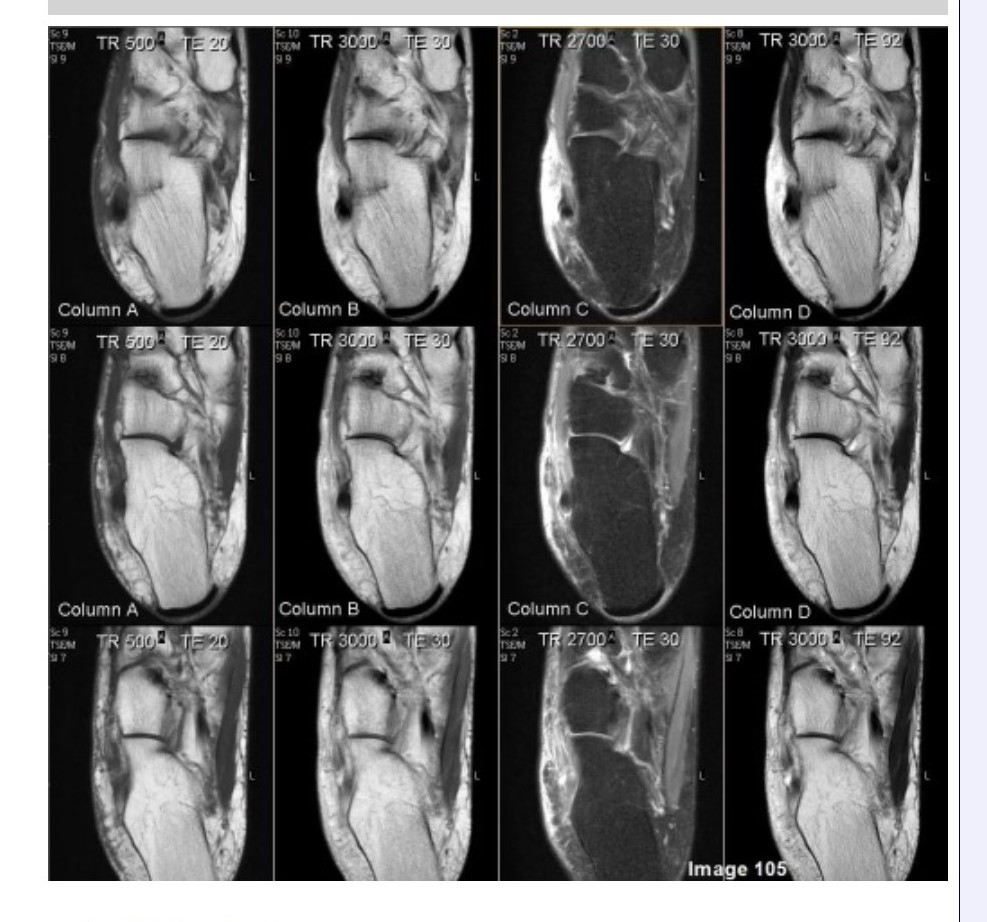
Column C in Image 105 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. Proton density with fat suppression
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
D. Proton density with fat suppression
Which of the following sets of parameters would show edema as hyperintense?
A. 400 TR, 20 TE
B. 1600 TR, 30 TE
C. 3500 TR , 35 TE
D. 4000 TR, 90 TE
D. 4000 TR, 90 TE
T2 weighted sequences (long TR -- >2000 and long TE >80) will yield hyperintense(bright) signal from fluid (edema)
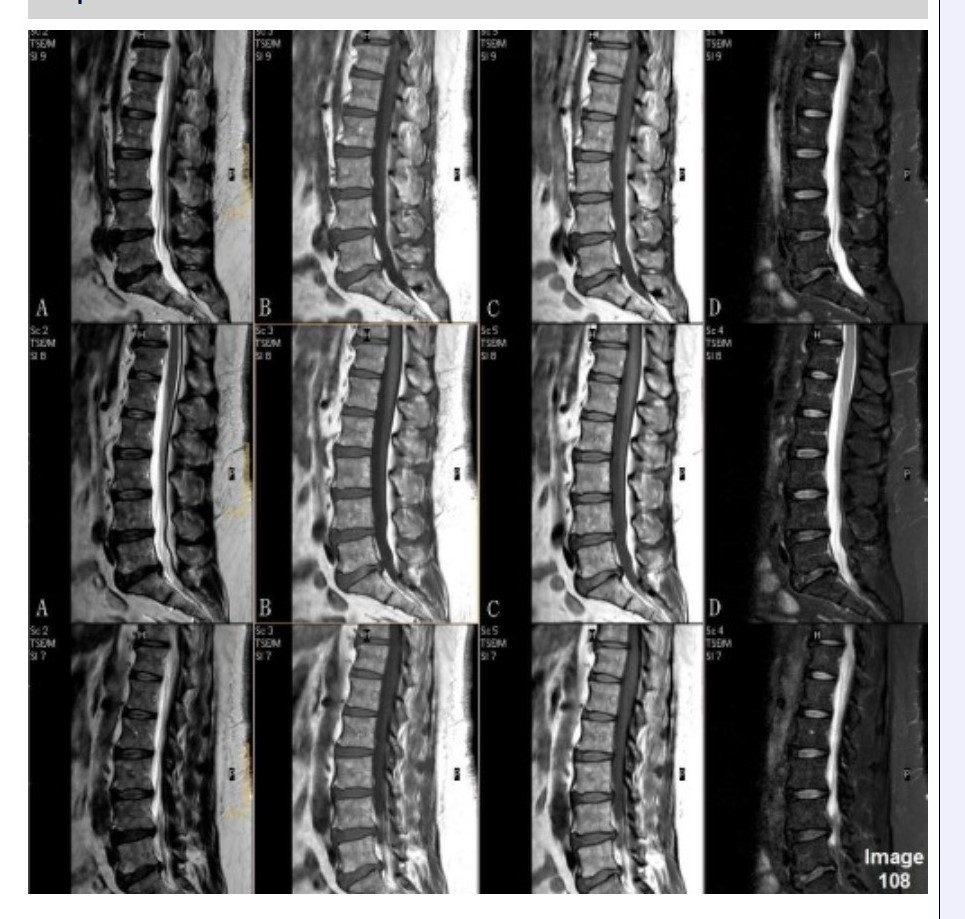
Column C in Image 108 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
A. Proton density
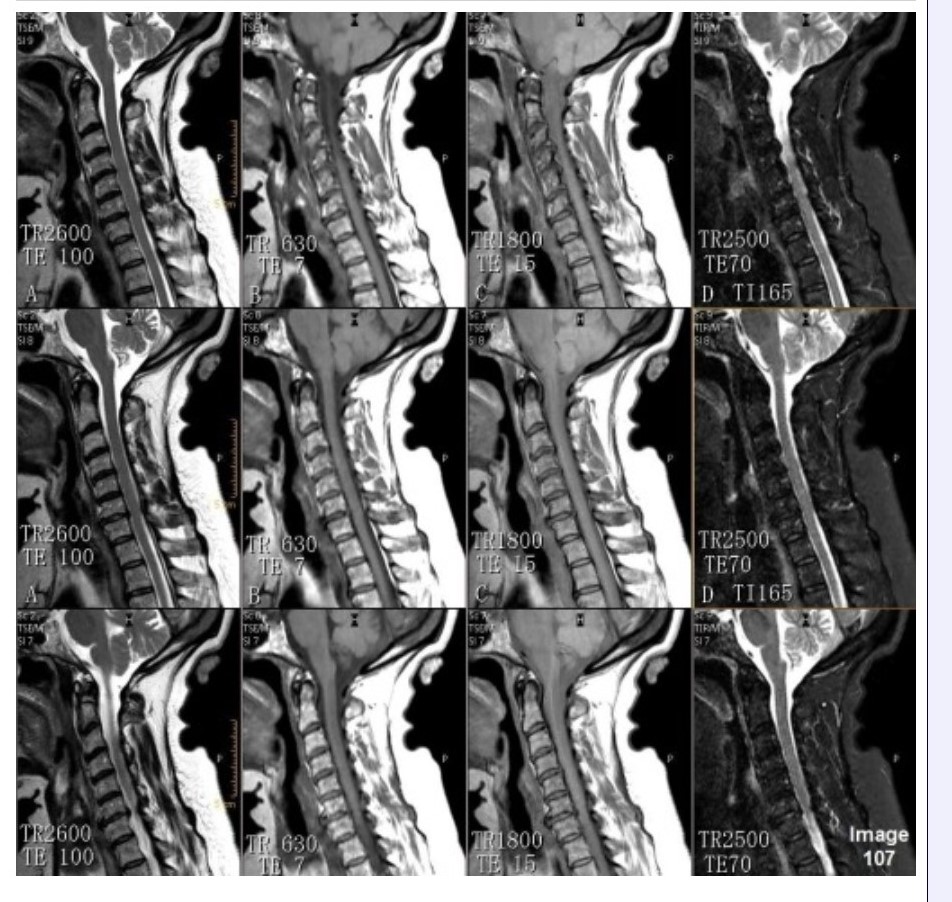
Column A in Image 107 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
C.T2 weighted
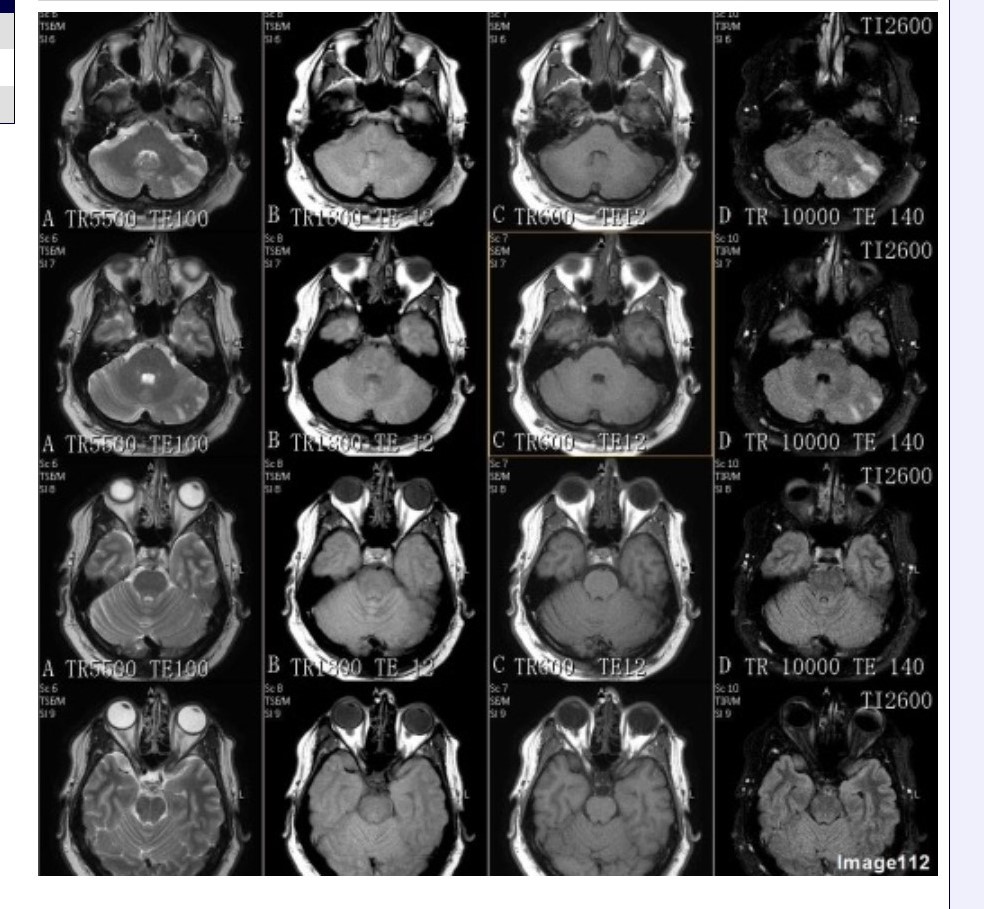
Column B in Image 112 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
F. T2* gradient echo
A. Proton density
The spin echo combination of Long TR with Short TE results in a Proton Density image
Chemical or spectral fat suppression techniques suppress fat signal based on the:
A. Amount of fat being imaged
B. Presence of T1 relaxation in the tissue
C. Presence of T2 relaxation in the tissue
D. Precessional frequency of fat
D. Precessional frequency of fat
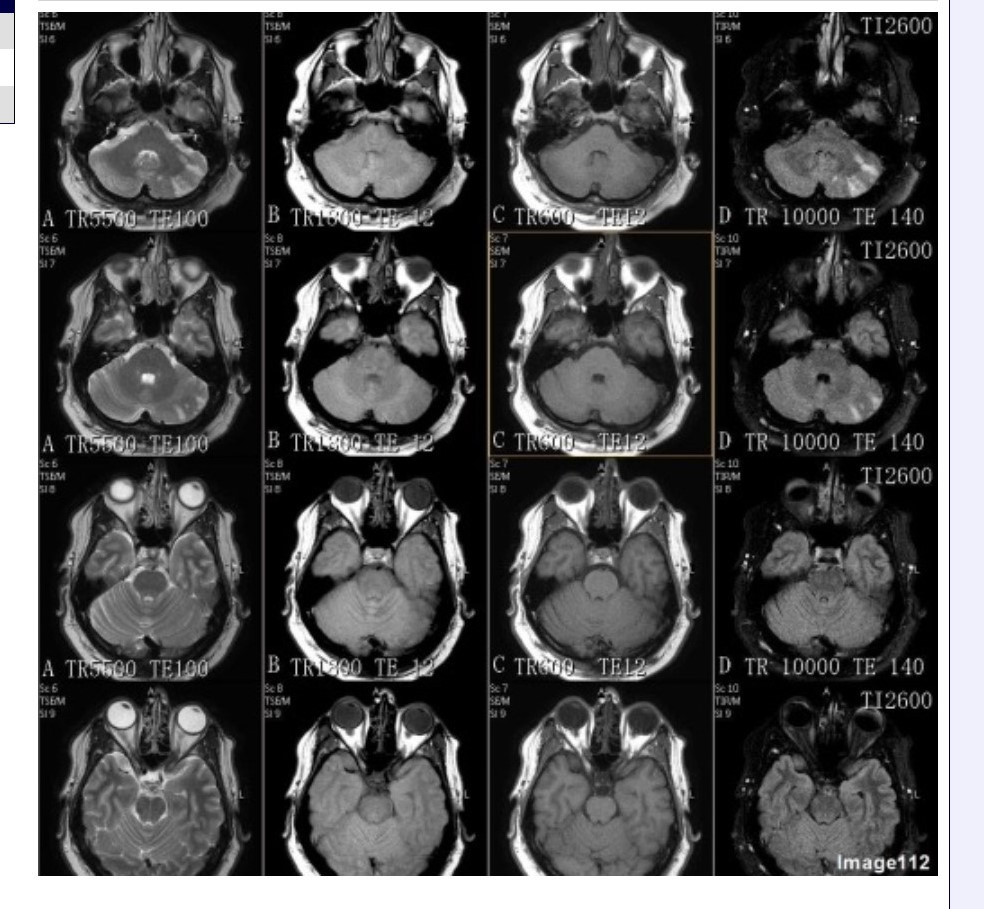
Column A in Image 112 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
F. T2* gradient echo
C. T2 weighted
Long TR + Long TE = T2 weighting
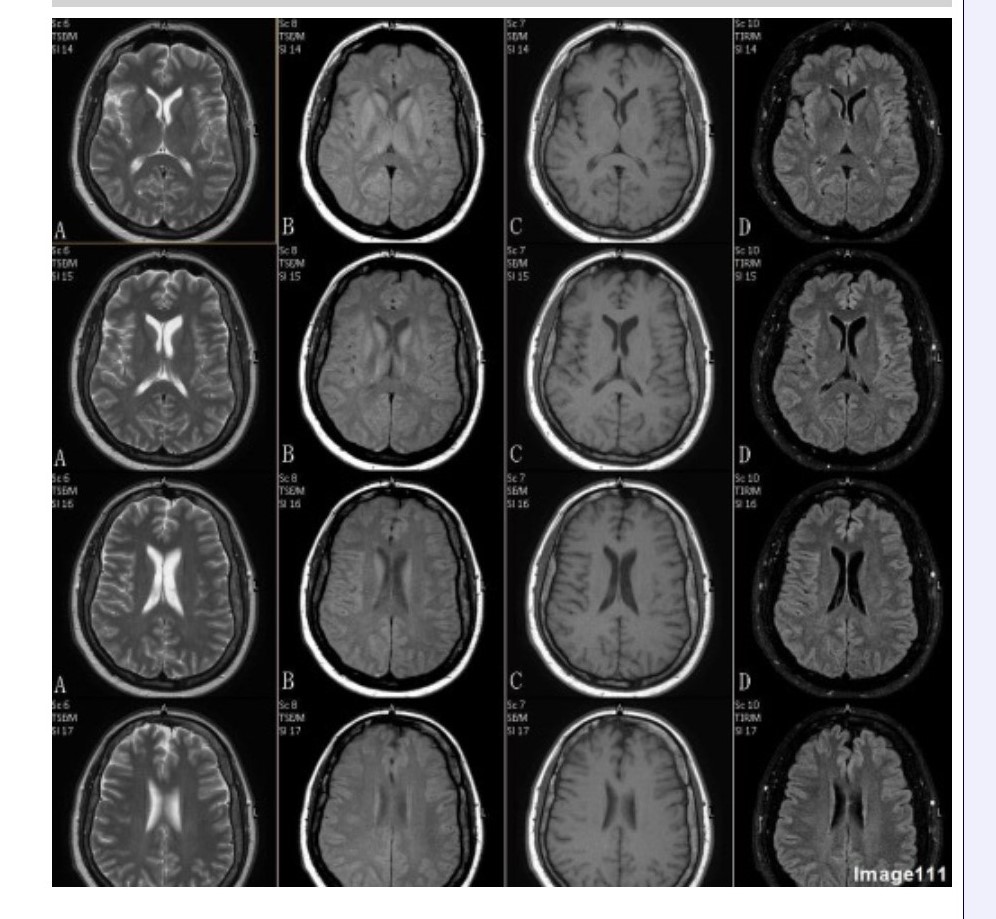
Column D in Image 111 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
F. T2* gradient echo
D. T2 FLAIR
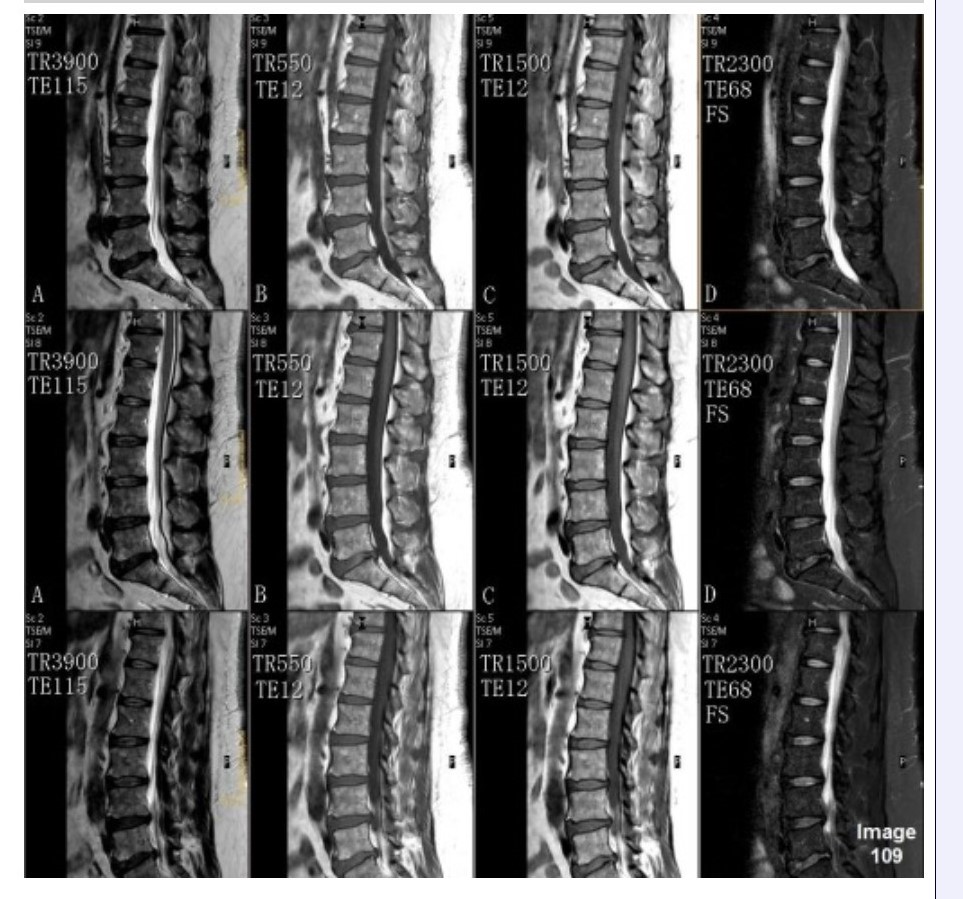
Column B in Image 109 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
B. T1 weighted
What is wrong with a T2 weighted, fast spin echo image that has a 1.1 second TR and a 90 millisecond TE?
A. The ETL will degrade the image resolution
B. The TE will yield insufficient T2 weighted contrast
C. The TR does not sufficiently minimize the T1 weighted contrast
D. All of the above
C. The TR does not sufficiently minimize the T1 weighted contrast
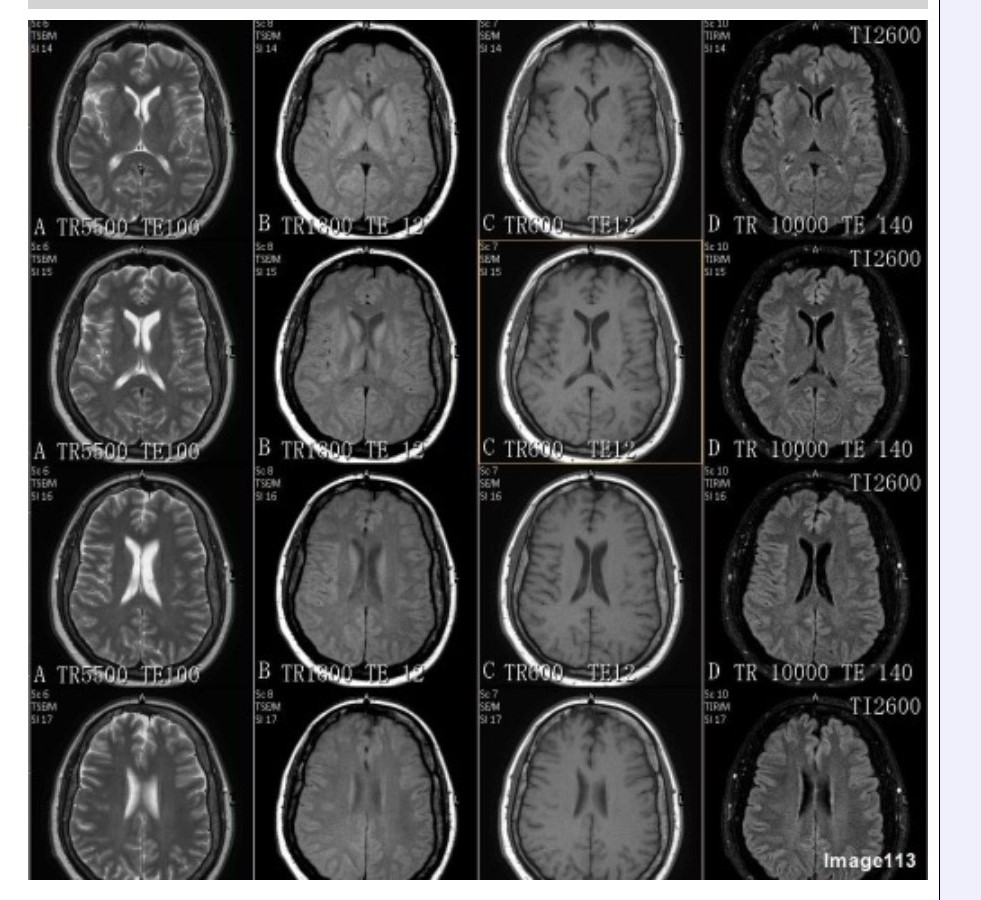
Which sequence's column in Image 113 would be repeated following the administration of a GBCA (gadolinium based contrast agent)?
A. Column A
B. Column B
C. Column C
D. Column D
C. Column C
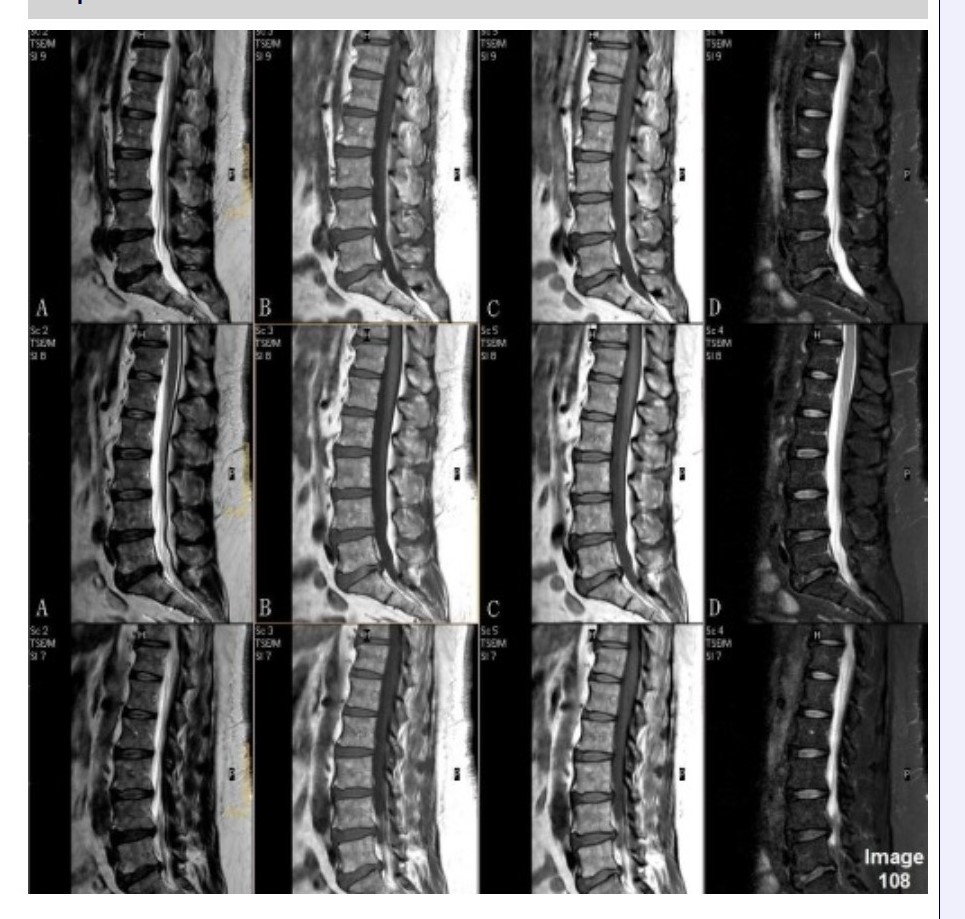
Column D in Image 108 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
D. T2 FLAIR
Structures that will always appear black on an MR image include all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Air
B. CSF
C. Cortical bone
D. Tendons/Ligaments
E. Metal susceptibility artifacts
B. CSF
T1 is useful for __________, whereas T2 is utilized for depicting __________.
A. Blood; anatomy
B. Anatomy; blood
C. Pathology; anatomy
D. Anatomy; pathology
D. Anatomy; pathology
T1 is useful for anatomy, whereas T2 is utilized for depicting pathology(edema)
Presaturation pulses typically occur:
A. Prior to the TE
B. At the time 1/2 TE
C. Prior to the excitation pulse
D. Between the 90° RF pulse and the 180° pulse
C. Prior to the excitation pulse
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A. T2 contrast is maximized with long TE's
B. T1 contrast is maximized with short TR's
C. Flip angle can control image contrast weighting
D. T1 weighting is adjusted with short TE's
D. T1 weighting is adjusted with short TE's
All of the following are examples of INTRINSIC contrast parameters in tissues EXCEPT:
A. ADC (apparent diffusion coefficient)
B. TR
C. T1 time
D. T2 time
E. Proton density
B. TR
Intrinsic parameters in tissues are those that are specific to each tissue, inherent, and cannot be changed, such as ADC, T1/T2 time, specific proton density, and flow.
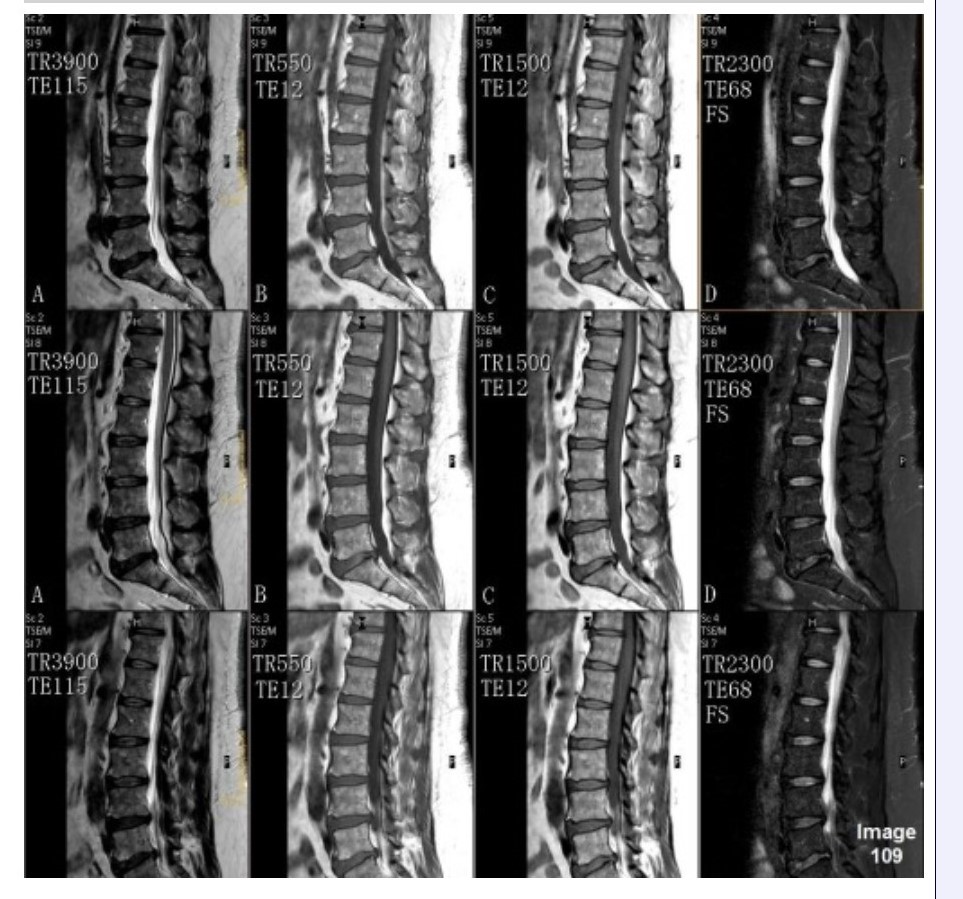
Column D in Image 109 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
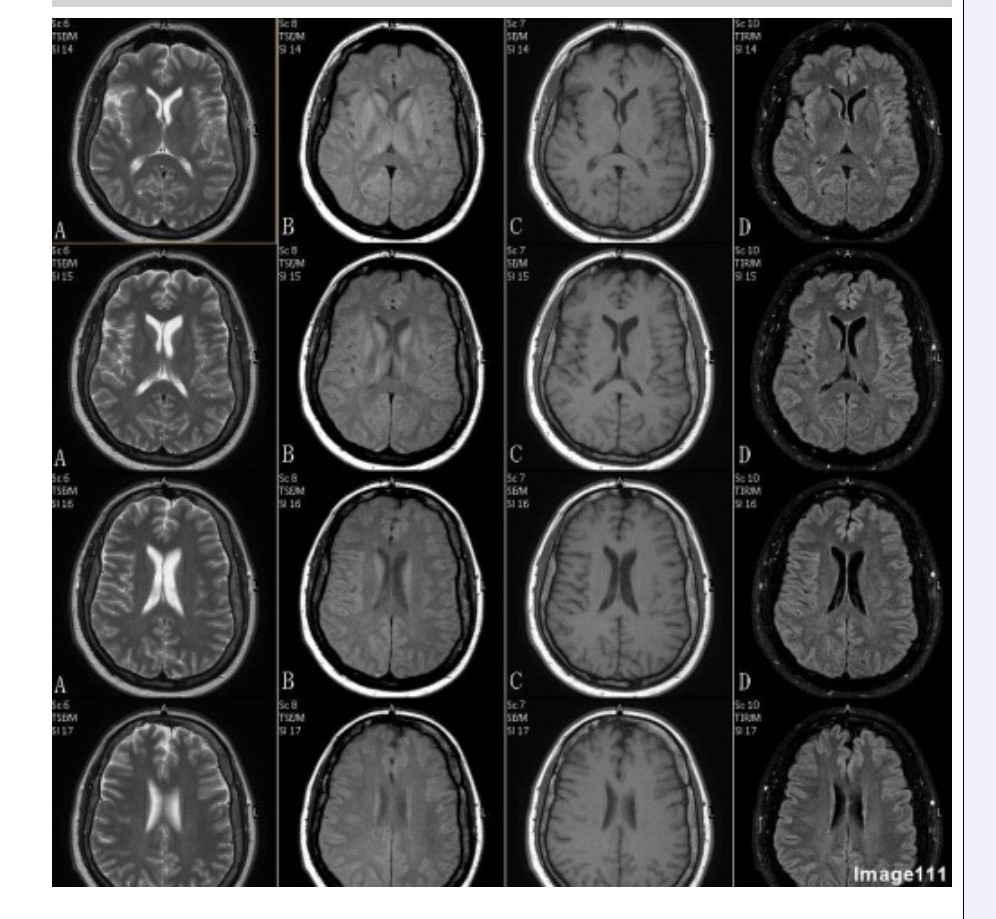
Column A in Image 111 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
F. T2* gradient echo
C. T2 weighted
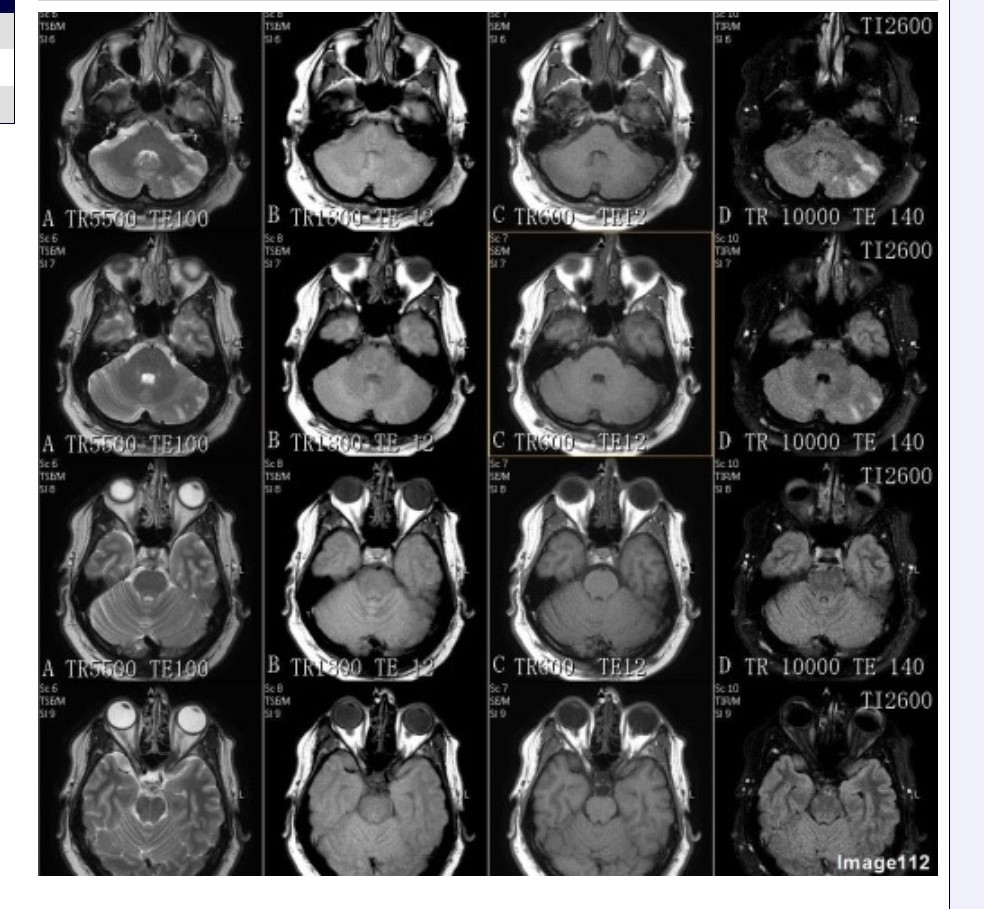
Column C in Image 112 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. T2 weighted with fat suppression
F. T2* gradient echo
B. T1 weighted
Short TR + Short TE = T1 weighting
All of the following are properties of T1 weighting EXCEPT:
A. Short TR, short TE are the parameter requirements
B. Spin lattice
C. Transverse magnetization
D. Timed at 63% recovery
E. Contrast is controlled by TR
C. Transverse magnetization
T1 relaxation time is the recovery of 63% longitudinal magnetization of a specific tissue.
A T1 weighted image will have a repetition time (TR) in the range of:
A. 25 - 40 ms
B. 80 - 120 ms
C. 350 - 700 ms
D. 2000 - 6000 ms
C. 350 - 700 ms
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding spin echo sequences?
A. T1 contrast is maximized with short TR's
B. PD contrast is maximized with multiple echo train lengths
C. T2 contrast is maximized with short TE's
D. None of the above
A. T1 contrast is maximized with short TR's
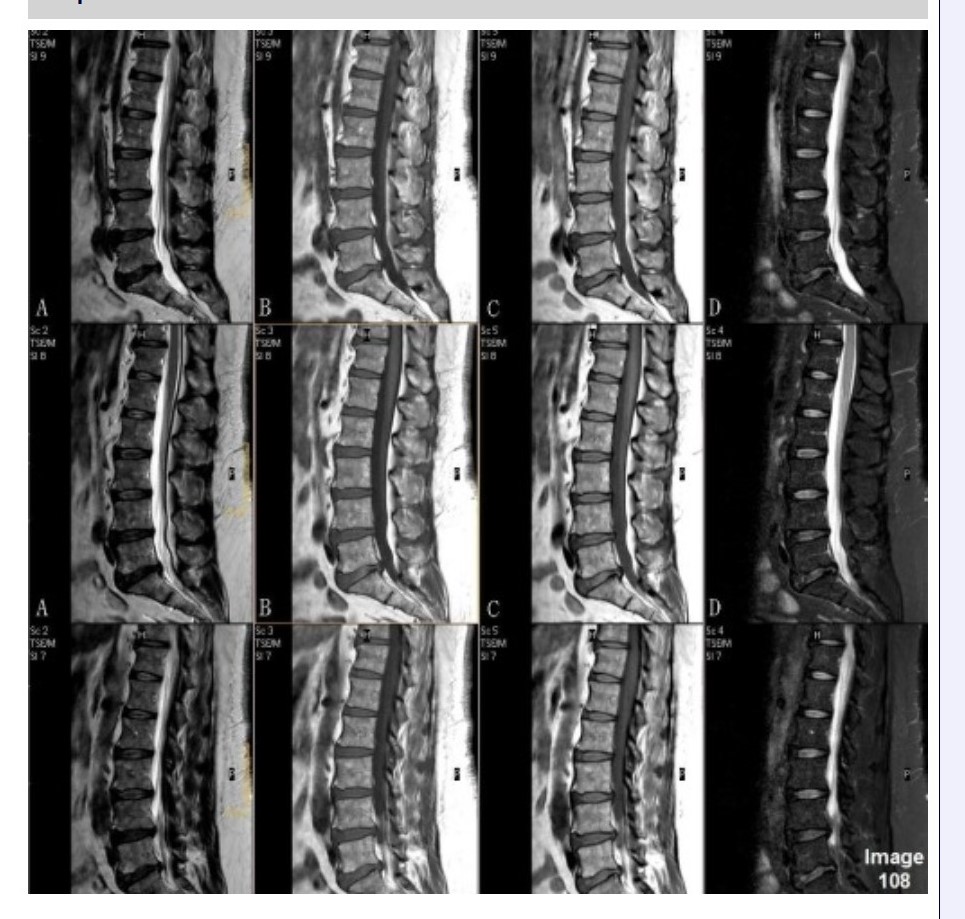
Column A in Image 108 corresponds to which MRI pulse sequence?
A. Proton density
B. T1 weighted
C. T2 weighted
D. T2 FLAIR
E. STIR
C. T2 weighted